Effect of Metal Ions on the Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Mechanical Properties of Alginate/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
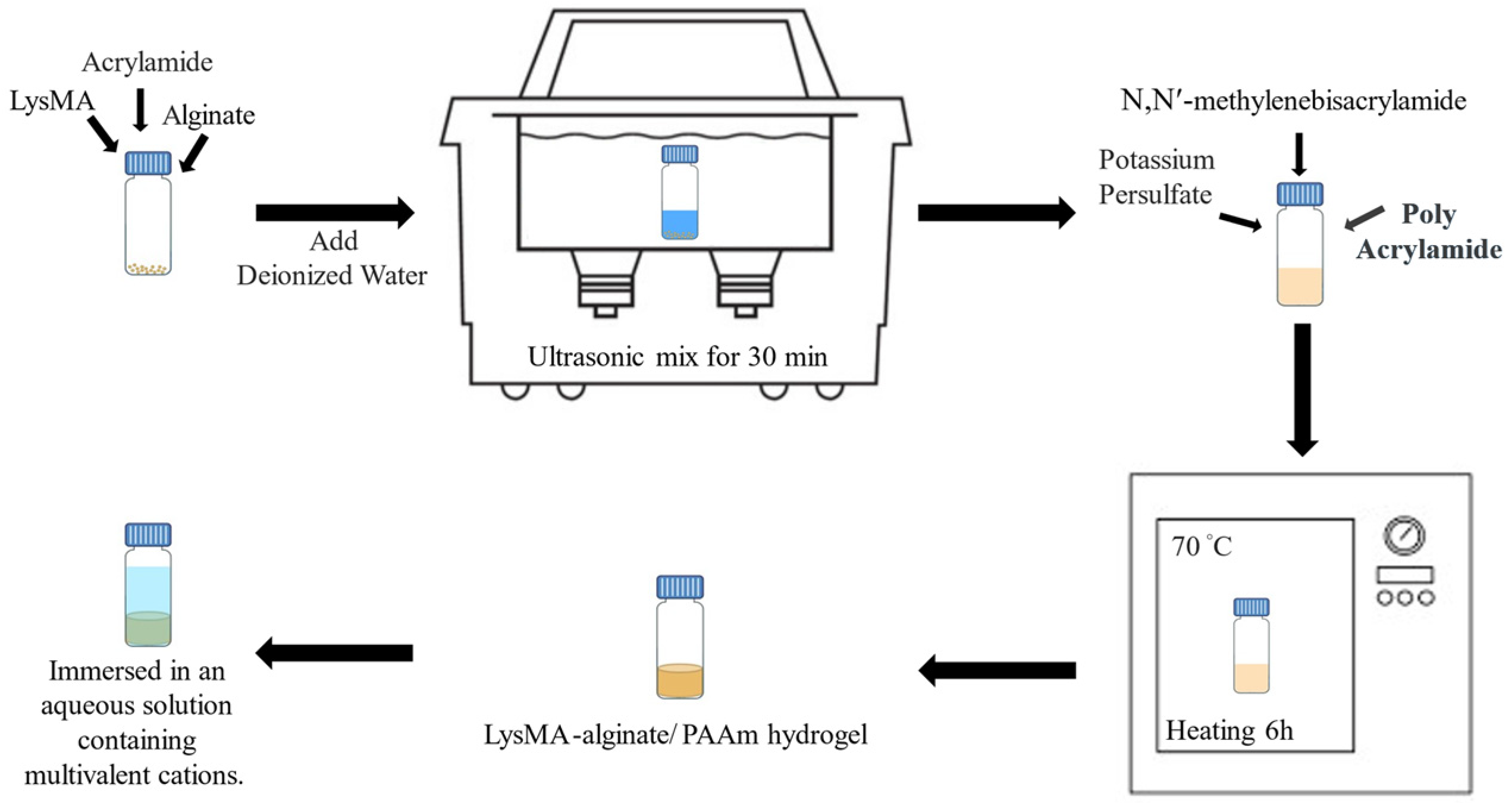
2.2. Composite Hydrogel (CH) Preparation Protocol
2.3. Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Fabrication of Composite Hydrogels
3.2. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties of Composite Hydrogels
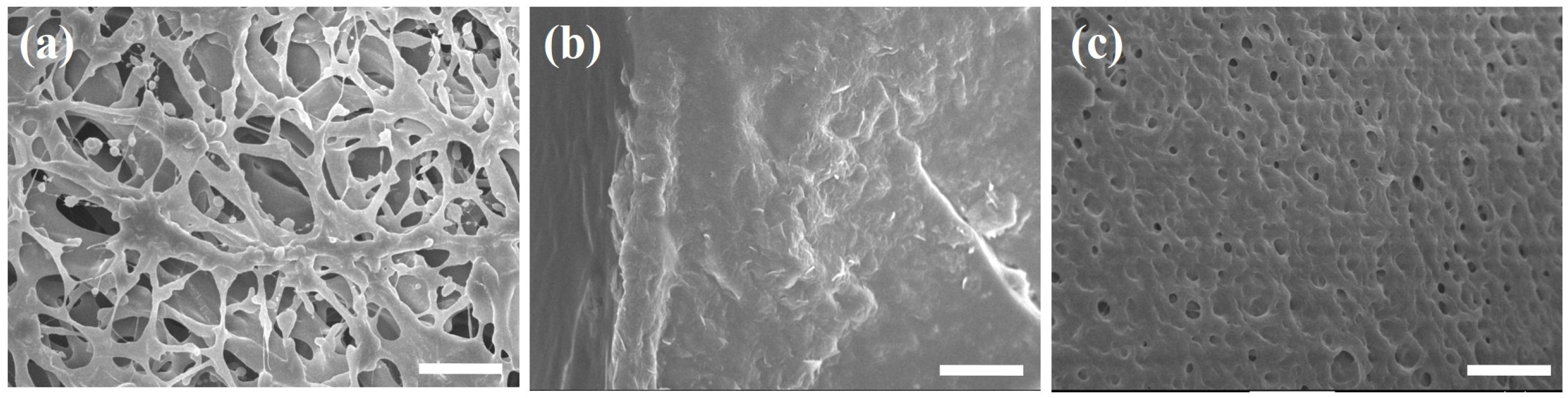
3.3. Microstructural Analysis of Composite Hydrogels
3.4. Testing of Composite Hydrogel Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAAM | Polyacrylamide |
| CH | Composite hydrogels |
| AAM | Acrylamide |
| LysMA | Methacrylated lysine |
| MBAA | N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide |
| G′ | Storage modulus |
| G″ | Loss modulus |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy |
References
- Trinadha Rao, M.; Chvs, P.; Yamini, M.; Prasad, C. Hydrogels the Three Dimensional Networks: A Review. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. 2021, 13, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Hydrogels: A review on their versatile applications for efficient and stable oil–water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 6919–6953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madduma-Bandarage, U.S.K.; Madihally, S.V. Synthetic hydrogels: Synthesis, novel trends, and applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lao, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogels for Flexible Electronics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 9681–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Chaturvedi, P.; Llamas-Garro, I.; Velázquez-González, J.S.; Dubey, R.; Mishra, S.K. Smart materials for flexible electronics and devices: Hydrogel. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12984–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöller, K.; To, D.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Biomedical applications of functional hydrogels: Innovative developments, relevant clinical trials and advanced products. Biomaterials 2025, 312, 122718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revete, A.; Aparicio, A.; Cisterna, B.A.; Revete, J.; Luis, L.; Ibarra, E.; Segura González, E.A.; Molino, J.; Reginensi, D. Advancements in the Use of Hydrogels for Regenerative Medicine: Properties and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biomater. 2022, 2022, 3606765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Stojanović, G.M.; Abdullah, M.F.B.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Marei, H.E.; Ashammakhi, N.; Hasan, A. Fundamental properties of smart hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buwalda, S.J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for Therapeutic Delivery: Current Developments and Future Directions. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesharwani, P.; Bisht, A.; Alexander, A.; Dave, V.; Sharma, S. Biomedical applications of hydrogels in drug delivery system: An update. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Ren, J. Polypyrrole-doped conductive self-healing multifunctional composite hydrogels with a dual crosslinked network. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 8363–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Ren, Z.; Liu, X.; Ling, Q.; Li, Z.; Gu, H. A Multifunctional, Self-Healing, Self-Adhesive, and Conductive Sodium Alginate/Poly(vinyl alcohol) Composite Hydrogel as a Flexible Strain Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 11344–11355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Preparation schemes and applications of multifunctional PVA composite hydrogels. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 508, 160946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Liu, T.; Jiang, Y.; He, B.; Hao, H. Multifunctional hydrogel sensor with Tough, self-healing capabilities and highly sensitive for motion monitoring and wound healing. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 497, 154890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Sawut, A.; Simayi, R.; Abudiwayiti, A. Preparation and Performance of Multifunctional Composite Hydrogel Based on Xanthate Lignin/Chitosan/Poly(acrylic acid) with Underwater Adhesion and Sensing Properties. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 14726–14739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.; Gutti, P.; Behera, B.; Mishra, D. Anionic species from multivalent metal salts are differentially retained during aqueous ionic gelation of sodium alginate and could fine-tune the hydrogel properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malektaj, H.; Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Mechanical Properties of Alginate Hydrogels Cross-Linked with Multivalent Cations. Polymers 2023, 15, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, J.; Han, S. The synthesis and characteristics of sodium alginate/graphene oxide composite films crosslinked with multivalent cations. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinelli, N.; Sabando, C.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S.; Bouza, R.; Castaño, J.; Valverde, J.C.; Rubilar, R.; Frizzo, M.; Recio-Sánchez, G. Sodium alginate-g-polyacrylamide hydrogel for water retention and plant growth promotion in water-deficient soils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos-Terrones, Y.A. A Review of the Strategic Use of Sodium Alginate Polymer in the Immobilization of Microorganisms for Water Recycling. Polymers 2024, 16, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, P.; Upadhyay, T.K.; Alshammari, N.; Saeed, M.; Kesari, K. Alginate-Chitosan Biodegradable and Biocompatible Based Hydrogel for Breast Cancer Immunotherapy and Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 3515–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Tan, H. Alginate-Based Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 1285–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Guo, W.; He, S.; Liu, W. Alginate-based hydrogels mediated biomedical applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyen, N.T.T.; Hamid, Z.A.A.; Tram, N.X.T.; Ahmad, N. Fabrication of alginate microspheres for drug delivery: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Ao, Q. Preparation of Alginate-Based Biomaterials and Their Applications in Biomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, K.; An, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Recent Development of Alginate-Based Materials and Their Versatile Functions in Biomedicine, Flexible Electronics, and Environmental Uses. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1302–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metha, C.; Pawar, S.; Suvarna, V. Recent advancements in alginate-based films for active food packaging applications. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 1246–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournaki, S.K.; Aleman, R.S.; Hasani-Azhdari, M.; Marcia, J.; Yadav, A.; Moncada, M. Current Review: Alginate in the Food Applications. J 2024, 7, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanisaadi, M.; Kennedy, J.F.; Rabiei, A.; Riseh, R.S.; Taheri, A. Nature’s coatings: Sodium alginate as a novel coating in safeguarding plants from frost damages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, A.; Dardari, O.; Metomo, F.N.N.N.; Essamlali, Y.; Akil, A.; Amadine, O.; Aboulhrouz, S.; Zahouily, M. Effect of sodium alginate-based superabsorbent hydrogel on tomato growth under different water deficit conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, K.; Zhang, X.; Teng, M.; Huang, Z. Integrated Instillation Technology for the Synthesis of a pH-Responsive Sodium Alginate/Biomass Charcoal Soil Conditioner for Controlled Release of Humic Acid and Soil Remediation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13386–13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milos, F.; del Campo, A. Polyacrylamide Hydrogels as Versatile Biomimetic Platforms to Study Cell-Materials Interactions. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2400404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.; Hwang, H.; Fontenot, J.F.; Lee, C.; Jung, J.P.; Kim, M. Tailoring Physical Properties of Dual-Network Acrylamide Hydrogel Composites by Engineering Molecular Structures of the Cross-linked Network. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 30028–30039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Qiao, Z.; Dou, B.; Xu, H.; Meng, F.; Huang, J. Polyacrylamide-Based Hydrogel with Biocompatibility and Tunable Stiffness for Three-Dimensional Cell Culture. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhman, D.; Batyrbekuly, D.; Myrzakhmetov, B.; Zhumagali, K.; Issabek, K.; Sultan-Akhmetov, O.; Umirov, N.; Konarov, A.; Bakenov, Z. Polyacrylamide-based hydrogel electrolyte for modulating water activity in aqueous hybrid batteries. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 40222–40233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Manna, S.; Roy, S.; Nandi, S.K.; Basak, P. Polymeric biomaterials-based tissue engineering for wound healing: A systemic review. Burn. Trauma 2023, 11, tkac058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.-L.; Guo, F.-L.; Li, Y.-Q.; Wang, D.-Y.; Huang, P.; Fu, S.-Y. Polyacrylamide Hydrogel Composite E-skin Fully Mimicking Human Skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 32084–32093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Wadhwa, R.; Rishi, M.; Kalra, J.; Teja, A.; Bhatia, D.D.; Gupta, D. High-Performance Polyacrylamide Hydrogel-Based Wearable Sensors for Electrocardiography Monitoring and Motion Sensing. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2025, 7, 4025–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, R.; Xiao, L.; Iqbal, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; et al. Flexible Bicolorimetric Polyacrylamide/Chitosan Hydrogels for Smart Real-Time Monitoring and Promotion of Wound Healing. Adv. Func. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosiak, J.; Burozak, K.; Pȩkala, W. Polyacrylamide hydrogels as sustained release drug delivery dressing materials. Radiat. Phys. Chem. (1977) 1983, 22, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Liu, J.; Huo, P.; Ding, R.; Shen, X.; Mao, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.L. Ultra-stretchable and conductive polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan composite hydrogels with low modulus and fast self-recoverability as flexible strain sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Fan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, G. A Mechanically strong and Highly Conductive MXene/Polyacrylamide–alginate Composite Hydrogel with Double-network Structure for Flexible Wearable Sensor. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 9283–9294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Ma, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, J. A polyacrylamide/gelatin/tannic acid-modified carbon nanotube double network hydrogel with skin temperature-triggered adhesion and high sensitivity for wearable sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 14330–14342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liang, S.; Tang, X.-Z.; Yan, D.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.-Z. Tough and highly stretchable graphene oxide/polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14160–14167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-K.; Chen, P.-W.; Wang, H.-J.; Yeh, M.-Y. Alkyl Chain Length Effects of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids on Electrical and Mechanical Performances of Polyacrylamide/Alginate-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2021, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.S.; Islam, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Zaman, A.; Ahmed, T.; Biswas, S.; Sharmeen, S.; Rashid, T.U.; Rahman, M.M. Morphological Characterization of Hydrogels. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Mondal, M.I.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 819–863. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-J.; Chu, Y.-Z.; Chen, C.-K.; Liao, Y.-S.; Yeh, M.-Y. Preparation of conductive self-healing hydrogels via an interpenetrating polymer network method. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 6620–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, H.; Song, Z.; Yu, D.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, W. Progress in Research on Metal Ion Crosslinking Alginate-Based Gels. Gels 2025, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajighasem, A.; Kabiri, K. Cationic highly alcohol-swellable gels: Synthesis and characterization. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, L.; Yue, S.; Jia, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, D. Electrolytes for Aluminum-Ion Batteries: Progress and Outlook. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202402017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Eshaq, G.; Winkler, M.K.H.; Pihlajamäki, A. Magnetic biochar aluminum cross-linked composite beads for preferential phosphate separation from phosphate-rich effluents. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barltrop, J.A.; Owen, T.C.; Cory, A.H.; Cory, J.G. 5-(3-Carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4,5-Dimethylthiazolyl)-3-(4-Sulfophenyl)Tetrazolium, Inner Salt (MTS) and Related Analogs of 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazolyl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Reducing to Purple Water-Soluble Formazans as Cell-Viability Indicators. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1991, 1, 611–614. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices-Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Massana Roquero, D.; Othman, A.; Melman, A.; Katz, E. Iron(iii)-cross-linked alginate hydrogels: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1849–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Transparent and conductive amino acid-tackified hydrogels as wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Hydrogel | Tensile Strength (kPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | G′ (Pa) | G″ (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 823.7 ± 2.9 | 123.5 ± 2.8 | 95.8 ± 1.7 |
| CH-Al | 1.61 ± 0.04 | 412.9 ± 3.4 | 642.7 ± 4.5 | 248.1 ± 2.0 |
| CH-Fe | 2.03 ± 0.06 | 306.4 ± 2.1 | 1681.6 ± 10.2 | 534.7 ± 3.1 |
| Hydrogel | Rct (Ω) | Resistivity (Ω Cm) | Conductivity (μS/cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 39.91 ± 3.21 | 4989 ± 85 | 200.4 ± 12.9 |
| CH-Al | 12.40 ± 1.02 | 1550 ± 26 | 645.2 ± 31.0 |
| CH-Fe | 31.42 ± 5.10 | 3927 ± 102 | 254.7 ± 10.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.-K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chakravarthy, R.D.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Yeh, M.-Y. Effect of Metal Ions on the Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Mechanical Properties of Alginate/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels. Materials 2025, 18, 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163871
Chen C-K, Lin C-Y, Chakravarthy RD, Chen Y-H, Chen C-Y, Lin H-C, Yeh M-Y. Effect of Metal Ions on the Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Mechanical Properties of Alginate/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163871
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Chen-Kang, Chien-Yin Lin, Rajan Deepan Chakravarthy, Yu-Hsu Chen, Chieh-Yi Chen, Hsin-Chieh Lin, and Mei-Yu Yeh. 2025. "Effect of Metal Ions on the Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Mechanical Properties of Alginate/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels" Materials 18, no. 16: 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163871
APA StyleChen, C.-K., Lin, C.-Y., Chakravarthy, R. D., Chen, Y.-H., Chen, C.-Y., Lin, H.-C., & Yeh, M.-Y. (2025). Effect of Metal Ions on the Conductivity, Self-Healing, and Mechanical Properties of Alginate/Polyacrylamide Hydrogels. Materials, 18(16), 3871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163871








