Direct Reuse of Spent Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets
Abstract
1. Introduction
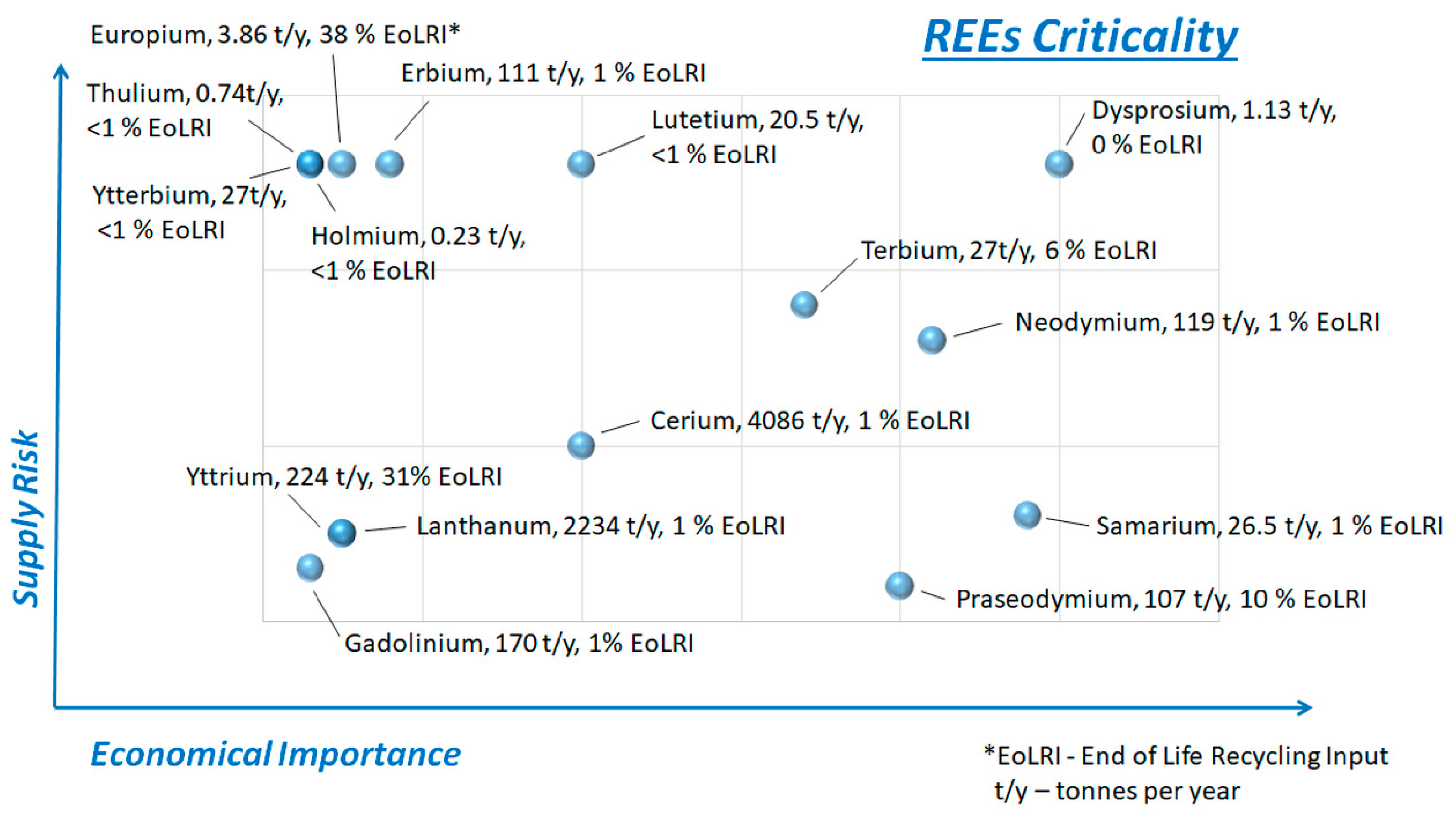
1.1. Rare Earth Elements Rank Among the Most Critical and Strategic Resource Materials
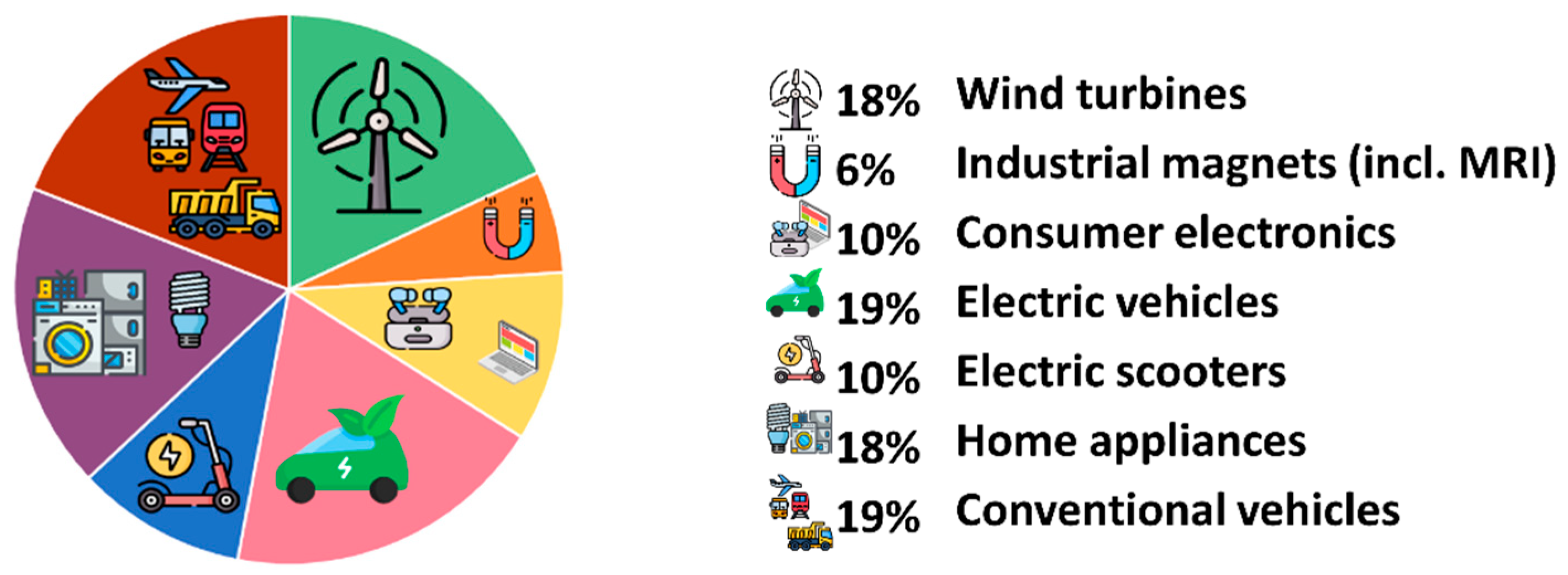
1.2. Nd–Fe–B Magnet’s Role in Green Energy and Carbon Reduction Strategy
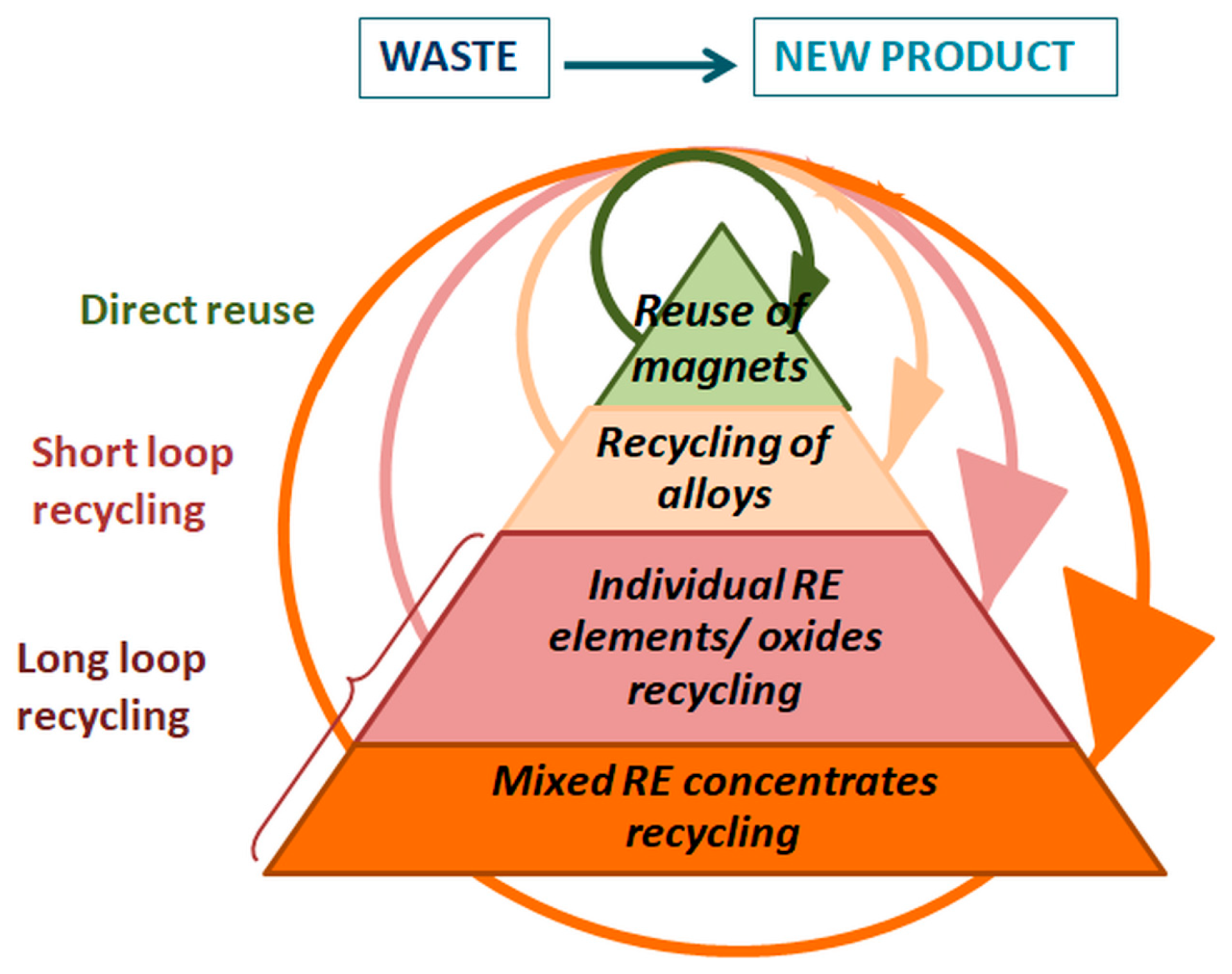
1.3. Recycling of Nd–Fe–B Magnets
1.4. Direct Recycling of EoL Nd–Fe–B Magnets from Electric Bike Motors
1.5. Mechanochemical Approach
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mechanochemical Processing
2.3. Characterization of Samples
3. Results
3.1. Elemental Analysis
3.2. Mechanochemical Treatment
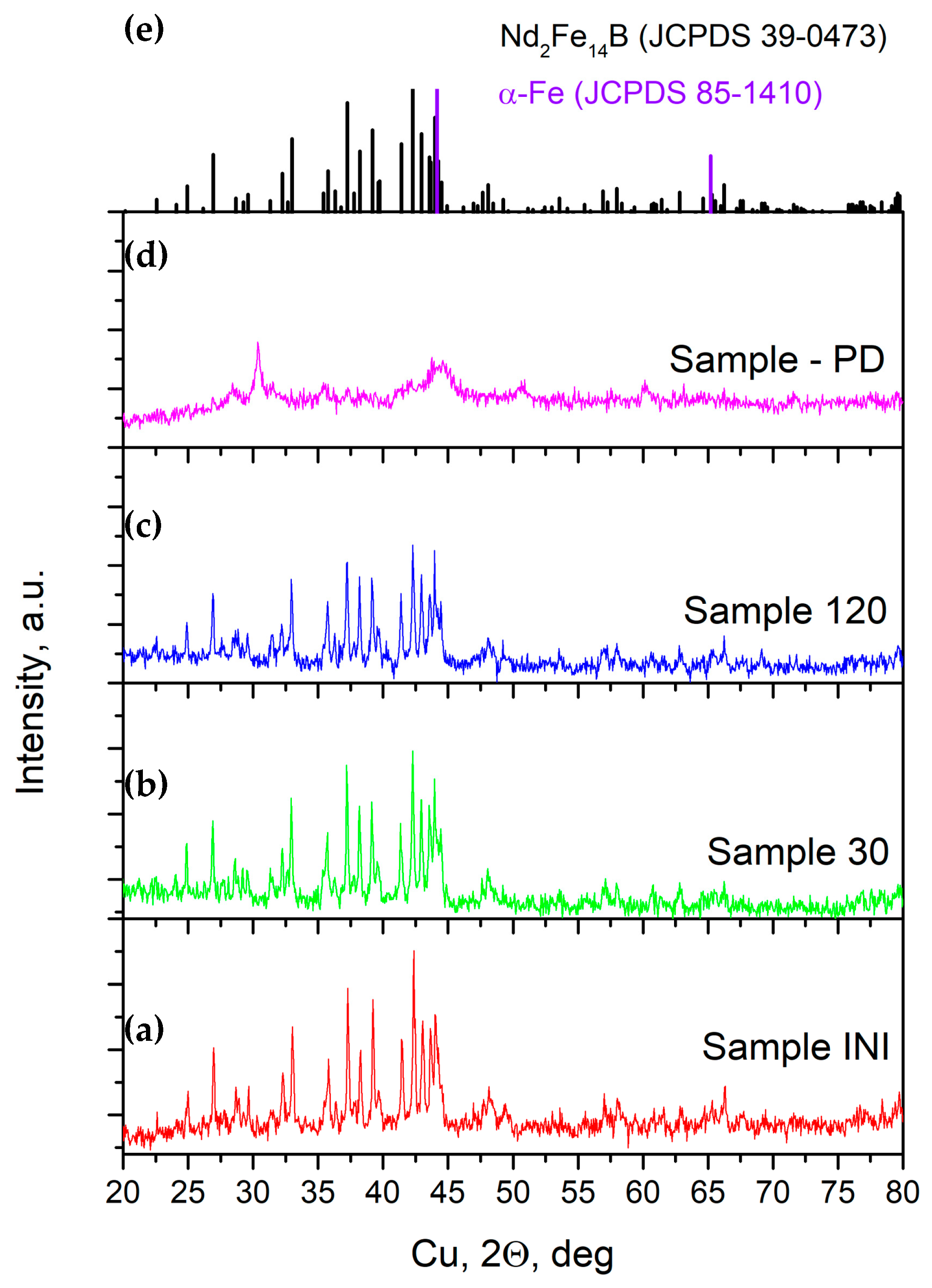
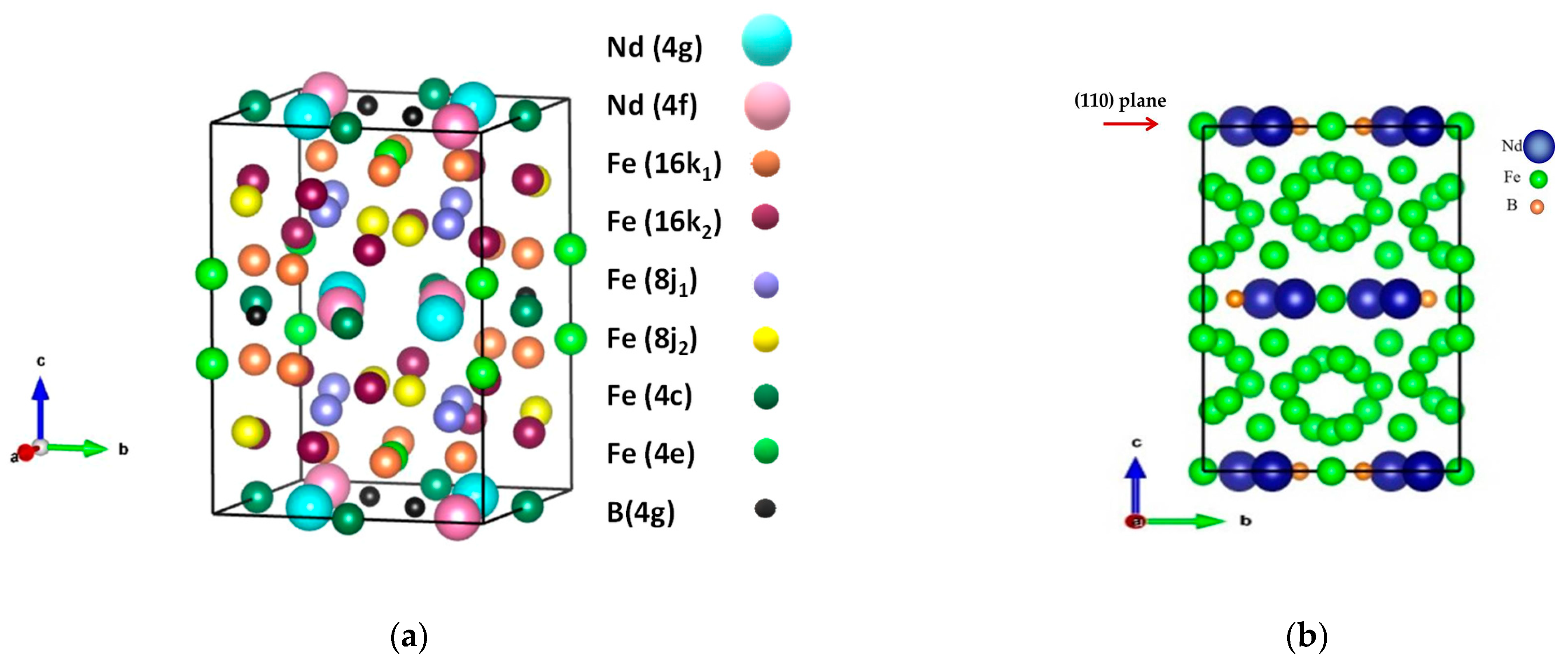
3.3. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
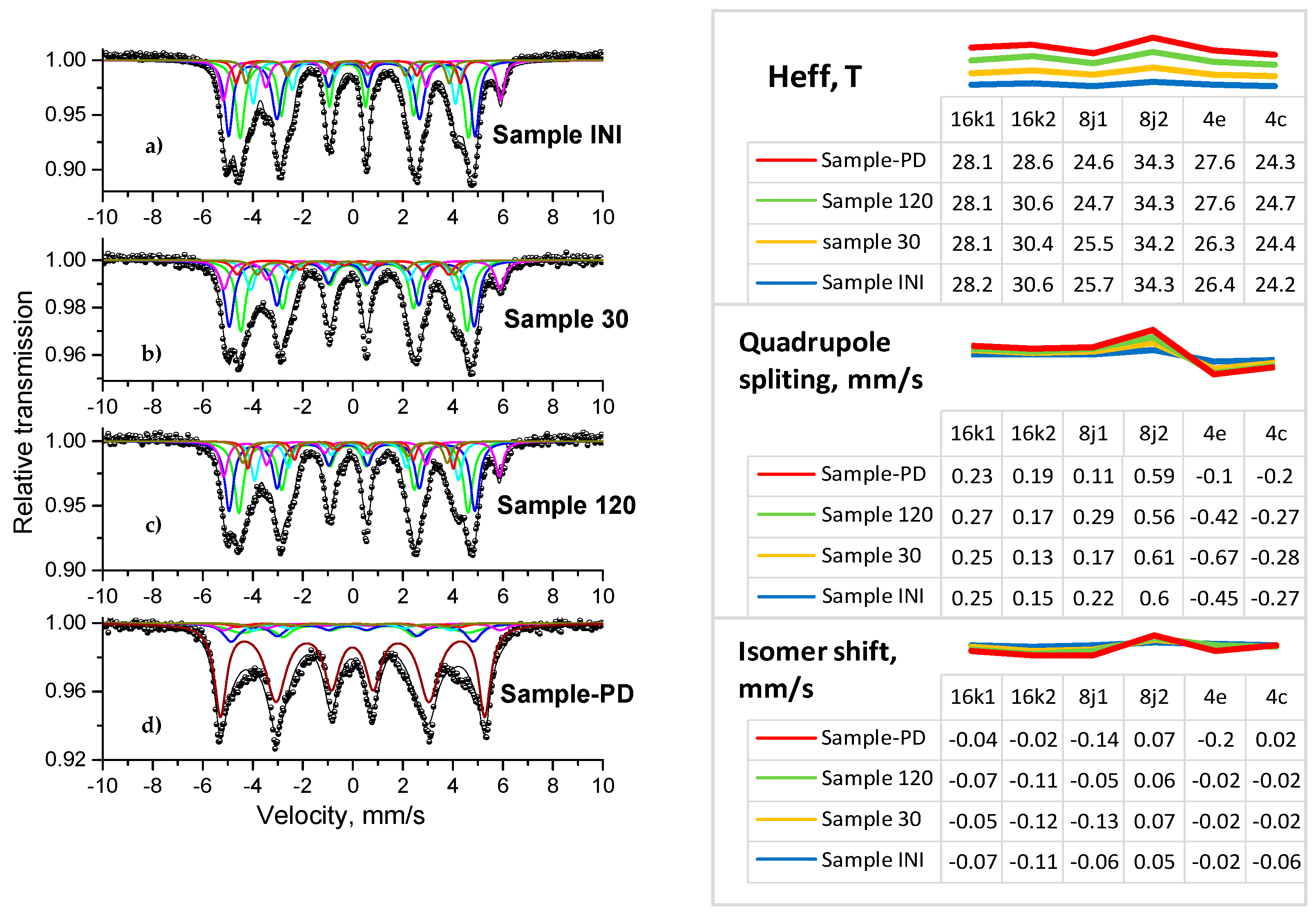
3.4. Mössbauer Analysis
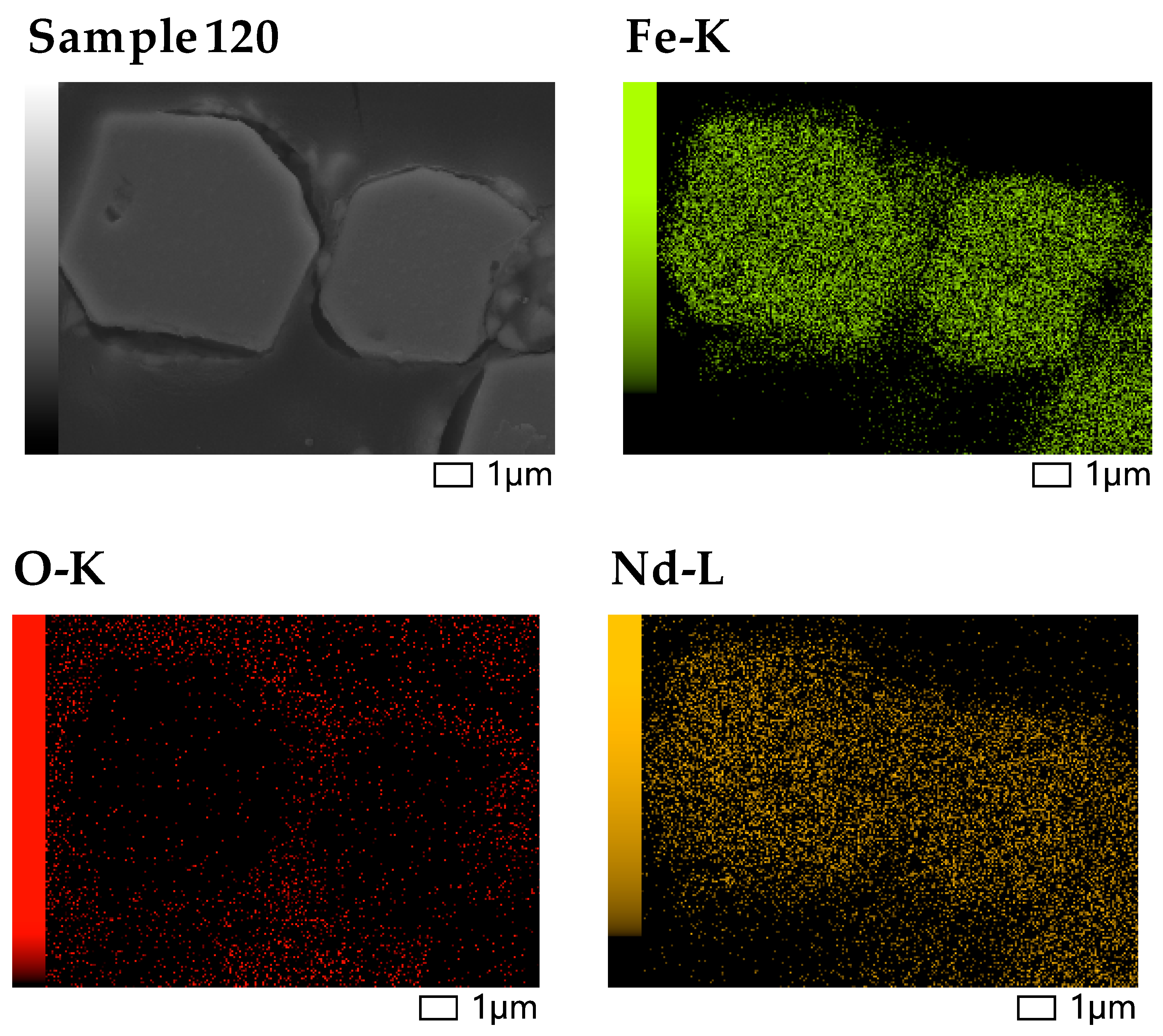
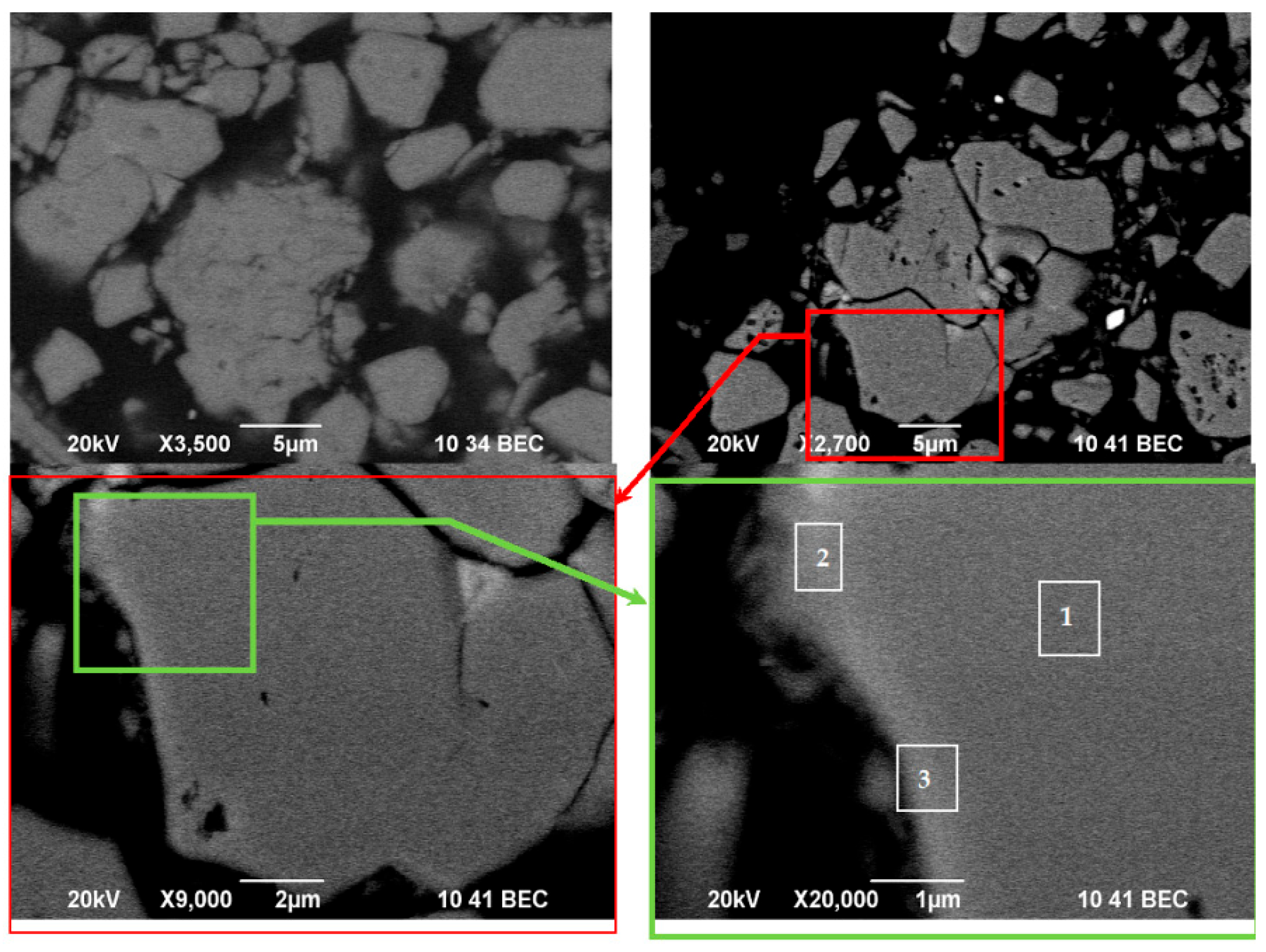
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS) Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample, wt.% | B | C | O | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zr | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Gd | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample INI | 2.27 | 5.64 | 2.66 | 0.01 | 59.55 | 0.27 | 2.53 | nd * | 1.07 | 0.15 | 5.13 | 15.8 | 0.09 | 3.16 | 1.27 |
| 2.43 | 9.62 | 2.42 | 0.02 | 51.85 | 0.2 | 4.48 | nd * | 0.67 | 0.24 | 4.73 | 15.2 | 0.24 | 3.18 | 1.79 | |
| 1.62 | 4.54 | 1.05 | 0.11 | 59.62 | 0.16 | 3.87 | nd * | 0.61 | 0.13 | 4.71 | 16.2 | 0.23 | 3.63 | 1.98 | |
| 1.53 | 4.01 | 0.88 | 0.09 | 60.65 | 0.12 | 3.64 | nd * | 0.69 | 0.21 | 4.69 | 16.2 | 0.19 | 3.8 | 1.64 | |
| 1.42 | 4.09 | 0.88 | 0.05 | 60.76 | 0.13 | 3.46 | nd * | 0.54 | 0.09 | 4.71 | 16.3 | 0.19 | 3.84 | 1.78 | |
| 1.67 | 4.32 | 0.95 | 0.12 | 59.75 | 0.25 | 3.45 | nd * | 0.63 | 0.13 | 4.77 | 16.6 | 0.31 | 4.03 | 1.42 | |
| 1.52 | 4.61 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 60.5 | 0.26 | 3.36 | nd * | 0.47 | 0.06 | 4.75 | 16.5 | 0.21 | 3.71 | 1.47 | |
| 1.36 | 4.07 | 0.9 | 0.09 | 60.78 | 0.2 | 3.3 | nd * | 0.58 | 0.17 | 4.83 | 16.7 | 0.23 | 3.72 | 1.54 | |
| 1.4 | 4.53 | 1.45 | 0.05 | 59.59 | 0.11 | 3.4 | nd * | 0.63 | 0.18 | 4.89 | 16.6 | 0.32 | 3.57 | 1.73 | |
| 1.49 | 4.73 | 0.95 | 0.05 | 60.22 | 0.1 | 3.43 | nd * | 0.57 | 0.16 | 4.78 | 16.4 | 0.35 | 3.7 | 1.49 | |
| 1.4 | 5.24 | 0.89 | 0.1 | 60.09 | 0.22 | 3.37 | nd * | 0.57 | 0.11 | 4.79 | 16.4 | 0.28 | 3.71 | 1.23 | |
| 4.15 | 6.32 | 1.42 | 0.1 | 55.67 | 0.27 | 4.06 | nd * | 0.6 | 0.27 | 4.71 | 15.7 | 0.22 | 3.43 | 1.28 | |
| Sample 30 | 1.71 | 8.76 | 3.63 | 0 | 55.12 | 0.27 | 3.95 | nd * | 0.53 | 0.09 | 4.37 | 15.2 | 0.1 | 3.45 | 1.29 |
| 1.25 | 3.93 | 1.16 | 0 | 61.29 | 0.07 | 3.36 | nd * | 0.53 | 0.04 | 4.54 | 16.6 | 0.18 | 3.65 | 1.57 | |
| 1.07 | 3.35 | 0.84 | 0 | 62.07 | 0.07 | 3.11 | nd * | 0.62 | 0.03 | 4.67 | 17.2 | 0.31 | 3.78 | 1.26 | |
| 1.06 | 3.18 | 0.84 | 0 | 61.94 | 0.14 | 3 | nd * | 0.62 | 0 | 4.71 | 17.3 | 0.31 | 3.79 | 1.5 | |
| 1.17 | 3.61 | 1.21 | 0 | 61.57 | 0.11 | 2.95 | nd * | 0.64 | 0.06 | 4.58 | 17.2 | 0.19 | 3.64 | 1.42 | |
| 0.89 | 3.54 | 1.32 | 0 | 61.64 | 0.2 | 3 | nd * | 0.66 | 0.15 | 4.43 | 17.2 | 0.24 | 3.76 | 1.3 | |
| 1.07 | 3.16 | 0.82 | 0 | 62.37 | 0.04 | 3 | nd * | 0.66 | nd * | 4.47 | 17.6 | 0.1 | 3.64 | 1.38 | |
| 1.31 | 3.72 | 0.91 | 0 | 61.47 | 0.06 | 3.14 | nd * | 0.49 | 0.09 | 4.86 | 16.9 | 0.26 | 3.72 | 1.43 | |
| 1.02 | 3.62 | 0.87 | 0 | 61.86 | 0.13 | 3.1 | nd * | 0.38 | 0.06 | 4.69 | 17.2 | 0.24 | 3.66 | 1.43 | |
| 1.77 | 13.18 | 2.97 | 0 | 53.69 | 0.25 | 3.25 | nd * | 0.45 | 0.04 | 4.26 | 14.6 | 0.23 | 3.35 | 0.54 | |
| Sample 120 | 1.87 | 13.13 | 3.97 | 0.63 | 52.3 | 1.32 | nd * | 0.02 | 4.48 | 15.57 | 0.17 | 13.4 | 3.52 | nd * | nd * |
| 0.94 | 2.56 | 0.85 | 0.61 | 63.09 | 1.12 | nd * | nd * | 5.15 | 17.72 | 0.37 | 14.75 | 4.02 | nd * | 0.66 | |
| 0.94 | 2.52 | 0.96 | 0.59 | 62.99 | 1.2 | nd * | nd * | 5.05 | 17.35 | 0.18 | 11.76 | 4.31 | nd * | 0.88 | |
| 0.89 | 2.47 | 1.05 | 0.6 | 63.18 | 1.07 | nd * | nd * | 5.15 | 17.11 | 0.24 | 12.78 | 4.26 | nd * | 0.79 | |
| 0.77 | 2.68 | 1.15 | 0.68 | 63.05 | 1.14 | nd * | nd * | 5.08 | 16.94 | 0.28 | 11.66 | 4.3 | nd * | 0.62 | |
| 0.86 | 2.53 | 1.07 | 0.63 | 62.71 | 1.09 | nd * | 0.03 | 5.18 | 17.25 | 0.34 | 12.69 | 4.13 | nd * | 0.89 | |
| 0.91 | 2.51 | 0.99 | 0.6 | 63.27 | 1 | nd * | 0.01 | 4.95 | 17.51 | 0.34 | 12.84 | 4.11 | nd * | 0.63 | |
| 0.69 | 3.31 | 1.14 | 0.39 | 61.42 | 0.64 | nd * | nd * | 5.37 | 17.98 | 0.35 | 14.84 | 4.23 | nd * | 0.72 | |
| Sample PD | 0.4 | 2.97 | 15.61 | 0.52 | 41.74 | 0.05 | 0.92 | 11.48 | 0.04 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 8.18 | 0.51 | 0.58 | 0.87 |
| 2.25 | 3.87 | 5.32 | 0.55 | 48.77 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.49 | 0.05 | 4.45 | 0.22 | 14.38 | 0.78 | 3.31 | 1.48 | |
| 1.73 | 3.82 | 4.78 | 0.57 | 49.76 | 0.00 | nd * | 2.34 | 0.18 | 4.72 | 0.16 | 15.23 | 0.7 | 3.34 | 1.41 | |
| 1.62 | 3.49 | 3.96 | 0.59 | 53.51 | nd * | nd * | 2.15 | nd * | 4.87 | 0.03 | 16.19 | 0.6 | 3.45 | 1.3 | |
| 1.5 | 3.41 | 4.04 | 0.56 | 52.16 | nd * | 0.00 | 2.08 | nd * | 4.73 | 0.83 | 15.31 | 0.84 | 3.31 | 1.33 | |
| 1.8 | 3.87 | 4.31 | 0.56 | 52.54 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.04 | 0.1 | 4.96 | 0.99 | 15.24 | 0.73 | 3.29 | 1.34 | |
| 1.75 | 3.72 | 4.1 | 0.6 | 52.14 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 2.17 | 0.13 | 4.89 | 0.48 | 15.28 | 0.7 | 3.44 | 1.45 | |
| 1.79 | 3.47 | 12.44 | 0.57 | 52.48 | nd * | 0.00 | 10.51 | nd * | 0.8 | 0.88 | 15.02 | 0.73 | nd * | 1.31 | |
| 1.04 | 9.20 | 10.84 | 0.5 | 52.18 | 0.00 | nd * | 11.18 | 0.06 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 12.35 | 0.6 | 0.00 | 1.38 |
References
- European Commission; Bobba, S.; Carrara, S.; Huisman, J.; Mathieux, F.; Pavel, C. Critical Raw Materials for Strategic Technologies and Sectors in the EU—A Foresight Study; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; ISBN 9789276153375. [Google Scholar]
- Lemonnier, V. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the European Council, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions, a Green Deal Industrial Plan for the Net-Zero Age; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Critical Raw Materials Resilience: Charting a Path towards Greater Security and Sustainability; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2020.
- RMIS—Critical, Strategic and Advanced Materials. Available online: https://rmis.jrc.ec.europa.eu/eu-critical-raw-materials (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Grohol, M.; Veeh, C. Study on the critical raw materials for the EU 2023—Final report, European Commission: Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs, Publications Office of the European Union, 2023. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2873/725585 (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Scrreen3, Factsheets Updates Based on the EU Factsheets 2020 Rare Earth Elements. Available online: https://scrreen.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/SCRREEN2_factsheets_REE-EUROSTAT.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Rare Earths Statistics and Information by National Minerals Information Center. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/centers/national-minerals-information-center/rare-earths-statistics-and-information (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Leal Filho, W.; Kotter, R.; Özuyar, P.G.; Abubakar, I.R.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Matandirotya, N.R. Understanding Rare Earth Elements as Critical Raw Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicka, E.; Guzik, K.; Galos, K. On the Possibilities of Critical Raw Materials Production from the EU’s Primary Sources. Resources 2021, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croat, J.J.; Ormerod, J. The history of permanent magnets. In Modern Permanent Magnets; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauß, R.; Burkhardt, C.; Carencotte, F.; Gasparon, M.; Gutfleisch, O.; Higgins, I.; Karajić, M.; Klossek, A.; Mäkinen, M.; Schäfer, B.; et al. Rare Earth Magnets and Motors: A European Call for Action, A Report by the Rare Earth Magnets and Motors Cluster of the European Raw Materials Alliance. A Report of Rare. 2021, pp. 1–35. Available online: https://eit.europa.eu/sites/default/files/2021_09-24_ree_cluster_report2.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Behrsing, T.; Blair, V.L.; Jaroschik, F.; Deacon, G.B.; Junk, P.C. Rare Earths—The Answer toEverything. Molecules 2024, 29, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, B. Environmental Impact of Modern Permanent Magnets. In Modern Permanent Magnets-Fundamentals and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollat, A.; Guyonnet, D.; Planchon, M.; Tuduri, J. Prospective Analysis of the Flows of Certain Rare Earths in Europe at the 2020 Horizon. Waste Manag. 2016, 49, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizos, V.; Righetti, E.; Kassab, A. Understanding the barriers to recycling critical raw materials for the energy transition: The case of rare earth permanent magnets. Energy Rep. 2024, 12, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, K. A Product Classification Approach to Optimize Circularity of Critical Resources—The Case of NdFeB Magnets. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.A.; Deng, S.; Jin, H.; Prodius, D.; Sutherland, J.W.; Nlebedim, I.C. Sustainable Recycling of Rare-Earth Elements from NdFeB Magnet Swarf: Techno-Economic and Environmental Perspectives. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 15915–15924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Afiuny, P.; McIntyre, T.; Yih, Y.; Sutherland, J. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of NdFeB Magnets: Virgin Production versus Magnet-to-Magnet Recycling. Procedia CIRP 2016, 48, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Burada, M.; Sobetkii, A.E.; Paneva, D.; Fironda, S.A.; Piticescu, R.-R. Green and Sustainable Rare Earth Element Recycling and Reuse from End-of-Life Permanent Magnets. Metals 2024, 14, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Buchert, M. Recycling of Rare Earths: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 51, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Sheridan, R.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O.; Buchert, M.; Steenari, B.M.; Van Gerven, T.; Jones, P.T.; et al. REE Recovery from End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnet Scrap: A Critical Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 3, 122–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró, L.T.; Méndez, G.V.; Ayres, R.U. Material Flow Analysis of Scarce Metals: Sources, Functions, End-Uses and Aspects for Future Supply. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2939–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becci, A.; Beolchini, F.; Amato, A.; Ippolito, M.; Innocenzi, V. Sustainable Strategies for the Exploitation of End-of-Life Permanent Magnets. Processes 2021, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nielen, S.S.; Sprecher, B.; Verhagen, T.J.; Kleijn, R. Towards Neodymium Recycling: Analysis of the Availability and Recyclability of European Waste Flows. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 394, 136252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanescu, D.; Cailean (Gavrilescu), D.; Teodosiu, C.; Fiore, S. Assessment of the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Management Systems Profile and Sustainability in Developed and Developing European Union Countries. Waste Manag. 2018, 73, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, E.; Rizos, V. The EU’s Quest for Strategic Raw Materials: What Role for Mining and Recycling? Intereconomics 2023, 58, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, E.; Rizos, V. Reducing Supply Risks for Critical Raw Materials: Evidence and Policy Options; CEPS: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.L.; Kim, H.; Pan, S.Y.; Tseng, P.C.; Lin, Y.P.; Chiang, P.C. Implementation of Green Chemistry Principles in Circular Economy System towards Sustainable Development Goals: Challenges and Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 136998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.; Buchert, M. Estimates of global REE recycling potentials from NdFeB magnet material. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 113, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, E.; Rizos, V.; Moreschi, M. Setting Standards for Critical Raw Materials: State of Play and Future Prospects; Centre for European Policy Studies: Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihne, T.; Hahn, R.; Wieprecht, N.; Franke, J.; Kühl, A. Approach for Advanced Mechanical Recycling Strategies of Rare Earth Magnets Applied in Traction Drives. In Congress of the German Academic Association for Production Technology; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormerod, J.; Karati, A.; Baghel, A.P.S.; Prodius, D.; Nlebedim, I.C. Sourcing, Refining and Recycling of Rare-Earth Magnets. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihne, T.; Hahn, R.; Kühl, A.; Franke, J. Approaches For The Physical Sorting Of Soft And Hard Magnetic Material Mixtures In The Context Of Rare Earth Recycling. In Proceedings of the 6 th Conference on Production Systems and Logistics, Honolulu, HI, USA, 8 July 2024; pp. 697–708. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, M.; Wirth, F.; Boschert, L.; Fleischer, J. An Approach for the Disassembly of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Rotors to Recover Rare Earth Materials. Procedia CIRP 2023, 116, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.; Abrahami, S.; Yang, Y.; Sprecher, B.; Li, Z.; Menad, N.-E.; Bru, K.; Marcon, T.; Rado, C.; Saje, B.; et al. Upscaling of Permanent Magnet Dismantling and Recycling through VALOMAG Project. Mater. Proc. 2021, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Cui, J.; Barnard, D.J.; Bond, L.J. Internal Defect Detection and Characterization of Samarium-Cobalt Sintered Magnets by Ultrasonic Testing Technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 570, 170524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kedous-lebouc, A.; Dubus, J.; Garbuio, L.; Personnaz, S. Direct reuse strategies of rare earth permanent magnets for PM electrical machines—An overview study. Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 86, 20901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Hu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, F.; Hu, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H. Technologies of Recycling REEs and Iron from NdFeB Scrap. Metals 2023, 13, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Yin, X.; Liu, W.; Lu, Q. Progress in Recycling of Nd-Fe-B Sintered Magnet Wastes. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 077506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Waal, F.F. Recycling Permanent Magnets from Offshore Wind Turbines—An E-Waste Approach. Master’s Thesis, TU Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Sahu, S.K. A Comprehensive Review on Recycling of Critical Raw Materials from Spent Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Magnet. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periyapperuma, K.; Sanchez-Cupido, L.; Pringle, J.M.; Pozo-Gonzalo, C.; Jones, M. Analysis of Sustainable Methods to Recover Neodymium. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 2, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Samadder, S.R. A Critical Review of the Pre-Processing and Metals Recovery Methods from e-Wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 320, 115887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakotnik, M.; Tudor, C.O.; Peiró, L.T.; Afiuny, P.; Skomski, R.; Hatch, G.P. Analysis of Energy Usage in Nd–Fe–B Magnet to Magnet Recycling. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogberg, S.; Holboll, J.; Mijatovic, N.; Jensen, B.B.; Bendixen, F.B. Direct Reuse of Rare Earth Permanent Magnets—Coating Integrity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowitt, S.M.; Werner, T.T.; Weng, Z.; Mudd, G.M. Recycling of the Rare Earth Elements. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, T.; Bertau, M. Recycling of Rare Earth Elements. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017, 2, 20160067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixandru, A.; Venkatesan, P.; Jönsson, C.; Poenaru, I.; Hall, B.; Yang, Y.; Walton, A.; Güth, K.; Gauß, R.; Gutfleisch, O. Identification and Recovery of Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets from Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M. An overview of NdFeB magnets recycling technologies. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 46, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopic, S.; Polat, B.; Chung, H.; Emil-Kaya, E.; Smiljanić, S.; Gürmen, S.; Friedrich, B. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements through Spent NdFeB Magnet Oxidation (First Part). Metals 2022, 12, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’am, A.C.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, S.W.; You, S.J. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Waste Permanent Magnet (WPMs) via Selective Leaching Using the Taguchi Method. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagianni, S.; Moschovi, A.M.; Sakkas, K.M.; Chalaris, M.; Yakoumis, I. Preprocessing and Leaching Methods for Extraction of REE from Permanent Magnets: A Scoping Review. AppliedChem 2022, 2, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poenaru, I.; Patroi, E.A.; Patroi, D.; Iorga, A.; Manta, E. HDDR as Advanced Processing Method and Recycling Technology to Address the Rare-Earth Resource Criticality in High Performance Nd2Fe14B Magnets Production. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 577, 170777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, F.S.; Yao, T.Q. An Environmentally Friendly Ball Milling Process for Recovery of Valuable Metals from E-Waste Scraps. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xu, Z. A Review of Current Progress of Supercritical Fluid Technologies for E-Waste Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 794–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Prasakti, L.; Stopic, S.R.; Feldhaus, D.; Cvetković, V.S.; Friedrich, B. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Spent NdFeB Magnets: Metal Extraction by Molten Salt Electrolysis (Third Part). Metals 2023, 13, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, A.; Hait, S. Comparative Assessment of Metallurgical Recovery of Metals from Electronic Waste with Special 1009 Emphasis on Bioleaching. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 6989–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Abe, T.; Martín-Cid, A.; Kawaguchi, S.; Suzuki, M.; Hirosawa, S.; Nakamura, T. Diagram of constituent crystalline phases in a Nd–Fe–B–Cu sintered magnet by in-situ high-temperature synchrotron X-ray diffraction and its thermodynamic interpretation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 892, 162188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, N.; Billington, D.; Tsuji, N.; Ueno, W.; Kotani, Y.; Kawaguchi, S.; Sugimoto, K.; Toyoki, K.; Fukagawa, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; et al. Quantitative identification of constituent phases in a Nd-Fe-B-Cu sintered magnet and temperature dependent change of electron density of Nd2Fe14B studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2019, 181, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, T.G.; Zhang, Y.; Hrkac, G.; Ciuta, G.; Dempsey, N.M.; Schrefl, T.; Gutfleisch, O.; Givord, D. Understanding the microstructure and coercivity of high performance NdFeB-based magnets. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, J.F.D.; Alcázar, G.A.P.; Colorado, H.D.; Tabares, J.A.; Zamora, L.E.; Garitaonandia, J.J.S. Systematic study of the dependence of magnetic and structural properties of Nd2Fe14B powders on the average particle size. J. Rare Earths 2020, 38, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Afiuny, P.; Dove, S.; Furlan, G.; Zakotnik, M.; Yih, Y.; Sutherland, J.W. Life Cycle Assessment of Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnet-to-Magnet Recycling for Electric Vehicle Motors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3796–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Ji, M.; Du, R.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yue, M.; et al. Understanding the coercivity enhancement mechanism of grain boundary diffused Nd-Fe-B magnets by comparing with commercial equivalent coercivity magnets. Mater. Charact. 2024, 210, 113817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K.; Sagawa, M. The origin of coercivity decrease in fine grained Nd–Fe–B sintered magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Cao, J.; Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Yu, H.; Hussain, M.; Liu, Z. Grain Boundary Diffusion Sources and Their Coating Methods for Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets. Metals 2021, 11, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazilkin, A.; Straumal, B.B.; Protasova, S.G.; Gorji, S.; Straumal, A.B.; Katter, M.; Schütz, G.; Barezky, B. Grain boundary oxide layers in NdFeB-based permanent magnets. Mater. Des. 2021, 199, 109417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehri-Amin, H.; Ohkubo, T.; Shima, T.; Hono, K. Grain boundary and interface chemistry of an Nd–Fe–B-based sintered magnet. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hono, K.; Sepehri-Amin, H. Strategy for high-coercivity Nd–Fe–B magnets. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Khoshsima, S.; Tomše, T.; Podmiljšak, B.; Šturm, S.; Burkhardt, C.; Žužek, K. Short-Loop Recycling of Nd-Fe-B Permanent Magnets: A Sustainable Solution for the RE2Fe14B Matrix Phase Recovery. Materials 2023, 16, 6565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirba, I.; Aravindhan, A.; Muneeb, M.; Gutfleisch, O. Grain size and coercivity tuning in Nd2Fe14B-based magnets prepared by high pressure hydrogen milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 582, 171018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cui, H.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P.; Liu, W.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, D.; Pang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.; et al. Magnetic property recovery in Nd-Fe-B bonded magnet wastes with chemical reaction and physical dissolution. J. Rare Earths 2021, 39, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumal, B.B.; Kucheev, Y.O.; Yatskovskaya, I.L.; Mogilnikova, I.V.; Schütz, G.; Nekrasov, A.N.; Baretzky, B. Grain boundary wetting in the NdFeB-based hard magnetic alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 8352–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothnagel, P.; Müller, K.H.; Eckert, D.; Handstein, A. The influence of particle size on the coercivity of sintered NdFeB magnets. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1991, 101, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.W.; Yu, J.H. Coercivity of Near Single Domain Size Nd2Fe14B-type Particles. J. Magn. 2012, 17, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, M.; Hirosawa, S.; Tokuhara, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Fujimura, S.; Tsubokawa, Y.; Shimizu, R. Dependence of coercivity on the anisotropy field in the Nd2Fe14B-type sintered magnets. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 3559–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapley, M.; Pauls, J.P.; Tansley, G.; Busch, A.; Gregory, S.D. Selective laser sintering of bonded magnets from flake and spherical powders. Scr. Mater. 2019, 172, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Korman, O.; Di Nardo, M.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C.; Ashcroft, I.; Hague, R.J.M.; Aboulkhair, N.T. Additive Manufacturing of Nd-Fe-BPermanent Magnets Their Application in Electrical Machines. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 138921–138931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Somashekara, M.; Paranthaman, M.P.; Kramer, M.; Haase, C.; Nlebedim, I.C. Functionalizing magnet additive manufacturing with in-situ magnetic field source. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 34, 101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandha, K.; Nlebedim, I.C.; Kunc, V.; Lara-Curzio, E.; Fredette, R.; Paranthaman, M.P. Additive manufacturing of highly dense anisotropic Nd–Fe–B bonded magnets. Scr. Mater. 2020, 183, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jones, K.; Sales, B.; Pries, J.L.; Nlebedim, I.; Jin, K.; Bei, H.; Post, B.K.; Kesler, M.S.; Rios, O.; et al. Fabrication of highly dense isotropic Nd-Fe-B nylon bonded magnets via extrusion-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fim, R.G.T.; Mascheroni, A.A.; Antunes, L.F.; Engerroff, J.B.E.; Ahrens, C.H.; Wendhausen, P.A.P. Increasing packing density of Additively Manufactured Nd-Fe-B bonded magnets. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 35, 101353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nlebedim, I.; Ucar, H.; Hatter, C.B.; McCallum, R.; McCall, S.K.; Kramer, M.; Paranthaman, M.P. Studies on in situ magnetic alignment of bonded anisotropic Nd-Fe-B alloy powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 422, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranthaman, M.P.; Nlebedim, I.C.; Johnson, F.; McCall, S.K. Additive Manufacturing of Permanent Magnets. Mater. Matters 2016, 11. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/BG/en/technical-documents/technical-article/materials-science-and-engineering/nanoparticle-and-microparticle-synthesis/additive-manufacturing-of-permanent-magnets?srsltid=AfmBOopTLCPnCs99y4Eg9VQ5HSD2v06yT9un3ud-uxuem4uMkh8eUOOY (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Baláž, P.; Achimovicová, M.; Baláž, M.; Billik, P.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Criado, J.M.; Delogu, F.; Dutková, E.; Gaffet, E.; Gotor, F.J.; et al. Hallmarks of Mechanochemistry: From Nanoparticles to Technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7571–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šepelák, V.; Becker, K.D. Mechanochemistry: From Mechanical Degradation to Novel Materials Properties. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2012, 49, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, P. Mechanochemistry in Nanoscience and Minerals Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Li, J. Recycling Metals from Wastes: A Novel Application of Mechanochemistry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5849–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Application of Mechanochemistry to Metal Recovery from Second-Hand Resources: A Technical Overview. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2015, 17, 1522–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Xiang, D.; Duan, G.; Mou, P. A Review of Mechanochemistry Applications in Waste Management. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baláž, P. Extractive Metallurgy of Activated Minerals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 10, p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Baláž, M. Environmental Mechanochemistry Recycling Waste into Materials Using High-Energy Ball Milling. In Environmental Mechanochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihan, Z.; Zhi, W.; Dong, W.; Yong, L.; Wanhai, X.; Chenghao, L.; Yang, L.; Jian, W.; Guobiao, L. A Green Process for Selective REEs Recovery from Rare Earth Waste through Mechanochemical Activation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, S.L.; Adams, C.J.; Bolm, C.; Braga, D.; Collier, P.; Friščić, T.; Grepioni, F.; Harris, K.D.M.; Hyett, G.; Jones, W.; et al. Mechanochemistry: Opportunities for New and Cleaner Synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 41, 413–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, S.; Rožić, L.; Grbić, B.; Radić, N.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Stojadinović, S. Structural, optical and photocatalytic properties of LaTi0.4Mg0.4Fe0.2O3 perovskite prepared by high-energy ball milling. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 297, 122085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, M.L.; Slobozeanu, A.E.; Larosa, C.; Paneva, D.; Yakoumis, I.; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z. Platinum Group Metals: Green Recovery from Spent Auto-Catalysts and Reuse in New Catalysts—A Review. Crystals 2023, 13, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Paneva, D.; Encheva, E.; Tsvetkov, M.; Krstić, J.; Grilli, M.L. Application of Mechanochemically Treated Waste Materials for Water Remediation. Phys. Status Solidi 2022, 219, 2100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, A.; Mingelgrin, U. Mechanochemistry: A Review of Surface Reactions and Environmental Applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67–68, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo, C.E.E.; Hernandez, J.S.T.; Salgado, M.J.R.; Tabares, J.A.; Maccari, F.; Cortes, A.; Alcázar, G.A.P. Processing and characterization of Nd2Fe14B microparticles prepared by surfactant-assisted ball milling. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.F.; Ding, J.; McCormick, P.G.; Street, R. Effect of mechanical milling on the structure and magnetic properties of Nd16Fe76B8. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1996, 29, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maât, N.; Lardé, R.; Nachbaur, V.; Le Breton, J.-M.; Isnard, O.; Pop, V.; Chicinaş, I. Investigation by Mössbauer spectroscopy atom probe tomography of the phase transformation of Nd-Fe-Balloys after high-energy ball milling. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 223905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabay, A.M.; Akdogan, N.G.; Marinescu, M.; Liu, J.F.; Hadjipanayis, G.C. Rare earth–cobalt hard magnetic nanoparticles and nanoflakes by high-energy milling. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 164213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeonidis, K.; Sarafidis, C.; Papastergiadis, E.; Angelakeris, M.; Tsiaoussis, I.; Kalogirou, O. Evolution of Nd2Fe14B nanoparticles magnetism during surfactant-assisted ball-milling. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, G.C.d.S.; Biondo, V.; Ferreira, R.F.; Tupan, L.F.d.S.; Nicolodi, S.; Ivashita, F.F.; Isnard, O.; Paesano, A. Structural and magnetic characterization of the Nd2Fe14B + 10%wt.Fe system subjected to high-energy milling. Hyperfine Interact. 2019, 240, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döbelin, N.; Kleeberg, R. Profex: A graphical user interface for the Rietveld refinement program BGMN. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gütlich, P.; Bill, E.; Trautwein, A.X. Trautwein, Mössbauer Spectroscopy and Transition Metal Chemistry, Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloyi, O.; Baloy, M.E.; Ngoepe, P.; Chauke, H. Effect of Gadolinium rare-earth element on Nd2Fe14B permanent magnet. MATEC Web Conf. 2022, 370, 09001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Kramer, M.J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Dennis, K.W.; McCallum, R.W. The mechanism of magnetic properties improvement and microstructure refinement of Zr in Nd2Fe14B. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08B511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Q. Microstructure refinement and magnetic properties enhancement for nanocomposite RE2Fe14B alloys by Zr additions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 460, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabekkodu, S.N.; Dosen, A.; Blanton, T.N. PDF-5+: A comprehensive Powder Diffraction File™ for materials characterization. Powder Diffr. 2024, 39, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, K.; Izumi, F. VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011, 44, 1272–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.-W.; Madavali, B.; Kim, D.-S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, M.-C.; Yang, C.-W.; Suryanarayana, C.; Hong, S.-J. Investigation of the magnetic properties and fracture behavior of Nd–Fe–B alloy powders during high-energy ball milling. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 096101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.C.; Lima, A.O.; dos Santos, M.N.L.; Souza, R.M.; Wendhausen, P.A.P.; Xavier, F.A. On the mechanical behavior of the sintered Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet during diamond scratching. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 94, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Grandjean, F. The Mössbauer Effect and its Application to Hard Permanent Magnetic Materials. In Supermagnets, Hard Magnetic Materials; NATO ASI Series; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 331, pp. 335–389. [Google Scholar]
- Van Noort, H.M.; de Mooij, D.B.; Buschow, K.H.J. 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy study of the magnetic properties of R2Fe14B compounds (R = Ce, Nd, Gd, Y). J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 5414–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.J.; Grandjean, F.; Pringle, O.A.; Fu, J. A Mössbauer Effect Study of the Re2Fe14B Magnets, Where RE Is Y, Pr, Nd, and Gd. Hyperfine Interact. 1990, 62, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Greneche, J.M. On the magnetism of grain boundary phase and its contribution to the abnormal openness of recoil loops in hot-deformed magnets. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 095002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Peng, B.; Liu, Y.; Greneche, J.M.; Yan, M. Evolution of REFe2 (RE = rare earth) phase in Nd-Ce-Fe-B magnets and resultant Ce segregation. Scr. Mater. 2019, 170, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Shao, X.; Que, Y.; Guo, B.; Bao, H.; Tang, G.; Yan, X.; Bao, J.; Yang, L.; Qin, L.; et al. Recent advances in mechanical properties of sintered NdFeB magnets. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1003, 175689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, D.; Huo, D.; Li, L.; Zhang, G. Structure and size-dependent properties of NdFeB nanoparticles and textured nano-flakes prepared from nanocrystalline ribbons. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 245003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




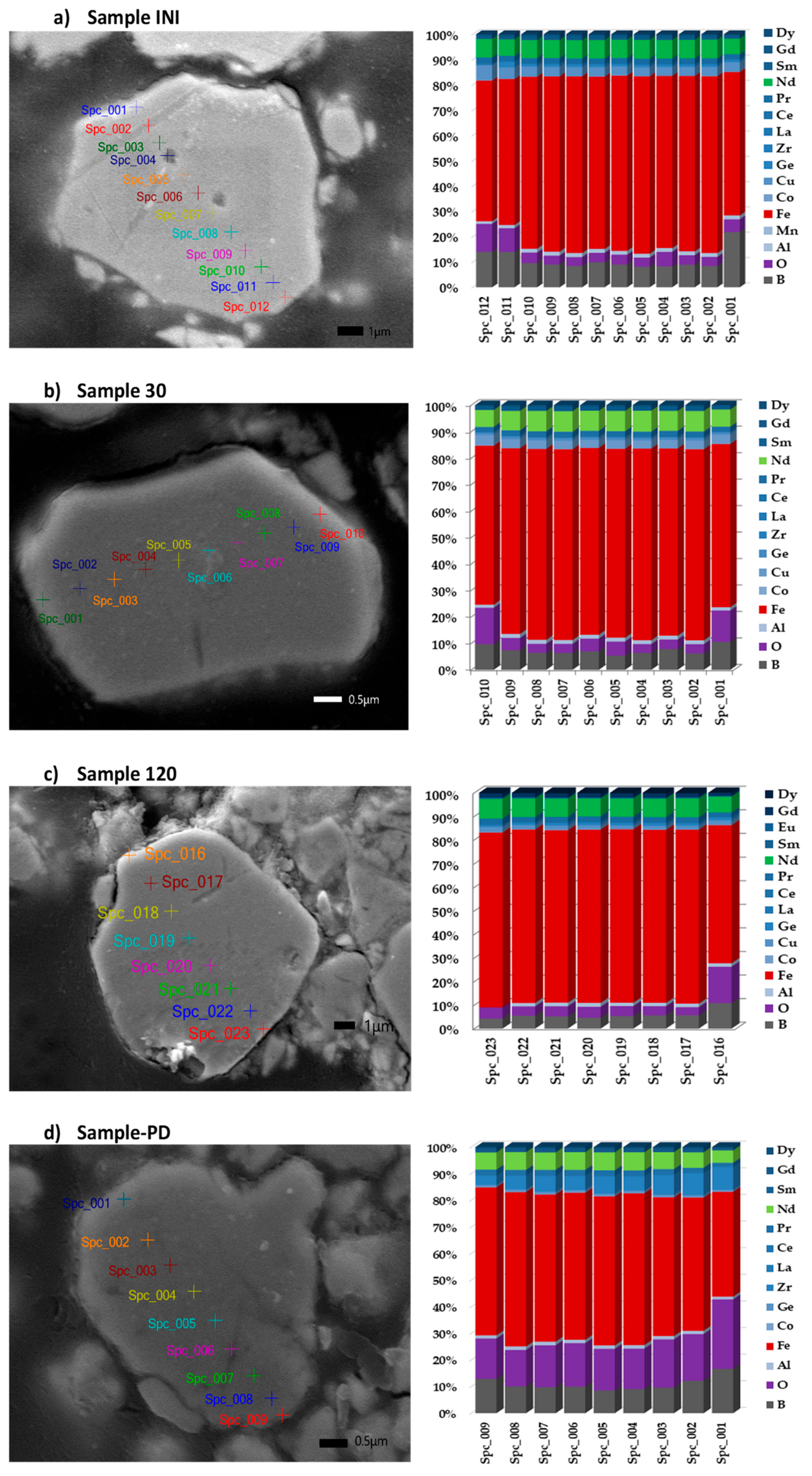
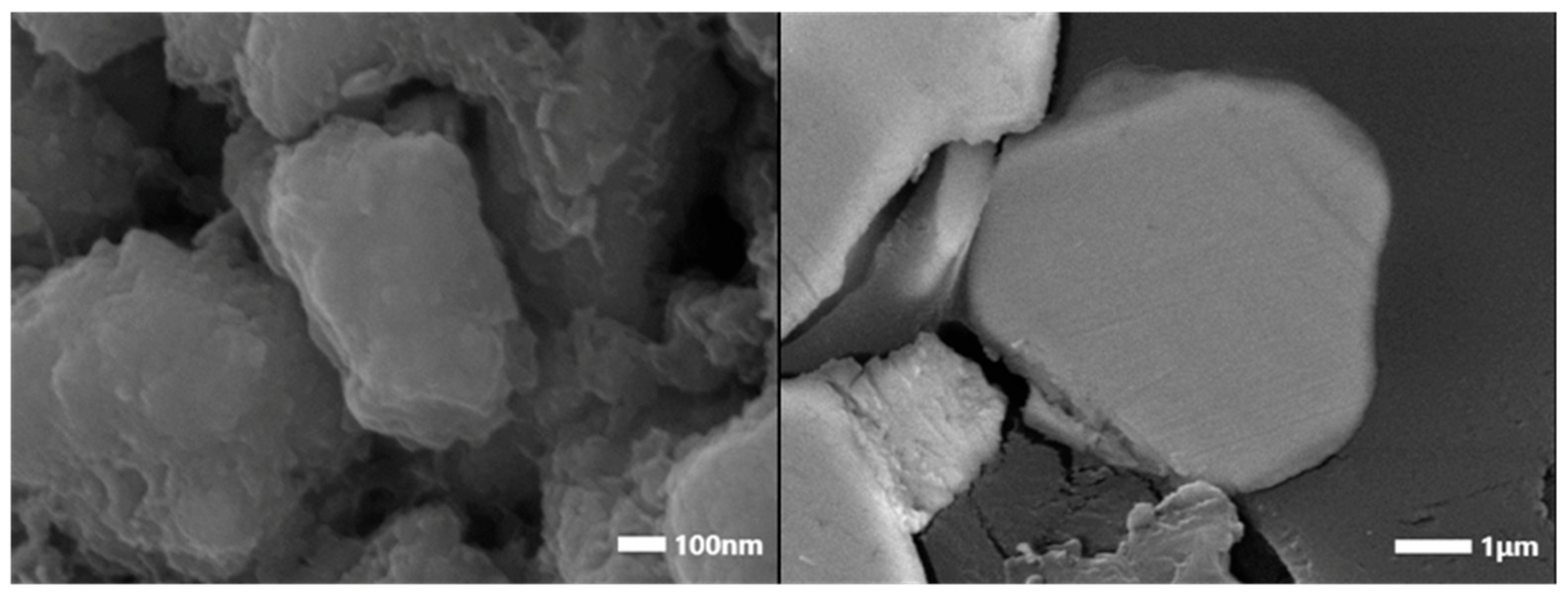
| Element | Nd | Sm | Pr | Dy | Gd | La | Ce | Fe | Co | Ni | Mn | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content wt.% | 17.8 | 0.04 | 4.6 | <0.005 | 4.7 | 0.89 | 0.081 | 63.2 | 0.47 | 0.005 | 0.016 | 0.18 |
| Sample | Phase Composition | Unite Cell Parameters | Mean Crystallite Size | Micro Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample INI | 100% Nd2Fe14B | a = b = 0.88006 ± 0.00011 c = 1.22129 ± 0.00018 c/a = 1.38773 | D(001) = 140 ± 4 nm D(100) = 82 ± 2 nm D(111) = 88 ± 2 nm | <ε2> = 3.8 × 10−4 ± 6 × 10−5 |
| Sample 30 | 100% Nd2Fe14B | a = 0.87984 ± 0.00011 c = 1.22061 ± 0.00017 c/a = 1.38793 | D(001) = 142± 5 nm D(100) = 83± 1 nm D(111) = 88 ± 1 nm | <ε2> = 7.2 × 10−4 ± 3 × 10−4 |
| Sample 120 | 100% Nd2Fe14B | a = b = 0.88013 ± 0.00020 c = 1.22123 ± 0.00031 c/a = 1.38755 | D(001) = 154 ± 7 nm D(100) = 78 ± 2 nm D(111) = 84 ± 4 nm | <ε2> = 11.0 × 10−4 ± 3 × 10−4 |
| Sample PD | 33% Nd2Fe14B | a = 0.88504 ± 0.00020 c = 1.22911 ± 0.00031 c/a = 1.38876 | D(001) = 41 ± 5 nm D(100) = 41 ± 5 nm D(111) = 41 ± 5 nm | <ε2> = 9.7 × 10−4 ± 7 × 10−4 |
| 67% α-Fe | a = b = c = 0.288 ± 0.00023 | D(001) = 32± 7 nm D(100) = 32 ± 7 nm D(111) = 32± 7 nm | <ε2> = 12.2 × 10−4 ± 4 × 10−4 | |
| ZrO2 contamination Amorphous phase | ||||
| Sample/Element Average wt.% | B | C | O | Mn | Fe | Co | Cu | Zr | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Gd | Dy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample INI | 1.86 | 5.98 | 1.29 | 0.07 | 61.81 | 0.62 | 1.38 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 0.07 | 4.79 | 16.22 | 0.24 | 3.62 | 1.41 |
| Sample 30 | 1.52 | 5.01 | 3.46 | 0.00 | 62.31 | 0.35 | 1.24 | nd * | 0.56 | 0.03 | 4.47 | 16.31 | 0.21 | 3.22 | 1.31 |
| Sample 120 | 0.98 | 3.96 | 5.43 | 0.03 | 63.52 | 2.25 | nd | 2.01 | 1.05 | 0.18 | 1.39 | 15.72 | 0.11 | 2.72 | 0.65 |
| Sample PD | 1.01 | 4.89 | 14.55 | 0.56 | 54.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 12.05 | 0.06 | 0.65 | nd * | 11.03 | 0.09 | nd * | 0.41 |
| Spectrum Label | O | Fe | Co | Mn | Cu | Nd | Sm | Pr | Dy | Gd | La | Ce |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.34 | 73.79 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 1.09 | 18.34 | 0.11 | 11.66 | 0.01 | 1.62 | 3.49 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 9.27 | 25.28 | 0.02 | nd * | 1.84 | 24.36 | 0.07 | 5.68 | nd * | 4.49 | 2.11 | 0.18 |
| 3 | 15.11 | 20.90 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 2.26 | 30.75 | 0.04 | 17.35 | 0.01 | 4.06 | 4.24 | 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z.; Paneva, D.; Fironda, S.A.; Piroeva, I.; Burada, M.; Sabeva, M.; Vasileva, A.; Ivanov, K.; Ranguelov, B.; Piticescu, R.R. Direct Reuse of Spent Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets. Materials 2025, 18, 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132946
Cherkezova-Zheleva Z, Paneva D, Fironda SA, Piroeva I, Burada M, Sabeva M, Vasileva A, Ivanov K, Ranguelov B, Piticescu RR. Direct Reuse of Spent Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets. Materials. 2025; 18(13):2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132946
Chicago/Turabian StyleCherkezova-Zheleva, Zara, Daniela Paneva, Sabina Andreea Fironda, Iskra Piroeva, Marian Burada, Maria Sabeva, Anna Vasileva, Kaloyan Ivanov, Bogdan Ranguelov, and Radu Robert Piticescu. 2025. "Direct Reuse of Spent Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets" Materials 18, no. 13: 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132946
APA StyleCherkezova-Zheleva, Z., Paneva, D., Fironda, S. A., Piroeva, I., Burada, M., Sabeva, M., Vasileva, A., Ivanov, K., Ranguelov, B., & Piticescu, R. R. (2025). Direct Reuse of Spent Nd–Fe–B Permanent Magnets. Materials, 18(13), 2946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132946











