Effect of Zinc, Magnesium, and Manganese Phosphate Coatings on the Corrosion Behaviour of Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material
2.2. Phosphating Process
2.3. Electrochemical Tests
3. Results
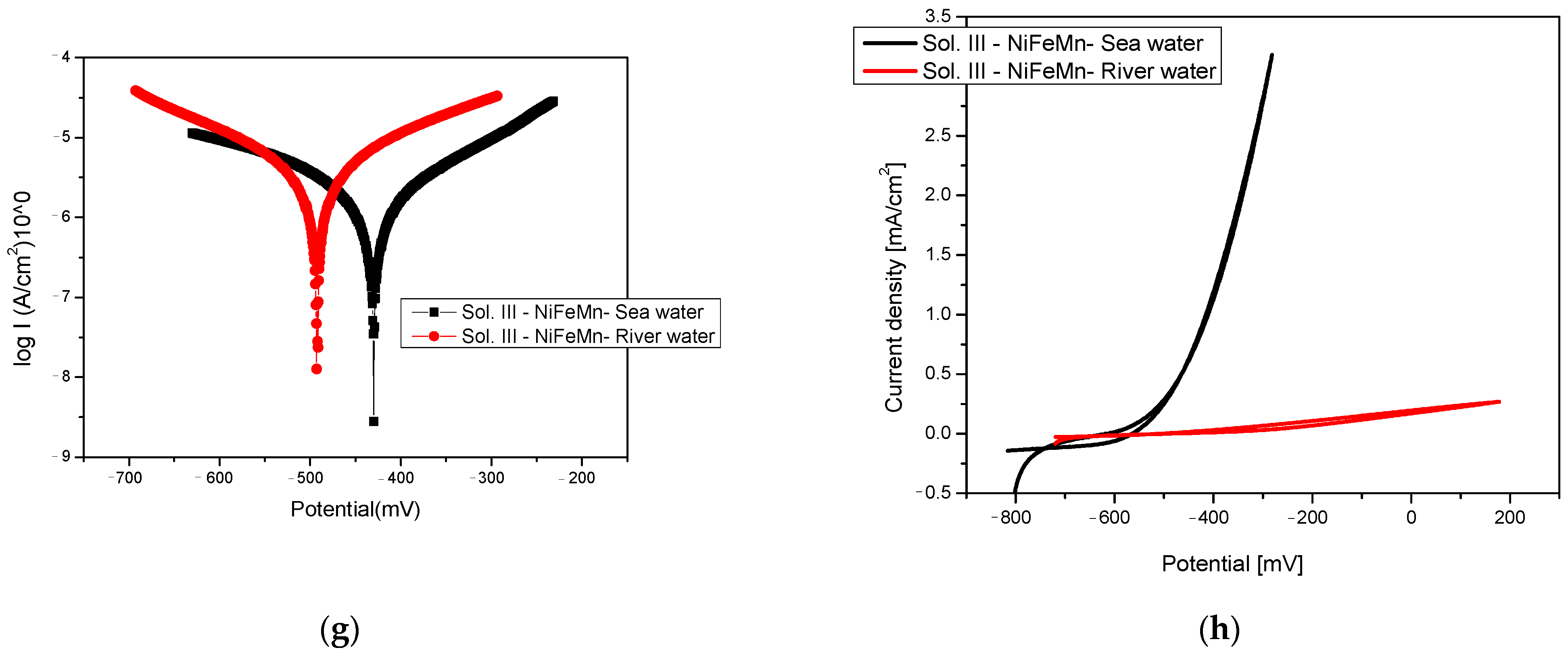
3.1. Corrosion Behaviour Evaluation
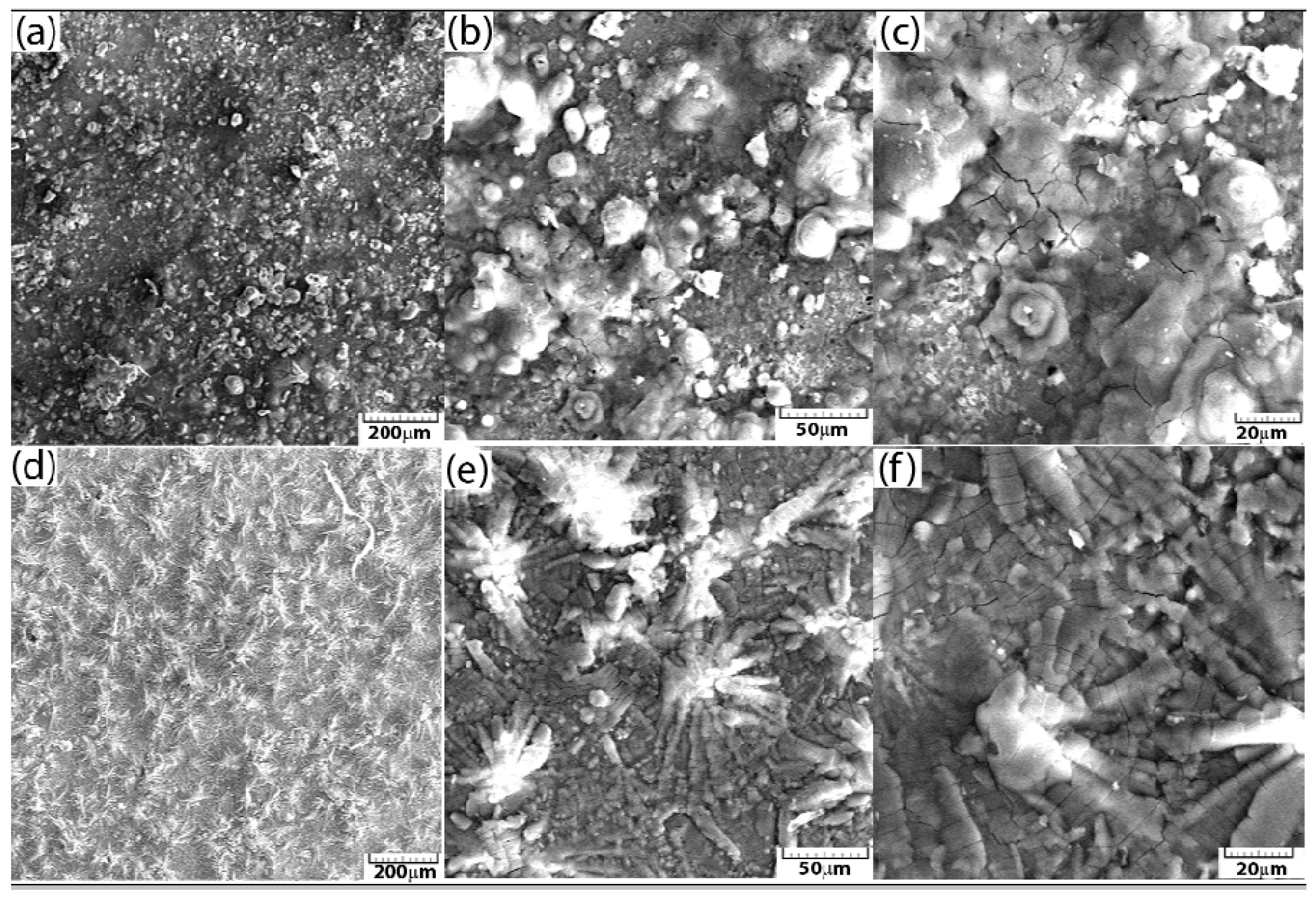
3.2. Morphology and Structure Analysis of Phosphate Layers After Corrosion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazar, P.; Cimpoesu, N.; Istrate, B.; Cazac, A.M.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.-P.; Benchea, M.; Berbecaru, A.C.; Badarau, G.; Vasilescu, G.D.; Popa, M.; et al. Microstructural and mechanical properties analysis of phosphate layers deposited on steel rebars for civil constructions. Coatings 2024, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.; Monteiro, P. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties and Materials; McGraw-Hill Education: Chicago, IL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9780071797870. [Google Scholar]
- Duffó, G.; Reinoso, M.; Ramos, C.; Farina, S. Characterization of steel rebars embedded in a 70-year old concrete structure. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, C.L.; Sergi, G. Developments in cathodic protection applied to reinforced concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2000, 12, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söylev, T.; Richardson, M. Corrosion inhibitors for steel in concrete: State of the art report. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarce, M.B.; Vazquez, M. Carbon steel passivity examined in alkaline solutions: The effect of chloride and nitrite ions. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5007–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, C.M.; Mammoliti, L.; Hope, B.B. Corrosion inhibitors in concrete. Part I: The principles. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1998, 28, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.B.; Hu, J.; Zuo, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Dong, S.G.; Du, R.G.; Lin, C.J. Synergistic inhibition effect of sodium tungstate and hexamethylene tetramine on reinforcing steel corrosion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, C555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etteyeb, N.; Sanchez, M.; Dhouibi, L.; Alonso, C.; Andrade, C.; Triki, E. Corrosion protection of steel reinforcement by a pretreatment in phosphate solutions: Assessment of passivity by electrochemical techniques. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Sun, W. Effects of phosphate on the chloride-induced corrosion behavior of reinforcing steel in mortars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 45, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B. Corrosion Inhibitors for Steel in Concrete. State of the Art Report; Maney Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Etteyeb, N.; Sánchez, M.; Dhouibi, L.; Alonso, M.C.; Takenouti, H.; Triki, E. Effectiveness of pretreatment method to hinder rebar corrosion in concrete. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahali, H.; Dhouibi, L.; Idrissi, H. Effect of Na3PO4 addition in mortar on stee reinforcement corrosion behavior in 3% NaCl solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastidas, D.M.; Criado, M.; La Iglesia, V.M.; Fajardo, S.; La Iglesia, A.; Bastidas, J.M. Comparative study of three sodium phosphates as corrosion inhibitors for steel reinforcements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 43, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, H.; Terryn, H.; De Graeve, I. Inhibitor evaluation in different simulated concrete pore solution for the, protection of steel rebars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B. Corrosion inhibitors for steel in concrete. In Proceedings of the Materials Week, International Congress on Advanced Materials, Munich, Germany, 25–28 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E.; Polder, R.B. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete: Prevention, Diagnosis, Repair; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Valcarce, M.B.; Lopez, C.; Vazquez, M. The role of chloride, nitrite and carbonate ions on carbon steel passivity studied in simulating concrete pore solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królikowski, A.; Kuziak, J. Impedance study on calcium nitrite as a penetrating corrosion inhibitor for steel in concrete. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 7845–7853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burduhos-Nergis, D.-P.; Sandu, A.V.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.-D.; Vizureanu, P.; Bejinariu, C. Phosphate Conversion Coating—A Short Review. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2023, 68, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, D.; Munoz, A.G.; Schultze, J.W. Formation of Zn–Ni alloys in the phosphating of Zn layers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 197, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banczek, E.P.; Rodrigues, P.R.P.; Costa, I. Evaluation of porosity and discontinuities in zinc phosphate coating by means of voltametric anodic dissolution (VAD). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creus, J.; Mazille, H.; Idrissi, H. Porosity evaluation of protective coatings onto steel, through electrochemical techniques. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 130, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.; Blawert, C.; Huang, Y.; Mendis, C.L.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Corrosion behavior of Mg–Gd–Zn based alloys in aqueous NaCl solution. J. Magnes. Alloys 2014, 2, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, Y.A.; Menezes, I.; Bonatti, R.S.; Bortolozo, A.D.; Osório, W.R. EIS Investigation of the Corrosion Behavior of Steel Bars Embedded into Modified Concretes with Eggshell Contents. Metals 2022, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Element | C | Si | Mn | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.75 | 0.045 | 0.045 | rest |
| Solution I | Solution II | Solution III |
|---|---|---|
| NaOH (7 g) | NaOH (0.9 g) | NaOH (0.75 g) |
| MgCO3 (8.5 g) | NaNO2 (0.6 g) | NaNO2 (0.45 g) |
| NaNO2 (0.4 g) | Na5P3O10 (0.1 g) | Na5P3O10 (0.05 g) |
| H3PO4 (85%, 23 mL) | H3PO4 (22 mL) | H3PO4 (7 mL) |
| HNO3 (11 mL) | HNO3 (0.4 mL) | |
| Zn (9 g) | Ni (0.03 g) | |
| Fe (0.03) | ||
| Mn (1.5 g) |
| Parameter | Reinforcing Steel | Sol. I—MgCO3 | Sol. II—Zn | Sol. III—NiFeMn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| River | Seawater | River | Seawater | River | Seawater | River | Seawater | |
| Er, mV(SCE) | −650.6 | −686.6 | −451.1 | −514.3 | −353 | −386.8 | −492.0 | −429.9 |
| Corrosion current density, µA/ cm2 | 3.937 | 3.762 | 10.393 | 23.221 | 0.028 | 0.187 | 3.78 | 3.059 |
| Rp, kohm/cm2 | 13.25 | 7.78 | 5.52 | 2.64 | 291 | 154.18 | 9.27 | 18.54 |
| Corrosion rate, µm/year | 45.35 | 43.34 | 226.35 | 421.47 | 0.258 | 3.060 | 47.68 | 40.82 |
| βa, mV/dec | 129 | 92 | 365 | 144 | 180 | 97 | 193 | 200 |
| −βc, mV/dec | 737 | 543 | 363 | 770 | 102 | 268 | 205 | 350 |
| Sample | Rs Ω·cm2 | Cext F/cm2 | CPE | Rext Ω·cm2 | CPE | Rct Ω·cm2 | W Ss1/2/cm2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q Ssn/cm2 | n | Q Ssn/cm2 | n | |||||||
| Reinforcing steel | River water | 317 | - | 1.69 × 10−4 | 0.74 | 4655 | - | - | - | - |
| Sea water | 13 | - | 1.09 × 10−4 | 0.77 | 4447 | - | - | - | - | |
| Sol. II/Zn | River water | 366 | 1.68 × 10−9 | - | - | 12,120 | 1.84 × 10−6 | 0.63 | 64,830 | 1.64 × 10−5 |
| Sea water | 175 | 4.12 × 10−9 | - | - | 2734 | 2.92 × 10−7 | 0.70 | 28,770 | 3.59 × 10−4 | |
| Element | At. No. | wt [%] | at [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 26 | 57.77 | 27.26 |
| O | 8 | 33.24 | 54.85 |
| C | 6 | 7.708 | 16.94 |
| Cl | 17 | 1.262 | 0.93 |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| Element | At. No. | wt [%] | at [%] | EDS Error [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O | 8 | 34.75 | 55.72 | 6.10 |
| Zn | 30 | 32.95 | 12.93 | 0.95 |
| P | 15 | 13.45 | 11.14 | 0.63 |
| Fe | 26 | 11.88 | 5.29 | 0.46 |
| C | 6 | 6.88 | 14.71 | 3.18 |
| Cl | 17 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cazac, A.-M.; Cioca, L.-I.; Lazar, P.; Badarau, G.; Cimpoesu, N.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.-P.; Iagaru, P.; Cimpoesu, R.; Cazac, A.; Bejinariu, C.; et al. Effect of Zinc, Magnesium, and Manganese Phosphate Coatings on the Corrosion Behaviour of Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133126
Cazac A-M, Cioca L-I, Lazar P, Badarau G, Cimpoesu N, Burduhos-Nergis D-P, Iagaru P, Cimpoesu R, Cazac A, Bejinariu C, et al. Effect of Zinc, Magnesium, and Manganese Phosphate Coatings on the Corrosion Behaviour of Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133126
Chicago/Turabian StyleCazac, Alin-Marian, Lucian-Ionel Cioca, Petru Lazar, Gheorghe Badarau, Nicanor Cimpoesu, Diana-Petronela Burduhos-Nergis, Pompilica Iagaru, Ramona Cimpoesu, Anca Cazac, Costica Bejinariu, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Zinc, Magnesium, and Manganese Phosphate Coatings on the Corrosion Behaviour of Steel" Materials 18, no. 13: 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133126
APA StyleCazac, A.-M., Cioca, L.-I., Lazar, P., Badarau, G., Cimpoesu, N., Burduhos-Nergis, D.-P., Iagaru, P., Cimpoesu, R., Cazac, A., Bejinariu, C., & Milea, A. (2025). Effect of Zinc, Magnesium, and Manganese Phosphate Coatings on the Corrosion Behaviour of Steel. Materials, 18(13), 3126. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133126













