Influence Mechanism of Waterborne Polyurethane on the Properties of Emulsified Asphalt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Base Asphalt
2.1.2. Anionic/Cationic Emulsifiers
2.1.3. Experimental Water
2.1.4. Hydrochloric Acid Modifier
2.1.5. Emulsifier
2.1.6. Different Ionic WPUs
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of Matrix Emulsified Asphalt
- (1)
- Heating of asphalt
- (2)
- Preparation of soap solution
- (3)
- Preparation of emulsified asphalt
- (4)
- Storage of emulsified asphalt
2.2.2. Preparation of WPU Modified Emulsified Asphalt
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Basic Performance Test
2.3.2. FTIR Test
2.3.3. AFM Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WPU-Modified Emulsified Asphalt Basic Properties
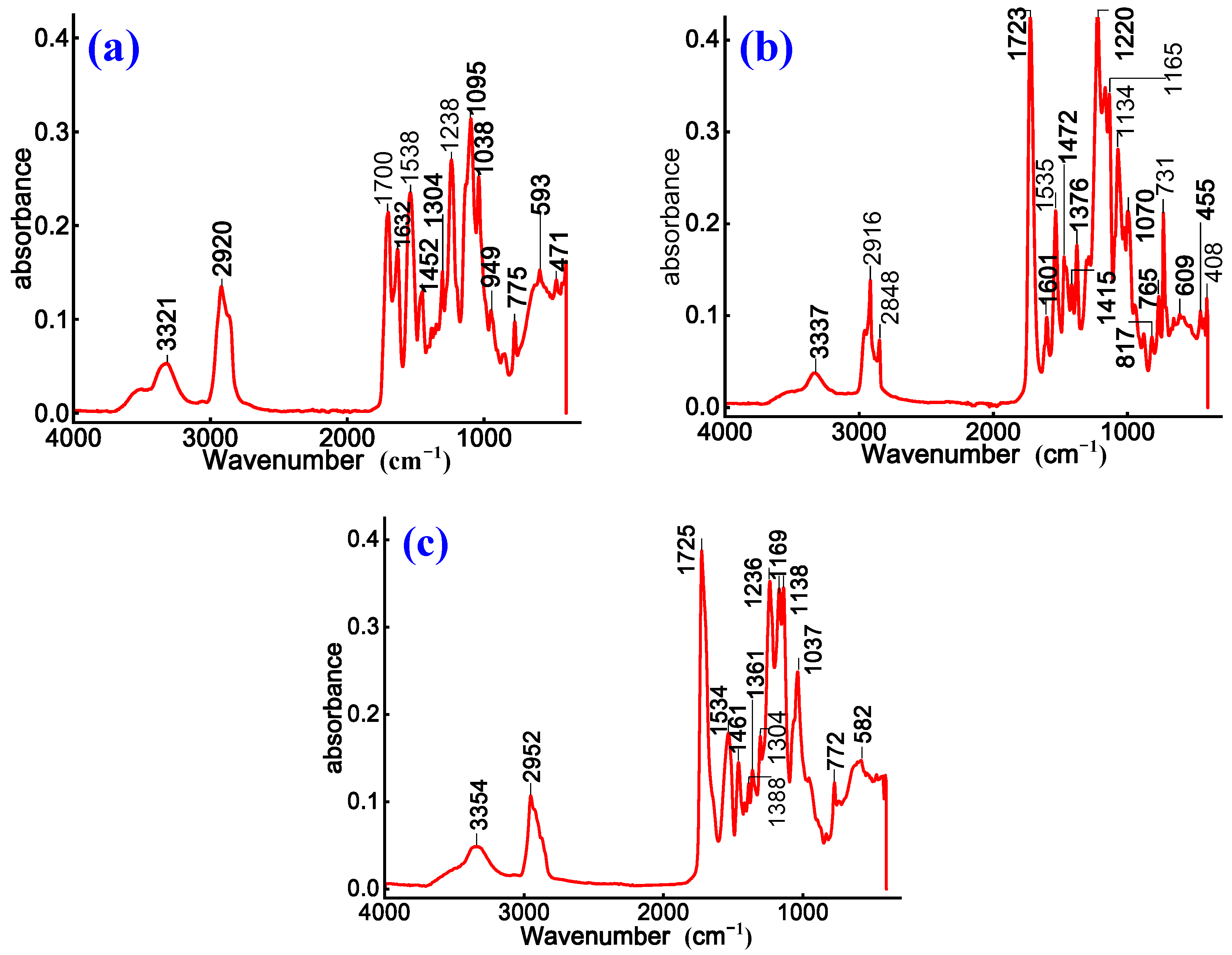
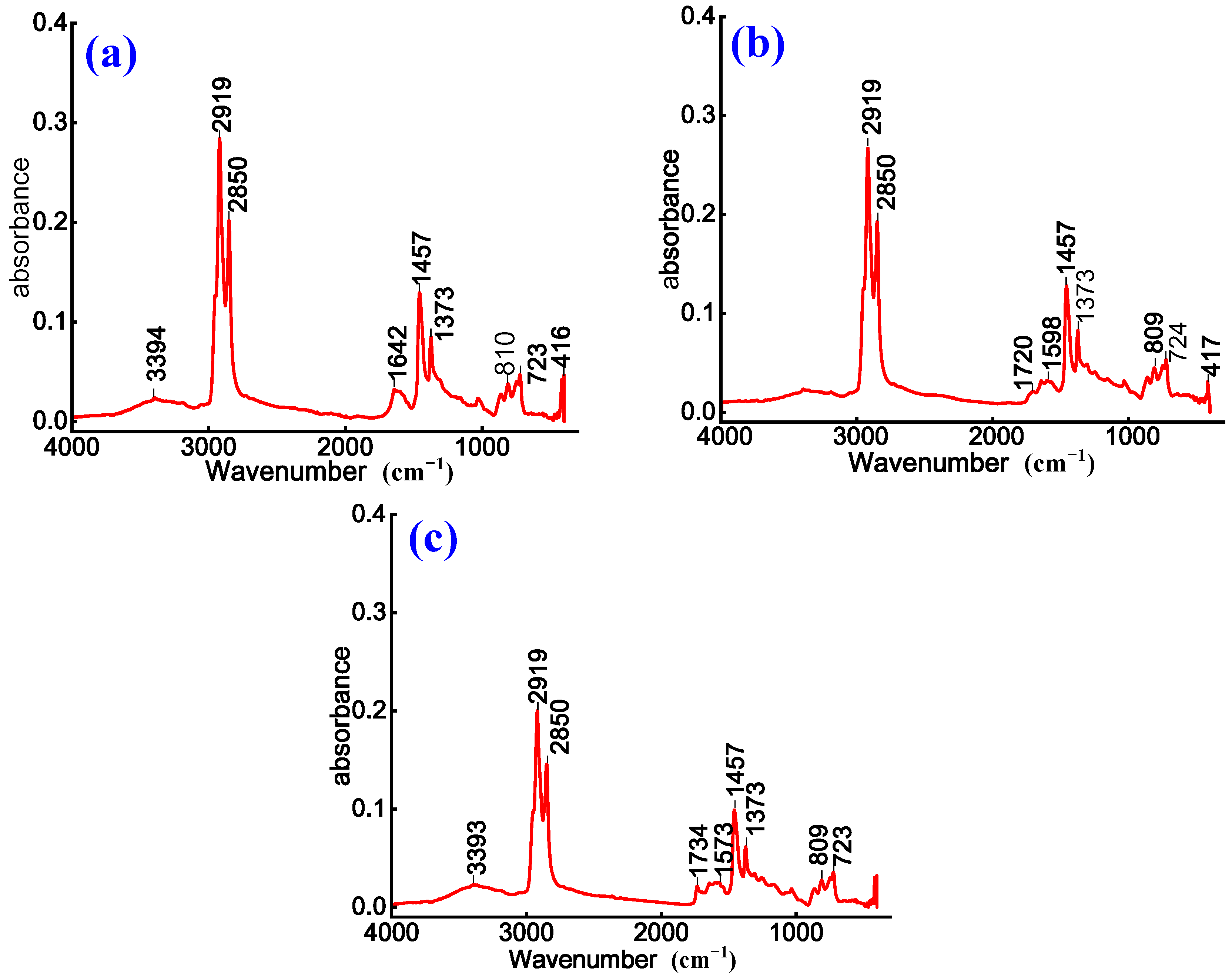
3.2. Effect of WPU on Chemical Composition and Functional Groups of Emulsified Asphalt
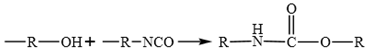
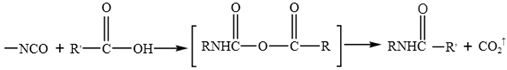

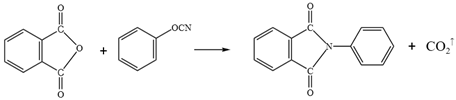
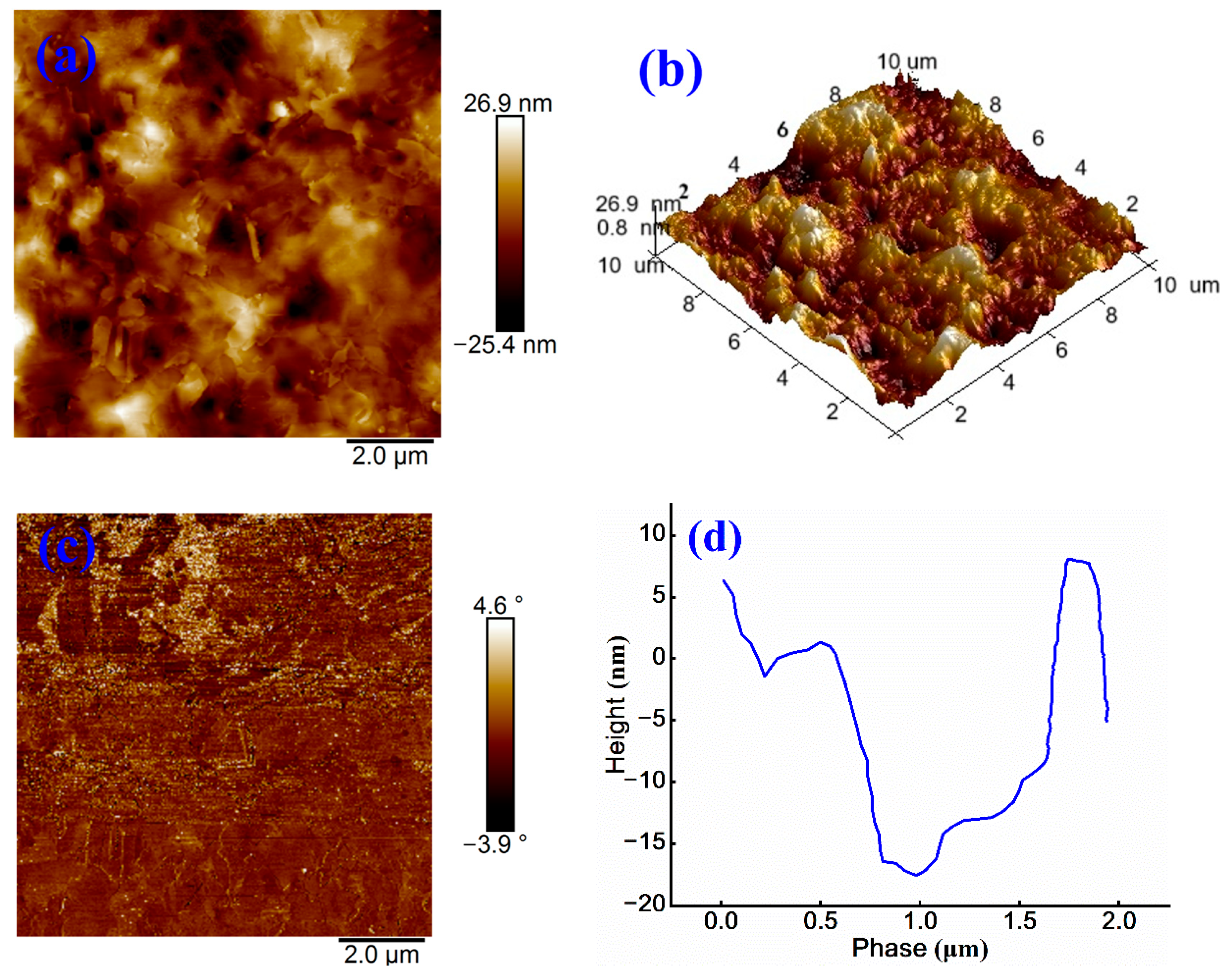
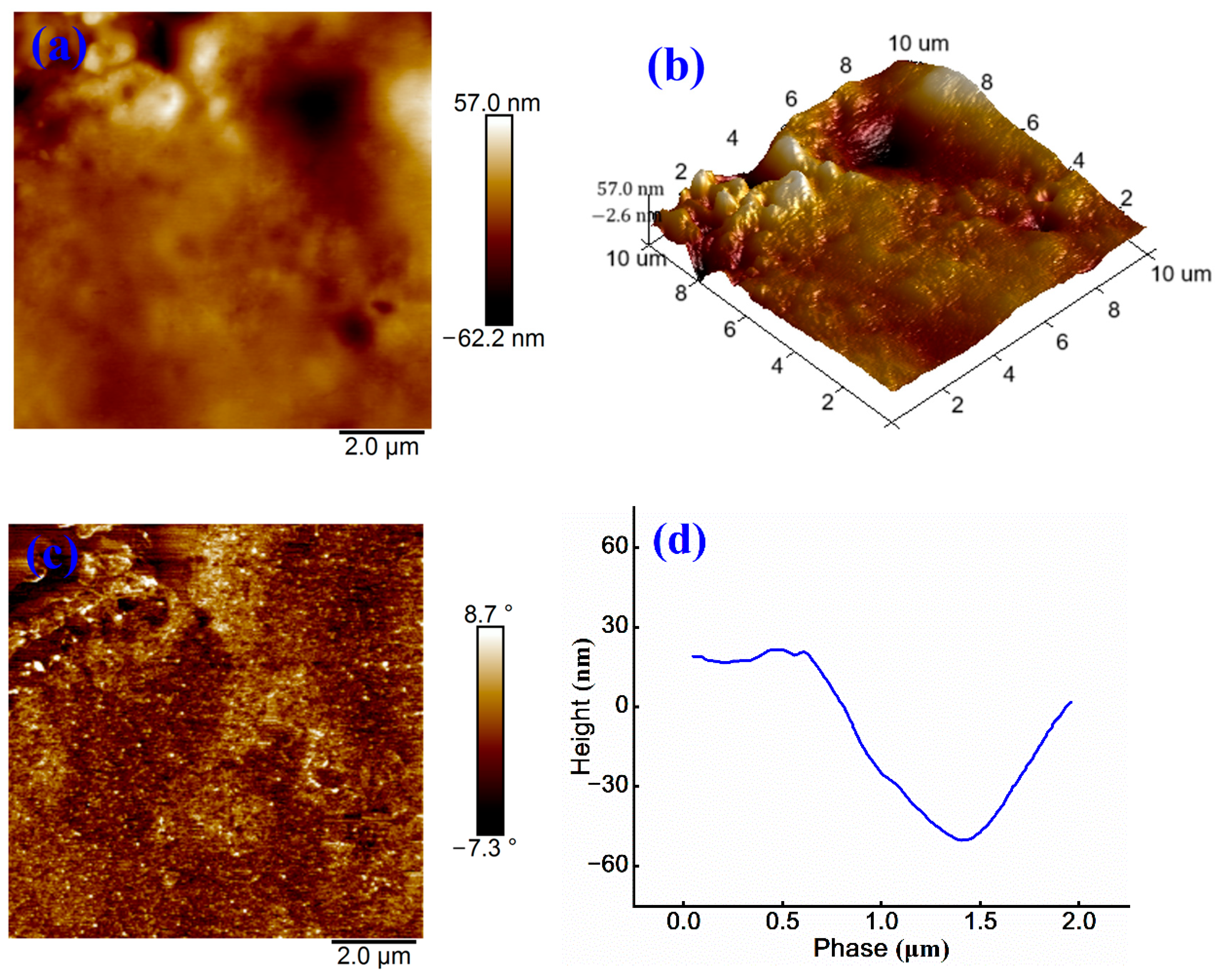
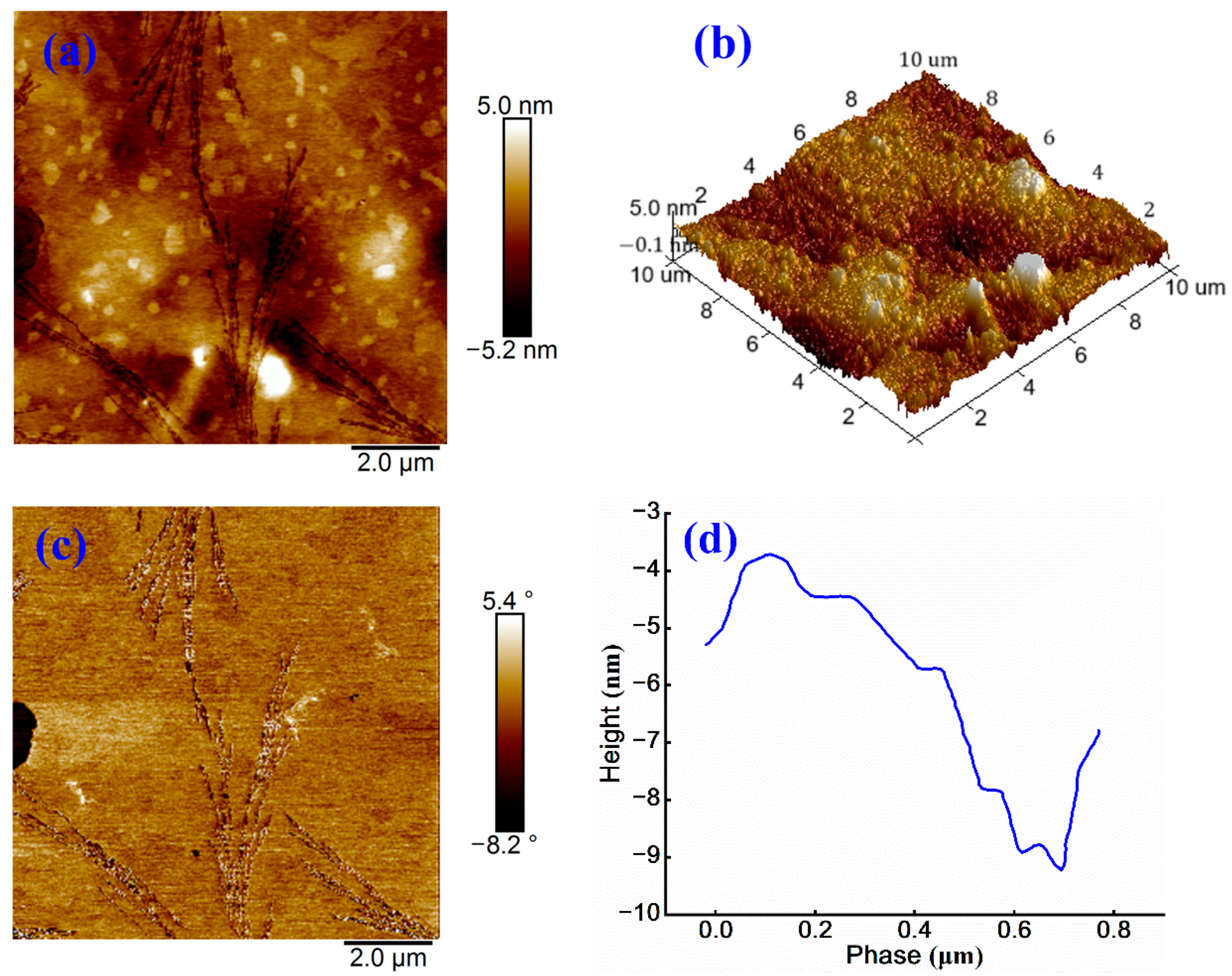
3.3. Influence of WPU on Micromorphology and Microstructure of Emulsified Asphalt
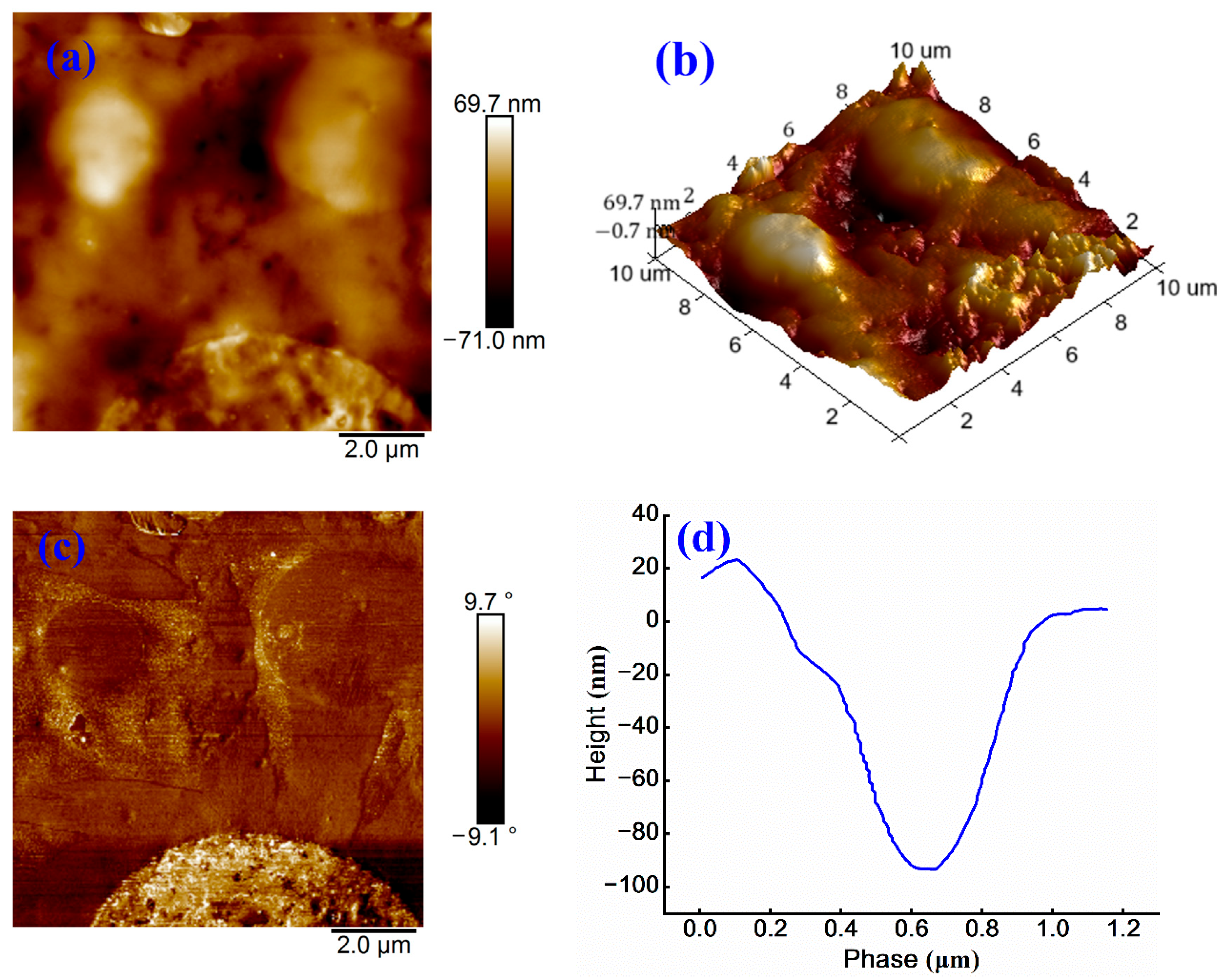
3.3.1. Influence of WPU on Surface Morphology of Emulsified Asphalt
3.3.2. Influence of WPU on Surface Roughness of Emulsified Asphalt
4. Conclusions
5. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, Y.; Chen, J.; Kong, W.; Hu, Y. Review of emulsified asphalt modification mechanisms and performance influencing factors. J. Road Eng. 2023, 3, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, A.; Hayati, P.; Goli, A. Advancing Pavement Preservation: Comprehensive Analysis and Optimization of Microsurfacing Mixtures with Stabilizers, Bitumen Types, Emulsifiers, and Fiber Impacts. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ding, J. Polyurethane-modified asphalt mechanism. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, V.; Cuadri, A.A.; García-Morales, M.; Partal, P. The development of polyurethane modified bitumen emulsions for cold mix applications. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 3407–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Yang, T.; He, Z.; Yu, L.; Xiao, H. Polyurethane as a modifier for road asphalt: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 356, 129058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keymanesh, M.R.; Ziari, H.; Zalnezhad, H.; Zalnezhad, M. Effects of lead time and manufacturing methods applied for polymer-modified bitumen emulsion (PMBE) on microsurfacing performance. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 23, 2271–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Liu, F.; Wei, T. Investigation of a novel blocked waterborne polyurethane emulsified asphalt mixture for pothole repair: Material development, road performance and construction parameters. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2025, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesami, S.; Sadeghi, V.; Azizi, A. Investigation of modified bitumen’s rheological properties with synthesized polyurethane by MDI-PPG reactive prepolymers. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2021, 34, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, Q. Research on rheological properties and modification mechanism of waterborne polyurethane modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 371, 130775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Liu, X.; Bi, H.; Wang, Z.; Qian, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Study on Preparation and Properties of Polyurethane-Epoxy Composite Emulsion Modified Emulsified Asphalt. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Symposium on Traffic Transportation and Civil Architecture (ISTTCA 2024), Tianjin, China, 21–23 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Cong, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hui, J.; Ye, M. Toughness modification of waterborne epoxy emulsified asphalt by waterborne polyurethane elastomer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 386, 131547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, V.L.; Hormaiztegui, M.E.V.; Amalvy, J.I.; Aranguren, M.I. Formulation, structure and properties of waterborne polyurethane coatings: A brief review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 489–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y. Preparation and Properties of Waterborne Polyurethane and SBS Composite-Modified Emulsified Asphalt. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavand, B.S.; Jola, B.G.; Didehban, K.; Mirshokraie, A. Modified bitumen emulsion by anionic polyurethane dispersion nanocomposites. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wan, C. Property improvement of epoxy emulsified asphalt modified by waterborne polyurethane in consideration of environmental benefits. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Liu, X.; Bi, H.; Wang, Z.; Qian, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Effect of evaporation temperature on evaporative residue properties of waterborne polyurethane modified emulsified asphalt. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2873, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Pang, B.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, D.; Bi, J.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, L. Durability enhancement of cement-based repair mortars through waterborne polyurethane modification: Experimental characterization and molecular dynamics simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y.; Li, F. Effect of ionic emulsifiers on the properties of emulsified asphalts: An experimental and simulation study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 347, 128503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Karimi, A.; Goli, A.; Hajikarimi, P.; Mohammadi, A.; Doctorsafaei, A.; Fini, E. Biobased polyurethane: A sustainable asphalt modifier with improved moisture resistance. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04023505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Asphalt and Asphalt Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JTG F40-2004; Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements. Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Honarkar, H. Waterborne polyurethanes: A review. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yeoh, G.H.; Kabir, I.I. Polyurethane Materials for Fire Retardancy: Synthesis, Structure, Properties, and Applications. Fire 2025, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Que, Y. Interaction between cement and asphalt emulsion and its influences on asphalt emulsion demulsification, cement hydration and rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Acierno, D. Structure-property relationships of waterborne polyurethane (WPU) in aqueous formulations. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2023, 29, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yuan, L.; Yi, J. Preparation and characterization of polyurethane-modified asphalt containing dynamic covalent bonds. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Xiang, S.; Bian, R.; Lin, R.; Wu, K.; Wang, T.; Cai, D. Study of MXene-filled polyurethane nanocomposites prepared via an emulsion method. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 168, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaneh, A.; Rostami, A.; Nazockdast, H. Thermoplastic polyurethane/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposites: Effect of nanoparticle content, shear, and thermal processing. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 4804–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lan, Y. Cohesion Performance of Tack Coat Materials between Polyurethane Mixture and Asphalt Mixture. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2024, 36, 04023534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, J.; Long, Q.; Sun, D.-X.; Qi, X.-D.; Yang, J.-H.; Wang, Y. Healable, Recyclable, and Ultra-Tough Waterborne Polyurethane Elastomer Achieved through High-Density Hydrogen Bonding Cross-Linking Strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 64333–64344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liu, W. Turning things around: From cationic/anionic complexation-induced nanoemulsion instability to toughened water-resistant waterborne polyurethanes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 18408–18421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, S.M.; Jadhav, S.M.; Patil, M.J.; Mestry, S.U.; Mahajan, U.R.; Mhaske, S.T. Recent developments in waterborne polyurethane dispersions (WPUDs): A mini-review on thermal and mechanical properties improvement. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 5709–5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Y.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Qin, Y.; Tang, D.; Oh, S.-K. Fabrication of silane and nano-silica composite modified Bio-based WPU and its interfacial bonding mechanism with cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 371, 130819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Z.; Liang, F.; Fan, H.; Xiang, J.; Chen, Y. Poly(methylmethacrylate) microspheres with matting characteristic prepared by dispersion polymerization. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2019, 24, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Ou, J. Investigation on the wetting behavior of asphalt emulsion on aggregate for asphalt emulsion mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad, S.; Idris, I.I.; Hassan, M.; Mohammad, L.N. Self-healing capability and mechanical properties of asphalt mixtures prepared with light-activated polyurethane prepolymer modified asphalt binder. Transp. Res. Rec. 2025, 2679, 710–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Chen, B.; Dong, F.; Zu, Y.; Wang, S.; Si, J.; Huang, J. Repurposing waste polyurethane into cleaner asphalt pavement materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Technical Indexes | Unit | Test Results | Standard Requirements | Experimental Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 5 s, 100 g) | 0.1 mm | 70 | 60–80 | T0604 |
| Ductility (10 °C) | cm | 18 | ≥15 | T0605 |
| Softening point | °C | 50 | ≥47 | T0606 |
| Parameter | Specification Requirements | Test Results | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Cationic | Brown viscous liquid | |
| Anionic | Light yellow liquid | ||
| Active substance content | Cationic | 70 ± 2 | 69 |
| Anionic | 70 | ||
| pH value | Cationic | 6–8 | 7.6 |
| Anionic | |||
| Free amine content (%) | Cationic | ≤2 | 1.25 |
| Anionic | 1.23 | ||
| Density (g/cm3) | Cationic | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Anionic | 1.05 | 1.05 | |
| Effective ingredient (%) | Cationic | 50 | 50 |
| Anionic | 40 | 40 | |
| Test Specimens | Acid | Alkali |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | HCl | NaOH |
| Molecular weight | 36.5 | 40.0 |
| Concentration/% | 36–38 | 5% |
| Color | Colorless | White |
| Density/(g/cm3) | 1.18 | 1.05 |
| Test Items | Quality Indicators | Measured | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residual on sieve (1.18 mm)/% | Cationic | <0.1 | 0.005 |
| Anionic | 0.003 | ||
| Particle Polarity | Cationic | Cationic | Cationic |
| Anionic | Anionic | Anionic | |
| Particle size/μm | Cationic | ≤7 | 4.41 |
| Anionic | 4.30 | ||
| Standard viscosity/(Pa.s) | Cationic | 8–25 | 12 |
| Anionic | 15 | ||
| Storage stability (1d, 25 °C)/% | Cationic | <1 | 0.4 |
| Anionic | 0.3 | ||
| Content/% | Cationic | ≥60 | 63.7 |
| Anionic | 62.8 | ||
| Penetration/(0.1 mm) | Cationic | 40–120 | 75 |
| Anionic | 50–300 | 79 | |
| Softening point/°C | Cationic | ≥42 | 52.9 |
| Anionic | 53.1 | ||
| Ductility/cm | Cationic | ≥40 | 52.5 |
| Anionic | 90.3 | ||
| Type | Designation | Solids Content (%) | pH Value | Viscosity Value (mPa.s) | Color | Specific Gravity (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Cationic WPU | 38 ± 1 | 3–7 | <200 | Milky white | 1.06 ± 0.02 |
| B | Anionic WPU | 30 ± 1 | 6–9 | ≥100 | 1.05 | |
| 20 °C | ||||||
| C | Non-ionic WPU | 6–8 | >100 |
| Test Items | Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Cationic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Non-ionic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Anionic Emulsified Asphalt | Anionic WPU + Anionic Emulsified Asphalt | Non-ionic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residual on sieve (1.18 mm)/% | 0.005 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.015 | 0.002 |
| Particle polarity | C | C | C | A | A | A |
| Standard viscosity /(Pa.s) | 12 | 16 | 15 | 15 | 17 | 16 |
| Storage stability (1d, 25 °C)/% | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Solid content (%) | 65 | 63.7 | 62.8 | 65 | 62.8 | 62.8 |
| Penetration/0.1 mm | 75 | 60.3 | 59.3 | 79 | 70 | 63.3 |
| Softening point/°C | 52.9 | 54.1 | 53.8 | 53.1 | 54 | 53.9 |
| Ductility (15 °C)/cm | 52.5 | 43.2 | 36.4 | 90.3 | 44.7 | 28.7 |
| Sample Name | Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Cationic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Non-ionic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt | Anionic Emulsified Asphalt | Anionic WPU + Anionic Emulsified Asphalt | Non-ionic WPU + Cationic Emulsified Asphalt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Rq/nm | 7.32 | 4.73 | 13.6 | 1.75 | 1.63 | 19.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.; Hou, S.; Jin, R.; Zhong, X.; Zou, X. Influence Mechanism of Waterborne Polyurethane on the Properties of Emulsified Asphalt. Materials 2025, 18, 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143280
Tan J, Hou S, Jin R, Zhong X, Zou X. Influence Mechanism of Waterborne Polyurethane on the Properties of Emulsified Asphalt. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143280
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jian, Shuguang Hou, Rui Jin, Xiao Zhong, and Xiaoxi Zou. 2025. "Influence Mechanism of Waterborne Polyurethane on the Properties of Emulsified Asphalt" Materials 18, no. 14: 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143280
APA StyleTan, J., Hou, S., Jin, R., Zhong, X., & Zou, X. (2025). Influence Mechanism of Waterborne Polyurethane on the Properties of Emulsified Asphalt. Materials, 18(14), 3280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143280







