Prediction of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Compressive Strength Based on Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Prediction Model Development
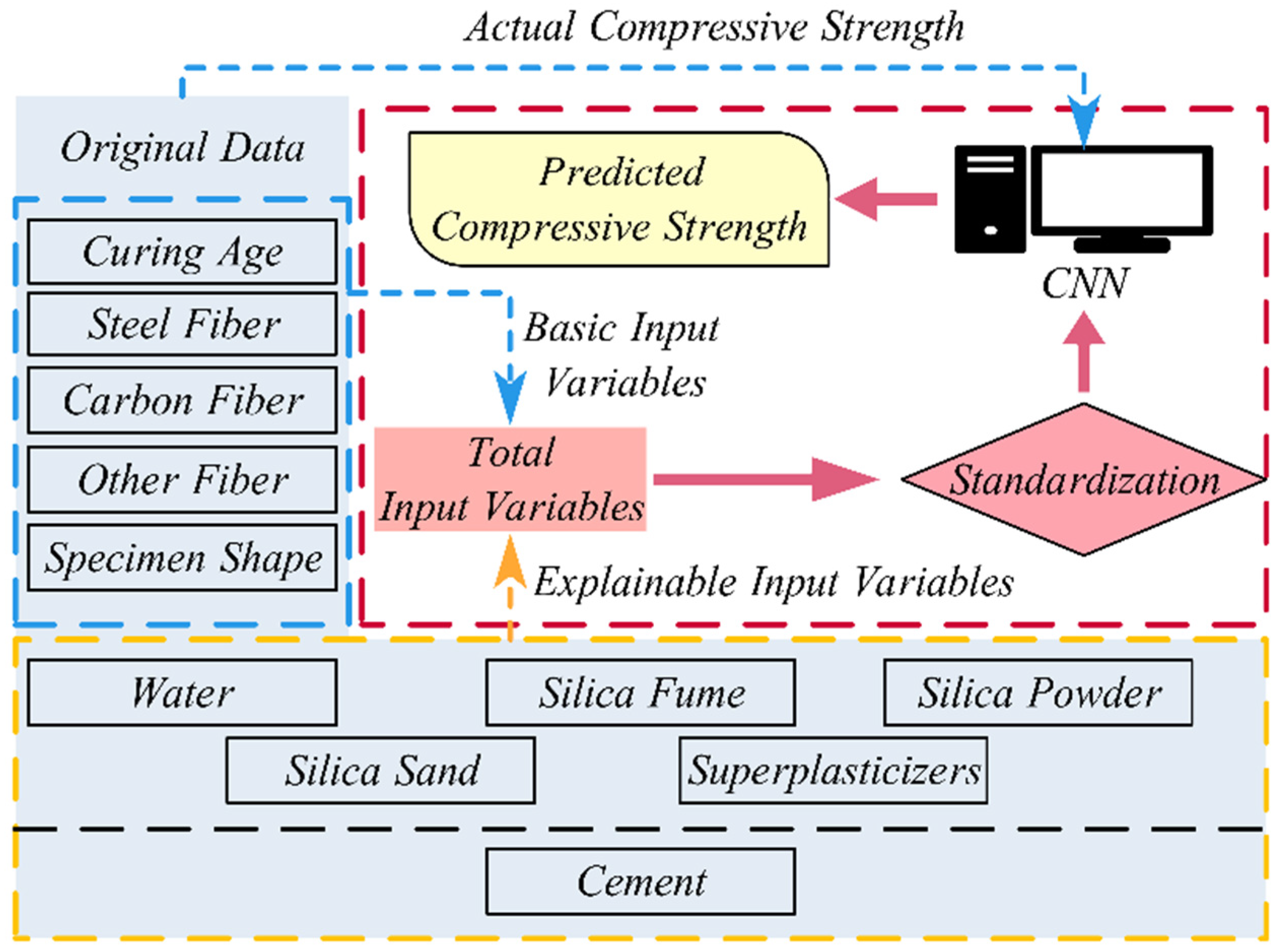
2.1. Data Sources and Information Processing
2.1.1. Data Sources
2.1.2. Data Processing
2.2. Prediction Model Development and Detailed Information
2.2.1. CNN Model Structure
2.2.2. Detailed Information on CNN Model
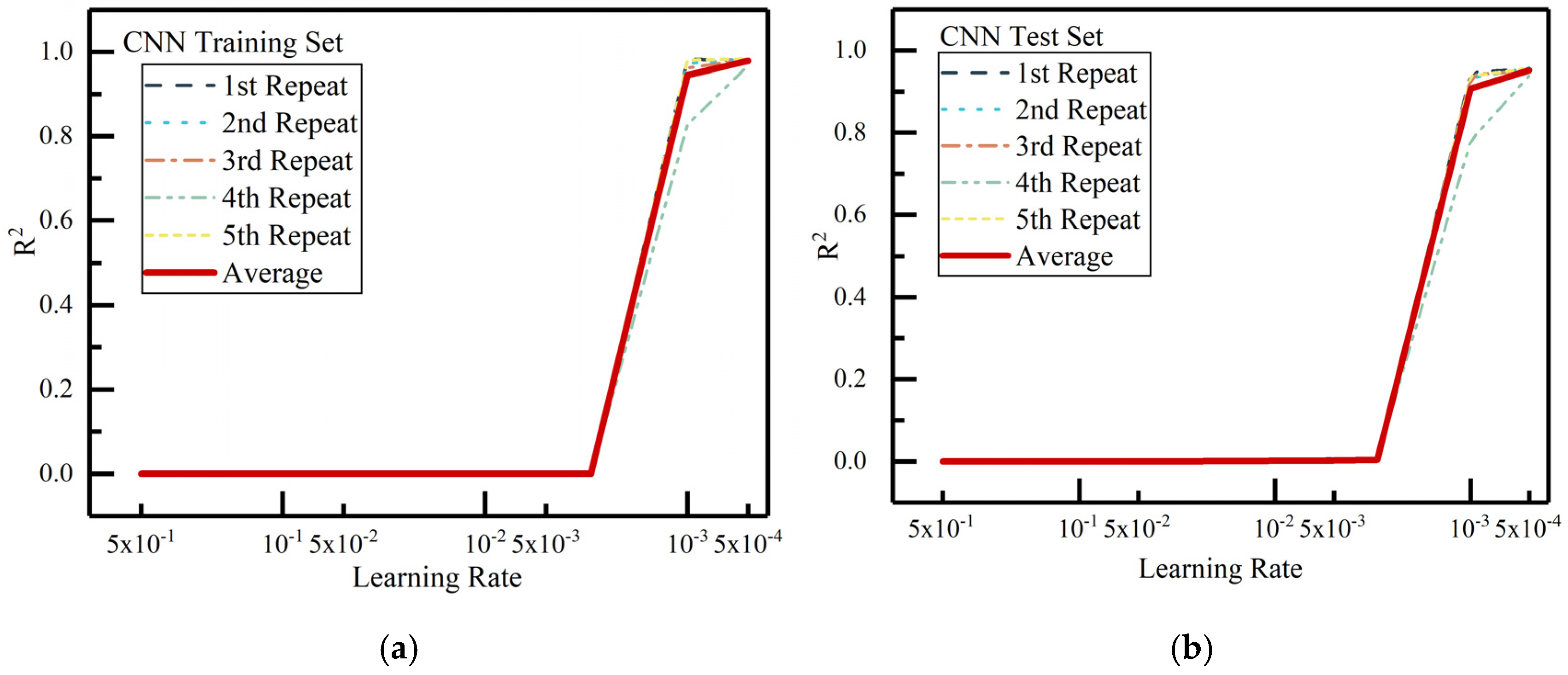
2.2.3. Evaluation Metrics for CNN Model Training
3. Model Prediction Results and Analysis
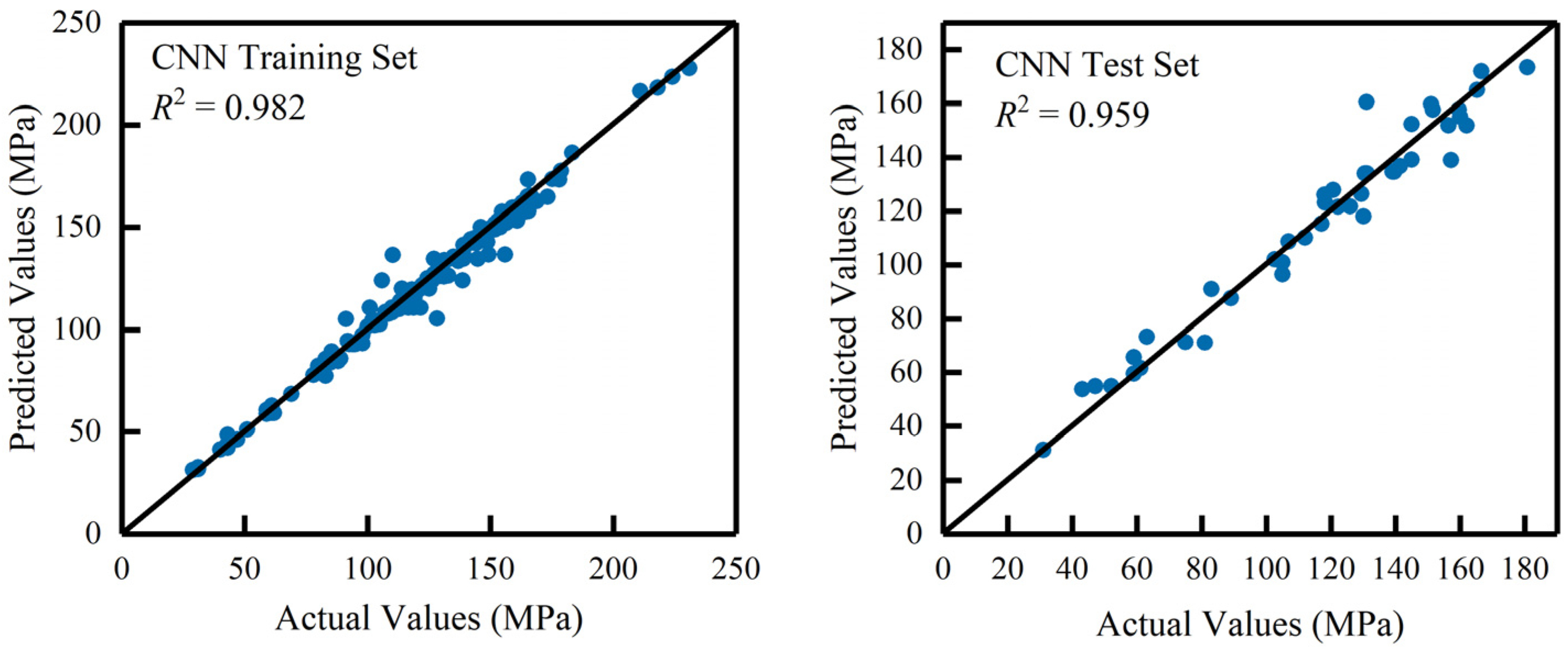
3.1. CNN Model Prediction Performance
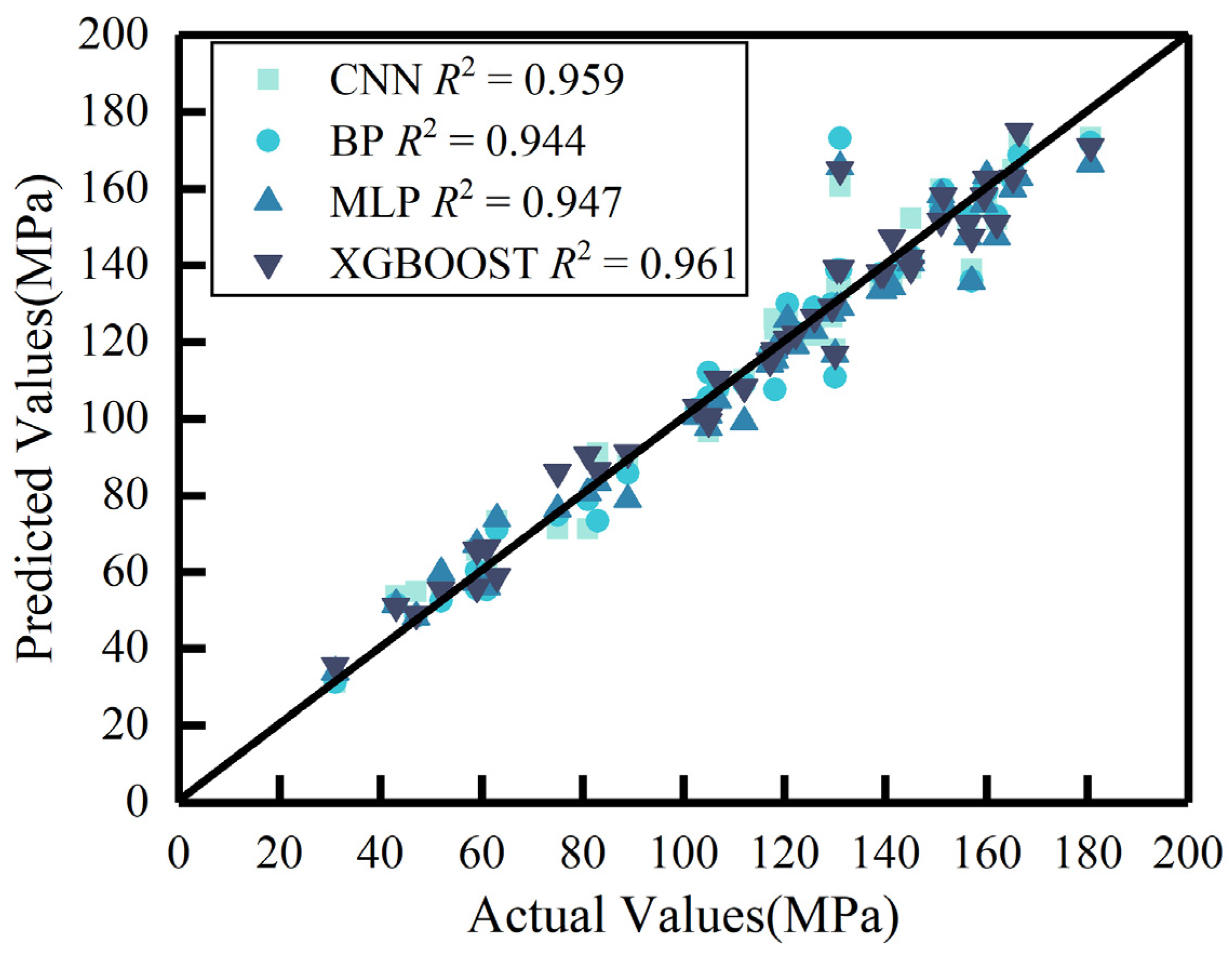
3.2. Comparison of CNN with Other Common Machine Learning Methods
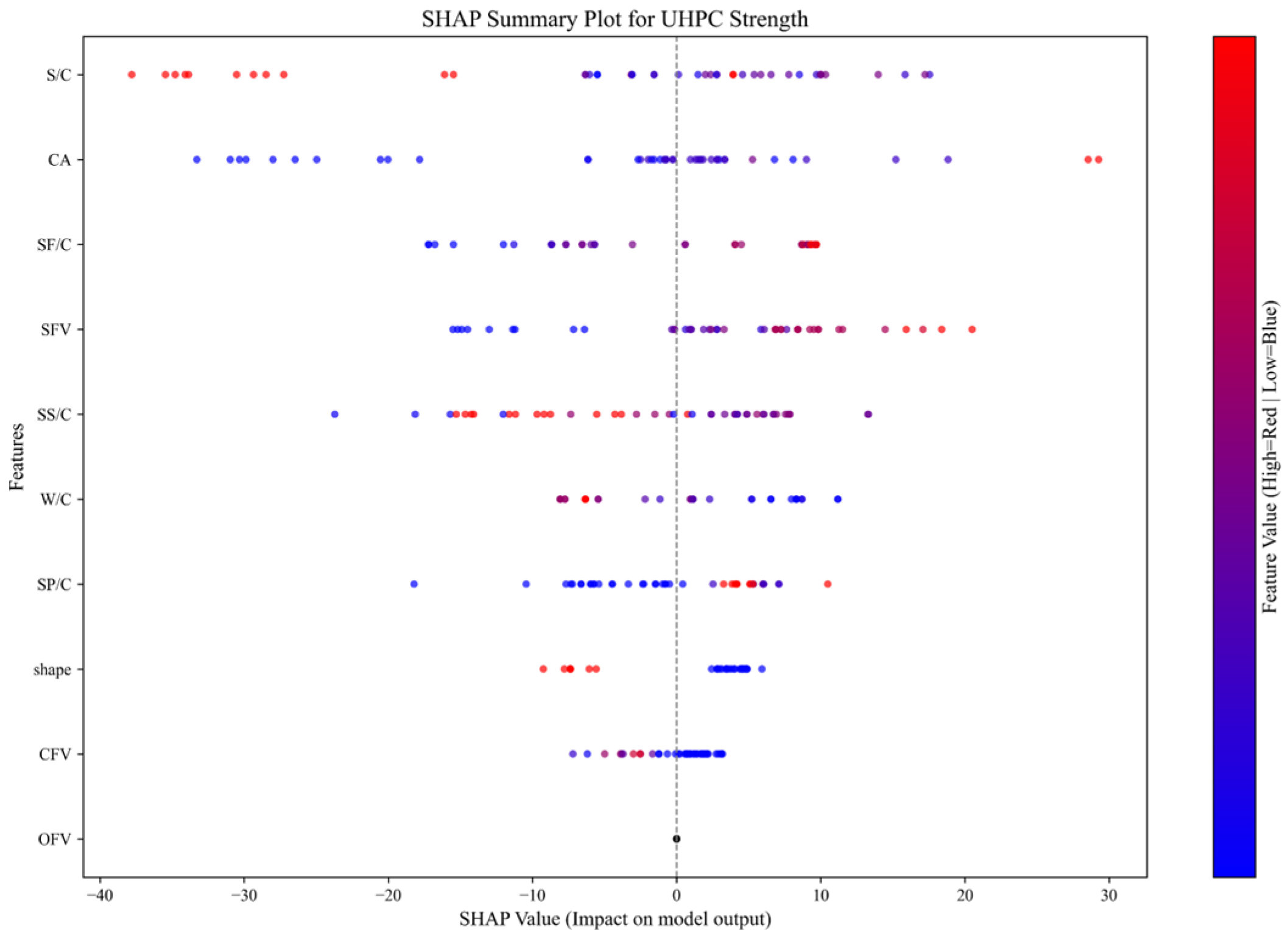
3.3. Interpretability of the CNN Model
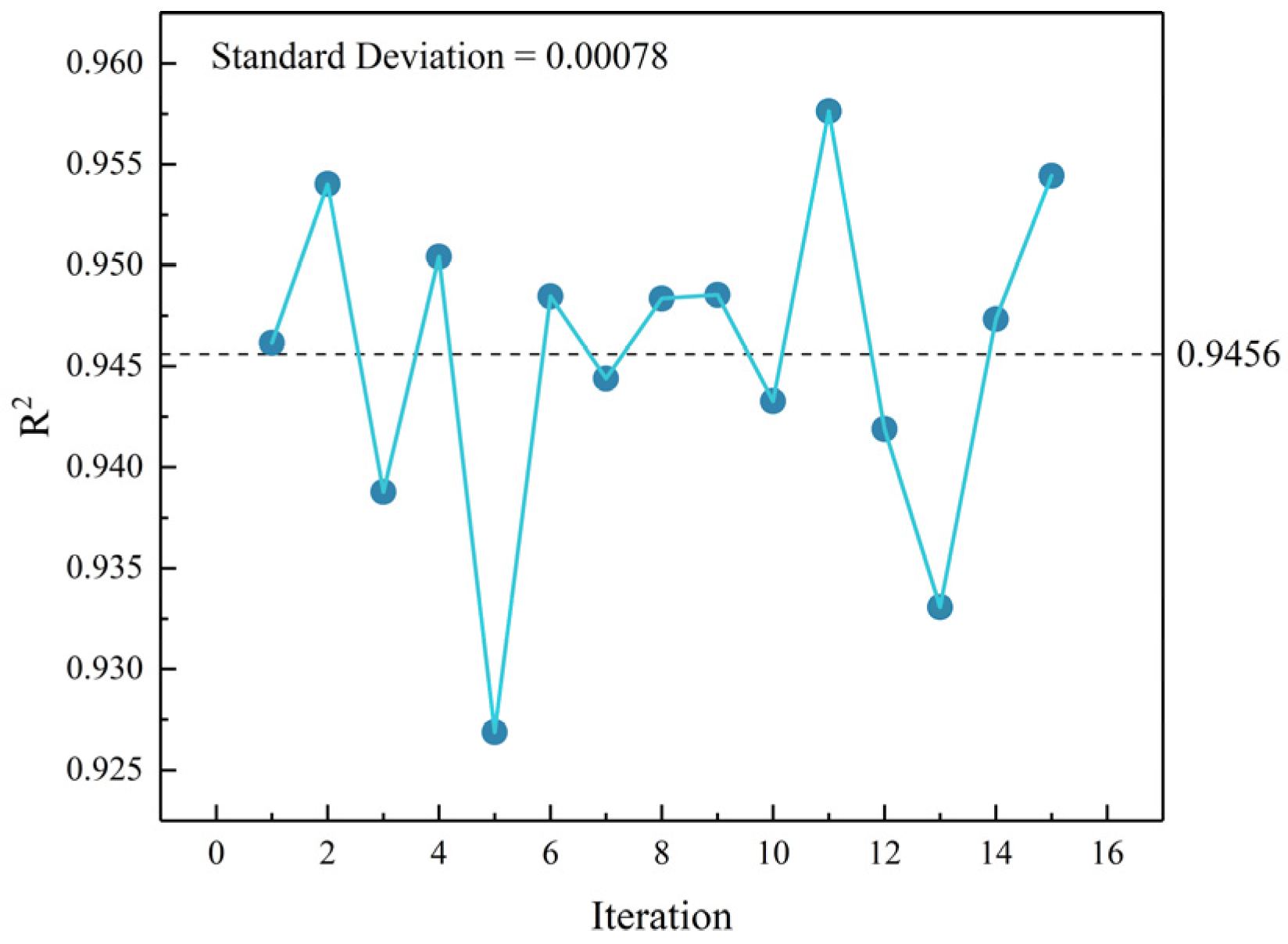
3.4. Stability of the CNN Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qaidi, S.M.A.; Atrushi, D.S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Ahmed, H.U.; Faraj, R.H.; Emad, W.; Tayeh, B.A.; Najm, H.M. Ultra-high-performance geopolymer concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.-Y.; Oh, T.; Banthia, N. Nanomaterials in ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC)—A review. Cement Concr. Comp. 2022, 134, 104730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal, S.; Mansour, W.; Agwa, I.; Nasr, M.; Abadel, A.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Akeed, M.H. Application of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete in Bridge Engineering: Current Status, Limitations, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Buildings 2023, 13, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Wang, B.; Zhu, H.T.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.Z.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhou, X.M. Ultra-high performance concrete: Mix design, raw materials and curing regimes-A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Huang, S.S.; Onaizi, A.M.; Makul, N.; Abdelgader, H.S.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Recent trends in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Current status, challenges, and future prospects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 352, 129029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeyad, A.M.; Hakeem, I.Y.; Amin, M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Agwa, I.S. Effect of aggregate and fibre types on ultra-high-performance concrete designed for radiation shielding. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 58, 104960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Hakeem, I.Y.; Zeyad, A.M.; Tayeh, B.A.; Maglad, A.M.; Agwa, I.S. Influence of recycled aggregates and carbon nanofibres on properties of ultra-high-performance concrete under elevated temperatures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Rui, Y.; Shui, Z.H.; Fan, D.Q.; Wang, J.N.; Yu, Y.H.; Luo, Q.Q.; Hong, X. Development of an environmental Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC) incorporating carbonated recycled coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 362, 129657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Rui, Y.; Shui, Z.H.; Fan, D.Q.; Wang, J.N.; Yu, Y.H.; Luo, Q.Q.; Hong, X. Effect of carbon nanotube and graphite nanoplatelet on composition, structure, and nano-mechanical properties of C-S-H in UHPC. Cement Concr. Res. 2022, 154, 106713. [Google Scholar]
- Lao, J.C.; Ma, R.Y.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.N.; Yao, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Xie, T.Y.; Huang, B.T. Fly ash-dominated High-Strength Engineered/Strain-Hardening Geopolymer Composites (HS-EGC/SHGC): Influence of alkalinity and environmental assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 447, 141182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.A.; Ahmed, N.; Almeshal, I.; Tayeh, B.A.; Elgamal, M.S. Experimental study and theoretical prediction of mechanical properties of ultra-high-performance concrete incorporated with nanorice husk ash burning at different temperature treatments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75380–75401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.H.; Ma, Y.W.; Fu, J.Y.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, X.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, H. Utilization of fibers in ultra-high performance concrete: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 241, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.Y.; Liu, J.Z.; Yang, K.; Zhang, S.H.; Han, F.Y.; Sha, J.F.; Zheng, X. Role of silica fume on hydration and strength development of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.S.; Gao, X.J.; Zhang, H.Z. Utilization of hybrid sisal and steel fibers to improve elevated temperature resistance of ultra-high performance concrete. Cement Concr. Comp. 2022, 130, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, J.C.; Xu, L.Y.; Huang, B.T.; Dai, J.G.; Shah, S.P. Strain-hardening Ultra-High-Performance Geopolymer Concrete (UHPGC): Matrix design and effect of steel fibers. Compos. Commun. 2020, 30, 101081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.Z.; Gu, M.G.; Zhang, S.F.; Jiang, H.B.; Fang, Z.C.; Hu, J.X. Effects of Steel Fiber and Specimen Geometric Dimensions on the Mechanical Properties of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Wang, B.N.; Hubler, M.H. Carbon nanofibers (CNFs) dispersed in ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Mechanical property, workability and permeability investigation. Cement Concr. Comp. 2022, 131, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.T.; Zhu, J.X.; Weng, K.F.; Li, V.C.; Dai, J.G. Ultra-high-strength engineered/strain-hardening cementitious composites (ECC/SHCC): Material design and effect of fiber hybridization. Cement Concr. Comp. 2022, 129, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.C.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.W. Influence of fibers on the mechanical properties and durability of ultra-high-performance concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 52, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Wei, Q.A.; Shang, H.S.; Liu, X.Y. Creep behaviour of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC): A review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 69, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakeem, I.Y.; Amin, M.; Abdelsalam, B.A.A.; Tayeh, B.A.; Althoey, F.; Agwa, I.S. Effects of nano-silica and micro-steel fiber on the engineering properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2022, 82, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Bennett, T.; Visintin, P. Plastic and early-age shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Experimental study of the effect of water to binder ratios, silica fume dosages under controlled curing conditions. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Y.; Huang, B.T.; Lao, J.C.; Dai, J.G. Tailoring strain-hardening behavior of high-strength Engineered Cementitious Composites (ECC) using hybrid silica sand and artificial geopolymer aggregates. Mater. Des. 2020, 220, 110876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Wu, M.M.; Shen, W.G.; Li, J.W.; Zhao, D.Q.; Li, P.F.; Wu, J.L. Performance and microstructure of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) with silica fume replaced by inert mineral powders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.S.; Tang, J.H.; Hu, X.; Yu, C.; Han, F.Y.; Sun, S.W.; Deng, W.L.; Liu, J.P. The influence of curing regimes on hydration, microstructure and compressive strength of ultra-high performance concrete: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, E.L.; Fu, S.Y.; Wu, C.Q.; Lv, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Feng, Y.; Shui, Z.H.; Yu, R. Value-added utilization of phosphogypsum industrial by-products in producing green Ultra-High performance Concrete: Detailed reaction kinetics and microstructure evolution mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, H.; Mostofinejad, D. Microstructure of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC)—A review study. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 50, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Xiang, Y. Behavior and constitutive model of ultra-high-performance concrete under monotonic and cyclic tensile loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.W.; Song, R.T.; Li, J.; Guo, T.F.; Li, X.D.; Yang, J.C.; Yan, Z.X. Effect of steel fiber type and content on the dynamic tensile properties of ultra-high performance cementitious composites (UHPCC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabduljabbar, H.; Khan, M.; Awan, H.H.; Eldin, S.M.; Alyousef, R.; Mohamed, A.M. Predicting ultra-high-performance concrete compressive strength using gene expression programming method. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e02074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.S.; Tang, J.H.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.C.; Yu, C.; Han, F.Y.; Liu, J.P. Influence of silica fume and thermal curing on long-term hydration, microstructure and compressive strength of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 395, 132370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.S.; Chen, G.F.; Gao, J.M. Elucidating the role of recycled concrete powder in low-carbon ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC): Multi-performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 441, 137520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.S.; Diao, C.R.; Wang, X.W.; Qing, L.B. Effect of the orientation of steel fiber on the strength of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 406, 133431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, B.C.; Liu, B.; Li, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, J.J.; Ding, P. Using rice husk ash in alkali-activated ultra-high-performance concrete: Flowability, early age strength and elasticity modulus. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 443, 137771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berloco, F.; Bevilacqua, V.; Colucci, S. Distributed Analytics for Big Data: A Survey. Neurocomputing 2024, 574, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Kumar, A. Survey of Deep-Learning Techniques in Big-Data Analytics. Wireless Pers. Commun. 2022, 126, 1321–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.M. Development of hybrid SVM-FA, DT-FA and MLR-FA models to predict the flexural strength (FS) of recycled concrete. Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1159079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadesh, P.; Khan, A.H.; Priya, B.S.; Asheeka, A.; Zoubir, Z.; Magbool, H.M.; Alam, S.; Bakather, O.Y. Artificial neural network, machine learning modelling of compressive strength of recycled coarse aggregate based self-compacting concrete. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P.J.; Pan, F. Machine-Learning-Based Comprehensive Properties Prediction and Mixture Design Optimization of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Kashem, A. Hybrid machine learning approach to prediction of the compressive and flexural strengths of UHPC and parametric analysis with shapley additive explanations. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Nguyen, T.A.; Ly, H.B. Ensemble XGBoost schemes for improved compressive strength prediction of UHPC. Structures 2023, 57, 105062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, J. Graph Neural Network for Traffic Forecasting: A Survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 207, 117921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaka, V.S.; Meena, S.V.; Rani, G.; Sinwar, D.; Kavita, K.; Ijaz, M.F.; Woźniak, M. A Survey of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Applied for Prediction of Plant Leaf Diseases. Sensors 2021, 21, 4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwartz-Ziv, R.; Armon, A. Tabular Data: Deep Learning Is Not All You Need. Inf. Fusion 2022, 81, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, R.Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.H. Comparative study on the effect of steel and plastic synthetic fibers on the dynamic compression properties and microstructure of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Compos. Struct. 2023, 324, 117570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocelić, A.; Baričević, A.; Smrkić, M.F. Synergistic integration of waste fibres and supplementary cementitious materials to enhance sustainability of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2024, 20, e02772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Li, W.Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhou, Y.W.; Wu, H.L.; Wang, P.; Ke, L.Y.W.; Yu, J. Axial compressive behavior and failure mechanism of CFRP partially confined ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 426, 136104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Nie, X.F.; Yu, T. Compressive behavior of FRP-confined ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) and ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete (UHPFRC). Compos. Struct. 2023, 312, 116879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, G.; Yu, T.; Fernando, D. Stress-strain models for ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) and ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete (UHPFRC) under triaxial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 370, 130658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.Q.; Lu, J.X.; Liu, K.N.; Ban, J.X.; Yu, R.; Poon, C.S. Multi-scale design of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) composites with centroplasm theory. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 281, 111562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Q.; Aloisio, A.; Contento, A.; Yang, Z.X.; Hu, N.; Briseghella, B. A piece-wise linear model for modelling the tension-stiffening effect in steel-reinforced UHPC composites. Compos. Struct. 2024, 345, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiew, S.Y.; Teoh, K.B.; Raman, S.N.; Hung, C.-C.; Chaen, Y.X.; Kong, D. A unified tensile constitutive model for mono/hybrid fibre-reinforced ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC). Cement Concr. Comp. 2024, 150, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.L.; Fang, Z.; Peng, F.; Luo, H.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, Q. Behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete under combined tensile and bending action. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksefidi, S.; Ghalehnovi, M.; Brito, J.D. Bond behaviour of high-strength steel rebars in normal (NSC) and ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC). J. Build. Eng. 2021, 33, 101592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.X.; Luo, R.H.; Su, J.Y.; Guo, Y.C.; Chen, W.S. Coarse synthetic fibers (PP and POM) as a replacement to steel fibers in UHPC: Tensile behavior, environmental and economic assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412, 134654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, K.N.; Yin, T.Y.; Tang, L.W.; Ding, M.X.; Shui, Z.H. Comparative study on the effect of steel and polyoxymethylene fibers on the characteristics of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC). Cement Concr. Comp. 2022, 127, 104418. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.N.; Xu, L.H.; Yin, C.R.; Cui, K.; Chi, Y. Constitutive behavior of ultra-high-performance steel fiber reinforced concrete under monotonic and cyclic tension. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 68, 105991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Xu, L.H.; Chi, Y.; Cui, K.; Yin, C.R.; Li, B. Cyclic tensile behavior of ultra-high performance concrete with hybrid steel-polypropylene fiber: Experimental study and analytical model. Compos. Struct. 2023, 321, 117255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Wille, K. Direct tensile behavior of steel fiber reinforced ultra-high performance concrete at high strain rates using modified split Hopkinson tension bar. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 246, 110259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.P.; Qiu, J.F.; Hou, C.G.; Huang, J.J. Impact of reinforcing ratio and fiber volume on flexural hardening behavior of steel reinforced UHPC beams. Eng. Struct. 2023, 285, 116067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Yan, J.C.; Lin, Y.Z.; Fan, F. Influence of shear connectors on the ultimate capacity of steel-UHPC-steel slabs subjected to concentrated loads. Eng. Struct. 2021, 231, 111763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.Y.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Yao, W.; Wang, Z.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Wei, Y.Q.; Wei, Z.H.; Guan, X.Q. Accurate prediction of concrete compressive strength based on explainable features using deep learning. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Features | Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity [31] | 0.91 | |
| Recycled Concrete Powder/Recycled Paste Powder Content [32] | - | |
| Steel Fiber [33] | 0.87 | |
| Age [34] | 0.98 |
| Author | Main Variable |
|---|---|
| Shuo Zhao et al. [45] | Plastic synthetic fiber, steel fiber |
| Antonija Ocelić et al. [46] | Recycled tire steel fiber, carbon fiber |
| Weiwen Li et al. [47] | Fiber-reinforced polymer |
| J.J. Wang et al. [48] | Fiber-reinforced polymer |
| S.S. Zhang et al. [49] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Dingqiang Fan et al. [50] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Junqing Xue et al. [51] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Shack Yee Hiew et al. [52] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Xin TIAN et al. [28] | Steel fiber volume fraction, fiber shape |
| Zilong Tang et al. [53] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Samaneh Khaksefidi et al. [54] | Concrete strength |
| Jia-Xiang Lin et al. [55] | Polypropylene fiber, polyoxymethylene fiber |
| Yu Rui et al. [56] | Steel fiber, polyoxymethylene fiber |
| Shunan Wang et al. [57] | Steel fiber volume fraction, fiber aspect ratio |
| Shunan Wang et al. [58] | Steel–polypropylene hybrid fiber |
| Mostafa Hassan et al. [59] | Steel fiber volume fraction |
| Kewei Liu et al. [29] | Fly ash, blast furnace slag, steel fiber type |
| Yang Zhang et al. [60] | Fiber volume fraction |
| Zefang Wang et al. [61] | Steel fiber volume fraction, shear connector |
| Parameter | Original Data | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | Dealt Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | 28 | 23.018 | 22.705 | 0.219 |
| W/C | 0.230 | 0.284 | 0.103 | −0.518 |
| SS/C | 1.589 | 1.384 | 0.676 | 0.303 |
| SP/C | 0 | 0.323 | 0.503 | −0.642 |
| SF/C | 0.212 | 0.255 | 0.160 | −0.267 |
| S/C | 0.027 | 0.048 | 0.020 | −1.008 |
| SFV | 0.500 | 1.059 | 0.979 | −0.572 |
| CFV | 1.500 | 0.348 | 0.676 | 1.703 |
| OFV | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| shape | 0 | 0.361 | 0.480 | −0.751 |
| Data Set | Performance Measures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE (MPa) | MAPE (%) | MAE (MPa) | |
| Training set | 0.982 | 4.809 | 2.423 | 2.765 |
| Test set | 0.959 | 7.762 | 5.550 | 5.724 |
| Method | R2 (This Paper) | Multimodal Extensibility | R2 (From Different Studies) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 0.959 | Native image input support, no feature engineering needed | 0.967 (conventional concrete) [62] |
| XGBOOST | 0.961 | Requires manual image feature extraction | 0.973 (UHPC) [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Yu, X.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Yang, J. Prediction of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Compressive Strength Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Materials 2025, 18, 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122851
Xu L, Yu X, Zhu C, Wang L, Yang J. Prediction of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Compressive Strength Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122851
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Li, Xiaochun Yu, Chenhui Zhu, Ling Wang, and Jie Yang. 2025. "Prediction of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Compressive Strength Based on Convolutional Neural Networks" Materials 18, no. 12: 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122851
APA StyleXu, L., Yu, X., Zhu, C., Wang, L., & Yang, J. (2025). Prediction of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) Compressive Strength Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Materials, 18(12), 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122851






