Anomalous Precipitation of the γ-Fe Phase in Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Alloys and Its Impact on Soft Magnetic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
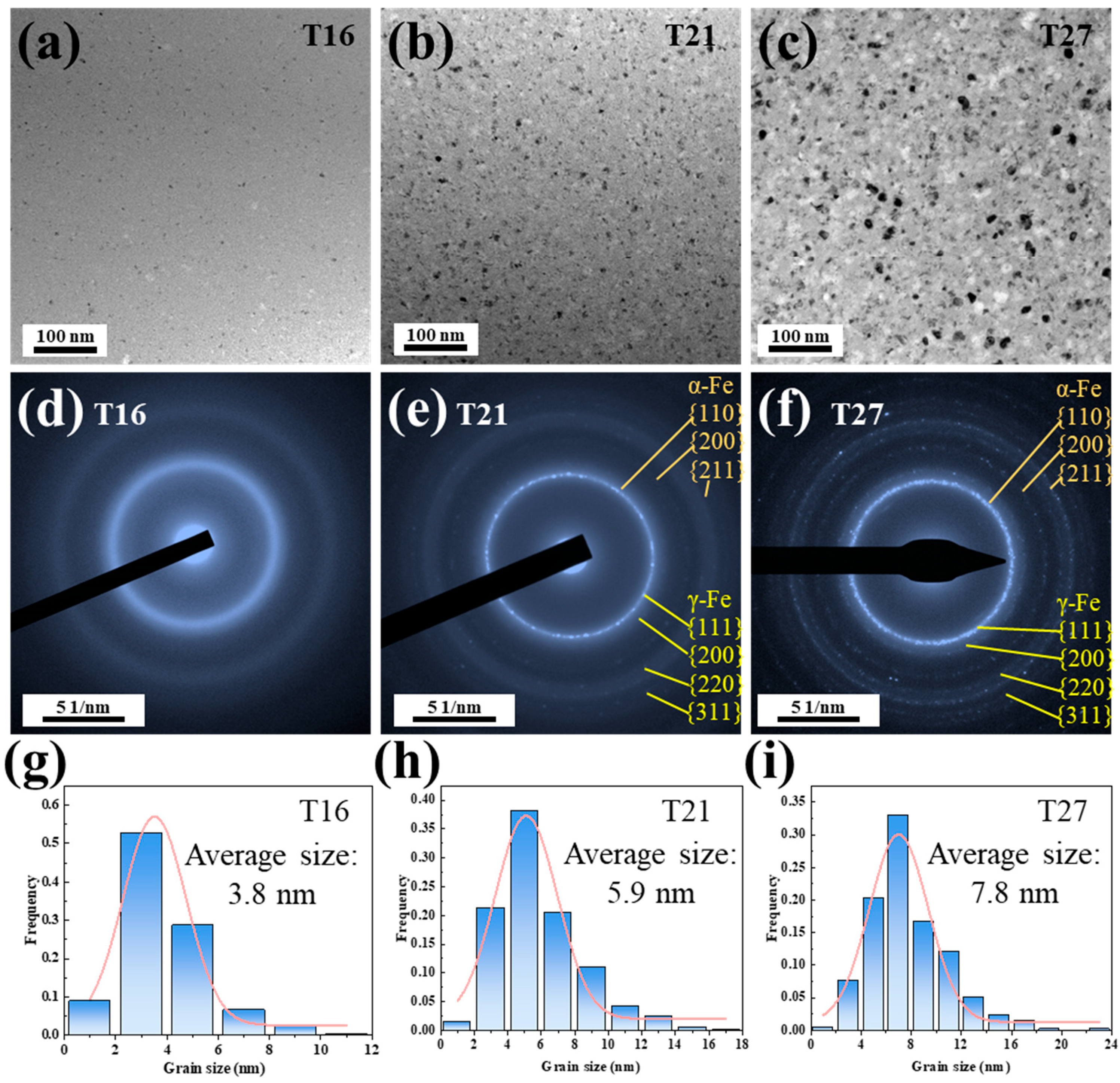
3.1. Microstructure and Thermal Properties
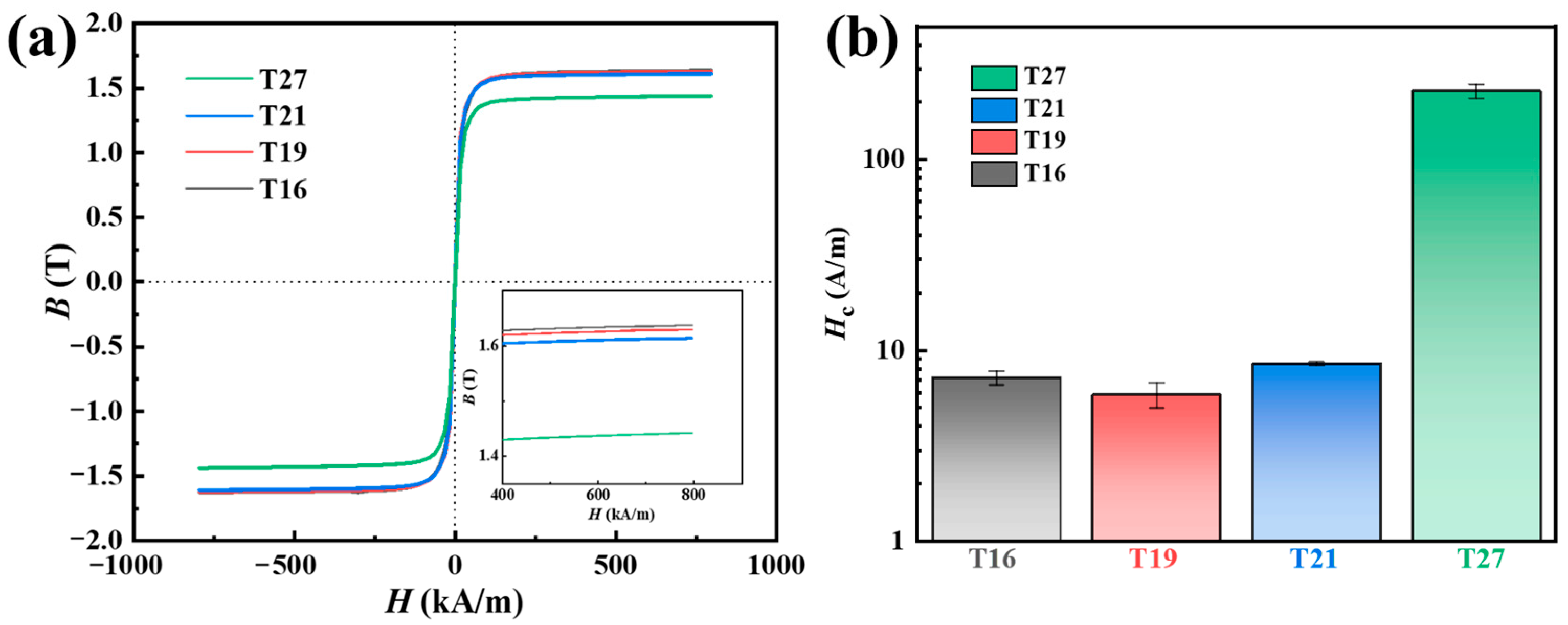
3.2. Crystallization Behavior and Magnetic Properties
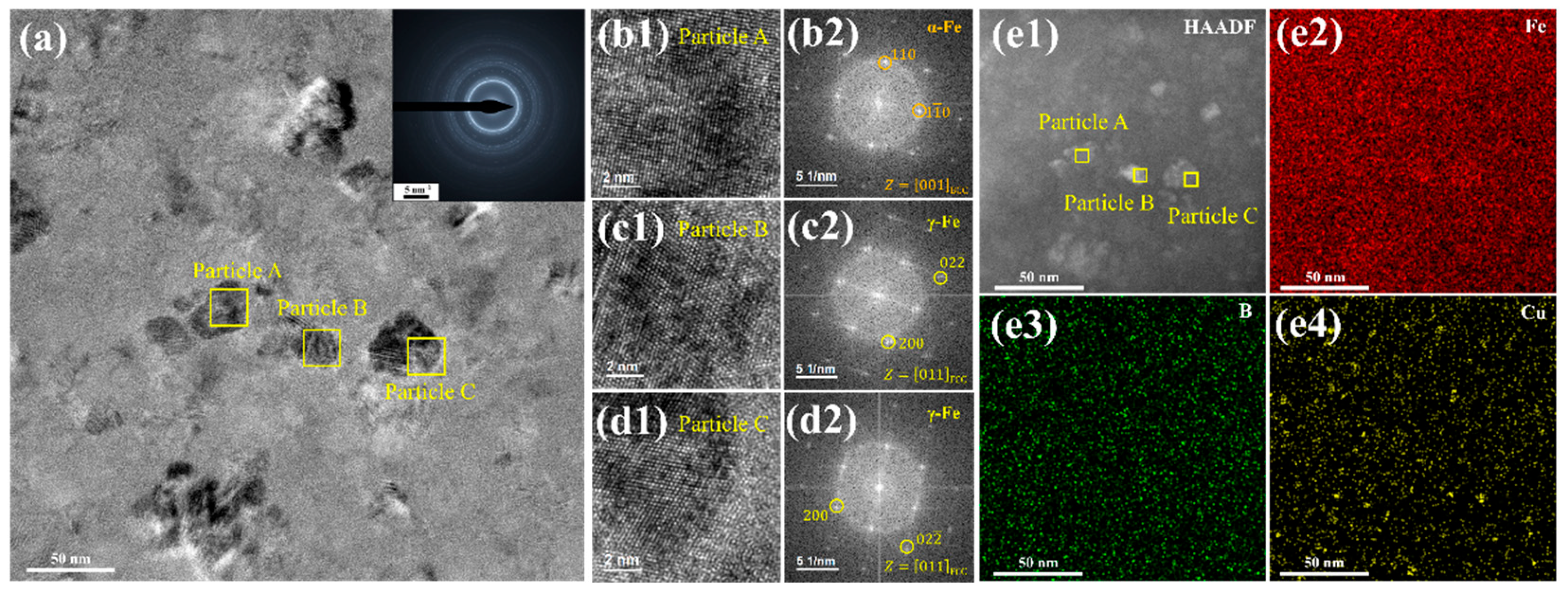
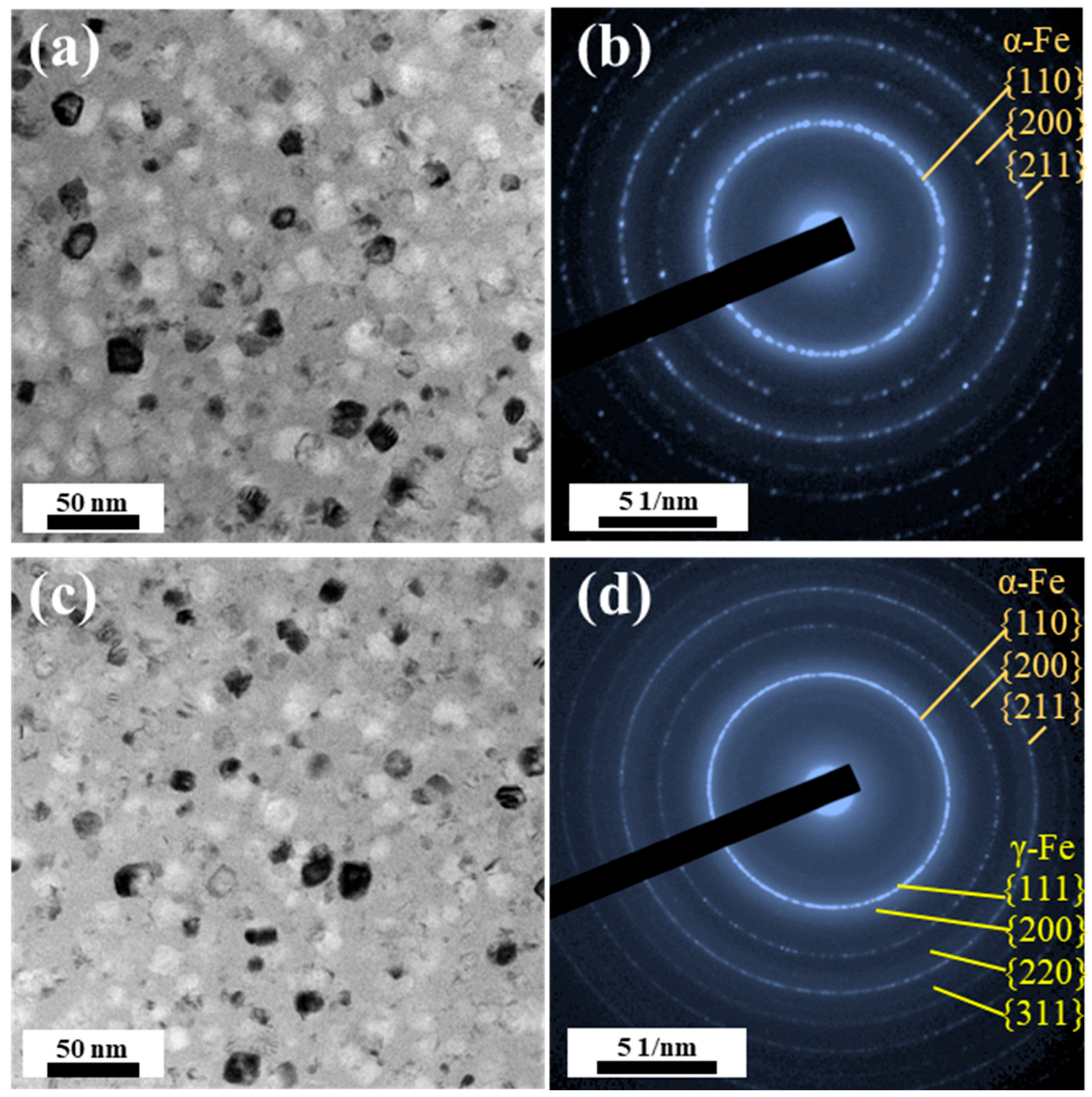
3.3. Formation of the γ-Fe Phase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silveyra, J.M.; Ferrara, E.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C. Soft magnetic materials for a sustainable and electrified world. Science 2018, 362, eaao0195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Shi, L.; Chen, S.; Shao, Y.; Chen, N.; Jia, J.-L. Research progress and application prospect of Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys. Acta Phys. Sin. 2018, 67, 016101. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Li, D.; Cai, M.; Di, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, Q.; Shen, B. Excellent magnetic softness-magnetization synergy and suppressed defect activation in soft magnetic amorphous alloys by magnetic field annealing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 116, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Modern soft magnets: Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 718–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzer, G. Anisotropies in soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 294, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheiratmand, T.; Hosseini, H.R.M. Finemet nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloy: Investigation of glass forming ability, crystallization mechanism, production techniques, magnetic softness and the effect of replacing the main constituents by other elements. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 408, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Makino, A.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Low core losses of nanocrystalline Fe–M–B (M = Zr, Hf, or Nb) alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 74, 3316–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.; Kataoka, N.; Inoue, A.; Makino, A.; Masumoto, T. High Saturation Magnetization and Soft Magnetic Properties of bcc Fe–Zr–B Alloys with Ultrafine Grain Structure. Mater. Trans. 1990, 31, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, Y.; Oguma, S.; Yamauchi, K. New Fe-based soft magnetic alloys composed of ultrafine grain structure. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6044–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Shao, Y.; Jia, J.; Lu, C.; Yao, K. Roles of Cu in Fe-based soft magnetic nanocrystalline alloys with high Fe content. Intermetallics 2024, 166, 108202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G.; Qiu, Z.; Luan, J.; Jiao, Z. Formation and crystallization behavior of Fe-based amorphous precursors with pre-existing α-Fe nanoparticles—Structure and magnetic properties of high-Cu-content Fe-Si-B-Cu-Nb nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 65, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Yoshizawa, Y. Cu addition effect on soft magnetic properties in Fe-Si-B alloy system. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 07E722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Ohkubo, T.; Ohta, M.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Hono, K. Three-dimensional atom probe study of Fe–B-based nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4463–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, L.; Zhang, W. The role of Cu content on structure and magnetic properties of Fe–Si–B–P–Cu nanocrystalline alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 54, 4400–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, Y.; Yubuta, K.; He, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Optimization of the structure and soft magnetic properties of a Fe87B13 nanocrystalline alloy by additions of Cu and Nb. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 166001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, D.; Ito, N.; Ohta, M. Recent progress in Fe-based amorphous and nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 501, 166373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-C.; Li, Y.-H.; Jia, X.-J.; He, A.-N.; Zhang, W. Effects of Ribbon Thickness on Structure and Soft Magnetic Properties of a High-Cu-Content FeBCuNb Nanocrystalline Alloy. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2021, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, Y. Estimation of critical cooling rates for formation of amorphous alloys from critical sizes. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Johnson, W.L. Formation of Ti–Zr–Cu–Ni bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 6514–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Kalb, J.A.; Thompson, C.V. Matching Glass-Forming Ability with the Density of the Amorphous Phase. Science 2008, 322, 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, H.; Luan, H.; Kang, J.; Jia, J.; Guo, W.; Su, Y.; Ding, H.; Chang, H.-S.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y.; et al. Accessing ultrastable glass via a bulk transformation. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Overney, G.; Toma, D. Structural properties of Fe crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, M.; Yoshizawa, Y. High Bs nanocrystalline Fe84−x−yCuxNbySi4B12 alloys (x = 0.0–1.4, y = 0.0–2.5). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 2220–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.X.; Song, Z.B.; Jain, A.; Wang, Y.G. Influence of Nb substitution for B on the microstructure, crystallization behavior and soft magnetic properties of FeBPCu alloys by two-step annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkova, D.A.; Bazlov, A.I.; Zanaeva, E.N.; Churyumov, A.Y.; Strochko, I.V.; Ubyivovk, E.V.; Inoue, A. (Fe-Ni)-based glassy alloy containing Nb and Cu with excellent soft magnetic properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 609, 122234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Tsukawaki, H.; Sakai, T.; Jonas, J.J. Effect of particle/matrix interfacial character on the high-temperature deformation and recrystallization behavior of Cu with dispersed Fe particles. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 4944–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Hu, C.; Mei, Y.; Hong, A.; Yang, Y.; Xu, K.; Yu, T.; Luo, X. Strain-induced fcc Fe nanocrystals confined in Al2O3 matrix. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 727, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memmel, N.; Detzel, T. Growth, structure and stability of ultrathin iron films on Cu(001). Surf. Sci. 1994, 307–309, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhou, N.; Rong, Y.; Chen, S.; Hsu, T.Y.; Zuyao, X. Size effect on the Fe nanocrystalline phase transformation. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, F.; Kaufmann, A.R. Magnetic Studies of Solid Solutions. I. Methods of Observations and Preliminary Results on the Precipitation of Iron from Copper. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, G.C.; Xu, X.Q.; Zhou, Y.H. Rapid solidification of bulk undercooled hypoperitectic Fe–Cu alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Phase Composition | Dav/Dα-Fe (nm) | Bs (T) | Hc (A/m) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Near Wheel | Near Free | Near Wheel | Near Middle | Near Free | |||
| T16 | Amorphous + α-Fe | Amorphous + α-Fe | 34.6 | 13.4 | 15.8 | 1.82 | 8.3 ± 0.1 |
| T19 | Amorphous + α-Fe | Amorphous + α-Fe | 34.8 | / | 14.3 | 1.76 | 13.6 ± 1.1 |
| T21 | Amorphous + α-Fe | Amorphous + α-Fe + micro γ-Fe | 34.2 | 10.9 | 14.1 | 1.72 | 38.4 ± 0.6 |
| T27 | Amorphous + α-Fe | Amorphous + α-Fe + γ-Fe + Fe3B | 34.2 | / | / | 1.60 | 455.9 ± 2.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Shi, L.; Wang, R.; Jia, J.; Guo, W.; Su, Y.; Bu, H.; Xiang, S.; Yang, W.; Fu, M.; et al. Anomalous Precipitation of the γ-Fe Phase in Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Alloys and Its Impact on Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122867
Wu Y, Shi L, Wang R, Jia J, Guo W, Su Y, Bu H, Xiang S, Yang W, Fu M, et al. Anomalous Precipitation of the γ-Fe Phase in Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Alloys and Its Impact on Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122867
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, You, Lingxiang Shi, Ranbin Wang, Jili Jia, Wenhui Guo, Yunshuai Su, Hengtong Bu, Siqi Xiang, Weihong Yang, Mingli Fu, and et al. 2025. "Anomalous Precipitation of the γ-Fe Phase in Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Alloys and Its Impact on Soft Magnetic Properties" Materials 18, no. 12: 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122867
APA StyleWu, Y., Shi, L., Wang, R., Jia, J., Guo, W., Su, Y., Bu, H., Xiang, S., Yang, W., Fu, M., Shao, Y., & Yao, K. (2025). Anomalous Precipitation of the γ-Fe Phase in Fe-Based Nanocrystalline Alloys and Its Impact on Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials, 18(12), 2867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122867






