Changes in Implant Surface Characteristics and Wettability Induced by Smoking In Vitro: A Preliminary Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
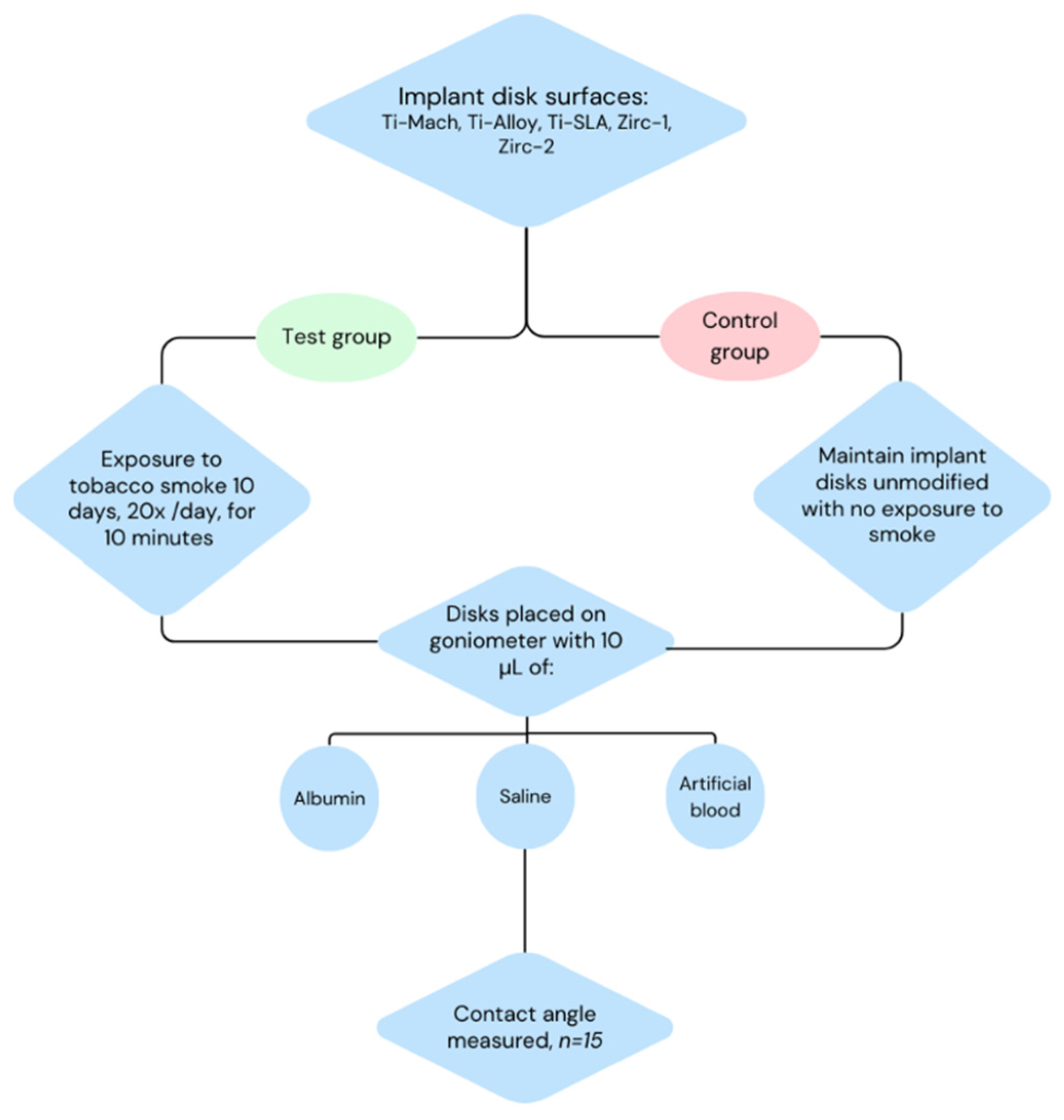
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Contact Angle Determination
2.3. Occasional Smoking, Primary Effects of Nicotine
2.4. Heavy Smoking
2.5. Surface Roughness Analysis
2.6. CRIS Guidelines
3. Results
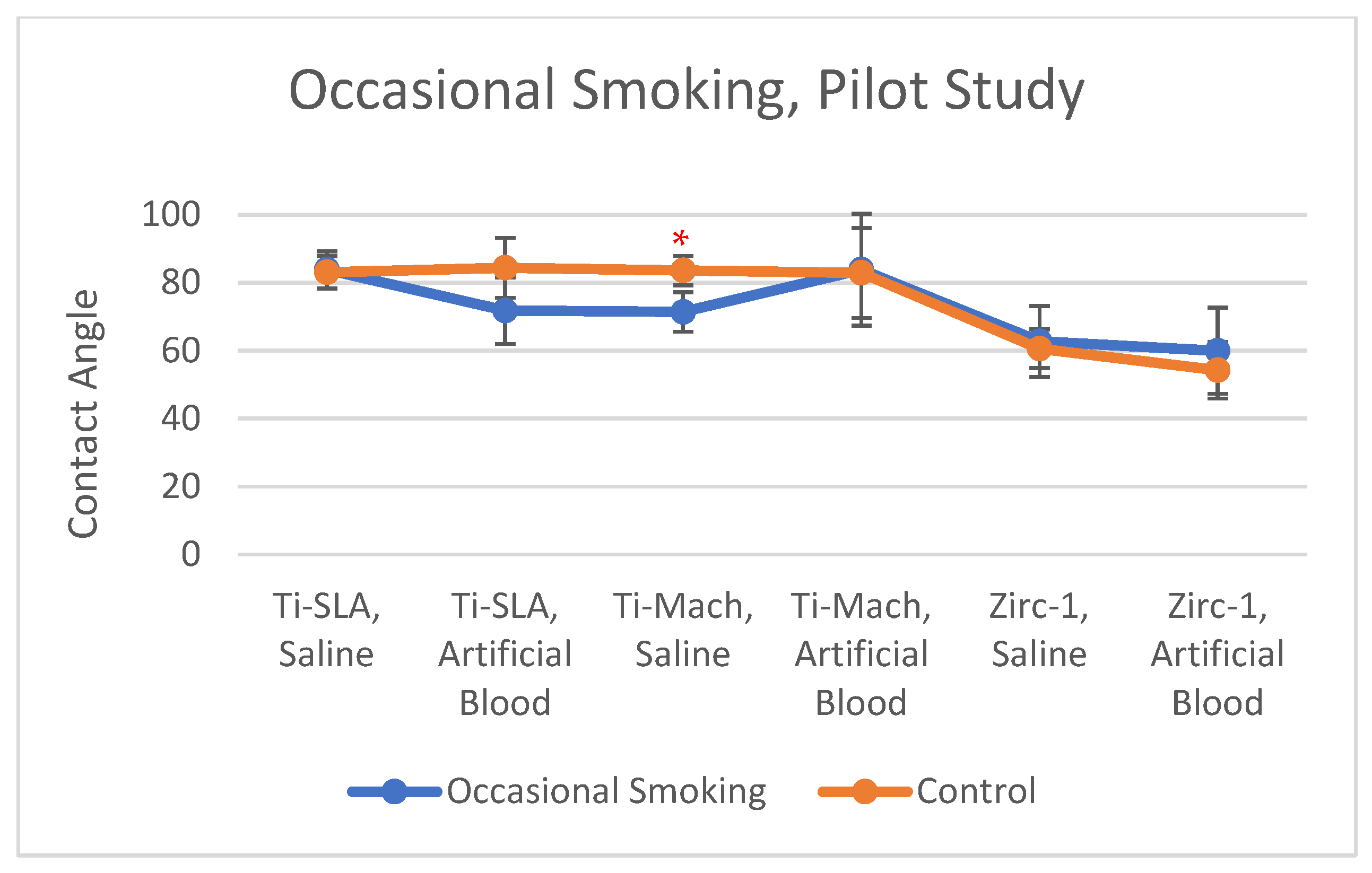
3.1. Occasional Smoking
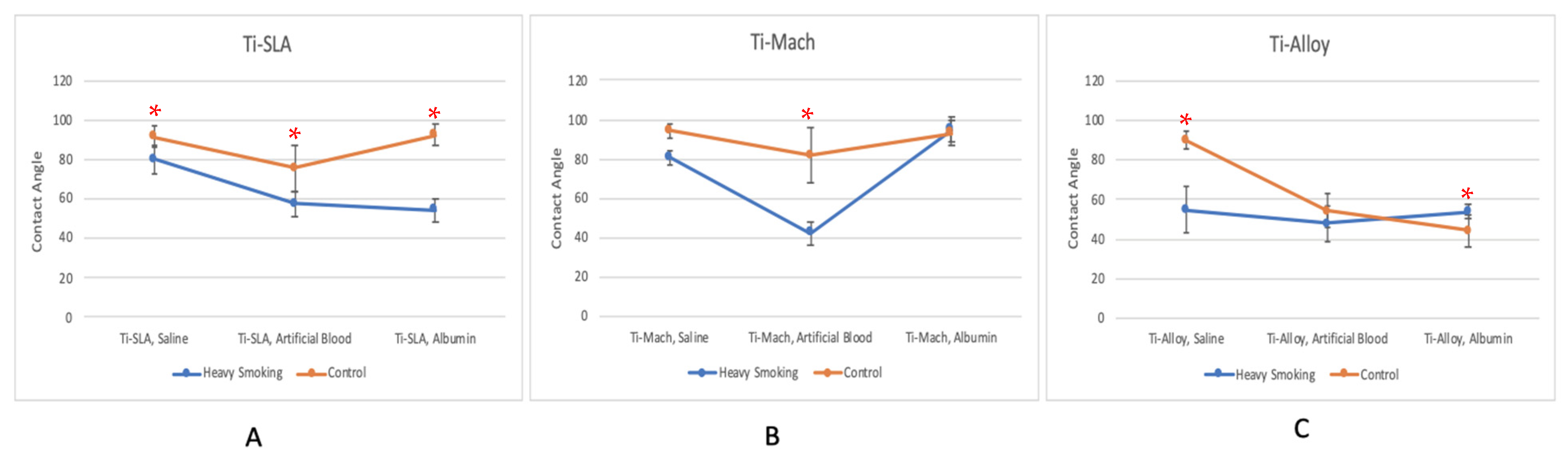
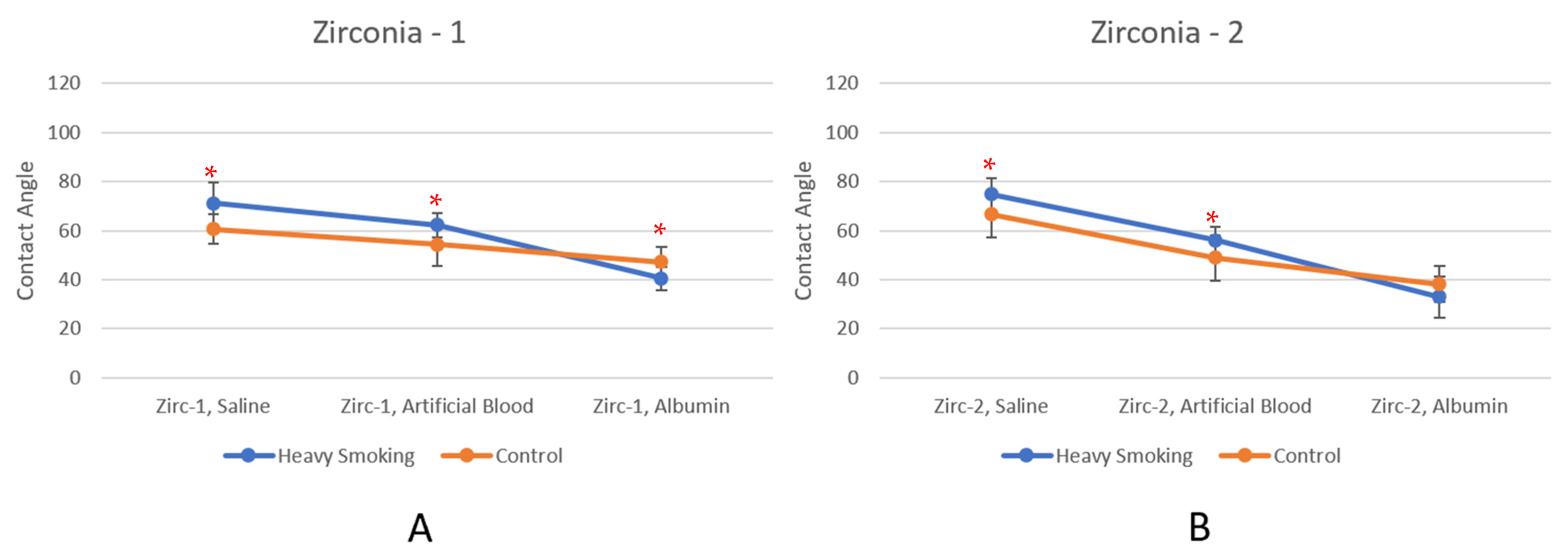
3.2. Heavy Smoking
3.3. Surface Rougness Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Vendor List
- Ossila, Sheffield, UK.
- Swiss Dental Solutions, Konstanz, Germany.
- W.O. Larsen Lotus pipe aromatic tobacco 100 g flavored by cocco, vanilla, Copenhagen, Denmark.
- Lampire Biological, Pipersville, PA, USA.
- Patent, Altendorf, Switzerland.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rupp, F.; Gittens, R.A.; Scheideler, L.; Marmur, A.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces I: Theoretical and experimental aspects. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2894–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, N.P.; Salvi, G.E.; Huynh-Ba, G.; Ivanovski, S.; Donos, N.; Bosshardt, D.D. Early osseointegration to hydrophilic and hydrophobic implant surfaces in humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 22, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gittens, R.A.; Scheideler, L.; Rupp, F.; Hyzy, S.L.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces II: Biological and clinical aspects. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, M.; Guo, W.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, X.; He, H.; et al. Surface texture fabricated by ultrafast laser treatment for manipulating wettability and cell adhesion performance of Ti6Al4V. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 489, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A. Smoking, haemostatic factors, and cardiovascular risk. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Xu, Z.; Shu, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, F. Influence of Physicochemical Characteristics on the Effective Moisture Diffusivity in Tobacco. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvers, K.; Scheuermann, T.S.; Romero, D.R.; Basora, B.; Luo, X.; Ahluwalia, J.S. Classifying a smoker scale in adult daily and nondaily smokers. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2014, 16, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krithikadatta, J.; Datta, M.; Gopikrishna, V. CRIS Guidelines (Checklist for Reporting In-vitro Studies): A concept note on the need for standardized guidelines for improving quality and transparency in reporting in-vitro studies in experimental dental research. J. Conserv. Dent. 2014, 17, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, R.; Haimböck, W.; Mailath, G.; Watzek, G. The relationship of smoking on peri-implant tissue: A retrospective study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 76, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.I.; Luime, J.J.; Uçkay, I.; Hannouche, D.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Lübbeke, A. Is there an association between smoking status and prosthetic joint infection after primary total joint arthroplasty? J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, N.; Takemoto, S.; Kawazoe, T.; Suzuki, S. Nicotine at a Low Concentration Promotes Wound Healing. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 145, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, J.; Jang, J.J.; Uma Sundram Dayoub, H.; Fajardo, L.F.; Cooke, J.P. Nicotine Accelerates Angiogenesis and Wound Healing in Genetically Diabetic Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, P. Smoking and wound healing. Am. J. Med. 1992, 93, 22S24S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hom, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Yin, W.; Rubenstein, D.A. Platelet activation, adhesion, inflammation, and aggregation potential are altered in the presence of electronic cigarette extracts of variable nicotine concentrations. Platelets 2016, 27, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretorius, E.; Oberholzer, H.M.; van der Spuy, W.J.; Meiring, J.H. Smoking and coagulation: The sticky fibrin phenomenon. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2010, 34, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royhman, D.; Dominguez-Benetton, X.; Yuan, J.C.-C.; Shokuhfar, T.; Takoudis, C.; Mathew, M.T.; Sukotjo, C. Nicotine corrosion on a Ti-6Al-4V dental implant. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, e352–e363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shao, S.Y.; Chen, W.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.M.; Qiu, J. Cigarette Smoke Extract Exposure: Effects on the Interactions between Titanium Surface and Osteoblasts. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8759568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkeyah, F.; El Sergany, O.; Shamel, M.; Al Ankily, M. Effect of conventional cigarette smoking and recent heated tobacco products on CAD/CAM restorative materials. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, M.; Jin, M.; Chen, S.; Tan, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T. Review: Osseointegration of titanium-based and zirconia implants: Novel perspective on features, influencing factors and improvements. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 16020–16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.S.; Biswas, S.; Sarangi, S.; Chaurasia, A.; Reddy, M.P.; Jose, A.T.; Kashwani, R. Impact of smoking on dental implant: A review. Bioinformation 2024, 20, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teughels, W.; Eldere, J.V.; Steenberghe Dvan Cassiman, J.J.; Fives-Taylor, P.; Quirynen, M. Influence of Nicotine and Cotinine on Epithelial Colonization by Periodontopathogens. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özlu, T.; Çelik, I.; Öztuna, F.; Bülbül, Y.; Özsu, Ş. Streptococcus pneumoniae Adherence in Rats under Different Degrees and Durations of Cigarette Smoke. Respiration 2007, 75, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baboni, F.B.; Guariza Filho, O.; Moreno, A.N.; Ribeiro, A. Influence of cigarette smoke condensate on cariogenic and candidal biofilm formation on orthodontic materials. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 138, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.S.; McGovern, J.G.; Adair, C.G.; Woolfson, A.D.; Gorman, S.P. Conditioning film and environmental effects on the adherence of Candida spp. to silicone and poly(vinylchloride) biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2001, 12, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baboni, F.B.; Barp, D.; de Azevedo Izidoro, A.C.S.; Samaranayake, L.P.; Ribeiro, A. Enhancement of Candida albicans Virulence After Exposition to Cigarette Mainstream Smoke. Mycopathologia 2009, 168, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semlali, A.; Killer, K.; Alanazi, H.; Chmielewski, W.; Rouabhia, M. Cigarette smoke condensate increases C. albicans adhesion, growth, biofilm formation, and EAP1, HWP1 and SAP2 gene expression. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, J.E.; Green, C.; Best, F.W.; Newell, M.P. Smoke composition. An extensive investigation of the water-soluble portion of cigarette smoke. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1977, 25, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
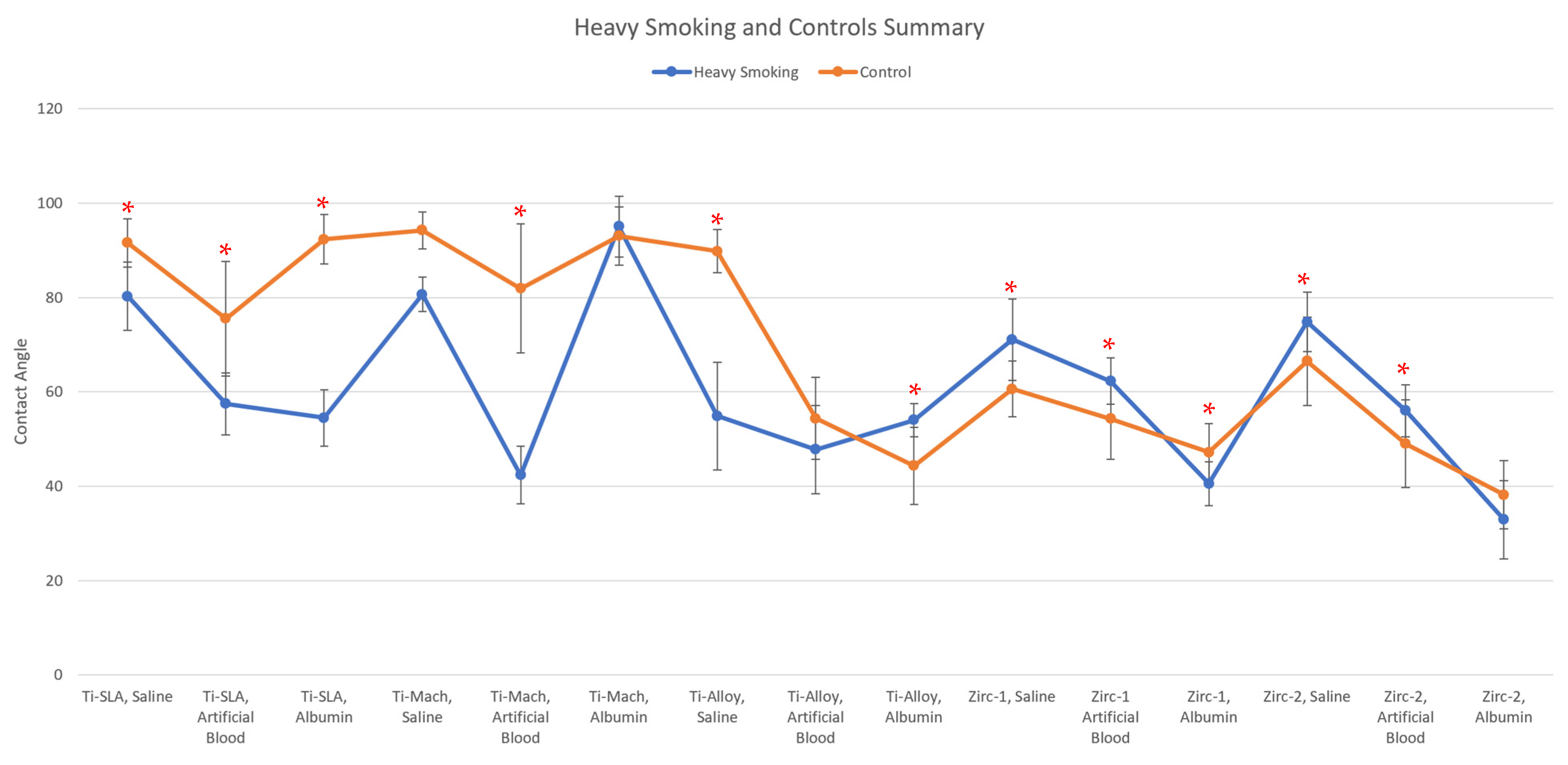
| Disk, Test Solution | Heavy Smoking (˚) | Control (˚) | % Change | p < 0.05 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-SLA, Saline | 80.25 | 91.59 | −12.38% | Yes |
| Ti-SLA, Artificial Blood | 57.45 | 75.50 | −23.91% | Yes |
| Ti-SLA, Albumin | 54.46 | 92.35 | −41.03% | Yes |
| Ti-Mach, Saline | 80.66 | 94.27 | −14.44% | No |
| Ti-Mach, Artificial Blood | 42.34 | 81.93 | −48.32% | Yes |
| Ti-Mach, Albumin | 95.02 | 93.04 | 2.12% | No |
| Ti-Alloy, Saline | 54.85 | 89.83 | −38.94% | Yes |
| Ti-Alloy, Artificial Blood | 47.77 | 54.35 | −12.12% | No |
| Ti-Alloy, Albumin | 54.02 | 44.30 | 21.96% | Yes |
| Zirc-1, Saline | 71.08 | 60.57 | 17.36% | Yes |
| Zirc-1 Artificial Blood | 62.25 | 54.26 | 14.74% | Yes |
| Zirc-1, Albumin | 40.51 | 47.19 | −14.15% | Yes |
| Zirc-2, Saline | 74.83 | 66.47 | 12.57% | Yes |
| Zirc-2, Artificial Blood | 56.01 | 49.00 | 14.32% | Yes |
| Zirc-2, Albumin | 32.92 | 38.16 | −13.74% | No |
| Material | Smoking Exposure | Sa (µm) | Sz (µm) | Sdr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti-Mach | Before | 0.72 | 4.52 | 5.98 |
| Ti-Mach | Light Smoking | 0.74 | 4.55 | 6.00 |
| Ti-Mach | Heavy Smoking | 0.75 | 4.58 | 6.10 |
| Zirc-1 | Before | 0.52 | 3.37 | 2.48 |
| Zirc-1 | Light Smoking | 0.53 | 3.42 | 2.56 |
| Zirc-1 | Heavy Smoking | 0.54 | 3.45 | 2.64 |
| Ti-SLA | Before | 1.23 | 7.59 | 8.74 |
| Ti-SLA | Light Smoking | 1.22 | 7.55 | 8.71 |
| Ti-SLA | Heavy Smoking | 1.25 | 7.64 | 8.83 |
| Zirc-2 | Before | 0.60 | 3.58 | 3.04 |
| Zirc-2 | Light Smoking | 0.61 | 3.59 | 3.12 |
| Zirc-2 | Heavy Smoking | 0.63 | 3.61 | 3.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohana, D.; Anderson, N.K.; Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G.E. Changes in Implant Surface Characteristics and Wettability Induced by Smoking In Vitro: A Preliminary Investigation. Materials 2025, 18, 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122844
Ohana D, Anderson NK, Delgado-Ruiz R, Romanos GE. Changes in Implant Surface Characteristics and Wettability Induced by Smoking In Vitro: A Preliminary Investigation. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122844
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhana, Danielle, Nina K. Anderson, Rafael Delgado-Ruiz, and Georgios E. Romanos. 2025. "Changes in Implant Surface Characteristics and Wettability Induced by Smoking In Vitro: A Preliminary Investigation" Materials 18, no. 12: 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122844
APA StyleOhana, D., Anderson, N. K., Delgado-Ruiz, R., & Romanos, G. E. (2025). Changes in Implant Surface Characteristics and Wettability Induced by Smoking In Vitro: A Preliminary Investigation. Materials, 18(12), 2844. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122844








