Microscopy Study of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steels Under Continuous Casting Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
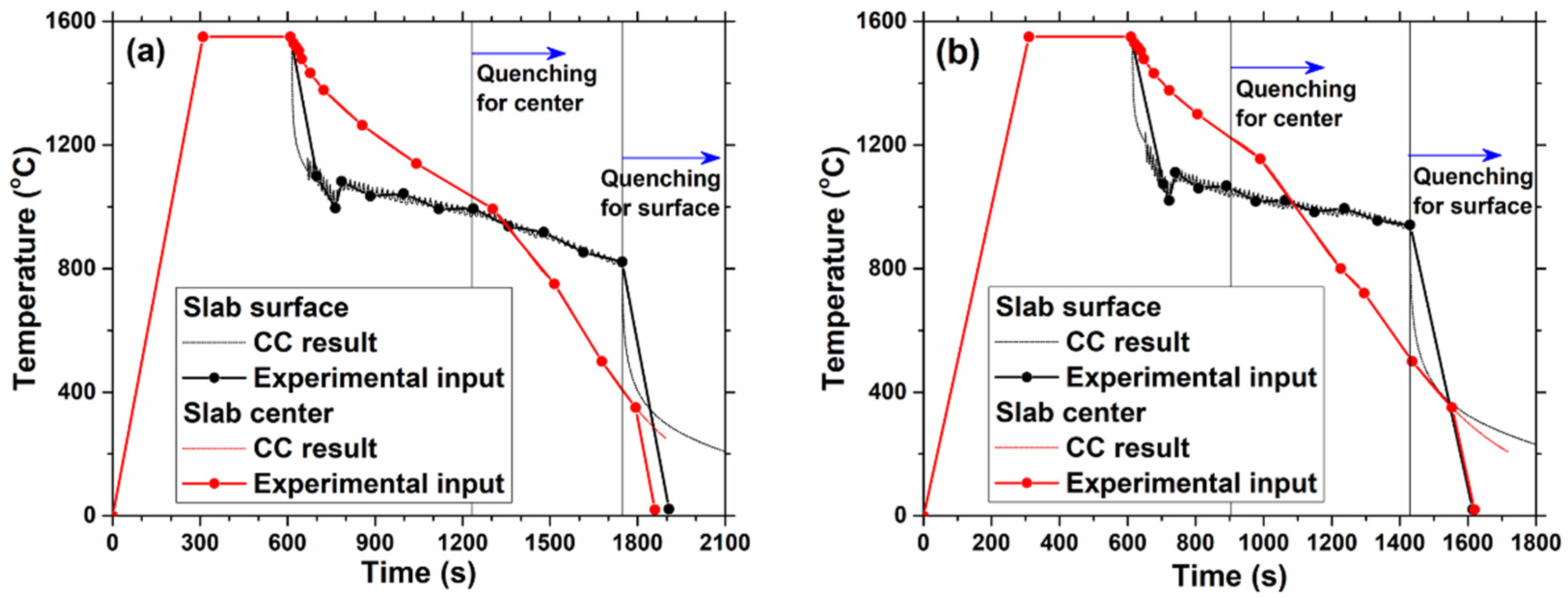
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Measurements
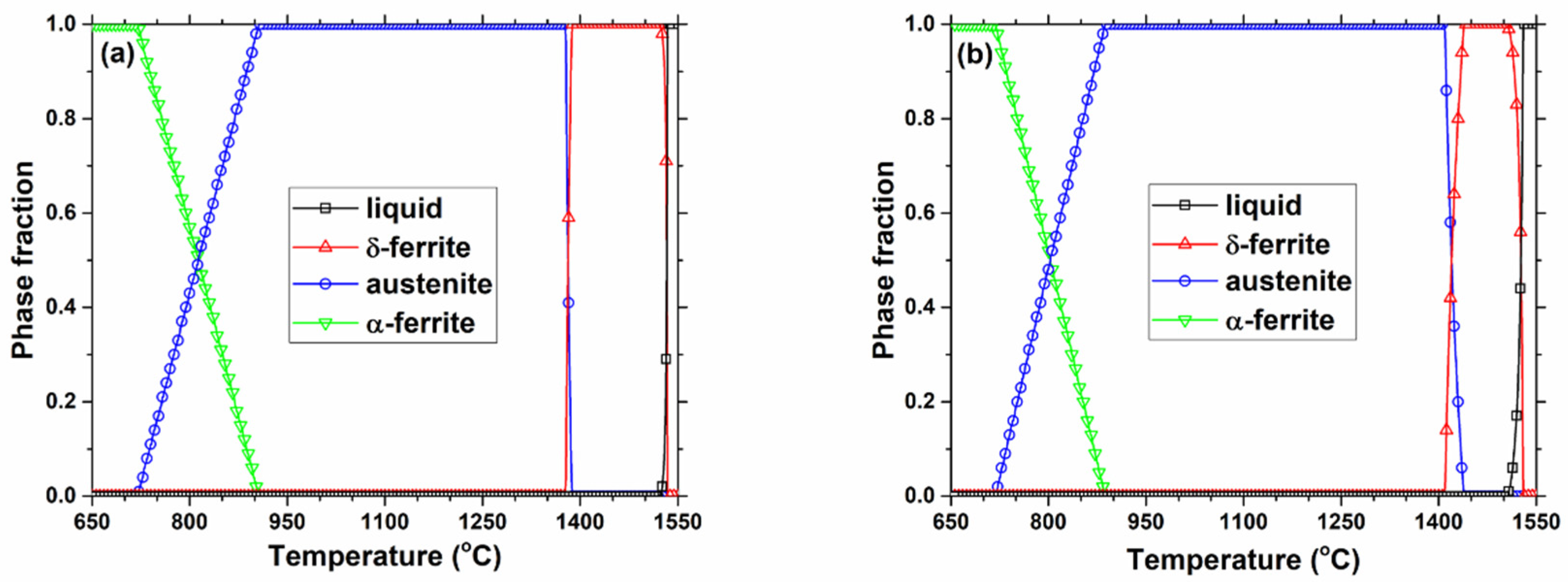
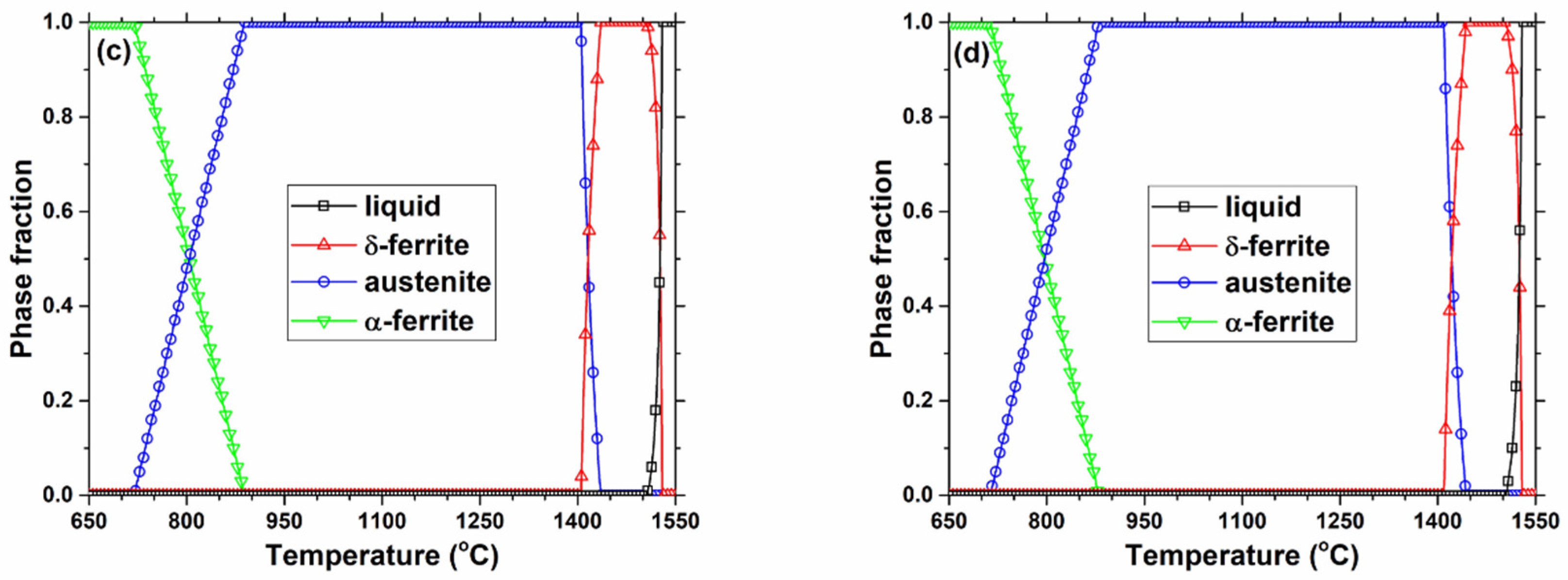
3. Thermodynamic Model Calculation of Equilibrium Precipitation
4. Results
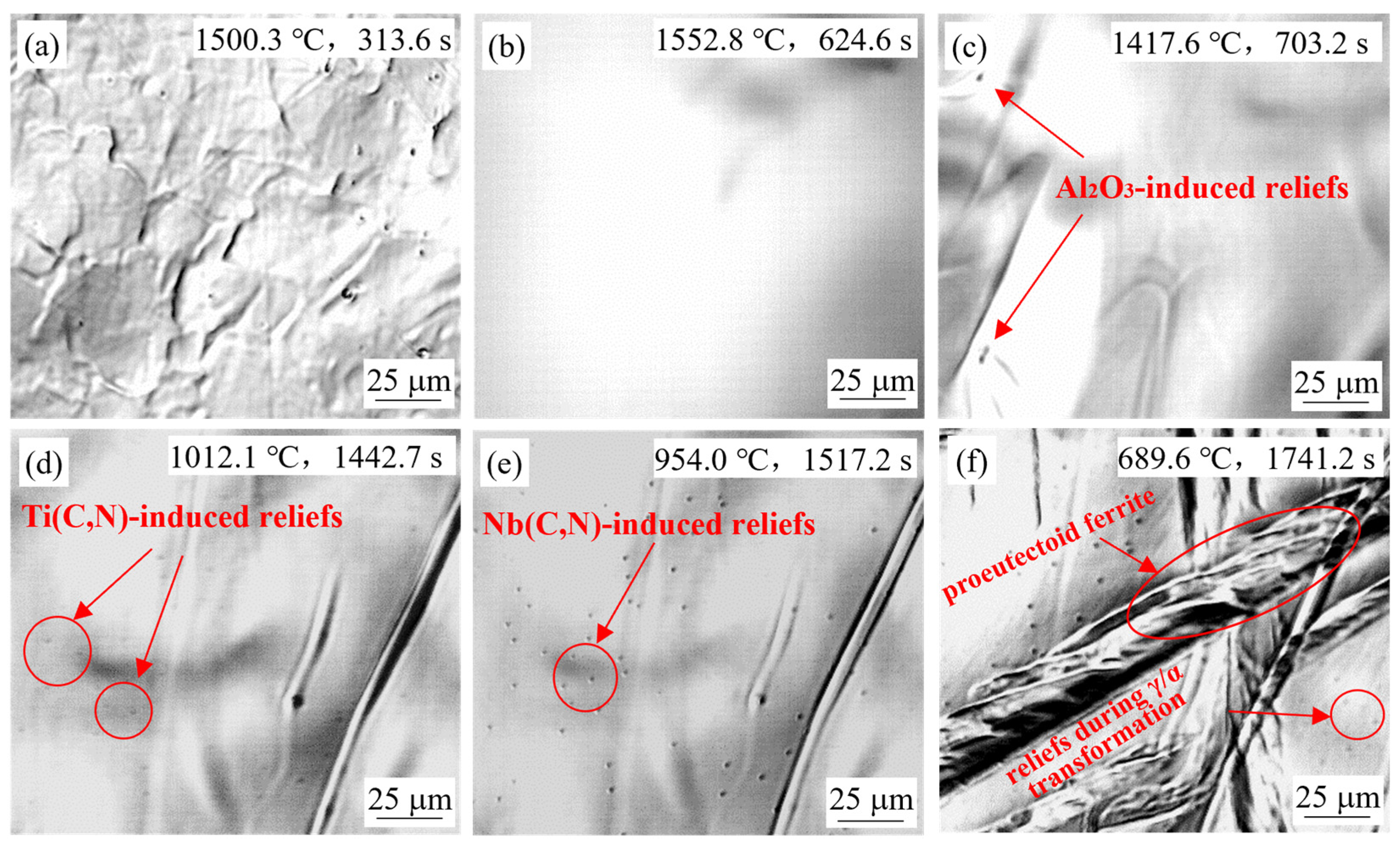
4.1. General In-Situ Observations of High-Temperature Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
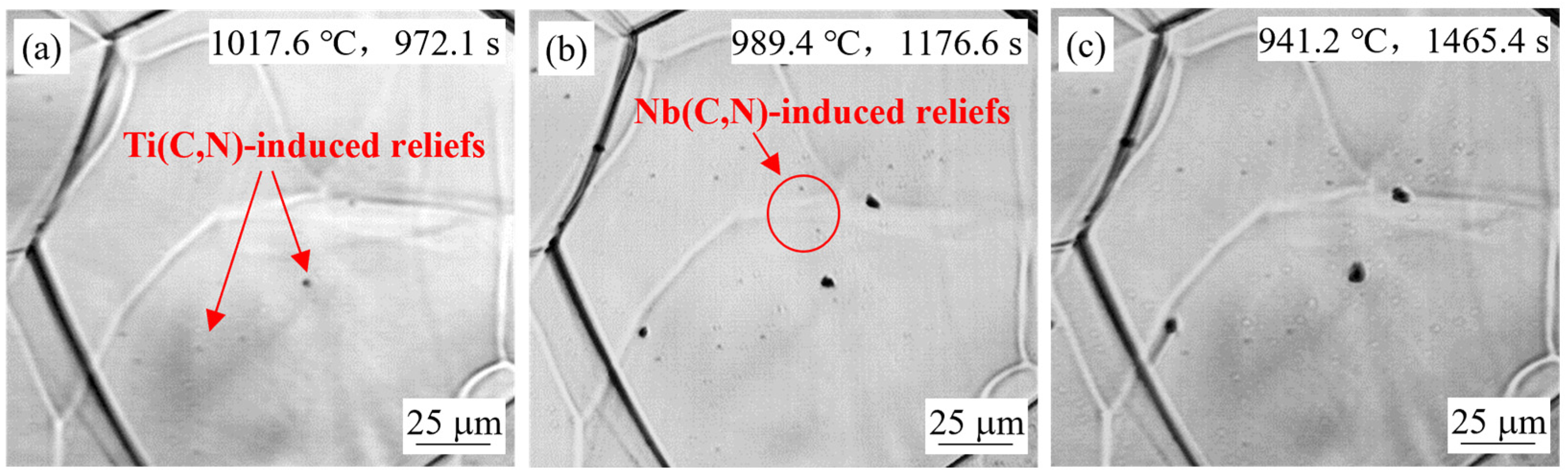
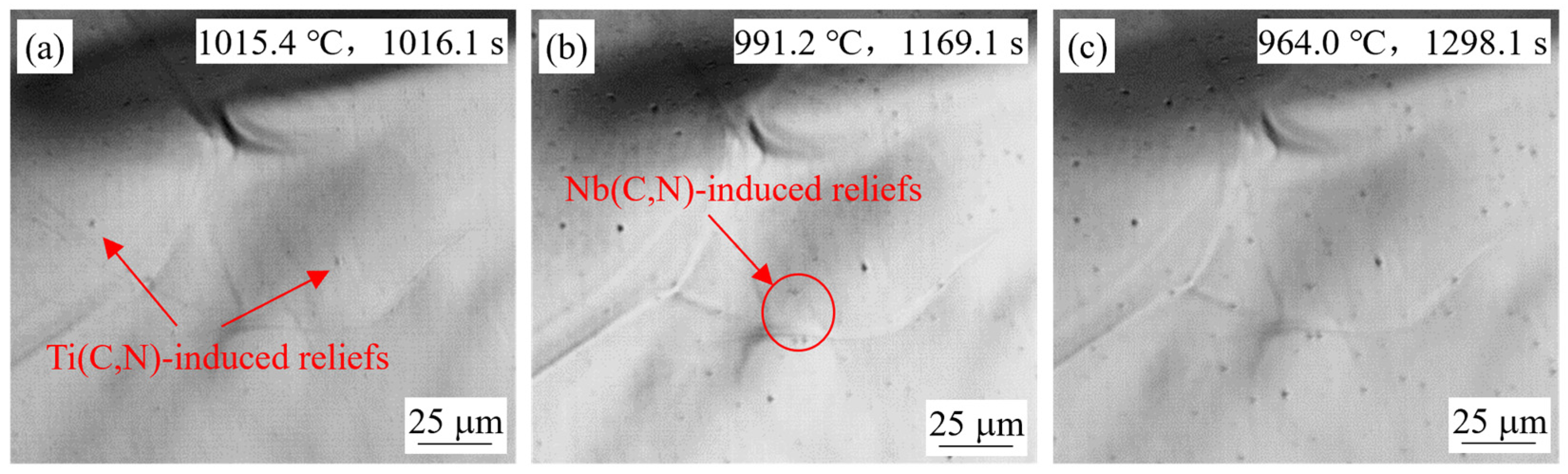
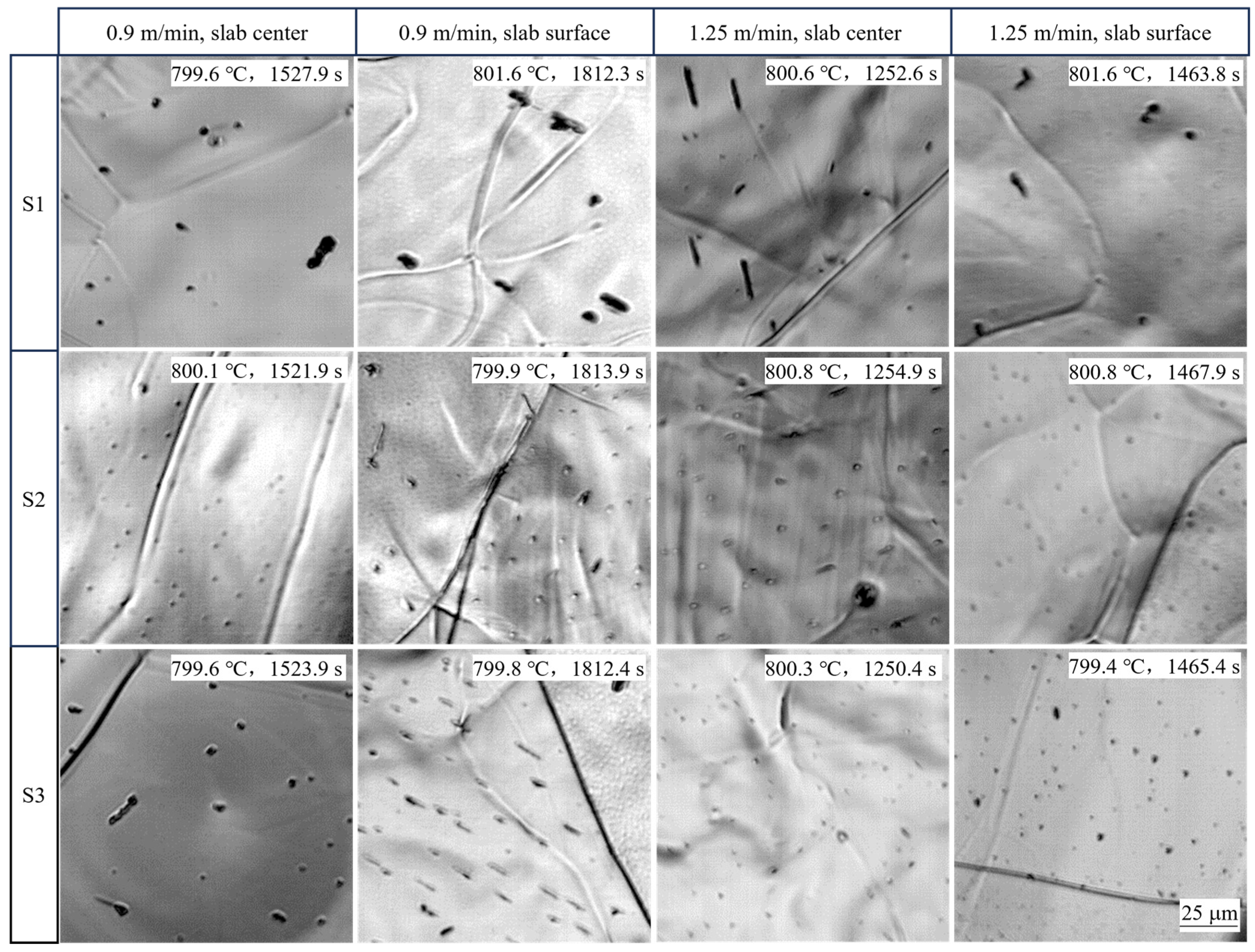
4.1.1. Effect of Slab Position
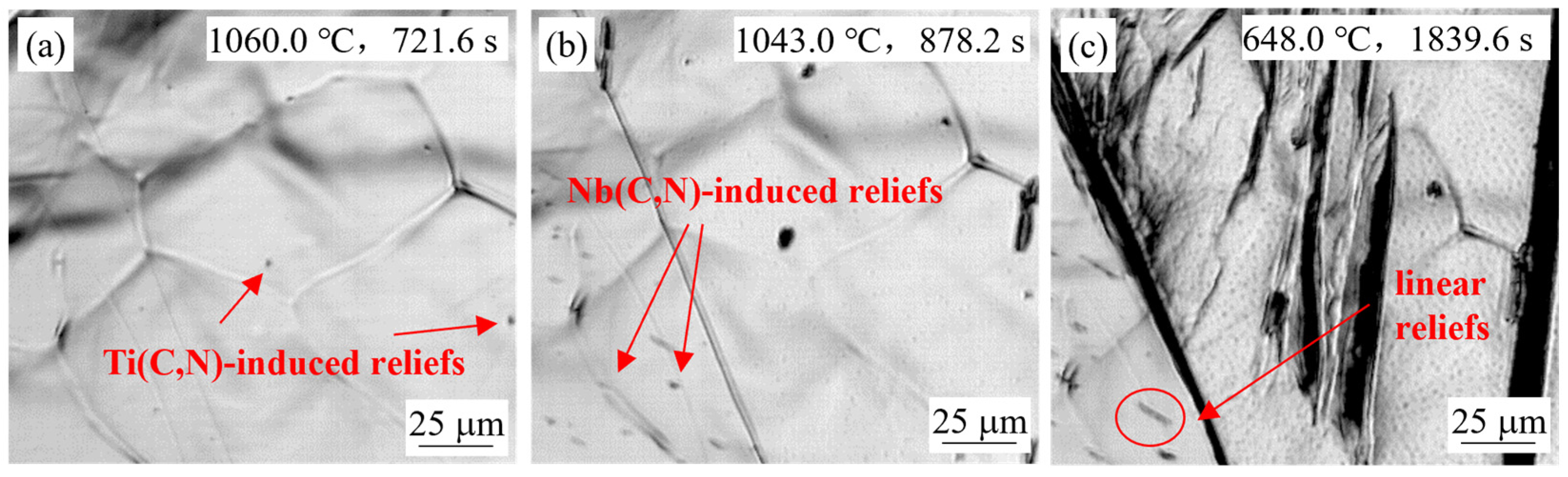
4.1.2. Effect of Casting Speed
4.1.3. Effect of Steel Composition
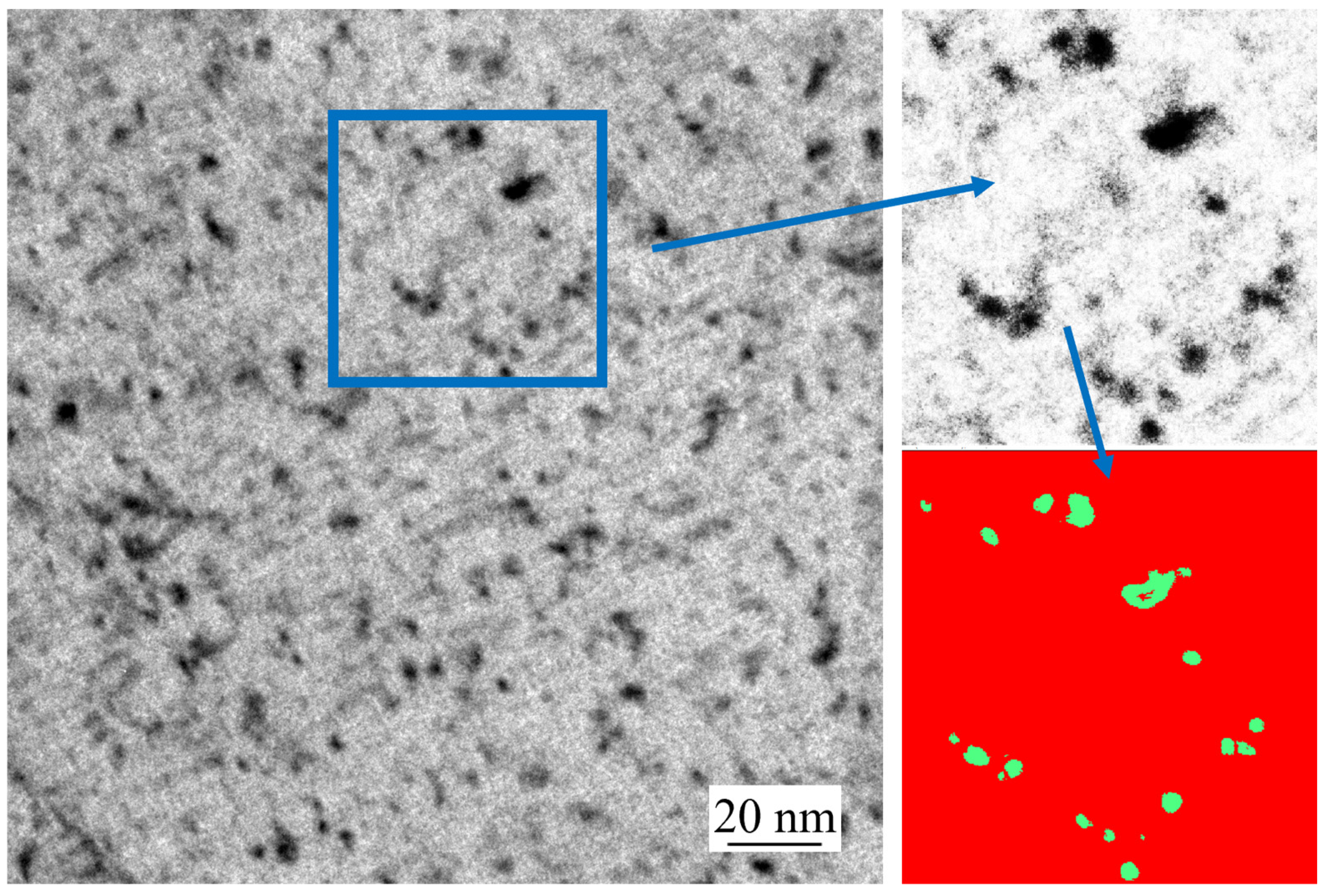
4.2. Characterization by Transmission Electron Microscopy
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- Small reliefs observed on the sample surface during HTCLSM were confirmed to result from internal precipitation of (Ti,Nb)(C,N). These reliefs appeared sequentially as temperature decreased during cooling. The formation of reliefs depended on the simulated slab position, the casting speed, and the steel composition. The reliefs formed earlier on the slab surface than in the slab center due to earlier cooling, and their size was larger. The reliefs appeared later with increasing casting speed, and their size was smaller. When the titanium or niobium content in the steel increased, the surface reliefs appeared earlier, and their number increased.
- (2)
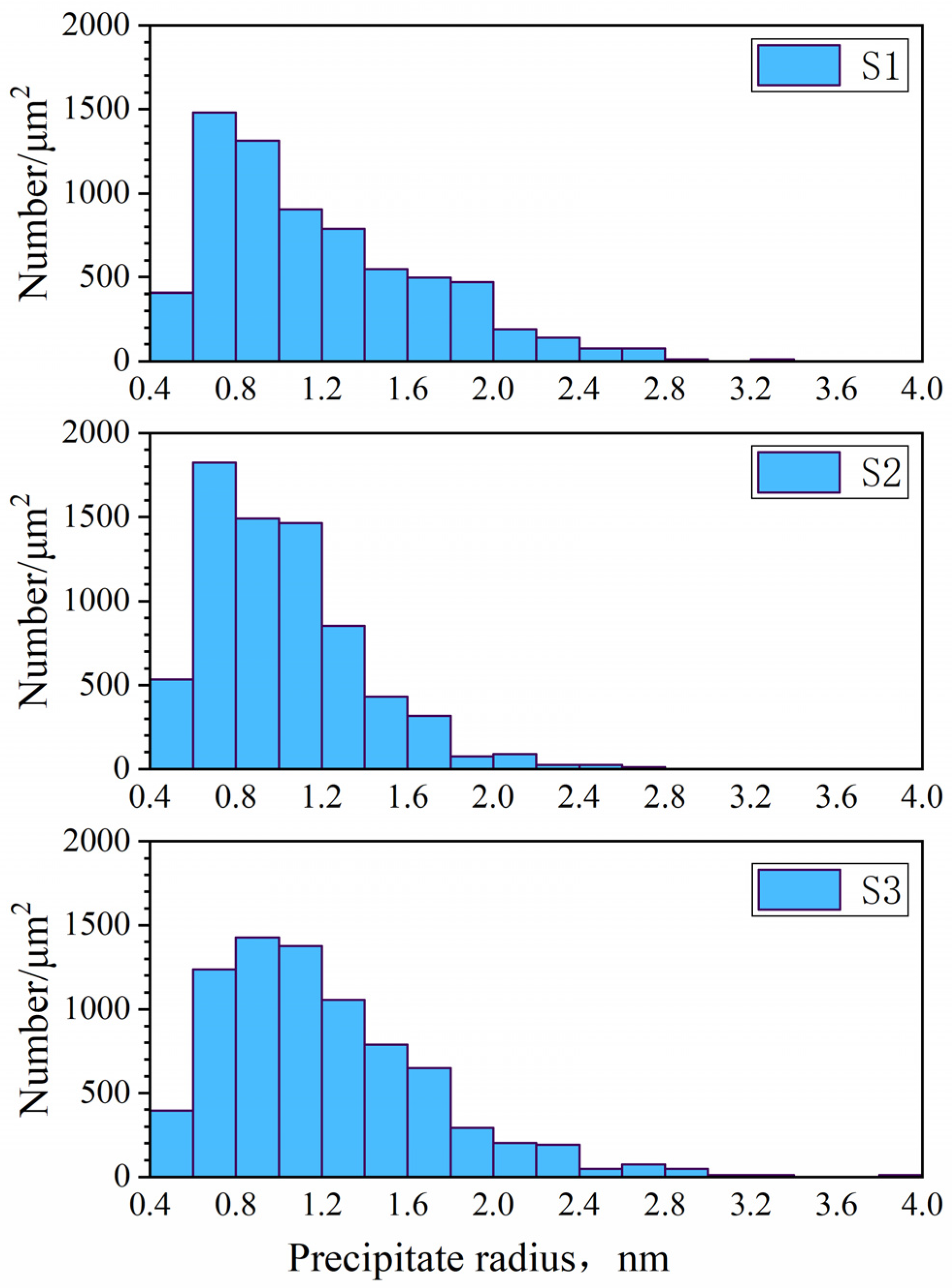
- TEM measurements showed that the precipitate radii of the simulated continuous casting experiments were mostly distributed within 2 nm, with a few larger precipitates at 2–4 nm. The average radius of precipitates decreased with increasing distance from the casting surface, casting speed, or titanium or niobium content in the steel sample.
- (3)
- The surface relief morphologies observed by HTCLSM showed a strong positive qualitative correlation with the number and sizes of precipitates measured by TEM, although the TEM precipitate size distributions showed much larger numbers of much smaller particles. Therefore, the relatively easy in-situ observation of micron-scale surface reliefs using HTCLSM was demonstrated to be an effective tool for indirect characterization of nanoscale secondary phase precipitation inside steel samples.
- (4)
- The experimental measurements presented here can serve as a benchmark for future modeling studies to predict starting times and precipitate size distributions of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) precipitation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amos, W.B.; White, J.G. How the confocal laser scanning microscope entered biological research. Biol. Cell 2003, 95, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagali, N. (Ed.) Confocal Laser Microscopy: Principles and Applications in Medicine, Biology, and the Food Sciences; BoD—Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tata, B.V.R.; Raj, B. Confocal laser scanning microscopy: Applications in material science and technology. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1998, 21, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlon, D.N.; Todd, I.; Peekstok, E.; Rainforth, W.M.; Zwaag, S.V.D. The application of laser scanning confocal microscopy to tribological research. Wear 2001, 251, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Li, F.; Lu, C. Visualization of materials using the confocal laser scanning microscopy technique. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2408–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, D.; Qu, T.; Hou, D.; Hu, S.; Tian, J.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Z. An investigation of single-phased metallic solidification process using high-temperature confocal laser scanning microscope combined with differential scanning colorimetry. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2025, 32, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Mu, W. In situ observation of solidification and crystallization of low-alloy steels: A review. Metals 2023, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. In-situ observation of nonmetallic inclusions in steel using confocal scanning laser microscopy: A review. Int. J. Min. Metall. Mater. 2025, 32, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippenaar, R.J.; Phelan, D.J. Delta-ferrite recovery structures in low-carbon steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.; Janik, V.; Rijkenberg, A.; Sridhar, S. Analysis of the extent of interphase precipitation in V-HSLA steels through in-situ characterization of the γ/α transformation. Mater. Charact. 2016, 115, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, K.; Meng, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, Y. Influence of cooling rate on secondary phase precipitation and proeutectoid phase transformation of micro-alloyed steel containing vanadium. Met. Mater. Int. 2016, 22, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Bu, S.; Shen, M.; Miao, X.; Li, X. The investigation of precipitation behavior of titanium compounds for high titanium steel based on in situ observation. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0275049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Chen, K.-W. A study of the engineering properties of CLSM with a new type of slag. Constr. Build. 2016, 102, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Hedström, P.; Shibata, H.; Jönsson, P.G.; Nakajima, K. High-temperature confocal laser scanning microscopy studies of ferrite formation in inclusion-engineered steels: A review. JOM 2018, 70, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Feng, L.; Sun, H.; Han, X. Phase-field simulation and high-temperature confocal laser scanning microscope experimental study of martensite transformation during the disk laser quenching process. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2024, 238, 1605–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Lan, C. A review on high temperature confocal scanning laser microscope applied in steel materials. Phys. Exam. Test 2019, 37, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Thomas, B.G.; Dyer, M.S.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Model of microalloy precipitation during continuous casting and reheating. Iron Steel Technol. 2011, 773–783. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wilson, J.A.; Crowther, D.N.; Mitchell, P.S.; Craven, A.J.; Baker, T.N. The effects of vanadium, niobium, titanium and zirconium on the microstructure and mechanical properties of thin slab cast steels. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeArdo, A.J.; Hua, M.J.; Cho, K.G.; Garcia, C.I. On strength of microalloyed steels: An interpretive review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2009, 25, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervynckt, S.; Verbeken, K.; Lopez, B.; Jonas, J.J. Modern HSLA steels and role of non-recrystallisation temperature. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.N. Microalloyed steels. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2016, 43, 264–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Jin, R.; Han, L.; Xie, D.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.; Shi, J. Effect of Ti and TiNb microalloying on microstructures and mechanical properties of 2200 MPa low-alloy ultra-high-strength steels. Metals 2025, 15, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Saito, Y.; Shiotani, K. Effect of microalloyed nitride forming elements on precipitation of carbonitride and high temperature ductility of continuously cast low carbon Nb containing steel slab. ISIJ Int. 1995, 35, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.; Kang, K.; Park, C. Effects of cooling rate and isothermal holding on the precipitation behavior during continuous casting of Nb-Ti bearing HSLA steels. Scripta Mater. 2004, 49, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kashif, E.; Asakura, K.; Koseki, T.; Shibata, K. Effect of boron, niobium and titanium on grain growth in ultra high purity 18% Cr ferritic stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, S.; Ramisetti, N.K.; Misra, R.D.K.; Hartmann, J.; Jansto, S.G. Microstructure and high strength-toughness combination of a new 700 mpa Nb-microalloyed pipeline steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 478, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, E.S. A review of strand casting factors affecting transverse cracking. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Clean Steel, Balatonfüred, Hungary, 10–12 June 2002; pp. 324–338. [Google Scholar]
- Mintz, B.; Yue, S.; Jonas, J.J. Hot ductility of steels and its relationship to the problem of transhverse cracking during continuous casting. Int. Mater. Rev. 1991, 36, 187–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Karjalainen, L.P.; Porter, D.A.; Liimatainen, H.-M.; Zhang, Y. The influence of Ti on the hot ductility of Nb-bearing steels in simulated continuous casting process. ISIJ Int. 2002, 42, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charleux, M.; Poole, W.J.; Militzer, M.; Deschamps, A. Precipitation behavior and its effect on strengthening of an HSLA-Nb/Ti steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2001, 32, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrard, F.; Donnadieu, P.; Deschamps, A.; Barges, P. TEM study of NbC heterogeneous precipitation in ferrite. Philos. Mag. 2006, 86, 4271–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, A.J.; He, K.; Craven, L.A.J.; Baker, T.N. Complex heterogeneous precipitation in titanium-niobium microalloyed Al-killed HSLA steels-I. (Ti,Nb)(C,N) particles. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 3857–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Wen, G.; Wang, W. Effect of cooling rates on the second-phase precipitation and proeutectoid phase transformation of a Nb–Ti microalloyed steel slab. Steel Res. Int. 2013, 84, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T. Study on Mechanisms of Microstructure Evolution and Second Phase Precipitation of Microalloyed Hypo-Peritectic Steels During Solidification Process. Ph.D. Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q. Characterization and control of secondary phase precipitation of Nb-V-Ti microalloyed steel during continuous casting process. ISIJ Int. 2022, 62, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L. Study on Solidification Characteristics of V-Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel and Crack Control of Continuous Casting Bloom. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology, Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Paddock, S.W. Principles and practices of laser scanning confocal microscopy. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Thomas, B.G. Heat-transfer and solidification model of continuous slab casting: CON1D. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Petrus, B.; Thomas, B.G. Prediction of Ideal Machine Taper at SSAB [Private Report]; Continuous Casting Consortium, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Thomas, B.G.; O’malley, R. Equilibrium model of precipitation in microalloyed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. The Physical Metallurgy of Microalloyed Steels; The Institute of Materials: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Turkdogan, E.T. Fundamental of Steelmaking; The institute of Materials: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Frisk, K. Thermodynamic modelling of multicomponent cubic Nb, Ti and V carbides/carbonitrides. Calphad 2008, 32, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.F. Determination of precipitation-time-temperature (PTT) diagrams for Nb, Ti or V micro-alloyed steels. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 32, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Ha, Y.-S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-K. Dissolution and precipitation kinetics of Nb(C,N) in austenite of a low-carbon Nb-microalloyed steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2009, 40, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. Kinetics of (Ti, Nb)(C, N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steel. Master’s Thesis, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Dong, Z.; Yang, X.; Liang, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; Luo, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; et al. The trends of in situ focused ion beam technology: Toward preparing transmission electron microscopy lamella and devices at the atomic scale. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Kirkaldy, J.S. Carbonitride precipitate growth in titanium/niobium microalloyed steels. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 22, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolinska, M.; Gustavsson, F.; Hedström, P. Revisiting the applications of the extraction replica sample preparation technique for analysis of precipitates in engineering alloys. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, K.C. Nucleation in solid: The induction and steady state effects. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1980, 13, 205–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Kampmann, R.; Voorhees, P.W. Homogeneous Second-Phase Precipitation; WileyVCH GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]





| C | O | N | Nb | Ti | V | Si | Mn | Al | S | P | Ni | Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 0.004 | 0.0029 | 0.0066 | 0.0008 | 0.003 | 0.0005 | 0.018 | 0.073 | 0.027 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.017 | 0.044 |
| S1 | 0.048 | 0.0023 | 0.0011 | 0.026 | 0.003 | 0.0004 | 0.032 | 0.070 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.17 | 0.079 |
| S2 | 0.047 | 0.0022 | 0.0011 | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.0005 | 0.032 | 0.071 | 0.006 | 0.006 | 0.010 | 0.15 | 0.076 |
| S3 | 0.053 | 0.0021 | 0.0013 | 0.052 | 0.012 | 0.0007 | 0.032 | 0.071 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.20 | 0.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Liu, D.; Wang, W.; Thomas, B.G.; Wu, T.; Xu, K.; Zhang, Z. Microscopy Study of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steels Under Continuous Casting Conditions. Materials 2025, 18, 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153445
Xu F, Liu D, Wang W, Thomas BG, Wu T, Xu K, Zhang Z. Microscopy Study of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steels Under Continuous Casting Conditions. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153445
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fangyong, Daoyao Liu, Wei Wang, Brian G. Thomas, Tianxu Wu, Kun Xu, and Zhan Zhang. 2025. "Microscopy Study of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steels Under Continuous Casting Conditions" Materials 18, no. 15: 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153445
APA StyleXu, F., Liu, D., Wang, W., Thomas, B. G., Wu, T., Xu, K., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Microscopy Study of (Ti,Nb)(C,N) Precipitation in Microalloyed Steels Under Continuous Casting Conditions. Materials, 18(15), 3445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153445







