Evaluation of Printability, Color Difference, Translucency, and Surface Roughness over Time in a 3D-Printed TiO2-Containing Denture Base Resin: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of TiO2-Modified Denture Base Resin
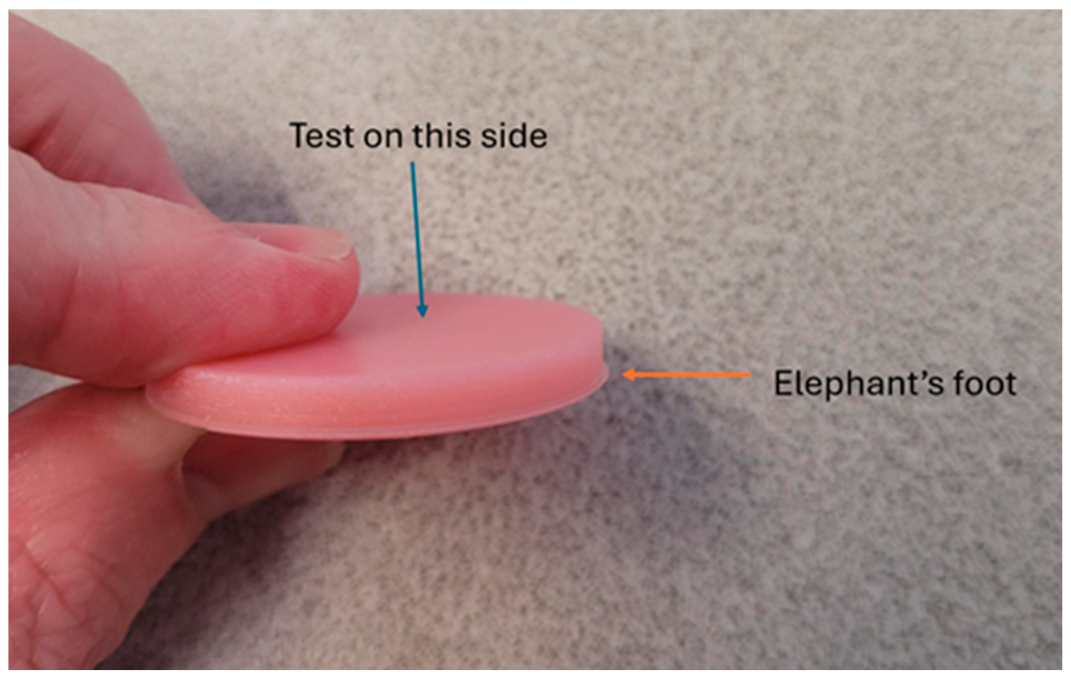
2.2. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.3. Color and Translucency Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Printability of TiO2-Modified Denture Base Resin
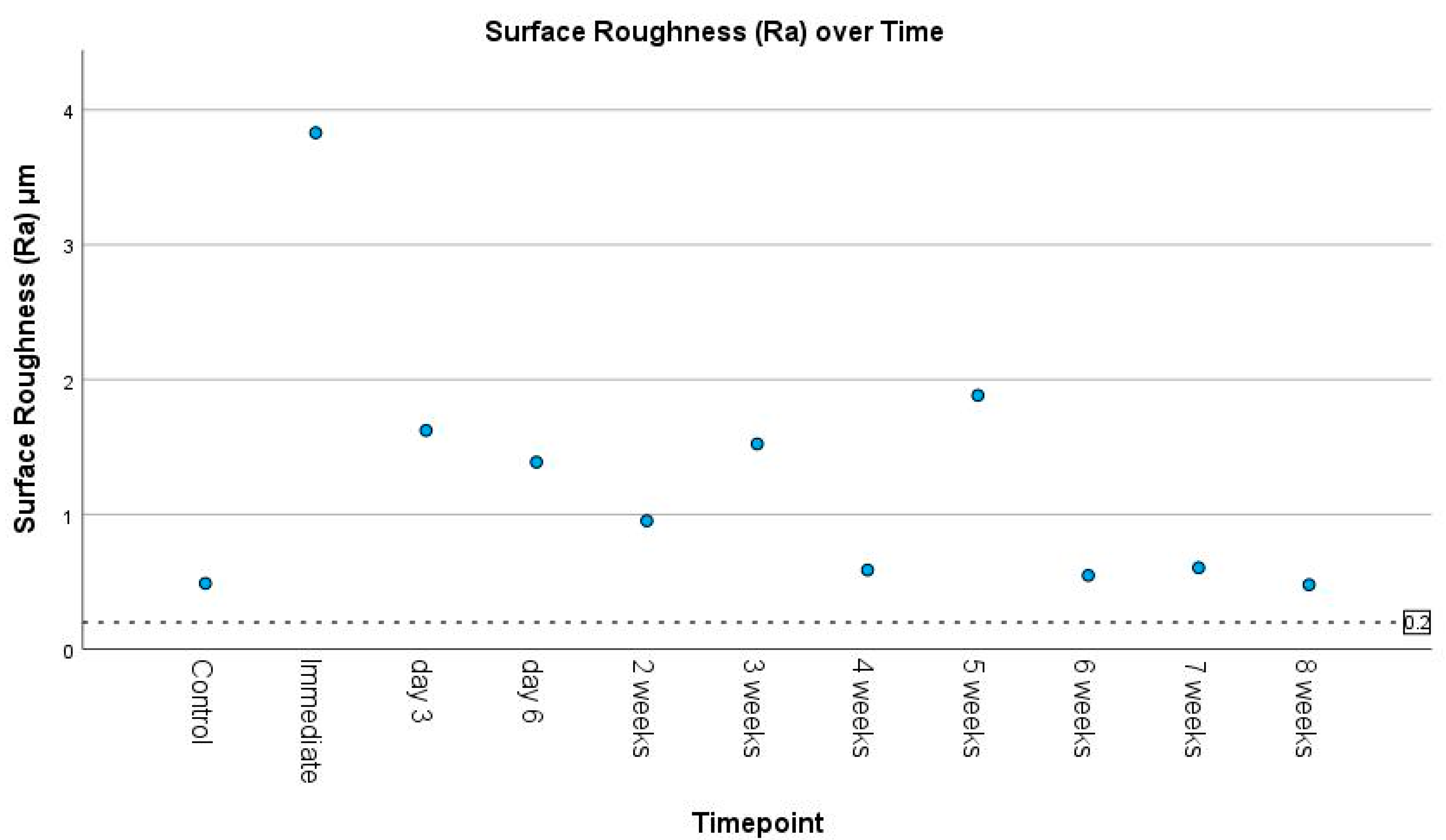
3.2. Surface Roughness
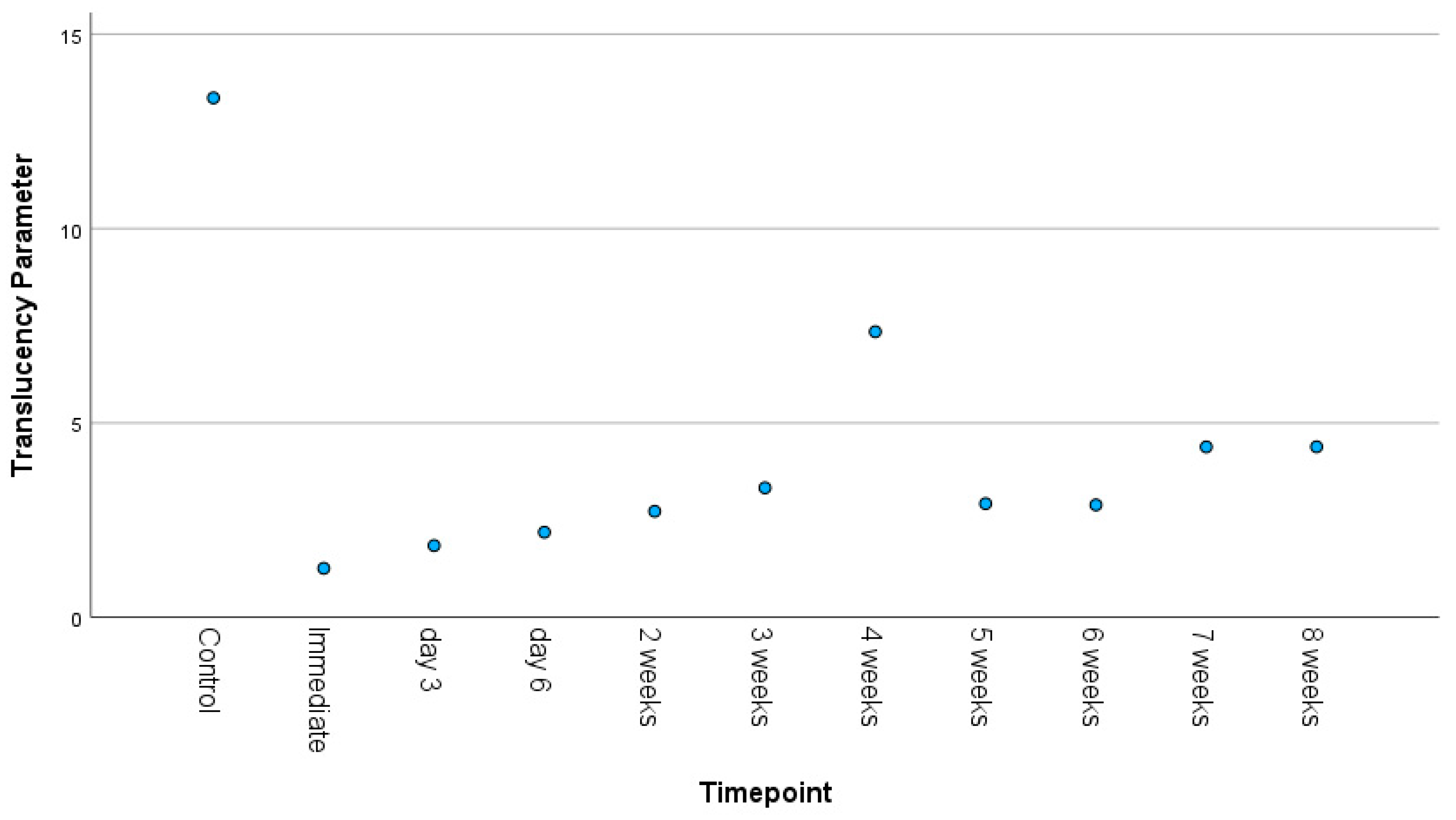
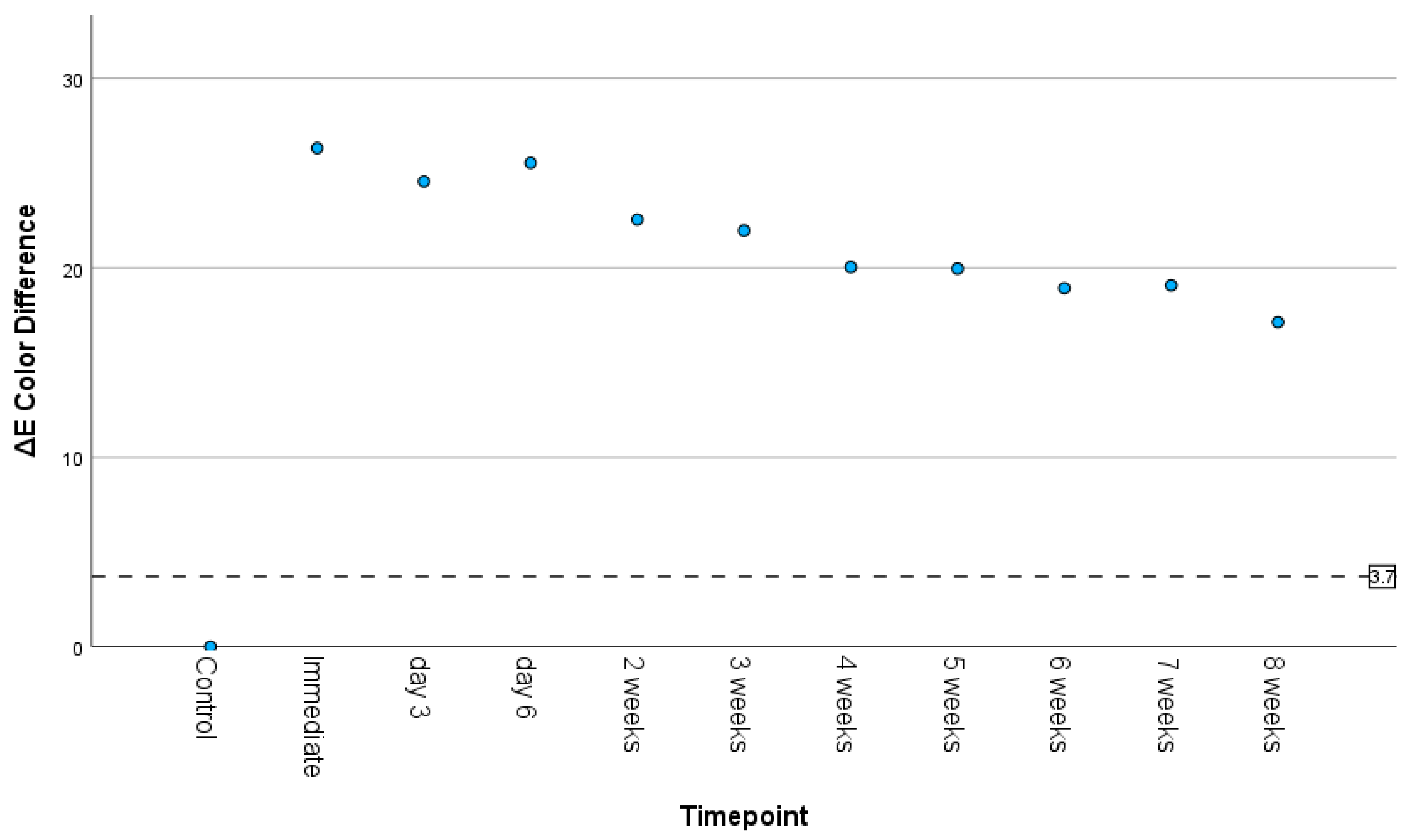
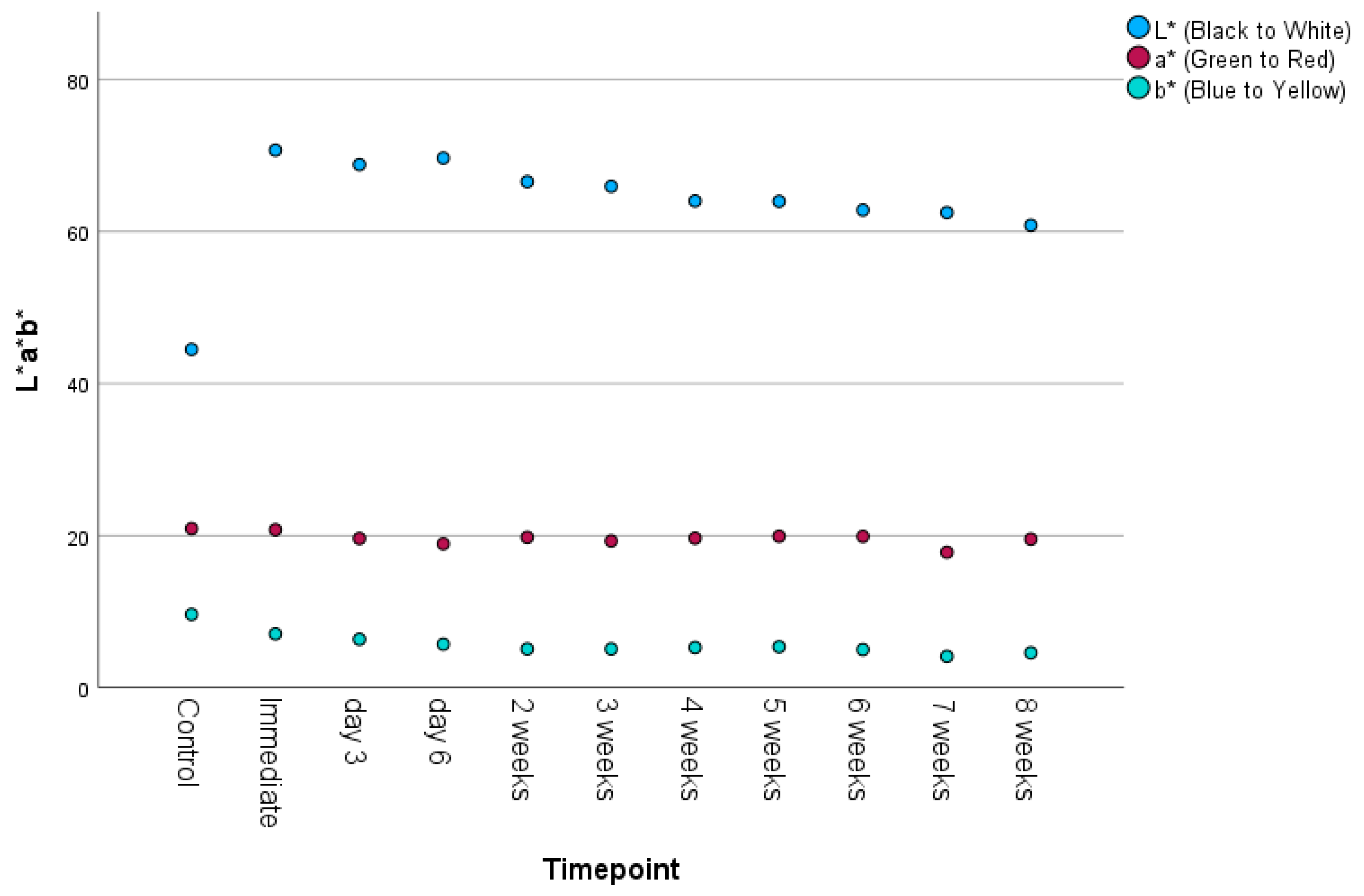
3.3. Color Difference and Translucency
3.4. Correlations Between Timepoint and Surface Roughness, Color Difference, and Translucency
3.5. Correlations Between Surface Roughness and Color Difference, and Translucency
3.6. Limitations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- TiO2 additions to a denture polymer produced significant changes in surface roughness and color that were not clinically acceptable.
- Although printability of the resin–TiO2 mixture was maintained for 7 weeks, mixture homogeneity is questioned.
- Dentures printed with TiO2 nanoparticles may require two-stage printing and a coating application.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| SLA | Stereolithography |
| Ra | Roughness Average |
| STL | Standard Tessellation Language |
| CIE Lab* | Commission Internationale de l’Éclairage color space |
References
- Dye, B.; Thornton-Evans, G.; Li, X.; Iafolla, T. Dental caries and tooth loss in adults in the United States, 2011–2012. NCHS Data Brief 2015, 2015, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; He, J.; He, H.; Yuan, X.; Su, X.; Zeng, X. Long-term trends in the burden of edentulism in China over three decades: A Joinpoint regression and age-period-cohort analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2019. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1099194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, E.; de Souza, R.F.; Kabawat, M.; Feine, J.S. The impact of edentulism on oral and general health. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013, 498305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandinejad, A.; Floriani, F.; Lin, W.S.; Naimi-Akbar, A. Clinical outcomes of milled, 3D-printed, and conventional complete dentures in edentulous patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. 2024, 33, 736–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, B.J. 3D Printing of Complete Dentures: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2024, 37, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nett, J.E.; Marchillo, K.; Spiegel, C.A.; Andes, D.R. Development and validation of an in vivo Candida albicans biofilm denture model. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3650–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannah, V.E.; O’Donnell, L.; Robertson, D.; Ramage, G. Denture Stomatitis: Causes, Cures and Prevention. Prim. Dent. J. 2017, 6, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iinuma, T.; Arai, Y.; Abe, Y.; Takayama, M.; Fukumoto, M.; Fukui, Y.; Iwase, T.; Takebayashi, T.; Hirose, N.; Gionhaku, N.; et al. Denture wearing during sleep doubles the risk of pneumonia in the very elderly. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 28s–36s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, D.R.; Gorup, L.F.; Takamiya, A.S.; de Camargo, E.R.; Filho, A.C.; Barbosa, D.B. Silver distribution and release from an antimicrobial denture base resin containing silver colloidal nanoparticles. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 21, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Neto, F.N.d.; Sala, R.L.; Fernandes, R.A.; Oliveira Xavier, T.P.; Cruz, S.A.; Paranhos, C.M.; Monteiro, D.R.; Barbosa, D.B.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Camargo, E.R.d. Effect of synthetic colloidal nanoparticles in acrylic resin of dental use. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaee, M.Z.; Akhavan, A.; Sheikh, N.; Sodagar, A. Antibacterial effects of a new dental acrylic resin containing silver nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, S.; Nedel, F.; de Carvalho, R.V.; Lund, R.G.; Cenci, M.S.; Pereira-Cenci, T.; Demarco, F.F.; Piva, E. Characterization of an antimicrobial dental resin adhesive containing zinc methacrylate. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Chu, L.; Rawls, H.R.; Norling, B.K.; Cardenas, H.L.; Whang, K. Development of an antimicrobial resin—A pilot study. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Evans, J.L.; Hamlet, S.; Love, R.M. Incorporation of antimicrobial agents in denture base resin: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyth, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Baraness-Hadar, L.; Yudovin-Farber, I.; Domb, A.J.; Weiss, E.I. Surface antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of incorporated polyethylenimine nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4157–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Jo, Y.H.; Yoon, H.I.; Han, J.S. Antifungal effect, surface roughness, and cytotoxicity of three-dimensionally printed denture base with phytoncide-filled microcapsules: An in-vitro study. J. Dent. 2022, 120, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Mangal, U.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, M.J.; Jin, J.; Yu, J.H.; Choi, S.H. Durable Oral Biofilm Resistance of 3D-Printed Dental Base Polymers Containing Zwitterionic Materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totu, E.E.; Nechifor, A.C.; Nechifor, G.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Cristache, C.M. Poly(methyl methacrylate) with TiO2 nanoparticles inclusion for stereolitographic complete denture manufacturing—The fututre in dental care for elderly edentulous patients? J. Dent. 2017, 59, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taormina, G.; Sciancalepore, C.; Bondioli, F.; Messori, M. Special Resins for Stereolithography: In Situ Generation of Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2018, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-G.; Yang, J.; Jia, Y.-G.; Lu, B.; Ren, L. TiO2 and PEEK Reinforced 3D Printing PMMA Composite Resin for Dental Denture Base Applications. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaikh, A.A.; Khattar, A.; Almindil, I.A.; Alsaif, M.H.; Akhtar, S.; Khan, S.Q.; Gad, M.M. 3D-Printed Nanocomposite Denture-Base Resins: Effect of ZrO2 Nanoparticles on the Mechanical and Surface Properties In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristache, C.M.; Totu, E.E.; Iorgulescu, G.; Pantazi, A.; Dorobantu, D.; Nechifor, A.C.; Isildak, I.; Burlibasa, M.; Nechifor, G.; Enachescu, M. Eighteen Months Follow-Up with Patient-Centered Outcomes Assessment of Complete Dentures Manufactured Using a Hybrid Nanocomposite and Additive CAD/CAM Protocol. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Barrera, L.; Chu, L.; Whang, K. Development of an antimicrobial, 3D printable denture base material with K18 quaternary ammonium silane-functionalized methyl methacrylate and filler. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2024, 131, 1251.e1251–1251.e1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarazi, A.; Jadaan, L.; McBain, A.J.; Haider, J.; Kushnerev, E.; Yates, J.M.; Alhotan, A.; Silikas, N.; Devlin, H. 3D-printed nanocomposite denture base resin: The effect of incorporating TiO2 nanoparticles on the growth of Candida albicans. J. Prosthodont. 2024, 33, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaurani, P.; Hindocha, A.D.; Jayasinghe, R.M.; Pai, U.Y.; Batra, K.; Price, C. Effect of addition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the antimicrobial properties, surface roughness and surface hardness of polymethyl methacrylate: A Systematic Review. F1000Research 2023, 12, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zguris, Z. How mechanical properties of stereolithography 3D prints are affected by UV curing. In Formlabs White Paper; Formlabs Inc.: Somerville, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- ISO EN. 4287; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)–Surface Texture: Profile Method–Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997.
- ISO D. TR 28642: 2016; Dentistry—Guidance on Colour Measurement. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Johnston, W.M.; Ma, T.; Kienle, B.H. Translucency parameter of colorants for maxillofacial prostheses. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1995, 8, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Khashayar, G.; Bain, P.A.; Salari, S.; Dozic, A.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Feilzer, A.J. Perceptibility and acceptability thresholds for colour differences in dentistry. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollenl, C.M.L.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer Fernandez, P.; Unkovskiy, A.; Benkendorff, V.; Klink, A.; Spintzyk, S. Surface Characteristics of Milled and 3D Printed Denture Base Materials Following Polishing and Coating: An In-Vitro Study. Materials 2020, 13, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.M.; Fouda, S.M.; Abualsaud, R.; Alshahrani, F.A.; Al-Thobity, A.M.; Khan, S.Q.; Akhtar, S.; Ateeq, I.S.; Helal, M.A.; Al-Harbi, F.A. Strength and Surface Properties of a 3D-Printed Denture Base Polymer. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 31, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.N.; Alsahafi, T.; Clark, W.A.; Felton, D.; Sulaiman, T.A. Evaluation of surface roughness of differently manufactured denture base materials. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025, 133, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raszewski, Z.; Chojnacka, K.; Mikulewicz, M. Effects of Surface Preparation Methods on the Color Stability of 3D-Printed Dental Restorations. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzade, Z.; Alihemmati, M.; Hakimaneh, S.M.R.; Shayegh, S.S.; Bafandeh, M.A.; Mohammadi, Z. Comparison of Color Stability and Surface Roughness of Interim Crowns Fabricated by Conventional, Milling and 3D Printing Methods. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2025, 11, e70119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Kim, J.-E.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Ryu, J.J. Printing accuracy, mechanical properties, surface characteristics, and microbial adhesion of 3D-printed resins with various printing orientations. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2020, 124, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhamdi, M.A.; Fouda, S.M.; Al-Dulaijan, Y.A.; Khan, S.Q.; El Zayat, M.; Al Munif, R.; Albazroun, Z.; Amer, F.H.; Al Ammary, A.T.; Mahrous, A.A.; et al. Nanocomposite 3D printed resins containing titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles: An in vitro analysis of color, hardness, and surface roughness properties. Front. Dent. Med. 2025, 6, 1581461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Descriptive Statistics | N | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness (Ra, μm) | 11 | 0.479 | 3.83 | 1.264 | 0.995 |
| Translucency Parameter | 11 | 1.26 | 13.36 | 4.242 | 3.439 |
| ΔEab Color Difference | 11 | 0 | 26.32 | 19.640 | 7.145 |
| SCI L* | 11 | 44.5 | 70.69 | 63.658 | 7.091 |
| SCI a* | 11 | 17.81 | 20.92 | 19.646 | 0.840 |
| SCI b* | 11 | 4.12 | 9.64 | 5.76 | 1.518 |
| Correlation to Timepoint | Spearman’s ρ | Significance (2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness | −0.733 | 0.016 * |
| Translucency Parameter | 0.806 | 0.005 * |
| ΔEab color shift | −0.976 | <0.001 * |
| SCI L* | −0.988 | <0.001 * |
| SCI a* | −0.261 | 0.467 |
| SCI b* | −0.875 | <0.001 * |
| Correlation to Roughness | Spearman’s ρ | Significance (2-Tailed) |
|---|---|---|
| Translucency Parameter | −0.727 | 0.011 * |
| ΔEab color shift | 0.791 | 0.004 * |
| SCI L* | 0.773 | 0.005 * |
| SCI a* | 0.073 | 0.832 |
| SCI b* | 0.419 | 0.199 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bennett, G.; Beatty, M.W.; Simetich, B. Evaluation of Printability, Color Difference, Translucency, and Surface Roughness over Time in a 3D-Printed TiO2-Containing Denture Base Resin: A Pilot Study. Materials 2025, 18, 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153683
Bennett G, Beatty MW, Simetich B. Evaluation of Printability, Color Difference, Translucency, and Surface Roughness over Time in a 3D-Printed TiO2-Containing Denture Base Resin: A Pilot Study. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153683
Chicago/Turabian StyleBennett, Gregory, Mark W. Beatty, and Bobby Simetich. 2025. "Evaluation of Printability, Color Difference, Translucency, and Surface Roughness over Time in a 3D-Printed TiO2-Containing Denture Base Resin: A Pilot Study" Materials 18, no. 15: 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153683
APA StyleBennett, G., Beatty, M. W., & Simetich, B. (2025). Evaluation of Printability, Color Difference, Translucency, and Surface Roughness over Time in a 3D-Printed TiO2-Containing Denture Base Resin: A Pilot Study. Materials, 18(15), 3683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153683







