Deformable Fricke-XO-Gelatin Radiochromic Dosimeter of Ionizing Radiation and Its Applications in Quality Assurance Tests for Radiation Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fricke Gel Preparation
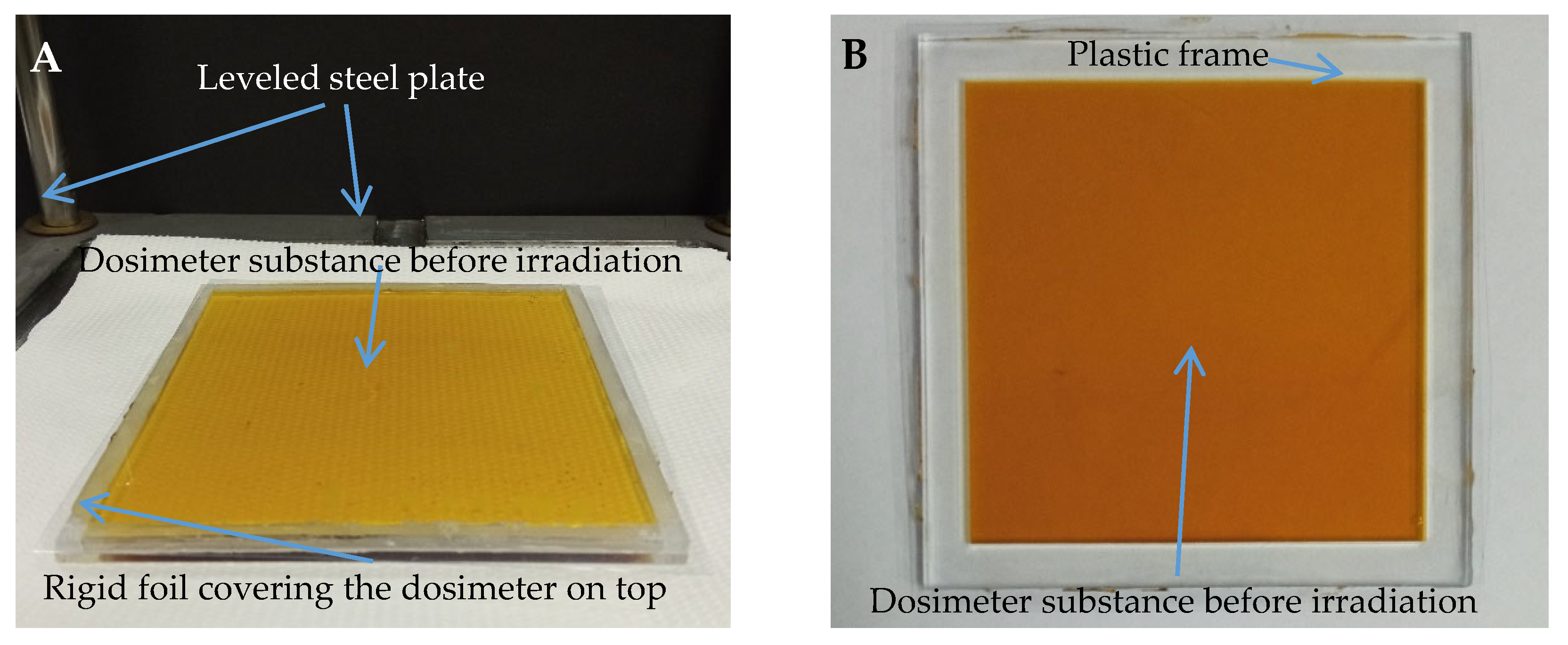
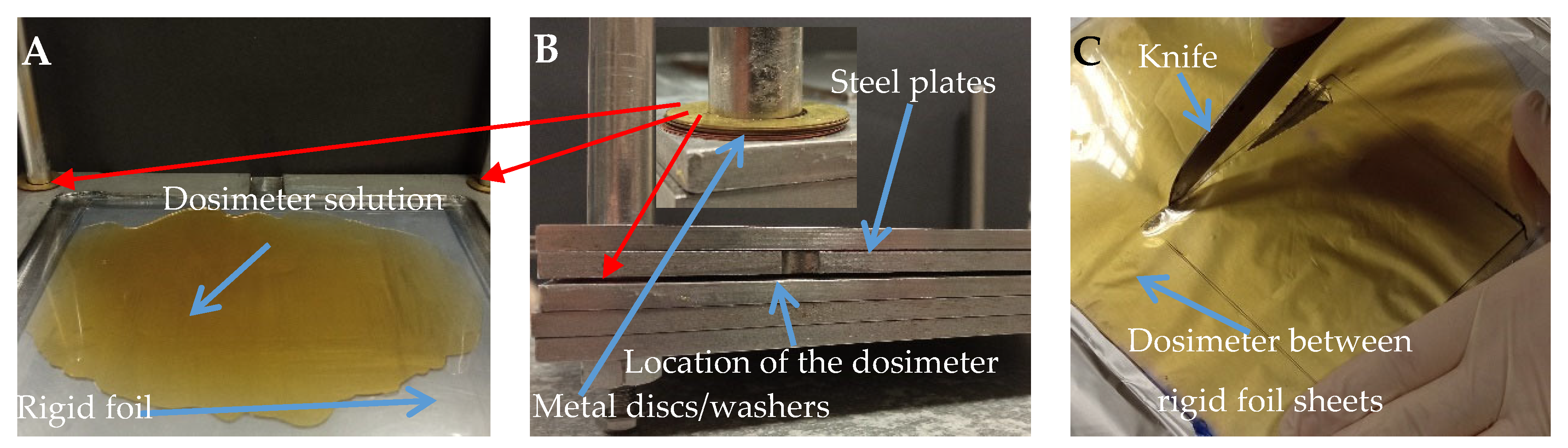
2.2. Preparation of the Samples
2.3. Chemical Stability Tests
2.4. Thermal Analysis
2.5. Mechanical Analysis
2.6. Irradiation
2.7. Readout and Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Properties of the Fricke-XO-Gelatin Dosimeter with Sorbitol
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the Fricke-XO-Gelatin Dosimeter with Sorbitol
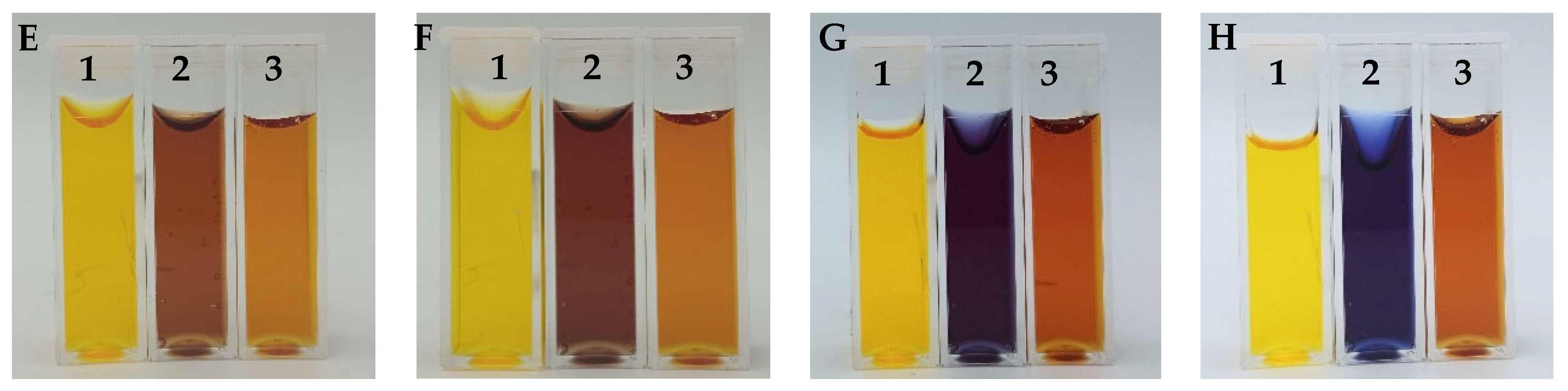
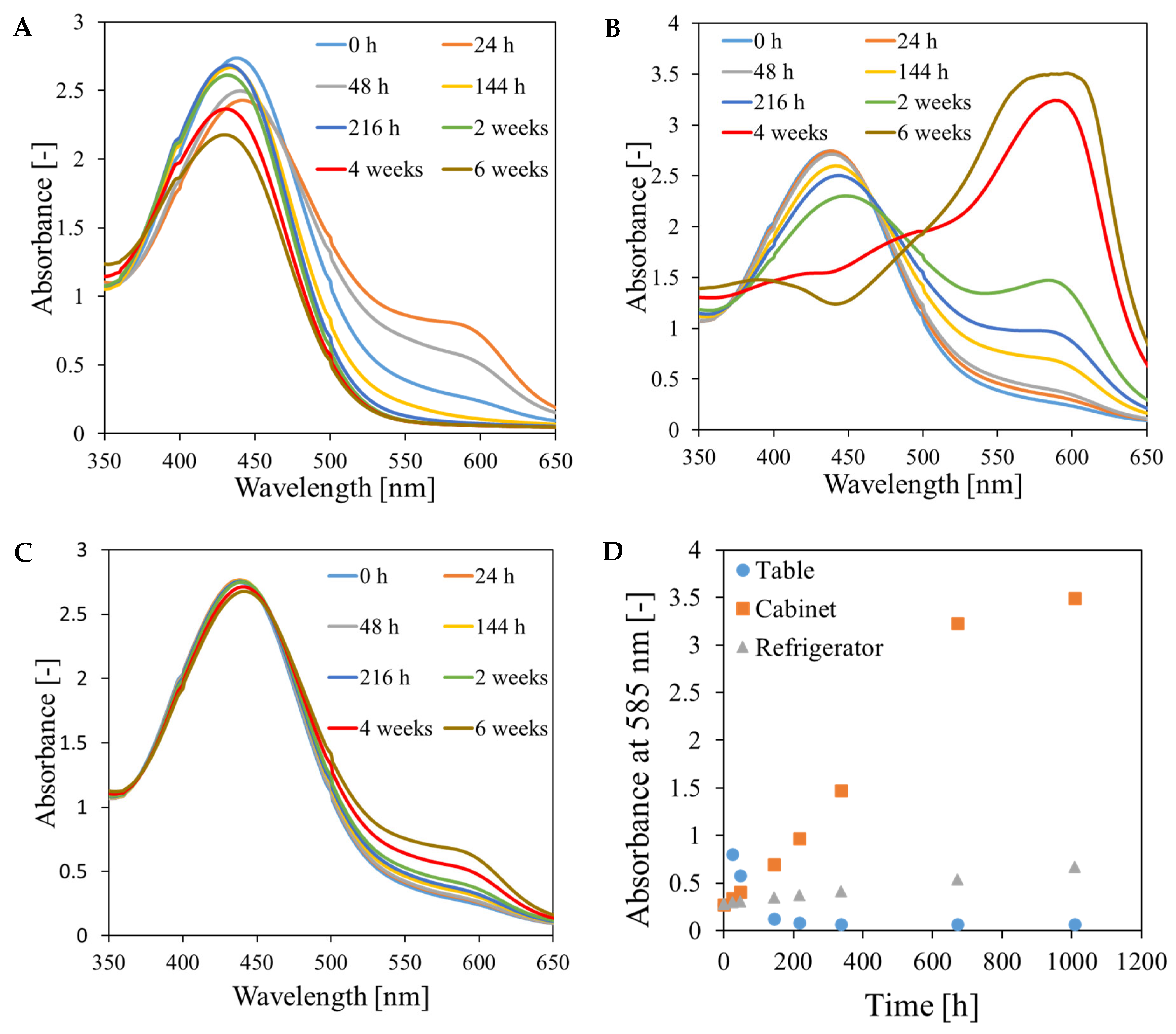
3.3. Chemical Stability of the Fricke-XO-Gelatin Dosimeter with Sorbitol
3.4. Dosimeter Response to Ionizing Radiation
3.5. Bolus and Thin Dosimeter Calibration
3.6. Applications of the Fricke-XO-Gelatine–Sorbitol Dosimeter
3.6.1. Coincidence Test of Radiation and Mechanical Isocenters
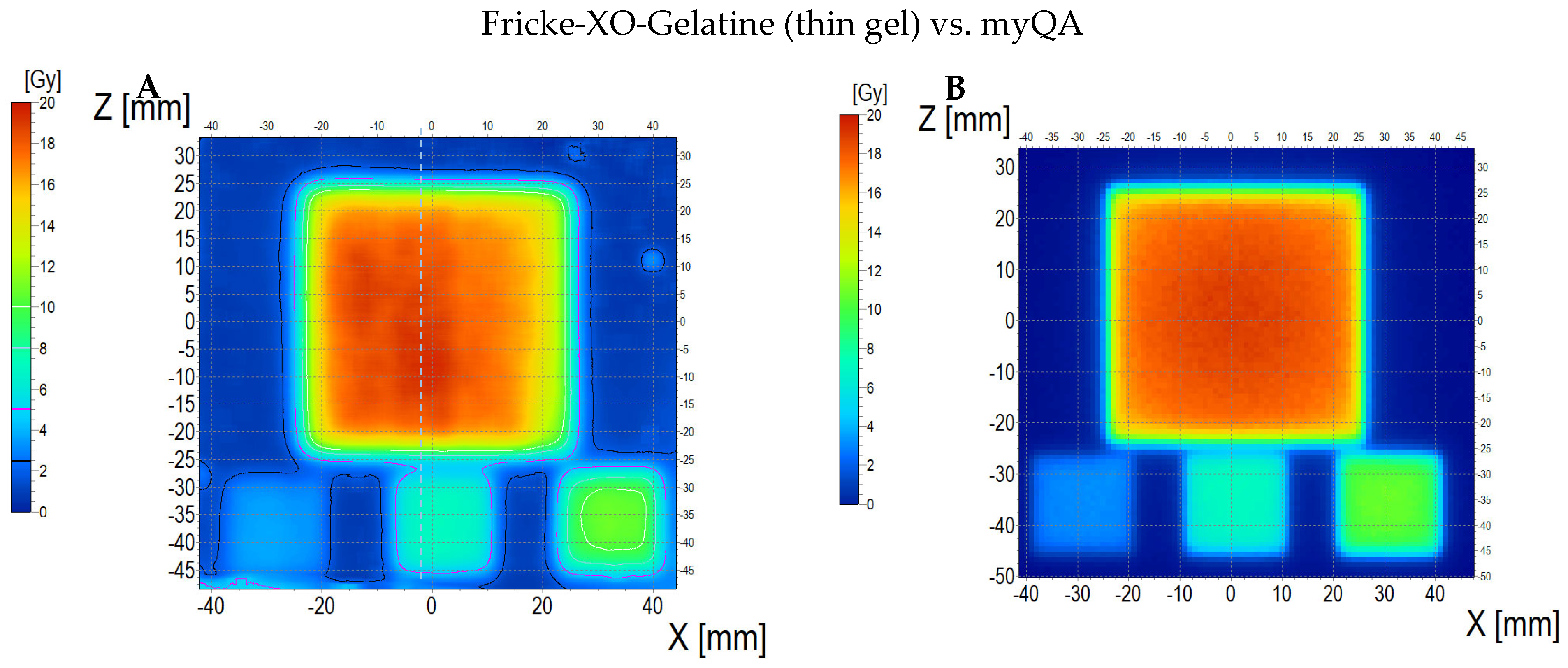
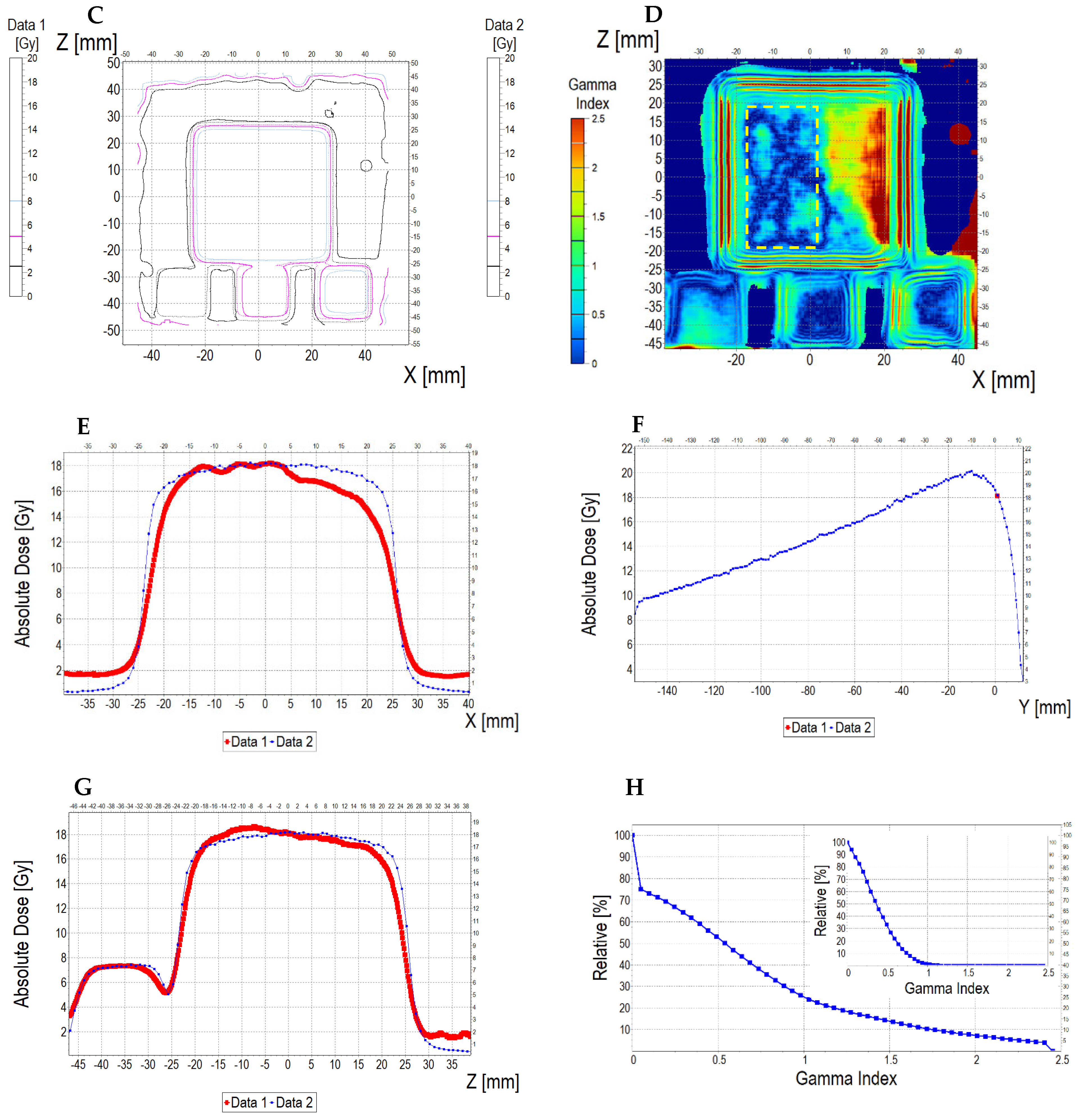
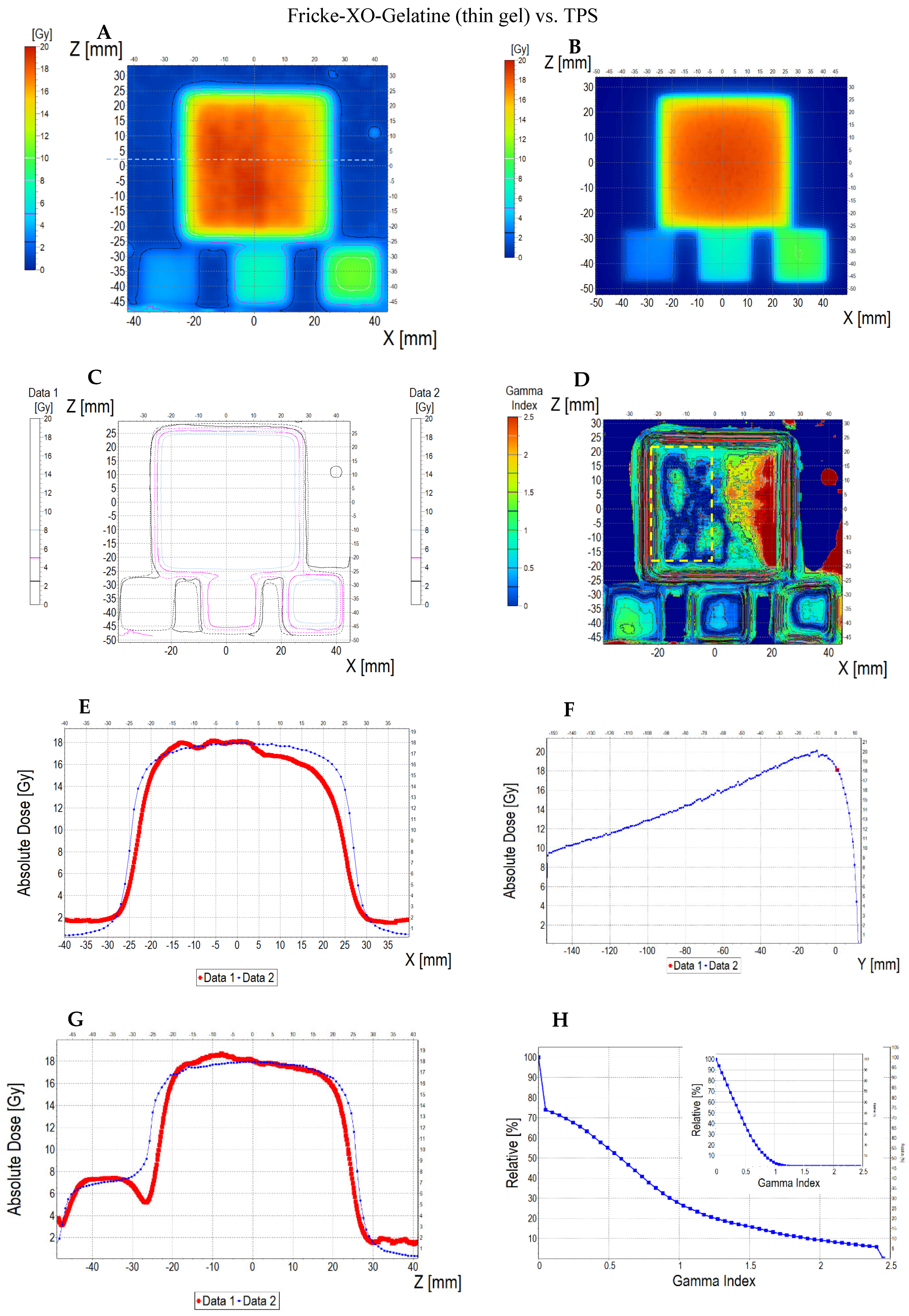
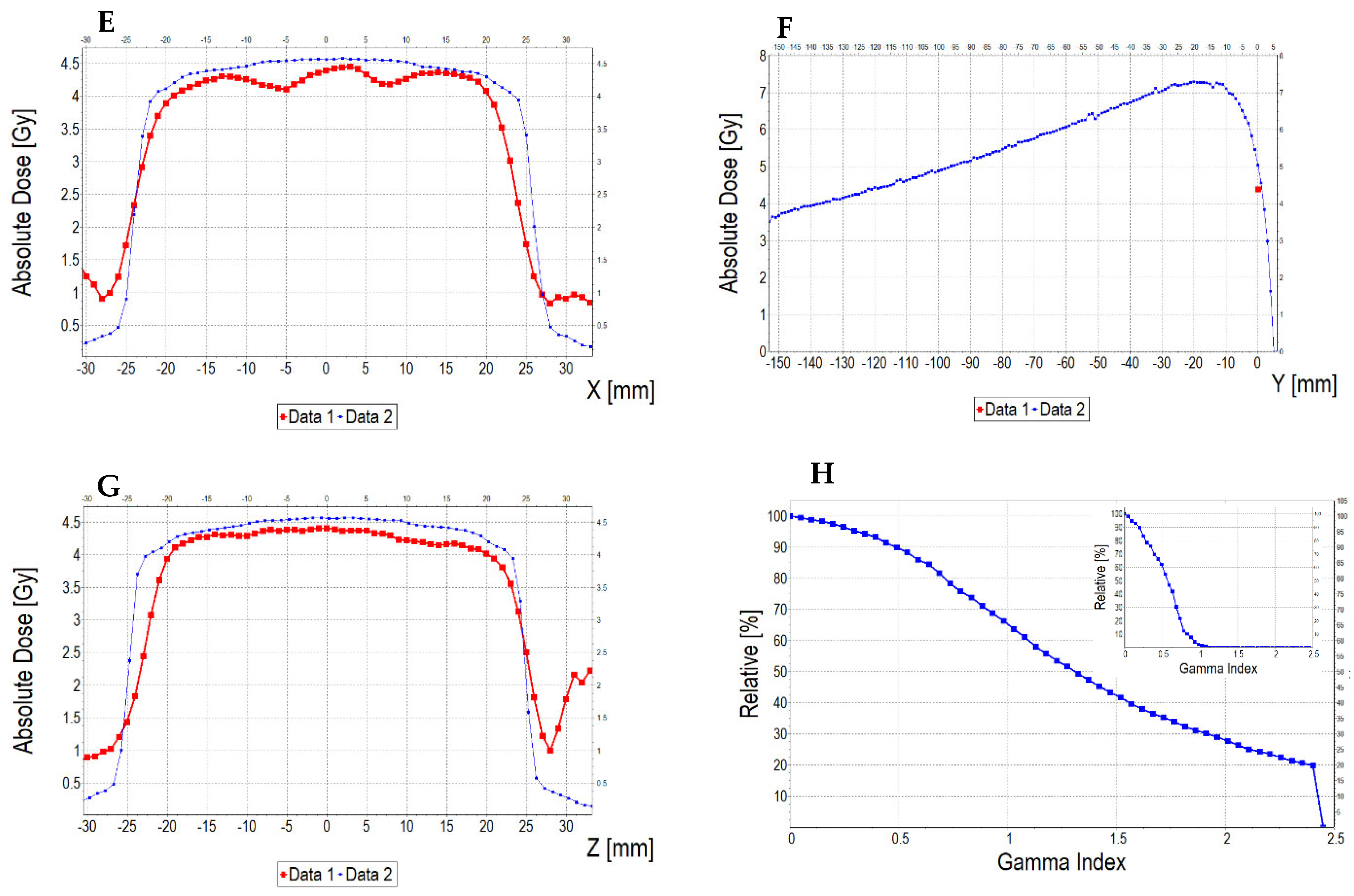
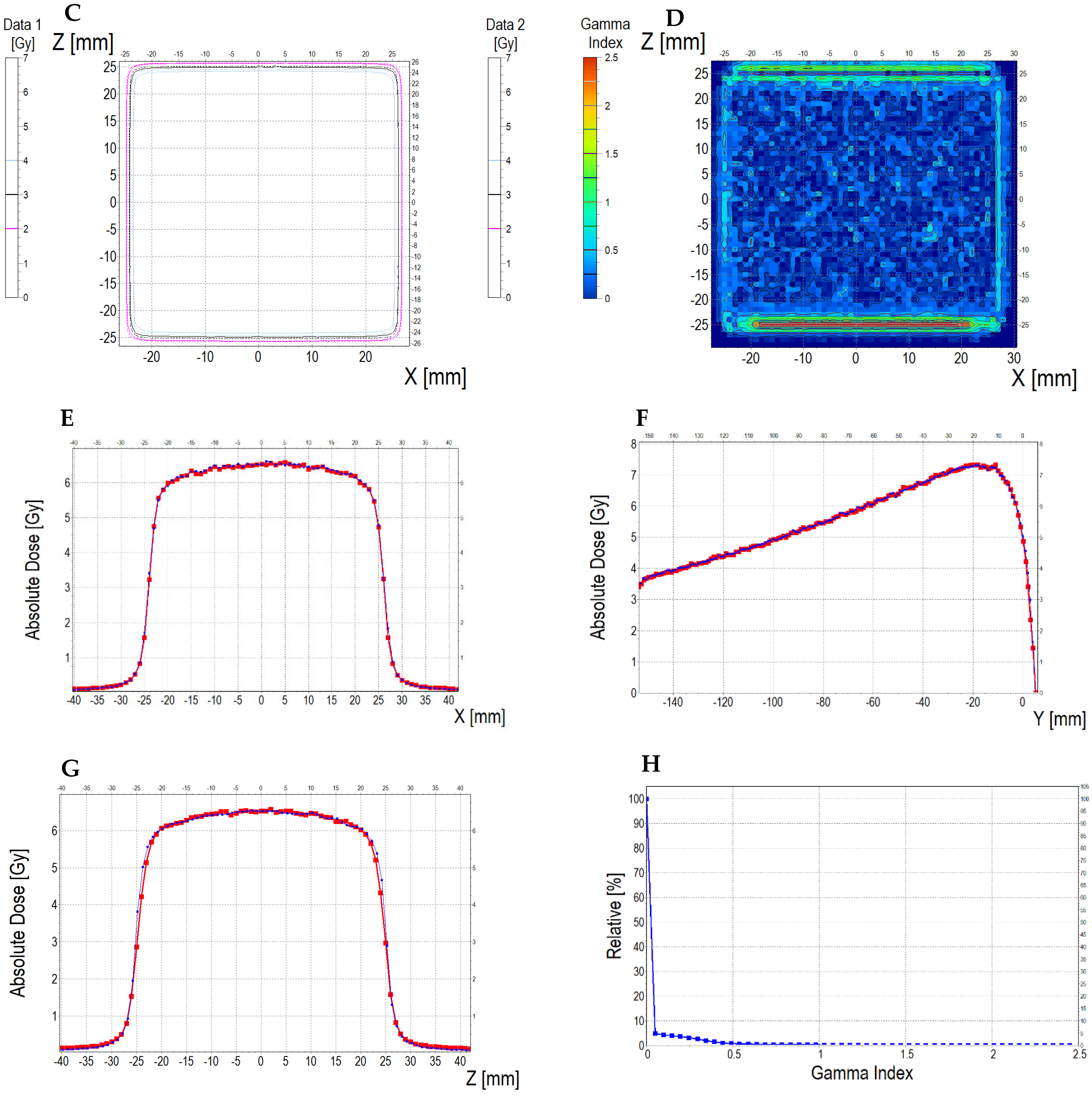
3.6.2. Treatment Planning Verification: Fricke-XO-Gelatine (Thin Gel)
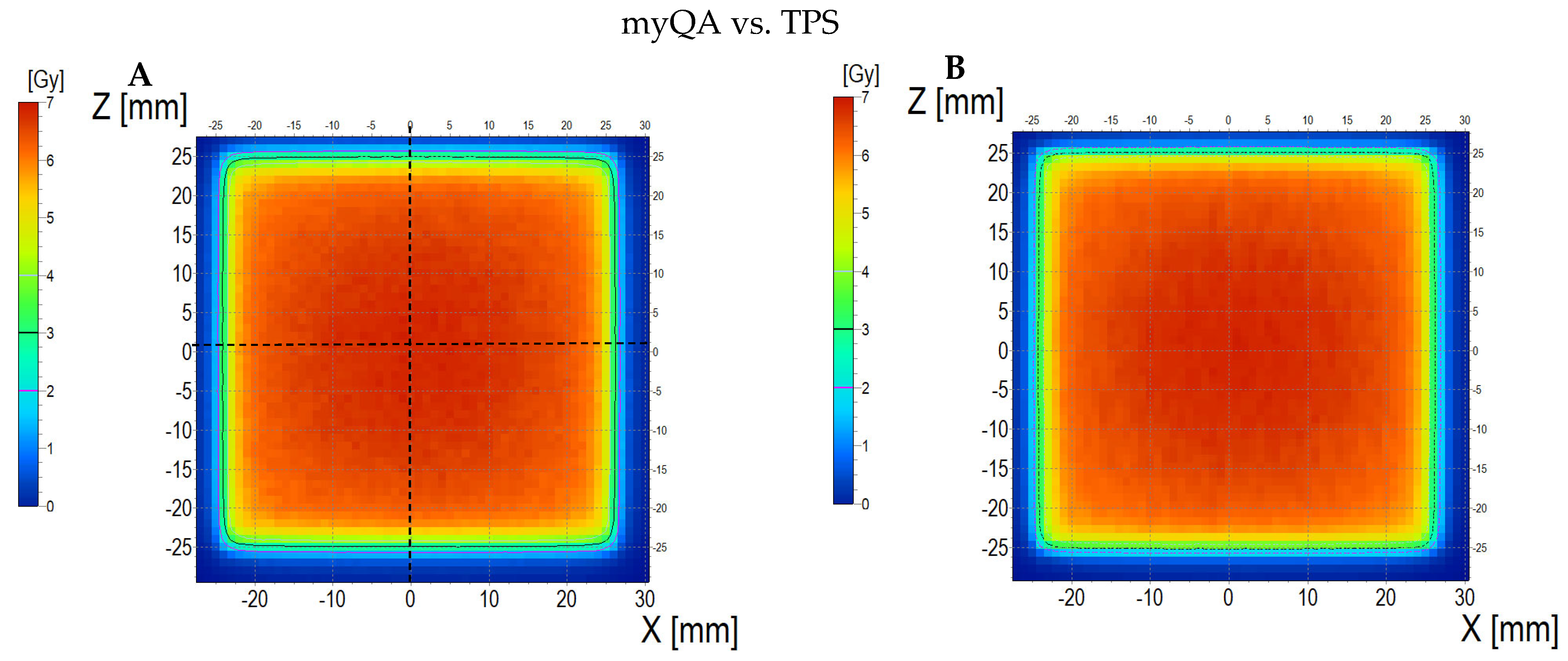
3.6.3. Treatment Planning Verification: Fricke-XO-Gelatine (Thick Gel)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldock, C.; De Deene, Y.; Doran, S.; Ibbott, G.; Jirasek, A.; Lepage, M.; McAuley, K.B.; Oldham, M.; Schreiner, L.J. Polymer gel dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, R1–R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Deene, Y. Radiation dosimetry by use of radiosensitive hydrogels and polymers: Mechanisms, state-of-the-art and perspective from 3D to 4D. Gels 2022, 8, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Warmington, L.; Gopishankar, N. Three-dimensional radiation dosimetry using polymer gel and solid radiochromic polymer: From basics to clinical applications. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchione, M.A.; Páez, S.L.; Strumia, M.C.; Valente, M.; Mattea, F. Chemical overview of gel dosimetry systems: A comprehensive review. Gels 2022, 8, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsh, S.; Mann, P.; Elter, A.; Runz, A.; Klüter, S.; Karger, C.P. Polymer gel-based measurements of the isocenter accuracy in an MR-LINAC. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1305, 012007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsh, S.; Mann, P.; Lang, C.; Hearing, P.; Runz, A.; Karger, C.P. Feasibility of polymer gel-based measurements of radiation isocenter accuracy in magnetic fields. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 11NT02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozicki, M.; Maras, P. On the measurement of radiation isocenter for medical accelerators using 3D polymer gel dosimetry. Introduction, application, and good practices. Measurement 2023, 221, 113585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.; Shin, W.G.; Son, J.; Choi, C.H.; Park, J.M.; Hwang, U.J.; Jin, K.; Jung, S. 3D star shot analysis using MAGAT gel dosimeter for integrated imaging and radiation isocenter verification of MR-Linac system. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Kozicki, M. On the use of the Fricke-Pluronic F-127 gel dosimeter for radiation isocenter testing of a medical linear accelerator. Materials 2024, 17, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, M.; Maras, P. An optical reusable 2D radiochromic gel-based system for ionising radiation measurements in radiotherapy. Molecules 2024, 29, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aon, E.; Brunetto, M.; Sansogne, R.; Castellano, G.; Valente, M. Novel Method Based on Fricke Gel Dosimeters for Dose Verification in IMRT Techniques. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA 12); Buenos Aires, Argentina, 19–24 October 2008, IRPA: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Valente, M.; Aon, E.; Brunetto, M.; Castellano, G.; Gallivanone, F.; Gambarini, G. Gel Dosimetry Measurements and Monte Carlo Modeling for External Radiotherapy Photon Beams: Comparison with a Treatment Planning System Dose Distribution. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2007, 580, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.L.; Ruda, H.E. In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy: Techniques, Applications, and Future Directions. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, U.J.; Taylor, L.; Dunn, L.; Kron, T.; Smith, R.L.; Franich, R.D. A Novel Methodology for 3D Deformable Dosimetry. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.J.; Foltz, W.D.; Velec, M.; Moseley, J.L.; Al-Mayah, A. A Novel Technique to Enable Experimental Validation of Deformable Dose Accumulation. Med. Phys. 2012, 39, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, T.; Das, S.; Adamovics, J.; Benning, R.; Oldham, M. On the Need for Comprehensive Validation of Deformable Image Registration, Investigated with a Novel 3D Deformable Dosimeter. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, L.P.; Høye, E.M.; Balling, P.; Muren, L.P.; Petersen, J.B.B.; Poulsen, P.R.; Yates, E.S.; Skyt, P.S. Determining the Mechanical Properties of a Radiochromic Silicone-Based 3D Dosimeter. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 5612–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Deene, Y.; Skyt, P.S.; Hill, R.; Booth, J.T. FlexyDos3D: A Deformable Anthropomorphic 3D Radiation Dosimeter: Radiation Properties. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 1543–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høye, E.M.; Skyt, P.S.; Yates, E.S.; Muren, L.P.; Petersen, J.B.B.; Balling, P. A New Dosimeter Formulation for Deformable 3D Dose Verification. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2015, 573, 012067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, H.; Morse, S. The Chemical Action of Roentgen Rays on Dilute Ferrous Sulphate Solutions as a Measure of Radiation Dose. Am. J. Roentgenol. Radium Ther. Nucl. Med. 1927, 18, 430–432. [Google Scholar]
- Gore, J.C.; Kang, Y.S.; Shultz, R.J. Measurement of radiation dose distributions by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 1984, 29, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bero, M.A.; Gilboy, W.B.; Glover, P.M. Radiochromic gel dosemeter for three-dimensional dosimetry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2001, 61, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, C.; Harris, P.J.; Piercy, A.R.; Healy, B. Experimental determination of the diffusion coefficient in two dimensions in ferrous sulphate gels using the finite element method. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2001, 24, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.G.; Jordan, K.J.; Battista, J.J. Optical CT reconstruction of 3D dose distributions using the ferrous–benzoic–xylenol (FBX) gel dosimeter. Med. Phys. 1998, 9, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, E.P.; Peppa, V.; Hourdakis, C.J.; Karaiskos, P.; Papagiannis, P. On the use of a novel Ferrous Xylenol-orange gelatin dosimeter for HDR brachytherapy commissioning and quality assurance testing. Phys. Med. 2018, 45, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.; Battista, J. Dose response of ferrous-xylenol orange gels: The effects of gel substrate, gelation time and dose fractionation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2004, 3, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magugliani, G.; Liosi, G.M.; Anderoli, S.; De Crescenzo, S.; Mossini, E.; Macerata, E.; Mariani, M. Characterization of Fricke-gelatin dosimeters for intraoperative Radiation Therapy dosimetry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 168, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, L.E.; Appleby, A.; Sommer, I. A new dosimeter based on ferrous sulphate solution and agarose gel. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991, 42, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.C.; Jordan, K.J.; Battista, J.J.; Van Dyk, J.; Rutt, B.K. Polyvinyl alcohol–Fricke hydrogel and cryogel: Two new gel dosimetry systems with low Fe3+ diffusion. Phys. Med. Biol. 2000, 45, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaeh, K.A.; Eyadeh, M.M.; Hailat, T.F.; Madas, B.G.; Aldweri, F.M.; Almomani, A.M.; Awad, S.I. Improvement on the performance of chemically cross-linked Fricke methylthymol-blue radiochromic gel dosimeter by addition of dimethyl sulfoxide. Radiat. Meas. 2021, 141, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Errico, F.; Lazzeri, L.; Dondi, D.; Mariani, M.; Marrale, M.; Souza, S.O.; Gambarini, S. Novel GTA-PVA Fricke gels for three-dimensional dose mapping in radiotherapy. Radiat. Meas. 2017, 106, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Jaszczak, M.; Kozicki, M. Anisotropic diffusion of Fe ions in Fricke-XO-Pluronic F-127 and Fricke-XO-Gelatine 3D radiotherapy dosimeters. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 155005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Kadłubowski, S.; Kozicki, M. Study of the Optimal Composition and Storage Conditions of the Fricke–XO–Pluronic F–127 Radiochromic Dosimeter. Materials 2022, 15, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Wach, R.; Kadłubowski, S.; Kozicki, M. Impact of Salt on Thermal Stability and Dose Response of the Fricke-XO-Pluronic F-127 3D Radiotherapy Dosimeter. Materials 2022, 15, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyadeh, M.M.; Rabaeh, K.A.; Alshomali, L.S.; Diamond, K.R.; Oglat, A.A. Evaluation of a novel physically cross-linked Fricke-xylenol orange-polyvinyl alcohol radio-chromic gel dosimeter for radiotherapy. Radiat. Meas. 2024, 177, 107263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, K.; Sekimoto, M. Effects of adding glycerol and sucrose to ferrous xylenol orange hydrogel. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 250, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Kozicki, M. Sorbitol to reduce Fe diffusion in a Fricke gel dosimeter and enhance its resistance to elongation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2799, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hartel, R.W. Citric acid and heating on gelatin hydrolysis and gelation in confectionery gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.F.; Accareddu, A.E.M.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Preparation and characterization of plasticized gelatin films cross-linked with low concentrations of Glutaraldehyde. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3282–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, T.; Zhang, Y. Effect of interaction between sorbitol and gelatin on gelatin properties and its mechanism under different citric acid concentrations. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, J.; Yao, X.; An, M.; Shi, Q.; Huang, X. 3D Printing Polymer-based Bolus Used for Radiotherapy. Int. J. Bioprint. 2021, 7, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Diao, W.; Xu, C.; Jia, L.; Li, H.; Li, B.; Jiang, X. Physical and Dosimetric Characterization of Silicone Rubber Bolus for Head Photon-Beam Radiotherapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241293267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sianturi, H.A.; Ginting, J.; Azhari; Rianna, M.; Marbun, R.G.A.; Sinaga, A.P.; Siregar, R.Y.M.; Sidaruk, L.; Silalahi, M.; Tampubolon, H.; et al. Enhancing Radiotherapy Bolus Characteristics through Comparative Analysis of Added Sawdust and Bagasse Powder: A Comprehensive Study of Physical and Mechanical Properties. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2733, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, O.V. Investigation of Surface Dose Accuracy of Two Dose Calculation Algorithms Using Thermoluminescent Dosimeters. GU J. Sci. 2023, 10, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykholeslami, N.; Parwaie, W.; Farzin, M.; Vaezzadeh, V.; Esfahani, M.; Geraily, G. An Investigation into the Surface Dose Using Eclipse Treatment Planning System and Film Dosimetry for Treatment of Breast Cancer. Front. Biomed. Technol. 2023, 10, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigamani, A.; Nambiraj, A.; Yadav, G.; Giribabu, A.; Srinivasan, K.; Gurusamy, V.; Raman, K.; Karunakaran, K.; Thiyagarajan, R. Surface Dose Measurements and Comparison of Unflattened and Flattened Photon Beams. J. Med. Phys. 2016, 41, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.G.; Pinto, D.F.S.; Borges, M.F.; Pereira, M.H.; Santos, J.A.M.; Cunha, L.T.; Lencart, J. Optimization of Skin Dose Using In-Vivo MOSFET Dose Measurements in Bolus/Non-Bolus Fraction Ratio: A VMAT and a 3DCRT Study. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, M.; Jaszczak, M.; Maras, P.; Kadłubowski, S. Measurement of the Radiation Dose and Radiation Isocenter of the TrueBeam Accelerator Using 3D Polymer Gel Dosimeters from the VIPAR Family with Different Chemical History. Measurement 2023, 221, 113452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maras, P.; Kozicki, M. Fast Isocenter Determination Using 3D Polymer Gel Dosimetry with Kilovoltage Cone-Beam CT Reading and the PolyGeVero-CT Software Package for Linac Quality Assurance in Radiotherapy. Materials 2022, 15, 6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozicki, M.; Maras, P.; Karwowski, A.C. Software for 3D Radiotherapy Dosimetry. Validation. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.F.; Ruseckaite, R.A. Tensile Properties, Barrier Properties, and Biodegradation in Soil of Compression—Molded Gelatin-Dialdehyde Starch Films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, S.; Garcia, M.A.; Pinotti, A. Correlations between Structural, Barrier, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Plasticized Gelatin Films. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatos, K.; Maras, P.; Kadłubowski, S.; Stempień, Z.; Dudek, M.; Kozicki, M. Tetrazolium Salts–Pluronic F-127 Gels for 3D Radiotherapy Dosimetry. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 095012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bero, M.A.; Abukassem, I. Detection of Ultraviolet Radiation Using Tissue Equivalent Radiochromic Gel Materials. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 164, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.E.; Hanley, J.; Bayouth, J.; Yin, F.F.; Simon, W.; Dresser, S.; Serago, C.; Aguirre, F.; Ma, L.; Arjomandy, B.; et al. Task Group 142 Report: Quality Assurance of Medical Accelerators. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, M.; Kroupa, B.; Georg, D. Interpretation and Evaluation of the γ Index and the γ Index Angle for the Verification of IMRT Hybrid Plans. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thwaites, D. Accuracy Required and Achievable in Radiotherapy Dosimetry: Have Modern Technology and Techniques Changed Our Views? J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 444, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Development of Procedures for In Vivo Dosimetry in Radiotherapy; IAEA Human Health Reports No. 8; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]


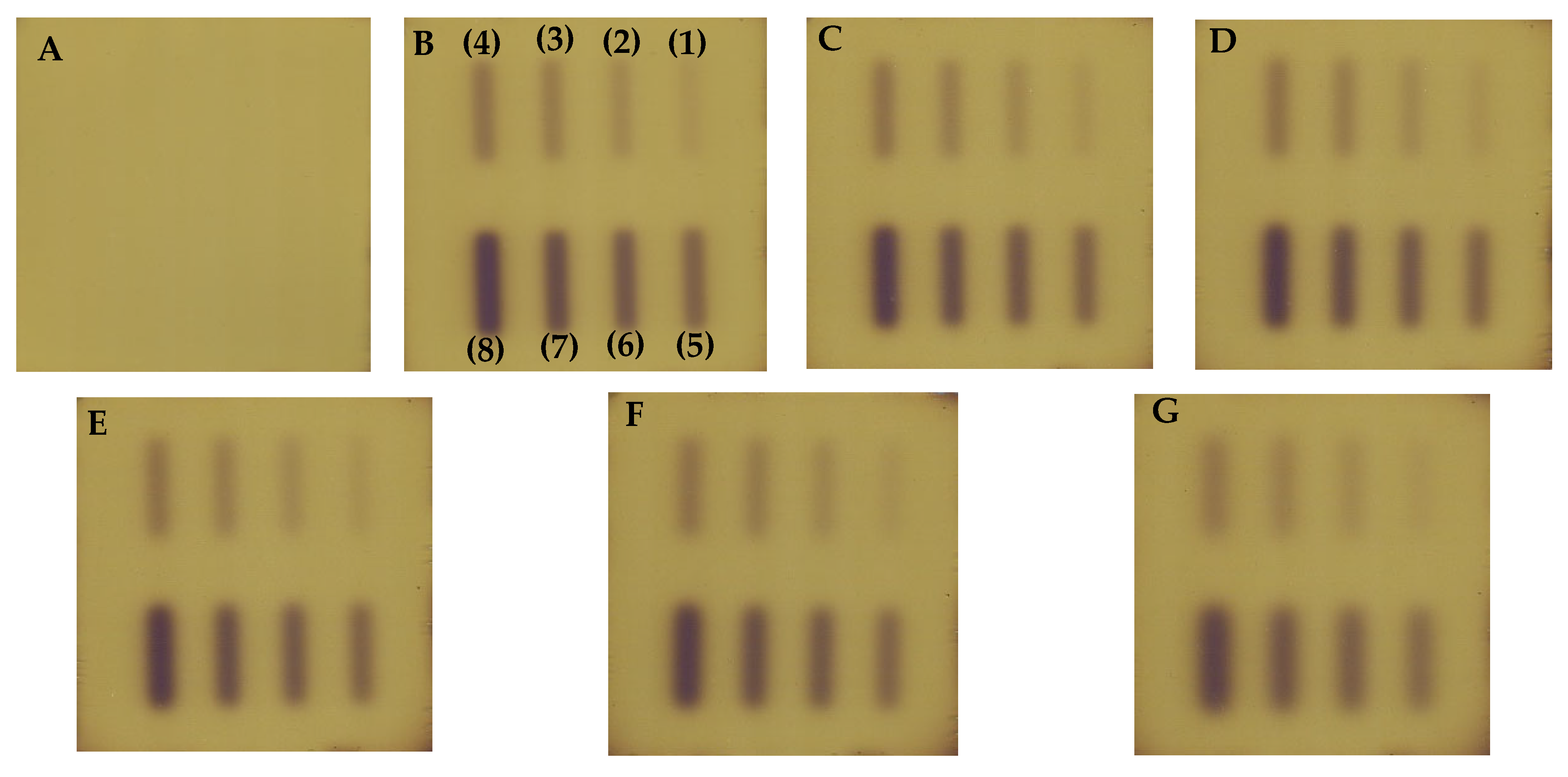
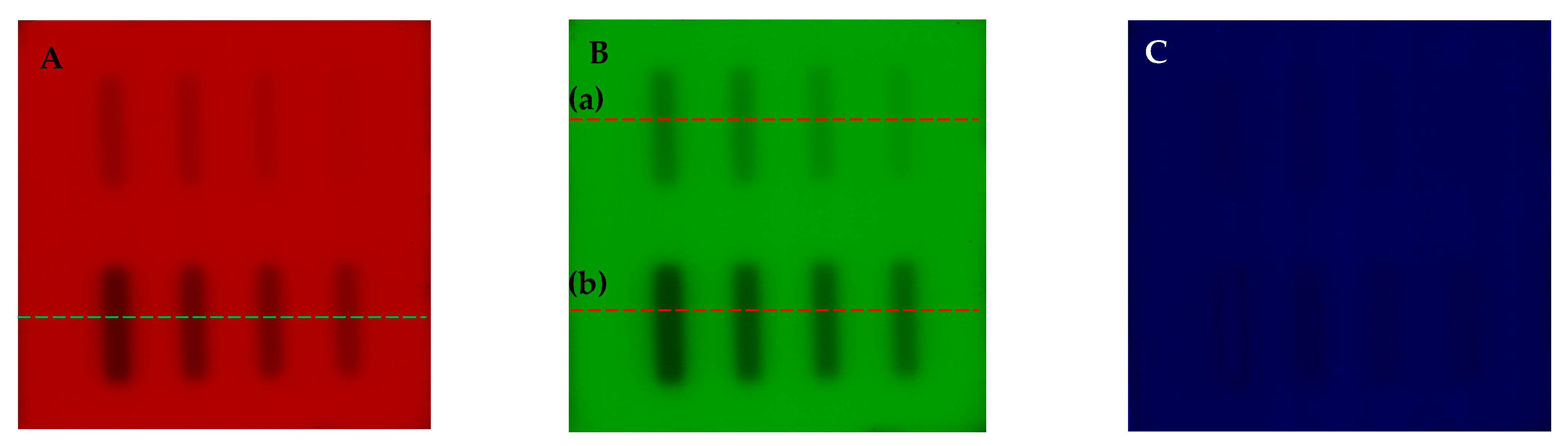
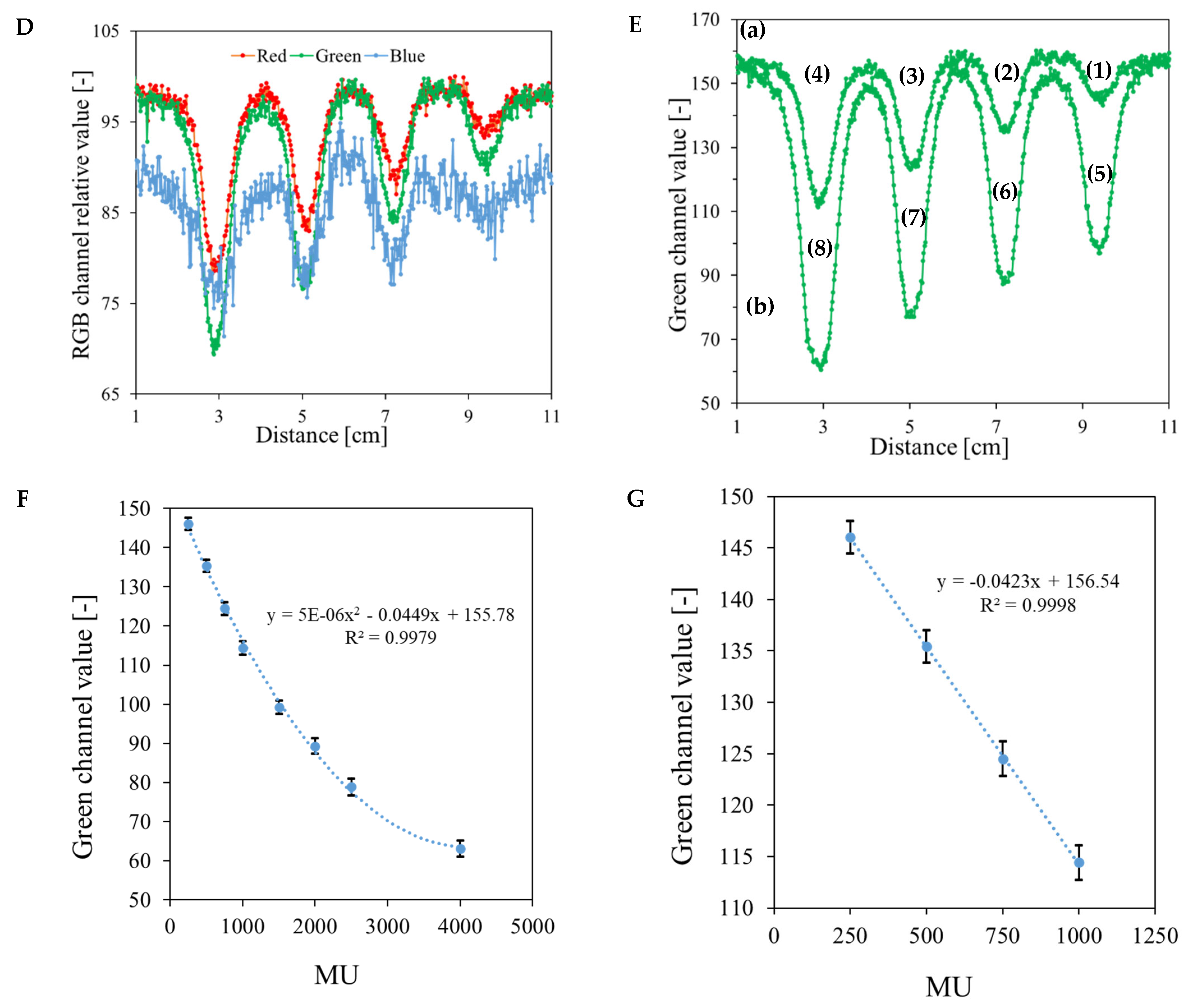
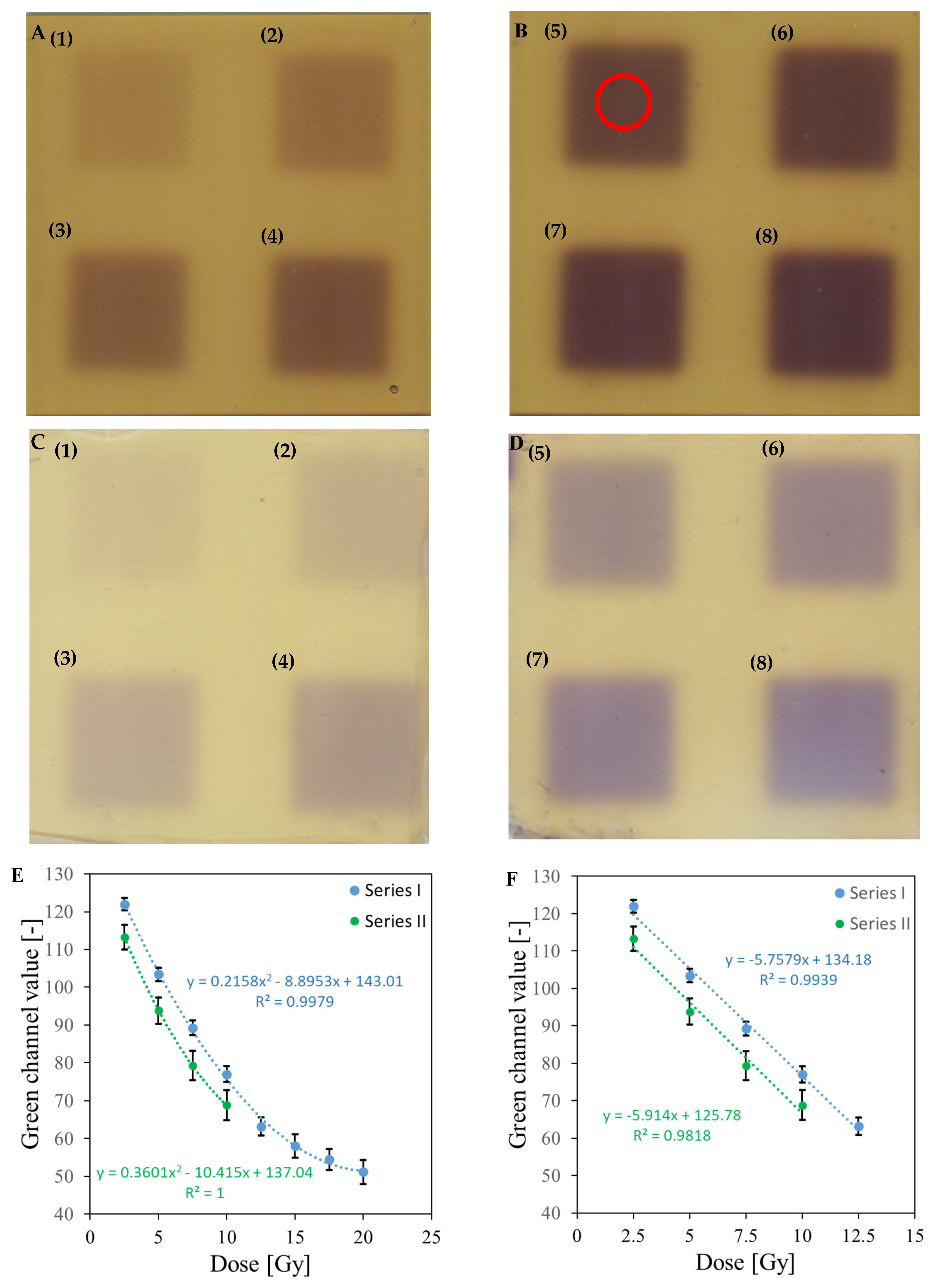
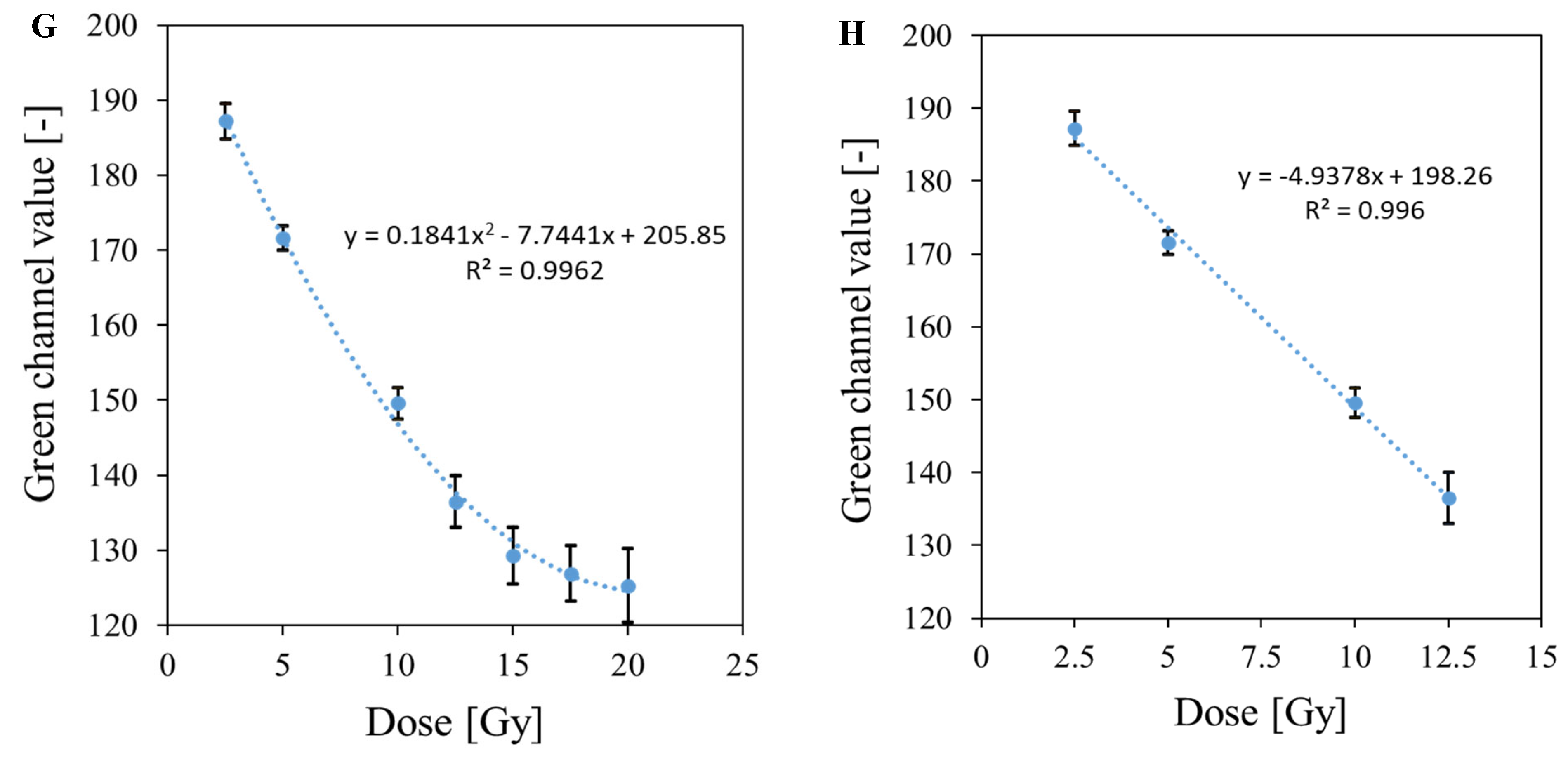


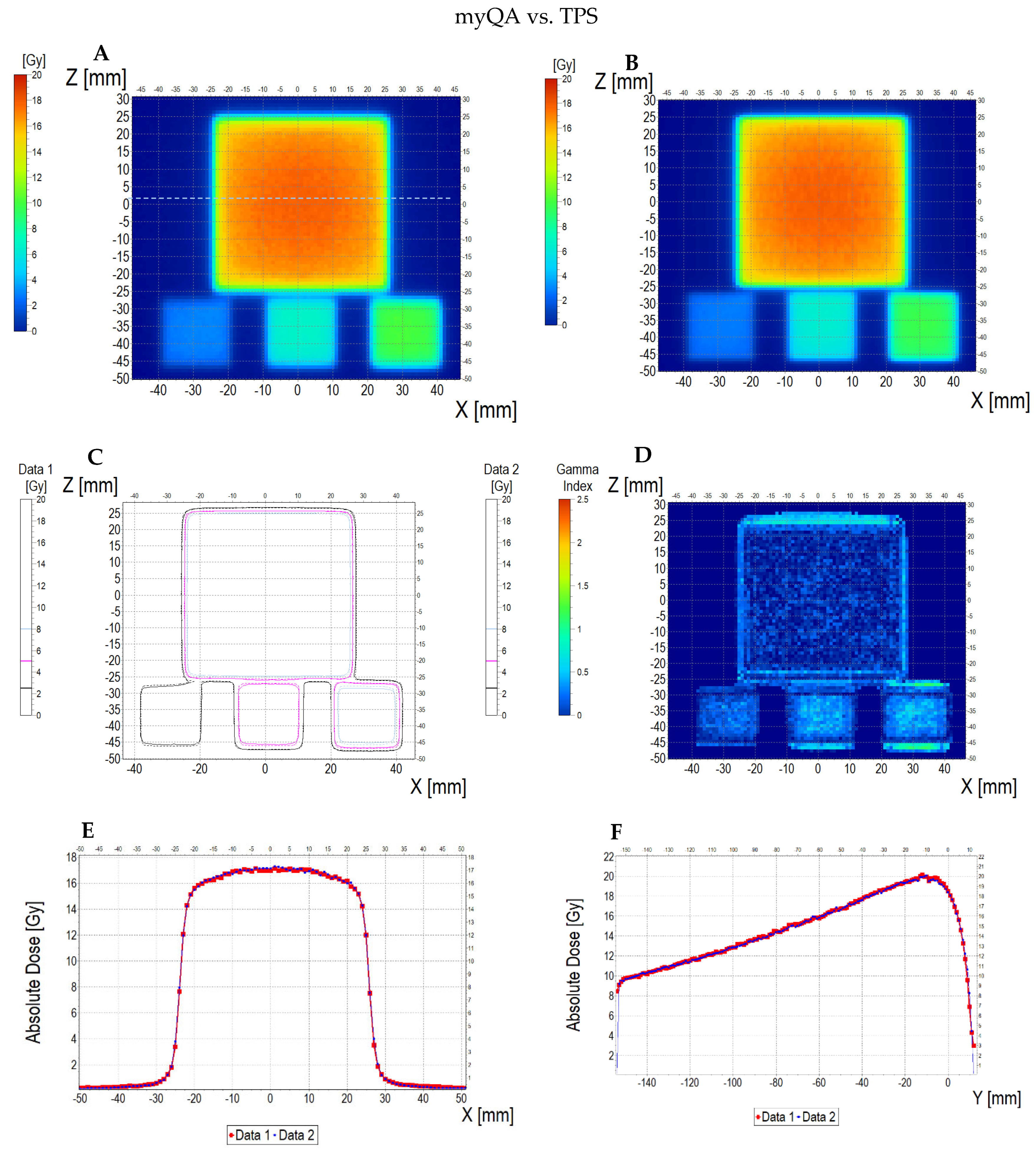
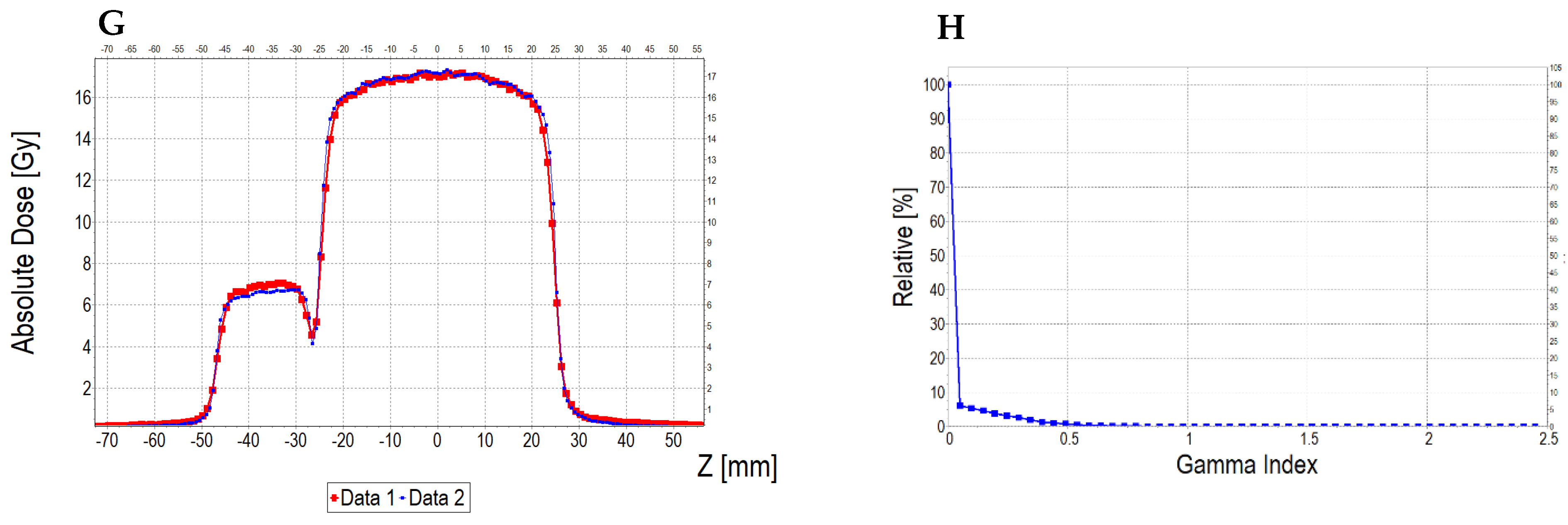
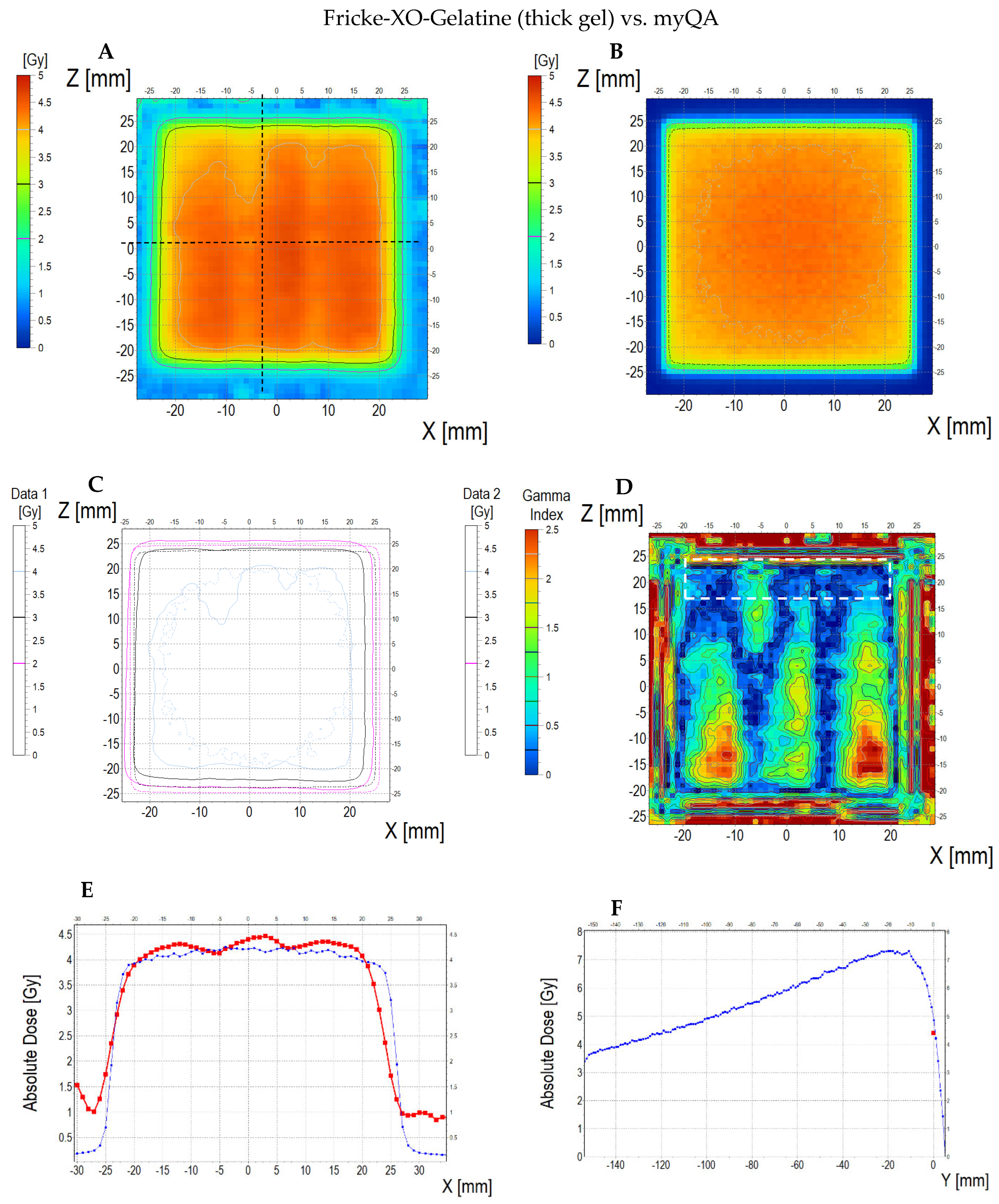
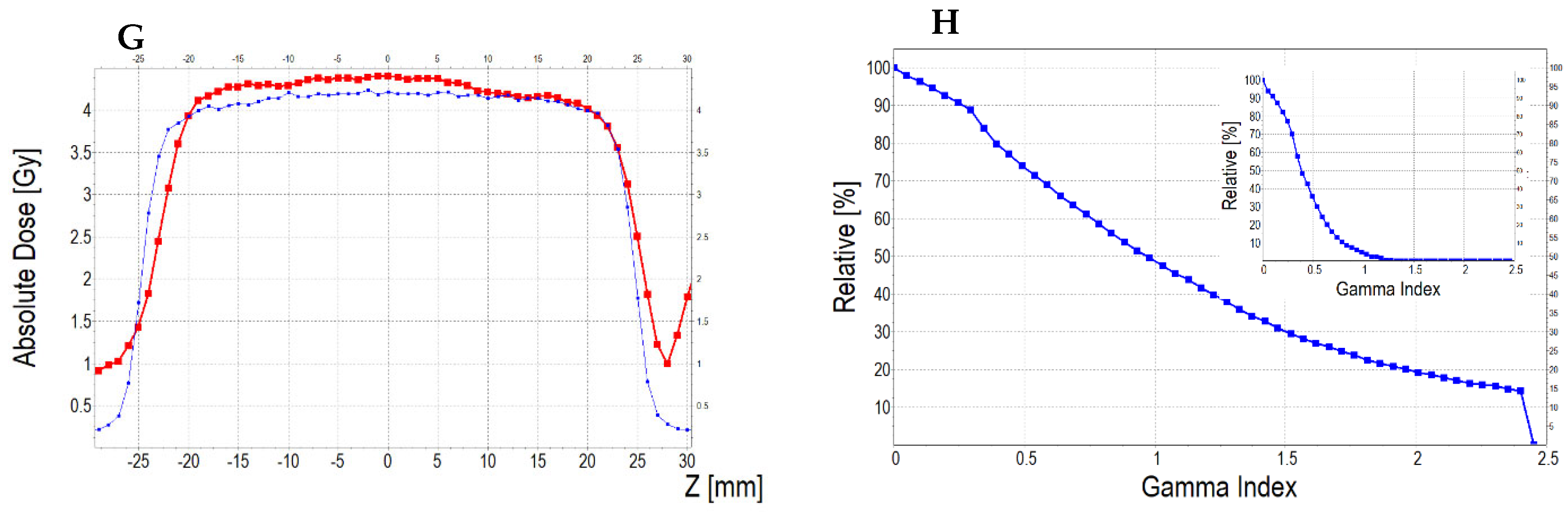

| No | Type of Dosimeter | Basic Reaction | Composition | Sensitivity | Linear Range | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fricke-XO-Gelatin with sorbitol (bolus) | Oxidation of Fe2+ ions | 7.96% gelatin, 50 mM H2SO4, 0.5 mM FAS, 0.165 mM XO, 23% sorbitol | 5.7579 Gy−1 | 12.5 Gy | This work |
| 2 | Fricke-XO-Gelatin with sorbitol (thin) | Oxidation of Fe2+ ions | 7.96% gelatin, 50 mM H2SO4, 0.5 mM FAS, 0.165 mM XO, 23% sorbitol | 4.9378 Gy−1 | 12.5 Gy | This work |
| 3 | DEFGEL | Polymerization of acrylamide monomers | 6% gelatin, 3% N,N’-methylene-bis-acrylamid, monomer 3% acrylamid monomer, 5 mM bis [tetrakis (hydroksymethyl-phosphonium)] sulfate, 0.01 mM hydroquinone | 0.02 cm−1 Gy−1 | 18.89 Gy (Maximum dose used in the study) | [14] |
| 4 | Polymer gel dosimeter enclosed using LDPE wraps | Polymerization of methacrylic acid monomers | 8% gelatin, 5% methacrylic acid, 50 mM bis [tetrakis (hydroksymethyl-phosphonium)] | 0.86 s−1 Gy−1 | 4 Gy (Maximum dose used in the study) | [15] |
| 5 | LMG-silicone | Oxidation of LMG to malachite green | Dow Corning SYLGARD® 184 Silicone Elastomer Kit (the ratio of curing agent to silicone elastomer was 1:10), 0.4 mM LMG, 200 mM chloroform | 0.012 cm−1 Gy−1 | 60 Gy (Maximum dose used in the study) | [19] |
| No. | Parameter | For Thin Fricke-XO-Gelatin Gel (Four Square Regions Irradiated) | For Thick Fricke-XO-Gelatin Gel (One Square Region Irradiated) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fricke-XO-Gelatin vs. myQA | Fricke-XO-Gelatin vs. TPS | myQA vs. TPS | Fricke-XO-Gelatin vs. myQA | Fricke-XO-Gelatin vs. TPS | myQA vs. TPS | ||||||||
| Fricke-XO-Gelatin (1) | myQA (2) | Fricke-XO-Gelatin (1) | TPS (2) | myQA (1) | TPS (2) | Fricke-XO-Gelatin (1) | myQA (2) | Fricke-XO-Gelatin (1) | TPS (2) | myQA (1) | TPS (2) | ||
| 1 | Minimum dose [Gy] | 12.06 | 15.23 | 12.06 | 15.42 | 15.23 | 15.42 | 3.54 | 3.67 | 3.54 | 3.86 | 3.67 | 3.86 |
| 2.95 | 2.54 | 2.95 | 2.63 | 2.54 | 2.63 | ||||||||
| 4.50 | 4.82 | 4.50 | 5.07 | 4.82 | 5.07 | ||||||||
| 7.04 | 6.94 | 7.04 | 7.36 | 6.94 | 7.36 | ||||||||
| 2 | Maximum dose [Gy] | 18.60 | 18.27 | 18.60 | 18.14 | 18.27 | 18.14 | 4.48 | 4.27 | 4.48 | 4.57 | 4.27 | 4.57 |
| 4.25 | 3.83 | 4.25 | 3.61 | 3.83 | 3.61 | ||||||||
| 7.42 | 7.45 | 7.42 | 7.10 | 7.45 | 7.10 | ||||||||
| 10.76 | 10.81 | 10.76 | 10.25 | 10.81 | 10.25 | ||||||||
| 3 | Mean dose [Gy] | 16.63 | 17.27 | 16.63 | 17.27 | 17.27 | 17.27 | 4.16 | 4.06 | 4.16 | 4.36 | 4.06 | 4.36 |
| 3.92 | 3.55 | 3.92 | 3.41 | 3.55 | 3.41 | ||||||||
| 6.77 | 6.95 | 6.77 | 6.73 | 6.95 | 6.73 | ||||||||
| 9.69 | 9.99 | 9.69 | 9.74 | 9.99 | 9.74 | ||||||||
| 4 | STD dose [Gy] | 1.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||||||||
| 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4 | ||||||||
| 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | ||||||||
| 5 | Mean dose difference [%] = 100 – (2) × 100/(1) | −3.85 | −3.85 | 0.00 | 2.40 | −4.81 | −7.39 | ||||||
| 9.44 | 13.01 | 3.94 | |||||||||||
| 2.66 | 0.59 | 3.17 | |||||||||||
| 3.10 | 0.52 | 2.50 | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piotrowski, M.; Maras, P.; Stempień, Z.; Wach, R.; Kozicki, M. Deformable Fricke-XO-Gelatin Radiochromic Dosimeter of Ionizing Radiation and Its Applications in Quality Assurance Tests for Radiation Therapy. Materials 2025, 18, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133135
Piotrowski M, Maras P, Stempień Z, Wach R, Kozicki M. Deformable Fricke-XO-Gelatin Radiochromic Dosimeter of Ionizing Radiation and Its Applications in Quality Assurance Tests for Radiation Therapy. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133135
Chicago/Turabian StylePiotrowski, Michał, Piotr Maras, Zbigniew Stempień, Radosław Wach, and Marek Kozicki. 2025. "Deformable Fricke-XO-Gelatin Radiochromic Dosimeter of Ionizing Radiation and Its Applications in Quality Assurance Tests for Radiation Therapy" Materials 18, no. 13: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133135
APA StylePiotrowski, M., Maras, P., Stempień, Z., Wach, R., & Kozicki, M. (2025). Deformable Fricke-XO-Gelatin Radiochromic Dosimeter of Ionizing Radiation and Its Applications in Quality Assurance Tests for Radiation Therapy. Materials, 18(13), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133135








