Synthesis of Biomass Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer and Its Performance on Cement-Based Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of AHEC
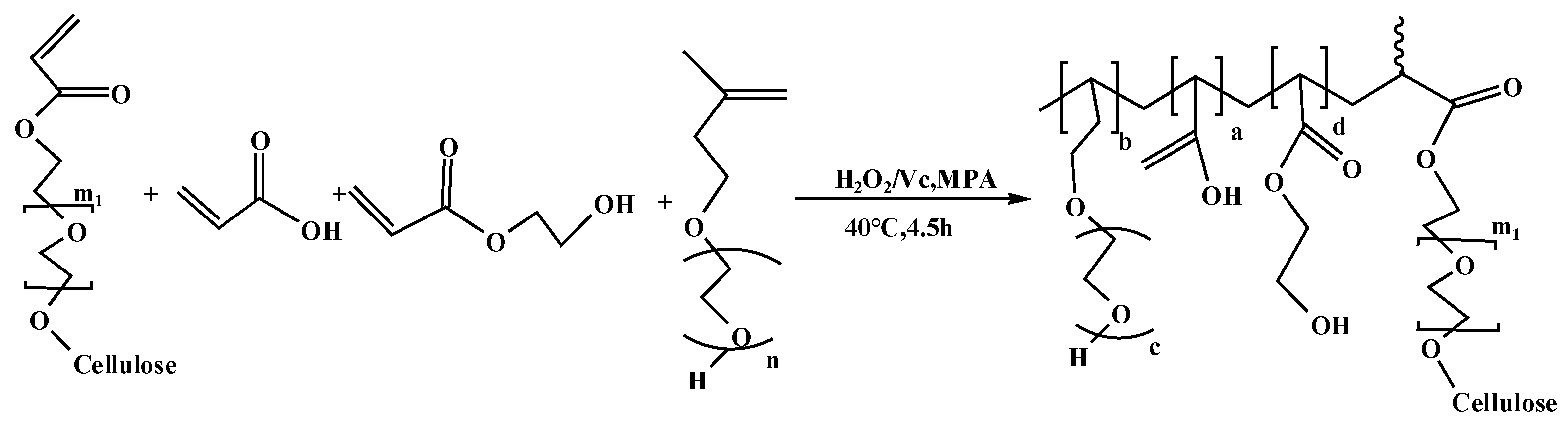
2.2.2. Synthesis of PCE-Cs
2.2.3. Iodine Value
2.2.4. Fluidity
2.2.5. Water Reduction Rate
2.2.6. Setting Time
2.2.7. Cement Mortar Strength
2.2.8. GPC
2.2.9. FTIR
2.2.10. ζ-Potential
2.2.11. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.12. Thickness of Adsorption Layer
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluidity of Cement Paste
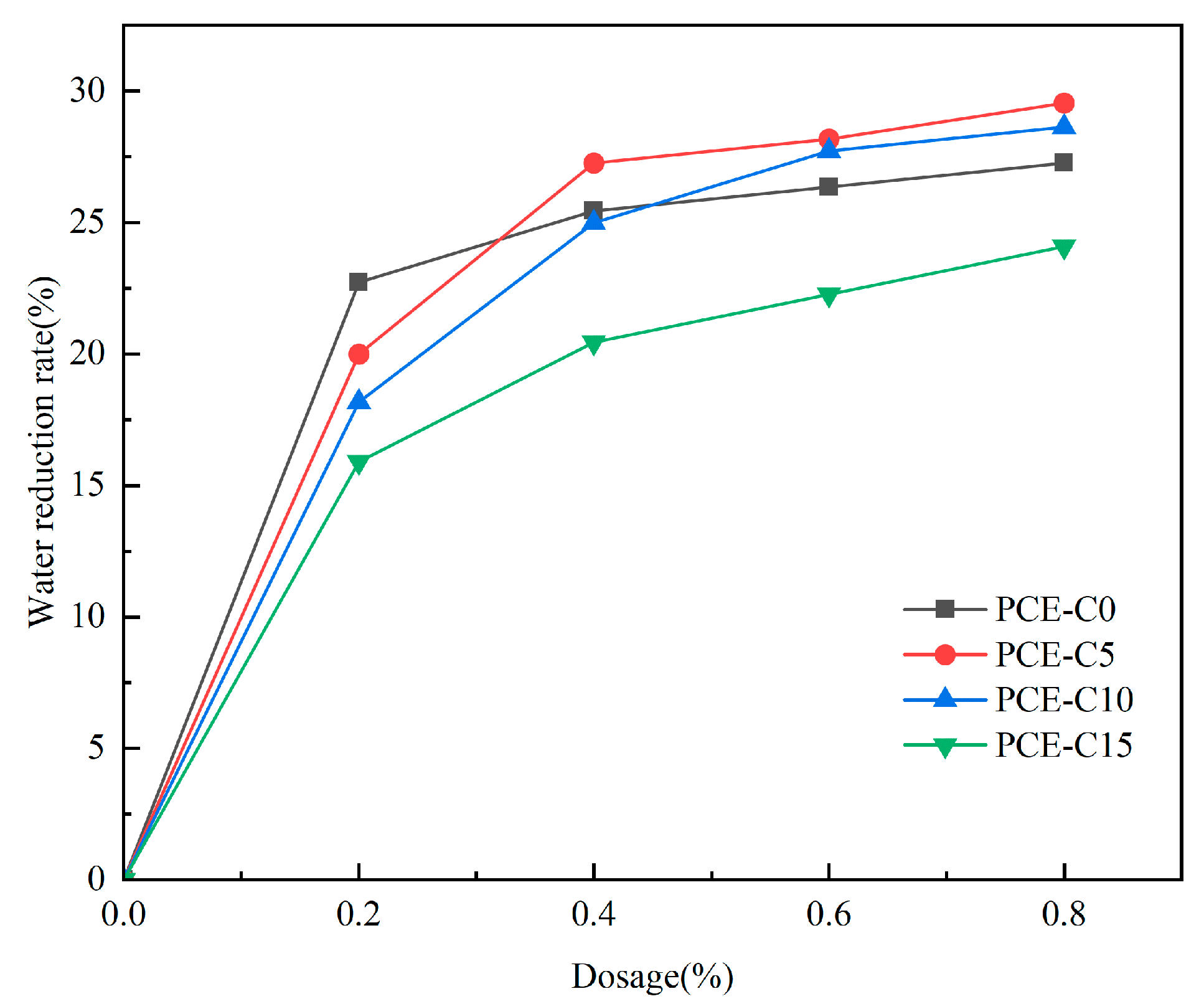
3.2. Water Reduction Rate of Cement Mortar
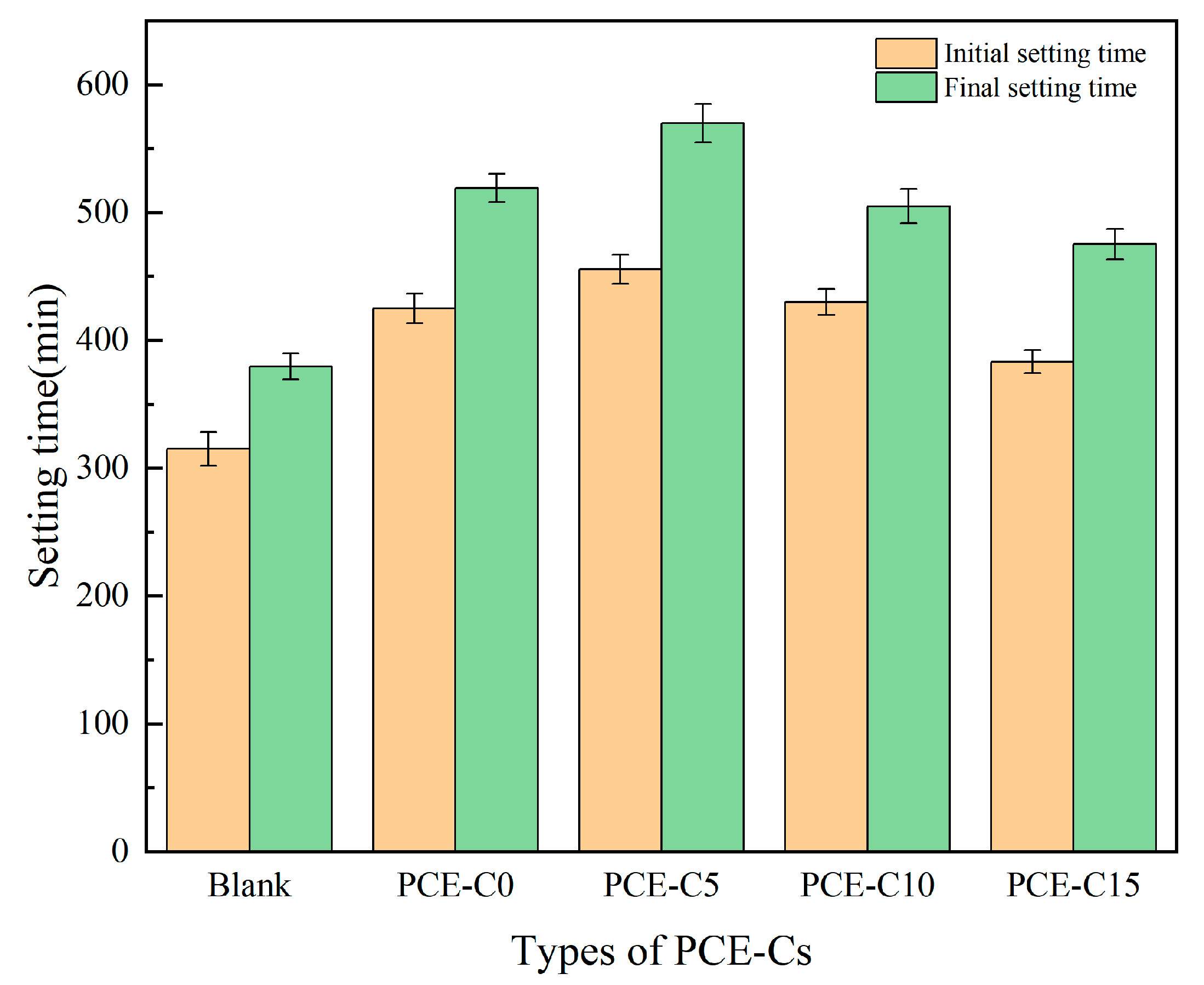
3.3. Setting Time of Cement
3.4. Mechanical Properties
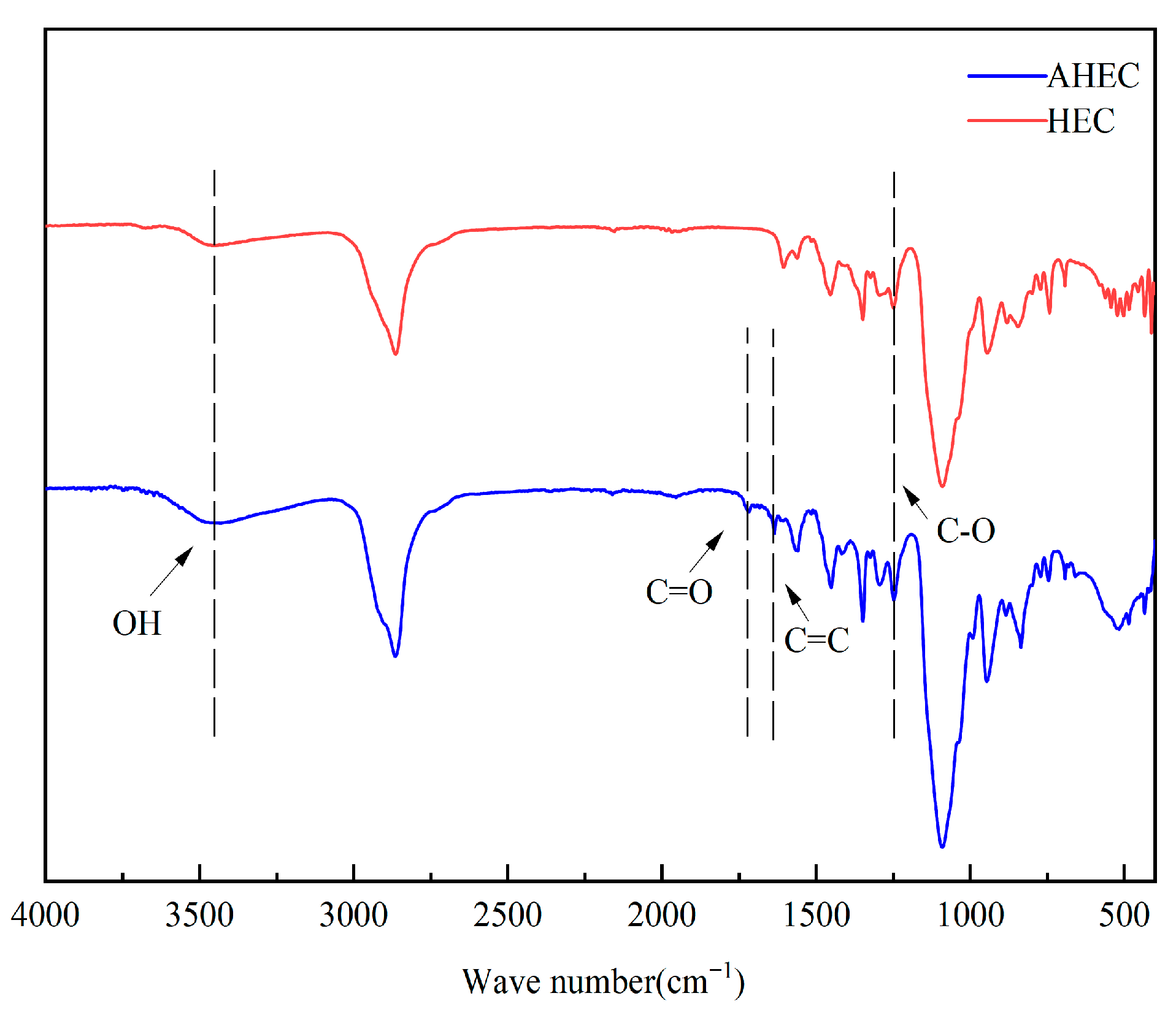
3.5. FTIR for HEC and AHEC
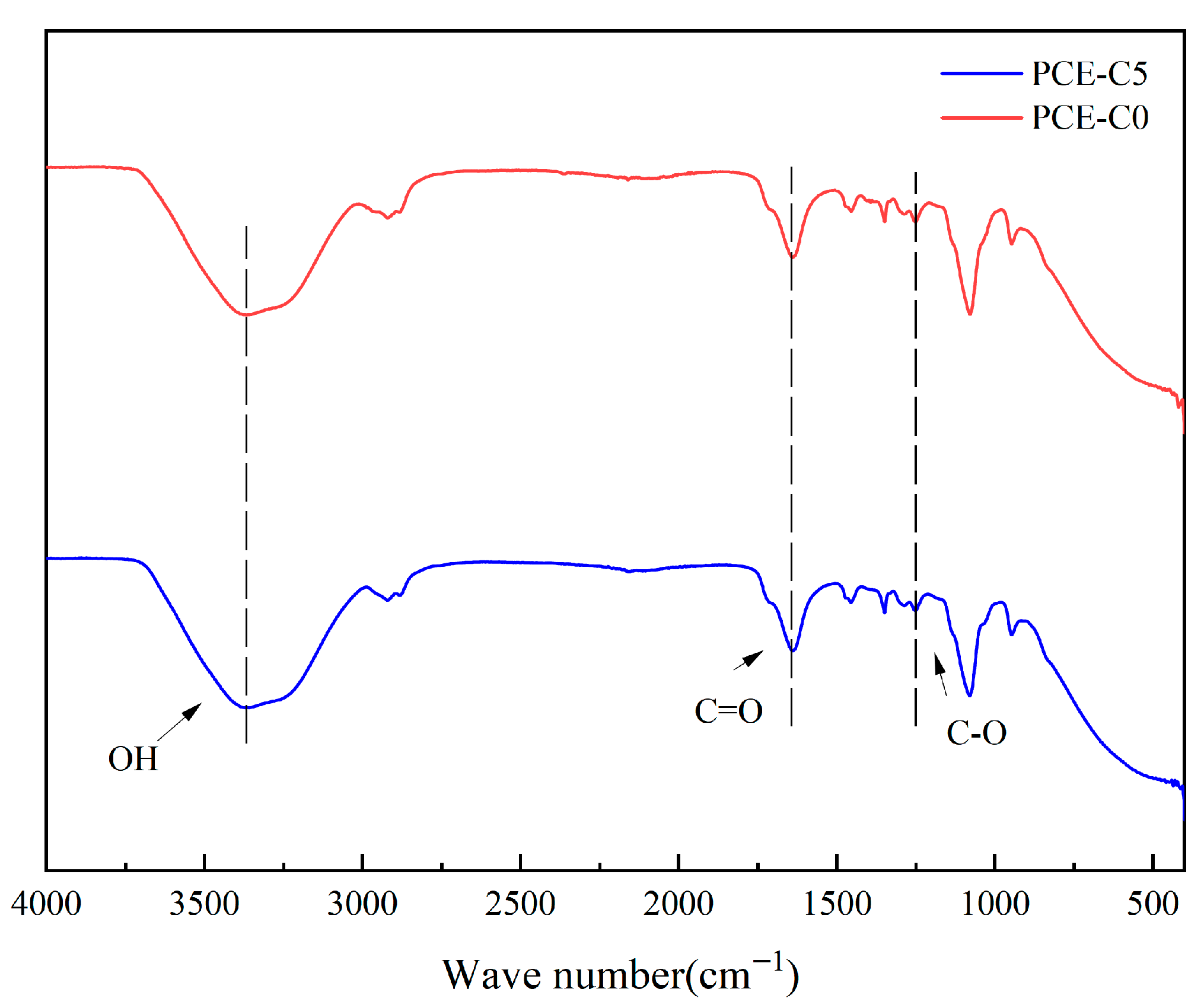
3.6. FTIR for PCE-C0 and PCE-C5
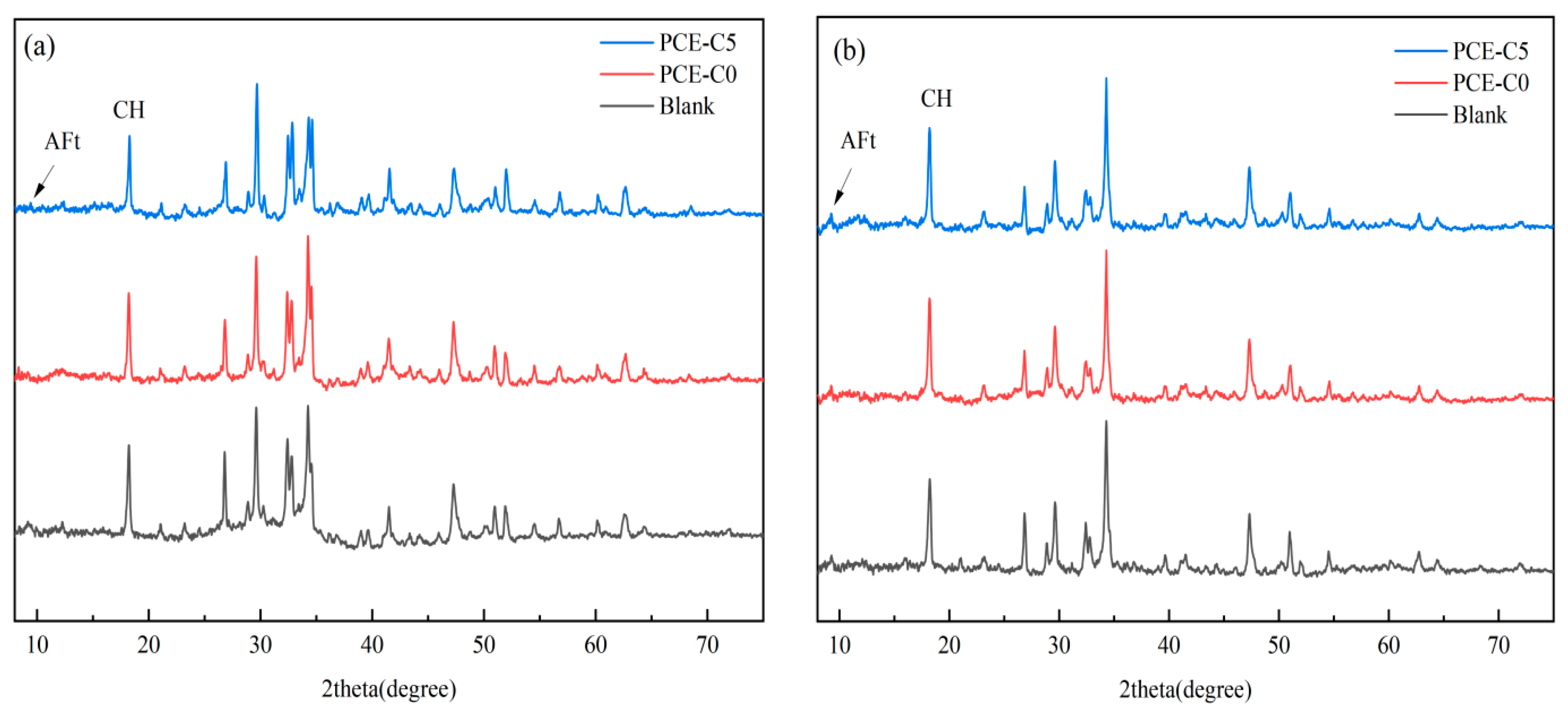
3.7. XRD Analysis of Cement Hydration Products
3.8. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC)
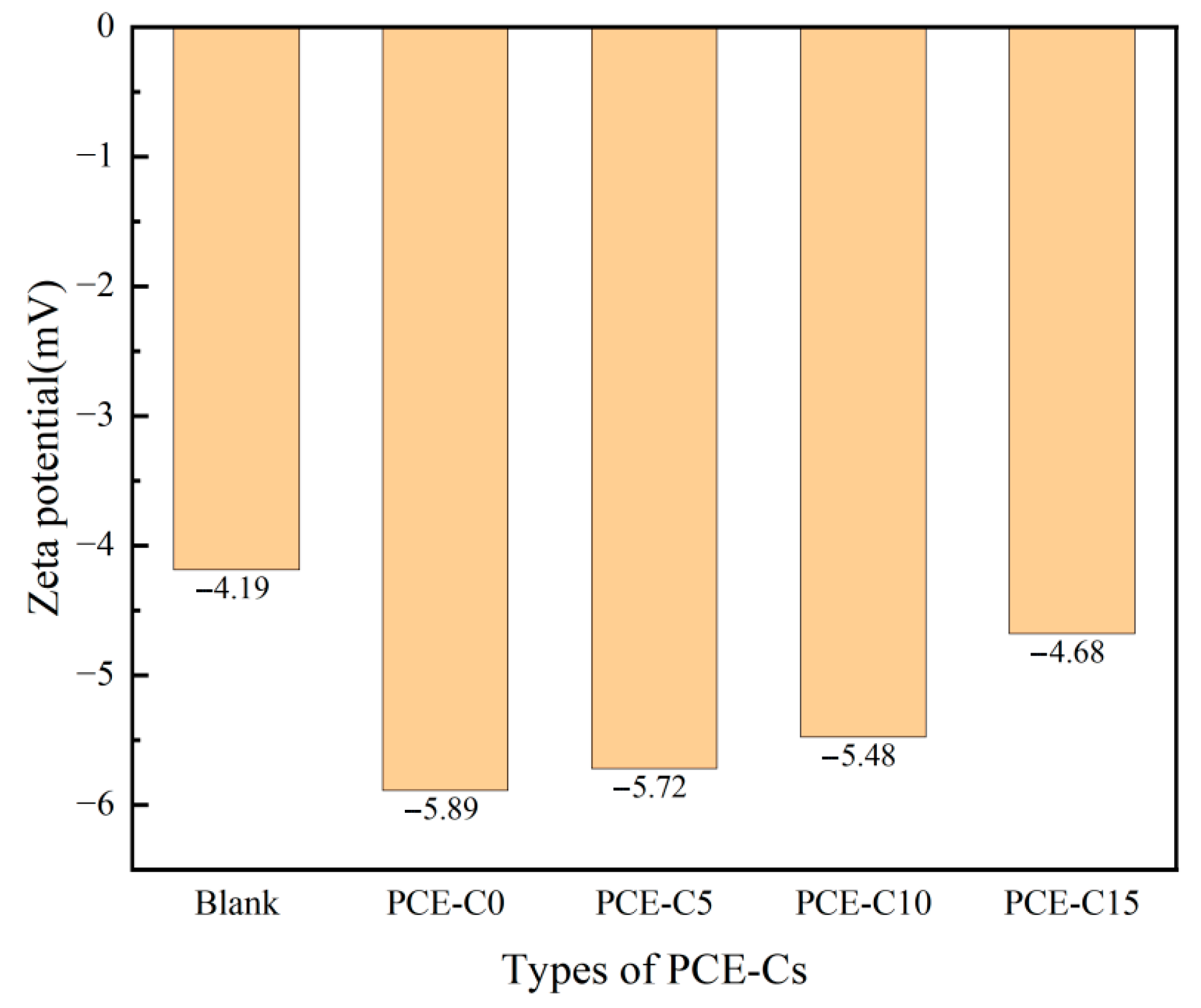
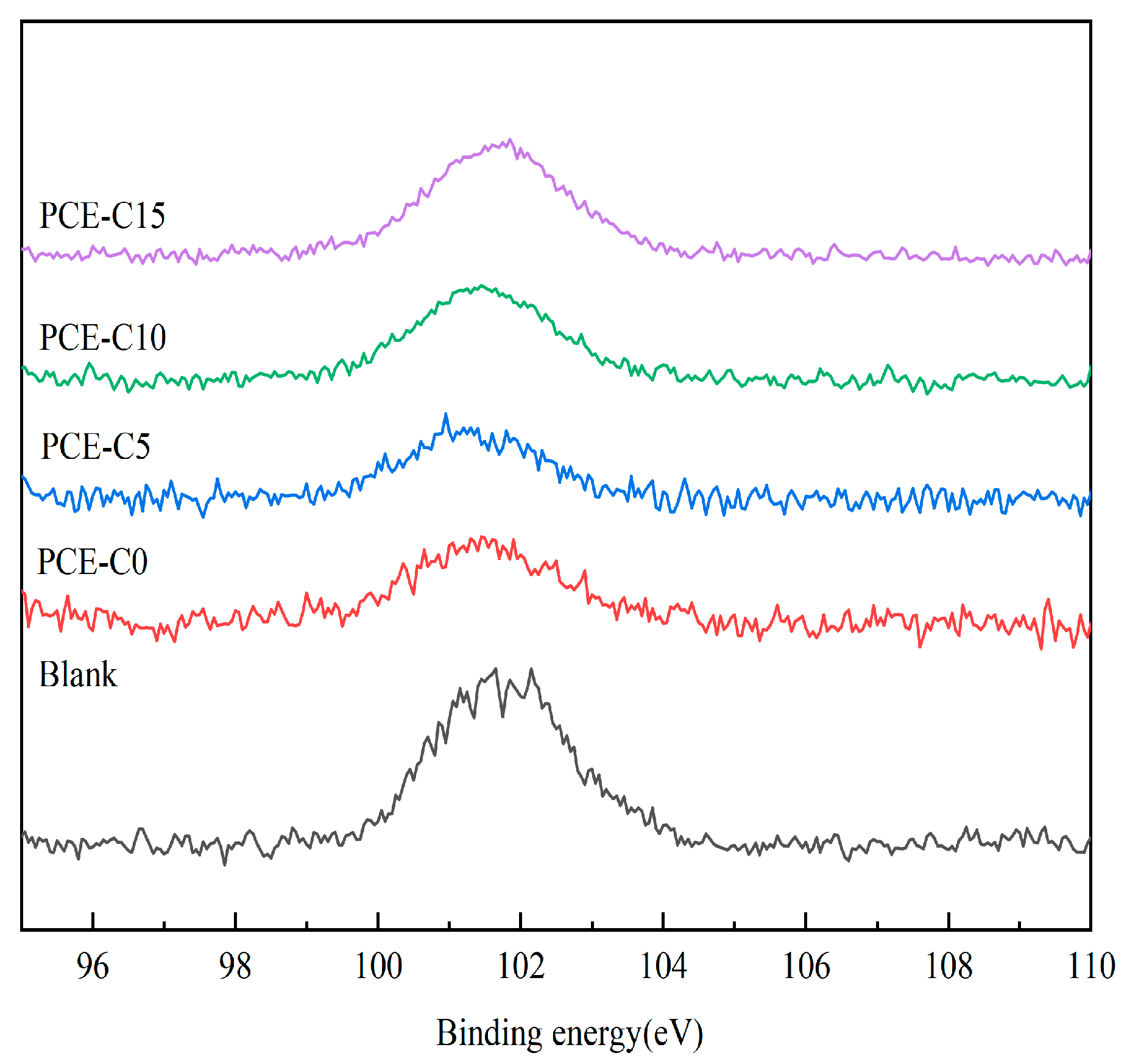
3.9. Zeta Potentials
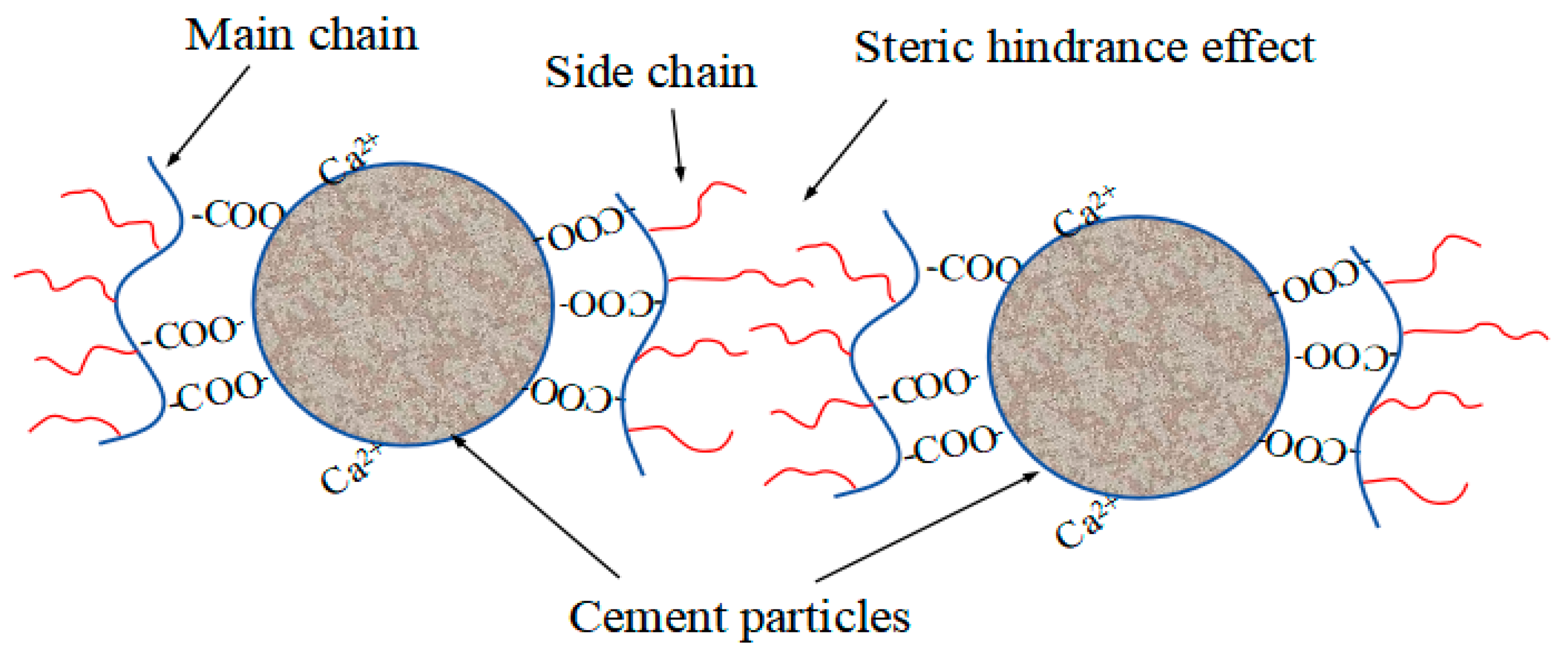
3.10. Adsorption Layer Thickness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, H.; Qian, C.; Zhao, F.; Qu, J.; Guo, J.; Danzinger, M. Improvement on microstructure of concrete by polycarboxylate superplasticizer (PCE) and its influence on durability of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 110, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Sakai, E.; Miao, C.W.; Yu, C.; Hong, J.X. Chemical admixtures—Chemistry, applications and their impact on concrete microstructure and durability. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Peng, X.; Yi, C.; Deng, Y. Effect of side chains and sulfonic groups on the performance of polycarboxylate-type superplasticizers in concentrated cement suspensions. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Bian, H. Method to assess the quality of casein used as superplasticizer in self-levelling compounds. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhov, A.; Shir, I.B.; Schmidt, A.; Kovler, K.; Diesendruck, C.E. Retardation mechanism of cement hydration by a comb polyphosphate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 128698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapeluszna, E.; Kotwica, Ł. The effect of various grinding aids on the properties of cement and its compatibility with acrylate-based superplasticizer. Materials 2022, 15, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Song, X.; Song, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, Q. A migrating and reactive polycarboxylate superplasticizer with coupled functions of new/old concrete interfacial agent and water reducer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 172, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, K.; Sakai, E.; Daimon, M.; Kitahara, A. Role of steric hindrance in the performance of superplasticizers for concrete. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 80, 2667–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zou, H.; Liang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Preparation and characterization of amphoteric polycarboxylate and the hydration mechanism study used in Portland cement. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 44018–44025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, L.; Sun, T. Synthesis of modified chitosan superplasticizer by amidation and sulfonation and its application performance and working mechanism. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3908–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guan, J.; Lai, G.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, S.; Lan, M.; Li, H. Novel designs of polycarboxylate superplasticizers for improving resistance in clay-contaminated concrete. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 55, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Cui, S.; Lan, M.; Li, H. Synthesis, characterization and performance of a polycarboxylate superplasticizer with amide structure. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 448, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, F.; Becker, S.; Pakusch, J.; Götz, T. Effects of the molecular architecture of comb-shaped superplasticizers on their performance in cementitious systems. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Somasundaran, P.; Miao, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Shen, J. Effect of the length of the side chains of comb-like copolymer dispersants on dispersion and rheological properties of concentrated cement suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Guo, H.; Lu, M. Study on dispersion, adsorption and flow retaining behaviors of cement mortars with TPEG-type polyether kind polycarboxylate superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 64, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Pang, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, D. Investigation on mechanical behaviors of a new sustainable composite material for fiber-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete under compressive low-cycle loadings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W.; Ma, Z. Unloading and reloading stress-strain relationship of recycled aggregate concrete reinforced with steel/polypropylene fibers under uniaxial low-cycle loadings. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Recent advances in regenerated cellulose materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yingping, Q.I.; Yongfeng, S.H.E.N.; Hua, L.I. Research progress on chemical modification and application of cellulose: A review. Mater. Sci. 2022, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, J.C.; Johns, M.A.; Galembeck, F.; Deneke, C.; Lanzoni, E.M.; Costa, C.A.; Sharma, R.I. Surface modified cellulose scaffolds for tissue engineering. Cellulose 2017, 24, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Ai, T.; Pang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K. Preparation and properties of retarded cellulose-based polycarboxylic superplasticizers. J. Polym. Res. 2025, 32, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Ying, W.F.; Yu, Y.P.; Chi, H.X. Effect of carboxylmethyl cellulose sulfate (CMC-S) on the hydration process of cement paste. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 838, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaiti, H.; Aerken, X. The structure and properties of sulfo-butylated celluluse ether (SBC) based water-reducing agents. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 556, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.C.; Klemm, D.; Einfeldt, L.; Albrecht, G. Dispersing agents for cement based on modified polysaccharides. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, H.; Silva, L.M.; Labrincha, J.A.; Ferreira, V.M. Effects of a water-retaining agent on the rheological behaviour of a single-coat render mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Li, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, T. Comparison of casein and polycarboxylate modified cellulose nanocrystals as superplasticizers in self-leveling mortars. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2022, 14, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Ju, B.Z.; Zhang, S.F.; Yang, J.Z. The study on the synthesis and action mechanism of starch succinate half ester as water-reducing agent with super retarding performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 71, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, I.E.; Ozkul, M.H. Utilization of polysaccharides as viscosity modifying agent in self-compacting concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, I.E.; Ozkul, M.H. Development of chemical admixtures for green and environmentally friendly concrete: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 389, 136116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patural, L.; Korb, J.P.; Govin, A.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B.; Devès, O. Nuclear magnetic relaxation dispersion investigations of water retention mechanism by cellulose ethers in mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Ruot, B. Current understanding of cellulose ethers impact on the hydration of C3A and C3A-sulphate systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, L. Effect of HEMC on the early hydration of Portland cement highlighted by isothermal calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2015, 119, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachaczek, W. Influence of Cellulose Ethers on the Consistency, Water Retention and Adhesion of Renovating Plasters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 471, 032020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, G.; Yong, Q. Preparation of lignosulfonates from biorefinery lignins by sulfomethylation and their application as a water reducer for concrete. Polymers 2018, 10, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, D.; Heublein, B.; Fink, H.P.; Bohn, A. Cellulose: Fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3358–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 13892-2020; Surface Active Agents-Determination of Iodine Value. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 8077-2012; Methods for Testing Uniformity of Concrete Admixture. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- GB/T 1346-2011; Test Methods for Water Requirement of Normal Consistency, Setting Time and Soundness of the Portland Cement. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- GB/T 17671-2021; Test Method of Cement Mortar Strength (ISO Method). Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Tan, H.; Zou, F.; Ma, B.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Jian, S. Effect of sodium tripolyphosphate on adsorbing behavior of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Sachsenhauser, B. Impact of molecular structure on zeta potential and adsorbed conformation of α-allyl-ω-methoxypolyethylene glycol-maleic anhydride superplasticizers. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2006, 4, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Winnefeld, F.; Plank, J. Multi-method approach to study influence of superplasticizers on cement suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourchez, J.; Grosseau, P.; Guyonnet, R.; Ruot, B. HEC influence on cement hydration measured by conductometry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Mishra, P.C.; Singh, V.K.; Narang, K.K. Effects of hydroxyethyl cellulose and oxalic acid on the properties of cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marliere, C.; Mabrouk, E.; Lamblet, M.; Coussot, P. How water retention in porous media with cellulose ethers works. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 1501–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Ouzia, A.; Juilland, P.; Mohamed, A.K. Advances in understanding cement hydration mechanisms. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zheng, D.; Qiu, X.; Yang, D.; Fan, L.; Zheng, J. A novel branched claw-shape lignin-based polycarboxylate superplasticizer: Preparation, performance and mechanism. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 119, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




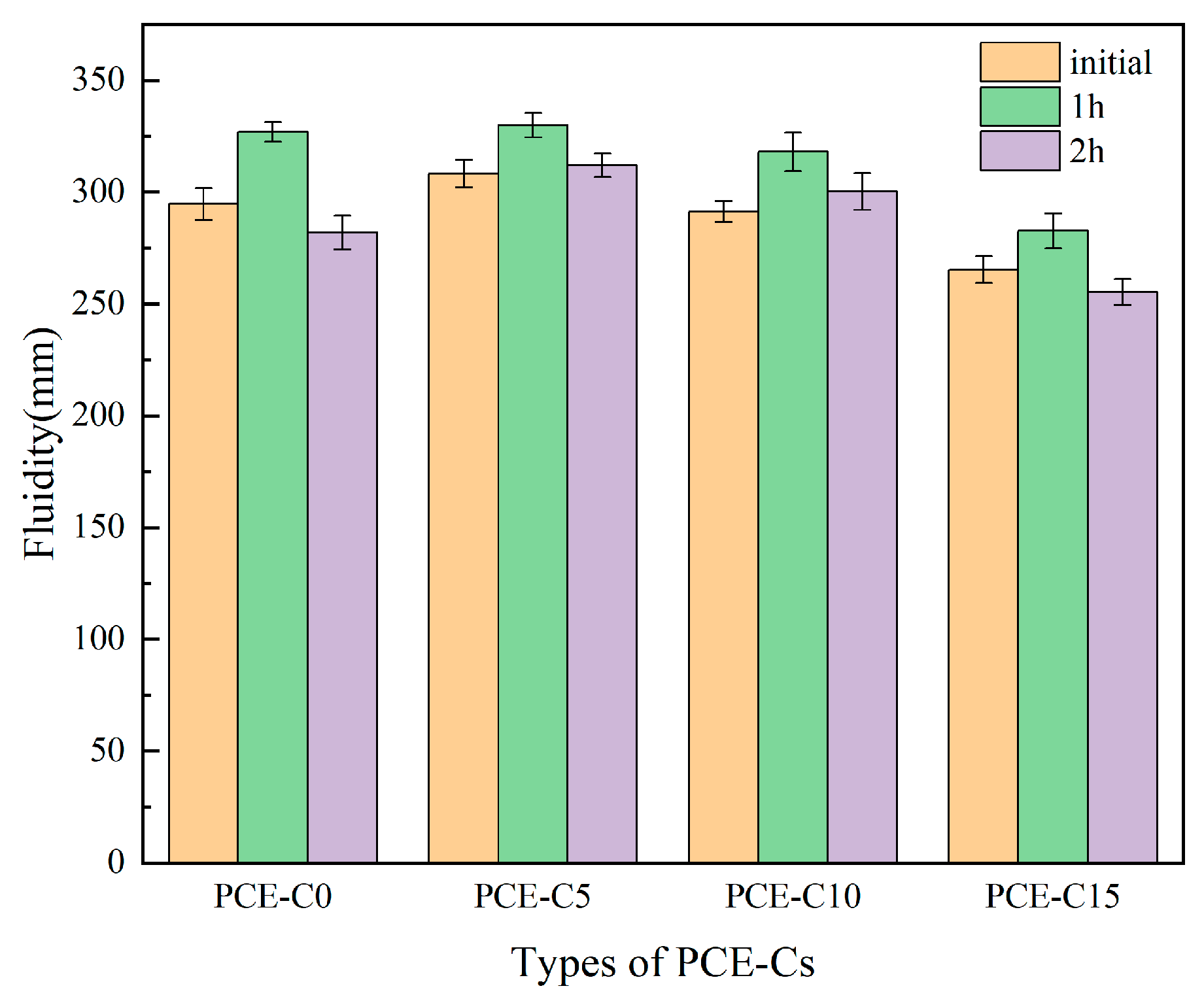
| Component | LOI | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | Fe2O3 | SO2 | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content(%) * | 2.98 | 5.85 | 70.45 | 1.31 | 3.03 | 18.99 | 2.79 |
| Specific Surface Area (m3/Kg) | Setting Time (min) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | 3d | 28d | 3d | 28d | |
| 367 | 315 | 380 | 23.6 | 45.1 | 4.6 | 7.4 |
| Aggregate Size | Proportion (%) | Percentage Passing (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31.5 | 26.5 | 19 | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | ||
| 20~30 mm | 45 | 98 | 67.4 | 3.9 | 0.8 | - | - | - | - |
| 10~20 mm | 55 | 100 | 100 | 96.9 | 75.0 | 6.9 | 5.3 | 0.6 | - |
| Aggregate Size | Fineness Modulus | Percentage Passing (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 0.15 | ||
| medium sand | 2.7 | 4 | 17 | 31 | 54 | 84 | 96 |
| Chemicals | Abbreviations |
|---|---|
| acrylic acid | AA |
| Hydroxyethyl acrylate | HEA |
| Isopentenyl polyoxyethylene ether | TPEG |
| Hydroxyethyl cellulose | HEC |
| ethylene oxide | EO |
| cyclohexane | CYH |
| P-toluenesulfonic acid | PTS |
| L-Ascorbic acid | Vc |
| mercaptopropionic acid | MPA |
| acryloyl hydroxyethyl cellulose | AHEC |
| Polycarboxylate superplasticizer | PCE |
| Biomass Polycarboxylate superplasticizer | PCE-Cs |
| calcium hydroxide | CH |
| Calcium Silicate Hydrate | C-S-H |
| Aluminate Ferrite tri-sulfate | AFt |
| PCE-Cs | TPEG/g | AHEC/g | AA/g | HEA/g | H2O2/g | Vc/g | MPA/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCE-C0 | 166 | / | 10 | 24.25 | 0.82 | 0.275 | 0.81 |
| PCE-C5 | 157.7 | 8.3 | 10 | 24.25 | 0.82 | 0.275 | 0.81 |
| PCE-C10 | 149.4 | 16.6 | 10 | 24.25 | 0.82 | 0.275 | 0.81 |
| PCE-C15 | 141.1 | 24.9 | 10 | 24.25 | 0.82 | 0.275 | 0.81 |
| PCE-Cs | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3d | 7d | 28d | 3d | 7d | 28d | |
| Blank | 23.6 | 35.2 | 45.1 | 4.6 | 5.7 | 7.4 |
| PCE-C0 | 34.7 | 46.3 | 58.0 | 6.1 | 7.4 | 8.7 |
| PCE-C5 | 35.2 | 47.8 | 59.8 | 6.5 | 7.6 | 9.1 |
| PCE-C10 | 33.8 | 47.0 | 56.5 | 5.8 | 7.0 | 8.4 |
| PCE-C15 | 32.6 | 44.7 | 53.4 | 5.6 | 6.9 | 8.1 |
| PCE-Cs | Mw (g/mol) | Mn (g/mol) | PDI | Polyether Monomer Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCE-C0 | 57,109 | 30,331 | 1.88 | 91.7 |
| PCE-C5 | 73,404 | 38,618 | 1.90 | 89.3 |
| PCE-C0 | PCE-C5 | PCE-C10 | PCE-C15 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hv/eV | 1486.60 | 1486.60 | 1486.60 | 1486.60 |
| Eb/eV | 101.45 | 101.30 | 101.50 | 101.60 |
| Ek/eV | 1385.15 | 1385.30 | 1385.10 | 1385.0 |
| I0 | 2012.41 | 2012.41 | 2012.41 | 2012.41 |
| I | 1296.52 | 1185.65 | 1351.54 | 1495.85 |
| b/nm | 1.80 | 2.17 | 1.63 | 1.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kou, Z.; Huang, K.; Chen, M.; Chu, H.; Zhou, L.; Yin, T. Synthesis of Biomass Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer and Its Performance on Cement-Based Materials. Materials 2025, 18, 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143416
Kou Z, Huang K, Chen M, Chu H, Zhou L, Yin T. Synthesis of Biomass Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer and Its Performance on Cement-Based Materials. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143416
Chicago/Turabian StyleKou, Zefeng, Kaijian Huang, Muhua Chen, Hongyan Chu, Linye Zhou, and Tianqi Yin. 2025. "Synthesis of Biomass Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer and Its Performance on Cement-Based Materials" Materials 18, no. 14: 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143416
APA StyleKou, Z., Huang, K., Chen, M., Chu, H., Zhou, L., & Yin, T. (2025). Synthesis of Biomass Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer and Its Performance on Cement-Based Materials. Materials, 18(14), 3416. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143416







