Experimental Study on RAP with High Recycling Content Based on High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Asphalt
2.2. Aggregates and Filler
3. Methods
3.1. Asphalt Performance Testing Methods
3.1.1. Basic Properties Testing Methods
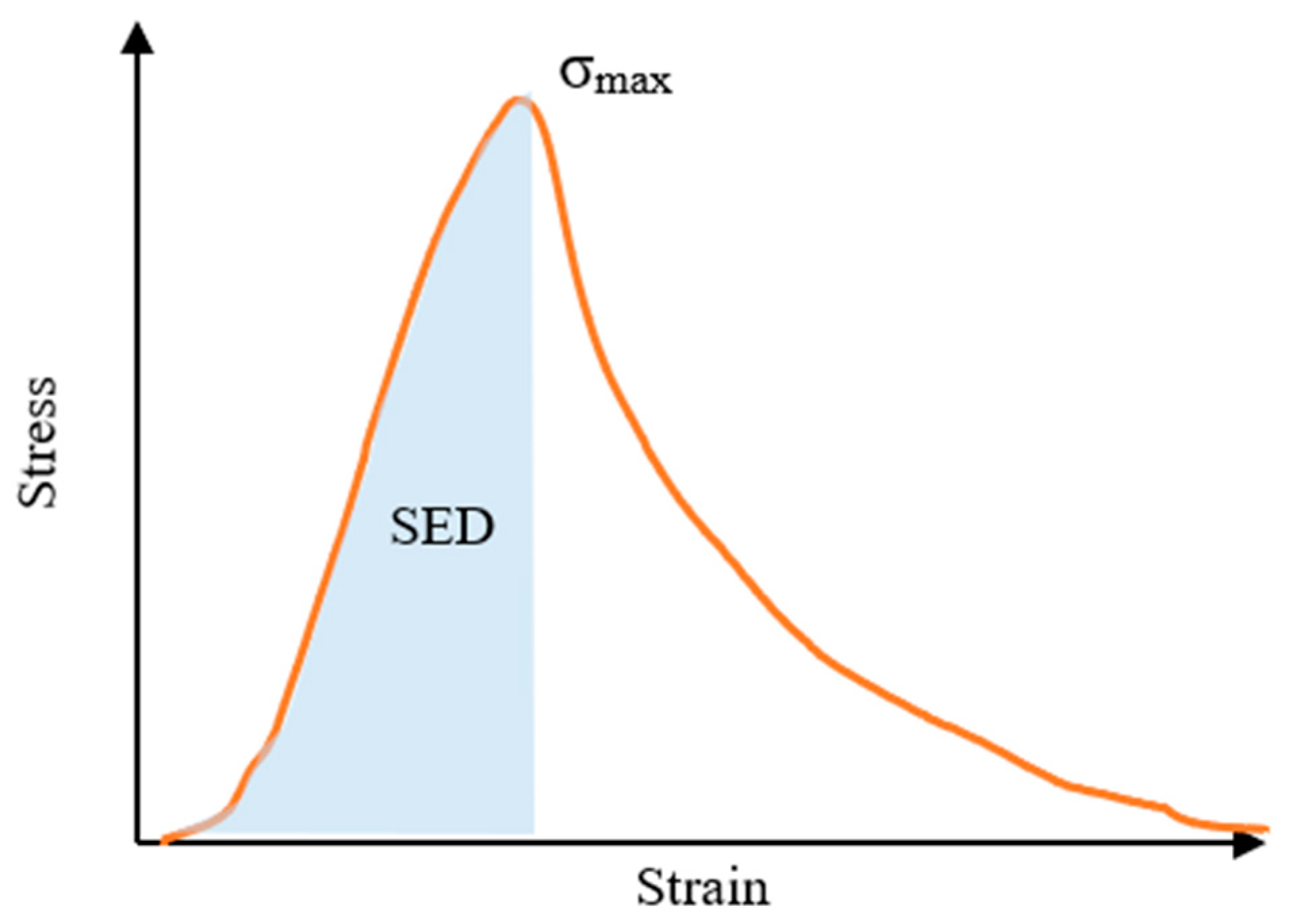
3.1.2. Linear Amplitude Sweep
3.1.3. Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR) Test
3.1.4. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Scan
3.2. Asphalt Mixture Performance Tests
3.2.1. Wheel Tracking Test
3.2.2. Low-Temperature Bending Beam Test
3.2.3. IDEAL Cracking Test (IDEAL-CT)
3.2.4. Dynamic Modulus Test
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Test Results of Asphalt Properties
4.1.1. Basic Properties Test Results
4.1.2. LAS Test Results
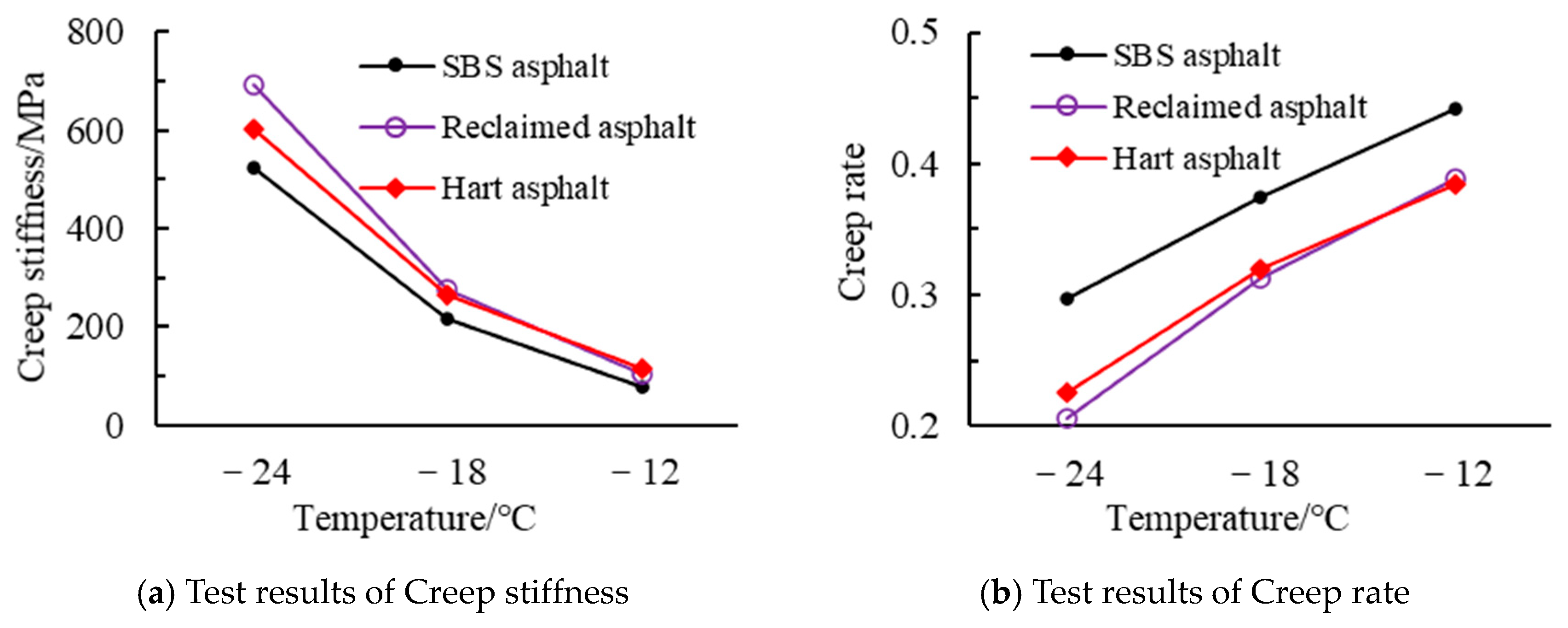
4.1.3. BBR Test Results
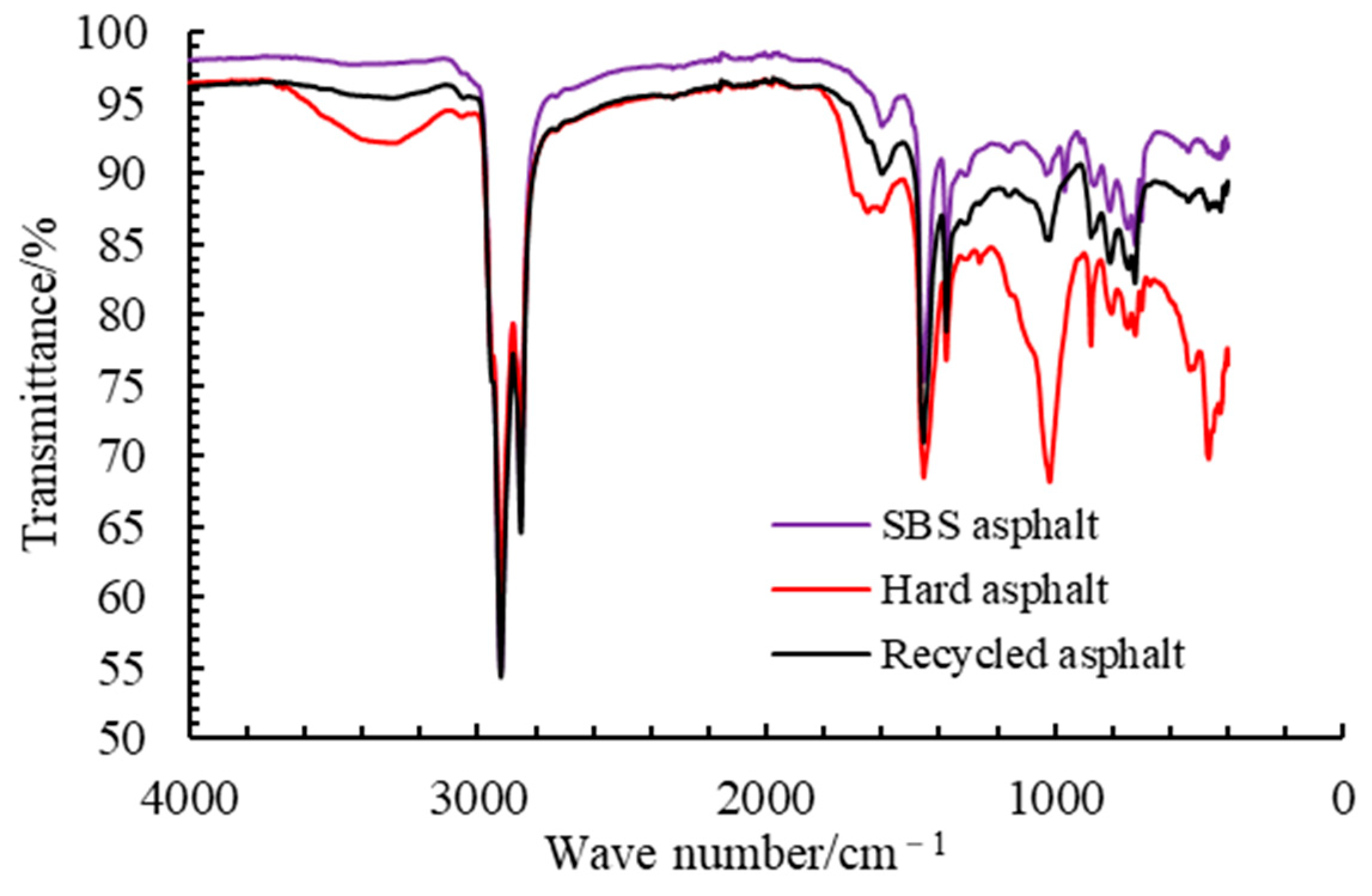
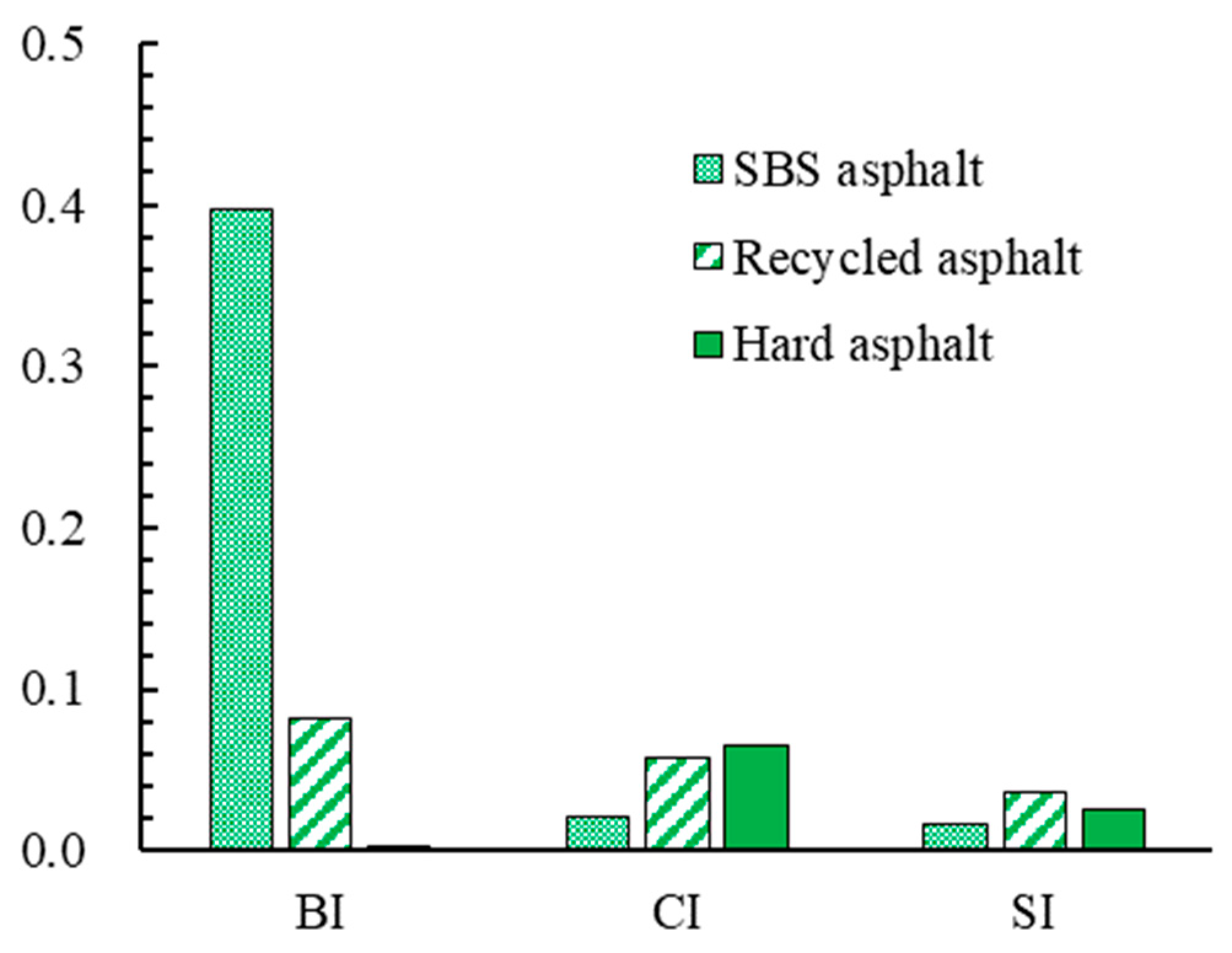
4.1.4. FTIR Test Results
4.2. Test Results of Asphalt Mixture Performance
4.2.1. Design of Asphalt Mixtures
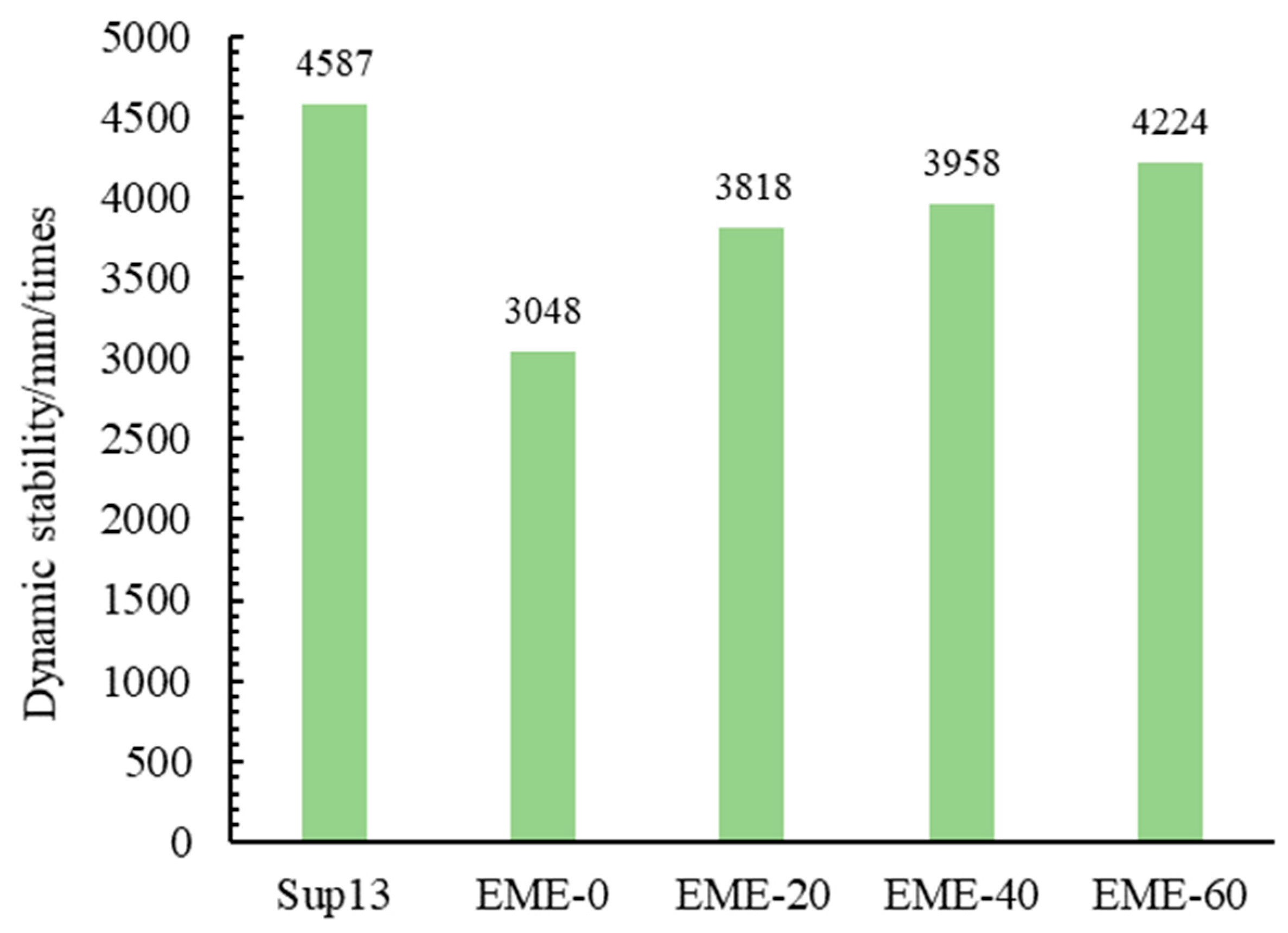
4.2.2. Wheel Tracking Test Results
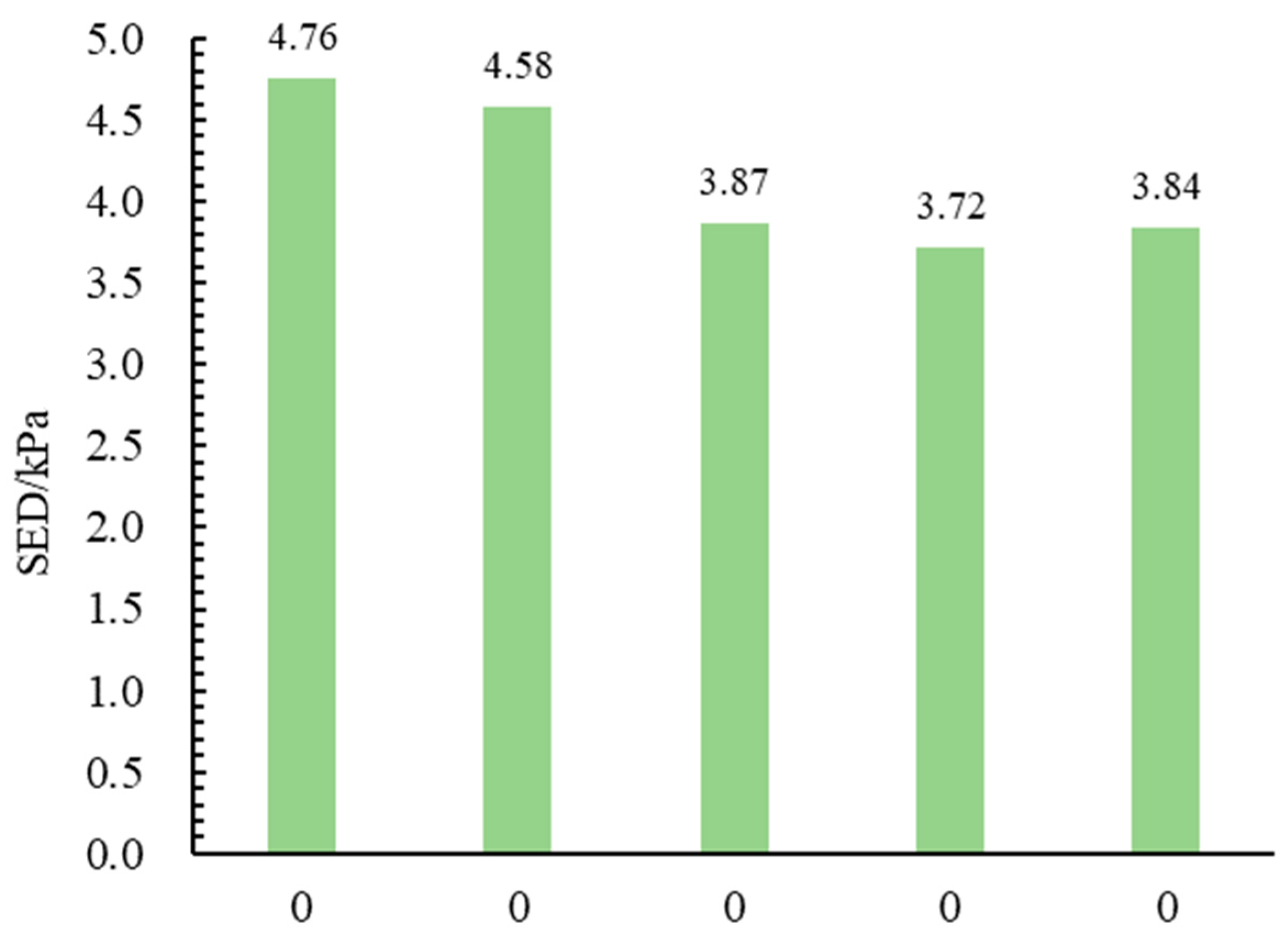
4.2.3. Low-Temperature Bending Beam Test Results
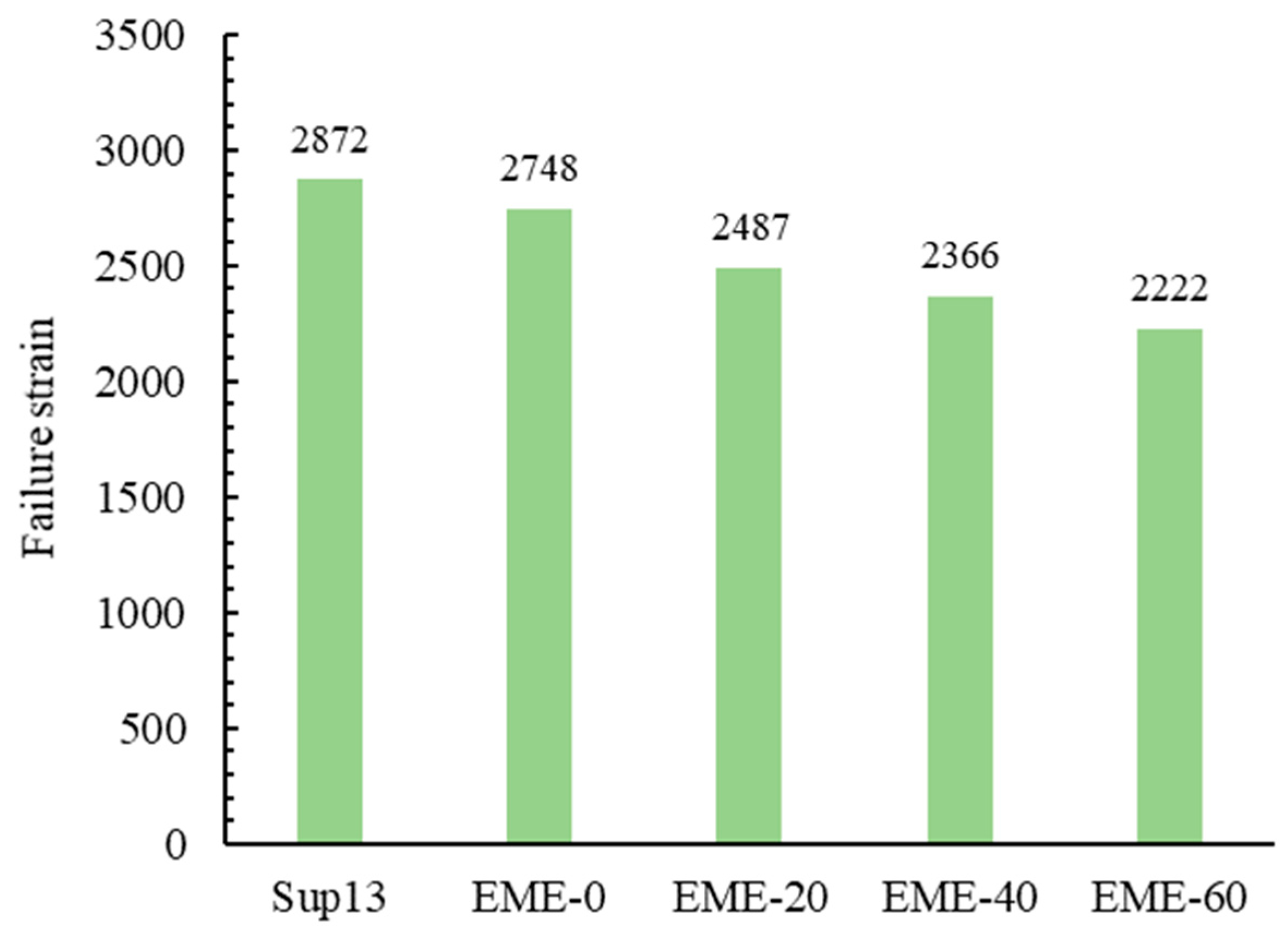
4.2.4. IDEAL-CT Test Results
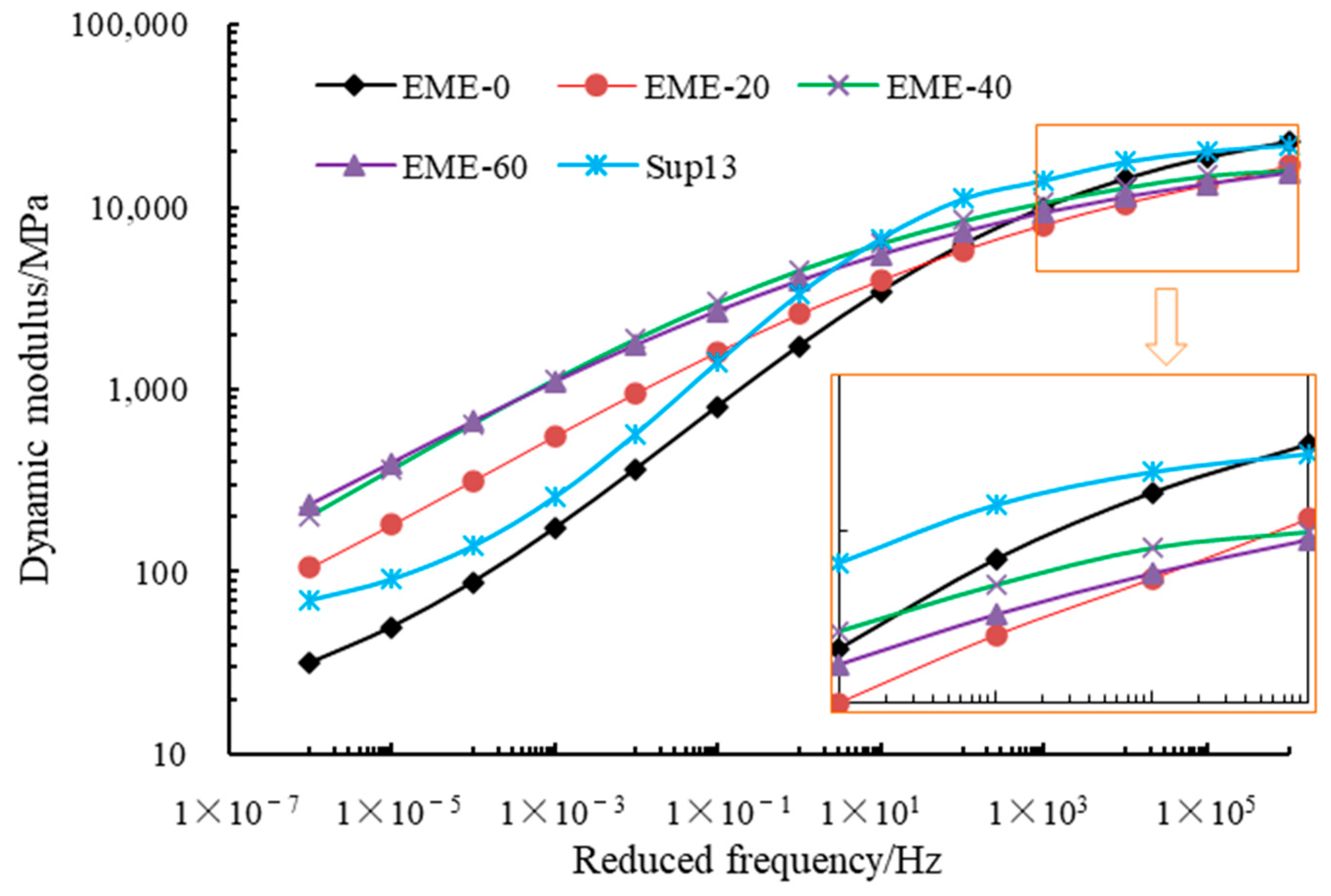
4.2.5. Dynamic Modulus Test Results
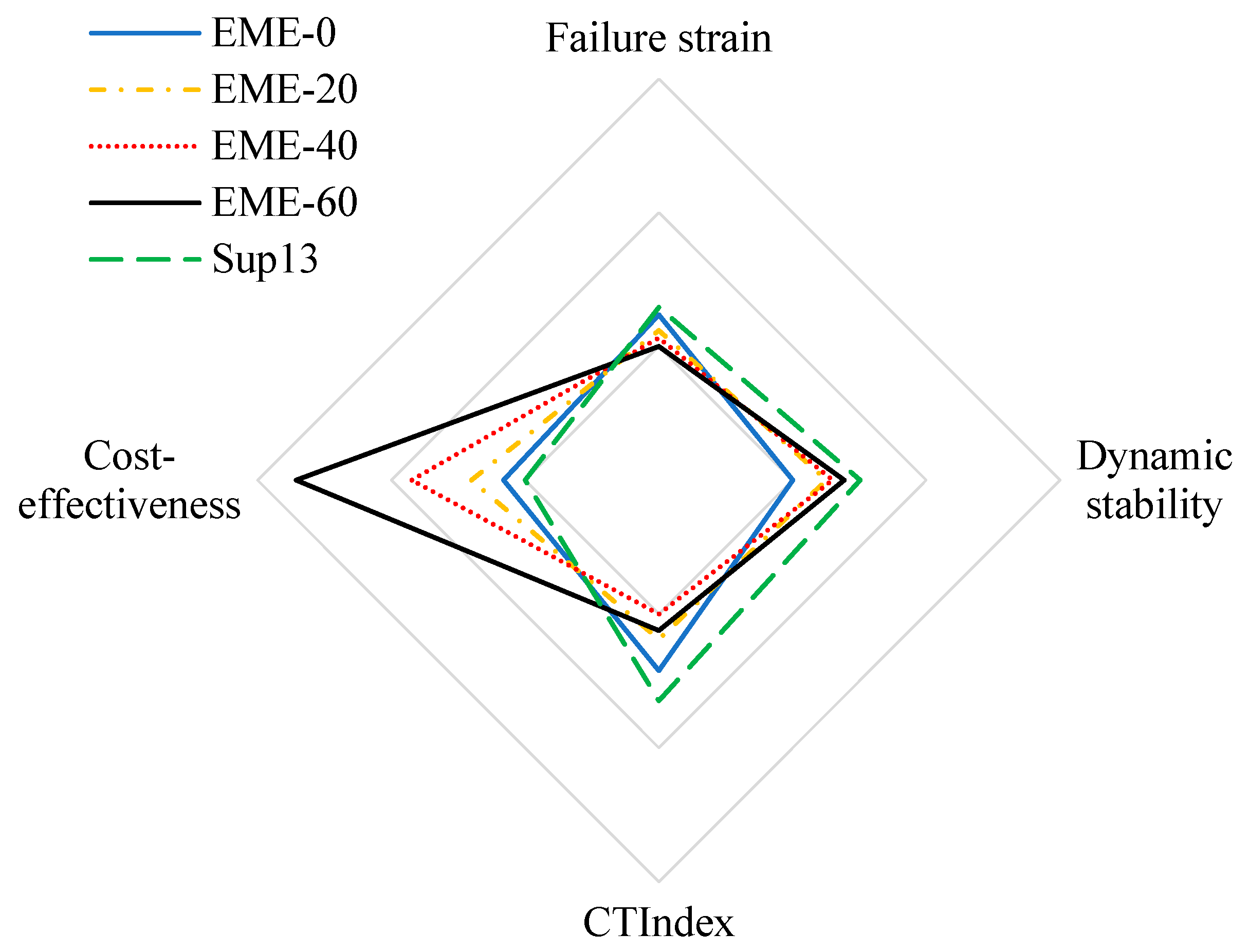
4.2.6. Comprehensive Analysis
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The technical performance and chemical functional groups of reclaimed asphalt are similar to those of hard asphalt, indicating that it is feasible to replace hard asphalt with reclaimed asphalt in the design of High-modulus Asphalt Mixtures.
- (2)
- With the increase in RAP content, the high-temperature performance of EME-13 increases by 20% to 60%; the low-temperature and medium-temperature cracking resistance decreases slightly by 10% to 20%; the dynamic modulus in the low-frequency range increases by 3 to 6 times, while the dynamic modulus in the high-frequency range decreases by 20% to 30%. RAP makes it easier for EME-13 to meet the modulus design requirements of High-modulus Asphalt Mixtures.
- (3)
- The pavement performance of modified asphalt Sup-13 is superior to that of EME-13, but its cost is also the highest. EME-13 with high RAP content has a significant economic advantage while having slightly lower pavement performance than Sup-13, making it highly cost-effective.
- (4)
- The aged characteristics of RAP binder are strategically compatible with the design requirements of High-modulus Asphalt Mixtures, which confirms the technical and economic viability of incorporating a high content (up to 60%) of RAP.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gulzar, S.; Fried, A.; Preciado, J.; Castorena, C.; Underwood, S.; Habbouche, J.; Boz, I. Towards sustainable roads: A state-of-the-art review on the use of recycling agents in recycled asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 406, 136994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y. Investigation on the effects of RAP proportions on the pavement performance of recycled asphalt mixtures. Front. Mater. 2022, 8, 842809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseer, F.; Arambula-Mercado, E.L. Performance of asphalt mixtures with high recycled materials content and recycling agents. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Han, Z.; Cheng, H.; Yang, R.; Yuan, J.; Jin, T. Low-temperature performance improvement strategies for high RAP content recycled asphalt mixtures: Focus on RAP gradation variability and mixing process. Fuel 2025, 387, 134362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Bian, X.; Jiang, X.; Hao, M.; Zhao, X.; Liu, J. Study on rheological properties of warm mix large proportion recycled asphalt. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Yi, J.; Xu, M.; Ai, X.; Cao, J.; Hu, W.; Gao, L.; Feng, D. Exploration of the design theory of crack-resistant rejuvenator for warm-mix recycled asphalt mixtures with high RAP contents. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Peng, A. Laboratory evaluation of foamed warm mix binders and mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Fu, H.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J. Research on the preparation and performance of biomimetic warm-mix regeneration for asphalt mixtures. Coatings 2024, 14, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Gazder, U.; Mamun, A.A.; Arifuzzaman, M.; Wahhab, H.I.A.-A.; Rahman, M.M. Predicting and optimizing the mechanical properties of rejuvenated asphalt mix with RAP content. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 37, 2071–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Mousavi, S.R.; Miri, M. Tensile-Tear cracking resistance of RAP incorporated asphalt mixtures, enhanced by warm mix asphalt additive and nano calcium carbonate. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2024, 132, 104467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielinski, J.C.; Huber, G.A. Evaluation of French high modulus asphalt (EME) in pavement structural design (MEPDG). J. Assoc. Asph. Paving Technol. 2011, 80, 697–718. [Google Scholar]
- Bilema, M.; Aman, Y.B.; Hassan, N.A.; Al-Saffar, Z.; Ahmad, K.; Rogo, K. Performance of aged asphalt binder treated with various types of rejuvenators. Civ. Eng. J.-Tehran 2021, 7, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xing, C.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Tang, S.; Cheng, H. Comparative analysis of four styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) structure repair agents in the rejuvenation of aged SBS-modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 141232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Arraigada, M.; Poulikakos, L.D. 100% recycled high-modulus asphalt concrete mixture design and validation using vehicle simulator. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y. Recycling aged asphalt using hard asphalt binder for hot-mixing recycled asphalt mixture. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Test Standard Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- AASHTO T101; Standard Method of Test for Estimating Damage Tolerance of Asphalt Binders Using The Linear Amplitude Sweep. AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- AASHTO T313; Standard Method of Test for Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Asphalt Binder Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Zhou, F.; Im, S.; Sun, L.; Scullion, T. Development of an IDEAL cracking test for asphalt mix design and QC/QA. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18 (Suppl. S4), 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO T313; Standard Method of Test for Determining Dynamic Modulus of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA). AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2022.
- Wang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Cui, P.; Lin, J.; Li, M.; Chen, Z. Correlation of asphalt performance indicators and ageing degrees: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, I.G.N.; Hofko, B.; Mirwald, J.; Grothe, H. Effect of thermal and oxidative ageing on asphalt binders rheology and chemical composition. Materials 2020, 13, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Baek, J.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.Y. Fatigue performance evaluation of SBS modified mastic asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhou, C.; Yu, P.; Song, X. Evaluation of ageing behaviors of asphalt binders using FTIR tests. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Tao, J.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y. Ageing mechanism of a diatomite-modified asphalt binder using Fourier-transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis. Materials 2019, 12, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hao, P. Low-temperature performance of asphalt mixtures modified by microencapsulated phase change materials with various graphene contents. Coatings 2022, 12, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullapudi, R.S.; Sudhakar Reddy, K. Relationship between rheological properties of RAP binders and cohesive surface free energy. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Min, Z.; Chen, F.; Huang, W. Adhesion behavior and microscopic mechanism of epoxy asphalt-RAP aggregate interface. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Ge, D.; Wang, J.; Malburg, L.; You, Z. Reconstruction of asphalt pavements with crumb rubber modified asphalt mixture in cold region: Material characterization, construction, and performance. Materials 2023, 16, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Duan, S.; Zhu, H. Research on improving the durability of bridge pavement using a high-modulus asphalt mixture. Materials 2021, 14, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, M.; Fuentes, L.; Liu, H.; Khalili, M.; Walubita, L.F. Evaluating fatigue resistance based on viscoelastic properties of asphalt mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2023, 24, 2126976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Aggregate Size (mm) | Percentage Passing (%) at the Following Sieves (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.0 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| 10–15 | 100 | 86.2 | 30.7 | 4.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| 5–10 | 100 | 94.9 | 76.8 | 5.1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 3–5 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 58.1 | 12.9 | 7.8 | 6.4 | 4.8 | 1.6 | 0.8 |
| 0–3 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 95.1 | 72.4 | 51.9 | 31.8 | 15.7 | 11.5 | 8.1 |
| RAP | 100 | 98 | 90.2 | 67.9 | 47 | 35.5 | 22.4 | 13.1 | 9 | 3.4 |
| Filler | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 96.5 | 83.6 |
| Asphalt Type | Basic Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility (cm) | |
| SBS asphalt | 56.3 | 81.5 | 30.4 |
| Reclaimed asphalt | 28.6 | 67.0 | 3.2 |
| Hard asphalt | 25.7 | 63.5 | 4.5 |
| Type of Asphalt | Modal A | Modal B | Nf at Different Strains (ε) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.50 | 5.00 | 10.00 | |||
| SBS asphalt | 1,380,000 | 2.784 | 107,652 | 15,626 | 2268 |
| Reclaimed asphalt | 1,082,300 | 3.411 | 47,531 | 4468 | 420 |
| Hard asphalt | 739,700 | 3.463 | 30,969 | 2808 | 255 |
| Mixture Type | Percentage Passing (%) at the Following Sieves (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.0 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| EME-0 | 100.0 | 95.8 | 77.6 | 46.0 | 29.1 | 22.3 | 16.0 | 11.6 | 9.3 | 6.3 |
| EME-20 | 100.0 | 95.5 | 77.7 | 47.5 | 29.8 | 22.9 | 16.4 | 11.3 | 9.0 | 6.5 |
| EME-40 | 100.0 | 95.6 | 78.5 | 46.4 | 28.8 | 22.5 | 16.3 | 11.7 | 9.2 | 6.1 |
| EME-60 | 100.0 | 95.2 | 76.5 | 46.5 | 29.4 | 23.4 | 17.5 | 11.9 | 9.3 | 5.9 |
| Sup13 | 100 | 94.3 | 69.2 | 44.3 | 34.1 | 24.1 | 15.8 | 8.9 | 7.0 | 5.1 |
| Mixture Type | RAP Content/% | Asphalt Content (%) | Air Void (%)/ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recycled Asphalt Content (%) | Extra Asphalt Content (%) | |||
| EME-0 | 0 | 0 | 5.3 | 3.2 |
| EME-20 | 20 | 1.0 | 4.3 | 3.3 |
| EME-40 | 40 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 3.2 |
| EME-60 | 60 | 3.0 | 2.3 | 3.1 |
| Sup13 | 0 | 0 | 4.9 | 4.0 |
| Mixture Type | Gf (J/m2) | |m75| | CTIndex |
|---|---|---|---|
| EME-0 | 14,380.3 | 1.90 | 257.3 |
| EME-20 | 10,983.2 | 1.95 | 214.8 |
| EME-40 | 7982.5 | 2.11 | 180.9 |
| EME-60 | 8313.4 | 2.01 | 203.1 |
| Sup13 | 11,372.3 | 1.67 | 298.2 |
| Mixture Type | EME-0 | EME-20 | EME-40 | EME-60 | Sup13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price (USD/ton) | 54.9 | 45.5 | 34.5 | 23.5 | 63.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Wu, Z.; Li, B. Experimental Study on RAP with High Recycling Content Based on High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2025, 18, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122835
Wang X, Wu B, Wu Z, Li B. Experimental Study on RAP with High Recycling Content Based on High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122835
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Bangwei Wu, Zhengguang Wu, and Bo Li. 2025. "Experimental Study on RAP with High Recycling Content Based on High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture" Materials 18, no. 12: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122835
APA StyleWang, X., Wu, B., Wu, Z., & Li, B. (2025). Experimental Study on RAP with High Recycling Content Based on High-Modulus Asphalt Mixture. Materials, 18(12), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122835







