Shear Strength of Lightweight Concrete Structural Elements Reinforced with FRP Bars: Experimental Studies vs. Code Predictions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Review of Experimental Works
3. Review of Provision Documents
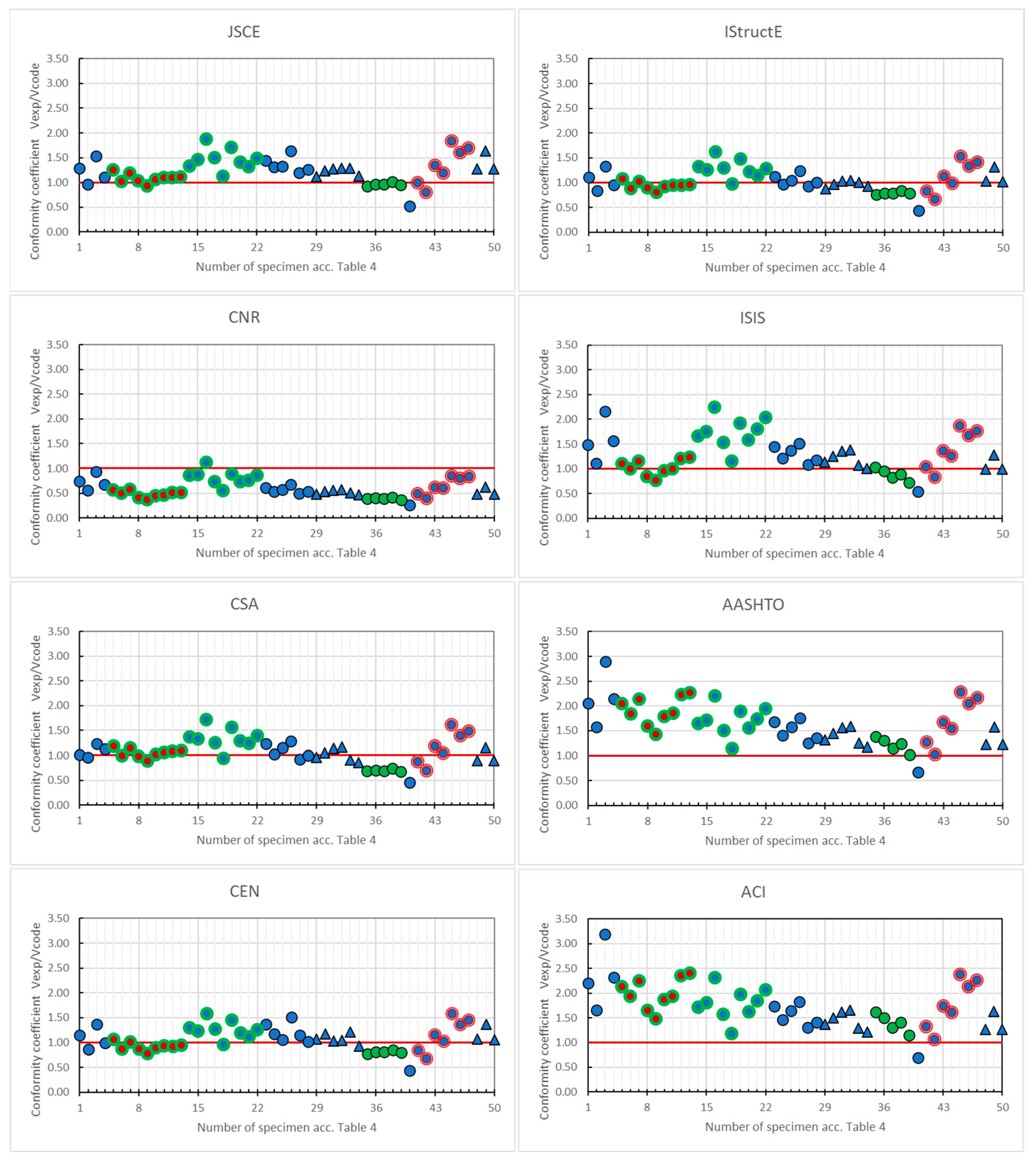
4. Code vs. Experiment–Comparison and Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Identifying the calculation procedures that best align with experimental results for lightweight concrete (LWC) and fibre-reinforced polymer (FRP) structural elements presents significant challenges. This complexity arises from the numerous research variables, each of which necessitates specific modifications to empirical calculation formulas.
- The analysis indicates that three procedures consistently demonstrate good compliance and the lowest variability: those outlined in the IStructE [30], CSA [33], and CEN [35] codes. In contrast, the procedures found in American codes, such as AASHTO [34] and ACI [36], tend to overestimate results significantly.
- Moreover, the findings suggest that adopting a single code procedure for the entire population of test results is more effective than modifying separate procedures for different lightweight concretes and FRP bars to enhance compliance.
- Among the analysed procedures, the most recent CEN [35] method aligns best with the experimental results related to the shear strength of FRP bar-reinforced lightweight concrete elements that lack stirrups. The conformity coefficient (Vexp/Vcode) for the CEN [35] procedure is very close to 1.0. Consequently, the authors did not propose a new formula, despite noting that none of the existing formulas is entirely adequate.
- One potential improvement to the CEN procedure is to assess how certain parameters (fc, ρf, Ef) affect the Vcode value. This evaluation could help achieve higher conformity coefficient values.
- Additionally, artificial neural networks (ANNs) could be utilised to enhance the procedure. However, the existing database of single test results for LWC/FRP elements, which currently contains only 50 entries, needs to be expanded.
- Moreover, it may be beneficial to use the database for NWC/FRP elements, which includes 326 entries collected from 1993 to 2016. This larger dataset could allow for adjustments, such as modifying the density of concrete.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FRP reinforcement ratio | |
| shear span | |
| maximum aggregate size | |
| width of cross-section | |
| distance from extreme compression fibre to centroid of tension reinforcement | |
| compressive strength of concrete | |
| tensile strength of concrete | |
| height of cross-section | |
| span length | |
| modulus of elasticity of concrete | |
| modulus of elasticity of FRP | |
| modulus of elasticity of steel | |
| bending moment due to the applied load | |
| shear force due to the applied load |
References
- Thienel, K.C.; Haller, T.; Beuntner, N. Lightweight concrete—From basics to innovations. Materials 2020, 13, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.X. Recent advances in high strength lightweight concrete: From development strategies to practical applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.L.; Spiesz, P.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Ultra-lightweight concrete: Conceptual design and performance evaluation. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2015, 61, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.E.; Kahn, L.F. Lightweight concrete reduces weight and increases span length of pretensioned concrete bridge girders. PCI J. 2002, 47, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, C.J.; Cousins, T.E.; Nassar, A.J.; Gomez, J.P. Demonstration of use of high-performance lightweight concrete in bridge superstructure in Virginia. J. Perform. Constr. Fac. 2005, 19, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwowski, T.W.; Rajchel, M. Structural performance of a hybrid FRP composite—Lightweight concrete bridge girder. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 2019, 174, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vives, I.; Varona, F.B.; Tenza-Abril, A.J.; Pereiro-Barceló, J. A parametric study to assess lightweight aggregate concrete for future sustainable construction of reinforced concrete beams. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Tan, K.H.; Dai, J.; Ang, K.K.; Nguyen, H.P. Behavior of concrete modular multi-purpose floating structures. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 229, 108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, Y.; Gupta, T.; Sharma, R.; Panwar, N.L.; Siddique, S. A comprehensive review on the performance of structural lightweight aggregate concrete for sustainable construction. Constr. Mater. 2021, 1, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.F.; Rehman, Z.; Kuruc, M.; Medve, I.; Bačinskas, D.; Čurpek, J.; Čekon, M.; Ijaz, N.; Ansari, W.S. Lightweight concrete from a perspective of sustainable reuse of waste byproducts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Chang, J.; Yang, J.; Ke, X.; Duan, Z. Life cycle sustainable assessment of natural vs artificial lightweight aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 367, 133064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Normal and high-strength lightweight self-compacting concrete incorporating perlite, scoria, and polystyrene aggregates at elevated temperatures. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifan, M.; Nagaratnam, B.; Thamboo, J.; Poologanathan, K.; Corradi, M. Development and prospectives of lightweight high strength concrete using lightweight aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiater, A.; Siwowski, T.W. Lightweight concrete bridge deck slabs reinforced with GFRP composite bars. Roads Bridges 2017, 16, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.A.; Anagreh, A.; Tošić, N.; Alkhabbaz, O.; Alshwaiki, M.E.; Černý, R. Structural performance of lightweight aggregate concrete reinforced by glass or basalt fiber reinforced polymer bars. Polymers 2022, 14, 2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Pantelides, C.P. Shear strength of GFRP reinforced precast lightweight concrete panels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengar, H.A.; Zarrinkolaei, F.A.; Bozorgnasab, M. Shear capacity of lightweight concrete beam reinforced with glass fiber-reinforced polymer bars. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehany, S.; Mohamed, H.M.; Benmokrane, B. Flexural strength and serviceability of GFRP-reinforced lightweight self-consolidating concrete beams. J. Compos. Constr. 2022, 26, 04022020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiater, A.; Siwowski, T. Serviceability and ultimate behaviour of GFRP reinforced lightweight concrete slabs: Experimental test versus code prediction. Compos. Struct. 2020, 239, 112020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiater, A.; Siwowski, T. Research on fatigue life of lightweight concrete bridge decks reinforced with GFRP composite rebars. Roads Bridges 2024, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, E.C.; Massam, L.; Collins, M.P. Shear strength of large concrete members with FRP reinforcement. J. Compos. Constr. 2010, 14, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Zareef, M.A.; Elbisy, M.S.; Badawi, M. Evaluation of code provisions predicting the concrete shear strength of FRP-reinforced members without shear reinforcement. Compos. Struct. 2021, 275, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghandour, B.; Eltahawy, R.; Shedid, M.; Abdelrahman, A. Prediction of shear strength for CFRP reinforced concrete beams without stirrups. Eng. Struct. 2023, 284, 115946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.H.; Roh, Y.S.; Truong, G.T. Shear strength model of FRP-reinforced concrete beams without shear reinforcement. Structures 2024, 64, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Huckelbridge, A. Experimental analysis of crack growth in GFRP reinforced concrete. J. Bridge Eng. 2007, 12, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Oehlers, D.; Visintin, P. Shear strength of FRP RC beams and one-way slabs without stirrups. J. Compos. Constr. 2014, 18, 04014007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, A.; Lubell, A.S.; Bindiganavile, V.S. Shear response of lightweight steel fiber reinforced concrete elements without stirrups. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 3141–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Jang, H.S. Concrete shear strength of normal and lightweight concrete beams reinforced with FRP bars. J. Compos. Constr. 2014, 18, 04013038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JSCE. Recommendation for Design and Construction of Concrete Structures Using Continuous Fiber Reinforcing Materials; Japan Society of Civil Engineering: Tokyo, Japan, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- IStructE. Interim Guidance on the Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures Using Fibre Composite Reinforcement; Institution of Structural Engineers: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- CNR DT 203–2006; Recommendations for the Design, Realization and Control of Structures in Concrete Reinforced with Fiber-Reinforced Composite Bars. Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche—National Research Council: Rome, Italy, 2006.
- ISIS. Reinforcing Concrete Structures with Fibre Reinforced Polymers. Design Manual No. 3; Canadian Network of Centres of Excellence on Intelligent Sensing for Innovative Structures: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- CSA S806-12; Design and Construction of Building Components with Fiber-Reinforced Polymers. Canadian Standards Association: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2012.
- AASHTO. Bridge Design Guide Specifications for GFRP Reinforced Concrete, 2nd ed.; American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- prEN 1992-1-1: 2021; Eurocode 2: Design of Concrete Structures—Part 1-1: General Rules—Rules for Buildings, Bridges and Civil Engineering Structures. European Committee for Standardization (CEN): Brussels, Belgium, 2021.
- ACI Code 440.11-22; Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete Reinforced with Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) Bars—Code and Commentary. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2022.
- ACI Code 440.1R-06; Guide for the Design and Construction of Structural Concrete Reinforced with Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Bars. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2006.
- ACI Code 440.1R-15; Guide for the Design and Construction of Structural Concrete Reinforced with Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Bars. American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2015.
- CSA S806-02; Design and Construction of Building Components with Fibre-Reinforced Polymers. Canadian Standards Association: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2002.
- Vakili, S.E.; Homami, P.; Esfahani, M.R. Effect of fibers and hybrid fibers on the shear strength of lightweight concrete beams reinforced with GFRP bars. Structures 2019, 20, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA S6:19; Canadian Highway Bridge Design Code. Canadian Standards Association: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2019.
- Gao, D.; Zhang, C. Shear strength prediction model of FRP bar-reinforced concrete beams without stirrups. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 7516502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholostiakow, S.; Di Benedetti, M.; Guadagnini, M.; Kaszubska, M.; Szczech, D.; Kotynia, R. Shear Database of RC FRP Beams Without Shear Reinforcement; The University of Sheffield: Sheffield, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source, Year | Specimen | Dimensions | LWC | FRP | Shear Strength | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lt [m] | b [mm] | h [mm] | a [mm] | d [mm] | ρlc [kg/m3] | fc [MPa] | Fine Aggregate | Reinf. Type | Ef [GPa] | dmax [mm] | ρf [%] | Vexp [kN] | ||
| Bengar et al. [17], 2021 | G-L-D12-2.5 | 2.00 | 150 | 250 | 500 | 200 | 1824 | 21.0 | sand | GFRP | 66.40 | 10.00 | 0.750 | 20.00 |
| G-L-D12-4 | 2.00 | 150 | 250 | 800 | 200 | 1824 | 21.0 | sand | GFRP | 66.40 | 10.00 | 0.750 | 15.00 | |
| G-L-D16-2.5 | 2.00 | 150 | 250 | 500 | 200 | 1824 | 21.0 | sand | GFRP | 66.40 | 10.00 | 1.340 | 29.00 | |
| G-L-D16-4 | 2.00 | 150 | 250 | 800 | 200 | 1824 | 21.0 | sand | GFRP | 66.40 | 10.00 | 1.340 | 21.00 | |
| Kim & Jang [28], 2014 | C-L-18-R1-1 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 25.80 |
| C-L-18-R2-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 17.50 | |
| C-L-18-R2-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 20.30 | |
| C-L-27-R1-1 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 24.40 | |
| C-L-27-R1-2 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 21.90 | |
| C-L-27-R2-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 20.70 | |
| C-L-27-R2-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 146.20 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 21.50 | |
| C-L-27-R3-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 640.5 | 213.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 147.90 | 15.00 | 0.791 | 25.90 | |
| C-L-27-R3-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 640.5 | 213.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | CFRP | 147.90 | 15.00 | 0.791 | 26.40 | |
| G-L-18-R1-1 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 20.70 | |
| G-L-18-R2-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 16.30 | |
| G-L-18-R2-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 18.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 20.90 | |
| G-L-27-R1-1 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 23.20 | |
| G-L-27-R1-2 | 2.20 | 200 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.331 | 17.50 | |
| G-L-27-R2-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 21.90 | |
| G-L-27-R2-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 646.5 | 215.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 41.00 | 15.00 | 0.441 | 18.00 | |
| G-L-27-R3-1 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 640.5 | 213.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 40.00 | 15.00 | 0.791 | 20.20 | |
| G-L-27-R3-2 | 2.20 | 150 | 250 | 640.5 | 213.5 | 1800 | 27.0 | lightwieght | GFRP | 40.00 | 15.00 | 0.791 | 22.70 | |
| Liu & Pantelides [16], 2013 | #4 B1LW | 2.44 | 610 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 63.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.940 | 112.37 |
| #5 B1LW | 2.44 | 610 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 75.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.940 | 102.72 | |
| #6 B2LW | 2.44 | 610 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 60.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.940 | 103.12 | |
| #7 B1LW | 2.44 | 610 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 68.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.830 | 122.15 | |
| #10 B1LW | 2.90 | 610 | 273 | 1450 | 240 | 1970 | 63.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.790 | 99.80 | |
| #11 B2LW | 2.90 | 610 | 273 | 1450 | 240 | 1970 | 60.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.790 | 105.36 | |
| #14 B1LW | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 63.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.960 | 264.74 | |
| #15 B1LW | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 63.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.960 | 290.16 | |
| #16 B2LW | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 57.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.960 | 298.99 | |
| #17 B2LW | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 56.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.960 | 302.52 | |
| #19 B1LWD | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 63.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.540 | 249.23 | |
| #20 B2LWD | 2.44 | 1830 | 235 | 1220 | 202 | 1970 | 56.0 | sand | GFRP | 43.40 | 12.70 | 0.540 | 221.14 | |
| Mehany et al. [18], 2022 | LSBI-1.26 | 2.60 | 200 | 400 | 1000 | 333.3 | 1800 | 54.0 | sand | BFRP | 63.70 | 15.00 | 1.260 | 44.85 |
| LSBI-0.83 | 2.60 | 200 | 400 | 1000 | 333.3 | 1800 | 54.0 | sand | BFRP | 63.70 | 15.00 | 0.830 | 39.05 | |
| LSBII-0.86 | 2.60 | 200 | 400 | 1000 | 333.3 | 1800 | 54.0 | sand | BFRP | 64.80 | 15.00 | 0.860 | 42.10 | |
| LSBII-0.58 | 2.60 | 200 | 400 | 1000 | 333.3 | 1800 | 54.0 | sand | BFRP | 64.80 | 15.00 | 0.580 | 34.45 | |
| Vakili et al. [40], 2019 | LWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1530 | 31.9 | sand | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 4.41 |
| GLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1552 | 33.2 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 8.58 | |
| PLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1521 | 32.8 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 6.86 | |
| SLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1673 | 41.0 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 12.50 | |
| GPLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1565 | 30.9 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 10.05 | |
| GSLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1680 | 40.0 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 16.92 | |
| PSLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1588 | 32.8 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 13.73 | |
| GPSLWC | 1.40 | 100 | 200 | 550 | 170 | 1620 | 33.7 | sand + fibre | GFRP | 49.40 | 9.50 | 0.590 | 14.71 | |
| Wiater & Siwowski [19], 2020 | LC-D2a-G1 | 2.40 | 1000 | 180 | 600 | 151 | 1857 | 42.7 | sand | GFRP | 49.00 | 8.00 | 0.280 | 82.40 |
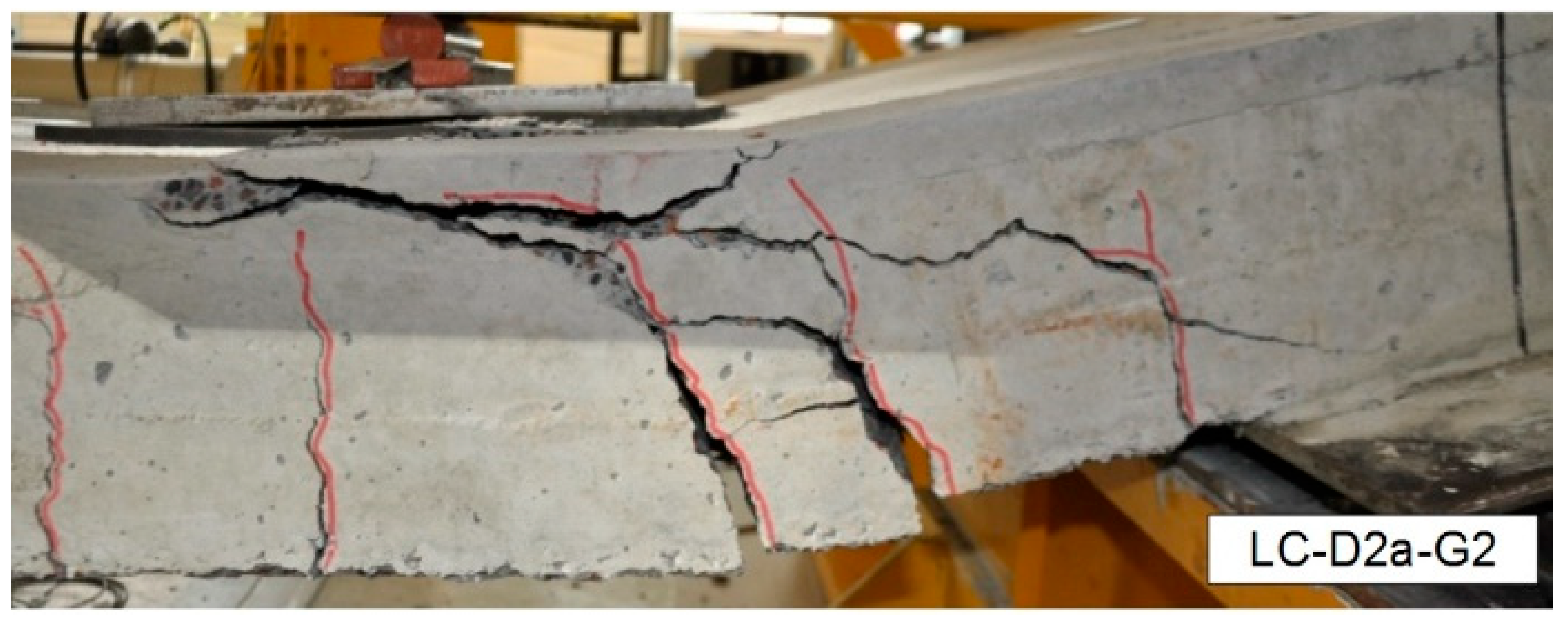
| LC-D2a-G2 | 2.40 | 1000 | 180 | 600 | 151 | 1857 | 42.7 | sand | GFRP | 49.00 | 8.00 | 0.280 | 106.20 | |
| LC-D2a-G0 | 2.40 | 1000 | 180 | 600 | 151 | 1857 | 42.7 | sand | GFRP | 49.00 | 8.00 | 0.280 | 82.20 | |
| No. | Code | Formulas for Calculating Vcode |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | JSCE [29] | no axial load |
| 2. | IStructE [30] | |
| 3. | CNR [31] | |
| 4. | ISIS [32] | For d < 300 mm: For d > 300 mm: |
| 5. | CSA [33] | |
| 6. | AASHTO [34] | |
| 7. | CEN [35] | |
| 8. | ACI [36] |
| Code/Parameters | b | d | h | fc | Ec | Ef | Es | ρf | ag | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSCE [29] | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| IStructE [30] | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| CNR [31] | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | + | - |
| ISIS [32] | + | + | - | - | + | - | + | + | - | - |
| CSA [33] | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | - | + | - |
| AASHTO [34] | + | + | - | + | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| CEN [35] | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | + | + |
| ACI [36] | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | + | - |
| Source | No. | Specimen | Vexp | Shear Strength Vcode [kN] According to Code Formulas 1 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [kN] | JSCE [29] | Istructe [30] | ISIS [31] | CNR [32] | CSA [33] | AASHTO [34] | CEN [35] | ACI [36] | |||
| Bengar et al. [17] | 1 | G-L-D12-2.5 | 20.00 | 15.57 | 18.02 | 13.46 | 26.94 | 19.86 | 9.71 | 19.44 | 9.07 |
| 2 | G-L-D12-4 | 15.00 | 15.57 | 18.02 | 13.46 | 26.94 | 15.70 | 9.55 | 16.62 | 9.07 | |
| 3 | G-L-D16-2.5 | 29.00 | 18.90 | 21.87 | 13.46 | 31.18 | 23.62 | 10.03 | 23.58 | 9.07 | |
| 4 | G-L-D16-4 | 21.00 | 18.90 | 21.87 | 13.46 | 31.18 | 18.67 | 9.76 | 20.16 | 9.07 | |
| Kim & Jang [28] | 5 | C-L-18-R1-1 | 25.80 | 20.66 | 23.91 | 23.45 | 45.52 | 21.65 | 12.58 | 25.57 | 12.07 |
| 6 | C-L-18-R2-1 | 17.50 | 17.05 | 19.73 | 17.59 | 35.27 | 17.68 | 9.49 | 21.10 | 9.05 | |
| 7 | C-L-18-R2-2 | 20.30 | 17.05 | 19.73 | 17.59 | 35.27 | 17.68 | 9.49 | 21.10 | 9.05 | |
| 8 | C-L-27-R1-1 | 24.40 | 23.65 | 27.37 | 28.73 | 59.65 | 24.78 | 15.36 | 29.27 | 14.78 | |
| 9 | C-L-27-R1-2 | 21.90 | 23.65 | 27.37 | 28.73 | 59.65 | 24.78 | 15.36 | 29.27 | 14.78 | |
| 10 | C-L-27-R2-1 | 20.70 | 19.52 | 22.59 | 21.54 | 46.21 | 20.24 | 11.57 | 24.16 | 11.09 | |
| 11 | C-L-27-R2-2 | 21.50 | 19.52 | 22.59 | 21.54 | 46.21 | 20.24 | 11.57 | 24.16 | 11.09 | |
| 12 | C-L-27-R3-1 | 25.90 | 23.64 | 27.36 | 21.47 | 50.81 | 24.00 | 11.64 | 29.28 | 10.98 | |
| 13 | C-L-27-R3-2 | 26.40 | 23.64 | 27.36 | 21.47 | 50.81 | 24.00 | 11.64 | 29.28 | 10.98 | |
| 14 | G-L-18-R1-1 | 20.70 | 15.52 | 15.56 | 12.42 | 24.11 | 15.08 | 12.58 | 16.74 | 12.07 | |
| 15 | G-L-18-R2-1 | 16.30 | 11.16 | 12.92 | 9.32 | 18.68 | 12.20 | 9.49 | 13.81 | 9.05 | |
| 16 | G-L-18-R2-2 | 20.90 | 11.16 | 12.92 | 9.32 | 18.68 | 12.20 | 9.49 | 13.81 | 9.05 | |
| 17 | G-L-27-R1-1 | 23.20 | 15.48 | 17.92 | 15.21 | 31.59 | 18.47 | 15.36 | 19.16 | 14.78 | |
| 18 | G-L-27-R1-2 | 17.50 | 15.48 | 17.92 | 15.21 | 31.59 | 18.47 | 15.36 | 19.16 | 14.78 | |
| 19 | G-L-27-R2-1 | 21.90 | 12.78 | 14.79 | 11.41 | 24.47 | 13.97 | 11.57 | 15.81 | 11.09 | |
| 20 | G-L-27-R2-2 | 18.00 | 12.78 | 14.79 | 11.41 | 24.47 | 13.97 | 11.57 | 15.81 | 11.09 | |
| 21 | G-L-27-R3-1 | 20.20 | 15.29 | 17.69 | 11.16 | 26.42 | 16.25 | 11.64 | 18.94 | 10.98 | |
| 22 | G-L-27-R3-2 | 22.70 | 15.29 | 17.69 | 11.16 | 26.42 | 16.25 | 11.64 | 18.94 | 10.98 | |
| Liu & Pantelides [16] | 23 | #4 B1LW | 112.37 | 77.90 | 99.64 | 77.45 | 182.28 | 91.44 | 67.00 | 68.33 | 64.55 |
| 24 | #5 B1LW | 102.72 | 77.90 | 105.61 | 84.51 | 194.31 | 99.77 | 73.02 | 73.34 | 70.43 | |
| 25 | #6 B2LW | 103.12 | 77.90 | 98.04 | 75.58 | 178.99 | 89.24 | 65.40 | 81.36 | 62.99 | |
| 26 | #7 B1LW | 122.15 | 74.73 | 98.06 | 80.47 | 182.26 | 95.00 | 69.47 | 67.21 | 67.06 | |
| 27 | #10 B1LW | 99.80 | 83.66 | 107.01 | 92.02 | 202.66 | 108.65 | 79.43 | 72.33 | 76.69 | |
| 28 | #11 B2LW | 105.36 | 83.66 | 105.28 | 89.80 | 199.00 | 106.03 | 77.54 | 86.12 | 74.84 | |
| 29 | #14 B1LW | 264.74 | 235.35 | 301.04 | 232.36 | 549.60 | 274.34 | 201.05 | 206.45 | 193.65 | |
| 30 | #15 B1LW | 290.16 | 235.35 | 301.04 | 232.36 | 549.60 | 274.34 | 201.05 | 206.45 | 193.65 | |
| 31 | #16 B2LW | 298.99 | 235.53 | 291.16 | 221.02 | 529.38 | 260.95 | 191.37 | 241.65 | 184.20 | |
| 32 | #17 B2LW | 302.52 | 235.35 | 289.45 | 219.06 | 525.85 | 258.65 | 189.70 | 240.22 | 182.57 | |
| 33 | #19 B1LWD | 249.23 | 194.27 | 248.50 | 232.36 | 491.31 | 274.34 | 199.86 | 170.42 | 193.65 | |
| 34 | #20 B2LWD | 221.14 | 194.27 | 238.93 | 219.06 | 470.08 | 258.65 | 188.52 | 198.30 | 182.57 | |
| Mehany et al. [18] | 35 | LSBI-1.75 | 48.40 | 51.99 | 63.17 | 47.01 | 123.16 | 70.30 | 34.91 | 65.14 | 29.93 |
| 36 | LSBI-1.26 | 44.85 | 46.60 | 56.62 | 47.01 | 110.45 | 63.64 | 34.40 | 58.39 | 29.93 | |
| 37 | LSBI-0.83 | 39.05 | 40.54 | 49.26 | 47.01 | 99.30 | 56.18 | 33.97 | 50.80 | 29.93 | |
| 38 | LSBII-0.86 | 42.10 | 41.26 | 50.13 | 47.40 | 100.94 | 57.06 | 34.00 | 51.70 | 29.93 | |
| 39 | LSBII-0.58 | 34.45 | 36.18 | 43.96 | 47.40 | 93.62 | 50.80 | 33.71 | 45.34 | 29.93 | |
| Vakili et al. [40] | 40 | LWC | 4.41 | 8.51 | 10.22 | 8.11 | 17.00 | 9.72 | 6.63 | 10.19 | 6.34 |
| 41 | GLWC | 8.58 | 8.63 | 10.37 | 8.28 | 17.48 | 9.85 | 6.77 | 10.33 | 6.47 | |
| 42 | PLWC | 6.86 | 8.59 | 10.32 | 8.22 | 17.32 | 9.81 | 6.72 | 10.28 | 6.43 | |
| 43 | SLWC | 12.50 | 9.25 | 11.11 | 9.19 | 20.10 | 10.57 | 7.50 | 11.08 | 7.18 | |
| 44 | GPLWC | 10.05 | 8.43 | 10.12 | 7.99 | 16.67 | 9.62 | 6.53 | 10.09 | 6.24 | |
| 45 | GSLWC | 16.92 | 9.18 | 11.03 | 9.09 | 19.80 | 10.49 | 7.41 | 10.99 | 7.10 | |
| 46 | PSLWC | 13.73 | 8.59 | 10.32 | 8.22 | 17.32 | 9.81 | 6.72 | 10.28 | 6.43 | |
| 47 | GPSLWC | 14.71 | 8.67 | 10.41 | 8.34 | 17.64 | 9.89 | 6.81 | 10.38 | 6.51 | |
| Wiater & Siwowski [19] | 48 | LC-D2a-G1 | 82.40 | 64.82 | 80.22 | 83.03 | 169.25 | 92.26 | 67.19 | 73.89 | 65.12 |
| 49 | LC-D2a-G2 | 106.20 | 64.82 | 80.22 | 83.03 | 169.25 | 92.26 | 67.19 | 73.89 | 65.12 | |
| 50 | LC-D2a-G0 | 82.20 | 64.82 | 80.22 | 83.03 | 169.25 | 92.26 | 67.19 | 73.89 | 65.12 | |
| Code | JSCE [29] | IStructE [30] | ISIS [31] | CNR [32] | CSA [33] | AASHTO [34] | CEN [35] | ACI [36] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire population | MAX | 1.87 | 1.62 | 2.24 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 2.89 | 1.59 | 3.20 | |
| MIN | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.70 | ||
| AVG | 1.25 | 1.04 | 1.29 | 0.59 | 1.08 | 1.63 | 1.08 | 1.72 | ||
| SD | 0.27 | 0.23 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.45 | ||
| Type of tested members | beams | MAX | 1.87 | 1.62 | 2.24 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 2.89 | 1.59 | 3.20 |
| MIN | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.70 | ||
| AVG | 1.24 | 1.05 | 1.31 | 0.61 | 1.09 | 1.68 | 1.07 | 1.78 | ||
| SD | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 0.46 | ||
| slabs | MAX | 1.64 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 0.63 | 1.17 | 1.59 | 1.37 | 1.66 | |
| MIN | 1.12 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 1.17 | 0.93 | 1.21 | ||
| AVG | 1.28 | 1.02 | 1.16 | 0.53 | 1.00 | 1.37 | 1.11 | 1.42 | ||
| SD | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.18 | ||
| Type of reinforcement | GFRP | MAX | 1.87 | 1.62 | 2.24 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 2.89 | 1.59 | 3.20 |
| MIN | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.70 | ||
| AVG | 1.33 | 1.10 | 1.41 | 0.65 | 1.13 | 1.61 | 1.15 | 1.69 | ||
| SD | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.42 | 0.24 | 0.47 | ||
| CFRP | MAX | 1.25 | 1.08 | 1.23 | 0.58 | 1.19 | 2.27 | 1.06 | 2.40 | |
| MIN | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 0.88 | 1.43 | 0.79 | 1.48 | ||
| AVG | 1.09 | 0.94 | 1.03 | 0.48 | 1.05 | 1.91 | 0.92 | 2.00 | ||
| SD | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.31 | ||
| BFRP | MAX | 1.02 | 0.84 | 1.03 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 1.39 | 0.86 | 1.62 | |
| MIN | 0.93 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 1.02 | 0.78 | 1.15 | ||
| AVG | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.22 | 0.81 | 1.40 | ||
| SD | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.18 | ||
| Type of lightweight concrete | sand | MAX | 1.64 | 1.33 | 2.15 | 0.93 | 1.29 | 2.89 | 1.51 | 3.20 |
| MIN | 0.52 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.26 | 0.45 | 0.67 | 0.44 | 0.70 | ||
| AVG | 1.20 | 0.97 | 1.18 | 0.53 | 0.96 | 1.47 | 1.04 | 1.57 | ||
| SD | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.43 | 0.23 | 0.47 | ||
| all lightweight | MAX | 1.87 | 1.62 | 2.24 | 1.12 | 1.71 | 2.27 | 1.59 | 2.40 | |
| MIN | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.76 | 0.37 | 0.88 | 1.14 | 0.79 | 1.18 | ||
| AVG | 1.28 | 1.11 | 1.39 | 0.65 | 1.20 | 1.81 | 1.09 | 1.89 | ||
| SD | 0.26 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.22 | 0.33 | ||
| fibre | MAX | 1.84 | 1.53 | 1.86 | 0.85 | 1.61 | 2.28 | 1.58 | 2.38 | |
| MIN | 0.80 | 0.66 | 0.83 | 0.40 | 0.70 | 1.02 | 0.68 | 1.07 | ||
| AVG | 1.35 | 1.13 | 1.40 | 0.66 | 1.19 | 1.71 | 1.16 | 1.79 | ||
| SD | 0.38 | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.49 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiater, A.; Siwowski, T.W. Shear Strength of Lightweight Concrete Structural Elements Reinforced with FRP Bars: Experimental Studies vs. Code Predictions. Materials 2025, 18, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153525
Wiater A, Siwowski TW. Shear Strength of Lightweight Concrete Structural Elements Reinforced with FRP Bars: Experimental Studies vs. Code Predictions. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153525
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiater, Agnieszka, and Tomasz Wojciech Siwowski. 2025. "Shear Strength of Lightweight Concrete Structural Elements Reinforced with FRP Bars: Experimental Studies vs. Code Predictions" Materials 18, no. 15: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153525
APA StyleWiater, A., & Siwowski, T. W. (2025). Shear Strength of Lightweight Concrete Structural Elements Reinforced with FRP Bars: Experimental Studies vs. Code Predictions. Materials, 18(15), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153525









