Early Hydration Kinetics of Shell Ash-Based Cementitious Materials: A Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Methods
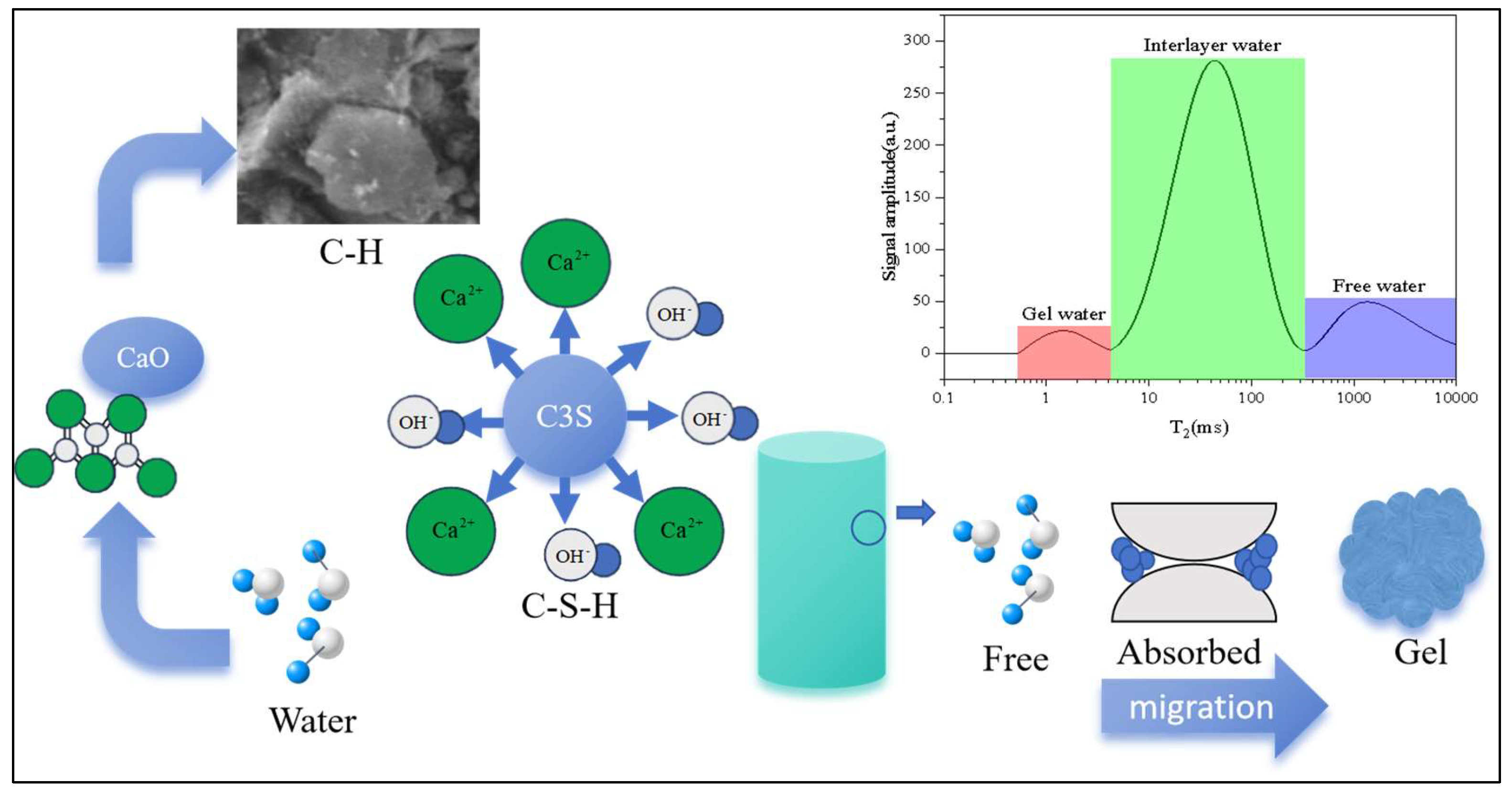
2.3.1. Low-Field NMR
2.3.2. The Krstulovic–Dabic Kinetic Model
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Early Moisture Changes in Cement Slurry
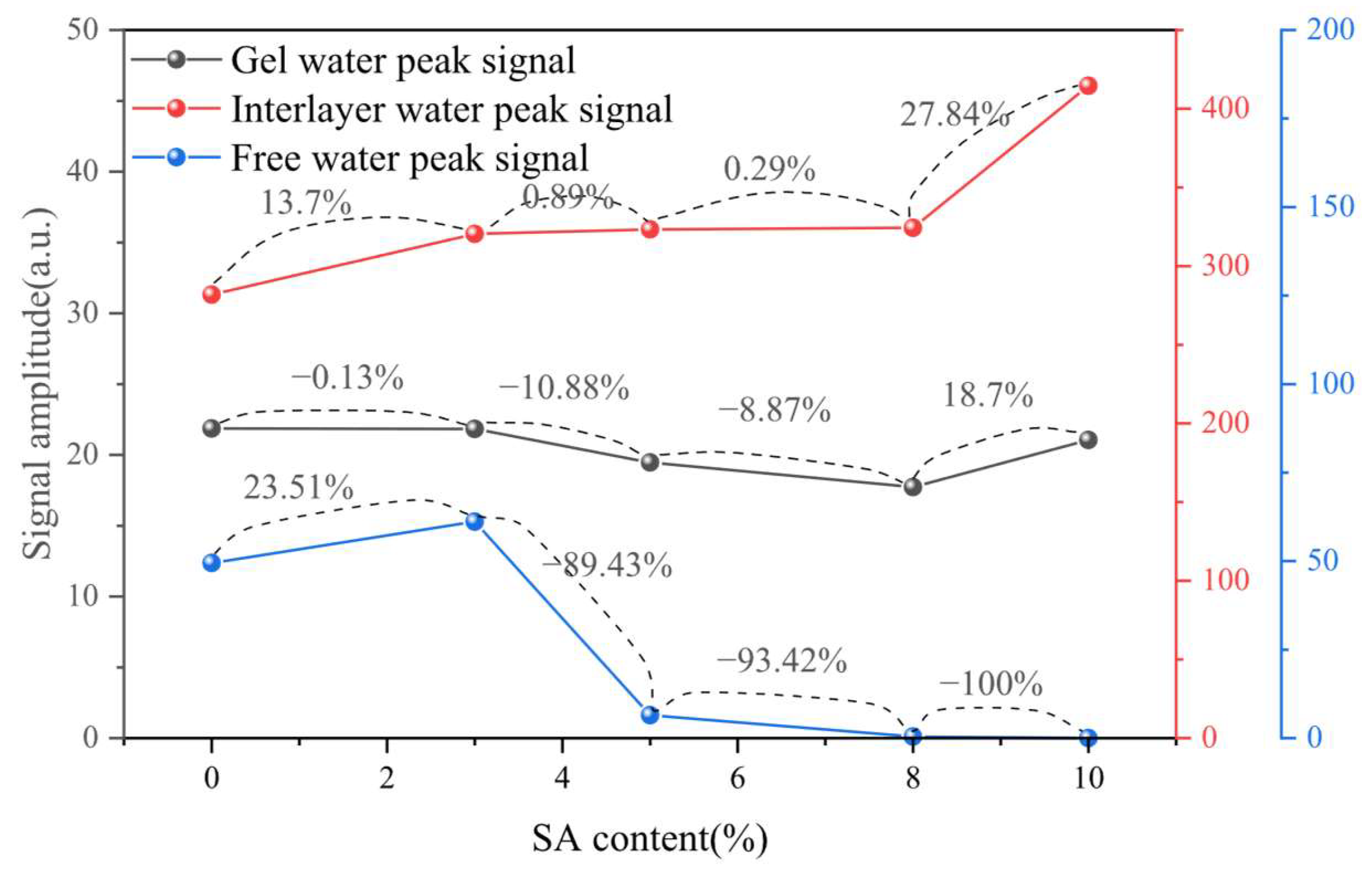
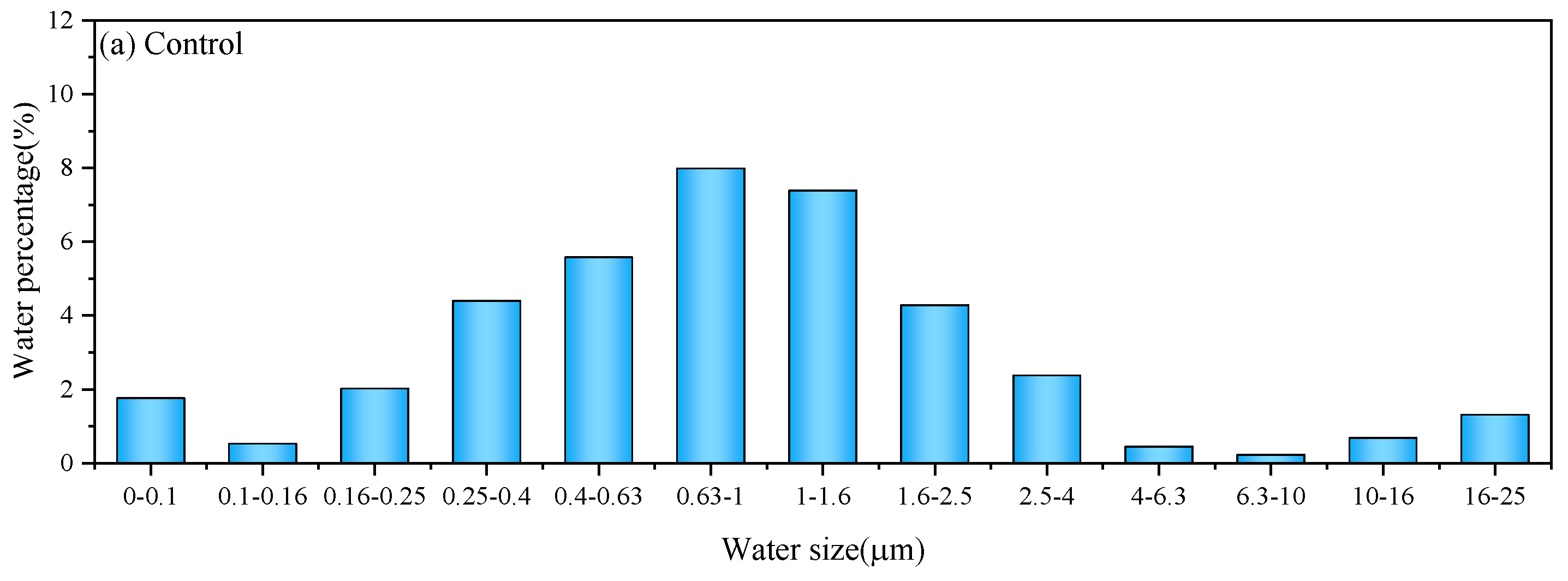
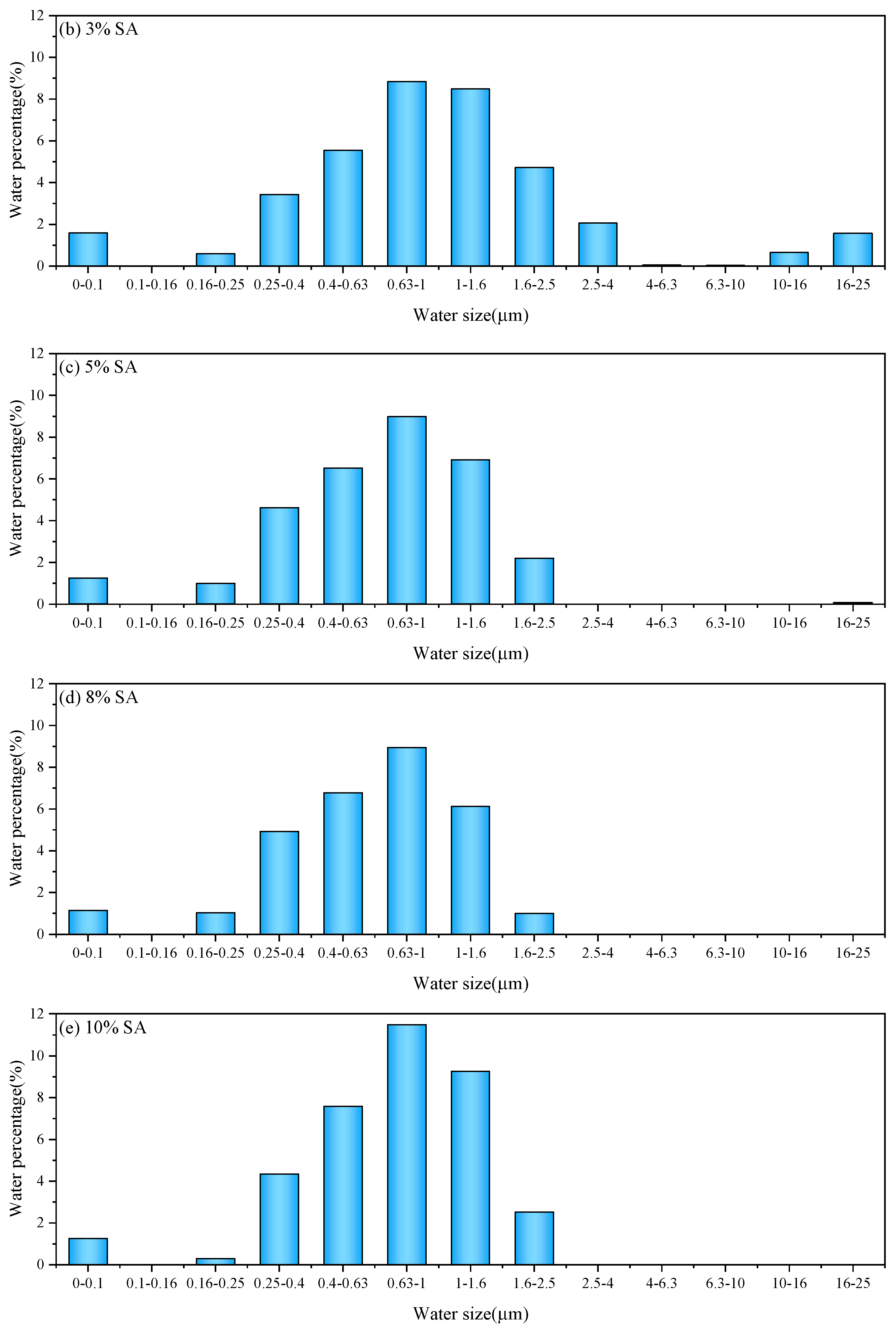
3.1.1. Water Distribution
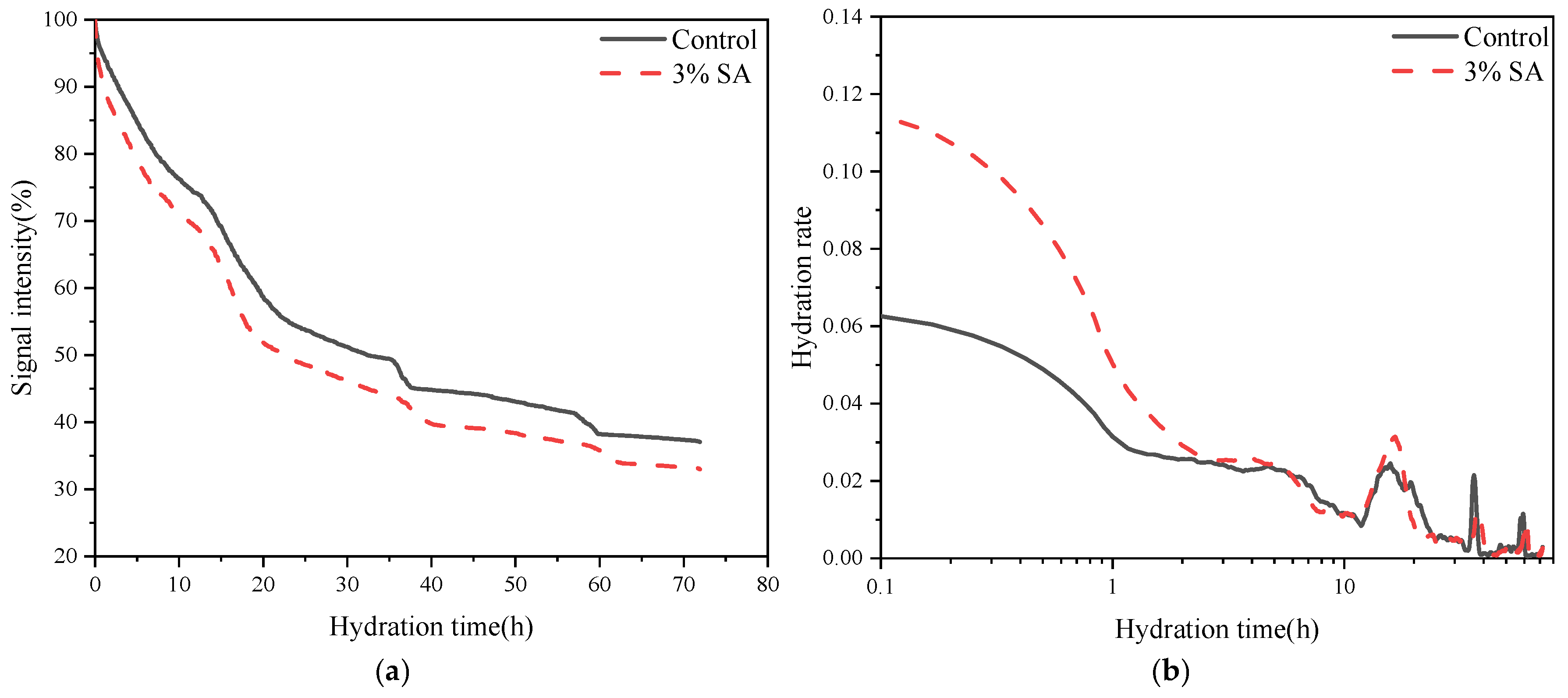
3.1.2. Moisture Ratio
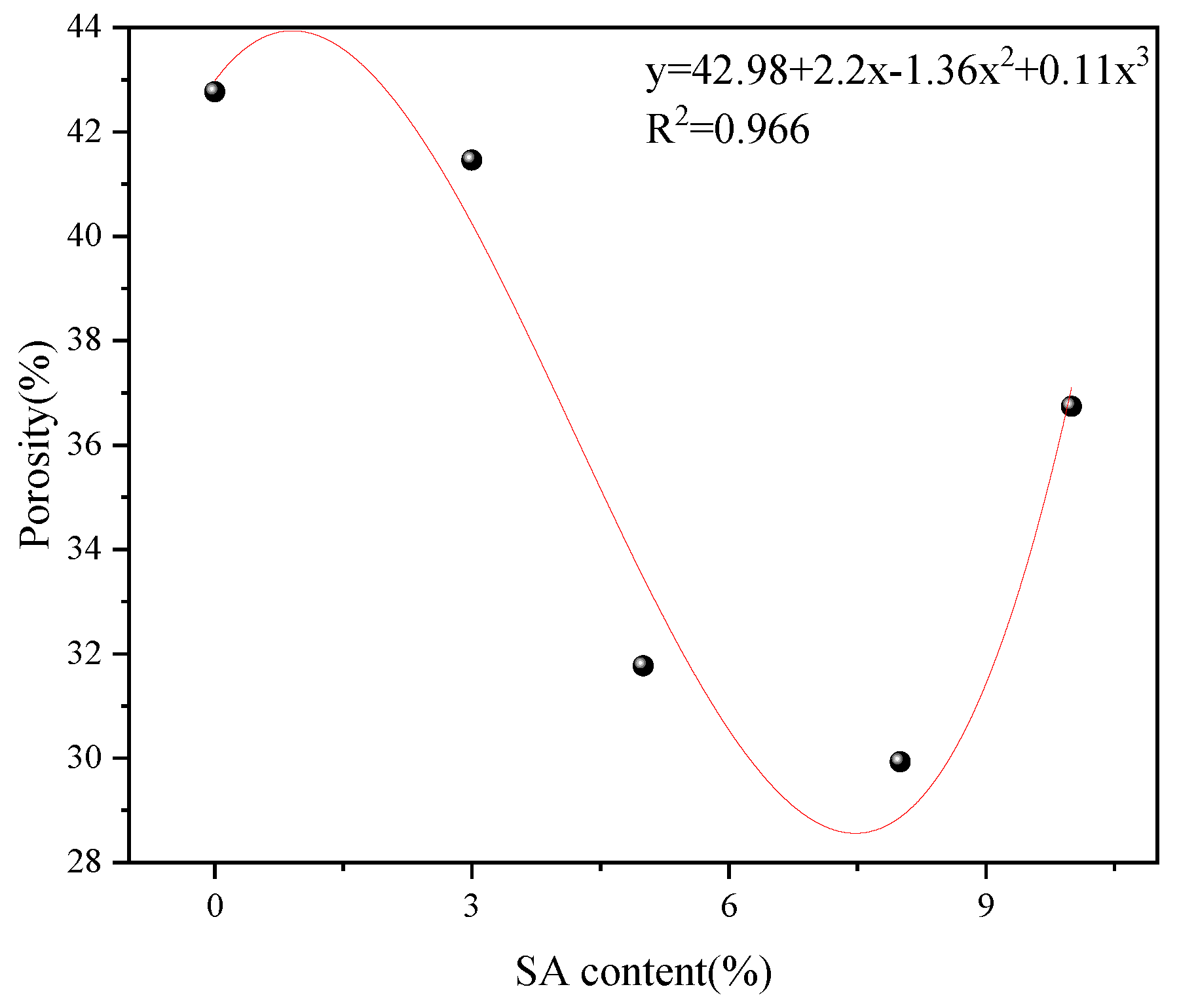
3.1.3. Porosity Analysis
3.2. Analysis of Hydration Dynamics of Shell Ash Based on NMR
3.2.1. Hydration Rate
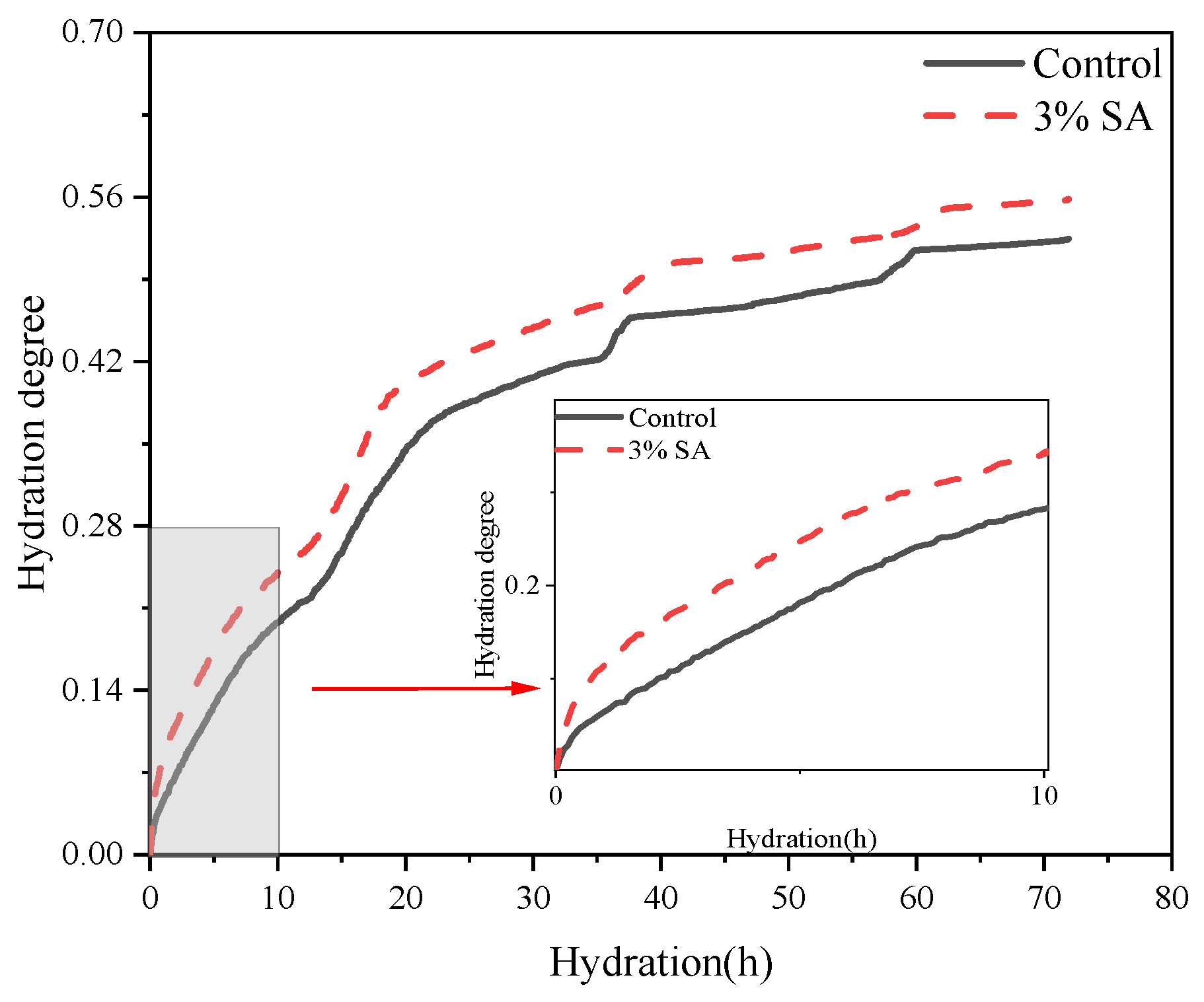
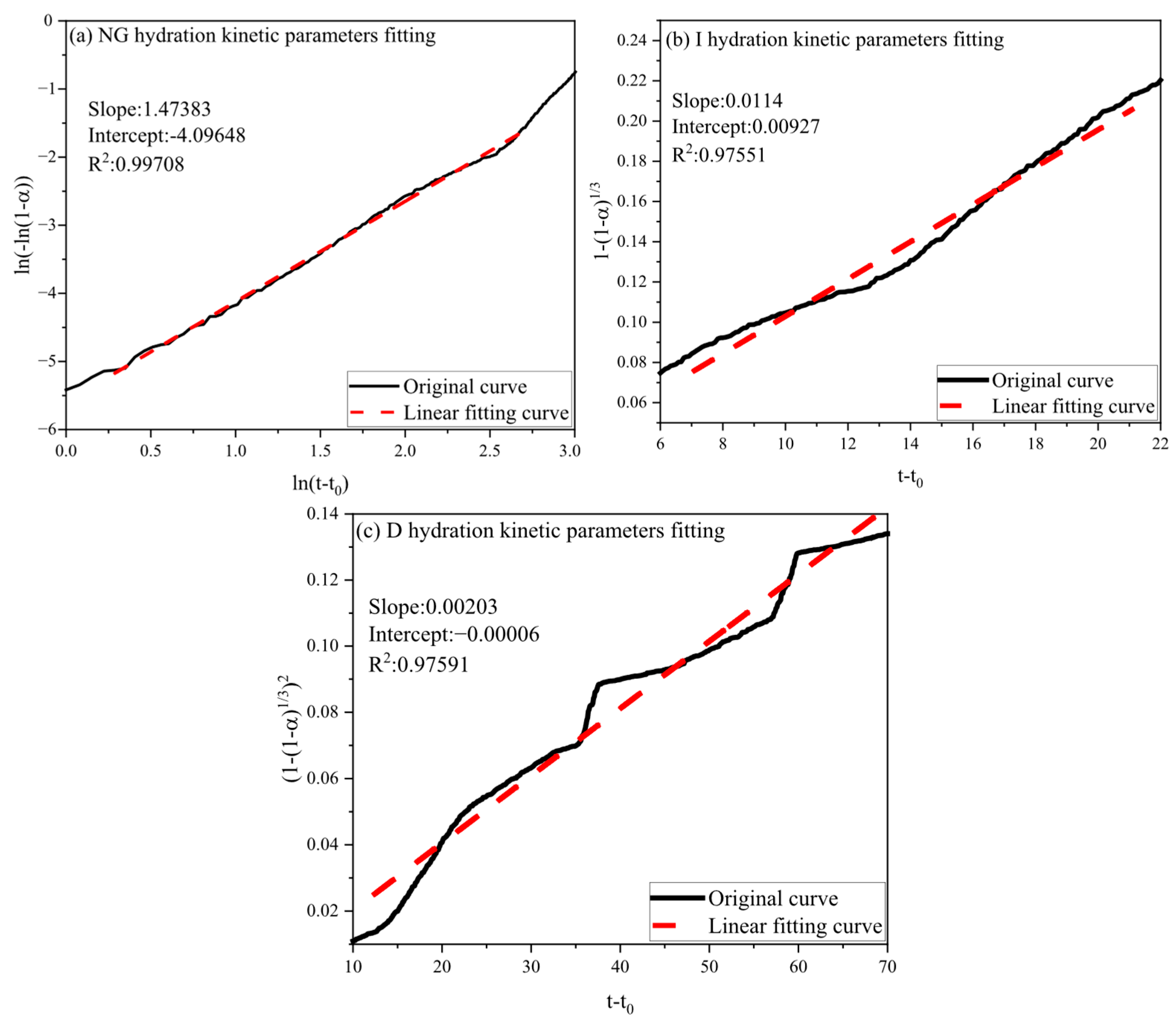
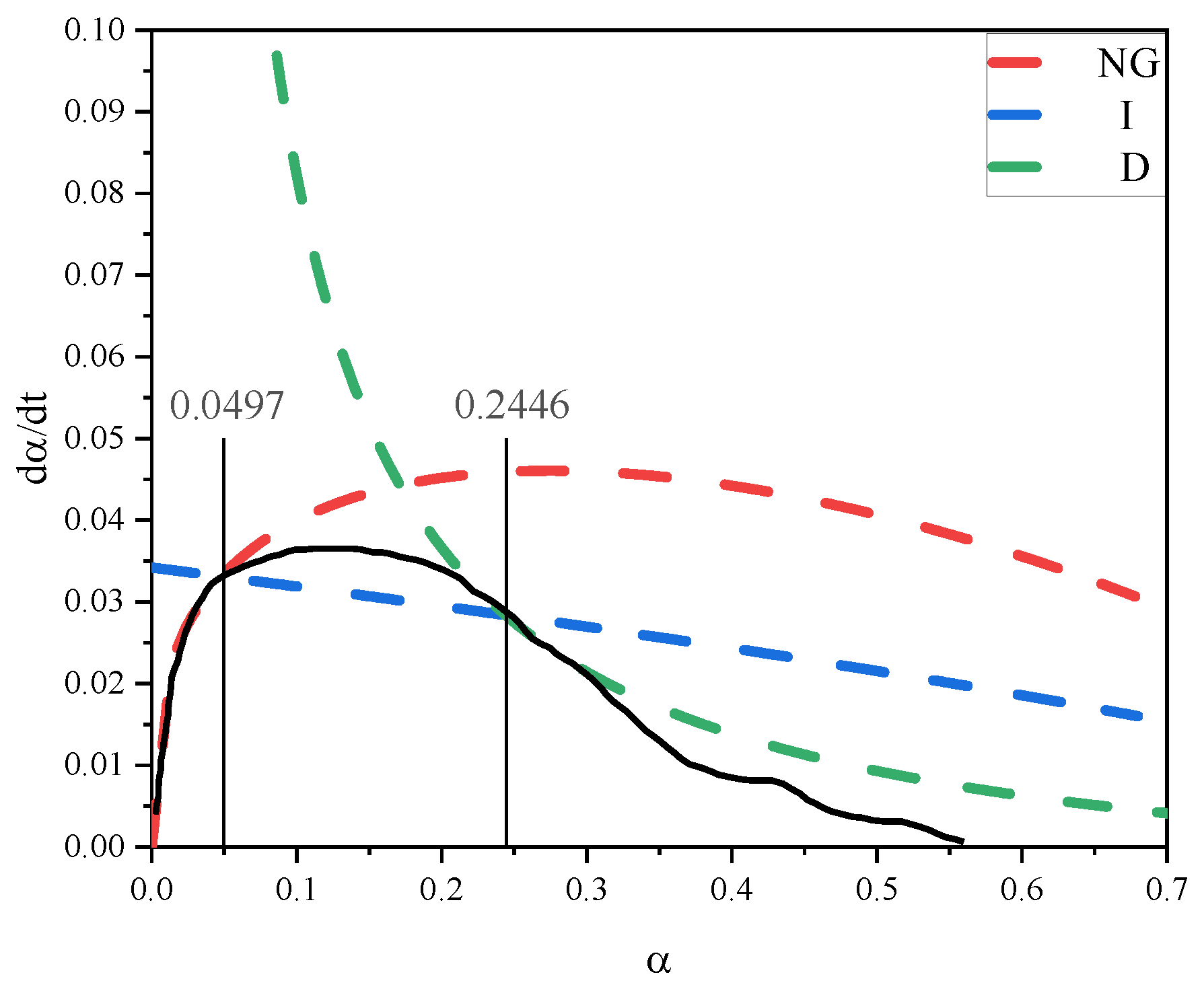
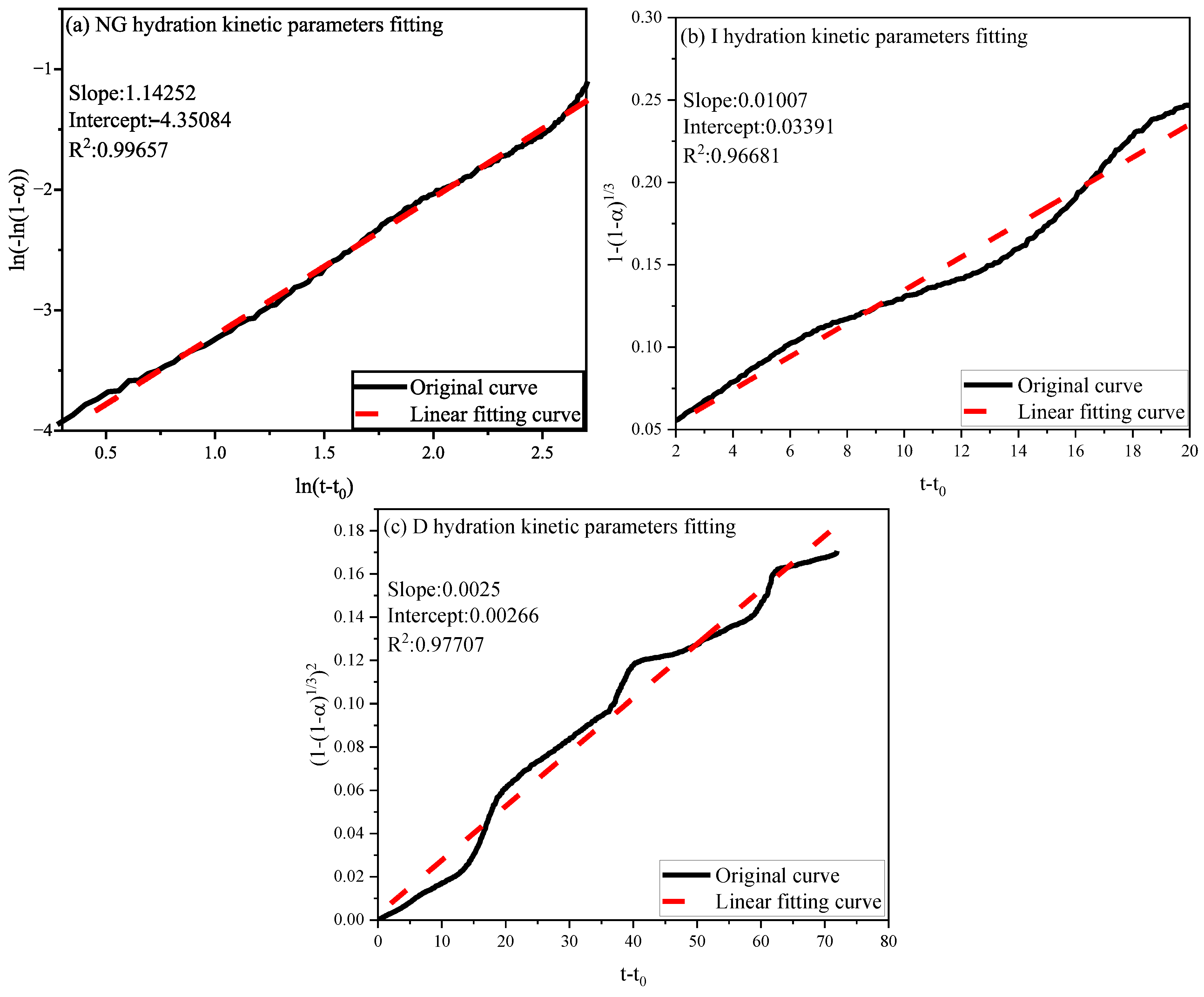
3.2.2. Hydration Kinetic Analysis
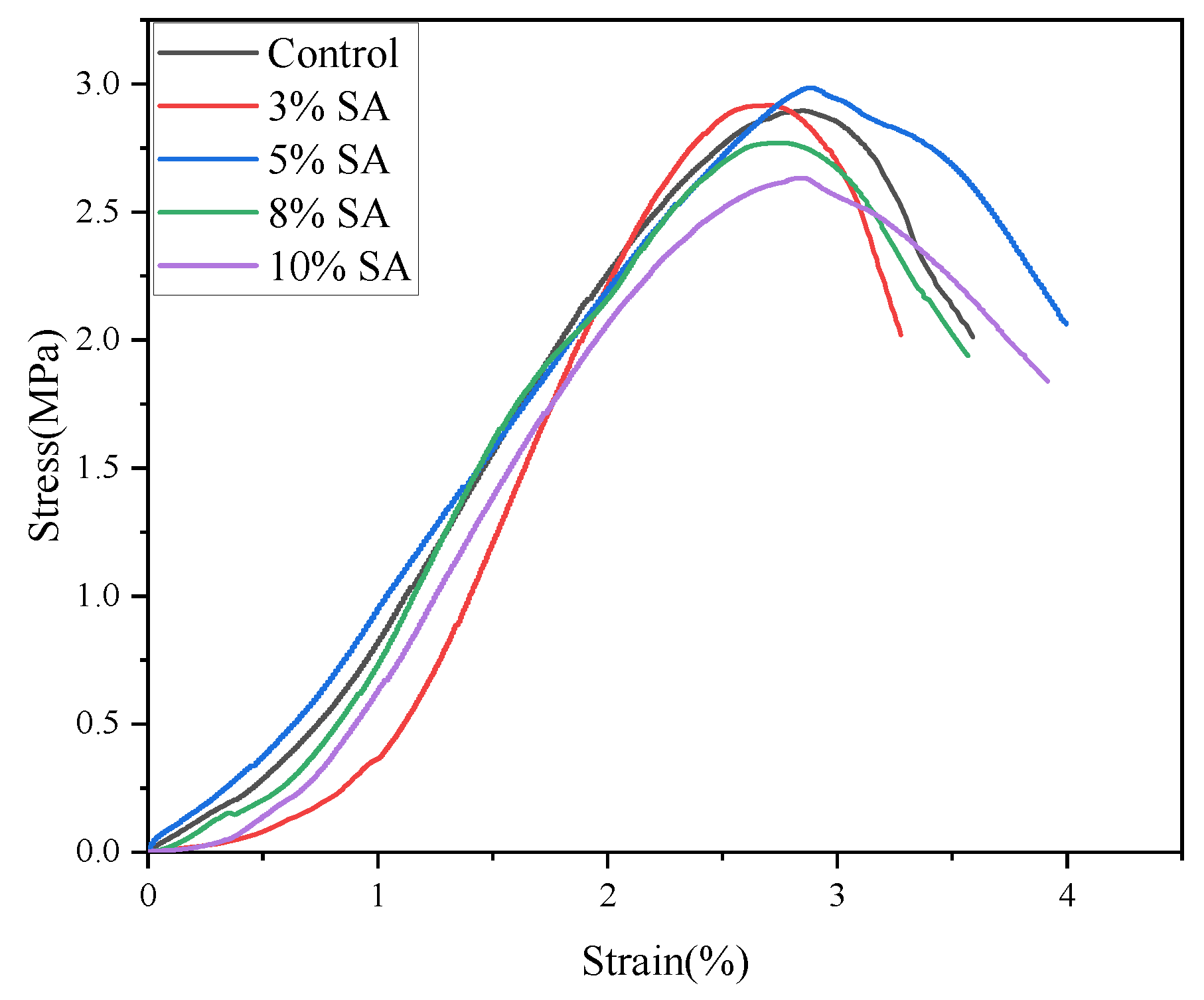
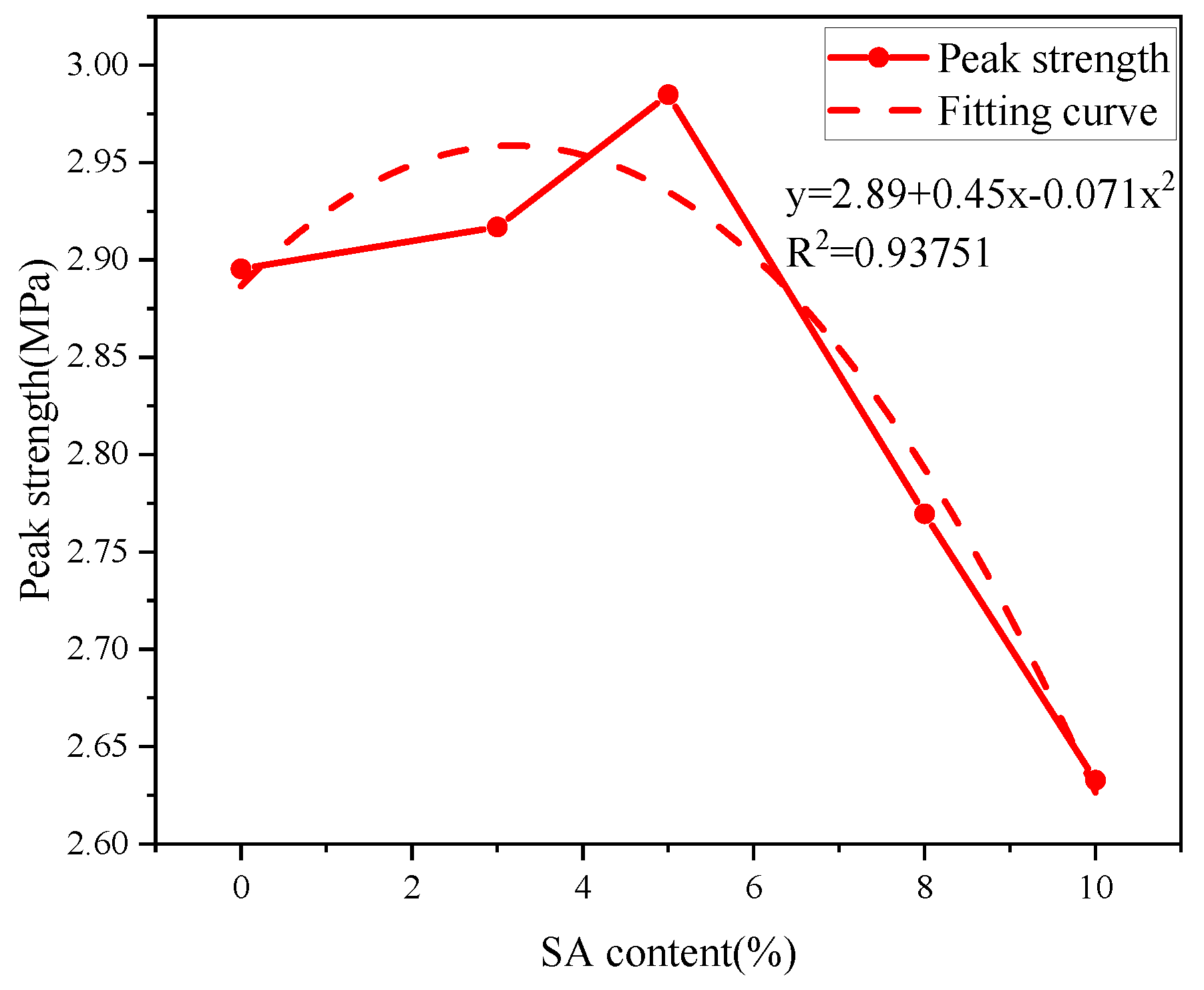
3.3. Effect of SA on the Early Strength
Analysis of Stress–Strain Curves
3.4. Multi-Scale Regulation Mechanism of Shell Ash Content on Hydration Dynamics and Microstructure Evolution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, L.; Krigsvoll, G.; Johansen, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Carbon emission of global construction sector. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.-X.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Internal pore evolution and early hydration characterization of fly ash cement backfill. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 72, 106716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusin, F.M.; Hasan, S.N.M.S.; Molahid, V.L.M.; Soomro, M.H. Dual adoption opportunities and prospects for mining and industrial waste recovery through an integrated carbon capture, utilization and storage. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 48, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, J.; Maboudian, R.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Does the hydration process of supplementary cementitious materials affect the aging creep of blended cement paste? Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 191, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahish, H.A.; Alfawzan, M.S.; Tayeh, B.A.; Abusogi, M.A.; Bakri, M. Effect of inclusion of natural pozzolan and silica fume in cement - based mortars on the compressive strength utilizing artificial neural networks and support vector machine. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fu, J.; Wang, J. The ratio optimization and hydration mechanism of multi source solid waste cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.; Karim, A.; Islam, M.T.; Ali, M.B.; Rahman, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Yahaya, F.M. A review of the mechanical properties and durability of concrete containing recycled seashells as a partial cement replacement. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, X.; Chen, E.; Fan, J.; Xiong, G. Properties of cement-based bricks with oyster-shells ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglad, A.M.; Mydin, M.A.O.; Datta, S.D.; Tayeh, B.A. Assessing the mechanical; durability, thermal and microstructural properties of sea shell ash based lightweight foamed concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 133018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelluri, S.; Hossiney, N. Performance evaluation of ternary blended geopolymer binders comprising of slag, fly ash and brick kiln rice husk ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sithole, T.; Mashifana, T.; Mahlangu, D.; Tchadjié, L. Effect of binary combination of waste gypsum and fly ash to produce building bricks. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2023, 31, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Ou, Y.; Liu, R. Transformation of fly ash into a fluffy C-S-H material: Enhancing chemical properties and advancing the utilization of portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Yue, J. Synergistic effect of red mud, desulfurized gypsum and fly ash in cementitious materials: Mechanical performances and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Qi, W.; Kong, F. Synthesis and characterization of cemented paste backfill: Reuse of multiple solid wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Li, J.; Xue, J.; Feng, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Performance of green binder developed from flue gas desulfurization gypsum incorporating Portland cement and large-volume fly ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, I.; Alqahtani, F.K. Effectiveness of extended curing for fly ash concrete against corrosion propagation under severe chloride exposure. Struct. Concr. 2021, 22, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, K.; He, Z. Influence of shell ash on pore structure and mechanical characteristics of cemented tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Peng, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, T.; Zhang, B. Improving the mechanical properties of mussel shell aggregate concrete by aggregate modification and mixture design. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqi, A.; Siddique, S.; Kim, H.-K.; Jang, J.G. Examining the potential of calcined oyster shell waste as additive in high volume slag cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez-zaki, H.; El Gharbi, B.; Diouri, A. Development of eco-friendly mortars incorporating glass and shell powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 159, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-García, C.; González-Fonteboa, B.; Martínez-Abella, F.; López, D.C. Performance of mussel shell as aggregate in plain concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, M.-Y.; Cho, H.-K.; Wang, X.-Y. Performance improvement of waste oyster-shell powder–cement binary system via carbonation curing. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Park, S.M.; Yang, B.J.; Jang, J.G. Calcined Oyster Shell Powder as an Expansive Additive in Cement Mortar. Materials 2019, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tong, T.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, P. Effect of pores and moisture on the mechanical properties of calcium silicate hydrate gels at mesoscale. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 452, 138998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, Z.; Ma, X.; Huo, Y.; Yang, Y. Preparation of C-S-H seeds from solid waste and its application as portland cement accelerator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 428, 136277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Cantero, A.; De La Torre, A.G.; Cuesta, A.; Santacruz, I.; Bernal, I.M.R.; Mazanec, O.; Dalla-Libera, A.; Borralleras, P.; Aranda, M.A.G. In situ synchrotron powder diffraction study of LC3 cement activation at very early ages by C-S-H nucleation seeding. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 178, 107463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, S.; Song, W. Distribution development of pore/crack expansion and particle structure of cemented solid-waste composites based on CT and 3D reconstruction techniques. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 376, 130966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Fu, J.; Zhaobo, M.; Bangyi, Z. Investigation of frozen rock behavior: Mechanical properties, pore structure, and strength under confining pressures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 234, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, H.; Jiang, Z.; Tian, G.; Wang, P.; Yu, S. Pore structure characteristics of artificial sand aggregate mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 94, 109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Song, W.; Fu, J. Study on shear behavior and microstructure of rock and cemented paste backfill interface. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; He, Z.; Cai, X.; Fu, S. Application of Low-Field NMR to the Pore Structure of Concrete. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2021, 52, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, W. Characterizing connectivity and tortuosity of pore network based on LF-NMR method to assess the water permeability of white cement mortar. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 93, 109862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, W.; Taheri, A.; Fu, J.; Zhao, T.; Tan, Y. Hydration mechanism and mechanical-thermal correlation of cemented paste backfill under different curing temperatures. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 85, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Tan, H.; Yang, Z.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Jian, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, J. C-S-H based nucleation seed prepared from waste glass powder and carbide slag and its application in portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Ji, Y. A novel method for semi-quantitative analysis of hydration degree of cement by 1H low-field NMR. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 141, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, Z. Exploration of microstructure characteristics and mechanical behaviors of thermal-damaged argillaceous sandstone via LF-NMR and µ-CT technologies. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energ. Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Weng, L.; Wu, L.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q. Experimental Study on the Grouting Diffusion Process in Fractured Sandstone with Flowing Water Based on the Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Technique. Rock. Mech. Rock. Eng. 2023, 56, 7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Li, W.; Shah, S.P.; Xu, J. Impact of synthetic C-S-H seeds on early hydration and pore structure evolution of cement pastes: A study by 1H low-field NMR and path analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 175, 107376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Fan, L.; Ma, C.; Yang, Q.; Du, X. Effects of ice content on compression characteristics of frozen sandstone by in-situ NMR technology. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energ. Geo-Resour. 2023, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophia, M.; Sakthieswaran, N. Waste shell powders as valuable bio- filler in gypsum plaster – Efficient waste management technique by effective utilization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zeng, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, J. Multi-scale investigation on composition-structure of C-(a)-S-H with different al/si ratios under attack of decalcification action. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 172, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, A.; Ma, K.; Yao, W.; Zuo, J.; Liao, G. Hydration kinetics of cementitious materials based on low-field NMR and isothermal calorimetry. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruct. 2022, 30, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
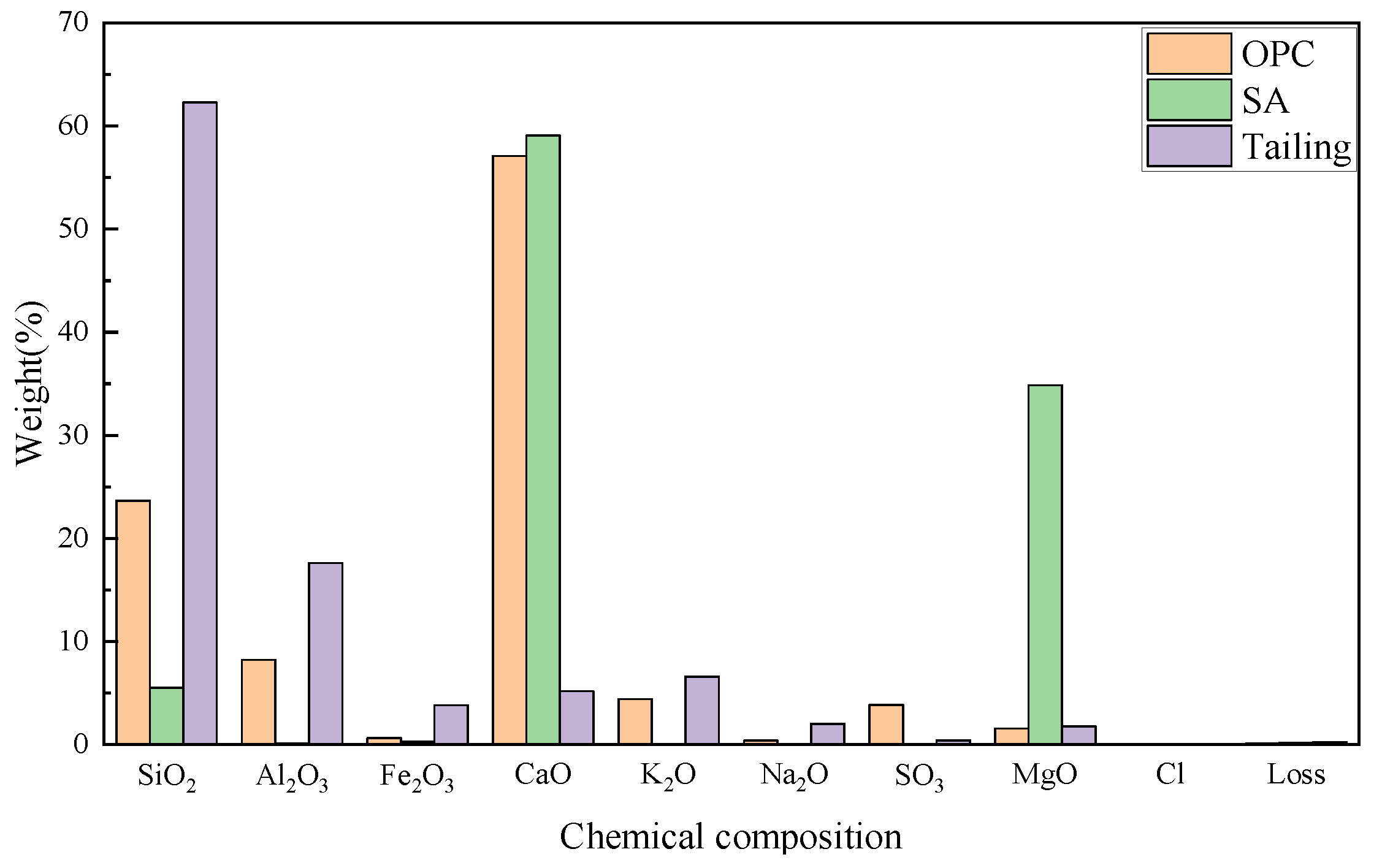
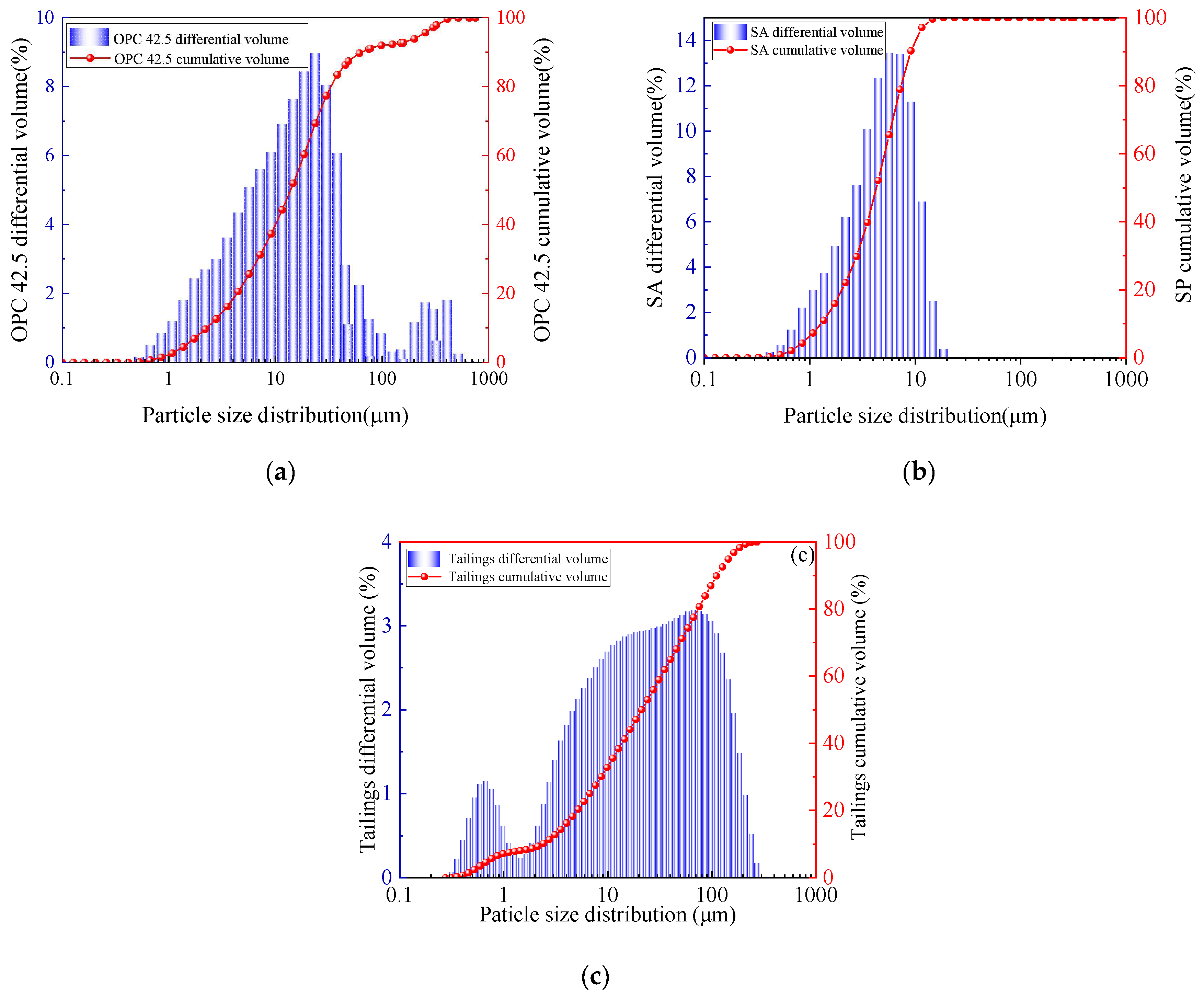

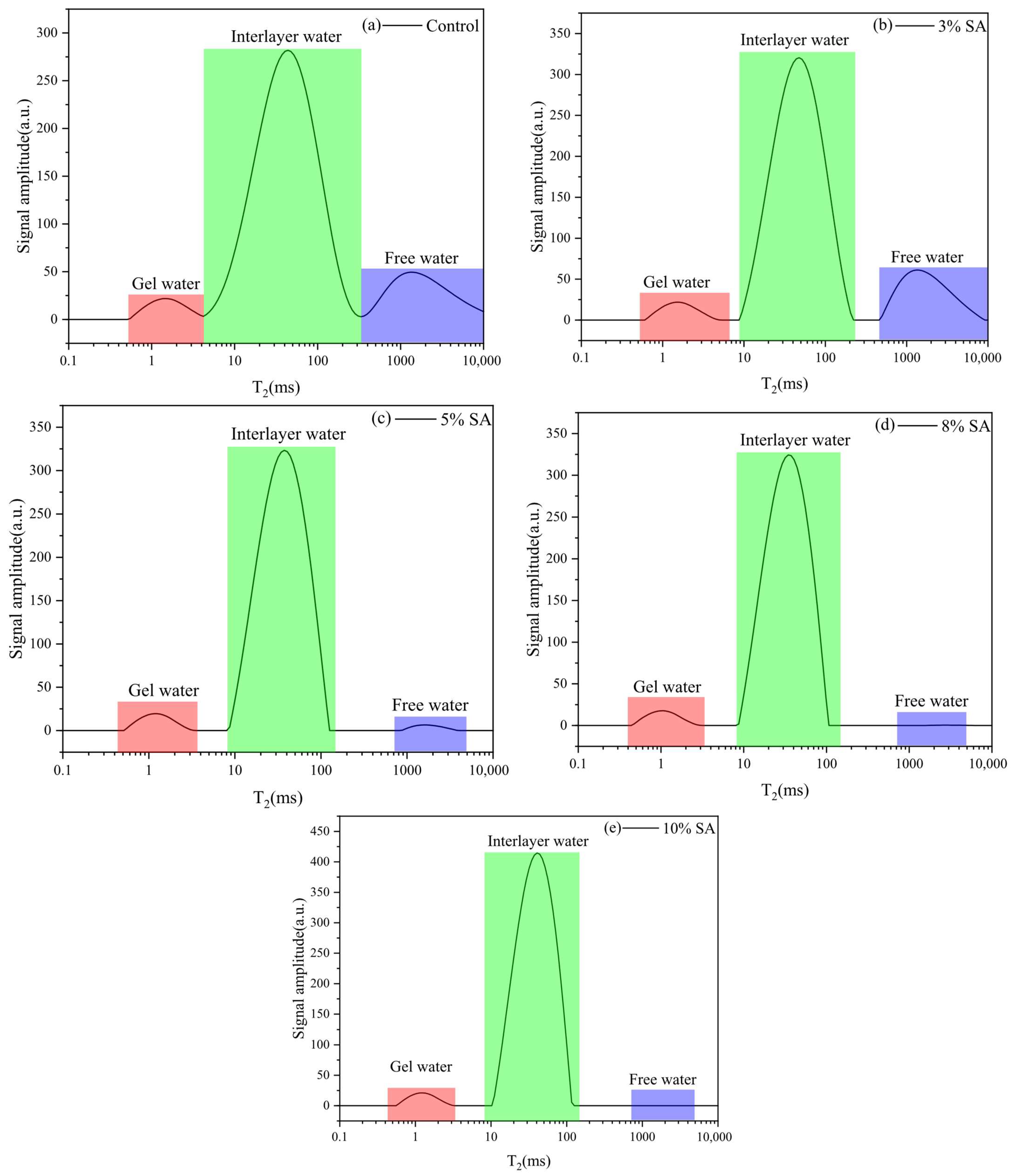

| Name | OPC | Tailing | Water | SA | c/t | w/c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 100 | 400 | 50 | 1:4 | 0.5 | |
| 3% SA | 97 | 3 | ||||
| 5% SA | 95 | 5 | ||||
| 8% SA | 92 | 8 | ||||
| 10% SA | 90 | 10 |
| Sample | n | K1′ | K2′ | K3′ | Mechanism | α1 | α2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.47383 | 0.062071 | 0.0114 | 0.00203 | NG-I-D | 0.0497 | 0.2446 |
| 3% SA | 1.4252 | 0.047227 | 0.01007 | 0.0025 | NG-I-D | 0.06886 | 0.3286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, K.; Fu, J. Early Hydration Kinetics of Shell Ash-Based Cementitious Materials: A Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study. Materials 2025, 18, 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143253
Tong C, Wang L, Wang K, Fu J. Early Hydration Kinetics of Shell Ash-Based Cementitious Materials: A Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143253
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Chuan, Liyuan Wang, Kun Wang, and Jianxin Fu. 2025. "Early Hydration Kinetics of Shell Ash-Based Cementitious Materials: A Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study" Materials 18, no. 14: 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143253
APA StyleTong, C., Wang, L., Wang, K., & Fu, J. (2025). Early Hydration Kinetics of Shell Ash-Based Cementitious Materials: A Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study. Materials, 18(14), 3253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143253






