Mg–Zn–Ca Alloy with Ultra-High Ductility and Strength Processed by Screw Rolling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results
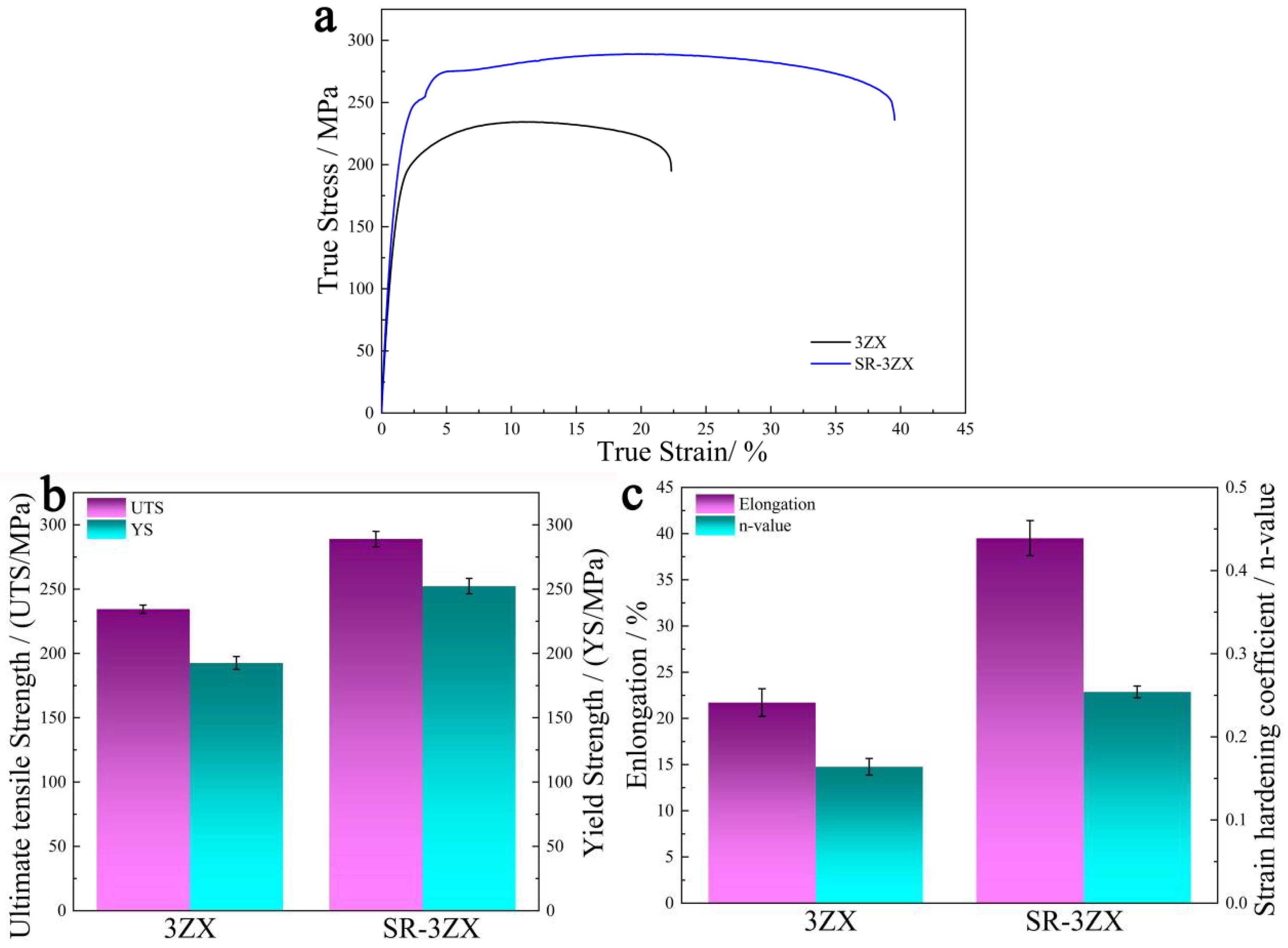
3.1. Tensile Properties
3.2. Microstructures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Ding, P.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Liu, D. In vitro and in vivo studies on the degradation and biosafety of Mg-Zn-Ca-Y alloy hemostatic clip with the carotid artery of SD rat model. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 115, 111093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Fukumoto, T.; Urade, T.; Kido, M.; Toyama, H.; Asari, S.; Ajiki, T.; Ikeo, N.; Mukai, T.; Ku, Y. Development of a new biodegradable operative clip made of a magnesium alloy: Evaluation of its safety and tolerability for canine cholecystectomy. Surgery 2017, 161, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Xiong, L.; Guo, X.; Yan, Y.; Yu, K.; Dai, Y.; et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of the effect of biodegradable magnesium alloys on osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Pan, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; et al. Mechanical properties and bio-corrosion behavior of Mg-Zn-Zr alloy influenced by rotary swaging. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Xu, H.; Song, F.; Wen, P.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, Y. Additive manufacturing of porous magnesium alloys for biodegradable orthopedic implants: Process, design, and modification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 182, 79–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, V.; Tardei, C.; Clicinschi, F.M. Biodegradable Mg alloys for orthopedic implants—A review. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1884–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Achieving high strength-ductility synergy in Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr alloy by controlling extrusion processes parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 916, 147342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Chen, T.; Bi, G.; Li, Y.; Tang, D.; Wang, X. Coordinating the deformation of a low-alloyed magnesium alloy for a superior combination of strength and ductility through core-shell structured reinforcements. Acta Mater. 2024, 281, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeo, N.; Nakamura, R.; Naka, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Yoshida, T.; Urade, T.; Fukushima, K.; Yabuuchi, H.; Fukumoto, T.; Ku, Y.; et al. Fabrication of a magnesium alloy with excellent ductility for biodegradable clips. Acta Biomater. 2016, 29, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holweg, P.; Berger, L.; Cihova, M.; Donohue, N.; Clement, B.; Schwarze, U.; Sommer, N.G.; Hohenberger, G.; van den Beucken, J.J.J.P.; Seibert, F.; et al. A lean magnesium–zinc–calcium alloy ZX00 used for bone fracture stabilization in a large growing-animal model. Acta Biomater. 2020, 113, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.H.; Avey, T.; Nam, K.H.; Dean, D.; Luo, A.A. In vitro and in vivo assessment of squeeze-cast Mg-Zn-Ca-Mn alloys for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2022, 150, 442–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Smith, C.; Sankar, J. Recent advances on the development of magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 4561–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, R.; Gao, Y. Enhanced strength-ductility synergy and activation of non-basal slip in as-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca alloy via heterostructure. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.P.; Geng, L.; Huang, L.J.; Zhang, X.X.; Dong, C.C. Enhanced mechanical properties in fine-grained Mg-1.0Zn-0.5Ca alloys prepared by extrusion at different temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horky, J.; Bryta, K.; Krystian, M.; Mozdzen, G.; Mingler, B.; Sajti, L. Improving mechanical properties of lean Mg–Zn–Ca alloy for absorbable implants via Double Equal Channel Angular Pressing (D-ECAP). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 826, 142002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Cai, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Song, C. Structural optimization and in vitro corrosion analysis of biodegradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy clip. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2025, 161, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, X.B.; Wang, Z.X.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, X.L.; Zhao, Y.Q. Study on cooling process of copper tube after three-roll planetary rolling. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 2020, 110, 104393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.K.; Hung, C.; Hsu, R.Q. The fnite element analysis on planetary rolling process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2001, 113, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.K.; Hung, C. Experimental and numerical analyses on three-roll planetary rolling process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 142, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, K. Simulation of deformation and temperaturein multi-pass three-roll rolling. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 92–93, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Niu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Huang, Q. Deformation law and bonding mechanism of 45 carbon steel/316L stainless steel cladding tubes fabricated by three-roll skew rolling bonding process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 325, 118277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.M.; Tsai, W.M.; Tsai, F.H.; Her, I. Analytical and experimental study on the spiral marks of the rolled product during three-roll planetary rolling processes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1555–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Molotnikov, A.; Diez, M.; Lapovok, R.; Kim, H.-E.; Wang, J.T.; Estrin, Y. Gradient structure produced by three roll planetary milling: Numerical simulation and microstructural observations. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, M.; Kim, H.E.; Serebryany, V.; Dobatkin, S.; Estrin, Y. Improving the mechanical properties of pure magnesium by three-roll planetary milling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 612, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, A.; Arthanari, S.; Shin, K.S. Improvement of corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of a magnesium alloy using screw rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 813, 152155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Shin, K.S. The dynamic recrystallization and mechanical property responses during hot screw rolling on pre-aged ZM6l magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 798, 140126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, M. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of Mg-Zn-Ca alloy operative clip. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, D.; Zhang, R.; Chen, M. Microstructure and Properties of Mg-3Zn-0.2Ca Alloy for Biomedical Application. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 0093–0098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, M.; Li, Z.; Yu, L. Mechanism study on improving the corrosion resistance of screw rolled Mg–Zn–Ca alloy by nano-MgO addition. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 31, 3104–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jain, A.; Brown, D.; Stoica, G.; Agnew, S.; Clausen, B.; Fielden, D.; Liaw, P. Twinning-detwinning behavior during the strain-controlled low-cycle fatigue testing of a wrought magnesium alloy, ZK60A. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Xin, R.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q. Improving tensile and compressive properties of magnesium alloy plates by pre-cold rolling. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, K.; Bu, Y.; Wu, J.; Fang, Y.; Meng, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Nanoprecipitates induced dislocation pinning and multiplication strategy for designing high strength, plasticity and conductivity Cu alloys. Scr. Mater. 2021, 195, 113741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Song, G.-L.; Yang, S.; Outeiro, J.; Dillon, O.; Puleo, D.; Jawahir, I. Grain refined and basal textured surface produced by burnishing for improved corrosion performance of AZ31B Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Xu, C.; Yan, H.; Lu, S.H.; Nakata, T.; Lao, C.S.; Chen, R.S.; Kamado, S.; Han, E.H. Correlation between dynamic recrystallization and formation of rare earth texture in a Mg-Zn-Gd magnesium alloy during extrusion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, V.; Li, A.; Komissarov, A.; Koltygin, A.; Tavolzhanskii, S.; Bautin, V.; Voropaeva, O.; Mukhametshina, A.; Tokar, A. Microstructure and mechanical and corrosion properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca–(Mn) biodegradable alloys. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležal, P.; Zapletal, J.; Fintová, S.; Trojanová, Z.; Greger, M.; Roupcová, P.; Podrábský, T. Influence of processing techniques on microstructure and mechanical properties of a biodegradable Mg-3Zn-2Ca alloy. Materials 2016, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shen, Y.; Shen, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.; Guan, S.; Kulyasova, O.B.; Valiev, R. In vitro and in vivo studies on pure Mg, Mg–1Ca and Mg–2Sr alloys processed by equal channel angular pressing. Nano Mater. Sci. 2020, 2, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradov, A.; Vasilev, E.; Kopylov, V.I.; Linderov, M.; Brilevesky, A.; Merson, D. High performance fine-grained biodegradable Mg-Zn-Ca alloys processed by severe plastic deformation. Metals 2019, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.B.; Chu, J.H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Kamado, S.; Zheng, M.Y. Ultra-fne grained Mg-Zn-Ca-Mn alloy with simultaneously improved strength and ductility processed by equal channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 785, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Blawert, C.; Zan, R.; Sun, Y.; Peng, H.; Ni, J.; Han, P.; Suo, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. A novel lean alloy of biodegradable Mg–2Zn with nanograins. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4333–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Qin, Z.; Yan, K. Mechanical properties and microstructure evolution of Mg-6 wt % Zn alloy during equal-channel angular pressing. Metals 2018, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Huang, X.; Chino, Y. A room temperature formable magnesium–silver–calcium sheet alloy with high ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 774, 138923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Sun, X. Achieving ultra-high strength and ductility in a rare-earth-free magnesium alloy via precisely controlled secondary hot extrusion process with an extremely low extrusion speed. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 5216–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.L.E.; Gupta, M. Development of Mg/Cu nanocomposites using microwave assisted rapid sintering. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.K.; Joshi, S.P.; Gupta, M. Hierarchical magnesium nano-composites for enhanced mechanical response. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6104–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.Q.; Dunand, D.C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium containing high volume fractions of yttria dispersoids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 277, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.C.; Chan, S.L.I. Tensile properties of nanometric Al2O3 particulate-reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, C.H.; Lukác, P. Strain hardening behaviour and the Taylor factor of pure magnesium. Philos. Mag. 2008, 88, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, M.; Munir, K.; Wen, C.; Li, Y. Magnesium matrix nanocomposites for orthopedic applications: A review from mechanical, corrosion, and biological perspectives. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, F.; Mahmudi, R.; Kang, J.Y.; Kim, H.S. Contributions of different strengthening mechanisms to the shear strength of an extruded Mg-4Zn-0.5Ca alloy. Philos. Mag. 2015, 95, 3452–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibnejad-Korayem, M.; Mahmudi, R.; Poole, W.J. Enhanced properties of Mg-based nano-composites reinforced with Al2O3 nano-particles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 519, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Kalhor, A.; Mirzadeh, H. Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) in advanced steels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 795, 140023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wei, R.; Feng, S.; Chen, C.; Han, Z.; Chen, L.; Wang, T.; Wu, S.; Li, F. Ultrahigh cryogenic strength and ductility in a duplex metastable ferrous medium-entropy alloy. Scr. Mater. 2023, 228, 115334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, H. Ultrafine also can be ductile: On the essence of Lüders band elongation in ultrafine-grained medium manganese steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 733, 220–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Luo, J. Non-equivalence contribution of geometrically necessary dislocation and statistically stored dislocation in work-hardened metals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 836, 142728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Rong, J.; Zha, M.; Wang, C.; Ma, P.; Jiang, Q. The synergy effect of fine and coarse grains on enhanced ductility of bimodal-structured Mg alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 780, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Location | Mg | Ca | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 58.66 | 0.97 | 40.37 |
| 2 | 64.05 | 15.03 | 20.92 |
| 3 | 59.83 | 1.01 | 39.16 |
| 4 | 61.82 | 14.33 | 23.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Sun, W.; Deng, L.; Zhao, L.; Shin, K.S.; Zhang, J. Mg–Zn–Ca Alloy with Ultra-High Ductility and Strength Processed by Screw Rolling. Materials 2025, 18, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112586
Zheng H, Sun W, Deng L, Zhao L, Shin KS, Zhang J. Mg–Zn–Ca Alloy with Ultra-High Ductility and Strength Processed by Screw Rolling. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112586
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Haoran, Weitao Sun, Lijun Deng, Li Zhao, Kwang Seon Shin, and Jian Zhang. 2025. "Mg–Zn–Ca Alloy with Ultra-High Ductility and Strength Processed by Screw Rolling" Materials 18, no. 11: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112586
APA StyleZheng, H., Sun, W., Deng, L., Zhao, L., Shin, K. S., & Zhang, J. (2025). Mg–Zn–Ca Alloy with Ultra-High Ductility and Strength Processed by Screw Rolling. Materials, 18(11), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112586







