Enhanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Performance in Sol–Gel Derived Al-Doped ZnO Thin Film Devices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical and Structural Characterization of AZO (0–4.0 wt% Al) Thin Films on Sapphire Substrates
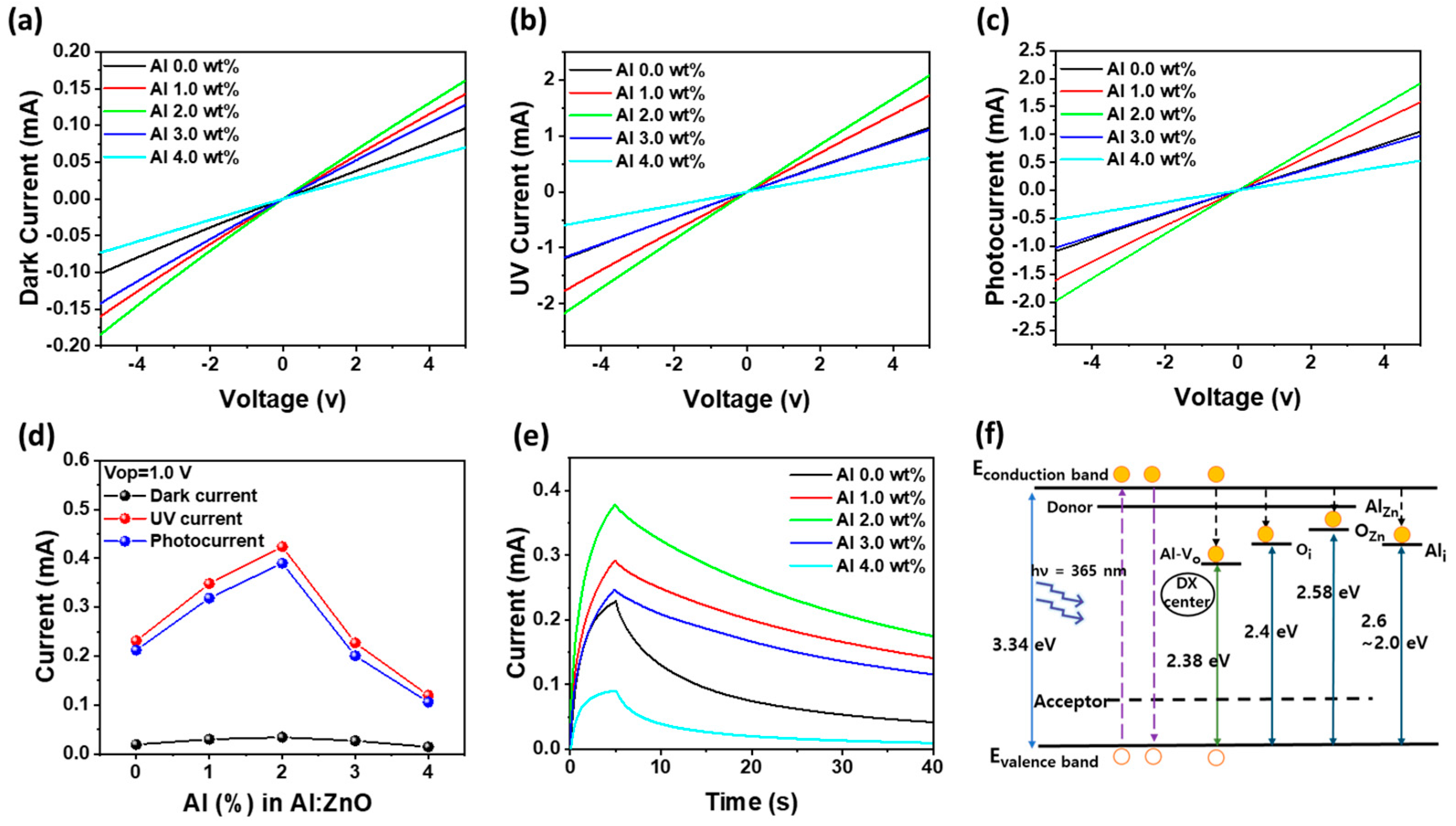
3.2. Electrical and Persistent Photoconductivity Characteristics of Al-Doped ZnO Devices
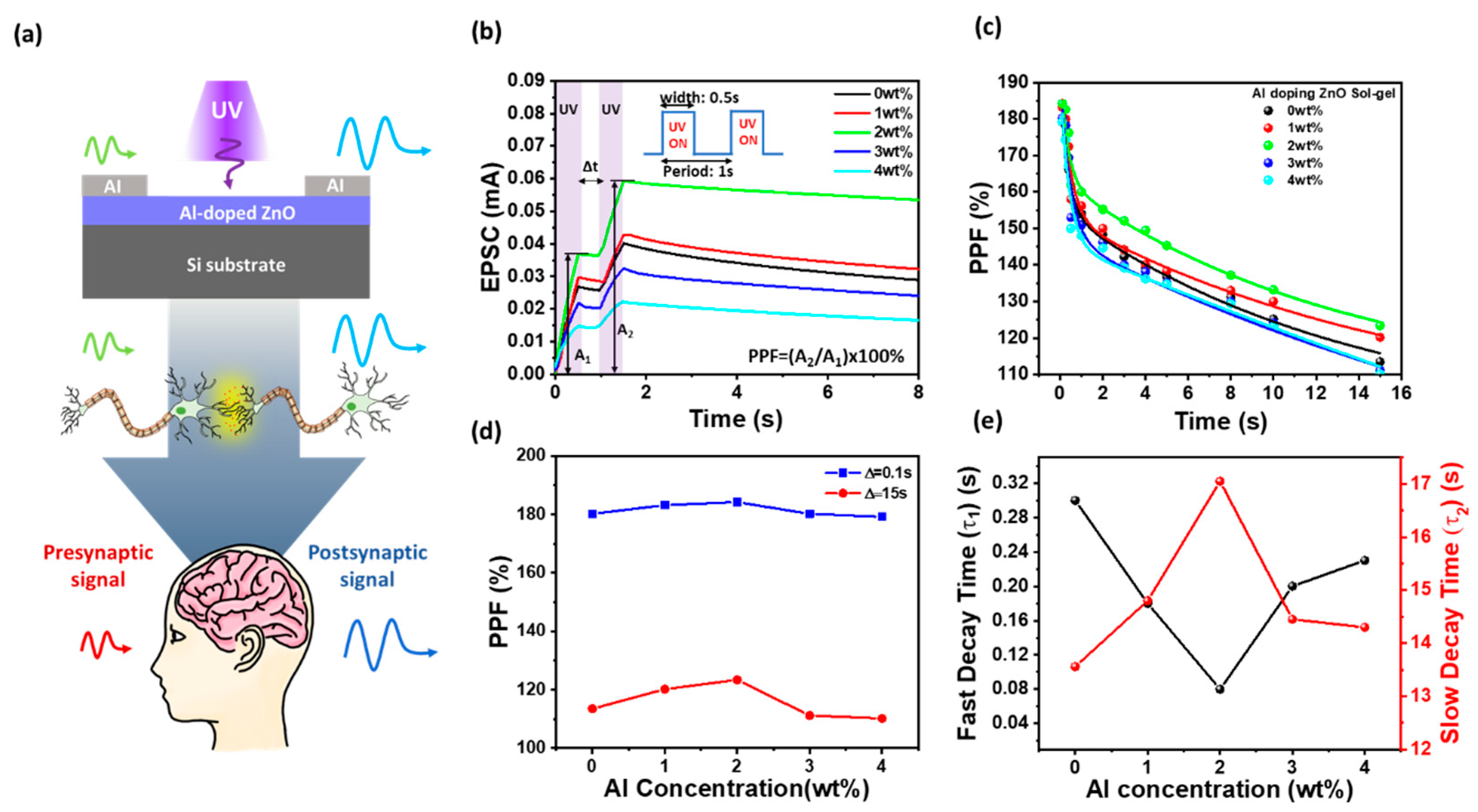
3.3. Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity and Paired-Pulse Facilitation in Al-Doped ZnO Devices
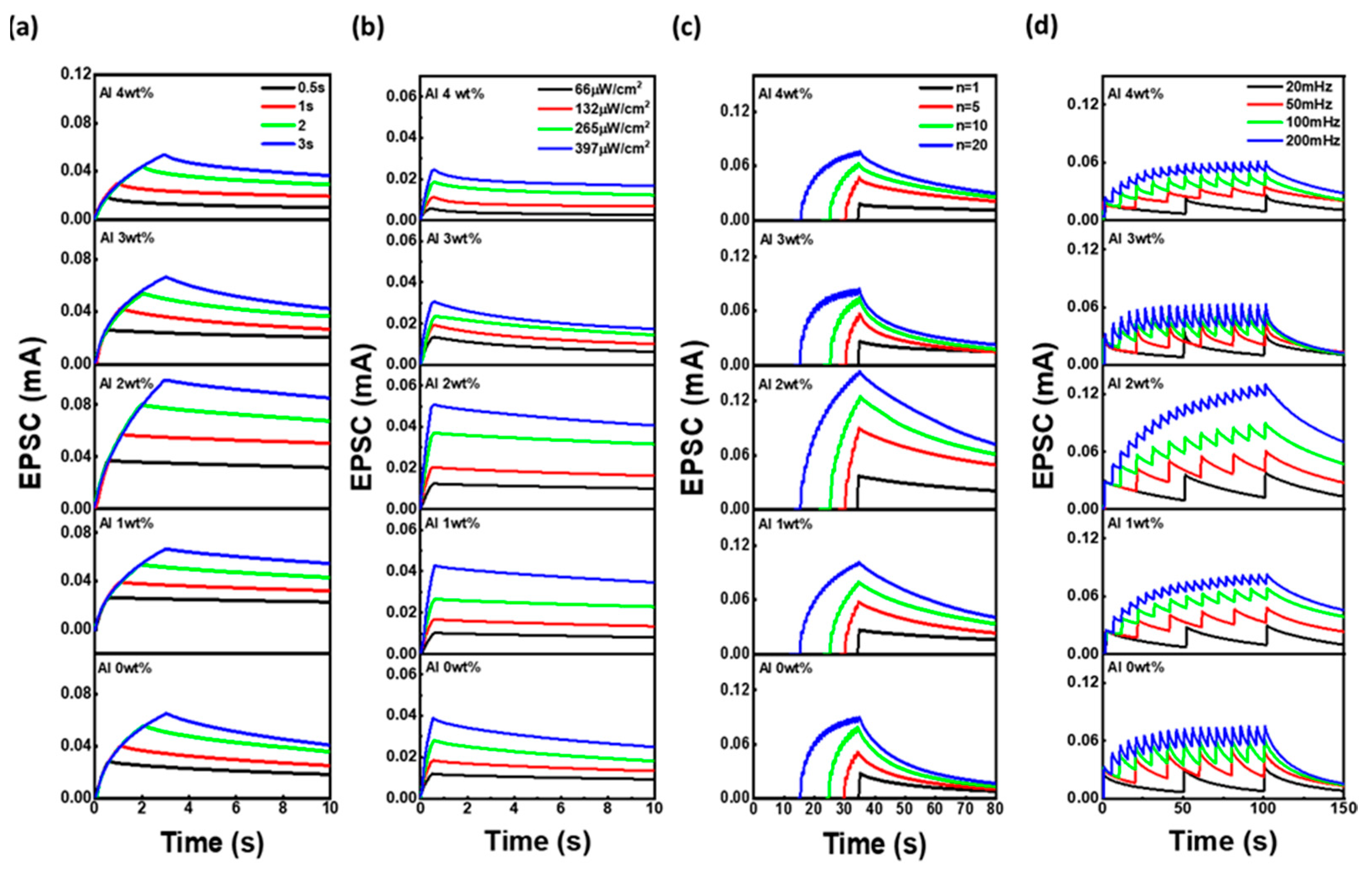
3.4. UV-Induced Synaptic Plasticity of Al/AZO/Al Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices Under Different Stimulation Conditions
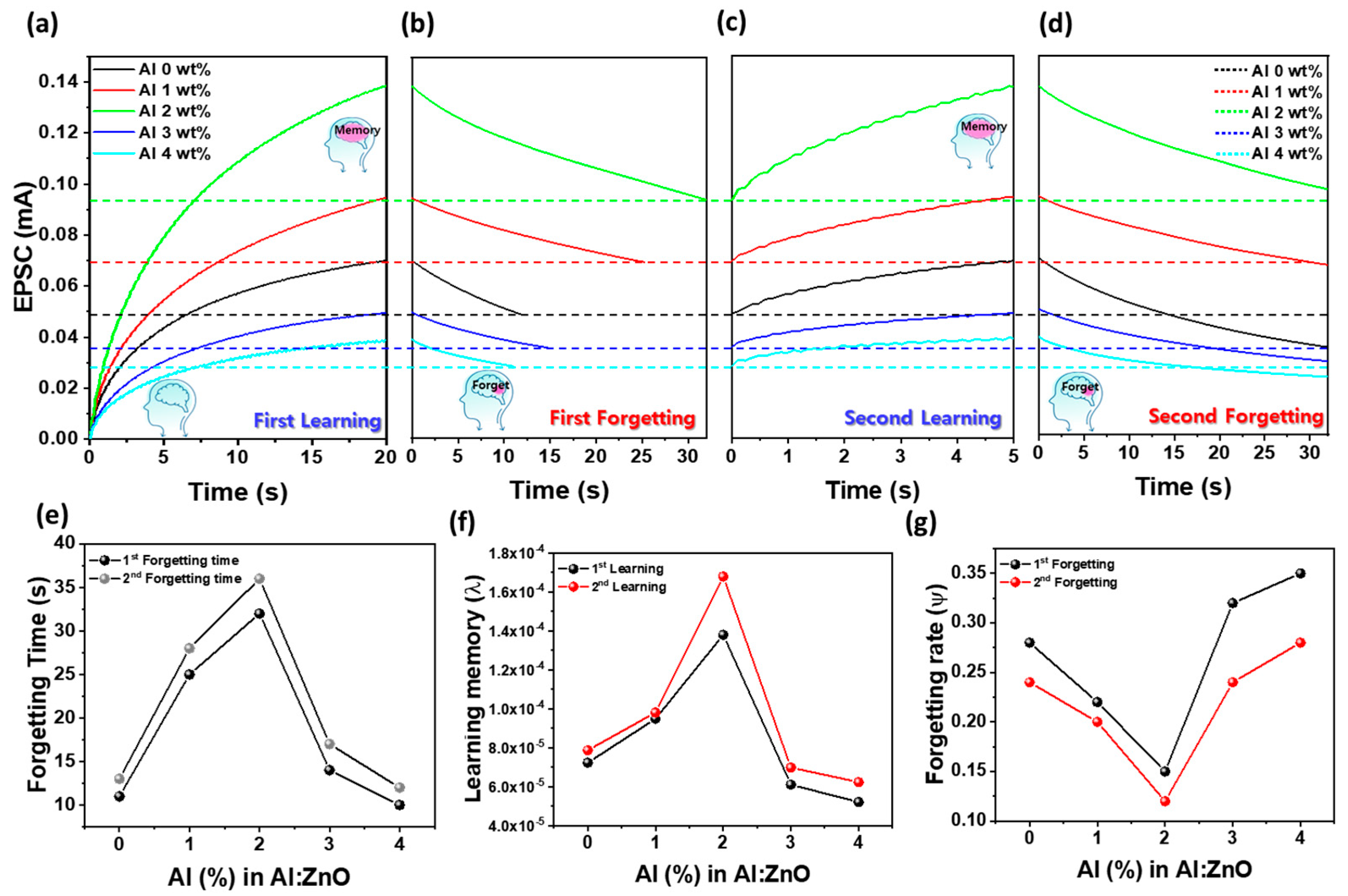
3.5. Al Concentration Effect on Learning, Forgetting, and Energy-Efficient Optical Synaptic Plasticity in AZO Optoelectronic Devices
3.6. Visual Memory Simulation and Long-Term Retention Behavior in AZO Optoelectronic Synaptic Device Arrays
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seok, H.; Lee, D.; Son, S.; Choi, H.; Kim, G.; Kim, T. Beyond von Neumann Architecture: Brain-Inspired Artificial Neuromorphic Devices and Integrated Computing. Adv. Electon. Mater. 2024, 10, 2300839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furber, S. Large-scale neuromorphic computing systems. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.H.; Chang, T.; Ebong, I.; Bhadviya, B.B.; Mazumder, P.; Lu, W. Nanoscale Memristor Device as Synapse in Neuromorphic Systems. Nano Lett. 2015, 10, 1297–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Recent Progress in Photonic Synapses for Neuromorphic Systems. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 2, 1900136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.; Ghosh, S.; Bhunia, R.; Chowdhury, A. Recent Developments in the State-of-the-Art Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices Based on 2D Materials: A Review. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 5299–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, K.-K.; Lee, S.-N. Enhanced Long-Term Memory Properties of ZnO Nanoparticle-Based Optical Synaptic Devices for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2300350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Hang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Han, S.; Chen, Z.; Peng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Zero-Power optoelectronic synaptic devices. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.L.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Jiang, Y.P.; Liu, Q.X.; Tang, X.G. In-sensor reservoir computing based on optoelectronic synaptic devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhu, C.Z.; Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J.; Wan, T.; Yan, W.; Chai, Y. Optoelectronic Devices for In-Sensor Computing. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 24007476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, G. Intelligent Optoelectronic Devices for Next-Generation Artificial Machine Vision. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2200668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.-J.; Choi, J.; Oh, J.-H.; Choi, D.-C.; Byun, J.; Ahn, S.-E.; Lee, S.-N. Oxide Semiconductor Memristor-Based Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices with Quaternary Memory Storage. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2024, 10, 2300863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Kwon, S.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.K. Recent Progress in Transistor-Based Optoelectronic Synapses: From Neuromorphic Computing to Artificial Sensory System. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeon, D.; Lee, S.N. Synaptic Plasticity and Memory Retention in ZnO–CNT Nanocomposite Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices. Materials 2025, 18, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, N.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Fu, H.; Gu, D.; Jiang, X.; Liu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, W. Nanostructured Materials and Architectures for Advanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Yang, Z.; Huang, J.; Shan, F. Recent Developments of Optoelectronic Synaptic Devices Based on Metal Halide Perovskites. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 16, 2211467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Noh, T.; Ahn, S.E.; Lee, S.N. Ultraviolet to red wavelength-dependent gallium oxide memristor-based multi-level optoelectronic synapse device. J. Alloys. Comps. 2025, 1017, 179053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-W.; Baek, S.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Lee, S.-N. A High-Photocurrent and Fast-Response Polarity-Controlled ZnO-Based UV Photodetector Grown by a Sol–Gel Process. Phys. Status Solidi 2021, 15, 2000501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revenant, C.; Benwadih, M.; Proux, O. Local structure around Zn and Ga in solution-processed In-Ga-Zn-O and implications for electronic properties. Phys. Status Solidi 2015, 9, 652–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, C.; Park, J.; Ismail, M.; Kim, S. Demonstration of electronic and optical synaptic properties modulation of reactively sputtered zinc-oxide-based artificial synapses. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 938, 168539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Li, D.; Yip, S.P.; Ho, J.C. Emerging optoelectronic artificial synapses and memristors based on low-dimensional nanomaterials. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 011303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Beom, K.; Kim, M.; Kang, C.J.; Yoon, T.S. Nonvolatile Memory and Artificial Synaptic Characteristics in Thin-Film Transistors with Atomic Layer Deposited HfOx Gate Insulator and ZnO Channel Layer. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Z.; Xu, C.; Duan, L.; Zhao, X.; Wu, H. Defects Control and Origins of Blue and Green Emissions in Sol-Gel ZnO Thin Films. Vacuum 2022, 202, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Znaidi, L. Sol–Gel-Deposited ZnO Thin Films: A Review. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 174, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musat, V.; Teixeira, B.; Fortunato, E.; Monteiro, R.C.C.; Vilarinho, P. Al-doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 180–181, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doni Pon, V.; Joseph Wilson, K.S.; Hariprasa, K.; Ganesh, V.; Elhosiny Ali, E.; Algarni, H.; Yahia, I.S. Enhancement of optoelectronic properties of ZnO thin films by Al doping for photodetector applications. Superlattices Microstruct. 2021, 151, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, V.; Kumar, M.; Kim, J.; Chung, H.J.; Yun, J.H. Persistent photoconductivity in Al-doped ZnO photoconductors under air, nitrogen and oxygen ambiance: Role of oxygen vacancies induced DX centers. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 8561–8590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Qin, F.; Shi, Z.; Xu, C. Burstein-Moss Effect Behind Au Surface Plasmon Enhanced Intrinsic Emission of ZnO Microdisks. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, D.C.; Mohanta, S.K.; Cho, H.K. A comparative analysis of deep level emission in ZnO layers deposited by various methods. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 013502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.P.; Tang, H.P.; Ye, Z.Z.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhao, B.H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.H. Temperature-dependent photoluminescence of quasialigned Al-doped ZnO nanorods. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 023104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusco, R.; Alarcon-Llado, E.; Ibanez, J.; Artus, L.; Jimenez, J.; Wang, B.; Callahan, M.J. Temperature dependence of Raman scattering in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 165202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Ghidelli, M.; Gondoni, P.; Casari, C.S.; Li Bassi, A. Multi-wavelength Raman scattering of nanostructured Al-doped zinc oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 073508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.Y. Memristor with Ag-Cluster-Doped TiO2 Films as Artificial Synapse for Neuroinspired Computing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, L.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D.; Pi, X. Optoelectronic Synaptic devices for Neuromorphic Computing. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, F.; Ji, X. Optical and electrical properties of Al-doped ZnO thin films by atomic layer deposition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 21, 17365–17374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, H.L.; Kim, Y.; Lee, T.W. Organic electronic synapses with low energy consumption. Joule 2021, 5, P794–P810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.J.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, E.H.; Kang, M.; Wang, G.; Kim, T.W. Ultrathin Conformable Organic Artificial Synapse for Wearable Intelligent Device Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, W. The Evolution of Silicon Wafer Cleaning Technology. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, D.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.-N. Enhanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Performance in Sol–Gel Derived Al-Doped ZnO Thin Film Devices. Materials 2025, 18, 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132931
Jeon D, Lee SH, Lee S-N. Enhanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Performance in Sol–Gel Derived Al-Doped ZnO Thin Film Devices. Materials. 2025; 18(13):2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132931
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Dabin, Seung Hun Lee, and Sung-Nam Lee. 2025. "Enhanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Performance in Sol–Gel Derived Al-Doped ZnO Thin Film Devices" Materials 18, no. 13: 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132931
APA StyleJeon, D., Lee, S. H., & Lee, S.-N. (2025). Enhanced Optoelectronic Synaptic Performance in Sol–Gel Derived Al-Doped ZnO Thin Film Devices. Materials, 18(13), 2931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132931






