Shaping the Structure and Properties of Stellite 6 Alloy by Addition of Ti and W via Laser Cladding
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Laser Processing
2.2. Macro- and Microstructural Examination with Penetrant Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Penetrant Tests
3.2. Macrostructure
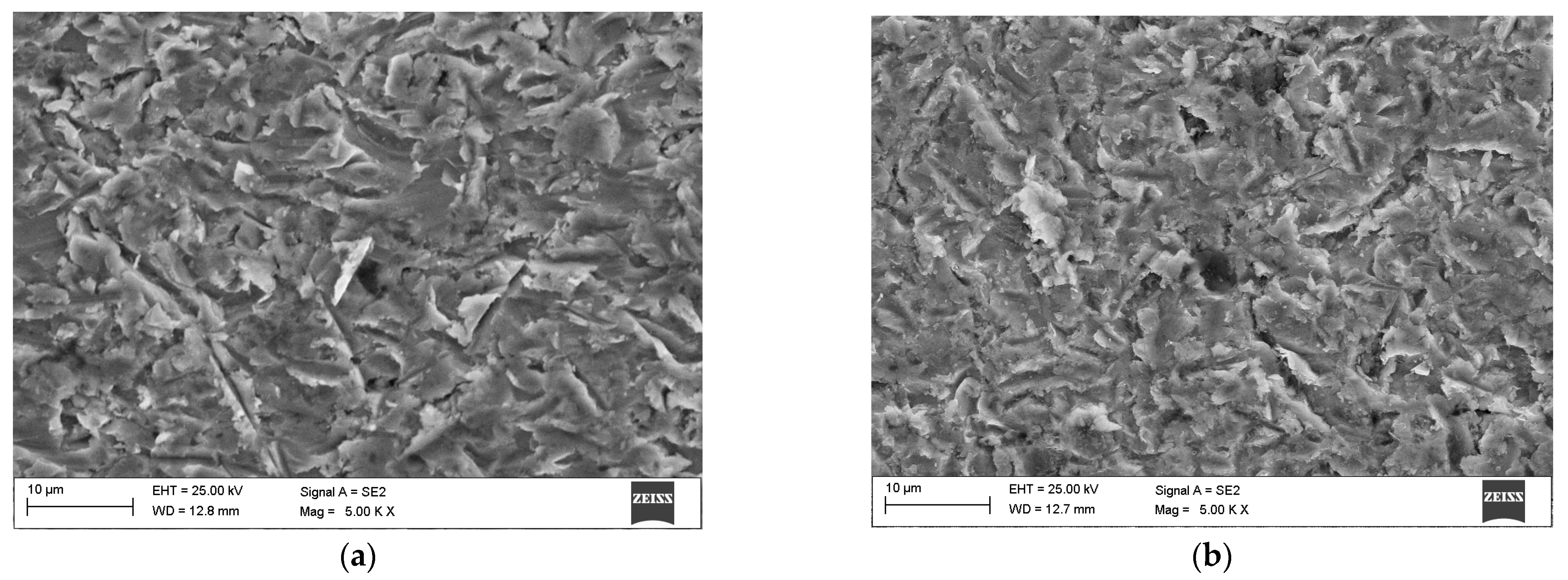
3.3. Microstructure
3.4. Microhardness
3.5. Solid Particle Erosion Tests
4. Conclusions
- Laser cladding of Co-Cr-W-C-Ti alloys produced defect-free coatings, where increased graphite and titanium content enhanced laser absorption, leading to greater coating thickness and higher dilution.
- The addition of titanium and increased carbon and tungsten content to the base Co-Cr-W-C alloy enabled the in situ formation of primary and eutectic (Ti,W)C carbides, where despite the formation of hard (Ti,W)C carbides, different powder compositions for laser cladding had only a moderate influence on the coating hardness.
- Transmission electron microscopy revealed a tungsten concentration gradient within primary (Ti,W)C carbides, indicating that TiC primary precipitates initially form at low tungsten levels (0.07 W/Ti % at. ratio) with progressively more tungsten dissolving into the carbide lattice reaching a W/Ti atomic ratio of 0.27 in the outer layer.
- Results from erosion testing showed that the inclusion of C and Ti to the Co-Cr-W-C alloy significantly influences erosive wear. The in situ synthesis of (Ti,W)C carbides enhanced the erosion resistance compared to the base alloy (M6 sample) at an impingement angle of 30°, while maintaining high erosion resistance at a 90° angle.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santerre, F.; El Khakani, M.; Chaker, M.; Dodelet, J. Properties of TiC thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 148, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupryński, A.; Wyględacz, B. Comparative Analysis of Laser and Plasma Surfacing by Nickel-Based Superalloy of Heat Resistant Steel. Materials 2020, 13, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloots, M.; Kunzeb, K.; Uggowitzer, P.; Wegener, K. Microstructural characteristics of the nickel-based alloy IN738LC and the cobalt-based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 658, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Encalada, A.I.; Stoyanov, P.; Makowiec, M.; Moreau, C.; Chromik, R.R. Wear of Stellite 6 Coatings Produced with High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel at Elevated Temperatures. Lubricants 2025, 13, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mi, G.; Xiong, L.; Jiang, P.; Shao, X.; Wang, C. Morphologies, microstructures and properties of TiC particle reinforced Inconel 625 coatings obtained by laser cladding with wire. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupryński, A.; Żuk, M. Matrix composite coatings deposited on AISI 4715 steel by powder plasma-transferred arc welding. Materials 2021, 14, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloczek, T.; Janicki, D.; Górka, J.; Kotarska, A. Effect of Ti and C alloyants on the microstructure of laser cladded cobalt-chromium coatings. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1182, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.P.; Ayers, J.D. LASER Melt-Particle Injection Processing. Surf. Eng. 1985, 1, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górka, J.; Poloczek, T.; Janicki, D.; Lont, A.; Topór, S.; Żuk, M.; Rzeźnikiewicz, A. Microstructure and Erosion Wear of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Co-Cr-W-C (Stellite 6) Laser-Cladded Coatings. Materials 2024, 17, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Li, K.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Cui, W.; Song, C.; Wang, C.; Jia, X.; et al. CW laser damage of ceramics induced by air filament. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2025, 8, 240296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenk, A.; Kurz, W. High-speed laser cladding: Solidification Conditions and Microstructure of a Cobalt-Based Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1993, 173, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxel, K.D.; Bandyopadhyay, A. First Demonstration of Additive Manufacturing of Cutting Tools Using Directed Energy Deposition System: Stellite™-Based Cutting Tools. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.D.; Ye, S.X.; Cheng, P.; Xie, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Guangshi, L.; Wenhe, W.; Xionggang, L. Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ TiC reinforced Stellite 6 coating using PTA cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 2656–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotarska, A.; Poloczek, T.; Janicki, D. Characterization of the Structure, Mechanical Properties and Erosive Resistance of the Laser Cladded Inconel 625-Based Coatings Reinforced by TiC Particles. Materials 2021, 14, 2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.S.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhou, J.S.; Liang, J. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser-cladded Co-Ti3SiC2 coating with Ni-based interlayer on copper alloy. Tribol. Int. 2022, 171, 107549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.B.; Zhu, G.X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, L. Tribological study of Ti3SiC2/Cu5Si/TiC reinforced Co-based coatings on SUS304 steel by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 432, 128064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, A.; Bialas, O.; Żuk, M.; Czupryński, A.; Sasu, D.; Adamiak, M. Hardfacing of mild steel with wear-resistant Ni-based powders containing tungsten carbide particles using powder plasma transferred arc welding technology. Mater. Sci.-Pol. 2022, 40, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poloczek, T.; Lont, A.; Górka, J. The Structure and Properties of Laser-Cladded Inconel 625/TiC Composite Coatings. Materials 2023, 16, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Chocyk, D.; Skic, A.; Kamiński, M.; Macek, W.; Turek, M. Effect of Nitrogen Ion Implantation on the Cavitation Erosion Resistance and Cobalt-Based Solid Solution Phase Transformations of HIPed Stellite 6. Materials 2021, 14, 2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolina, I.; Kobiela, K. Characterization of Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Stellite 6 Laser Surfaced Alloyed (LSA) with Rhenium. Coatings 2021, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D.; Czupryński, A.; Górka, J.; Matus, K. Effect of Cooling Rate on Microstructure of In Situ TiC-Reinforced Composite Surface Layers Synthesized on Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying. Materials 2024, 17, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahroozi, A.; Afsari, A.; Khakan, B.; Khalifeh, A.R. Microstructure and mechanical properties investigation of stellite 6 and Stellite 6/TiC coating on ASTM A105 steel produced by TIG welding process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Dávila, J.L.; Muñoz-Arroyo, R.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Martinez-Enriquez, A.I.; Alvarez-Vera, M.; Hernández-García, F.A. Cobalt-based PTA coatings effects of addition of TiC nanoparticles. Vacuum 2017, 143, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Cao, X.Y. Developing the ductility and thermal fatigue cracking property of laser-deposited Stellite 6 coatings by adding titanium and nickel. Mater. Des. 2019, 162, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A.; Jurči, P. Laser cladding process of Fe/WC metal matrix composite coatings on low-carbon steel using a Yb:YAG disk laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 136, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsoesie, S.; Rong, L.; Chen, C.; Yao, M. Erosion Resistance of Stellite Alloys under Solid-Particle Impact. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2013, 3, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, B.F.; Dupont, J.N.; Marder, A.R. Weld overlay coatings for erosion control. Wear 1995, 181–183, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; An, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Y. Microstructural Characteristics and Erosion Resistance of Laser Cladding Stellite 6 Alloy on a 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV Steel Surface. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 168, 109093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 10025-2; Hot Rolled Products of Structural Steels—Part 2: Technical Delivery Conditions for Non-Alloy Structural Steels. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- ASTM G76-04; Standard Test Method for Conducting Erosion Tests by Solid Particle Impingement Using Gas Jets. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004.
- Adamiak, M.; Czupryński, A.; Kopyść, A.; Monica, Z.; Olender, M.; Gwiazda, A. The Properties of Arc-Sprayed Aluminum Coatings on Armor-Grade Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostolaza, M.; Arrizubieta, J.I.; Cortina, M.; Lamikiz, A. Study of the reinforcement phase dilution into the metal matrix in functionally graded Stellite 6 and WC metal matrix composite by Laser Metal Deposition. Procedia CIRP 2020, 94, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xv, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, Y. Engineering Process Optimization and Quality Stability Control of High-Speed Laser Cladding Coatings Based on AHP-FCE. Coatings 2023, 13, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, F.A.; de Araújo, R.M.; Tay, F.R.; Niu, L.; Pucci, C.R. Effect of high-power-laser with and without graphite coating on bonding of resin cement to lithium disilicate ceramic. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zak, G.; Bates, P.J. Effect of Carbon Black on Light Transmission in Laser Welding of Thermoplastics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janicki, D. Shaping the Structure and Properties of Surface Layers of Ductile Cast Iron by Laser Alloying, 1st ed.; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2018; pp. 70–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Meiping, W.; Rui, H.; Yuling, G.; Xiaojin, M. Understanding Stellite-6 coating prepared by laser cladding: Convection and columnar-to-equiaxed transition. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Hua, C.; Qu, S.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, C.; Lu, H. Isothermal Transformation of γ-Co to ε-Co in Stellite 6 Coatings. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D.; Sharma, R.; Chakraborti, N. The Ti-Co-C System (Titanium-Cobalt-Carbon). J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 2000, 21, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S. High-Temperature Hardness and Wear Resistance of Stellite Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Carleton University, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.M.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.J. The microstructure and elevated temperature strength of tungsten–titanium carbide composite. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3541–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yao, J.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Yao, M.X.; Collier, R. Effects of Temperature on the Hardness and Wear Resistance of High-Tungsten Stellite Alloys. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Min, T.; Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Yi, D. The Electronic, Mechanical Properties and Theoretical Hardness of Chromium Carbides by First-Principles Calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5242–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, S.; Tabor, D. Work hardening in erosion due to single-particle impacts. Wear 1984, 98, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabnejad, H.; Mansouri, A.; Shirazi, S.A.; McLaury, B. Evaluation of Solid Particle Erosion Equations and Models for Oil and Gas Industry Applications. Proc. CIRP 2015, 38, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T. Erosive Wear Mechanisms of Materials—A Review of Understanding and Progresses. Materials 2025, 18, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
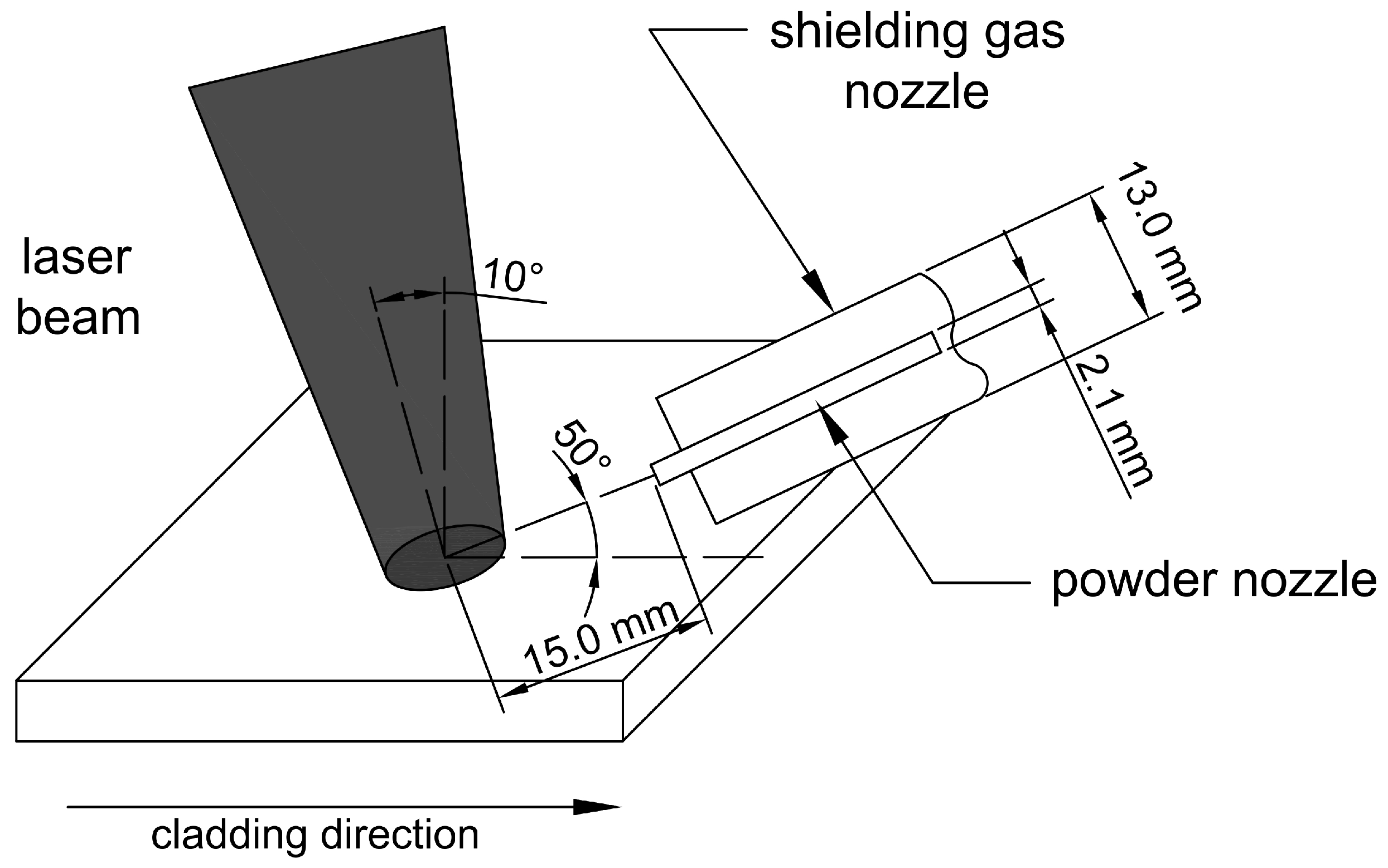

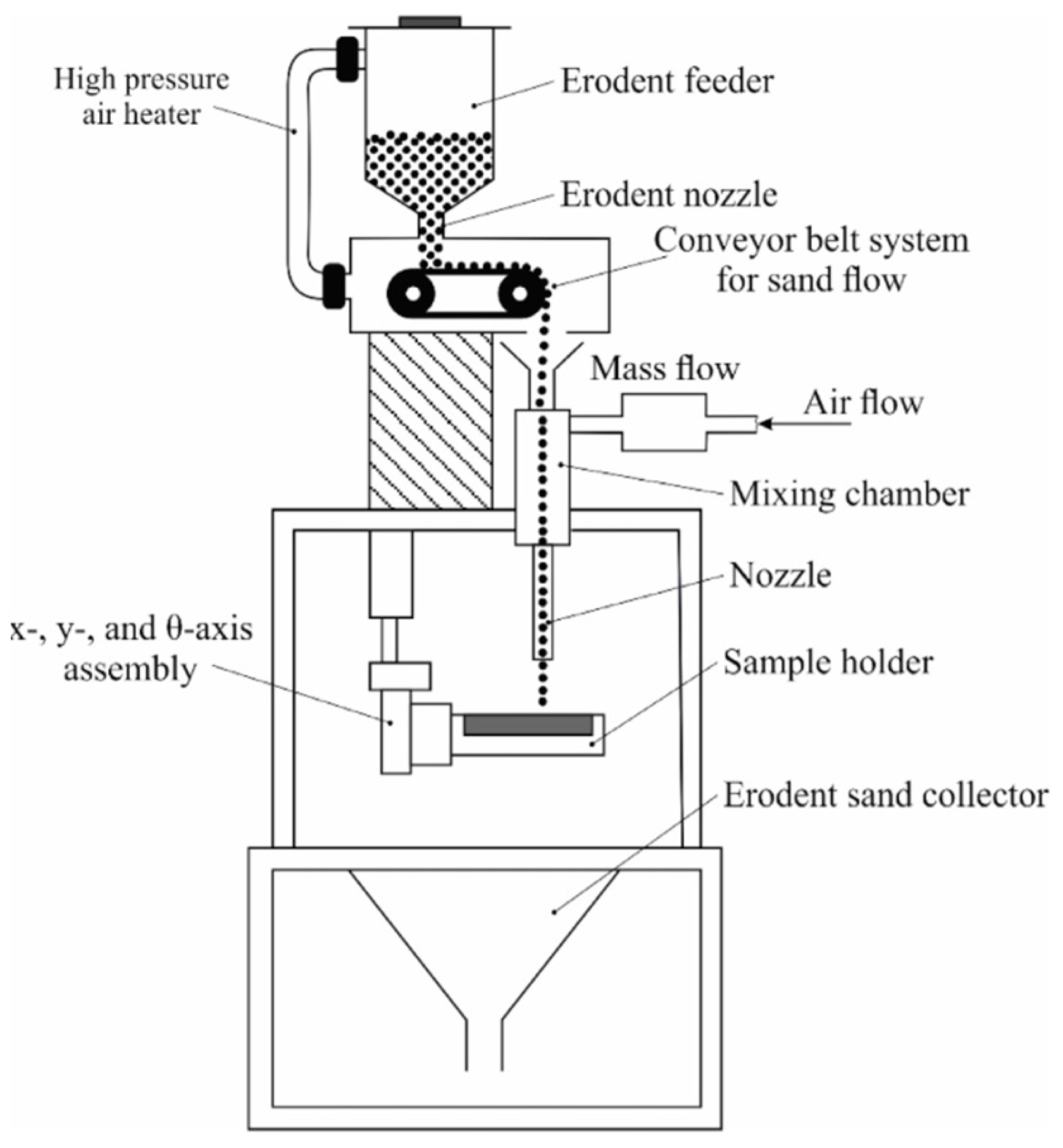

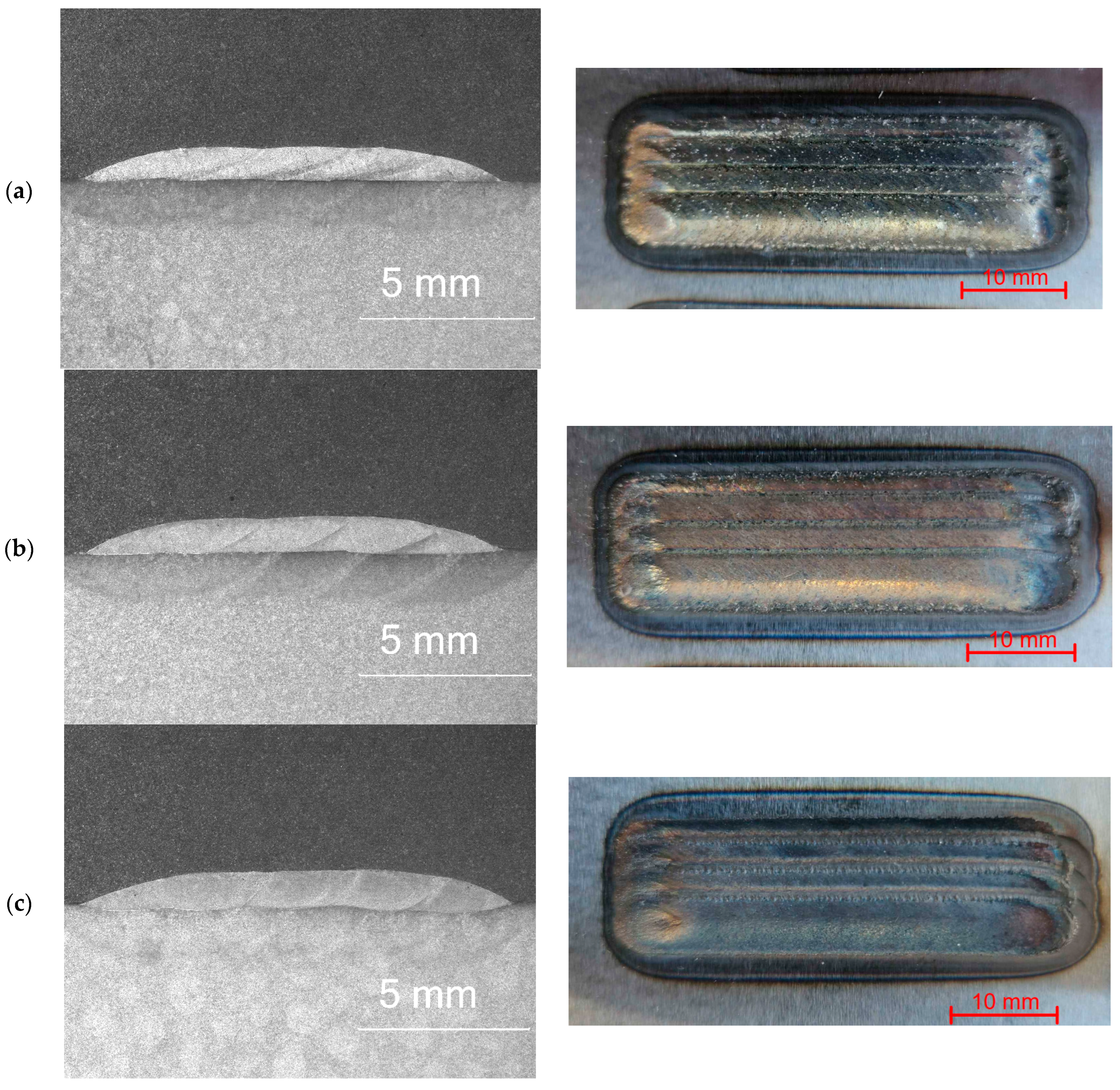

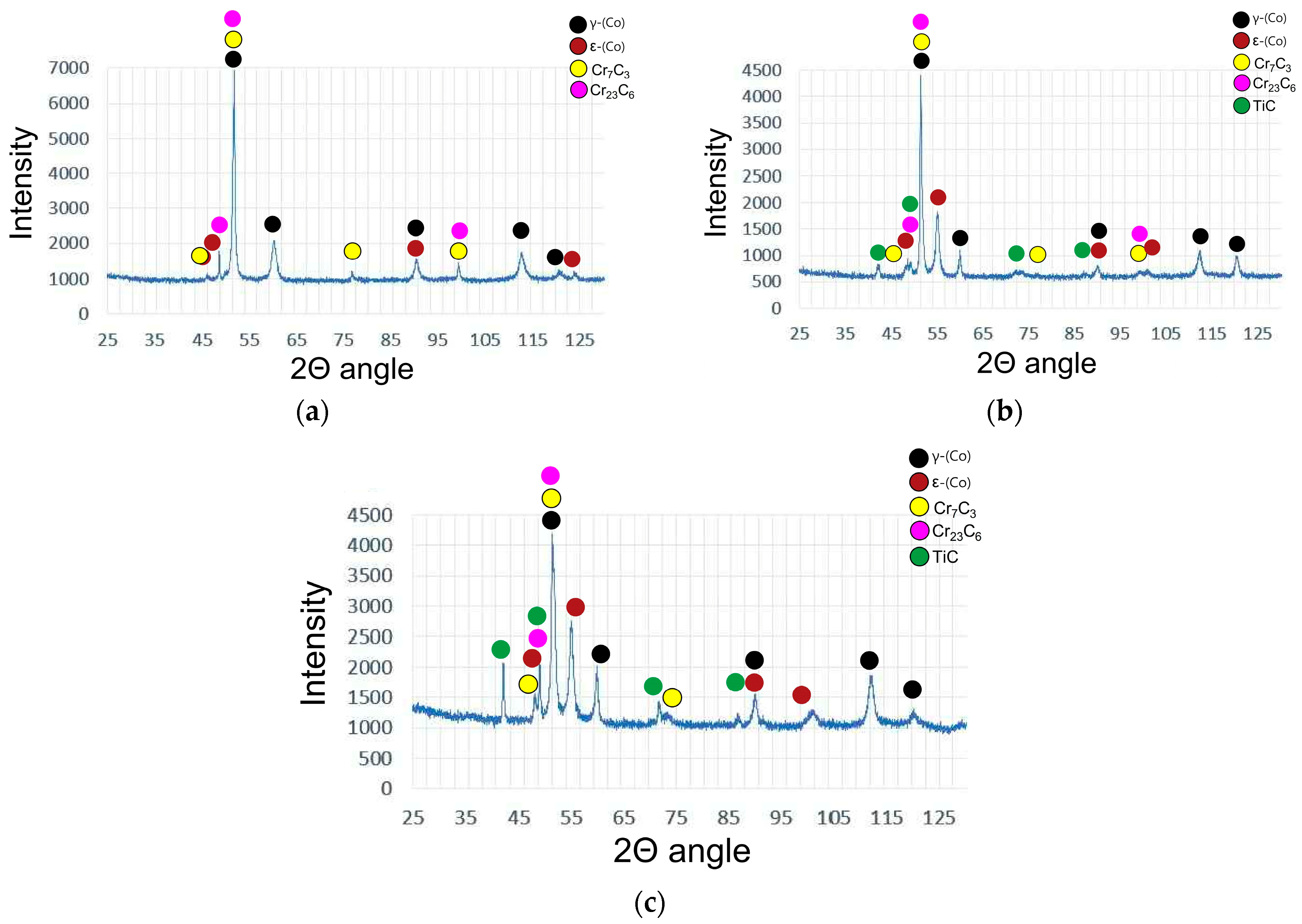


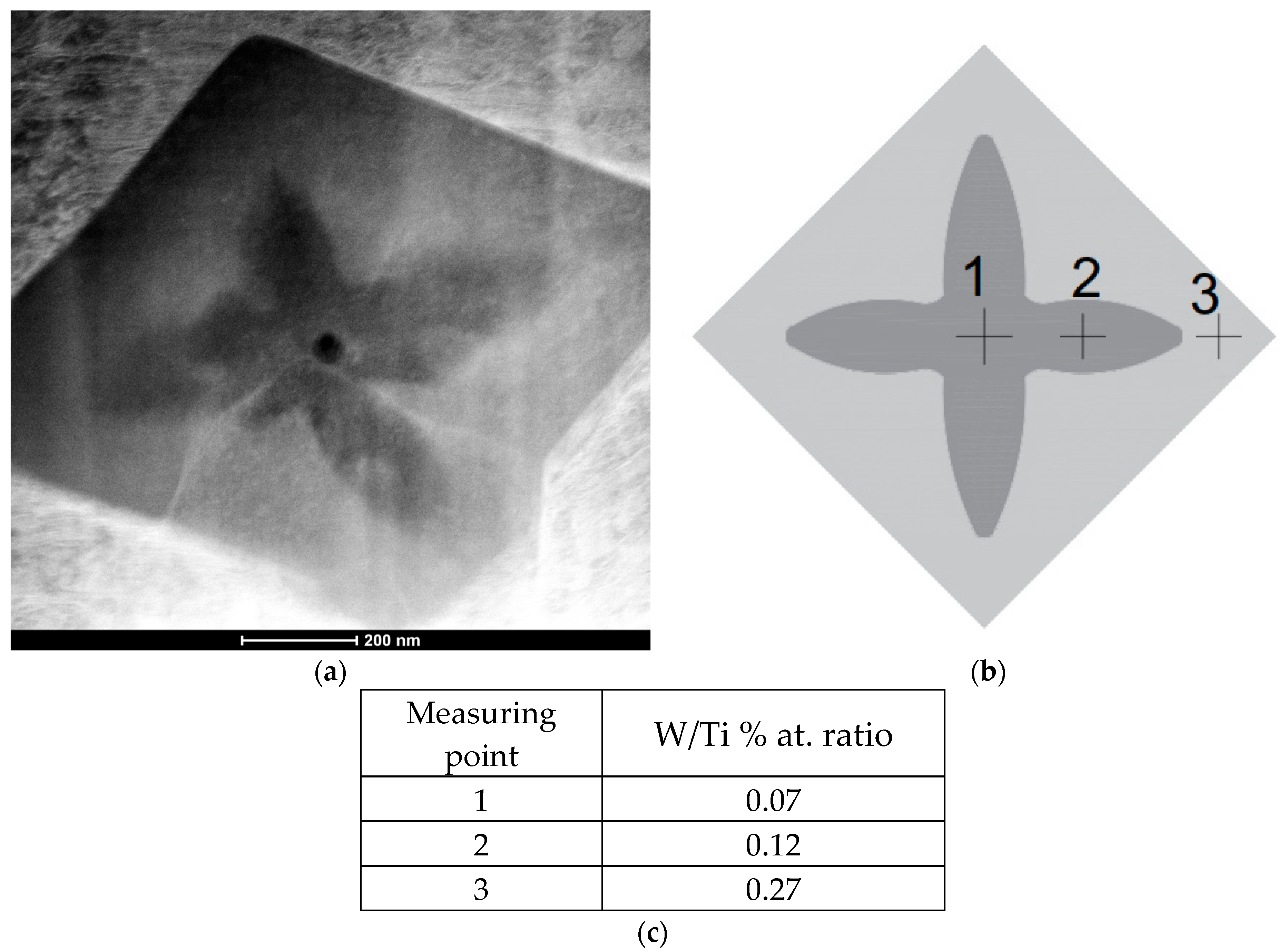
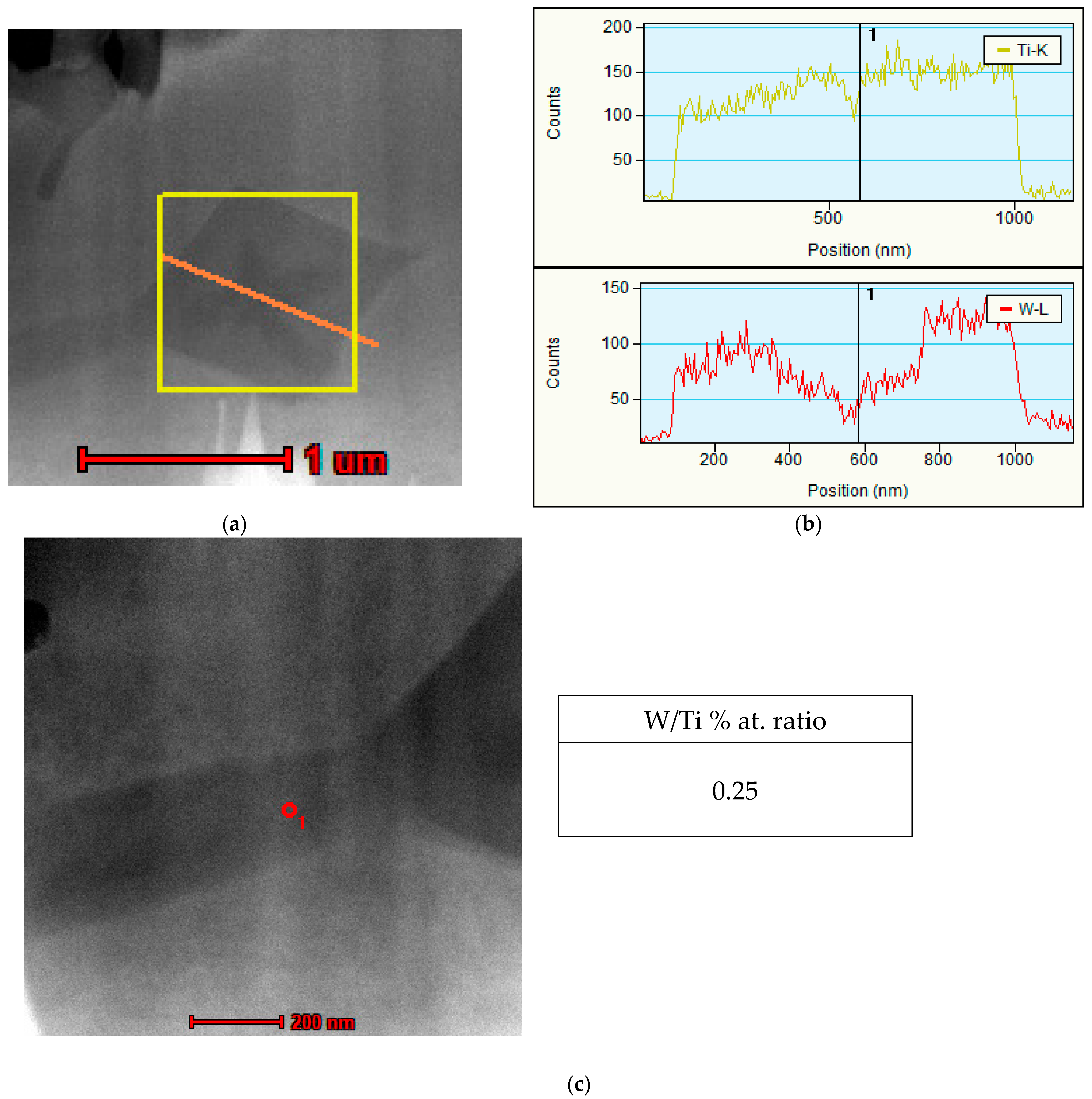


| Sample Designation | C | Co | Cr | Fe | Mn | Mo | Ni | Si | W | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 1.1 | balance | 27.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 4.4 | - |
| M6Ti | 1.1 | balance | 26.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 4.2 | 4.0 |
| M6TiCW | 3.0 | balance | 24.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 5.9 | 8.0 |
| Sample Designation | Width (mm) | Height (mm) | Cross-Sectional Area of the Melted Substrate (mm2) | Cross-Sectional Area of the Coating Buildup (mm2) | Cross-Sectional Area (mm2) | Dilution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 12.0 ± 0.1 | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 9.12 ± 0.12 | 9.27 ± 0.17 | 1.6 |
| M6Ti | 12.1 ± 0.1 | 0.96 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.10 | 9.52 ± 0.15 | 9.93 ± 0.25 | 4.2 |
| M6TiCW | 12.6 ± 0.2 | 1.01 ± 0.03 | 1.39 ± 0.12 | 9.73 ± 0.15 | 11.12 ± 0.27 | 12.5 |
| Sample Designation (Acc. to Table 1) | Average Volume Fraction of Primary (Ti,W)C Carbides [%] | Average Volume Fraction of Eutectic (Ti,W)C Carbides [%] | Average Volume Fraction of Co-Based Solid Solution [%] | Average Volume Fraction of Eutectic Consisting of M7C3/M23C6 Carbides [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | - | - | 65.3 ± 0.7 | 34.7 ± 0.7 |
| M6Ti | 8.0 ± 1.0 | 5.3 ± 1.0 | 86.1 ± 1.7 | 0.6 ± 0.3 |
| M6TiCW | 12.2 ± 0.3 | 6.1 ± 0.5 | 81.7 ± 0.7 | - |
| Sample Designation (Acc. to Table 1) | Average Erosion Rate [mg/min] | Average Erosion Value [mm3/g] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impingement Angle | 30° | 90° | 30° | 90° |
| M6 | 0.020 ± 0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.25 ± 0.02 |
| M6Ti | 0.026 ± 0.002 | 0.011 ± 0.002 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 0.18 ± 0.02 |
| M6TiCW | 0.013 ± 0.002 | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Górka, J.; Poloczek, T.; Janicki, D.; Lont, A. Shaping the Structure and Properties of Stellite 6 Alloy by Addition of Ti and W via Laser Cladding. Materials 2025, 18, 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173968
Górka J, Poloczek T, Janicki D, Lont A. Shaping the Structure and Properties of Stellite 6 Alloy by Addition of Ti and W via Laser Cladding. Materials. 2025; 18(17):3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173968
Chicago/Turabian StyleGórka, Jacek, Tomasz Poloczek, Damian Janicki, and Aleksandra Lont. 2025. "Shaping the Structure and Properties of Stellite 6 Alloy by Addition of Ti and W via Laser Cladding" Materials 18, no. 17: 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173968
APA StyleGórka, J., Poloczek, T., Janicki, D., & Lont, A. (2025). Shaping the Structure and Properties of Stellite 6 Alloy by Addition of Ti and W via Laser Cladding. Materials, 18(17), 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173968








