Multi-Physics Coupling of Rectangular Channels with Different Aspect Ratios in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
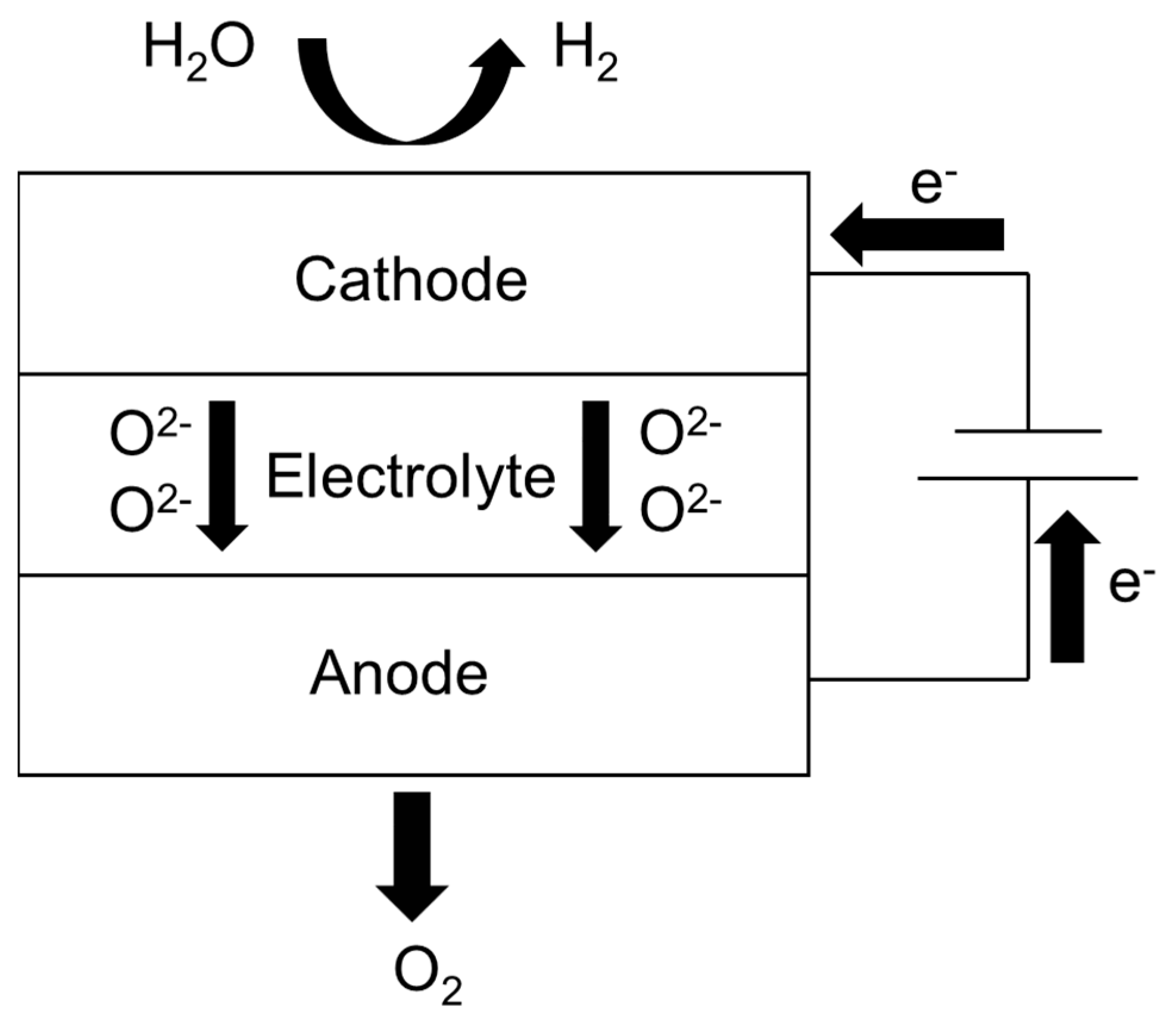
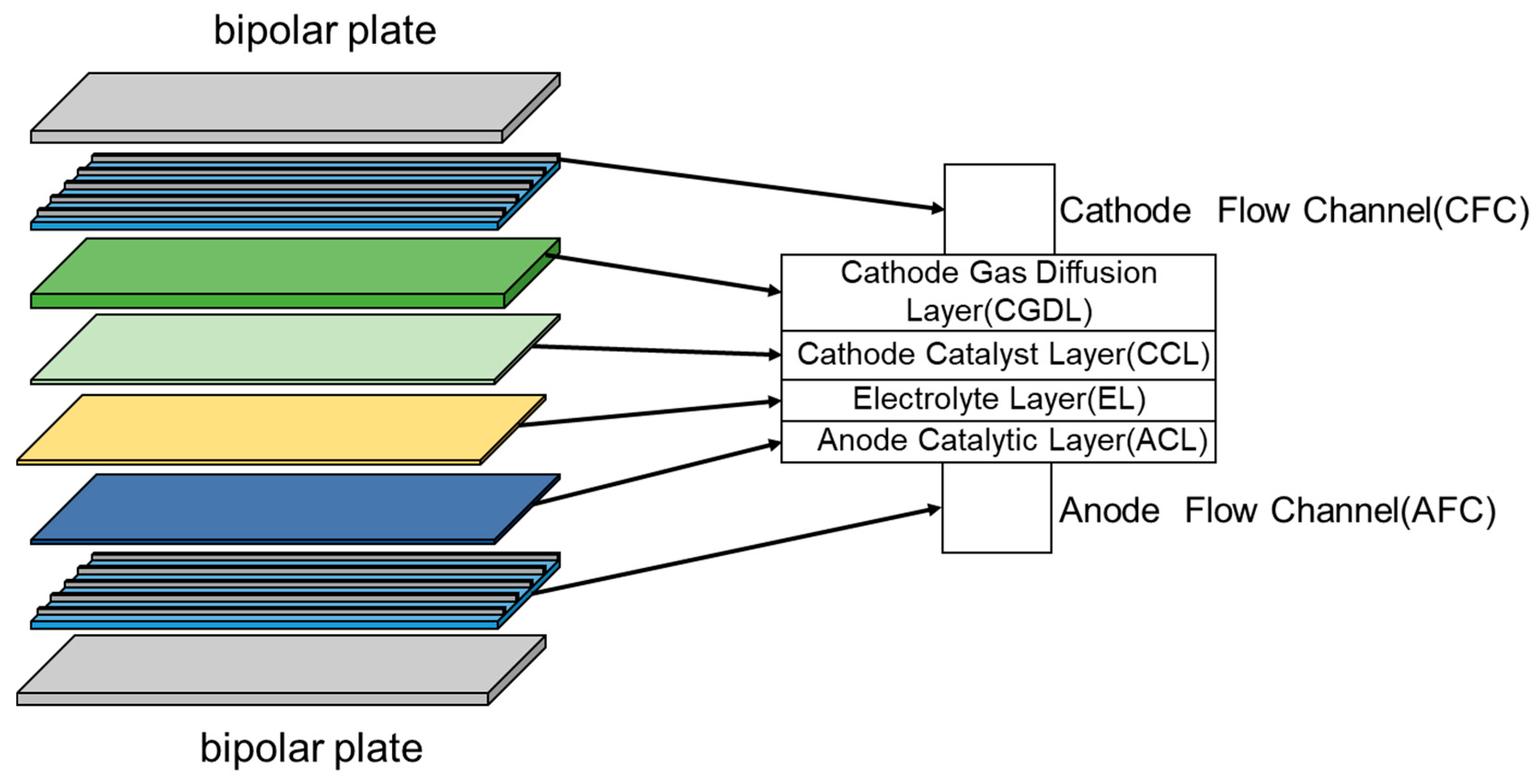
2. Model Establishment
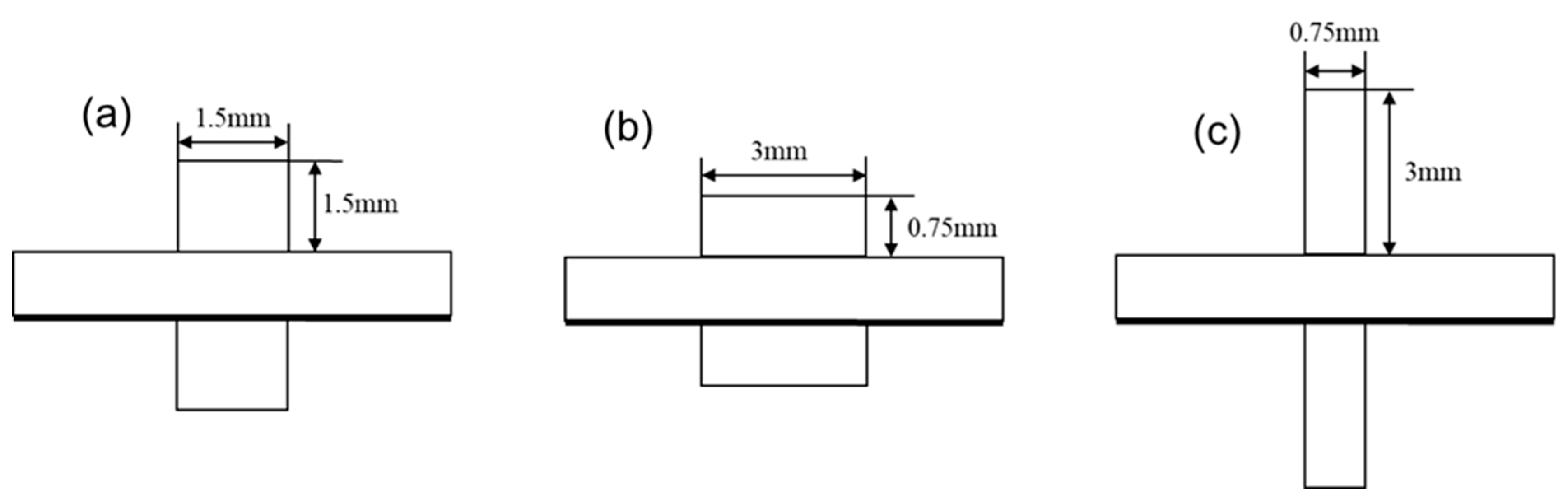
2.1. Geometric Model
2.2. Mathematical Model
2.2.1. Electrochemical Model
2.2.2. Conservation of Mass
2.2.3. Conservation of Momentum
2.2.4. Heat Transport
2.3. Boundary Conditions
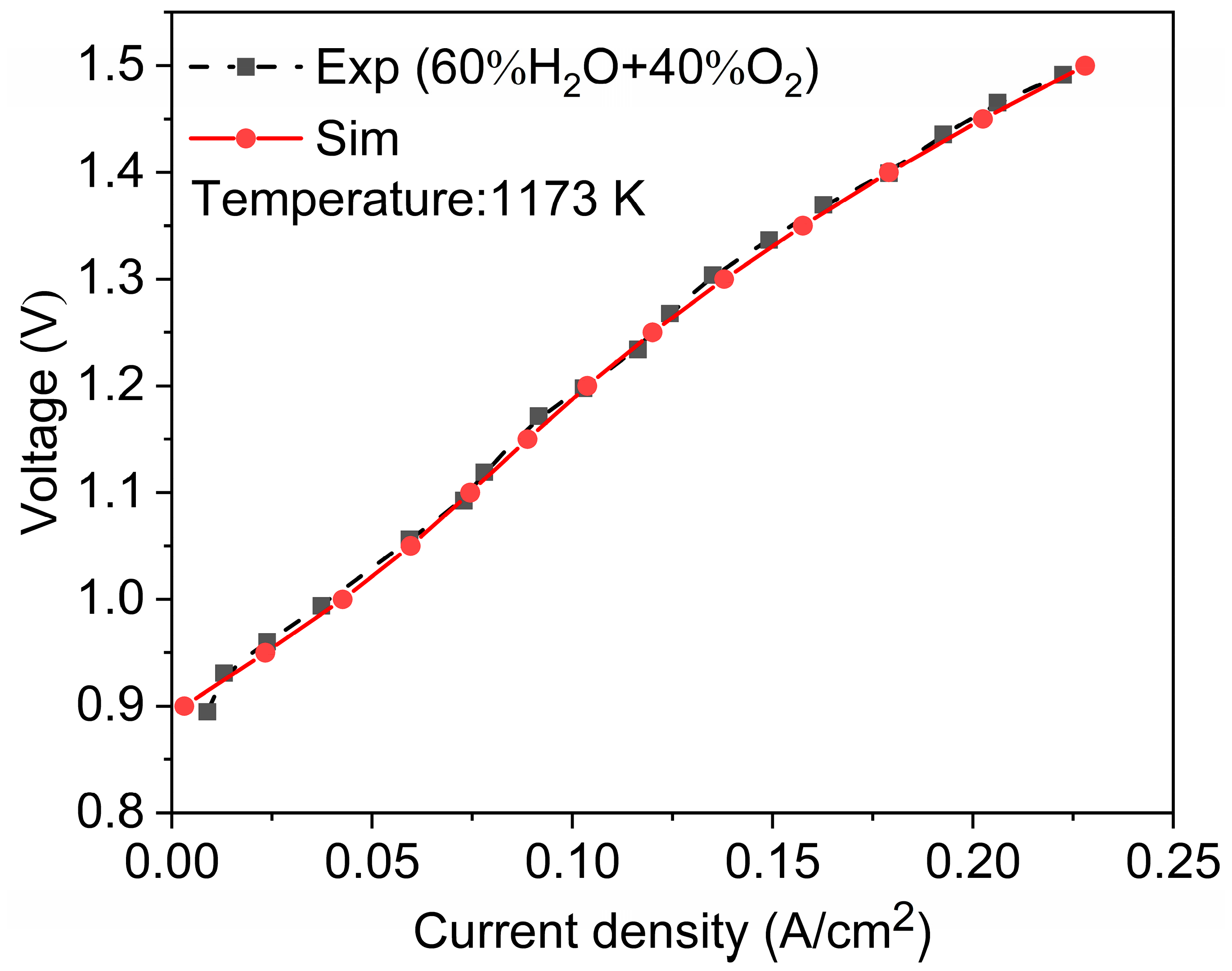
2.4. Model Validation
3. Results and Discussion
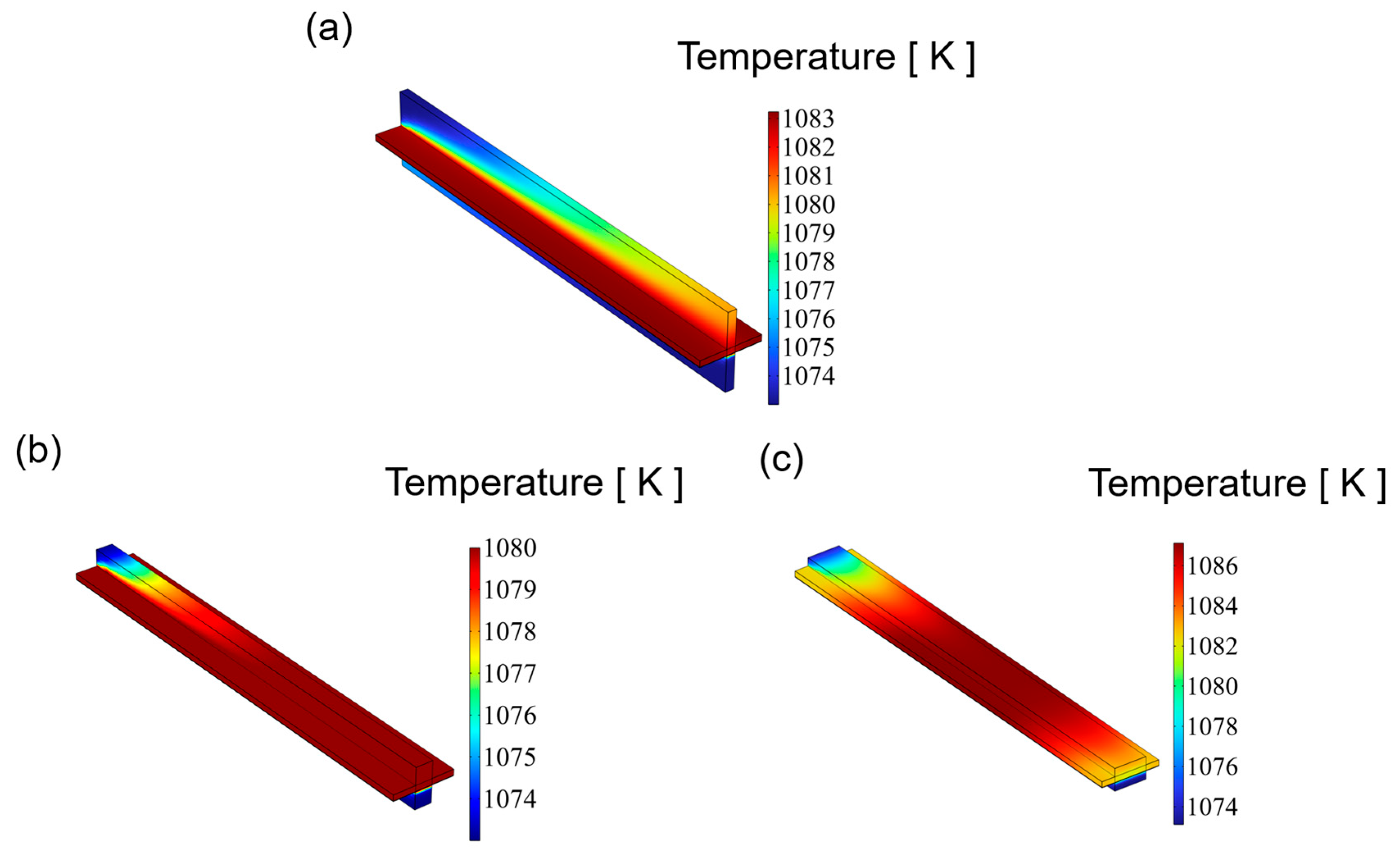
3.1. Temperature Distribution
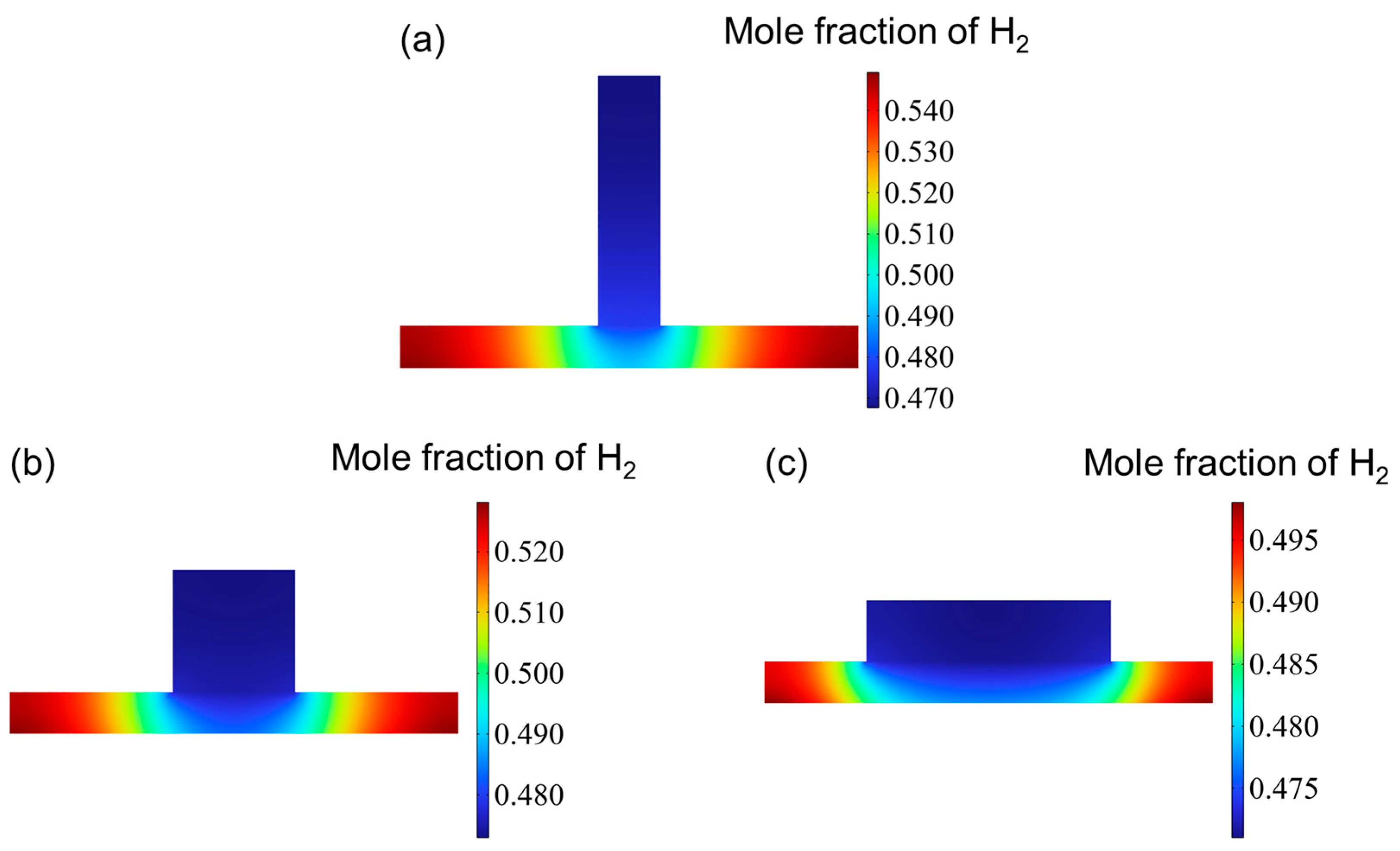
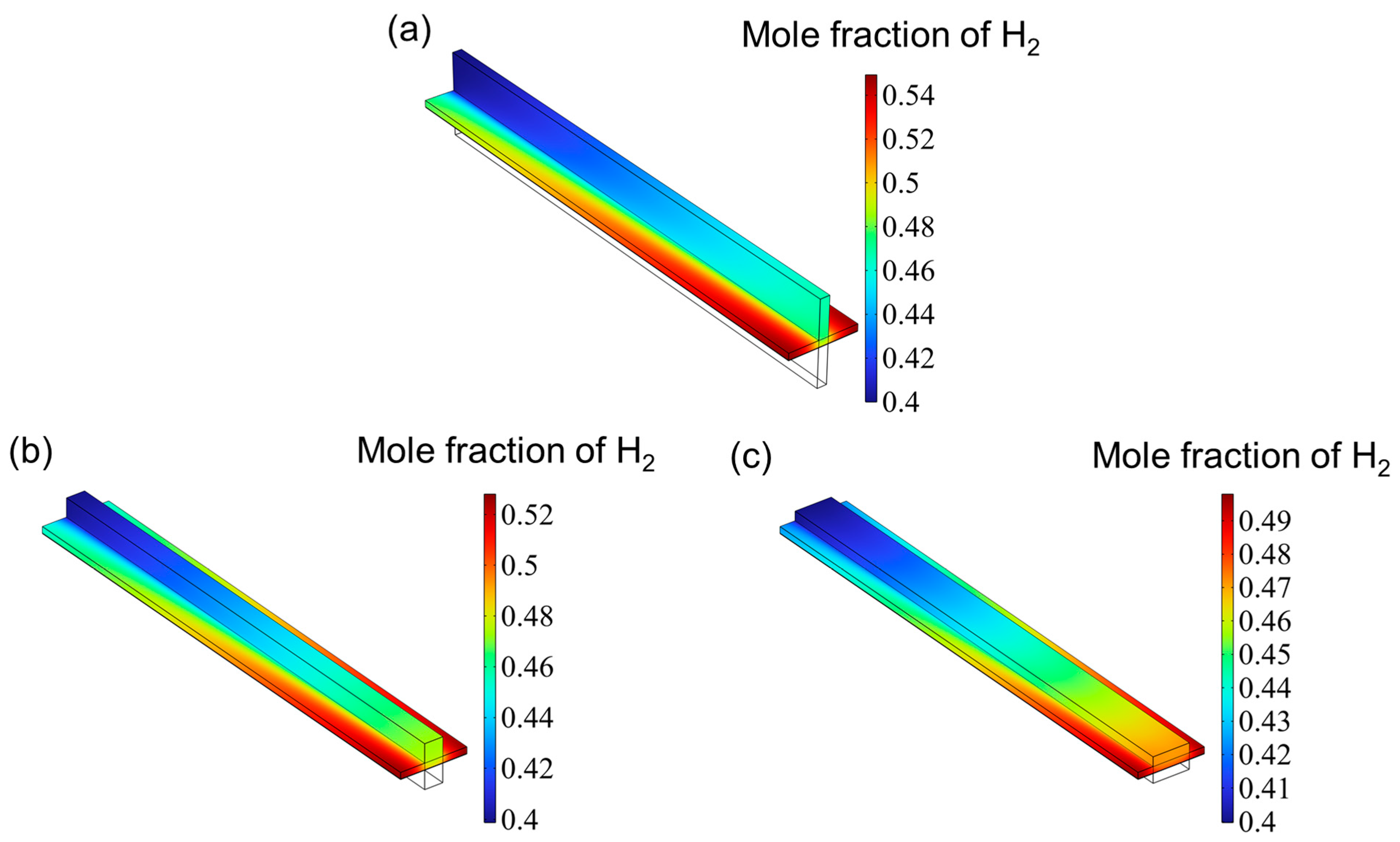
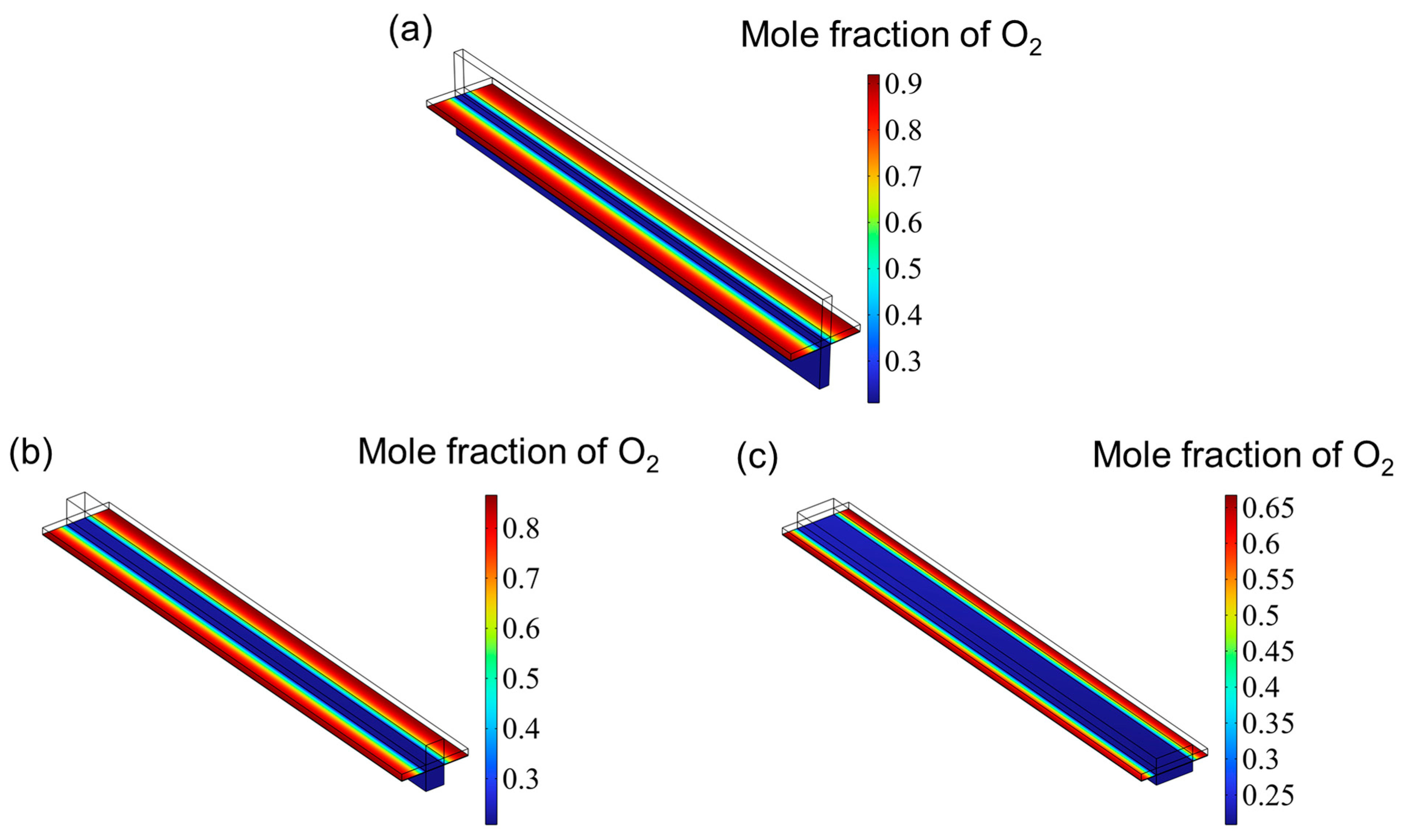
3.2. Gas Distribution
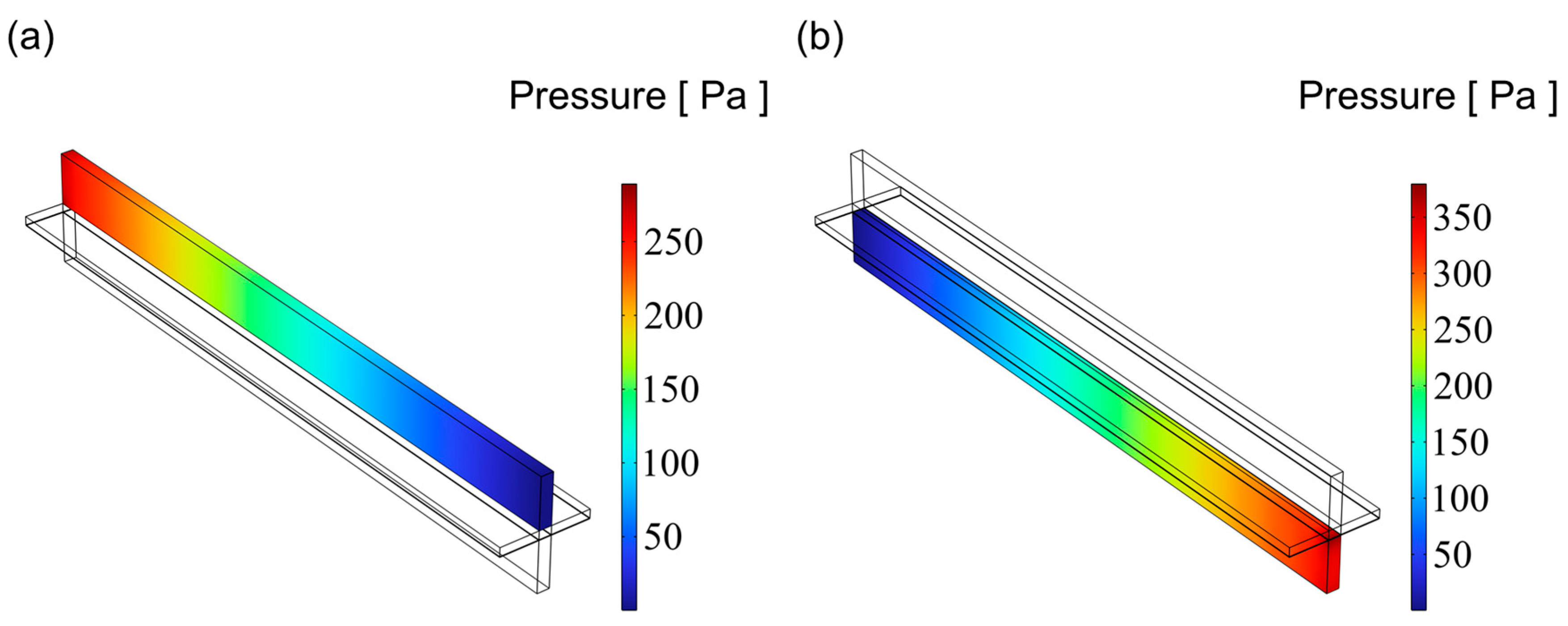
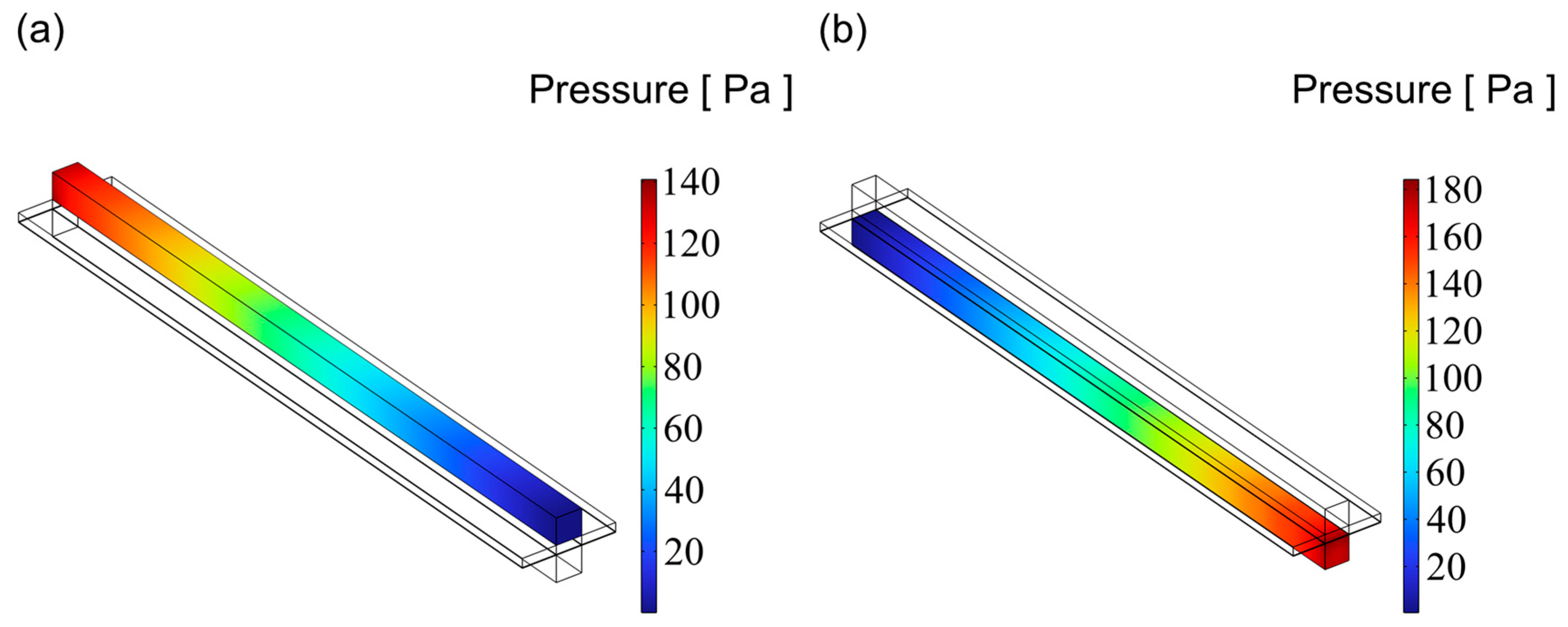
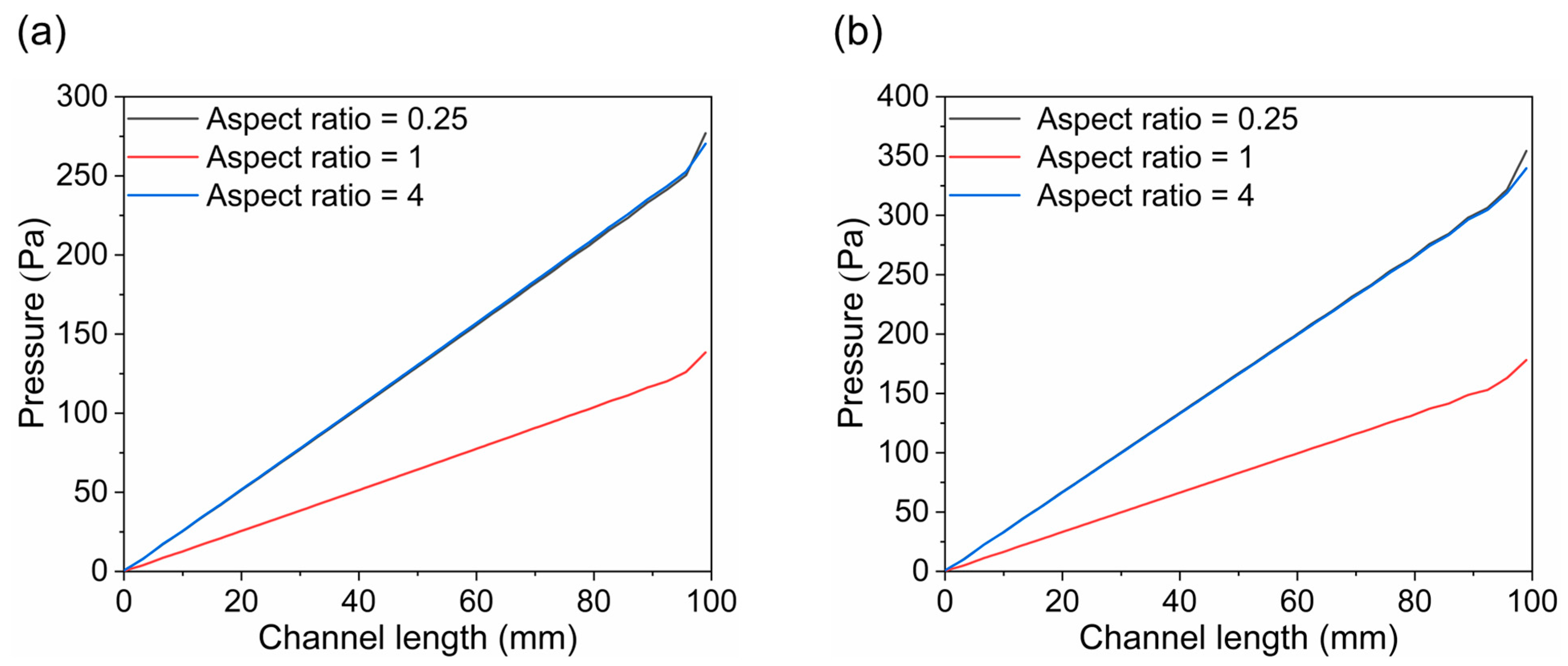
3.3. Pressure Distribution
3.4. Cell Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hauch, A.; Küngas, R.; Blennow, P.; Hansen, A.B.; Hansen, J.B.; Mathiesen, B.V.; Mogensen, M.B. Recent advances in solid oxide cell technology for electrolysis. Sci. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2020, 370, eaba6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. Solid Oxide Electrolysis of H2O and CO2 to Produce Hydrogen and Low-Carbon Fuels. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2021, 4, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, H.; Lv, H.; Bao, X. Pure CO2 electrolysis over an Ni/YSZ cathode in a solid oxide electrolysis cell. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. Energy Sustain. 2018, 6, 13661–13667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, F.; Sebold, D.; Brisse, A.; Schefold, J. Degradation phenomena in a solid oxide electrolysis cell after 9000 h of operation. J. Power Sources 2013, 223, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, S.; Zhu, X.; Yang, W. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 in solid oxide electrolysis cells. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, J. A review of high temperature co-electrolysis of H2O and CO2 to produce sustainable fuels using solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs): Advanced materials and technology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1427–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, S.D.; Jensen, S.H.; Hauch, A.; Mogensen, M.B. High Temperature Electrolysis in Alkaline Cells, Solid Proton Conducting Cells, and Solid Oxide Cells. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10697–10734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, S.B. Factors Governing Oxygen Reduction in Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Cathodes. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4791–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skafte, T.L.; Guan, Z.; Machala, M.L.; Gopal, C.B.; Monti, M.; Martinez, L.; Graves, C. Selective high-temperature CO2 electrolysis enabled by oxidized carbon intermediates. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Colón, B.C.; Ziesack, M.; Silver, P.A.; Nocera, D.G. Water splitting-biosynthetic system with CO2 reduction efficiencies exceeding photosynthesis. Sci. Am. Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2016, 352, 1210–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Høgh, J.V.T.; Nielsen, J.U.; Bentzen, J.J.; Ebbesen, S.D.; Hendriksen, P.V. High Temperature Co-Electrolysis of Steam and CO2 in an SOC Stack: Performance and Durability. Fuel Cells 2013, 13, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, S.D.; Høgh, J.; Nielsen, K.A.; Nielsen, J.U.; Mogensen, M. Durable SOC stacks for production of hydrogen and synthesis gas by high temperature electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 7363–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Tu, Z.; Hwa Chan, S. A novel flow field design with flow re-distribution for advanced thermal management in Solid oxide fuel cell. Appl. Energy 2023, 331, 120364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Zhao, D.; Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; Ni, M. New interconnector design optimization to balance electrical and mechanical performance of solid oxide fuel cell stack. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 3107–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, A.; Fei, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhu, L.; Huang, Z. Design of biomimetic leaf-like flow fields using three-dimensional numerical simulation for co-electrolysis in solid oxide electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 72, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tu, Z. Numerical simulation of flow channel geometries optimization for the planar solid oxide electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momma, A.; Kato, T.; Kaga, Y.; Nagata, S. Polarization Behavior of High Temperature Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells (SOEC). J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 105, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Leung, M.K.H.; Leung, D.Y.C. Parametric study of solid oxide fuel cell performance. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dang, Z.; Xi, G. Numerical study on thermal stress of solid oxide electrolyzer cell with various flow configurations. Appl. Energy 2024, 353, 122041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yin, Y.; Jiao, K.; Du, Q. Modelling of effect of pressure on co-electrolysis of water and carbon dioxide in solid oxide electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 3456–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; He, Q.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, D.; Ni, M. New interconnector designs for electrical performance enhancement of solid oxide fuel cells: A 3D modelling study. J. Power Sources 2022, 533, 231373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zhu, H.; Fei, Z.; Lin, Z. A modified dusty gas model in the form of a Fick’s model for the prediction of multicomponent mass transport in a solid oxide fuel cell anode. J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Mukhopadhyay, J.; Biswas, N.; Basu, R.N.; Das, P.K. Performance evaluation of different bipolar plate designs of 3D planar anode-supported SOFCs. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 123, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, Z.; Fu, M.; Ren, T.; Li, X. Thermal and electrochemical performance analysis of an integrated solar SOEC reactor for hydrogen production. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 229, 120603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Yuan, J.; Sundén, B. SOFC modeling considering hydrogen and carbon monoxide as electrochemical reactants. J. Power Sources 2013, 232, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Deng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, D.; Kupecki, J.; Wu, X.; Li, X. Modeling and analysis of cross-flow solid oxide electrolysis cell with oxygen electrode/electrolyte interface oxygen pressure characteristics for hydrogen production. J. Power Sources 2022, 529, 231248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values (m) |
|---|---|
| CGDL thickness | 5 × 10−4 |
| CCL thickness | 1 × 10−5 |
| EL thickness | 1 × 10−5 |
| ACL thickness | 2.5 × 10−5 |
| Gas channel width | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| Gas channel thickness | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| Gas channel length | 9.9 × 10−2 |
| Source Term Si | Expression |
|---|---|
| SH2 | |
| SH2O | |
| SO2 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity (S/m)(CGDL; CCL; ACL) | 2.03 × 105–66.09T; 3.27 × 106–1065.3T; 4.2 × 107/T × exp(–1150/T) |
| Ionic conductivity (S/m) (EL) | 3.34 × 104 × exp(–10300/T) |
| Porosity (CGDL; CCL; ACL) | 0.48; 0.335; 0.335 |
| Permeability (CGDL; CCL; ACL) | 1 × 10−13; 1 × 10−12; 1 × 10−12 |
| Density(kg/m−3) (CGDL; CCL; EL; ACL) | 4500; 4500; 8280; 6820 |
| Thermal conductivity (W/(m K)) (CGDL; CCL; EL; ACL) | 4; 4; 2; 4 |
| Specific heat capacity(J/(kg K)) (CGDL; CCL; EL; ACL) | 431; 431; 600; 470 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Operating pressure (atm) | 1 |
| Operating voltage (V) | 1.32 |
| Operating temperature (K) | 1073 |
| Inlet gas component of cathode | 60 vol% H2O, 40 vol% H2, |
| Inlet gas component of anode | 79 vol% N2, 21 vol% O2, |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, J.; Korte, C.; Qian, Z.; Chen, M.; Luo, J. Multi-Physics Coupling of Rectangular Channels with Different Aspect Ratios in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Materials 2025, 18, 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122827
Yao J, Korte C, Qian Z, Chen M, Luo J. Multi-Physics Coupling of Rectangular Channels with Different Aspect Ratios in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122827
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Jie, Carsten Korte, Zhengyang Qian, Ming Chen, and Jiangshui Luo. 2025. "Multi-Physics Coupling of Rectangular Channels with Different Aspect Ratios in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells" Materials 18, no. 12: 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122827
APA StyleYao, J., Korte, C., Qian, Z., Chen, M., & Luo, J. (2025). Multi-Physics Coupling of Rectangular Channels with Different Aspect Ratios in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells. Materials, 18(12), 2827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122827








