Flexible Moisture–Electric Generator Based on Vertically Graded GO–rGO/Ag Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Synthesis of GO
2.3. GO Synthesis for MEGs with Different Oxidation Levels
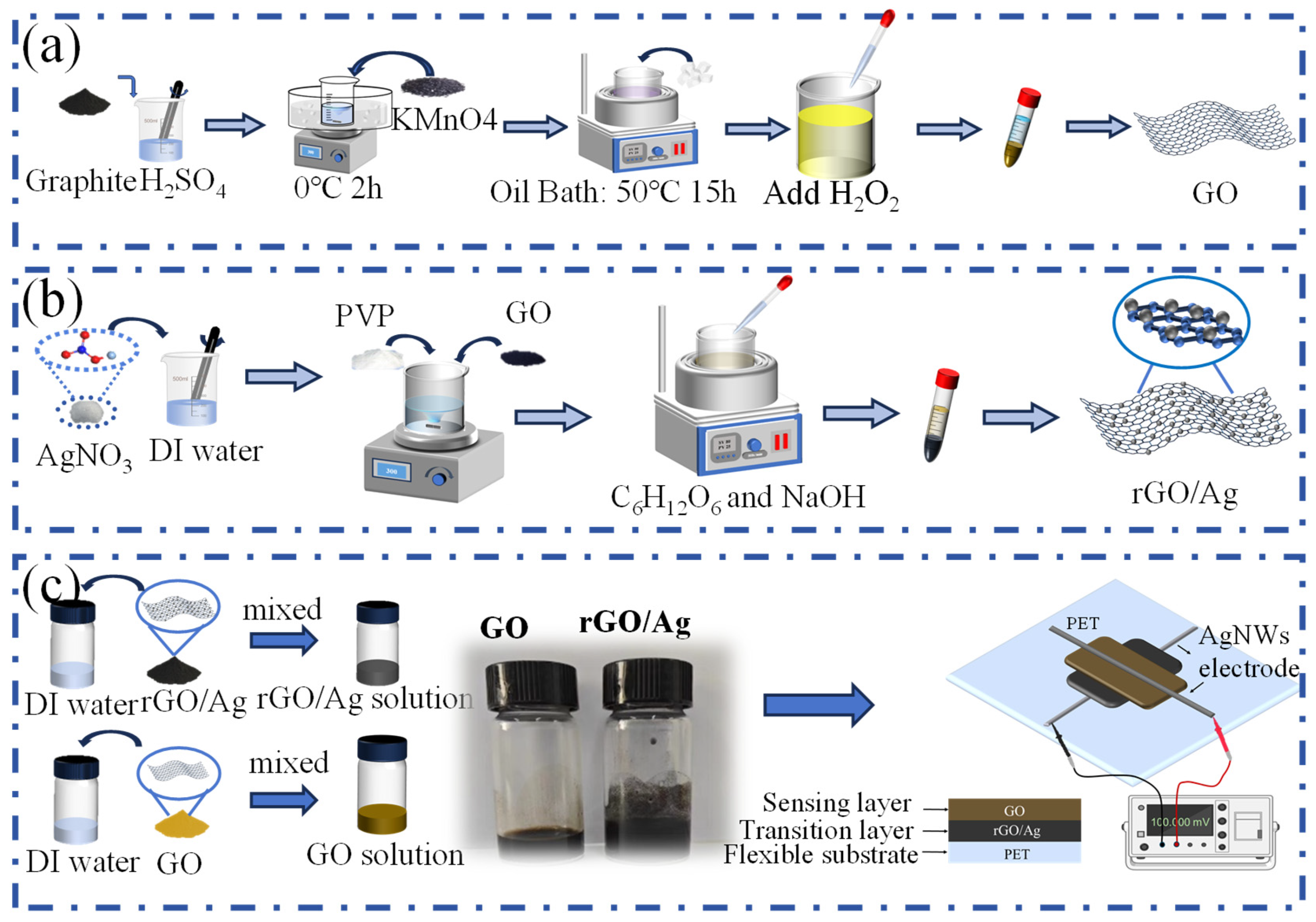
2.4. Synthesis of rGO/Ag
2.5. The Design and Assembly of the MEG
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
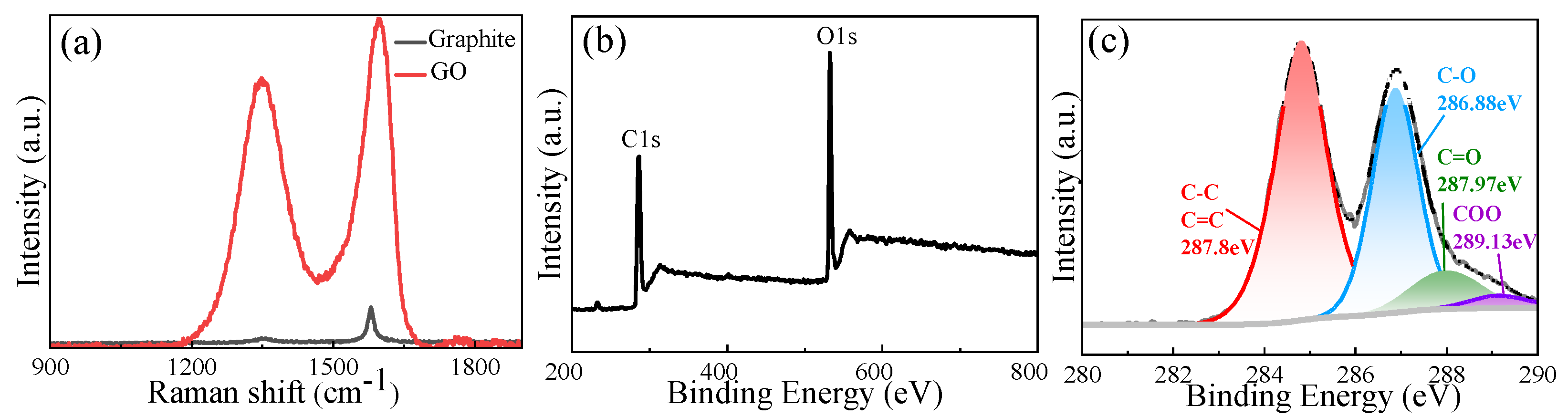
3.1. GO Structural Analysis
3.2. rGO/Ag Structural Analysis
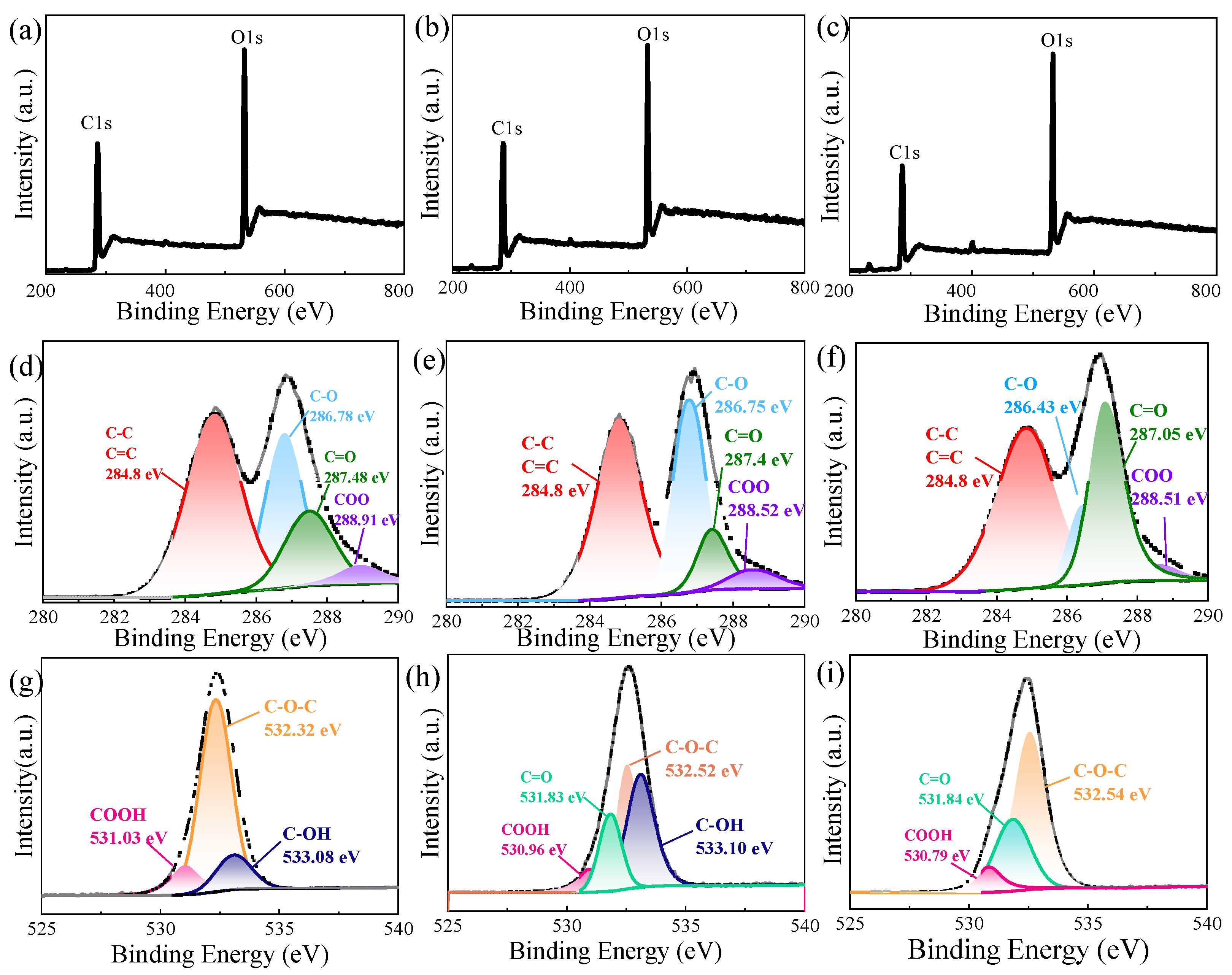
3.3. Structural Analysis of GO with Different Oxidation Degrees
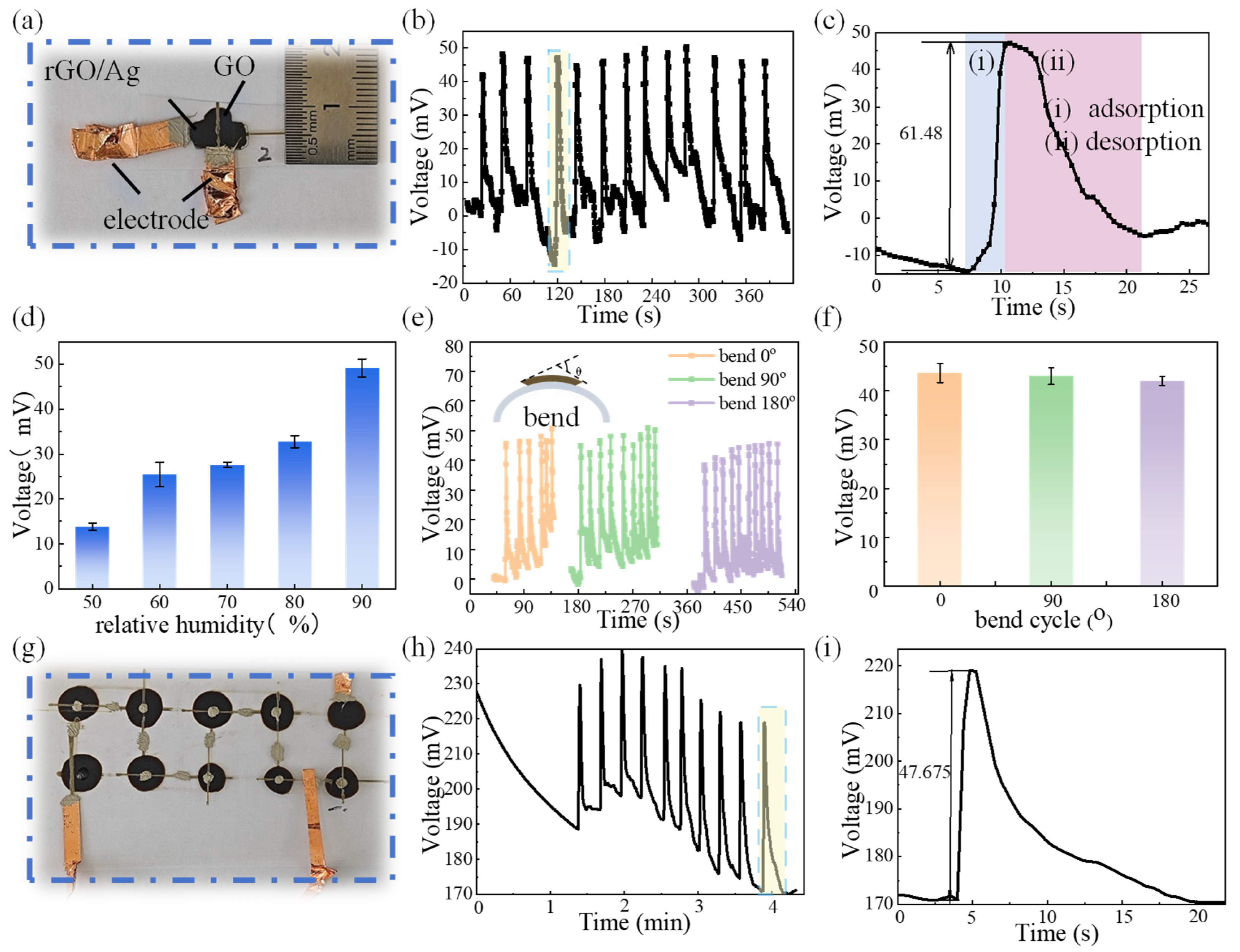
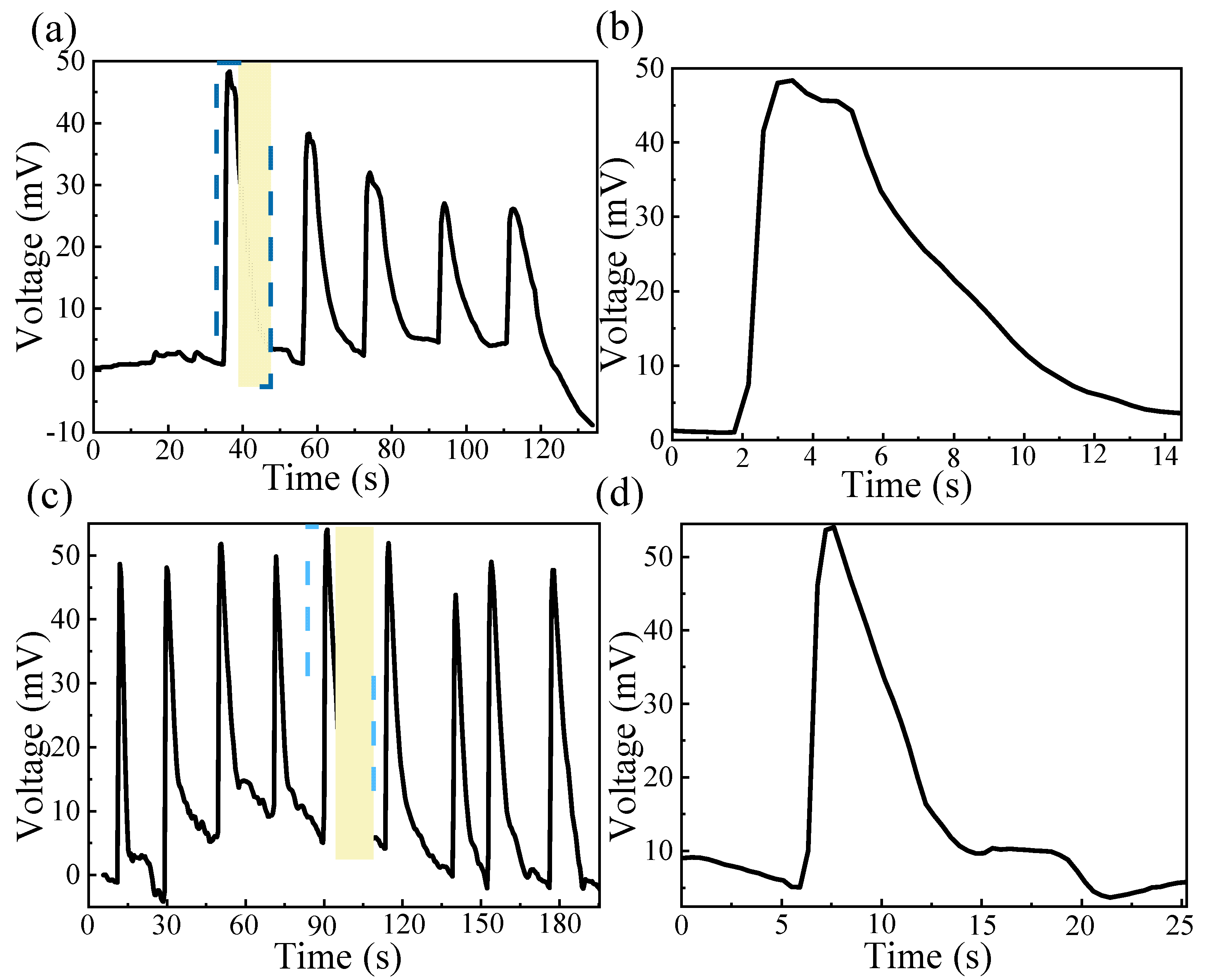
3.4. Output Performance of MEGs Under Moisture
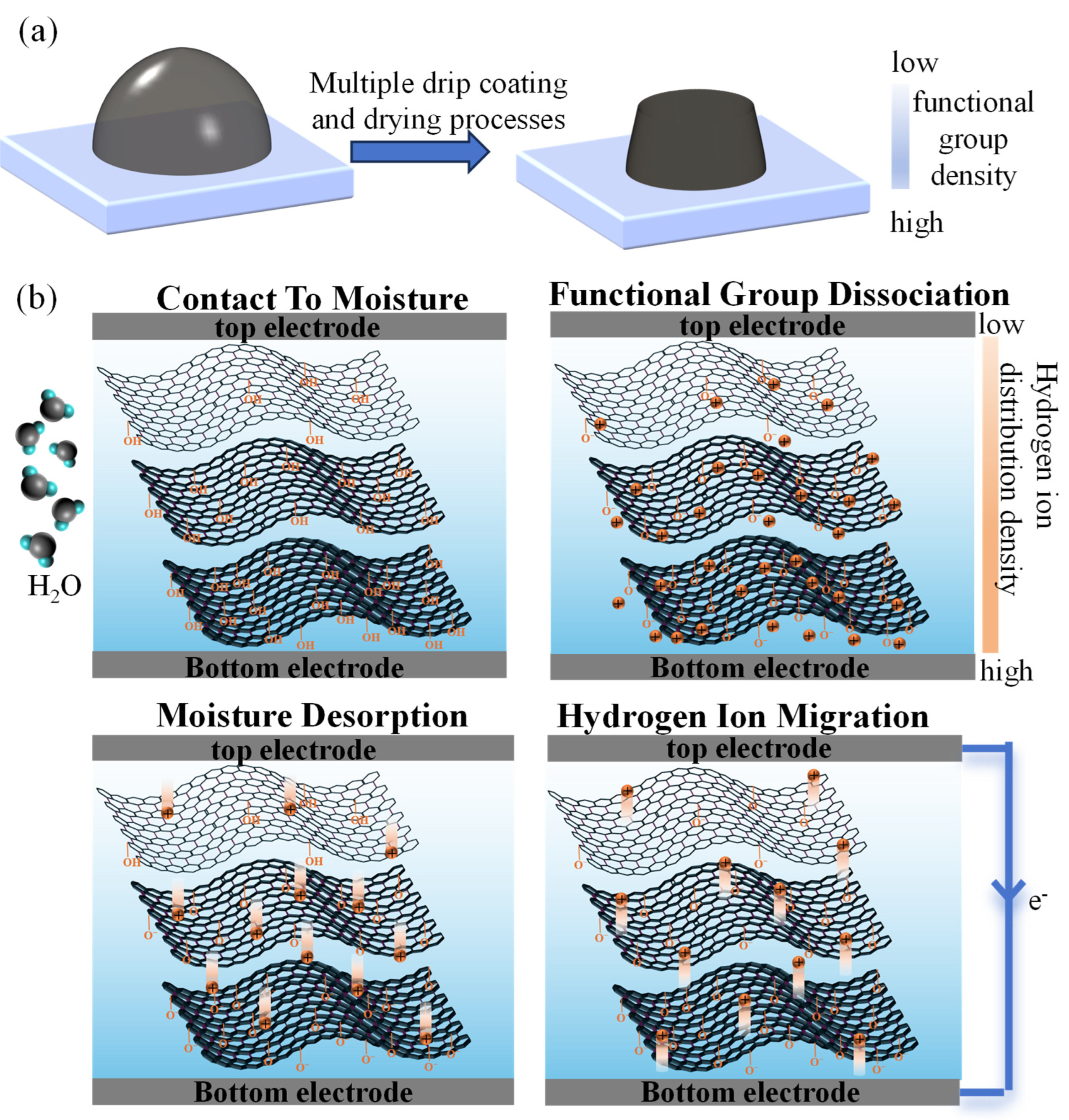
3.5. Mechanism Analysis
3.5.1. Power Generation Mechanism of MEGs
3.5.2. Investigating the Power Generation Effect of rGO/Ag Transition Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zang, S.; Chen, J.B.; Yamauchi, Y.; Sharshir, S.W.; Huang, H.Q.; Yun, J.H.; Wang, L.W.; Wang, C.; Lin, X.F.; Melhi, S.; et al. Moisture Power Generation: From Material Selection to Device Structure Optimization. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 19912–19930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Hou, S.H.; Wu, Z.X.; Wang, X.D.; Yin, L.; Liu, Y.J.; He, H.L.; Duan, S.C.; Wang, B.L.; Mao, J.; et al. Mechanical properties of thermoelectric generators. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 148, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Chen, Y.F.; Gao, Z.Q.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X.H. Advances in self-powered triboelectric pressure sensors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 20100–20130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustakim, N.S.M.; Kamaruzaman, D.; Abdullah, M.H.; Malek, M.F.; Parimon, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Abu Bakar, S.; Vasimalai, N.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mamat, M.H. Review of recent advances in piezoelectric material for nanogenerator application: Preparation methods, material selection, performance, applications, and future outlook. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 19003–19022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sum, M.Z.; Meng, Q.; Li, H.; Tian, Y.H. Polymer engineering in hydrogel-based moisture-electric generators for green energy harvesting. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Cheng, H.H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.P.; Liao, Q.H.; Yao, H.Z.; Shi, G.Q.; Qu, L.T. Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.J.; Zhou, M.; Yang, Q.F.; Yang, M.Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.X.; Yu, J.W. Flexible carbon dots composite paper for electricity generation from water vapor absorption. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 10639–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Ren, Q.Y.; Liu, S.F.; Sun, B.Q.; Lai, Y.C.; Zhang, X.H.; Liu, R.Y. Advances in asymmetric moist-electric generators with innovative heterogeneous structures. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 9406–9424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yang, P.H.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Ding, T.P.; Xue, G.B.; Chen, Q.; Feng, G.; Zhou, J. Induced Potential in Porous Carbon Films through Water Vapor Absorption. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8003–8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, R.; Ling, G.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Hao, C. Cu-Ag-C@Ni3S4 with core shell structure and rose derived carbon electrode materials: An environmentally friendly supercapacitor with high energy and power density. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guchait, A.; Pramanik, S.; Goswami, D.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Mondal, T. Elastomeric Ionic Hydrogel-Based Flexible Moisture-Electric Generator for Next-Generation Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 46844–46857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; He, T.C.; Huang, Y.X.; Cheng, H.H.; Li, C.; Xie, D.; Yang, P.F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Qu, L.T. Bilayer of polyelectrolyte films for spontaneous power generation in air up to an integrated 1,000 V output. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Tao, X.M.; Chen, W.; Mao, J.F.; Luo, H.; Lin, S.P.; Zhang, L.S.; Hao, J.H. Ionic Hydrogel for Efficient and Scalable Moisture-Electric Generation. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2200693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Zong, L.; Yang, W.Q.; Li, X.K.; You, J.; Wu, X.C.; Li, Z.H.; Li, C.X. Biological Nanofibrous Generator for Electricity Harvest from Moist Air Flow. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Saez, J.S.D.; Ao, X.; Yusuf, A.; Wang, D.Y. Highly-sensitive fire alarm system based on cellulose paper with low-temperature response and wireless signal conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 43, 134108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Gao, H.Y.; Ward, J.E.; Liu, X.R.; Yin, B.; Fu, T.D.; Chen, J.H.; Lovley, D.R.; Yao, J. Power generation from ambient humidity using protein nanowires. Nature 2020, 578, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.S.; Wang, Y.S.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Xu, H.; Tan, Y.S.; Li, Y.; Song, T.; Sun, B.Q. Constant Electricity Generation in Nanostructured Silicon by Evaporation-Driven Water Flow. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10619–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.X.; Ji, B.X.; Xu, T.; Gao, J.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.K.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L.T. Large-Scale Production of Flexible, High-Voltage Hydroelectric Films Based on Solid Oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30927–30935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.Z.; Xiao, M.; Zou, G.S.; Liu, L.; Duley, W.W.; Zhou, Y.N. Self-Powered Wearable Electronics Based on Moisture Enabled Electricity Generation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, R.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhu, G. Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of paraoxon ethyl in water and fruit samples based on defect-engineered graphene nanoribbons modified electrode. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, C.; Sun, C.; Yang, X. Simultaneously determination of trace Cd2+ and Pb2+ based on L-cysteine/graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Haroon Elrasheid, T.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhai, X.; Hu, X. Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide on an electrode for fast and sensitive determination of methylmercury in fish. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Qiu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Colorimetric aptasensor for the detection of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium using ZnFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide nanostructures as an effective peroxidase mimetics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 261, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, N.; Gong, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Selection and Application of ssDNA Aptamers against Clenbuterol Hydrochloride Based on ssDNA Library Immobilized SELEX. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J.; Peng, J. A Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Graphene Oxide Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles–Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Determination of Sunset Yellow in Soft Drinks. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Zou, X. Rapid determination of cadmium in rice using an all-solid RGO-enhanced light addressable potentiometric sensor. Food Chem. 2018, 261, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Tan, W.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; et al. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer probe based on functionalized graphene oxide and upconversion nanoparticles for sensitive and rapid detection of zearalenone. LWT 2021, 147, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, N.; Guo, Y.; Wang, K. A colorimetric biosensor for simultaneous ochratoxin A and aflatoxins B1 detection in agricultural products. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.S.; Ali, S.; Sabarinathan, D.; Murugavelu, M.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Recent progress on graphene quantum dots-based fluorescence sensors for food safety and quality assessment applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5765–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, W.; Ni, L. Immobilization of Horseradish Peroxidase on Multi-Armed Magnetic Graphene Oxide Composite: Improvement of Loading Amount and Catalytic Activity. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 57, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Cheng, H.H.; Zhang, Z.P.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L.T. Direct Power Generation from a Graphene Oxide Film under Moisture. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4351–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Dai, Y.T.; Zhang, H.; Luo, H.M.; Chen, Y.L. Preparation and Characterization of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Graphene Oxide Nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 7159–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Li, X.M.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y.; Fei, W.W.; Xue, M.M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.X.; Guo, W.L. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Cheng, H.H.; Yang, C.; Yao, H.Z.; Li, C.; Qu, L.T. All-region-applicable, continuous power supply of graphene oxide composite. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.M.; Tian, S.; Chen, X.; Liao, Y.F.; Jiang, F.; Ye, J.; He, Y.; Gui, Y.G.; Lian, Z.; Liu, G.; et al. A high-current and tunable moisture-enabled electric generator for wireless wearable electronics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 33039–33052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, D.; Duley, W.W.; Peng, P.; Xiao, M.; Feng, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Zou, G.S.; Zhou, Y.N. Moisture-Enabled Electricity Generation: From Physics and Materials to Self-Powered Applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2003722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Ding, X.T.; Cheng, H.H.; Han, G.Y.; Qu, L.T. Moisture-Enabled Electricity from Hygroscopic Materials: A New Type of Clean Energy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2209661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Huang, Y.X.; Qu, L.T.; Cheng, Q.L.; Shi, G.Q.; Jiang, L. Flexible in-plane graphene oxide moisture-electric converter for touchless interactive panel. Nano Energy 2018, 45, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.H.; Zhou, Q.H.; Shao, H.B.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L.T. Self-powered wearable graphene fiber for information expression. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Huang, Y.X.; Zhao, F.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.P.; Jiang, L.; Shi, G.Q.; Qu, L.T. Spontaneous power source in ambient air of a well-directionally reduced graphene oxide bulk. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2839–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, H.; Lee, H.; Yoon, D.; Jeon, S. Direct Fabrication of a Moisture-Driven Power Generator by Laser-Induced Graphitization with a Gradual Defocusing Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 26970–26975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xia, H.; Ni, Q.Q. A Wearable Sustainable Moisture-Induced Electricity Generator Based on rGO/GO/rGO Sandwich-Like Structural Film. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2021, 7, 2100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xia, H.; Ni, Q.Q. A sustainable, continuously expandable, wearable breath moisture-induced electricity generator. Carbon 2022, 194, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Qi, W.Z.; Cai, L.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.L.; Sun, M.X.; Yang, X.K.; Xiang, L.; Xie, D.; Ren, T.L. Enhanced room-temperature NO2− sensing performance of AgNPs/rGO nanocomposites. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 738, 136873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.Q.; Peng, B.L.; Xie, Z.J.; Du, S.; Zhang, L.B.; Zhu, J.T. Moist-Induced Electricity Generation by Electrospun Cellulose Acetate Membranes with Optimized Porous Structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57373–57381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.X.; Wang, K.X.; Ji, X.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Ma, Z.; Qiu, Y.F. A self-powered moisture detector using graphene oxide film constructed by asymmetric metal electrodes. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 810, 151880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Sun, S.; Lyu, W.Y.; Li, M.; Liu, W.D.; Shi, X.L.; Chen, Z.G. Advances in printing techniques for thermoelectric materials and devices. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belal, M.A.; Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Kaja, K.R.; Abdo, M.M.M.; Abd El-Moneim, A.; Janas, D.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kim, H.J. Advances in gas sensors using screen printing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 5447–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Hu, B.; Lan, S.; Wang, H. Flexographic and screen printing of carboxymethyl chitosan based edible inks for food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Arslan, M.; Li, Z.; Cen, S.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Xiao, J.; Zou, X. Application of Protein in Extrusion-Based 3D Food Printing: Current Status and Prospectus. Foods 2022, 11, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Qiu, G.; Zhao, P.; Awais, M.; Fan, B.; Huang, Y.; Tong, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, F. Regulation of rheological properties of soy protein isolate-beeswax based bigel inks for high-precision 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Wu, J.; Cai, L.; Li, M.; Dai, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Zhang, M. Effects of different hydrocolloids on the water migration, rheological and 3D printing characteristics of β-carotene loaded yam starch-based hydrogel. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Cen, S.; Liang, N.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Zou, X. Preparation of Pangasius hypophthalmus protein-stabilized pickering emulsions and 3D printing application. J. Food Eng. 2023, 341, 111333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, L.; Xu, Y.; Nie, M.; Li, D.; Zhou, C.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Rheological property, β-carotene stability and 3D printing characteristic of whey protein isolate emulsion gels by adding different polysaccharides. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, C.; Khin, M.N.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Design and development of dual-extruder food 3D printer based on selective compliance assembly robot arm and printing of various inks. J. Food Eng. 2024, 370, 111973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Feng, L.; Dai, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Yu, D. Improvement of 3D Printing Performance of Whey Protein Isolate Emulsion Gels by Regulating Rheological Properties: Effect of Polysaccharides Incorporation. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Chitrakar, B.; Xu, Y.; Wei, B.; Wang, B.; Lin, L.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H. Effect of various physical modifications of pea protein isolate (PPI) on 3D printing behavior and dysphagia properties of strawberry-PPI gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 158, 110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Fan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, W.; et al. Development and characterization of whole-grain buckwheat biscuit formula based on extruded 3D printing technology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 9766–9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, W.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. 4D printing system stimulated by curcumin/whey protein isolate nanoparticles: A comparative study of sensitive color change and post-processing. J. Food Eng. 2023, 342, 111357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, B.; Liang, N.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Paximada, P.; Xiaobo, Z. 4D printing of Pickering emulsion: Temperature-driven color changes. J. Food Eng. 2025, 386, 112258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beedasy, V.; Smith, P.J. Printed Electronics as Prepared by Inkjet Printing. Materials 2020, 13, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y.; Feng, J.Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.X.; Wu, Z.H.; Wen, J.Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.H. Electrohydrodynamic Printing of High-Resolution Self-Reduced Soldered Silver Nanowire Pattern for Wearable Flexible Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.X.; Feng, J.Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.Y.; Wen, J.Y.; Wang, S.; Tian, Y.H. Electrohydrodynamic Printing of Ultrafine and Highly Conductive Ag Electrodes for Various Flexible Electronics. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2300080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, Y.X.; Wen, J.Y.; Feng, J.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Sun, Q.; Tian, Y.H. Precision Control of Aerosol Jet Printing for Conformal Electronics Fabrication with Ultra-Fine and Wide-Range Resolution. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2025, 10, 2402114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.H.; Deng, Y.X.; Xiao, Y.K.; Cheng, H.H.; Zhang, P.P.; Huang, Y.X.; Shao, H.B.; Qu, L.T. Electric power generation via asymmetric moisturizing of graphene oxide for flexible, printable and portable electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.C.; Wang, H.Y.; Lu, B.; Guang, T.L.; Yang, C.; Huang, Y.X.; Cheng, H.H.; Qu, L.T. Fully printed planar moisture-enabled electric generator arrays for scalable function integration. Joule 2023, 7, 935–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.J.; Han, Y.F.; Cheng, H.; Xiong, Z.X.; Luo, B.; Ma, T.; Li, L.B.; Liu, S.N.; Chen, X.M.; Yi, C.L. Synthesized silver nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide/silver ink for aerosol jet printed conformal temperature sensor with a wide sensing range and excellent stability. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chi, F.Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, M.; Yao, B.W.; Li, Y.R.; Li, C.; Shi, G.Q. Synthesis of graphene oxide sheets with controlled sizes from sieved graphite flakes. Carbon 2016, 110, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimi, S.; Mazinani, S.; Bazargan, A.M.; Sharif, F. Effect of formulation and process on morphology and electrical conductivity of Ag-graphene hybrid inks. Synth. Met. 2021, 281, 116913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhang, L.H.; Wang, K.; Miao, L.J.; Lan, Q.F.; Jiang, K.M.; Lu, H.M.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Shen, B.; et al. Analysis of oxidation degree of graphite oxide and chemical structure of corresponding reduced graphite oxide by selecting different-sized original graphite. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17209–17217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaimin, N.S.; Hanifah, M.F.R.; Azhar, M.; Jaafar, J.; Aziz, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Rahman, M.A.; Aziz, F.; Yusof, N.; et al. The evolution of oxygen-functional groups of graphene oxide as a function of oxidation degree. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 278, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, M.A.; Heydaryan, K.; Khojasteh, H.; Montazer, A.H.; Eskandari, V. Green Synthesis of Ag NPs/rGO Nanocomposite for Use as a Non-enzymatic Sensor of H2O2. Plasmonics 2025, 20, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poostforush, M.; Azizi, H.; Ghasemi, I. Enhanced through-plane thermal conductive properties of Ag/rGO nanocomposite. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2019, 58, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvalkar, P.D.; Jagtap, A.S.; Prasad, N.R.; Yaul, A.R.; Sharma, K.K.K.; Ramteke, A.A. Bio-inspired preparation of Ag NPs, rGO, and Ag/rGO nanocomposites for acoustical, antioxidant, and plant growth regulatory studies. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.G.; Lv, S.H.; Liu, L.P.; Liu, X. High-quality preparation of graphene oxide via the Hummers’ method: Understanding the roles of the intercalator, oxidant, and graphite particle size. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.; Kim, S.J. The Chemical and structural analysis of graphene oxide with different degrees of oxidation. Carbon 2013, 53, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lin, J.G.; Lv, J.N.; Yang, Y.N.; He, X.J.; Liu, F.; Chen, N. Dynamic 3D hydrogen-bond network in siloxene-water system enables efficient moisture-enabled electricity generation. Nano Energy 2024, 131, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.B.; Xia, X.M.; Yang, R.J.; Yu, R.S.; Dai, F.F.; Chen, J.L.; Liu, W.; Wu, M.; Xu, J.; Chen, L. Selective reduction of epoxy groups in graphene oxide membrane for ultrahigh water permeation. Carbon 2021, 172, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Types of GO | Mixed Speed (rpm) | The Amount of KMnO4 (g) |
|---|---|---|
| GO-1 | 150 | 3 |
| GO-2 | 500 | 3 |
| GO-3 | 500 | 6 |
| Sample | Atomic Ratio (%) | O1 Element (%) | C/O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C C=C | C-O | C=O | COO | |||
| GO | 51.57 | 35.66 | 9.33 | 3.28 | 30.08 | 2.3 |
| rGO/Ag | 53.87 | 37.56 | 8.57 | — | 11.09 | 7.56 |
| Sample | Atomic Ratio (%) | O1 Element (%) | C/O Ratio | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-C C=C | C-O | C=O | COO | |||
| GO-1 | 49.18 | 28.29 | 16.2 | 4.33 | 30.02 | 2.33 |
| GO-2 | 47.82 | 34.84 | 11.72 | 5.56 | 31.81 | 2.14 |
| GO-3 | 49.45 | 12.58 | 34.28 | 3.69 | 36.26 | 1.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Li, G.; Wen, J.; Feng, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y. Flexible Moisture–Electric Generator Based on Vertically Graded GO–rGO/Ag Films. Materials 2025, 18, 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122766
Wang S, Li G, Wen J, Feng J, Zhang H, Tian Y. Flexible Moisture–Electric Generator Based on Vertically Graded GO–rGO/Ag Films. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122766
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shujun, Geng Li, Jiayue Wen, Jiayun Feng, He Zhang, and Yanhong Tian. 2025. "Flexible Moisture–Electric Generator Based on Vertically Graded GO–rGO/Ag Films" Materials 18, no. 12: 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122766
APA StyleWang, S., Li, G., Wen, J., Feng, J., Zhang, H., & Tian, Y. (2025). Flexible Moisture–Electric Generator Based on Vertically Graded GO–rGO/Ag Films. Materials, 18(12), 2766. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122766






