A Finite Element Analysis of a New Dental Implant Design: The Influence of the Diameter, Length, and Material of an Implant on Its Biomechanical Behavior
Highlights
- New approach paradigm for dental implants—from conical to cylindrical—with new features;
- A novel dental implant to improve the clinical planning and long-term longevity;
- FEM analysis of the mechanical behavior of a single-component cylindrical dental implant;
- Ti6Al4V alloy generates significantly lower bone stress/strains vs. Ti35Nb7Zr5Ta.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
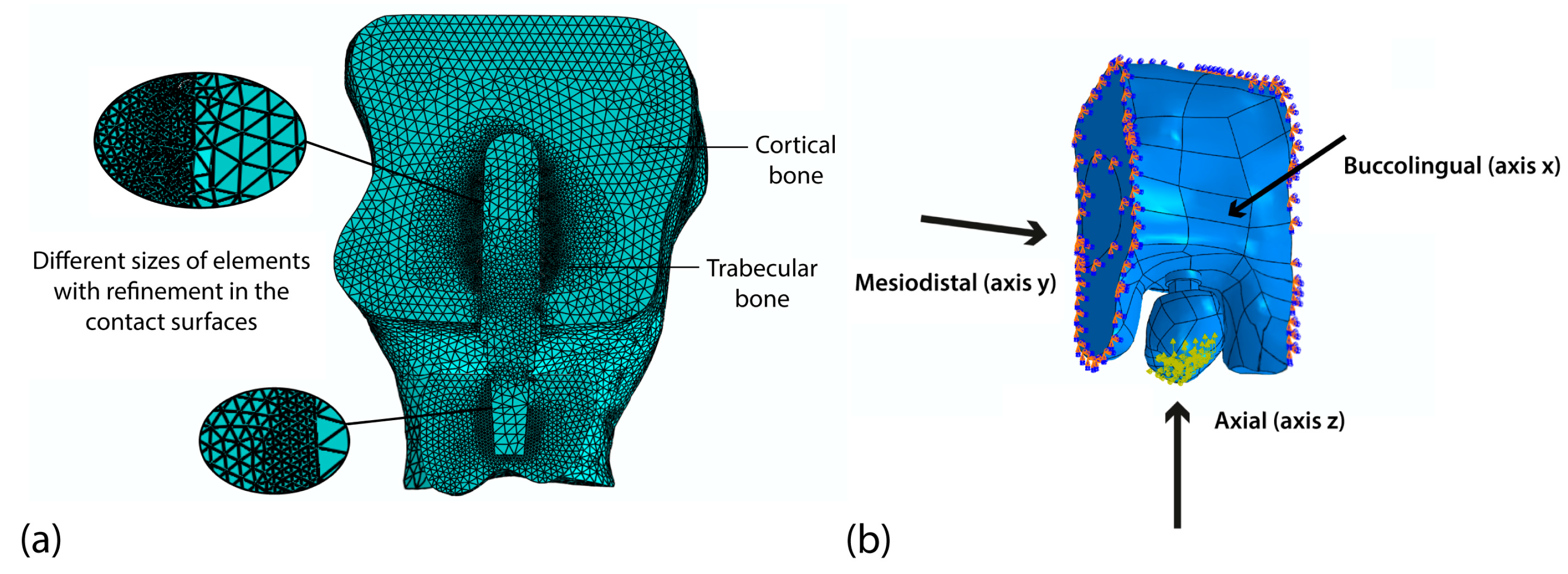
2.1. Dental Implant Models
2.2. The Assembly of the Crown Dental Implant System
2.3. Analysis Using the Finite Element Method
2.4. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
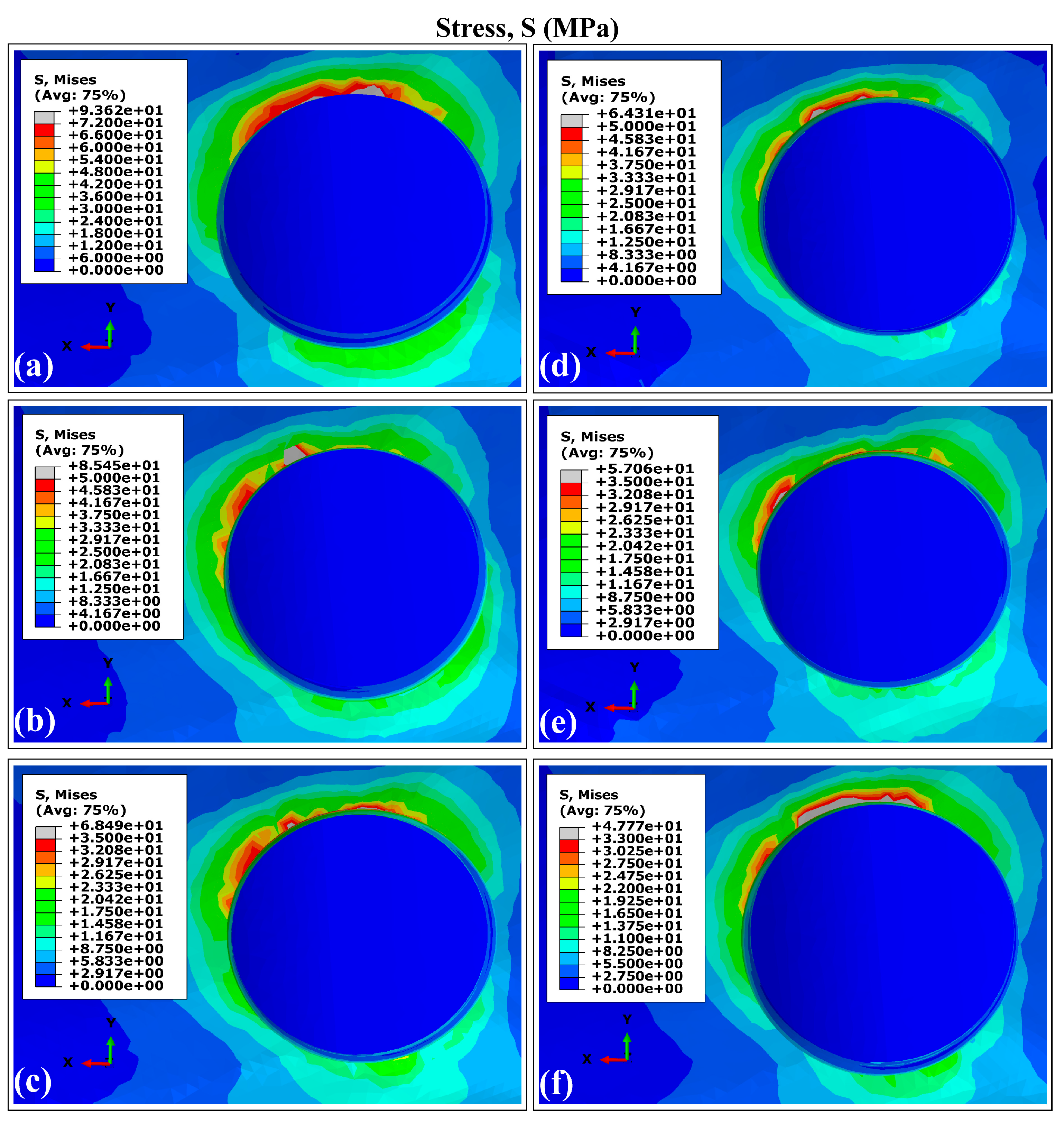
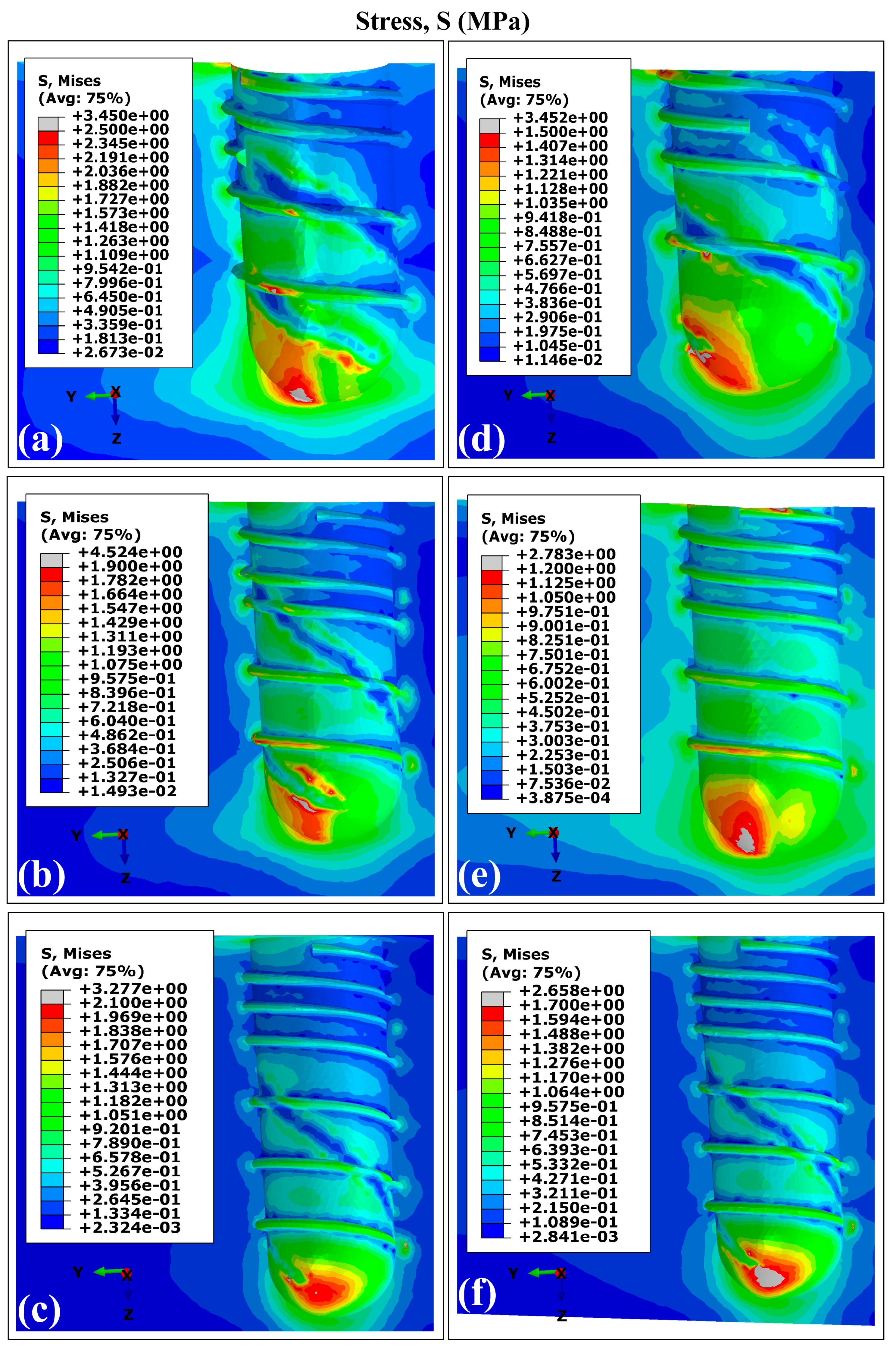
3.1. Stress and Strain Distribution Patterns in Cortical Bone Using Ti6Al4V (α+β Ti)
Stress and Strain Distribution Patterns in Cortical Bone Using Ti35Nb7Zr5Ta (β-Ti)
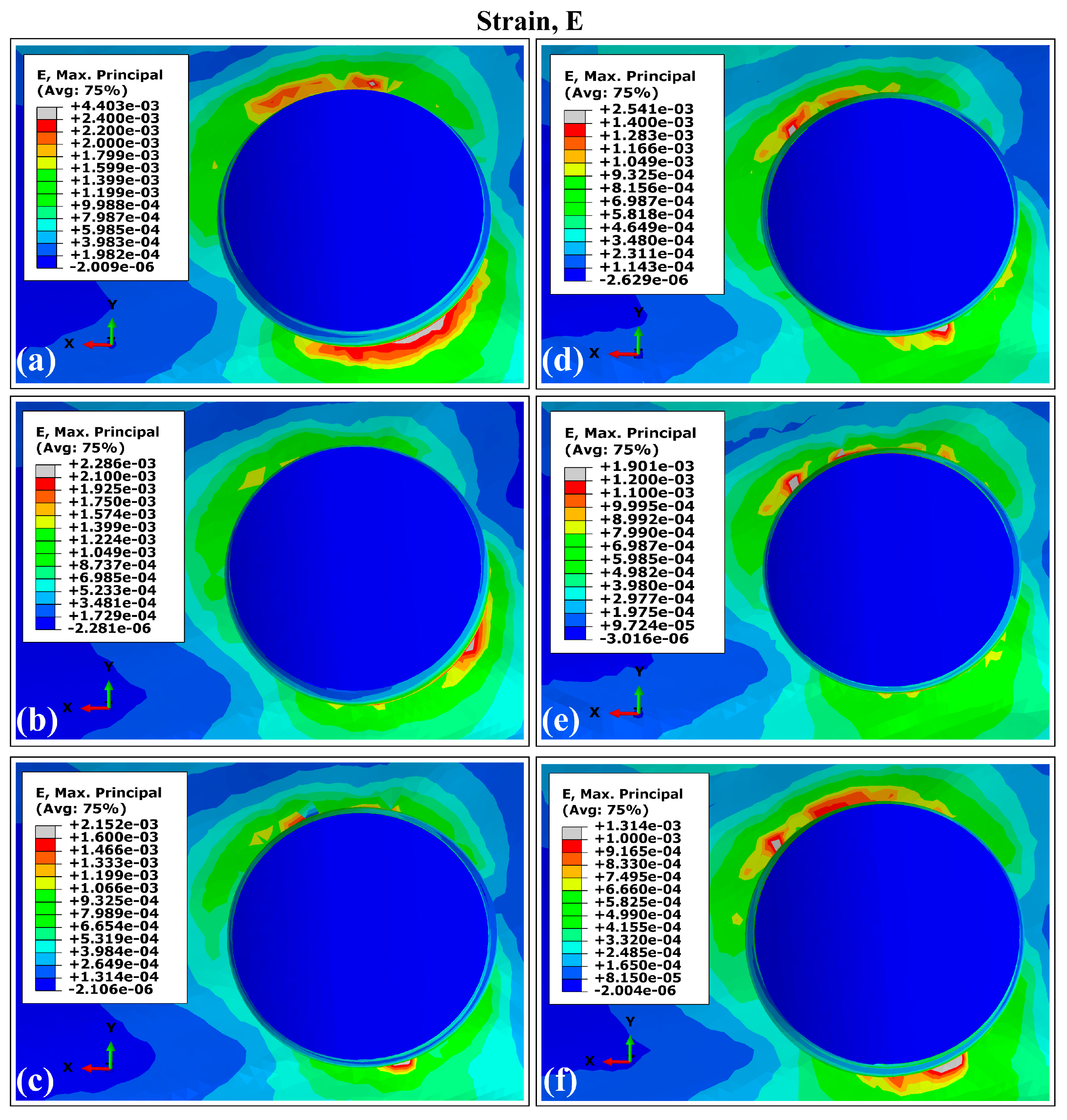
3.2. Distribution Patterns of Stresses and Strains in Trabecular Bone Using Ti6Al4V (α+β Ti)
Distribution Patterns of Stresses and Strains in Trabecular Bone Using Ti35Nb7Zr5Ta (β-Ti)
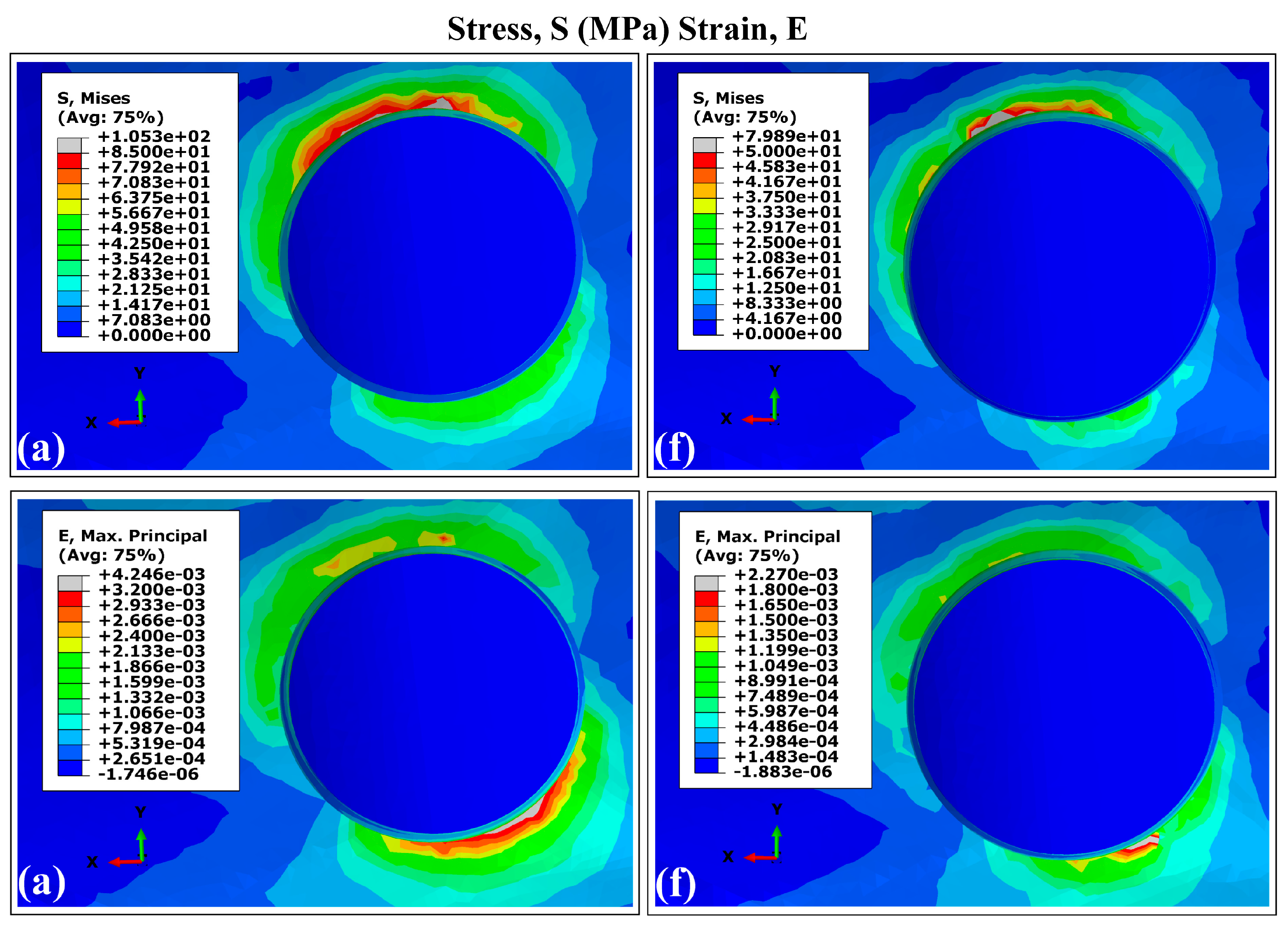
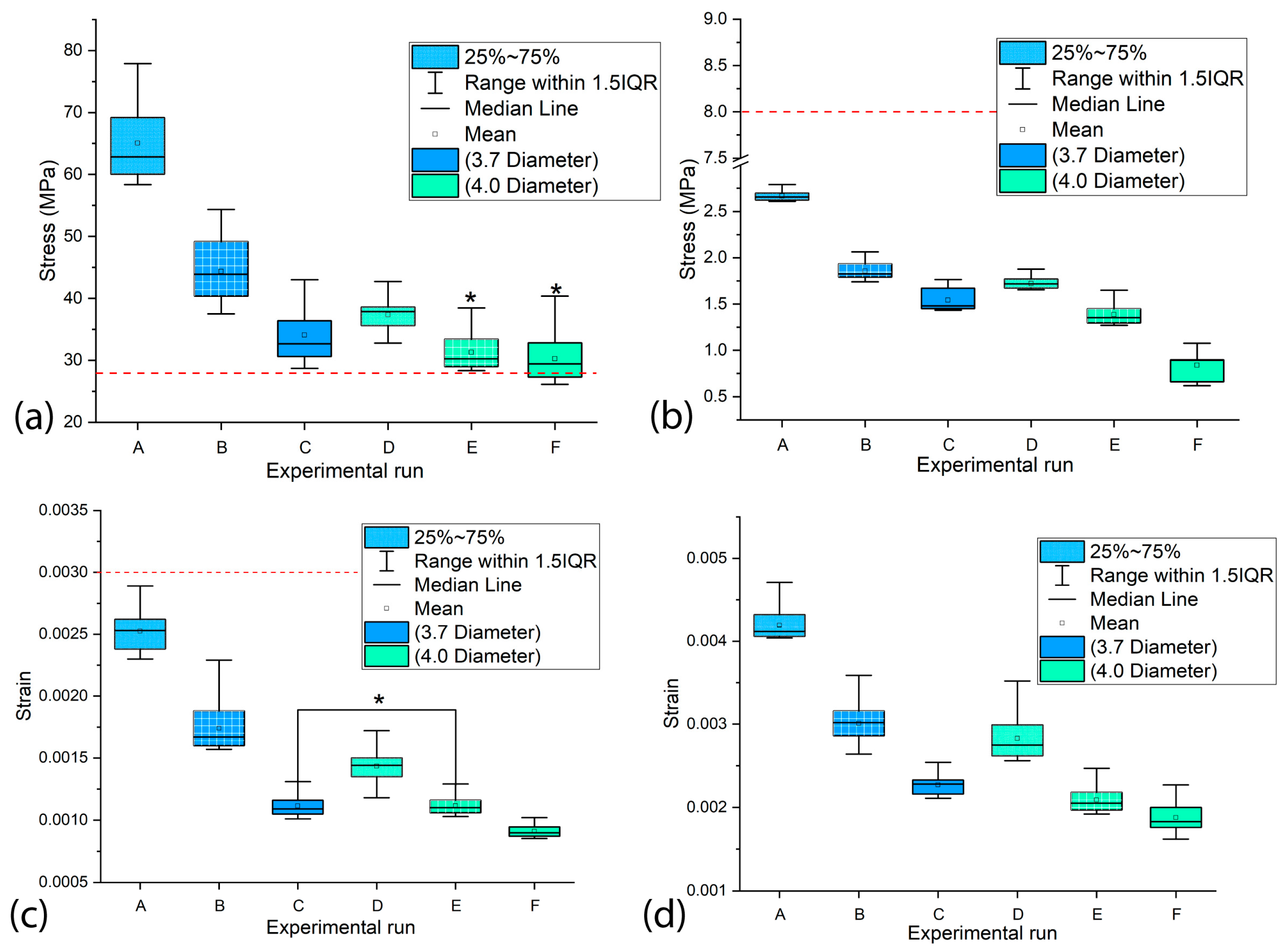
3.3. The Influence of the Diameter and Length of the Dental Implants on the Values of MVMES and MVMS in the Peri-Implant Bone
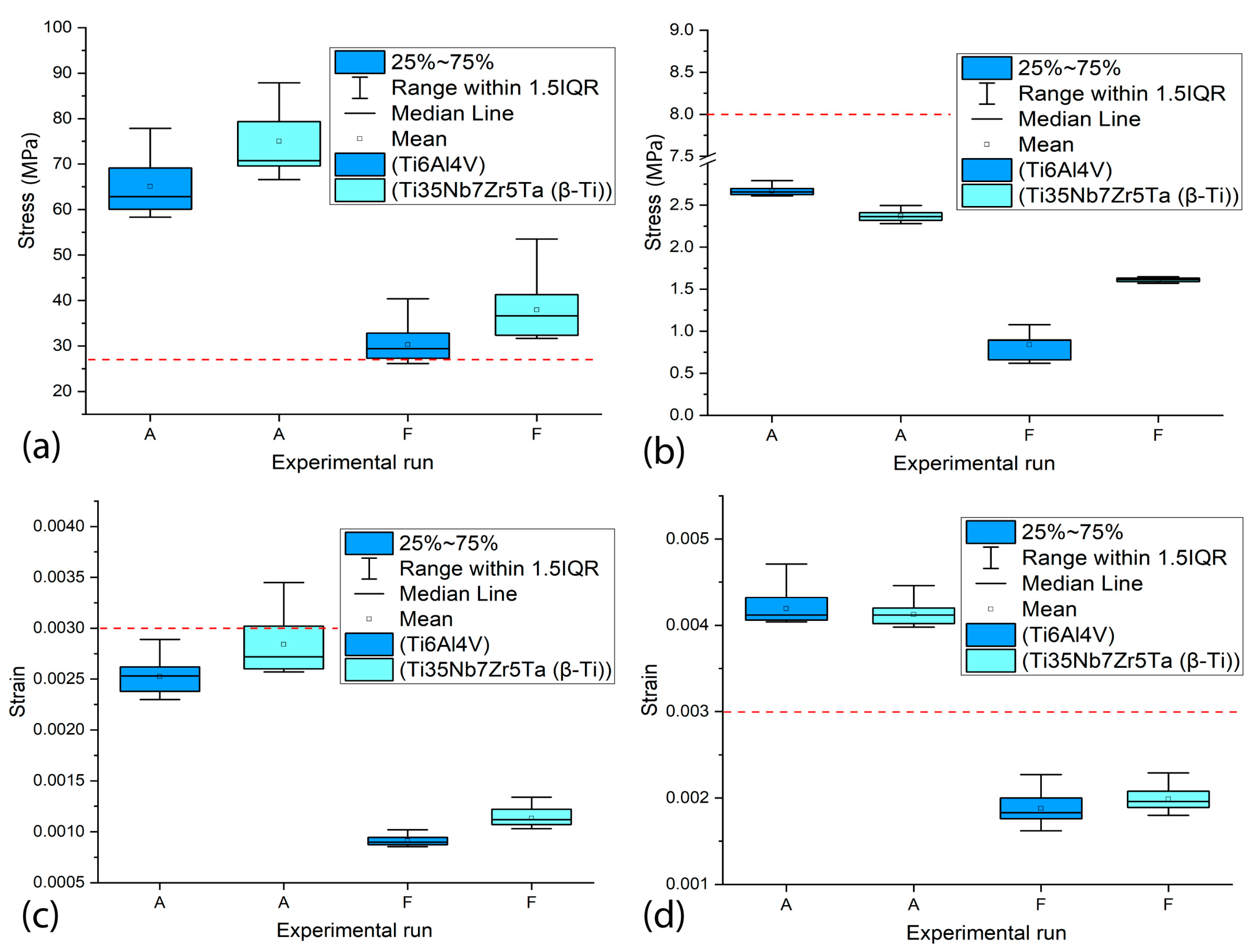
3.4. The Influence of the Type of Material on the Values of MVMES and MVMS in the Peri-Implant Bone
4. Conclusions
- Peak stress concentrations occurred in peri-implant cortical bone, particularly in the maxillary surface region adjacent to the implant neck. This mechanical behavior stems from the elevated Young’s modulus of the cortical bone, which enhances its load-bearing capacity. On the contrary, the maximum strain values were localized in the trabecular bone regions.
- Both the implant diameter and length demonstrated statistically significant effects (p < 0.05) on the peak equivalent stress and strain values in cortical and trabecular bone.
- Implant diameter emerged as the dominant variable affecting mechanical response, attributable to increased implant–bone contact area that promotes load dissipation and consequently reduces peri-implant stress/strain magnitudes.
- Superior biomechanical outcomes consistently correlated with larger implant dimensions, suggesting enhanced clinical performance potential for crown–implant systems featuring maximum diameter and length configurations.
- The material of the dental implant demonstrated a statistically significant influence (p < 0.05) on the maximum levels of stress and strain generated in the cortical and trabecular bones. In general, the Ti35Nb7Zr5Ta alloy implants showed higher maximum values of VMES and VMS than those generated by Ti6Al4V alloy implants.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| VMES | von Mises equivalent stress |
| VMS | von Mises strain |
| MVMES | Maximum von Mises equivalent stress |
| MVMS | Maximum von Mises strain |
References
- Alghamdi, H.S.; Jansen, J.A. The development and future of dental implants. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazli, L.; Khoramabadi, H.N.; Chahardehi, A.M.; Arsad, H.; Malekpouri, B.; Jazi, M.A.; Azizabadi, N. Factors influencing the failure of dental implants: A Systematic Review. J. Compos. Compd. 2019, 2, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Zeng, M.; Chu, H.; Gan, Z.; Duan, J.; Rong, M. The survival rates and risk factors of implants in the early stage: A retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanoglu Erbasar, G.N.; Hocaoğlu, T.P.; Erbasar, R.C. Risk factors associated with short dental implant success: A long-term retrospective evaluation of patients followed up for up to 9 years. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krisam, J.; Ott, L.; Schmitz, S.; Klotz, A.-L.; Seyidaliyeva, A.; Rammelsberg, P.; Zenthöfer, A. Factors affecting the early failure of implants placed in a dental practice with a specialization in implantology–a retrospective study. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimbalkar, S.; Dhatrak, P.; Gherde, C.; Joshi, S. A review article on factors affecting bone loss in dental implants. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 43, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, T. The effect of individuals’ oral hygiene habits and knowledge levels on peri-implant health and disease: A questionnaire-based observational study. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmqvist, S.; Erdenborg, J.; Johannsen, G.; Johannsen, A. Patient’s experiences of dental implants, peri-implantitis and its treatment-A qualitative interview study. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2024, 22, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, S.; Favril, C.; De Nutte, M.; Teughels, W.; Quirynen, M. Patient compliance as a risk factor for the outcome of implant treatment. Periodontology 2000 2019, 81, 209–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowsky, S.J. Occlusal overload with dental implants: A review. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Aguilar, L.; Gatti, A.; Abduo, J.; Lee, P.V.S.; Ackland, D. Load response of the natural tooth and dental implant: A comparative biomechanics study. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2019, 11, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szajek, K.; Wierszycki, M. Screw preload loss under occlusal load as a predictor of loosening risk in varying dental implant designs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 148, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pevida, E.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Diéguez-Pereira, M.; Estrada-Martínez, A.; Montalbán-Vadillo, O.; Jiménez-Garrudo, A. Consequences of peri-implant bone loss in the occlusal load transfer to the supporting bone in terms of magnitude of stress, strain, and stress distribution: A finite element analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 3087071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.A.; Calvo-Guirado, J.L.; Romanos, G.E. Effects of occlusal forces on the peri-implant-bone interface stability. Periodontology 2000 2019, 81, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagegni, A.; Abou-Ayash, S.; Rücker, G.; Algarny, A.; Att, W. The influence of prosthetic material on implant and prosthetic survival of implant-supported fixed complete dentures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2019, 63, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misch, C.E.; Resnik, R.R. Available bone and dental implant treatmentplans. In Misch’s Contemporary Implant Dentistry, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 415. [Google Scholar]
- Rues, S.; Schmitter, M.; Kappel, S.; Sonntag, R.; Kretzer, J.P.; Nadorf, J. Effect of bone quality and quantity on the primary stability of dental implants in a simulated bicortical placement. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 25, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, J.; Lapinska, B.; Nissan, J.; Lukomska-Szymanska, M. Factors Influencing Marginal Bone Loss around Dental Implants: A Narrative Review. Coatings 2021, 11, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, D.A.; Arosio, P.; Capparè, P.; Barbon, S.; Gherlone, E.F. Gherlone, Stability of dental implants and thickness of cortical bone: Clinical research and future perspectives. A systematic review. Materials 2021, 14, 7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarot, S.; Christensen, B.J.; Chapple, A.G.; Block, M.S. Block, Prediction of residual alveolar bone height in the posterior maxilla after dental extractions. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 80, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, M.; Fernández-Romero, E.; Vallecillo, C.; Toledano, R.; Osorio, M.T.; Vallecillo-Rivas, M. Short versus standard implants at sinus augmented sites: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 6681–6698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, J.; Kang, I.; Lee, H.; Noh, G. Effects of assessing the bone remodeling process in biomechanical finite element stability evaluations of dental implants. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 221, 106852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, S.; Müftü, S. The interplay between bone healing and remodeling around dental implants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, D. Osseous remodeling around dental implants. J. Oral Implant. 2019, 45, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherde, C.; Dhatrak, P.; Nimbalkar, S.; Joshi, S. A comprehensive review of factors affecting fatigue life of dental implants. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 43, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaie, B.; Khalili, S.M.R. Evaluation of fatigue life for dental implants using FEM analysis. Prosthesis 2021, 3, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Takashima, M.; Matsuzaki, N.; Takada, S. Marginal bone loss in dental implants: A literature review of risk factors and treatment strategies for prevention. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2024, 69, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, S.S.; Cabbar, F.; Guler, N. Local and systemic factors associated with marginal bone loss around dental implants: A retrospective clinical study. Quintessence Int. 2020, 51, 128–141. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, D.-B.; Jeng, Y.-R. Three-dimensional finite element investigation into effects of implant thread design and loading rate on stress distribution in dental implants and anisotropic bone. Materials 2021, 14, 6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, M.I.; Daud, R.; Ibrahim, I.; Mat, F.; Mansor, N.N. Mansor, Biomechanical overloading factors influencing the failure of dental implants: A review. In Symposium on Damage Mechanism in Materials and Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Lovatto, S.T.; Bassani, R.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; dos Santos, M.B.F. Influence of different implant geometry in clinical longevity and maintenance of marginal bone: A systematic review. J. Prosthodont. 2018, 28, e713–e721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, L.C.D.C.; Faot, F.; Madruga, M.d.M.; Marcello-Machado, R.M.; Bordin, D.; Cury, A.A.D.B. Effect of implant macrogeometry on peri-implant healing outcomes: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 23, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreve, S.; Ferreira, I.; Valente, M.L.d.C.; dos Reis, A.C. Relationship between dental implant macro-design and osseointegration: A systematic review. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero-Climent, M.; López-Jarana, P.; Lemos, B.F.; Gil, F.J.; Falcão, C.; Ríos-Santos, J.V.; Ríos-Carrasco, B. Relevant design aspects to improve the stability of titanium dental implants. Materials 2020, 13, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; de Ibarra, N.L.S.; Martín, I.M.; Rotaeche, L.S. Influence of dental implant diameter and bone quality on the biomechanics of single-crown restoration. A finite element analysis. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elleuch, S.; Jrad, H.; Kessentini, A.; Wali, M.; Dammak, F. Design optimization of implant geometrical characteristics enhancing primary stability using FEA of stress distribution around dental prosthesis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 24, 1035–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büyük, F.N.; Savran, E.; Karpat, F. Review on finite element analysis of dental implants. J. Dent. Implant Res. 2022, 41, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcinelli, C.; Valente, F.; Vasta, M.; Traini, T. Finite element analysis in implant dentistry: State of the art and future directions. Dent. Mater. 2023, 39, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudagi, V.; Shivakumar, S.; Talwade, P. Applications of finite element analysis in dentistry: A review. J. Int. Oral Health 2021, 13, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla, R.; Forero, L.; González-Estrada, O.A. Comparative study of the influence of dental implant design on the stress and strain distribution using the finite element method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1159, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreevich, S.Y.; Zurabovich, C.D.; Mikhailovich, A.V. The usage of the finite element analysis in the design of new dental implant systems. Int. J. Innov. Med. 2023, 1, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Jo, M.; Noh, G. Biomechanical effects of dental implant diameter, connection type, and bone density on microgap formation and fatigue failure: A finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 200, 105863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, L.; Cicciù, M.; D’amico, C.; Mauceri, R.; Oteri, G.; Cervino, G. Finite element method and von mises investigation on bone response to dynamic stress with a novel conical dental implant connection. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2976067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pammer, D. Evaluation of postoperative dental implant primary stability using 3D finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 22, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakir, S.M.; Muhsin, S.A.; Al Marza, R. Finite Element Modelling Based Studies for Dental Implants: Systematic Review. J. Tech. 2022, 4, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanaclocha, V.; Atienza, C.; Vanaclocha, A.; Peñuelas, A.; Gómez-Herrero, J.; Pérez-Carrió, F.; Diego-Leyda, J.A.; Sáiz-Sapena, N.; Vanaclocha, L. New Subperiosteal Dental Implant Design with Finite Element Analysis and Mechanical Validation: A Design Validation Study. Materials 2025, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-C.; Lin, D.-H.; Jiang, C.-P.; Lee, S.-Y. Design improvement and dynamic finite element analysis of novel ITI dental implant under dynamic chewing loads. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, S555–S561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommeti, V.K.; Pramanik, S.; Roy, S. Design of customized coated dental implants using finite element analysis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.; Naik, N. A comparative study on the effect of stress in dental implant structure using finite element analysis. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2019, 9, 709–717. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, J.V.C.; Celles, C.A.S.; de Andrade, C.S.A.F.; Afonso, C.R.M.; Nagay, B.E.; Barão, V.A.R. Recent advances and prospects in β-type titanium alloys for dental implants applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 6029–6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Yu, W.; Jin, M.; Wang, Y.; Shang, X.; Lin, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, E. Mechanobiologically optimized Ti–35Nb–2Ta–3Zr improves load transduction and enhances bone remodeling in tilted dental implant therapy. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Alevizakos, V.; Mitov, G.; Ahrens, A.; von See, C. The influence of implant site preparation and sterilization on the performance and wear of implant drills. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant 2021, 36, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, N.; Kunusoth, R.; Alwala, A.M.; Prakash, R.; Sampreethi, S.; Katkuri, S. Cylindrical Implant Versus Tapered Implant: A Comparative Study. Cureus 2022, 14, e29675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugova, S.; Abboud, M. Thermal Evaluation of Bone Drilling with a One-Drill Protocol. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- obau-Porrua, A.; González, J.E.; Rodríguez-Guerra, J.; González-Mederos, P.; Navarro, P.; de la Rosa, J.E.; Carbonell-González, M.; Araneda-Hernández, E.; Torres, Y. Biomechanical behavior of a new design of dental implant: Influence of the porosity and location in the maxilla. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3255–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robau-Porrua, A.; González, J.E.; Arancibia-Castillo, R.; Picardo, A.; Araneda-Hernández, E.; Torres, Y. Design, fabrication, and characterization of novel dental implants with porosity gradient obtained by Selective Laser Melting. Mater. Des. 2025, 251, 113660. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, Y.; Ruíz, J.G.; Ruiz-Valverde, O.; Pérez-Álvarez, M. Simulation of the influence of the platform switching of a model of dental implant on the bio-mechanics of maxillary bones. In Proceedings of the Dental Implants, Chicago, IL, USA, 29 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pevida, E.; Brizuela-Velasco, A.; Chávarri-Prado, D.; Jiménez-Garrudo, A.; Sánchez-Lasheras, F.; Solaberrieta-Méndez, E.; Diéguez-Pereira, M.; Fernández-González, F.J.; Dehesa-Ibarra, B.; Monticelli, F. Biomechanical Consequences of the Elastic Properties of Dental Implant Alloys on the Supporting Bone: Finite Element Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1850401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadad, A.A.; Romero-Resendiz, L.; Rossi, M.; Rodríguez-Albelo, L.; Lascano, S.; Afonso, C.R.; Alcudia, A.; Amigó, V.; Torres, Y. Findings and perspectives of β-Ti alloys with biomedical applications: Exploring beyond biomechanical and biofunctional behaviour. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3550–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellizzer, E.P.; Lemos, C.A.A.; Almeida, D.A.F.; Batista, V.E.D.S.; Júnior, J.F.S.; Verri, F.R. Biomechanical analysis of different implant-abutments interfaces in different bone types: An in silico analysis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 90, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.O. Biomechanical analysis of different implant-overdenture loading protocols under dynamic loads. J. Am. Sci. 2013, 9, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Himmlová, L.; Dostálová, T.; Kácovský, A.; Konvičková, S. Influence of implant length and diameter on stress distribution: A finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemineni, B.C.; Mahendra, J.; Nasina, J.; Mahendra, L.; Shivasubramanian, L.; Perika, S.B. Evaluation of maximum principal stress, von mises stress, and deformation on surrounding mandibular bone during insertion of an implant: A three-dimensional finite element study. Cureus 2020, 12, e9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretto, P.H.W.; dos Santos, M.B.F.; Spazzin, A.O.; Pereira, G.K.R.; Bacchi, A. Assessment of stress/strain in dental implants and abutments of alternative materials compared to conventional titanium alloy—3D non-linear finite element analysis. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 23, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; van den Beucken, J.J. Mechanical aspects of dental implants and osseointegration: A narrative review. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 103, 103574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Fraulob, M.; Haïat, G. Biomechanical behaviours of the bone–implant interface: A review. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20190259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, X.; Wan, Q.; Xie, G.; Pei, X. Biomechanical behavior analysis of four types of short implants with different placement depths using the finite element method. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023, 129, 447.e1–447.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robau-Porrua, A.; Pérez-Rodríguez, Y.; Soris-Rodríguez, L.M.; Pérez-Acosta, O.; González, J.E. The effect of diameter, length and elastic modulus of a dental implant on stress and strain levels in peri-implant bone: A 3D finite element analysis. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2020, 30, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Lan, J.; Ma, S. Porous structure design and mechanical behavior analysis based on TPMS for customized root analogue implant. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 115, 104222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, D.; Couto, R.; Fonseca, E.M.; Carreiras, A.R. Numerical analysis of the mechanical stimuli transferred from a dental implant to the bone. J. Comput. Appl. Res. Mech. Eng. (JCARME) 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Frost, H.M. Bone’s mechanostat: A 2003 update, The Anatomical record part a: Discoveries in molecular, cellular, and evolutionary biology: An official publication of the american association of anatomists. Anat. Rec. 2003, 275, 1081–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggi, L.; Cappelloni, I.; Di Girolamo, M.; Maceri, F.; Vairo, G. The influence of implant diameter and length on stress distribution of osseointegrated implants related to crestal bone geometry: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2008, 100, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Liao, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Effect of diameter and length on stress distribution of the alveolar crest around immediate loading implants. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2009, 11, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangsisied, S.; Chantarapanich, N.; Veerasakul, M.S.; Inglam, S. Effect of implant diameter and cortical bone thickness on biomechanical performance of short dental implant-supported distal cantilever: A finite element study. Eng. J. 2021, 25, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, K.; Sridevi, J.; Kalavathy, N.; Nagaranjani, P.; Sharmila, M.R. Evaluation of stress distribution in bone of different densities using different implant designs: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Indian Prosthodont. Soc. 2012, 13, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.-H.; Zhu, X.-H.; Xie, J.; Sohodeb, V.K.; Ding, X. Influence of Trabecular Bone on Peri-Implant Stress and Strain Based on Micro-CT Finite Element Modeling of Beagle Dog. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 3926941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, M.; Luo, L.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y. Effect of short implant crown-to-implant ratio on stress distribution in anisotropic bone with different osseointegration rates. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, H.; Shi, L.; Fok, A.S.; Ucer, C.; Devlin, H.; Horner, K.; Silikas, N. A mathematical model for simulating the bone remodeling process under mechanical stimulus. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experimental Run | Implant Parameter | |
|---|---|---|
| D (mm) | L (mm) | |
| A | 3.7 | 8 |
| B | 3.7 | 10 |
| C | 3.7 | 12 |
| D | 4.0 | 8 |
| E | 4.0 | 10 |
| F | 4.0 | 12 |
| Material | Young’s Modulus, E (MPa) | Shear Modulus, G (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio, ν | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V (dental implant) | 110,000 | - | 0.32 | [58] |
| Ti35Nb7Zr5Ta (β-Ti) (dental implant) | 55,000 | - | 0.32 | [59] |
| Feldspathic ceramic (crown) | 82,800 | - | 0.35 | [60] |
| Cortical bone | Ex = 17,900 * Ey = 26,600 Ez = 12,500 | Gyx = 4500 Gyz = 7100 Gxz= 5300 | νxy = 0.26 νxz = 0.31 νyz = 0.28 | [61] |
| Trabecular bone | Ex = 1148 Ey = 1148 Ez = 21 | Gyx = 68 Gyz = 434 Gxz = 68 | νxy = 0.05 νxz = 0.055 νyz = 0.322 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Mederos, P.; Rodríguez-Guerra, J.; González, J.E.; Picardo, A.; Torres, Y. A Finite Element Analysis of a New Dental Implant Design: The Influence of the Diameter, Length, and Material of an Implant on Its Biomechanical Behavior. Materials 2025, 18, 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122692
González-Mederos P, Rodríguez-Guerra J, González JE, Picardo A, Torres Y. A Finite Element Analysis of a New Dental Implant Design: The Influence of the Diameter, Length, and Material of an Implant on Its Biomechanical Behavior. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122692
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Mederos, Pedro, Jennifer Rodríguez-Guerra, Jesús E. González, Alberto Picardo, and Yadir Torres. 2025. "A Finite Element Analysis of a New Dental Implant Design: The Influence of the Diameter, Length, and Material of an Implant on Its Biomechanical Behavior" Materials 18, no. 12: 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122692
APA StyleGonzález-Mederos, P., Rodríguez-Guerra, J., González, J. E., Picardo, A., & Torres, Y. (2025). A Finite Element Analysis of a New Dental Implant Design: The Influence of the Diameter, Length, and Material of an Implant on Its Biomechanical Behavior. Materials, 18(12), 2692. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122692








