Effects of Ti Substitution by Zr on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Laves Phase AB2-Type Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Structural Characterizations
2.3. Hydrogen Absorption and Desorption Performance Tests
3. Results and Discussion
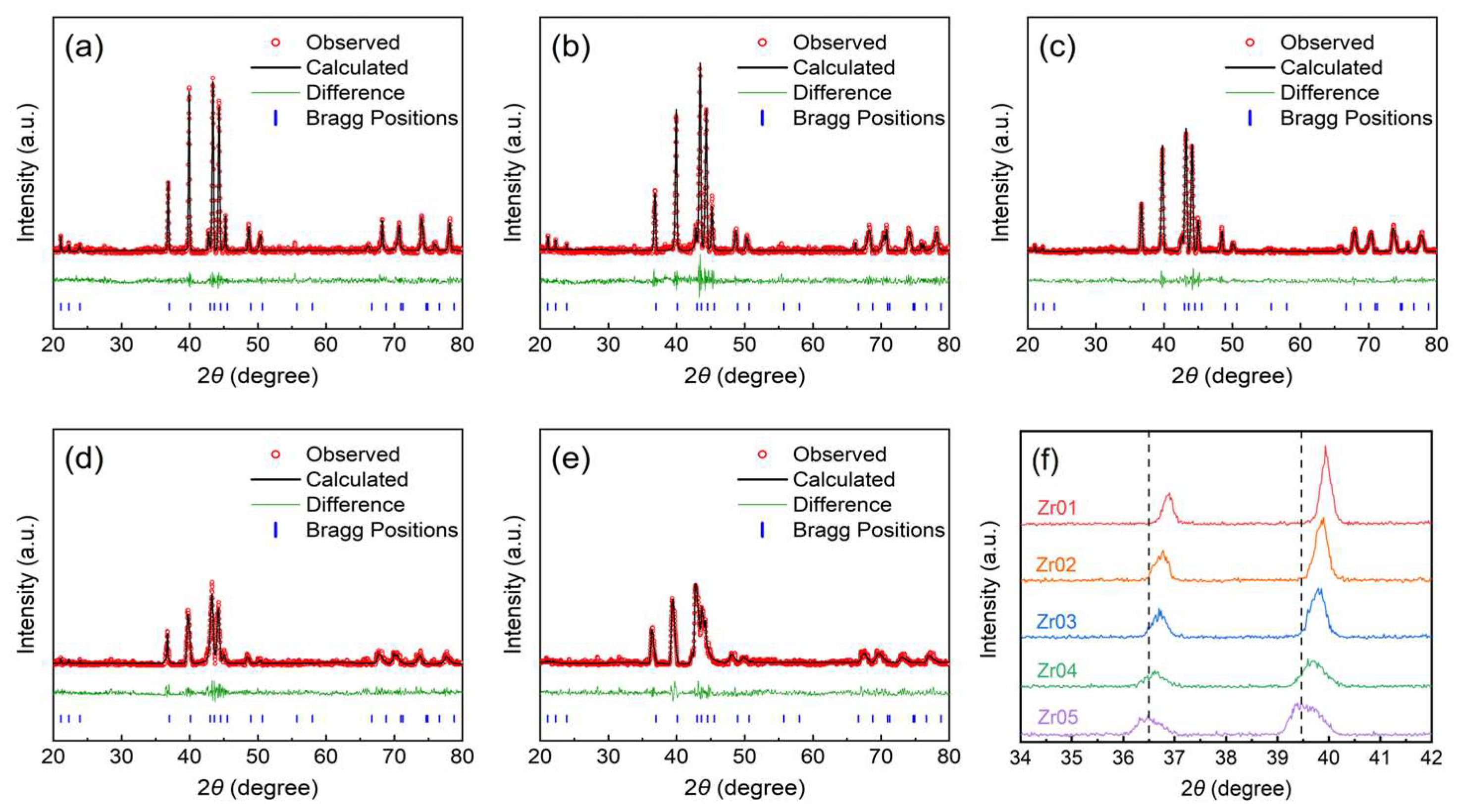
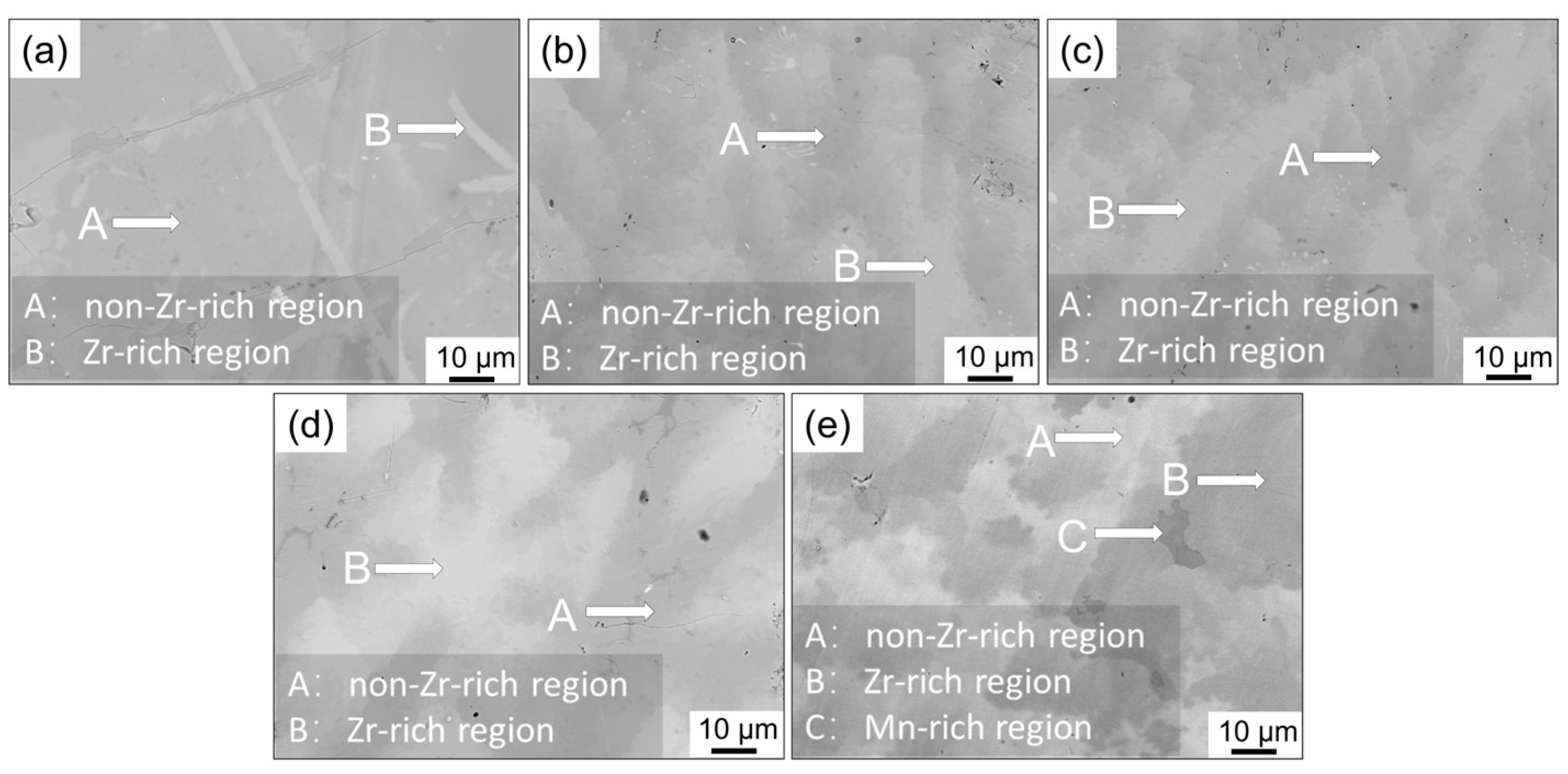
3.1. Microstructure Characteristics
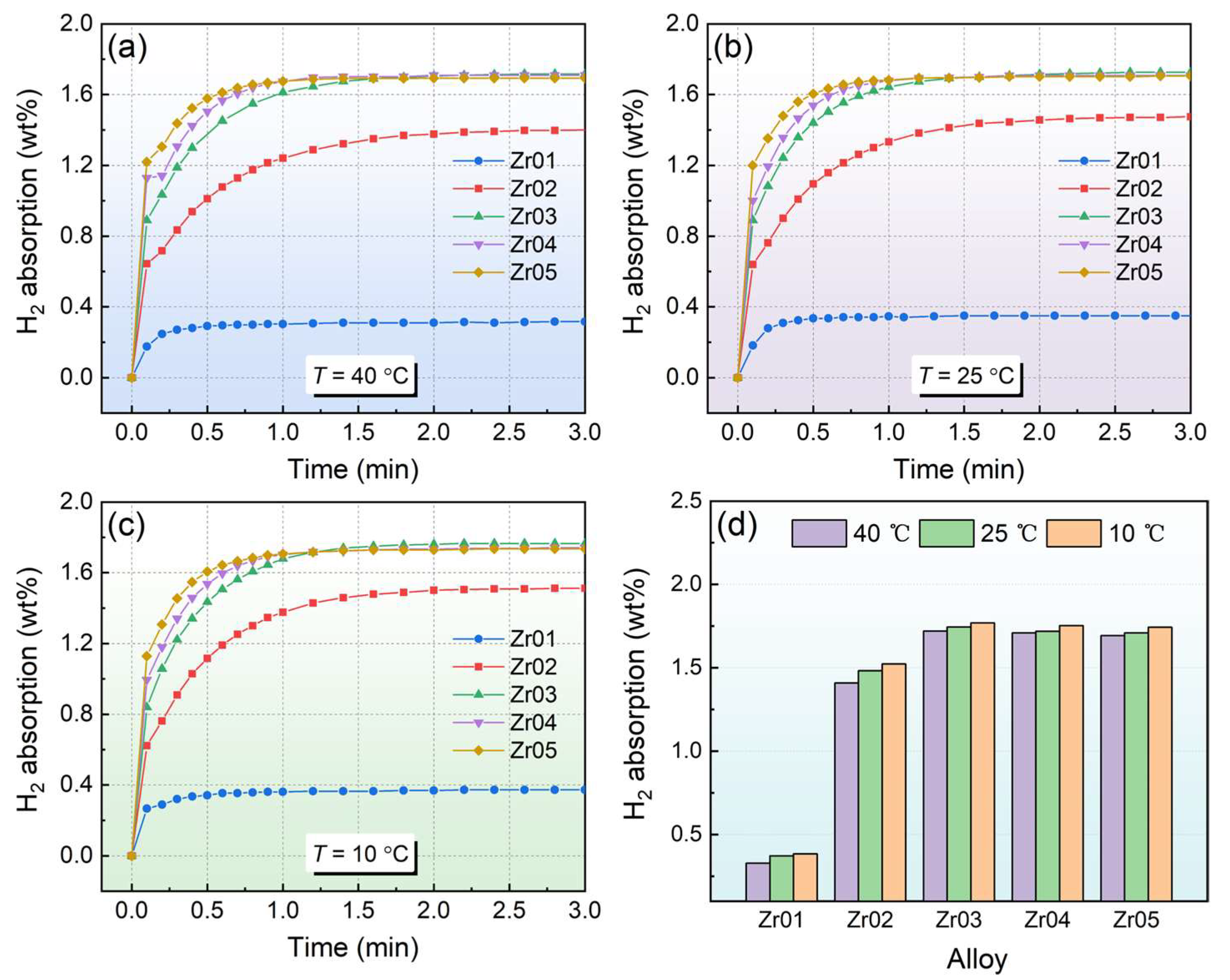
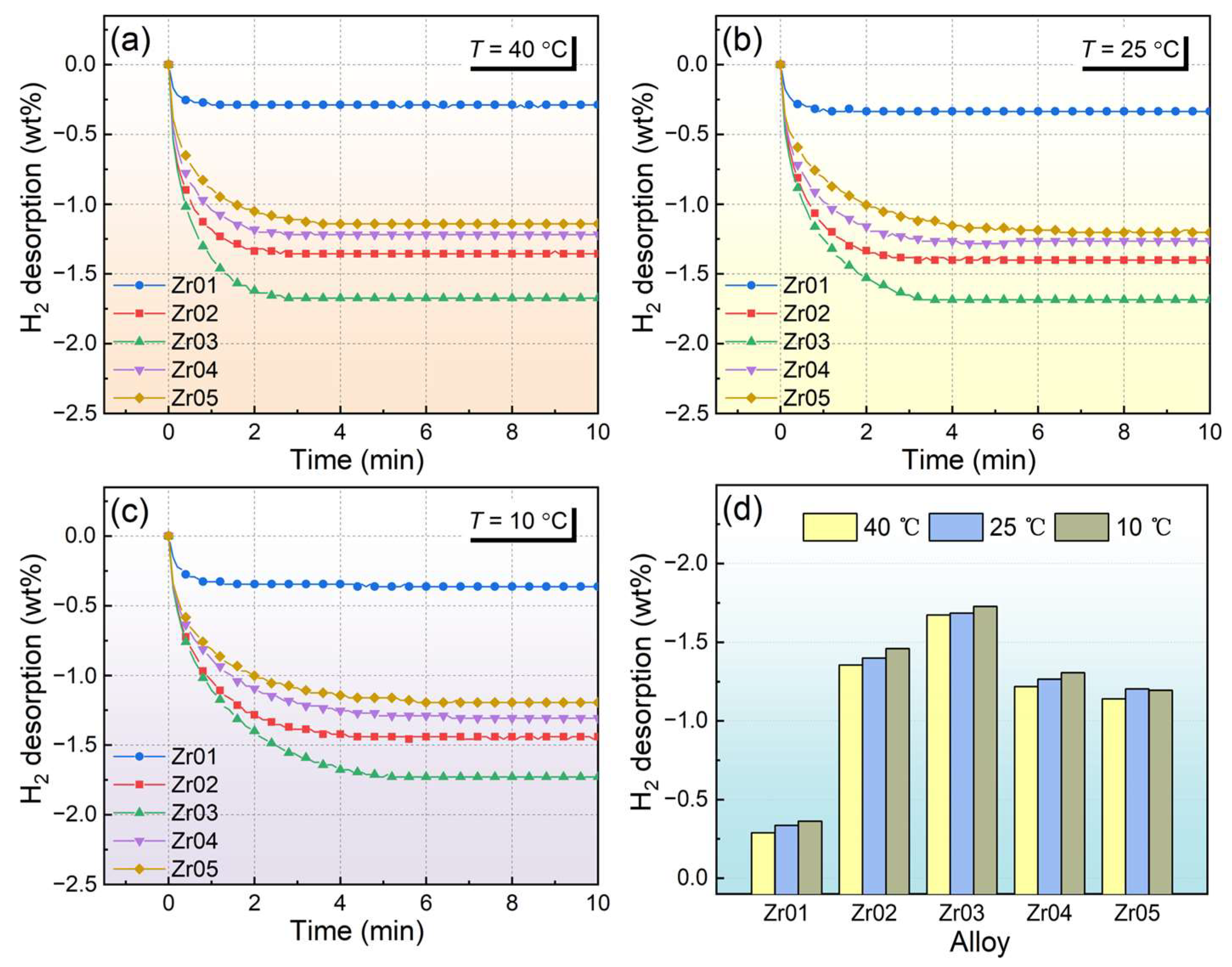
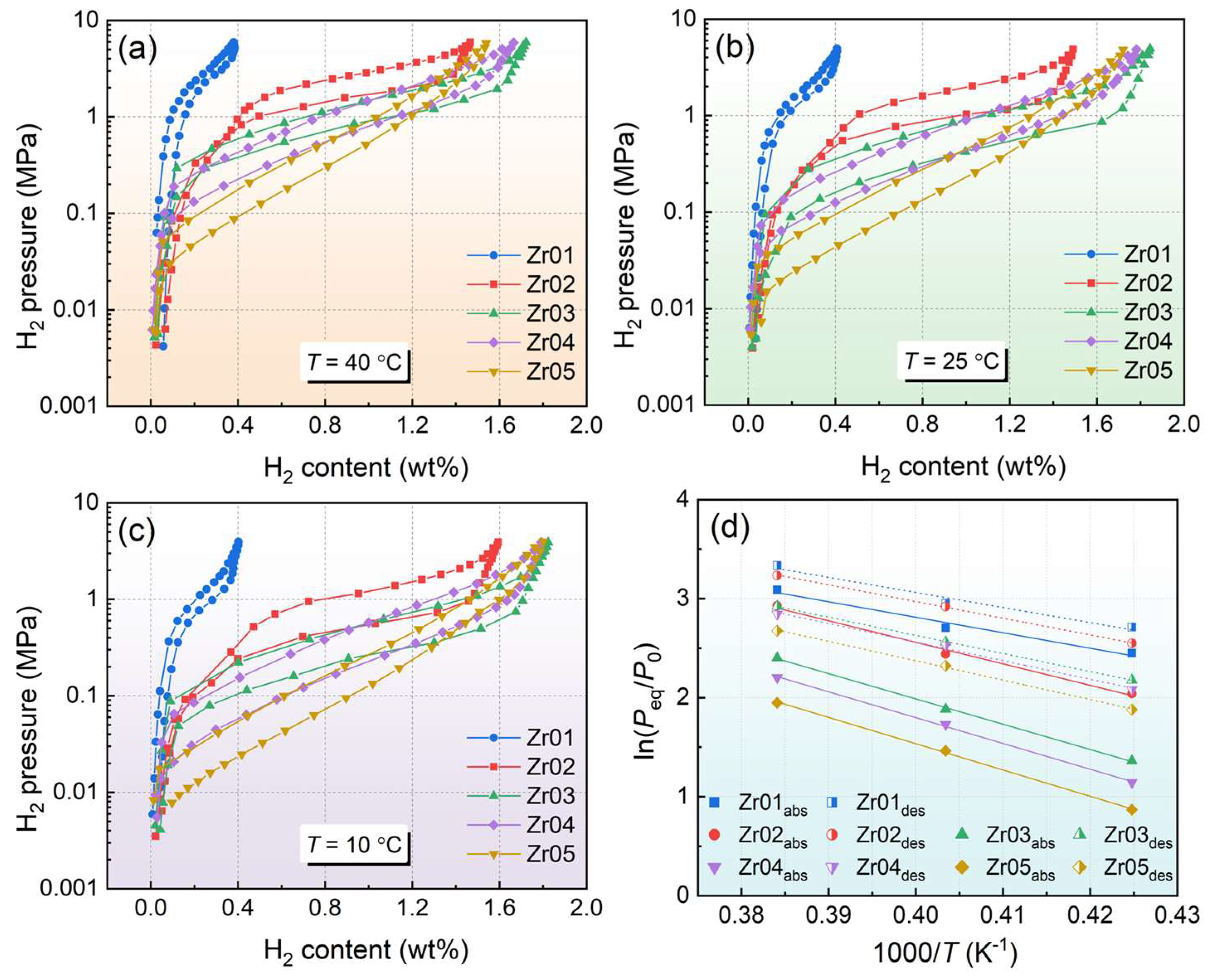
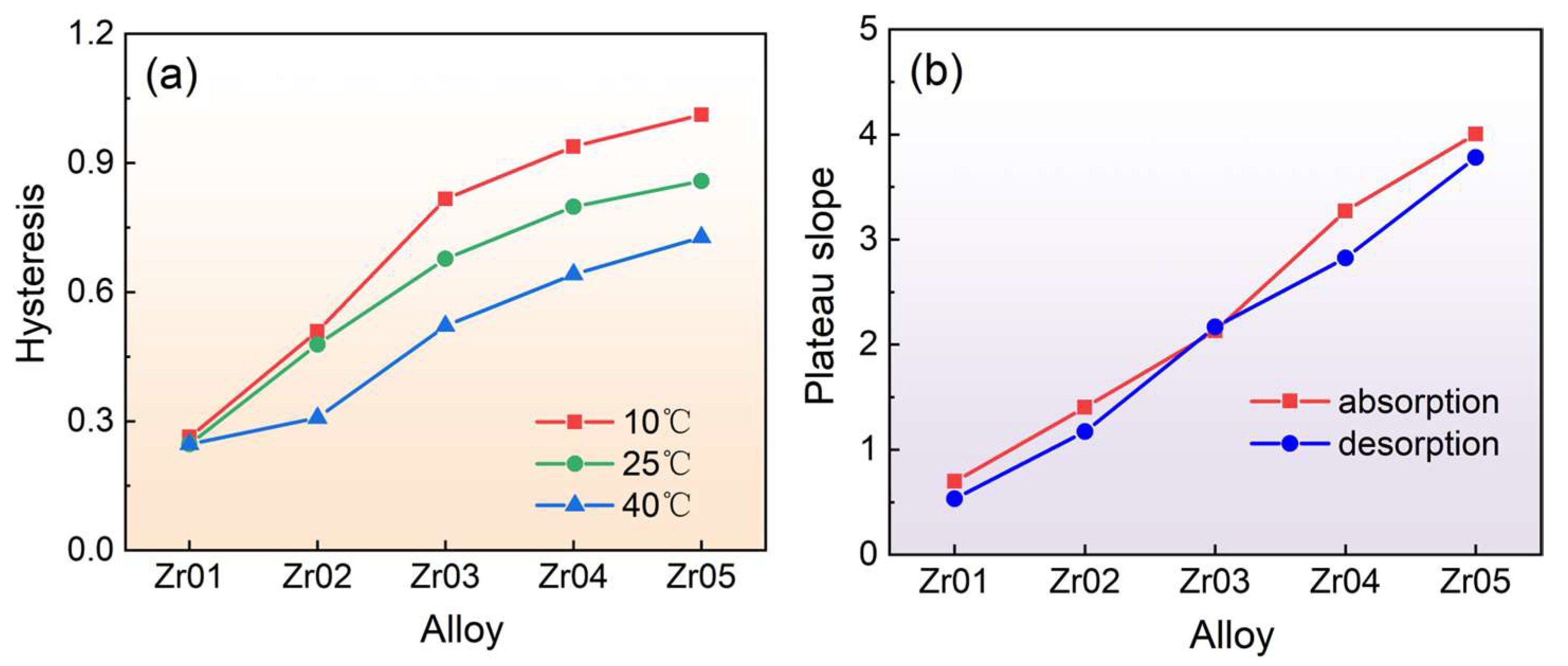
3.2. Hydrogen Absorption and Desorption Kinetic Properties
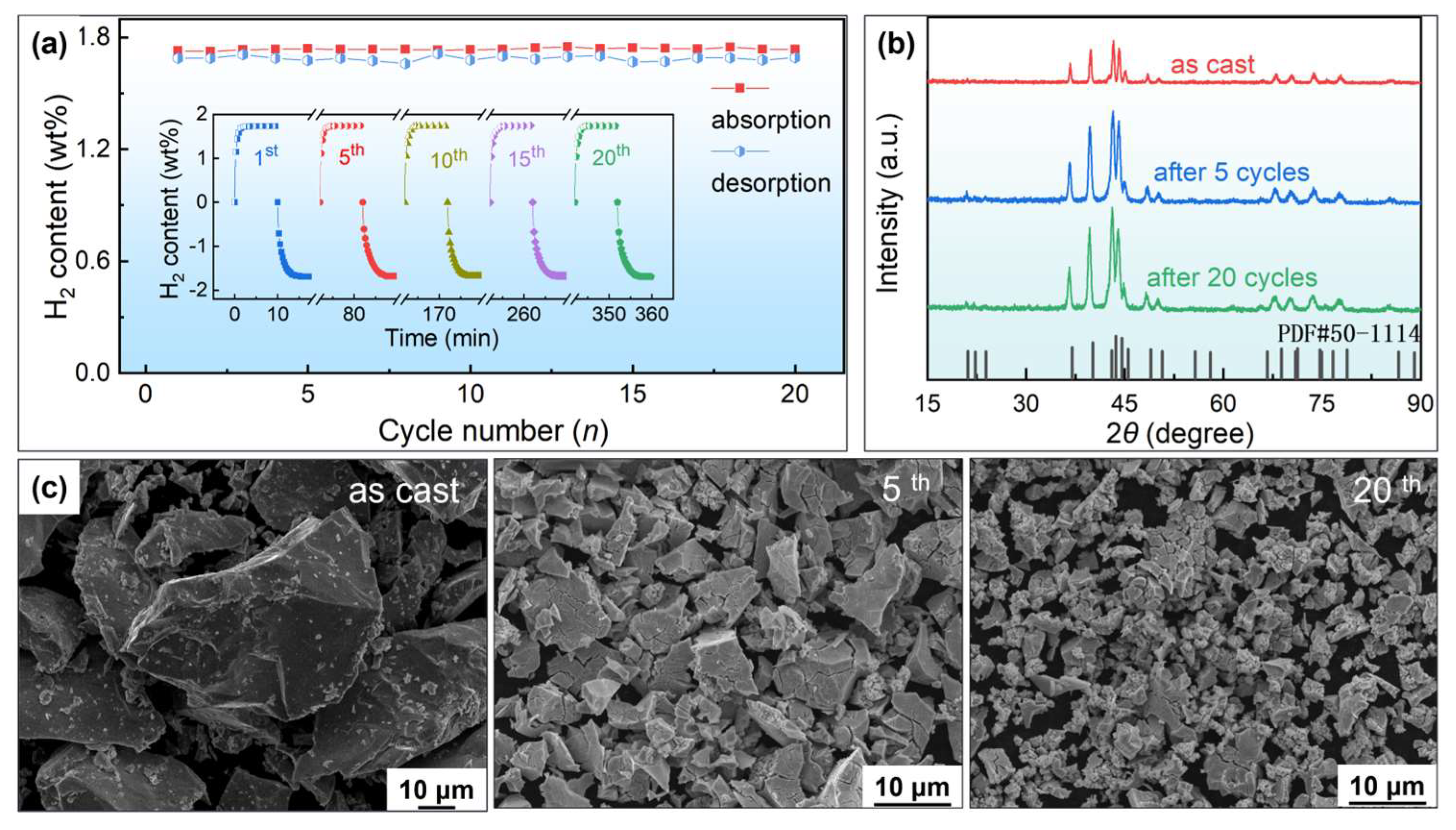
3.3. Cycling Performance
4. Conclusions
- A series of TiMn2-based alloys with varying Zr contents were prepared, with all these alloys exhibiting a single C14-type Laves phase structure. As the Zr content increased, both the lattice parameters and unit cell volume increased accordingly. SEM and EDS analysis indicates that the Zr distributions in the alloys are not uniform.
- Kinetic tests showed that the alloys exhibited good hydrogen absorption and desorption rates. The hydrogen storage capacity of the alloy first increases and then decreases with increasing Zr content. The Zr03 alloy demonstrated relatively high hydrogen absorption and desorption capacities, with a maximum hydrogen absorption of 1.77 wt% at 10 °C.
- Increasing the Zr content has been shown to effectively lower the plateau pressure in the alloys. The van ‘t Hoff fitting demonstrated that the Zr content influences the thermodynamic properties of the alloys, leading to increases in both the enthalpy change and entropy change. Specifically, the Zr05 alloy exhibited the largest absolute values for hydrogen absorption and desorption enthalpy and entropy changes, with values of 19.56 kJ·mol−1 H2/101.9 J·K−1·mol−1 H2 for absorption, and 26.56 kJ·mol−1 H2/121.6 J·K−1·mol−1 H2 for desorption. Moreover, the P-C-T curves of the alloys exhibit an obvious slope and a certain degree of hysteresis.
- Significant alloy particle pulverization occurs during the hydrogen absorption and desorption cyclic process. There is no noticeable capacity degradation and phase composition changes during hydrogenation cycles; the results suggest that the Zr03 alloy possesses good cycling stability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, S.A.; Razi, F.; Hewage, K.; Sadiq, R. The perspective of energy poverty and 1st energy crisis of green transition. Energy 2023, 275, 127487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, M.; Osman, A.I.; Mohamed, I.M.A.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Ihara, I.; Yap, P.-S.; Rooney, D.W. Strategies to save energy in the context of the energy crisis: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2003–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Luo, Q.; Li, Q.; Pan, F. Thermodynamic and kinetic regulation for Mg-based hydrogen storage materials: Challenges, strategies, and perspectives. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2406639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagar, R.; Srivastava, S.; Hudson, S.L.; Amaya, S.L.; Tanna, A.; Sharma, M.; Achayalingam, R.; Sonkaria, S.; Khare, V.; Srinivasan, S.S. Recent developments in state-of-the-art hydrogen energy technologies-Review of hydrogen storage materials. Sol. Compass 2023, 5, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Huang, Z.; Yang, L.; Gu, C.; Sun, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Recent advances in catalyst-modified Mg-based hydrogen storage materials. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 163, 182–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.R. Hydrogen storage methods: Review and current status. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, C.; Sui, Y.; Zhai, T.; Hou, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Y. Research progress in improved hydrogen storage properties of Mg-based alloys with metal-based materials and light metals. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1401–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Musyoka, N.M.; Langmi, H.W.; Mathe, M.; Liao, S. Current research trends and perspectives on materials-based hydrogen storage solutions: A critical review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirscher, M.; Yartys, V.A.; Baricco, M.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.; Blanchard, D.; Bowman, R.C.; Broom, D.P.; Buckley, C.E.; Chang, F.; Chen, P.; et al. Materials for hydrogen-based energy storage—Past, recent progress and future outlook. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 153548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhu, W.; Lu, C.; Ding, W.J.; Zou, J.X. Nanostructuring of Mg-Based Hydrogen Storage Materials: Recent Advances for Promoting Key Applications. Nano Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, F.; Balcerzak, M.; Winkelmann, F.; Zepon, G.; Felderhoff, M.; Marques, F. Review and outlook on high-entropy alloys for hydrogen storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5191–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, M.; Pourarian, F.; Sankar, S.G.; Wallace, W.E.; Zhang, L. TiMn2-based alloys as high hydrogen storage materials. Mat. Sci. Eng. B-Adv. 1995, 33, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-H.; Kim, D.-M.; Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y. Hydrogen storage properties of TiMn2-based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1996, 240, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, D.; Chen, D.; Yang, L.; Xiao, P.; Liu, J. Ti–Mn hydrogen storage alloys: From properties to applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 35744–35755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.W.; Martin, T.C.; Fursikov, P.V.; Zhidkov, M.V.; Khodos, I.I.; Fashu, S.; Lototskyy, M.V. Effect of preparation routes on the performance of a multi-component AB2-type hydrogen storage alloy. J. Phys. Energy 2024, 6, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandavel, M.; Bhat, V.V.; Rougier, A.; Aymard, L.; Nazri, G.A.; Tarascon, J.M. Improvement of hydrogen storage properties of the AB2 Laves phase alloys for automotive application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 3754–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Cao, Z.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, L.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L. Development of Ti-Zr-Mn-Cr-V based alloys for high-density hydrogen storage. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 875, 160035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon Monsalve, D.; Ulate-Kolitsky, E.; Martínez-Amariz, A.-D.; Huot, J. Effects of Ti substitution by Zr, on the microstructure and hydrogen storage properties OF Ti2−xZrxCrV (x = 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2) alloys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e35739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, W.F.; Liu, W.Q.; Yin, D.M.; Ding, N.; Zhao, S.L.; Xiu, H.X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Wang, C.L.; et al. Comprehensive improvement of AB2 hydrogen storage alloy: Substitution of rare earth elements for different A-side alloys. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, U.; Dieterich, M.; Pohl, A.; Dittmeyer, R.; Linder, M.; Fichtner, M. Study of the structural, thermodynamic and cyclic effects of vanadium and titanium substitution in laves-phase AB2 hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20103–20110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Yin, D.; Zhao, S.; Ding, N.; Liang, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; He, M.; Cheng, Y. Effects of Cu doping on the hydrogen storage performance of Ti-Mn-based, AB2-type alloys. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, L.; Jiang, Z.; Piao, M.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, L. Studies on Ti-Zr-Cr-Mn-Fe-V based alloys for hydrogen compression under mild thermal conditions of water bath. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, W.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Optimization of Ti-Zr-Cr-Fe alloys for 45 MPa metal hydride hydrogen compressors using orthogonal analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 889, 161629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Zhu, J.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Leng, H.; Liu, W.; Pan, T.; Han, X.; Lv, L. Effect of different metal element substitution on microstructural and comprehensive hydrogen storage performance of Ti0.9Zr0.1Mn0.95Cr0.7V0.2M0.15 (M = Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Mo) alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2024, 34, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, H.; Liu, W.; Yin, D.; Ding, N.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, S.; Liang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; et al. Multidimensional regulation of Ti-Zr-Cr-Mn hydrogen storage alloys via Y partial substitution. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 4211–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Ma, X.; Ding, X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Song, Q.; Cui, H. Study on hydrogen storage properties of Ti–V–Fe–Mn alloys by modifying Ti/V ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 67, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhao, X.; Deng, Y.; Ke, D.; Li, R.; Hu, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; HuangFu, Y.; Zou, S.; et al. Influence of the substitution Cr for Mn on structural and hydrogen storage performance of Ti0.9Zr0.1V0.45CrxMn1.5-x(x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.2) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, A.J.; Wadge, M.D.; Adams, M.; Manickam, K.; Ling, S.; Walker, G.S.; Grant, D.M. Stoichiometry and annealing condition on hydrogen capacity of TiCr2−x AB2 alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.; Nei, J.; Huang, B.; Fetcenko, M.A. Studies of off-stoichiometric AB2 metal hydride alloy: Part 2. Hydrogen storage and electrochemical properties. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 11146–11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandavel, M.; Ramaprabhu, S. The effect of non-stoichiometry on the hydrogen storage properties of Ti-substituted AB2 alloys. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 7501–7517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Xiong, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Yan, H. Hydrogen storage properties of AB2 type Ti–Zr–Cr–Mn–Fe based alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; He, J.; Li, J.; Luo, L.; Xi, H.; Yan, Y.; Wu, C.; Mu, S.; Lan, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Enhancing the Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti–Mn Alloys by Ti Occupying Mn Sites: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 5819–5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebossadri, S.; Book, D. Compositional effects on the hydrogen cycling stability of multicomponent Ti-Mn based alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 10722–10731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Chen, X.Y.; Ding, X.; Li, X.Z.; Guo, J.J.; Ding, H.S.; Su, Y.Q.; Fu, H.Z. Effects of Ti/Mn ratio on microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Ti-V-Mn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 748, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, K.; Grant, D.M.; Walker, G.S. Optimization of AB2 type alloy composition with superior hydrogen storage properties for stationary applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16288–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCusker, L.B.; Von Dreele, R.B.; Cox, D.E.; Louer, D.; Scardi, P. Rietveld refinement guidelines. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chang, S.-Y.; Hong, Y.-D.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J. Anomalous decrease in X-ray diffraction intensities of Cu–Ni–Al–Co–Cr–Fe–Si alloy systems with multi-principal elements. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 103, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, F.; Miao, G.; Ju, A.; Qu, X.; Li, P. Tuning of Zr content in TiMn2 based multinary alloys by powder metallurgy to fabricate superior hydrogen storage properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 682, 1040–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naorem, R.; Gupta, A.; Mantri, S.; Sethi, G.; ManiKrishna, K.V.; Pala, R.; Balani, K.; Subramaniam, A. A critical analysis of the X-ray diffraction intensities in concentrated multicomponent alloys. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 110, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobet, J.L.; Darriet, B. Relationship between hydrogen sorption properties and crystallography for TiMn2 based alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2000, 25, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, E. Thermodynamics of hydrogenation for Ti1−xZrxMnCr Laves phase alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 455, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrokhin, S.V.; Bezuglaya, T.N.; Verbetsky, V.N. Structure and hydrogen sorption properties of (Ti,Zr)–Mn–V alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330–332, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehouche, Z.; Savard, M.; Laurencelle, F.; Goyette, J. Ti–V–Mn based alloys for hydrogen compression system. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 400, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.B.; Wu, Z.; Xia, B.J.; Xu, N.X. Enhancement of hydrogen storage capacity of Ti–V–Cr–Mn BCC phase alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 372, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yao, M.; Feng, F.; Northwood, D.O. The application of mathematical models to the calculation of selected hydrogen storage properties (formation enthalpy and hysteresis) of AB2-type alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2000, 25, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-G.; Jang, H.-Y.; Han, S.-C.; Lee, P.S.; Lee, J.-Y. Hydrogen storage properties of TiMn2-based alloys for metal hydride heat pump. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2002, 329–331, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Xia, C.; Yang, T. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of Zr-based AB2-type high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Alloys | Lattice Parameters | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | c (Å) | ||
| Zr01 | 4.873 | 7.999 | 164.5 |
| Zr02 | 4.883 | 8.020 | 165.6 |
| Zr03 | 4.899 | 8.040 | 167.1 |
| Zr04 | 4.908 | 8.406 | 167.8 |
| Zr05 | 4.935 | 8.105 | 170.9 |
| Alloys | Regions | Element Fraction (at %) | Percentage of Zr Elements | Error % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | Zr | Mn | Cr | Fe | ||||
| Zr01 | A | 21.50 | 1.57 | 17.81 | 25.31 | 1.79 | 2.31% | 2.81% |
| B | 26.79 | 2.20 | 23.01 | 32.86 | 2.05 | 2.53% | 2.74% | |
| Zr02 | A | 29.95 | 3.56 | 34.80 | 29.05 | 2.64 | 3.56% | 2.80% |
| B | 26.99 | 5.29 | 32.07 | 32.91 | 2.74 | 5.29% | 2.80% | |
| Zr03 | A | 22.75 | 4.60 | 31.89 | 26.01 | 1.81 | 5.28% | 3.12% |
| B | 18.29 | 7.23 | 28.61 | 28.46 | 2.43 | 8.50% | 2.54% | |
| Zr04 | A | 18.55 | 4.06 | 42.12 | 21.06 | 1.54 | 5.65% | 2.68% |
| B | 14.06 | 10.14 | 35.28 | 24.92 | 1.73 | 11.77% | 2.14% | |
| Zr05 | A | 26.44 | 7.50 | 36.99 | 26.28 | 2.78 | 7.50% | 3.20% |
| B | 13.97 | 15.02 | 33.10 | 34.89 | 3.02 | 15.02% | 2.64% | |
| C | 4.60 | 0.01 | 54.50 | 28.77 | 0.78 | 0.01% | 2.70% | |
| Alloys | ∆Habs (kJ·mol−1 H2) | ∆Sabs (J·K−1·mol−1 H2) | ∆Hdes (kJ·mol−1 H2) | ∆Sdes (J·K−1·mol−1 H2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr01 | −15.23 | −91.5 | 15.64 | 90.7 |
| Zr02 | −16.85 | −97.1 | 21.73 | 112.5 |
| Zr03 | −18.31 | −99.5 | 25.54 | 122.0 |
| Zr04 | −18.77 | −100.7 | 26.05 | 122.2 |
| Zr05 | −19.56 | −101.9 | 26.56 | 121.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Shi, L.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.; Xia, C.; Yang, T. Effects of Ti Substitution by Zr on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Laves Phase AB2-Type Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153438
Guo X, Shi L, Ma C, Zhang W, Xia C, Yang T. Effects of Ti Substitution by Zr on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Laves Phase AB2-Type Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153438
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaowei, Lingxing Shi, Chuan Ma, Wentao Zhang, Chaoqun Xia, and Tai Yang. 2025. "Effects of Ti Substitution by Zr on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Laves Phase AB2-Type Alloy" Materials 18, no. 15: 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153438
APA StyleGuo, X., Shi, L., Ma, C., Zhang, W., Xia, C., & Yang, T. (2025). Effects of Ti Substitution by Zr on Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Laves Phase AB2-Type Alloy. Materials, 18(15), 3438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153438






