Experimental Study on Rheological Behavior of Firefighting Foams
Highlights
- Firefighting foam goes through linear, transition, and nonlinear viscoelastic regions.
- Firefighting foam exhibits ductile yielding and significant shear thinning.
- The creep and relaxation response of firefighting foam conforms to the Burgers model.
- The flow curve of firefighting foam conforms to the Herschel–Bulkley model.
- Foam drainage and coarsening have competing effects on foam rheology.
Abstract
1. Introduction
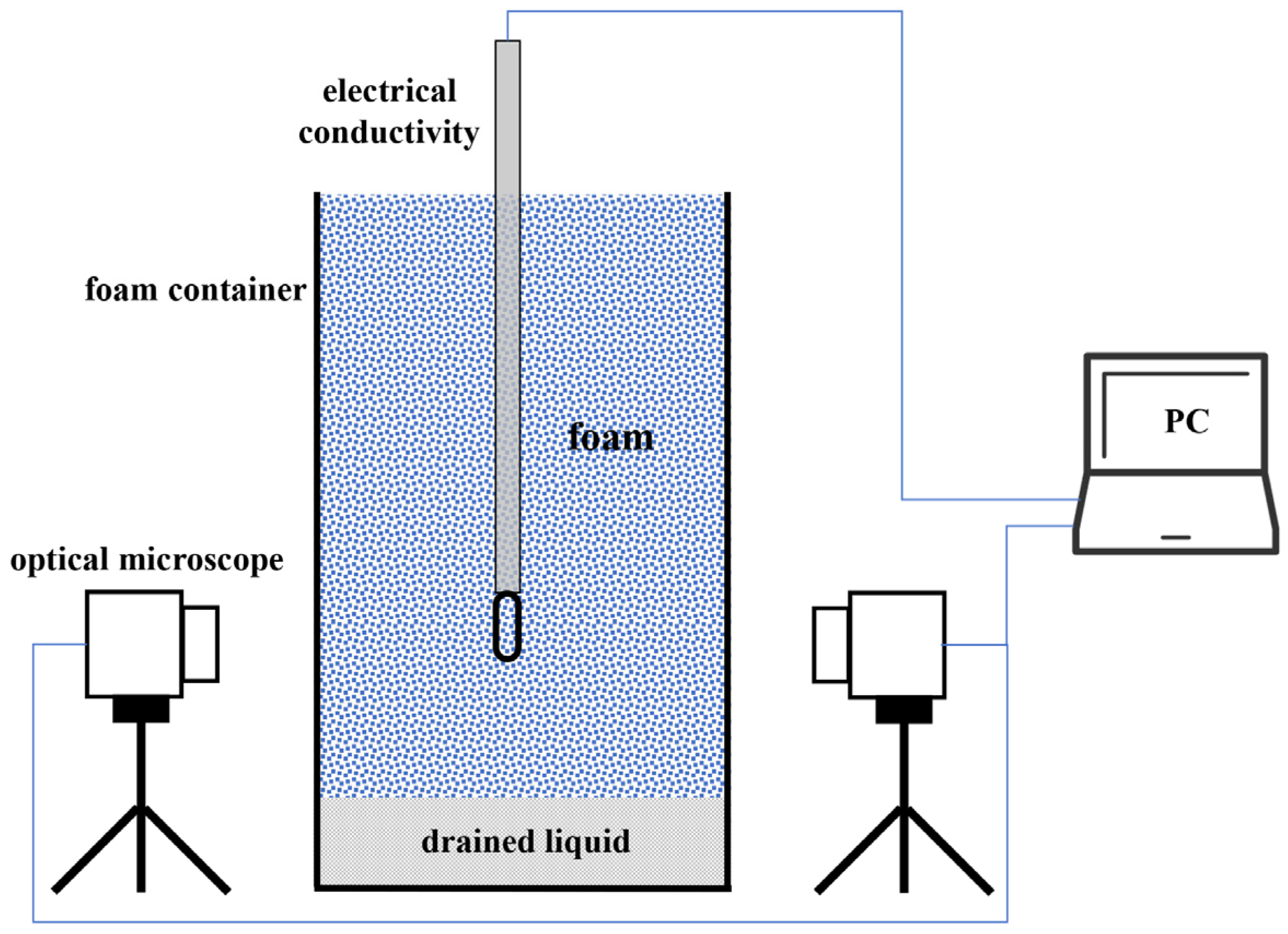
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Foam Concentrate and Firefighting Foam Production
2.2. Experimental Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
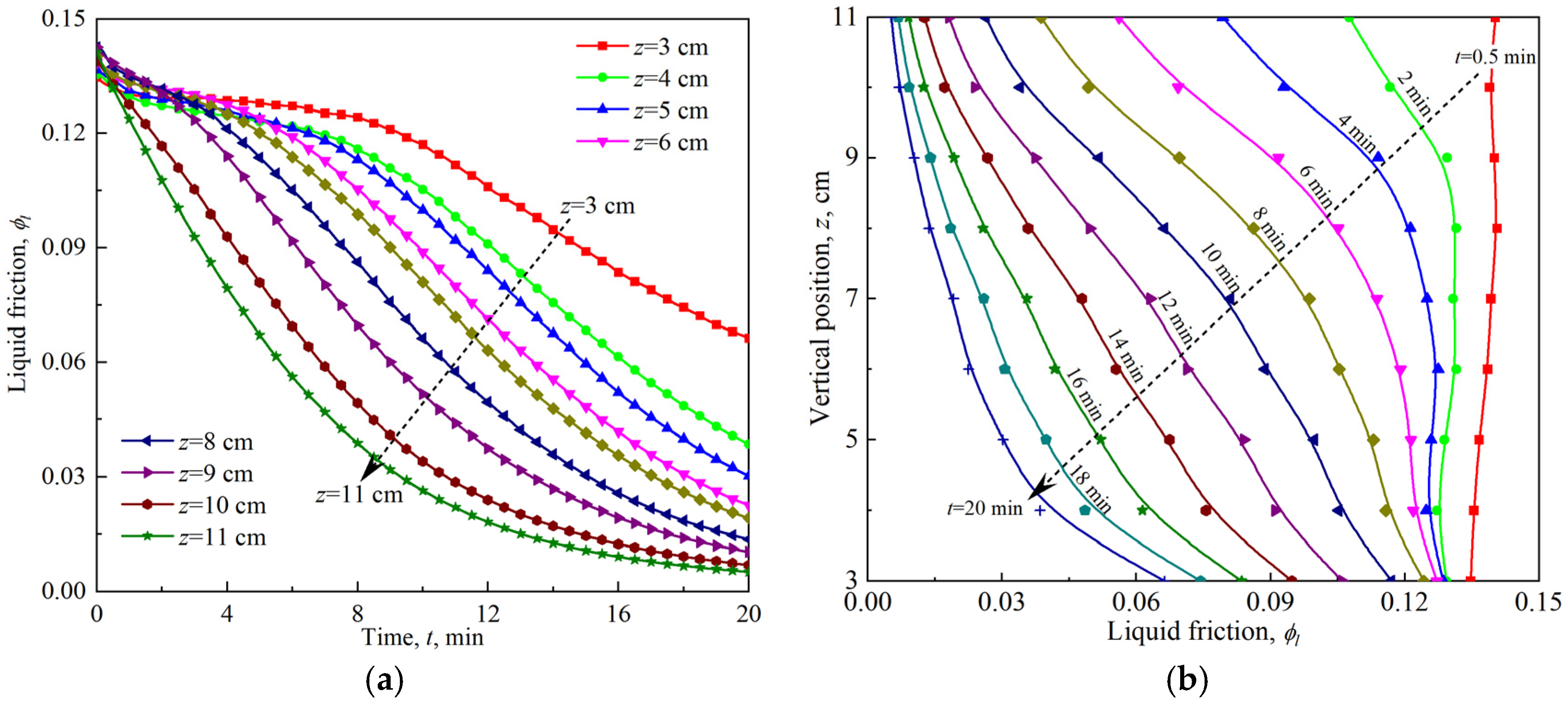
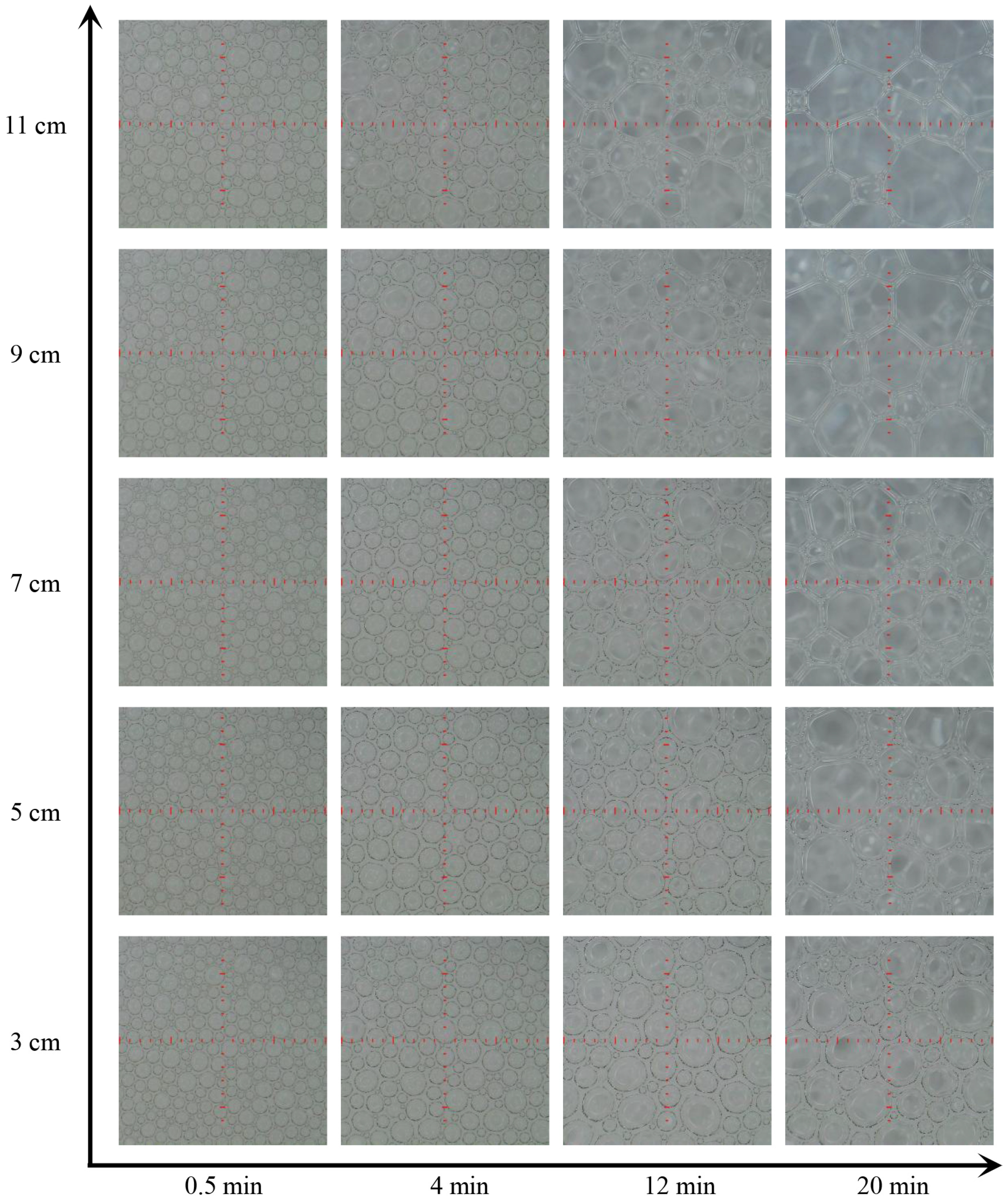
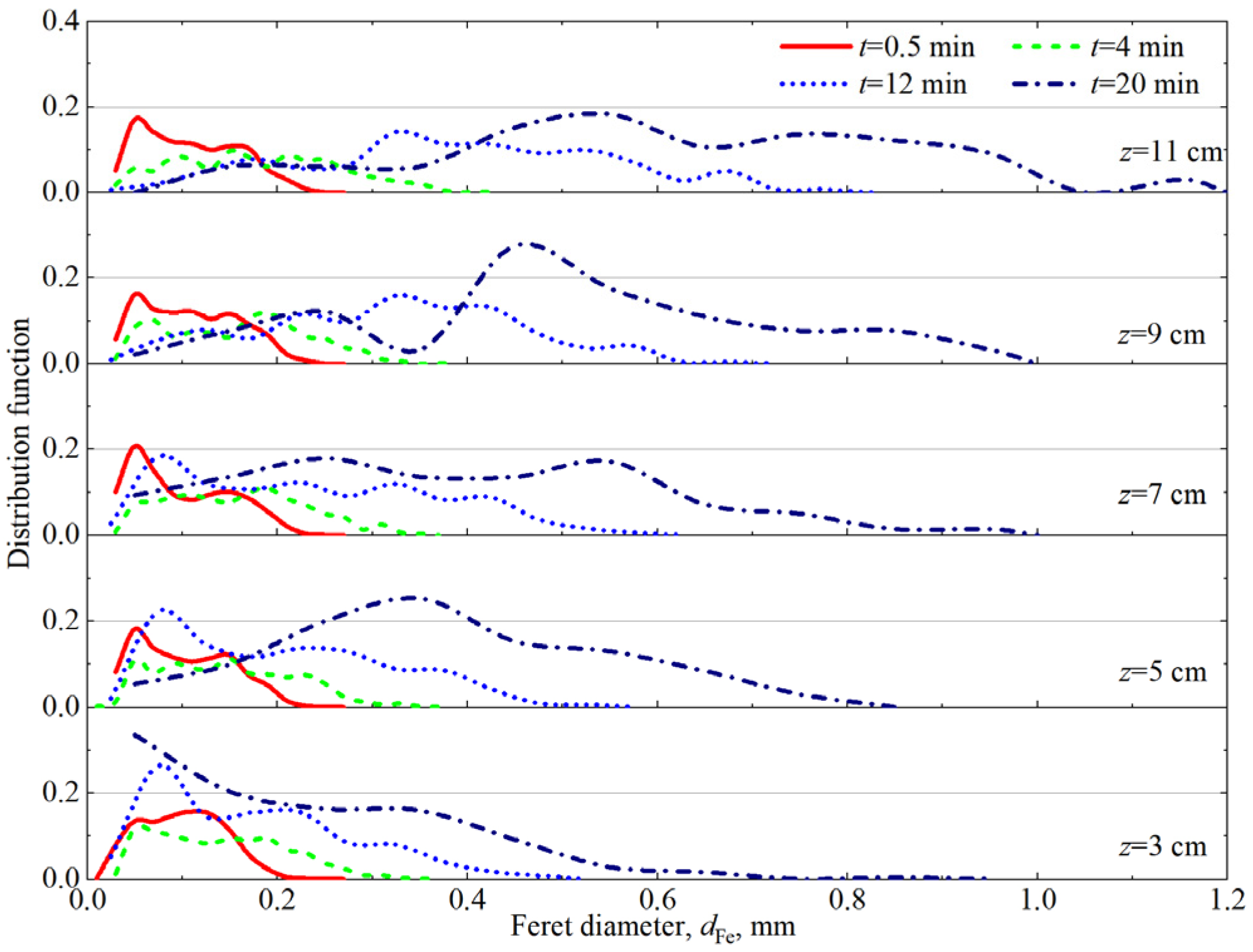
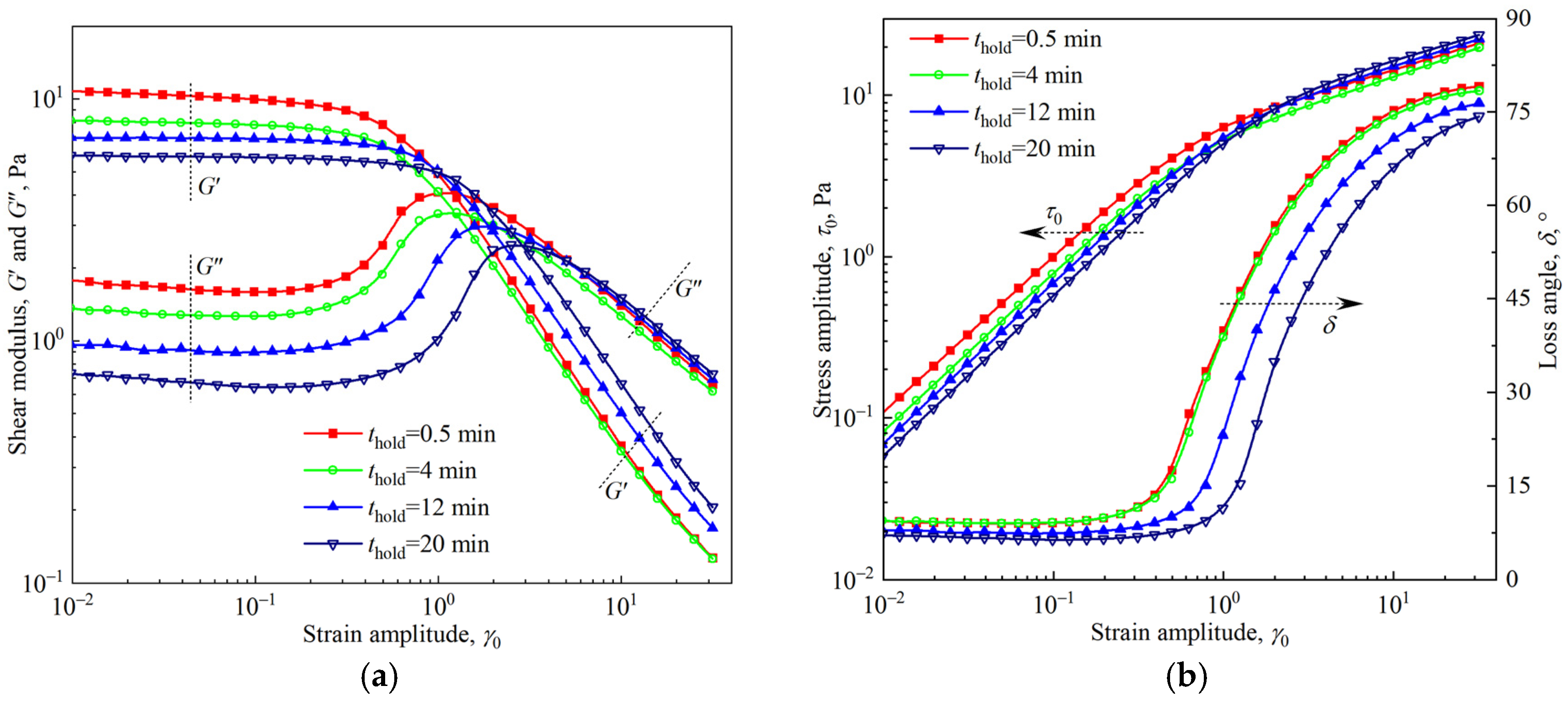
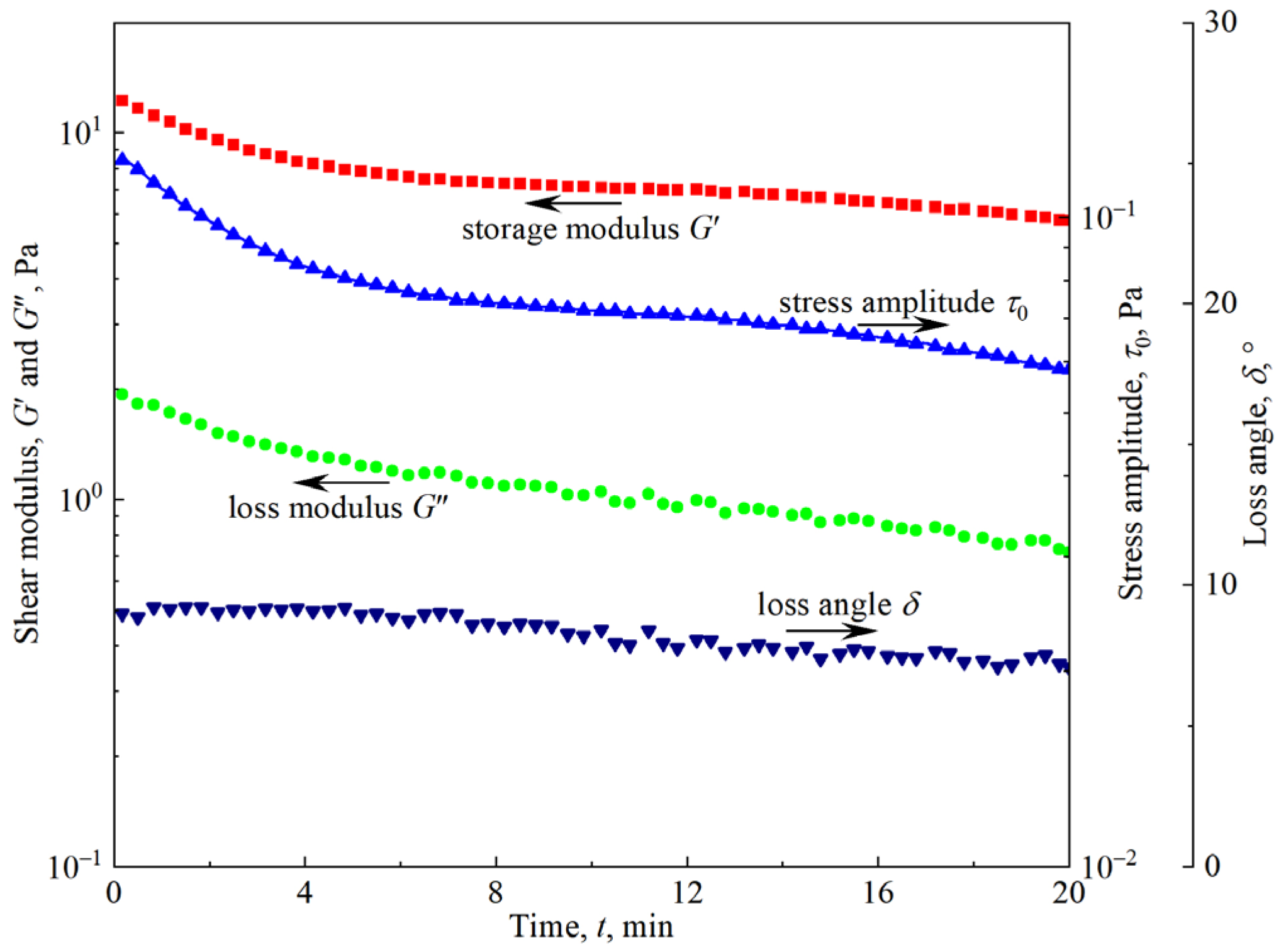
3.1. Foam Aging
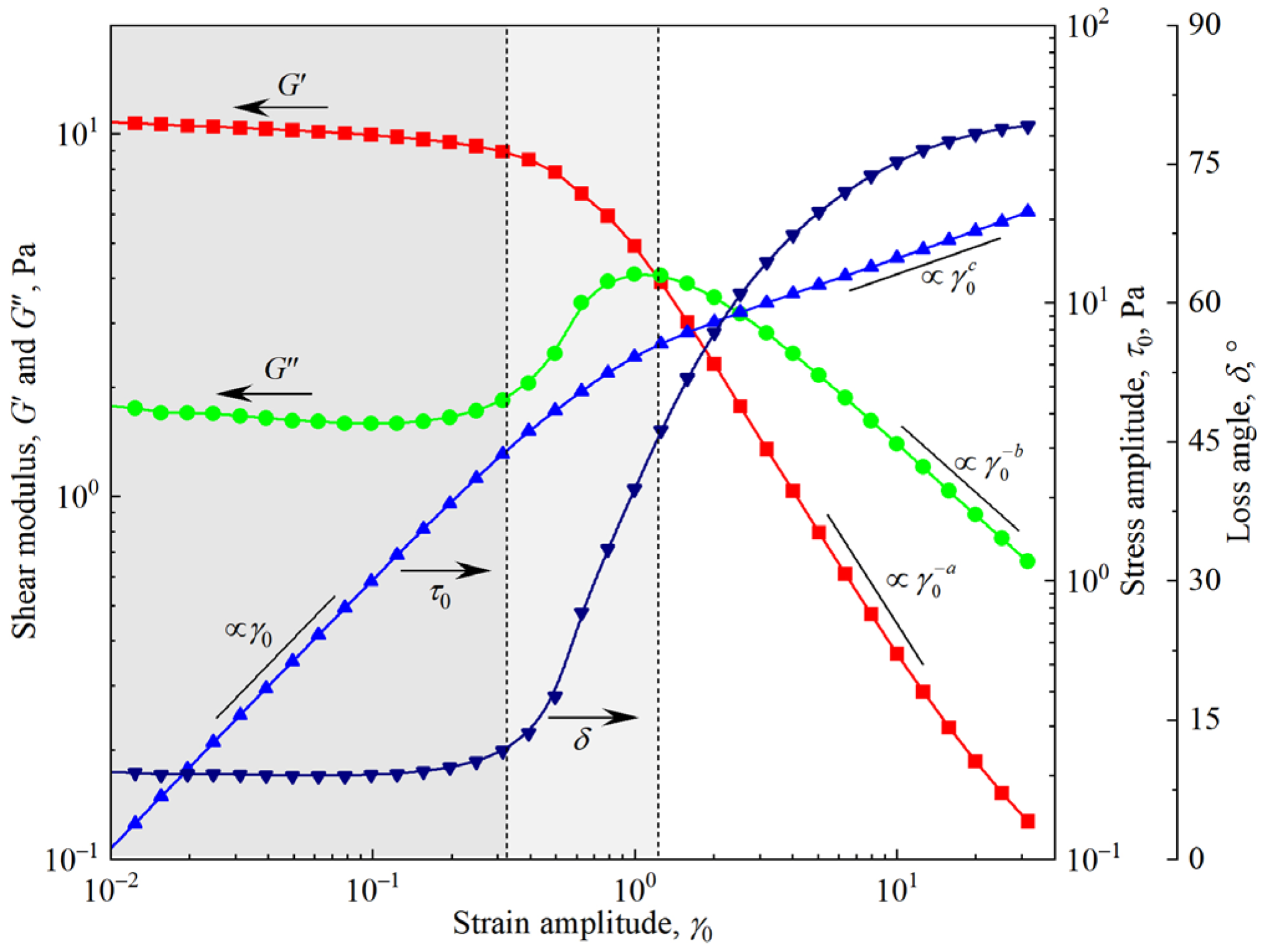
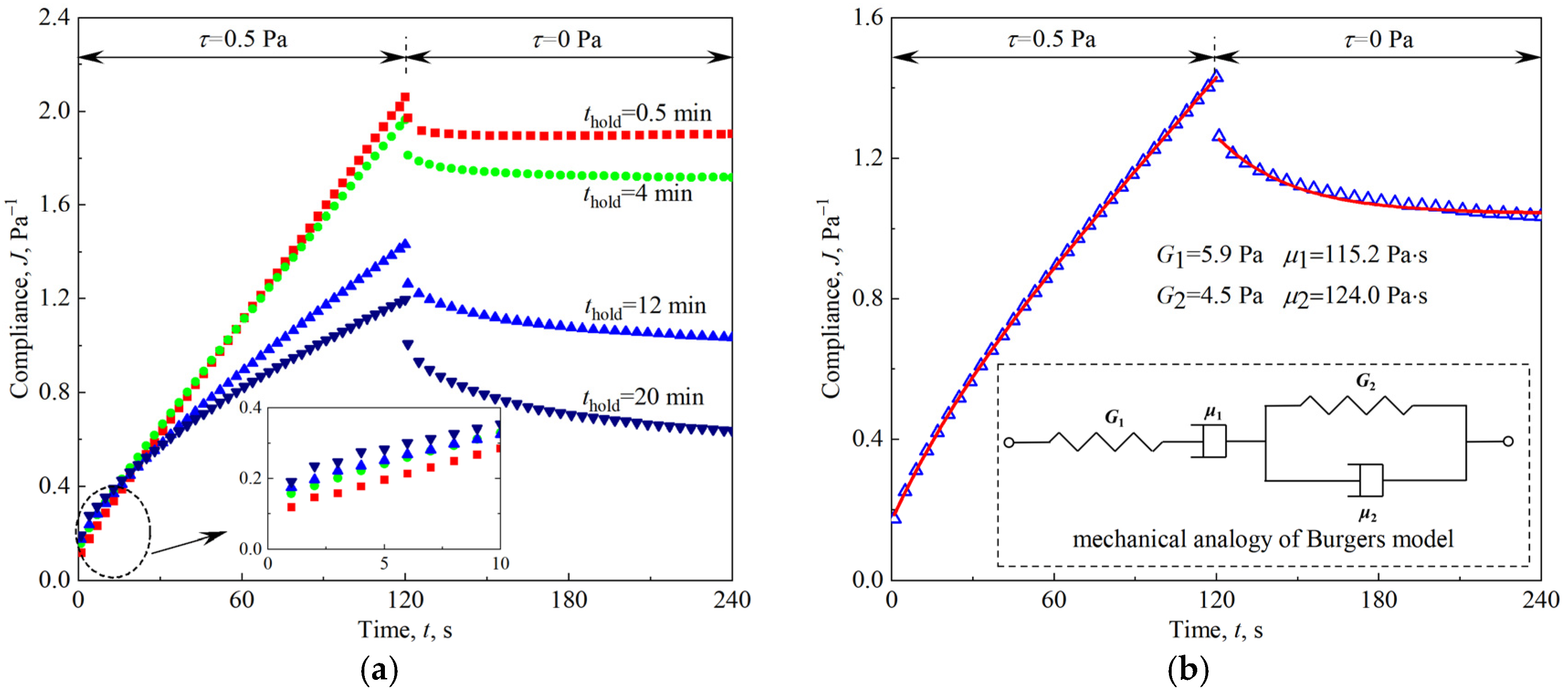
3.2. Viscoelasticity of Firefighting Foam
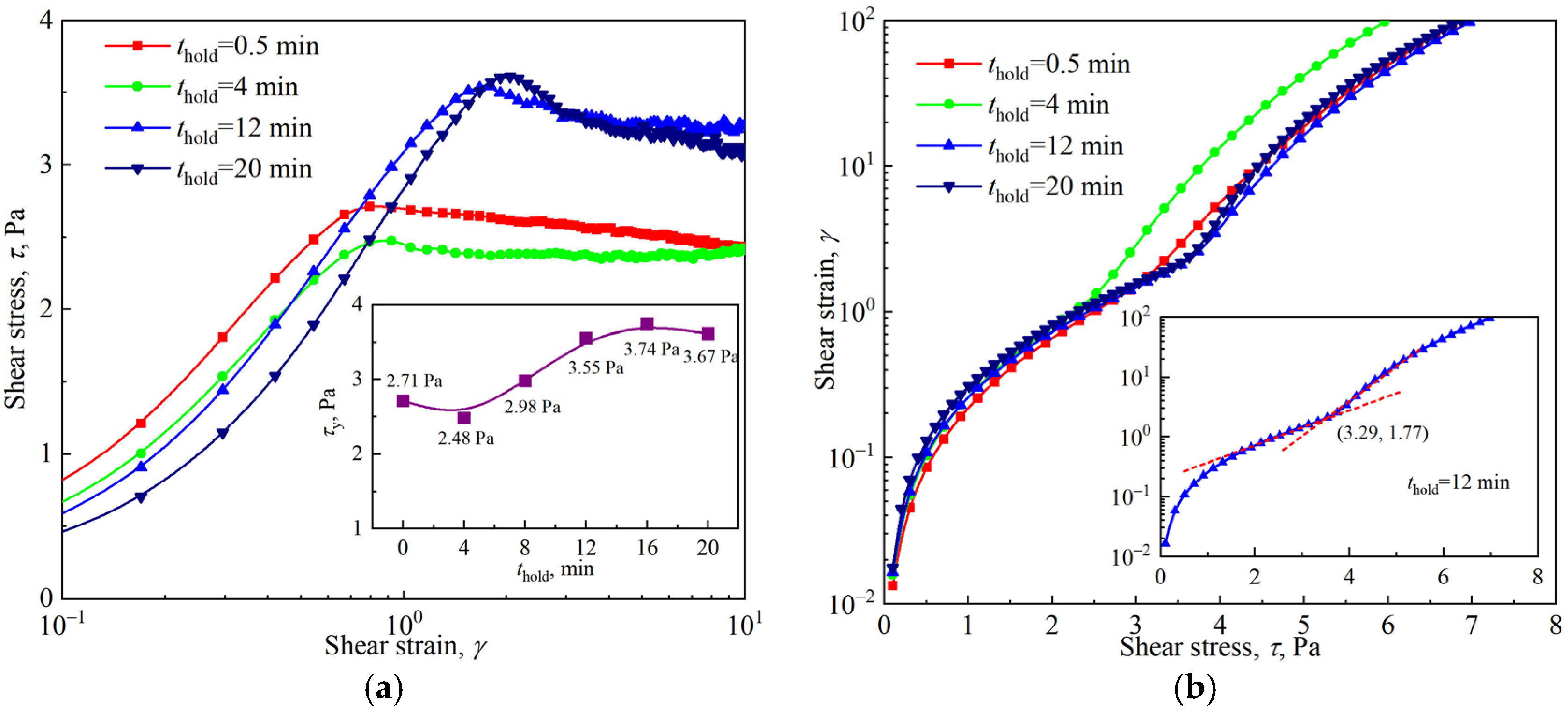
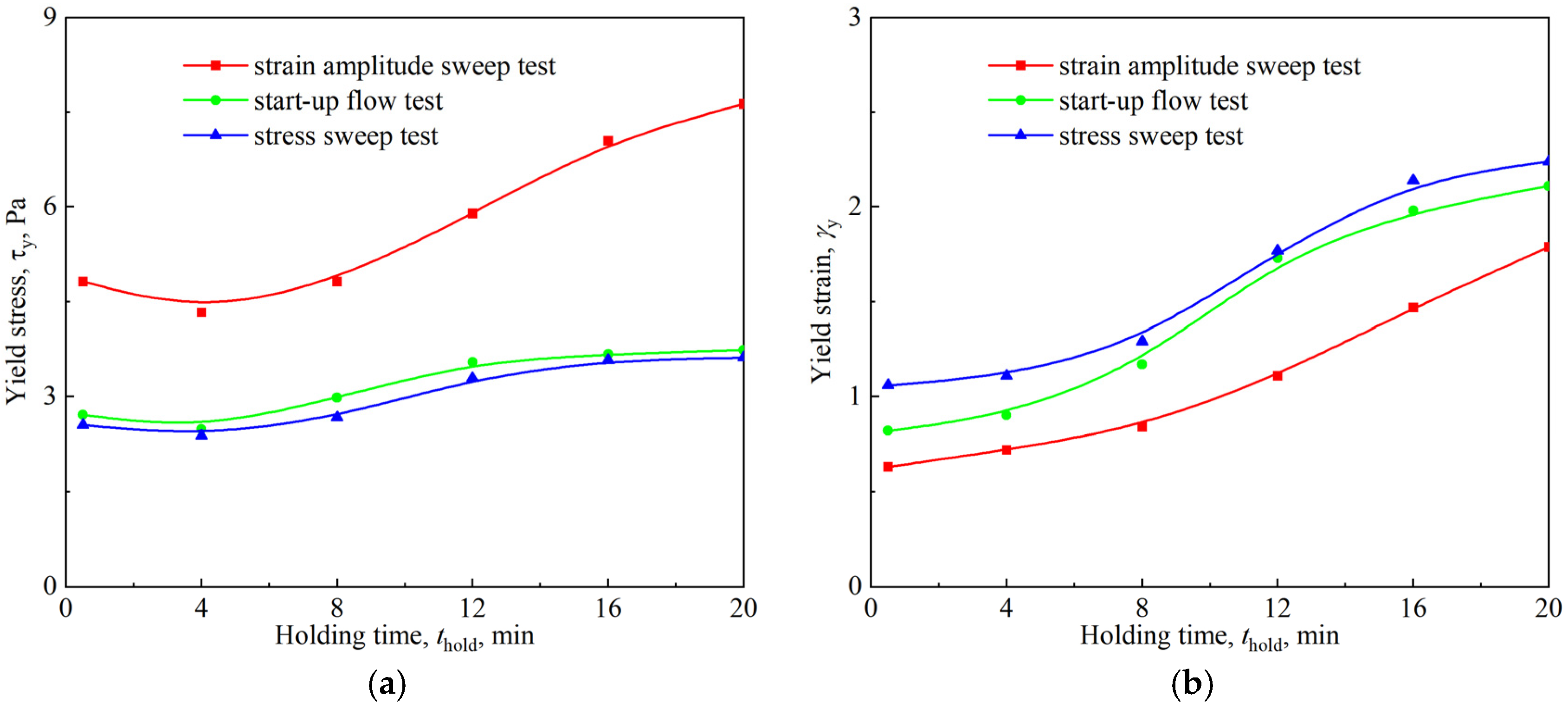
3.3. Yielding of the Firefighting Foam
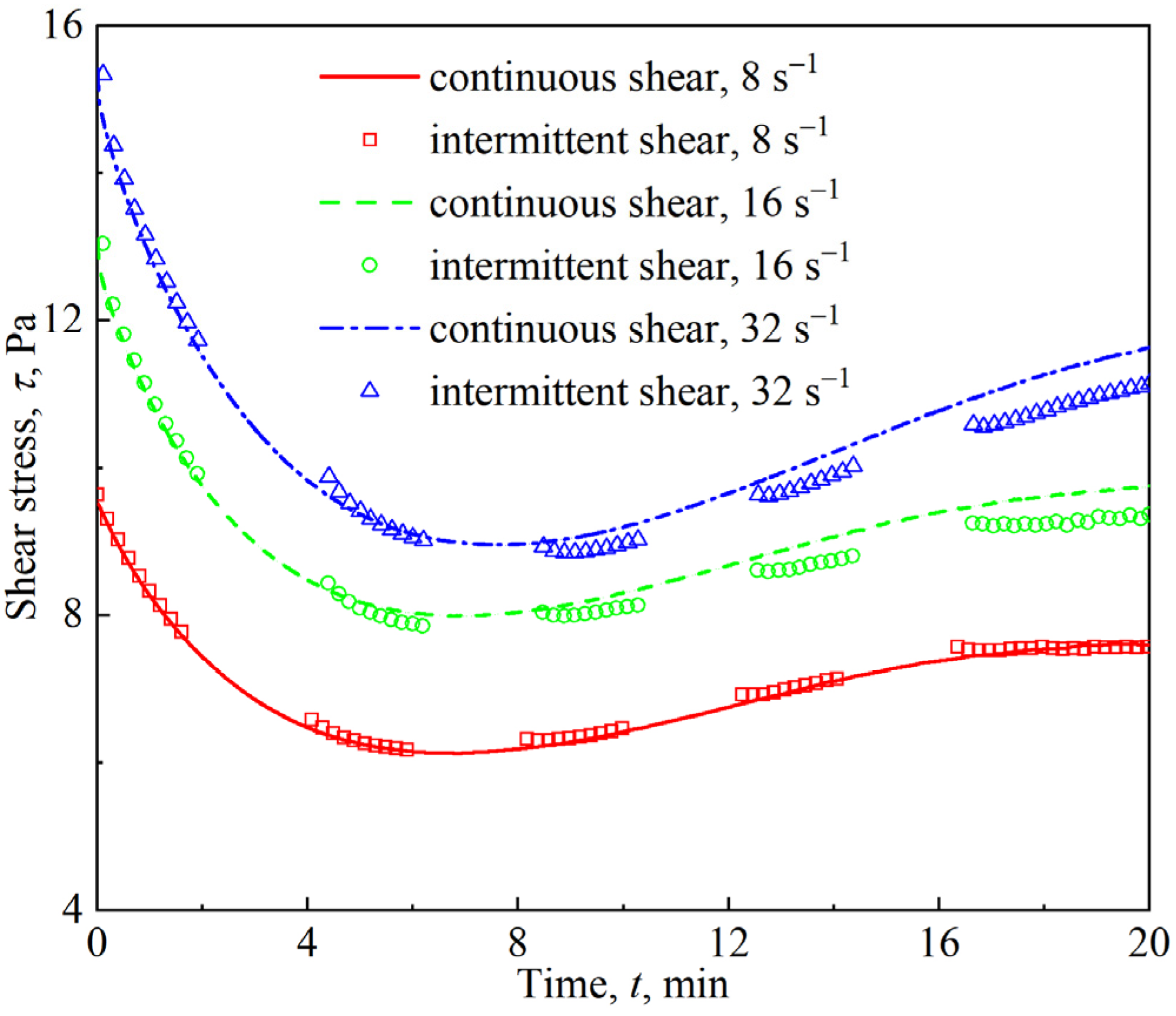
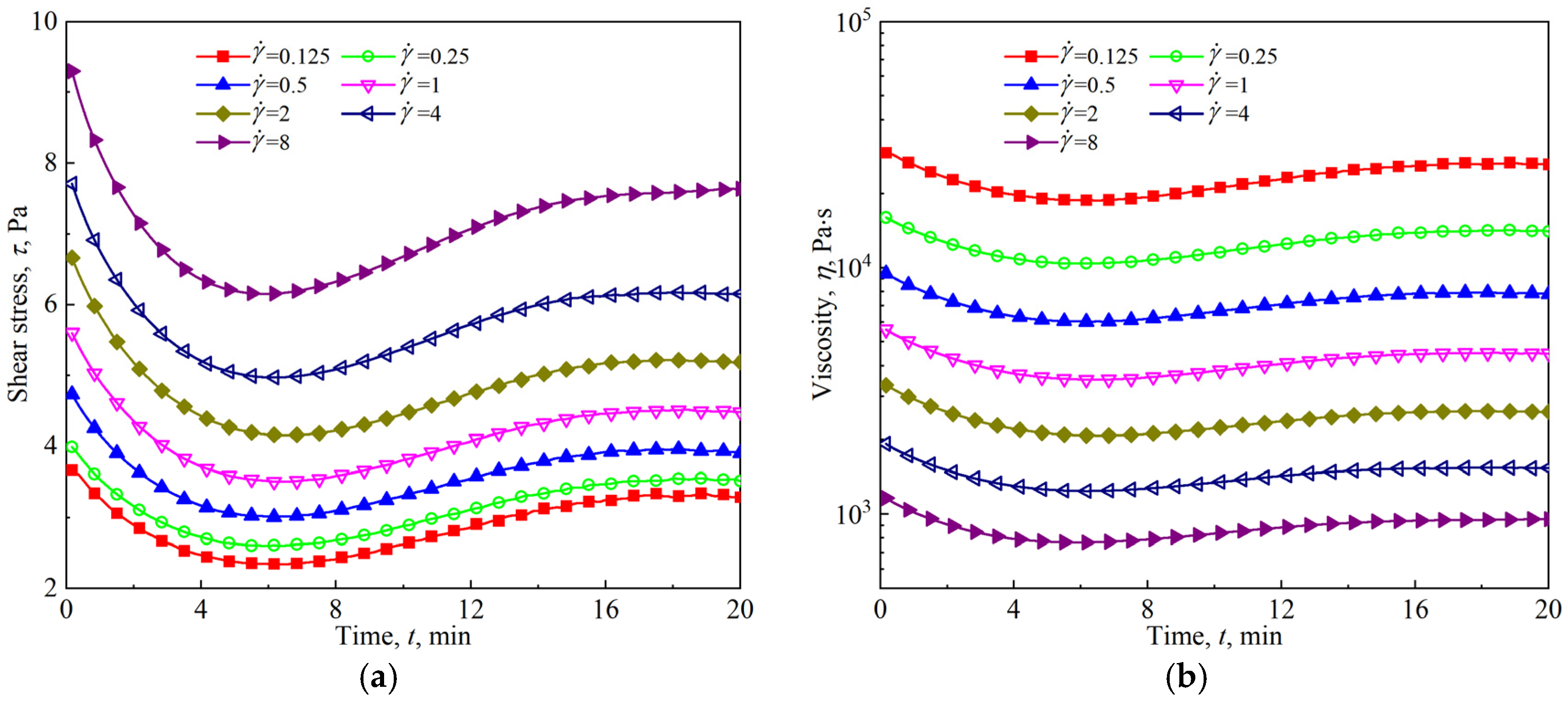
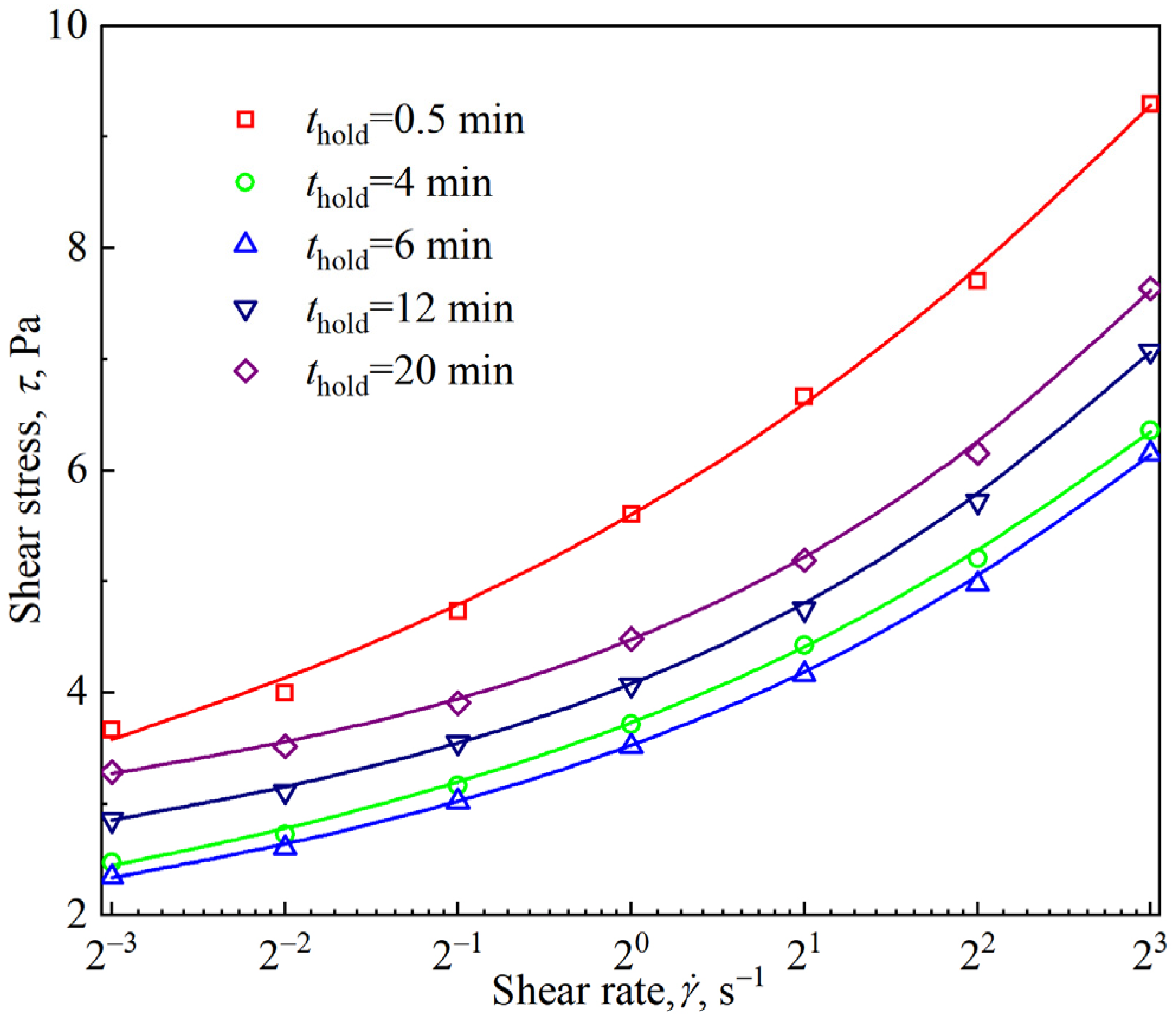
3.4. Viscous Flow of Firefighting Foam Under Slow Shear
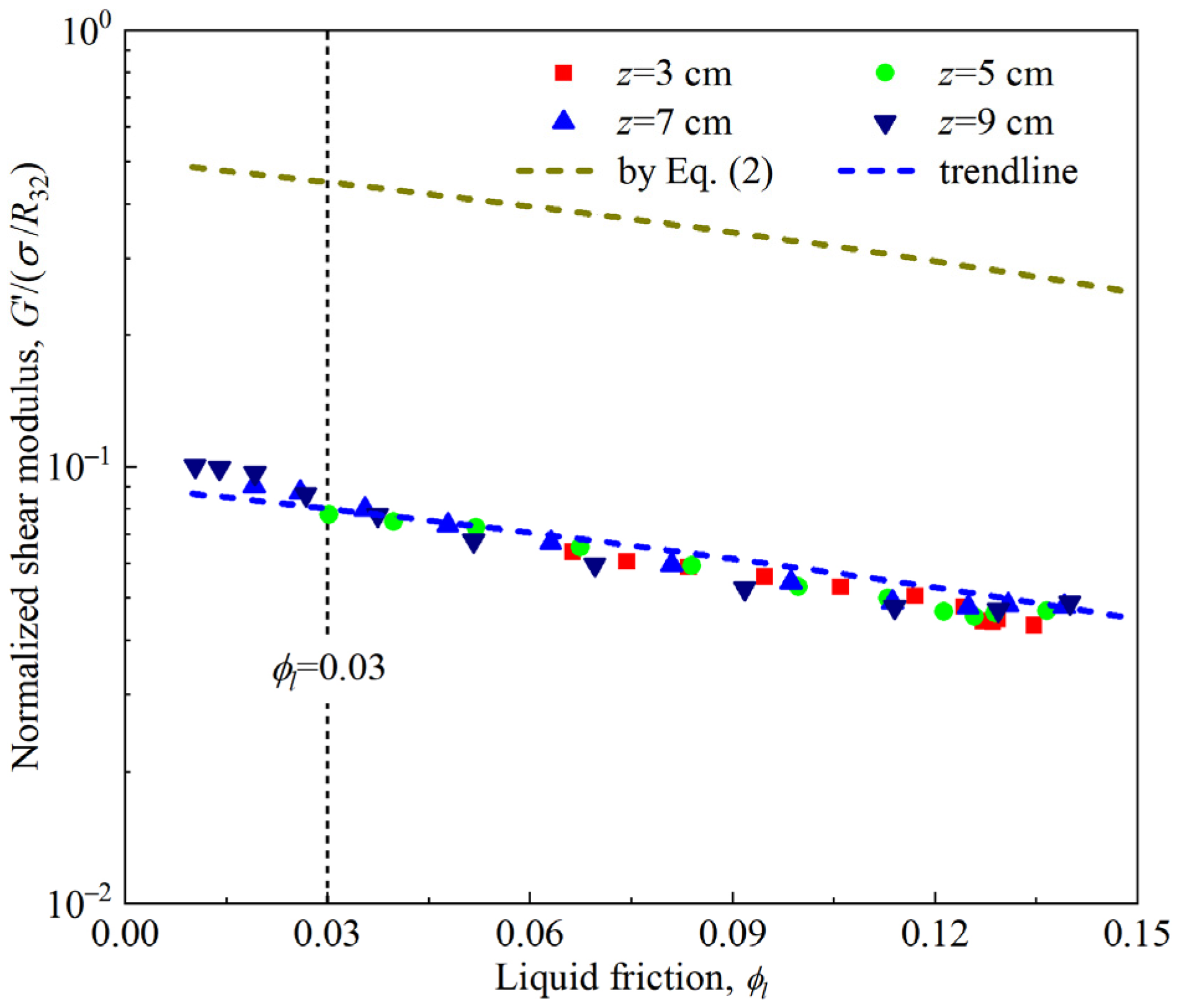
3.5. Competitive Effects of Foam Drainage and Coarsening on Foam Rheology
3.6. Limitations and Prospects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Nomenclature | |
| a, b, c | power law exponents |
| a1, a2 | empirical parameters in Equation (4) and Equation (5) |
| dFe | Feret diameter [mm] |
| f | frequency [Hz] |
| G′ | storage modulus [Pa] |
| G″ | loss modulus [Pa] |
| G1, G2 | parameters of the Burgers model (Equation (3)) [Pa] |
| J | compliance [Pa−1] |
| J∞ | residual compliance [Pa−1] |
| K | consistency factor [Pa.sn] |
| n | flow behavior index |
| r | bubble radius, equal to half the Feret diameter [mm] |
| R32 | Sauter mean radius, defined as R32 = <r3>/<r2> [mm] |
| RA | arithmetic mean radius, defined as RA = <r> [mm] |
| Ro | cubic mean radius, defined as Ro = <r3>1/3 [mm] |
| Rrms | mean square radius, defined as Rrms = <r2>1/2 [mm] |
| t | time [min] |
| thold | holding time [min] |
| Greek symbols | |
| γ | strain |
| γ0 | strain amplitude |
| γy | yield strain |
| shear rate [s−1] | |
| δ | loss angle [°] |
| μ1, μ2 | parameters of the Burgers model (Equation (3)) [Pa.s] |
| σ | surface tension of the foam solution [mN.m−1] |
| τ | shear stress [Pa] |
| τ0 | stress amplitude [Pa] |
| τy | yield stress [Pa] |
| ϕl | liquid friction (volume fraction of the liquid phase of a foam) |
| critical liquid fraction | |
| ϕl,0 | initial liquid friction |
| ψ | relative conductivity of firefighting foam, defined as ψ = ψfoam/ψsolution |
| ψfoam | conductivity of firefighting foam [mS.cm−1] |
| ψsolution | conductivity of the foam solution [mS.cm−1] |
References
- NFPA 11; Standard for Low-, Medium-, and High-Expansion Foam. NFPA: Quincy, MA, USA, 2024.
- NFPA 30; Flammable and combustible liquids code. NFPA: Quincy, MA, USA, 2024.
- Zhi, H.; Bao, Y.; Wang, L.; Mi, Y. Extinguishing performance of alcohol-resistant firefighting foams on polar flammable liquid fires. J. Fire Sci. 2020, 38, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, M.W.; Ananth, R. Fuel surface cooling by aqueous foam: A pool fire suppression mechanism. Fire Technol. 2015, 51, 667–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Bi, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhi, H.; Qiu, P. Experimental investigation of foam spread and extinguishment of the large-scale methanol pool fire. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 287, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.J.; Jiang, N.; Lu, S.X.; Li, C.H. Fluorinated and fluorine-free firefighting foams spread on heptane surface. Colloids Surf. A 2018, 552, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.; Lönnermark, A.; Persson, H. FOAMSPEX: Large scale foam application: Modelling of foam spread and extinguishment. Fire Technol. 2003, 3, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattimer, B.Y.; Trelles, J. Foam spread over a liquid pool. Fire Saf. J. 2007, 42, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, R.L.; Williams, F.W. A Review of the Performance of AFFF Systems Serving Helicopter Decks on U.S. Navy Surface Combatants; U.S. Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ranjbar, H.; Shahraki, B.H. Effect of aqueous film-forming foams on the evaporation rate of hydrocarbon fuels. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, P.; Nandini, D.; Tripathi, B.P. Firefighting aqueous film forming foam composition, properties and toxicity: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 2013–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgarr, J.; Mbonimpa, E.; Mcavoy, D.; Soltanian, M. Fate and transport of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) at aqueous film forming foam (AFFF) discharge sites: A review. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonough, C.A.; Choyke, S.; Barton, K.E.; Mass, S.; Higgins, C.P. Unsaturated PFOS and other PFASs in human serum and drinking water from an AFFF-impacted community. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8139–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, G.G.; Farley, J.P. Evaluation of the fire protection effectiveness of fluorine free firefighting foams. 2020. Available online: https://www.nfpa.org/education-and-research/research/fire-protection-research-foundation/projects-and-reports/evaluation-of-the-fire-protection-effectiveness-of-fluorine-free-firefighting-foams (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Gao, H.; Zhang, M.; Xia, J.J.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.K. Time and surfactant types dependent model of foams based on the Herschel–Bulkley model. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 509, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Géminard, J.C.; Pastenes, J.; Melo, F. Foam rheology at large deformation. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 042601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Lin, Q.; Song, B.; Xia, J. Rheological characterization and prediction model of compressed air Class A foam. J. Dispersion Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Addad, S.; Höhler, R. Rheology of foams and highly concentrated emulsions. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 19, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Merrer, M.; Lespiat, R.; Höhler, R.; Cohen-Addad, S. Linear and non-linear wall friction of wet foams. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrabi, S.A.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Jameson, G.J. Free drainage in aqueous foams: Model and experimental study. AIChE J. 2001, 47, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Qin, B.; Xu, Y.; Hao, M.; Shao, X.; Zhuo, H. Experimental investigation of the drainage characteristic and stability mechanism of gel-stabilized foam used to extinguish coal fire. Fuel 2022, 313, 122685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakalo, K.; Baumgarten, K.; Tighe, B.P.; Puisto, A. Coarsening and mechanics in the bubble model for wet foams. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 98, 012607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requier, A.; Guidolin, C.; Rio, E.; Galvani, N.; Cohen-Addad, S.; Pitois, O.; Salonen, A. Foam coarsening in a yield stress fluid. Soft Matter 2024, 20, 6023–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzan, M. Rheology of the wet surfactant foams and biofoams—A review. Tech. Trans. 2013, 1-Ch, 9–27. [Google Scholar]
- Denkov, N.D.; Tcholakova, S.; Golemanov, K.; Ananthpadmanabhan, K.P.; Lips, A. The role of surfactant type and bubble surface mobility in foam rheology. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 3389–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlier, F.; Khidas, Y.; Pitois, O. Yielding of complex liquid foams. J. Rheol. 2017, 61, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexis, M.; Willenbacher, N. Yield stress and elasticity of aqueous foams from protein and surfactant solutions—The role of continuous phase viscosity and interfacial properties. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 459, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, M.J.; Conroy, M.W.; Dougherty, J.A.; Otto, N.; Williams, B.A.; Ananth, R.; Fleming, J.W. Bubble coarsening dynamics in fluorinated and non-fluorinated firefighting foams. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 470, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrabi, S.A.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; Jameson, G.J. A comparative study of drainage characteristics in AFFF and FFFP compressed-air fire-fighting foams. Fire Saf. J. 2002, 37, 21–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.E.; Chiesa, P.J. A new foam rheometer for studying fire fighting foams. Fire Technol. 1976, 12, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, B.S.; Dlugogorski, B.Z.; G.Jameson, J. Rheology of fire-fighting foams. Fire Saf. J. 1998, 31, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, K.; Marze, S.; Saint-Jalmes, A.; Durian, D.J. Electrical conductivity of dispersions: From dry foams to dilute suspensions. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, 6301–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P. Foam Engineering: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cantat, I.; Cohen-Addad, S.; Elias, F.; Graner, F.; Höhler, R.; Pitois, O.; Rouyer, F.; Saint-Jalmes, A. Foams: Structure and Dynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Höhler, R.; Cohenaddad, S. Rheology of liquid foam. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouyer, F.; Cohen-Addad, S.; Höhler, R. Is the yield stress of aqueous foam a well-defined quantity? Colloids Surf. A 2005, 263, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| t/min | RA/mm | R32/mm | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z = 3 cm | z = 5 cm | z = 7 cm | z = 9 cm | z = 11 cm | z = 3 cm | z = 5 cm | z = 7 cm | z = 9 cm | z = 11 cm | |
| 0.5 | 0.0502 ± 0.0213 | 0.0511 ± 0.0243 | 0.0495 ± 0.0257 | 0.0543 ± 0.0250 | 0.0540 ± 0.0253 | 0.0662 ± 0.0006 | 0.0714 ± 0.0007 | 0.0730 ± 0.0007 | 0.0745 ± 0.0007 | 0.0749 ± 0.0008 |
| 4 | 0.0703 ± 0.0339 | 0.0734 ± 0.0345 | 0.0795 ± 0.0353 | 0.0793 ± 0.0361 | 0.0896 ± 0.0414 | 0.0992 ± 0.0016 | 0.1020 ± 0.0016 | 0.1071 ± 0.0016 | 0.1073 ± 0.0015 | 0.1224 ± 0.0020 |
| 8 | 0.0810 ± 0.0437 | 0.0854 ± 0.0453 | 0.0958 ± 0.0499 | 0.1031 ± 0.0552 | 0.1312 ± 0.0670 | 0.1226 ± 0.0028 | 0.1279 ± 0.0027 | 0.1392 ± 0.0025 | 0.1527 ± 0.0030 | 0.1876 ± 0.0043 |
| 12 | 0.0873 ± 0.0521 | 0.1025 ± 0.0582 | 0.1168 ± 0.0665 | 0.1585 ± 0.0668 | 0.1939 ± 0.0790 | 0.1416 ± 0.0039 | 0.1583 ± 0.0037 | 0.1789 ± 0.0039 | 0.2065 ± 0.0050 | 0.2487 ± 0.0067 |
| 16 | 0.0985 ± 0.0634 | 0.1382 ± 0.0768 | 0.1586 ± 0.0847 | 0.1989 ± 0.1003 | 0.2417 ± 0.1064 | 0.1697 ± 0.0053 | 0.2091 ± 0.0057 | 0.2296 ± 0.0059 | 0.2783 ± 0.0075 | 0.3197 ± 0.0104 |
| 20 | 0.1099 ± 0.0774 | 0.1864 ± 0.0830 | 0.2215 ± 0.1073 | 0.2493 ± 0.1055 | 0.3036 ± 0.1220 | 0.2065 ± 0.0110 | 0.2516 ± 0.0088 | 0.2920 ± 0.0119 | 0.3251 ± 0.0122 | 0.3877 ± 0.0152 |
| thold/min | G1/Pa | μ1/Pa·s | G2/Pa | μ2/Pa·s | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 62.7 ± 0.1 | 23.8 ± 1.1 | 327.8 ± 39.4 | 0.0015 |
| 4 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 69.5 ± 0.2 | 10.8 ± 0.4 | 225.1 ± 13.6 | 0.0018 |
| 8 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | 84.1 ± 0.2 | 8.3 ± 0.2 | 152.4 ± 5.8 | 0.0015 |
| 12 | 5.9 ± 0.1 | 115.2 ± 0.7 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 124.0 ± 2.7 | 0.0017 |
| 16 | 5.4 ± 0.1 | 142.3 ± 1.4 | 3.9 ± 0.1 | 109.4 ± 2.5 | 0.0021 |
| 20 | 4.9 ± 0.1 | 173.9 ± 3.8 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 98.0 ± 3.0 | 0.0034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Y.; Zhi, H.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J. Experimental Study on Rheological Behavior of Firefighting Foams. Materials 2025, 18, 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143236
Bao Y, Zhi H, Wang L, Fan Y, Wang J. Experimental Study on Rheological Behavior of Firefighting Foams. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143236
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Youquan, Huiqiang Zhi, Lu Wang, Yakun Fan, and Junqi Wang. 2025. "Experimental Study on Rheological Behavior of Firefighting Foams" Materials 18, no. 14: 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143236
APA StyleBao, Y., Zhi, H., Wang, L., Fan, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Experimental Study on Rheological Behavior of Firefighting Foams. Materials, 18(14), 3236. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143236






