Tailoring Microstructure and Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites Fabricated via Infiltration Sintering: Effects of Graphene Addition and Skeleton Relative Density
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
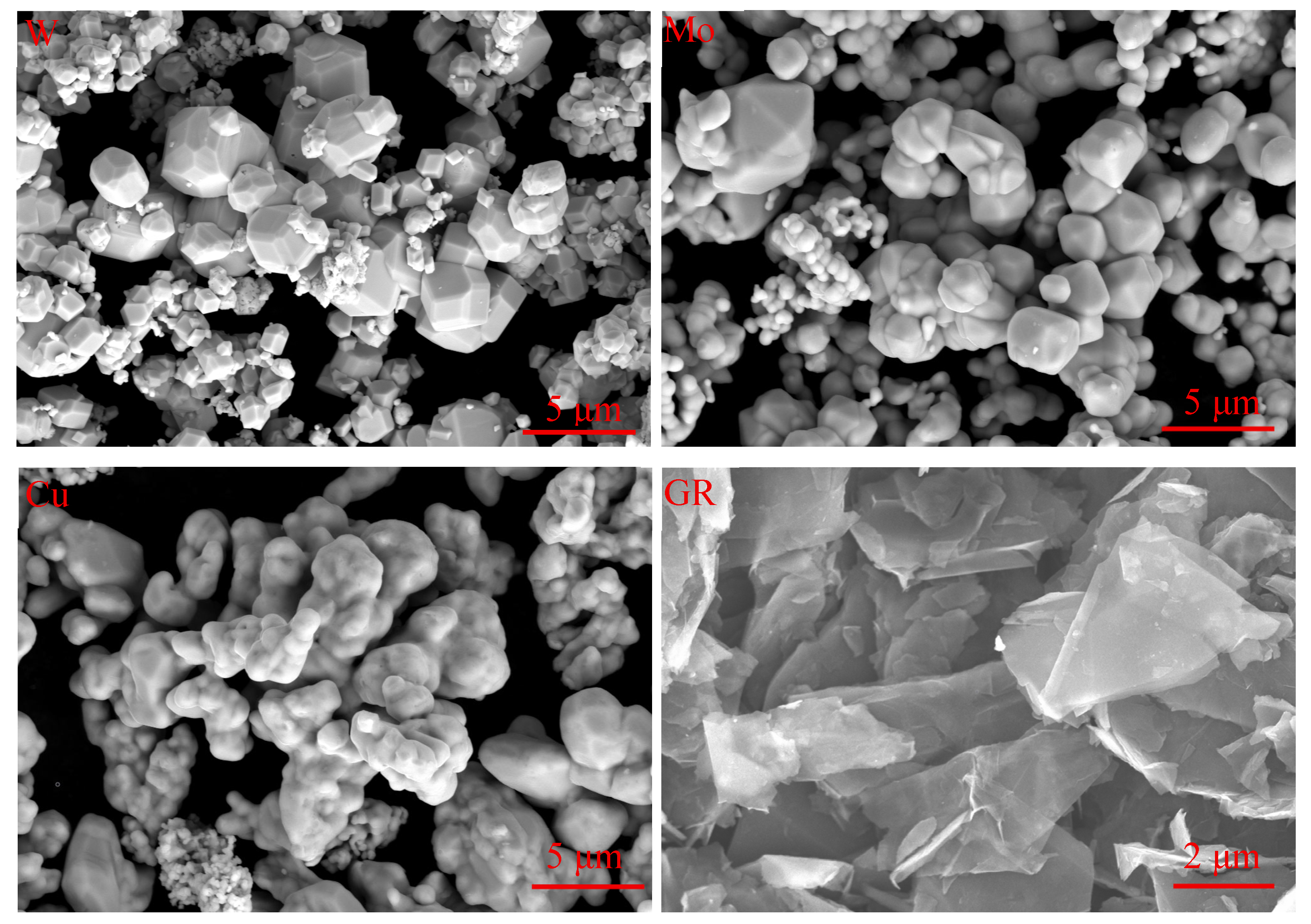
2.1. Materials
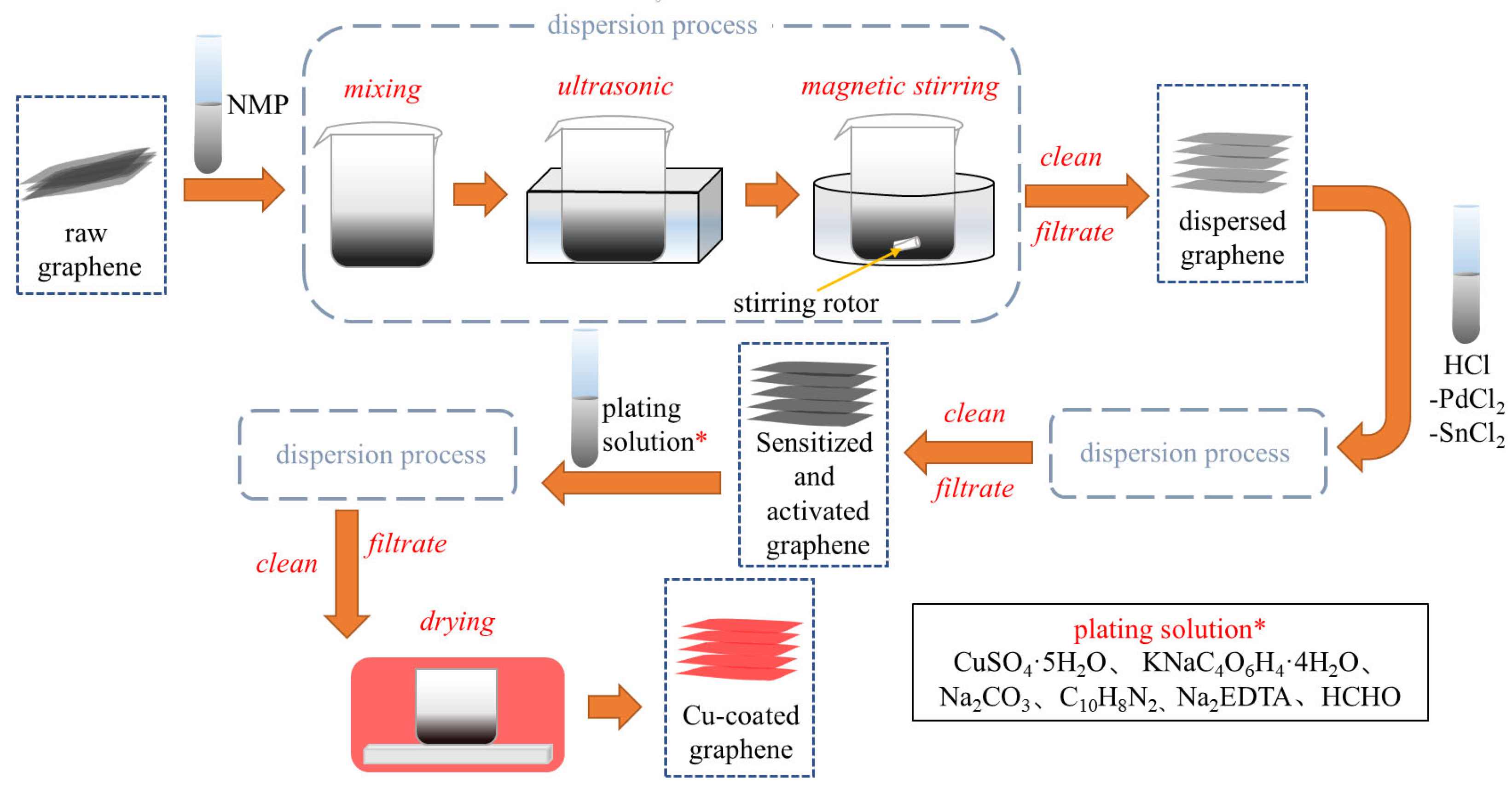
2.2. Graphene Surface Modification
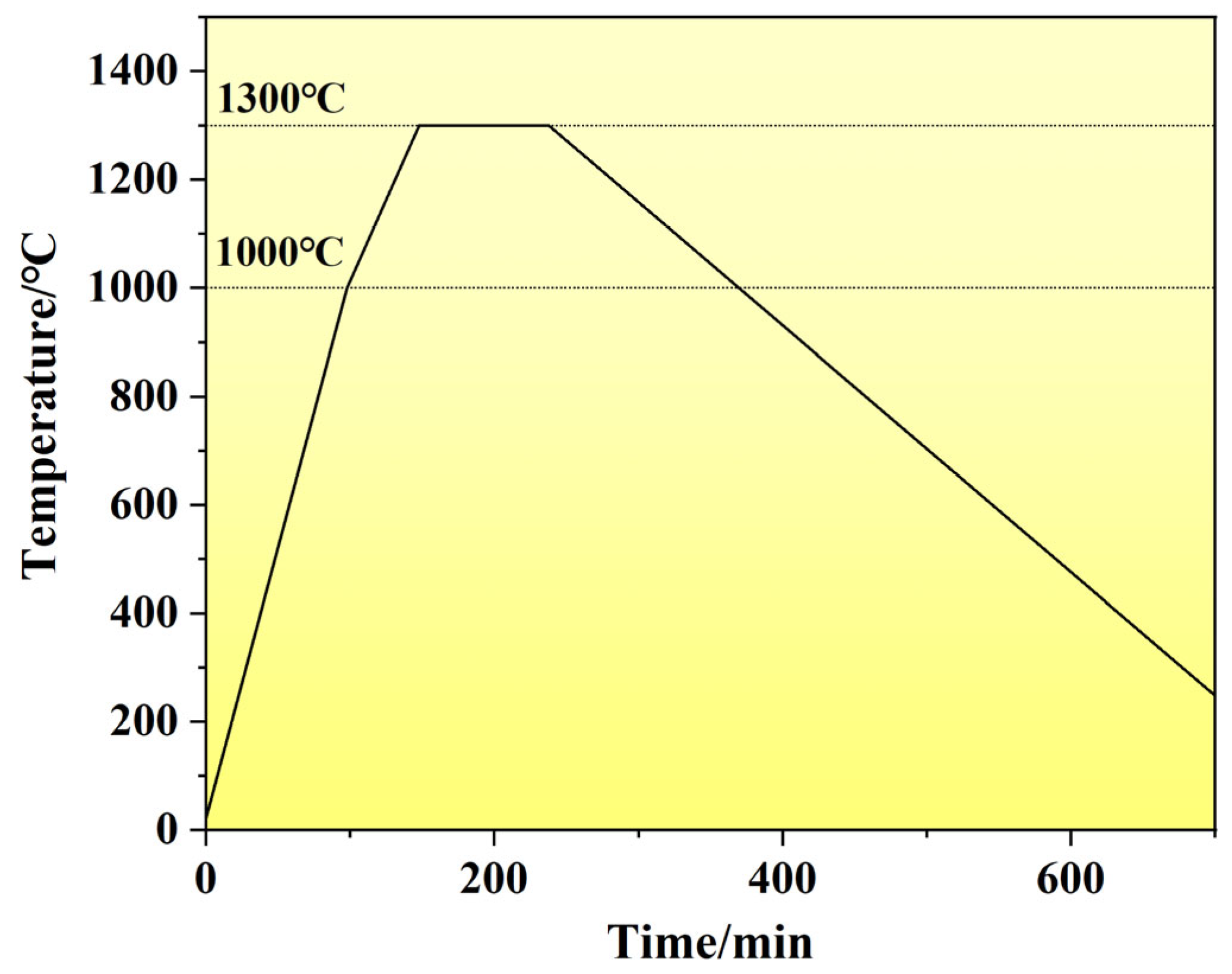
2.3. Preparation of Cu@Gr-Reinforced W-Mo-Cu Composites
2.4. Testing and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
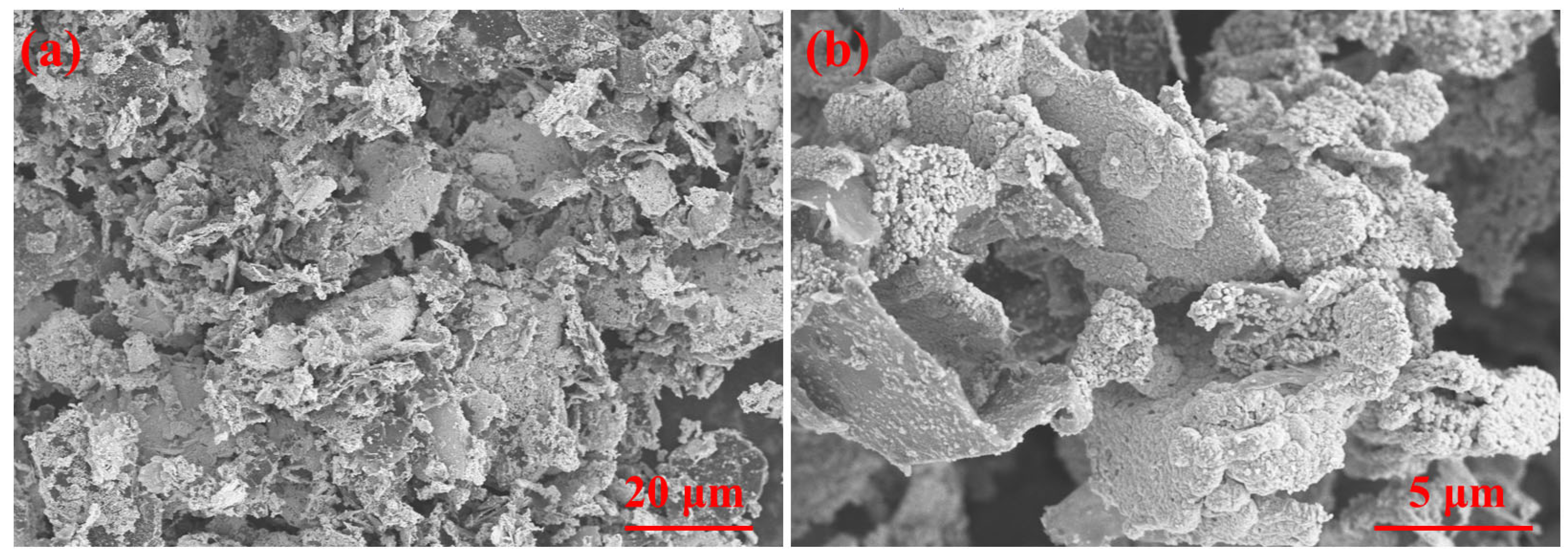
3.1. Influence of Cu@Gr Contents on the Microstructure and Properties of Cu@Gr/W-Mo-Cu Composites
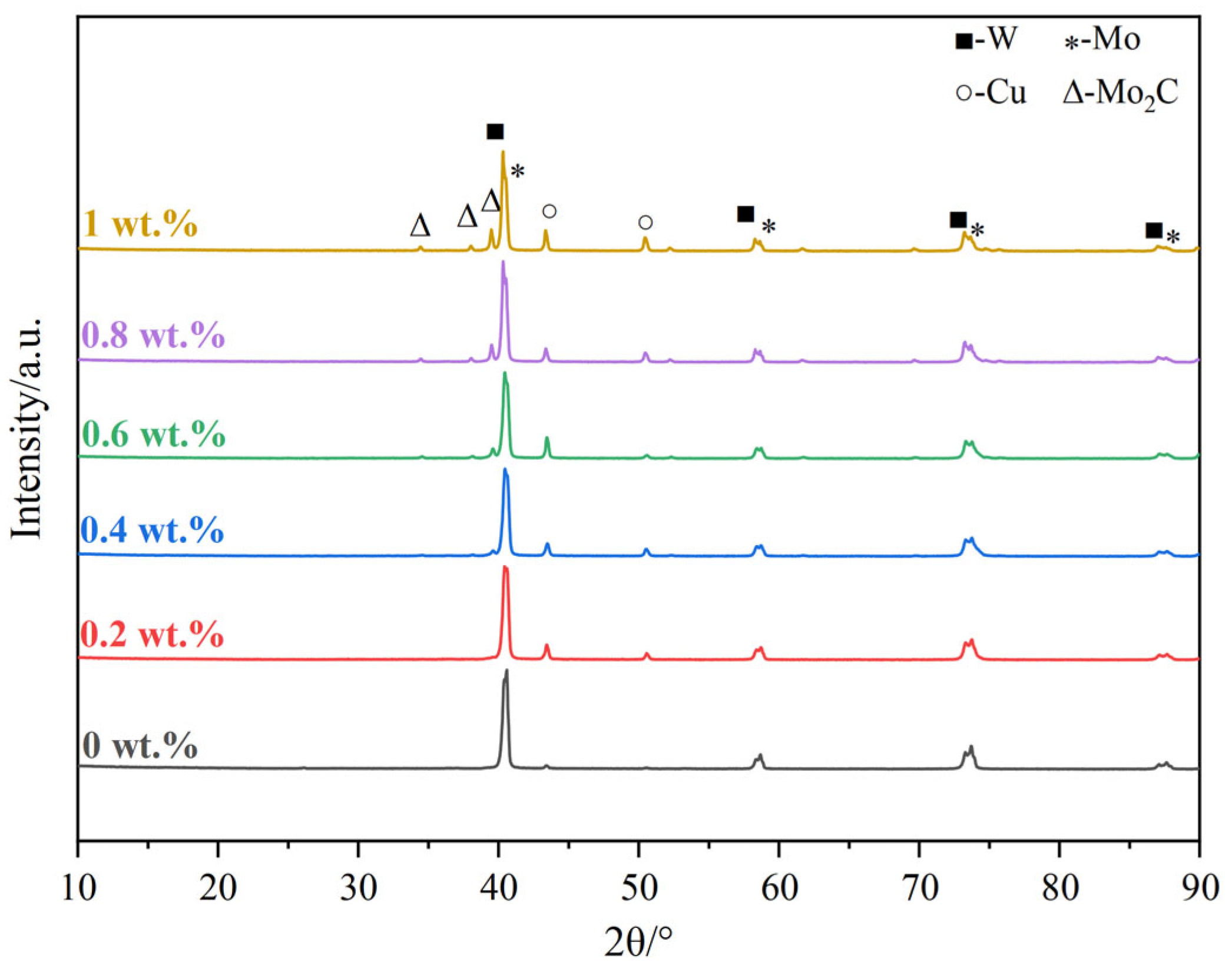
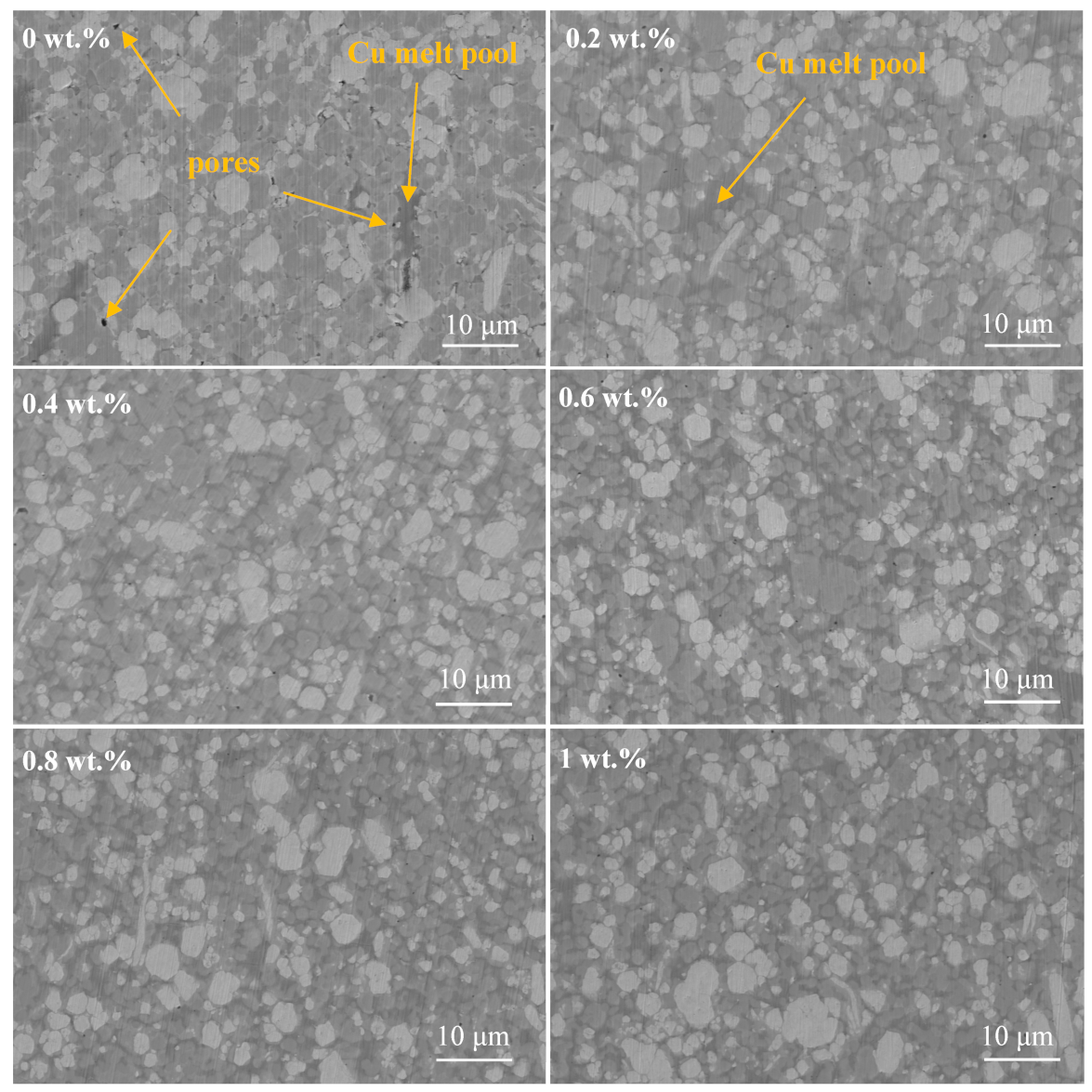
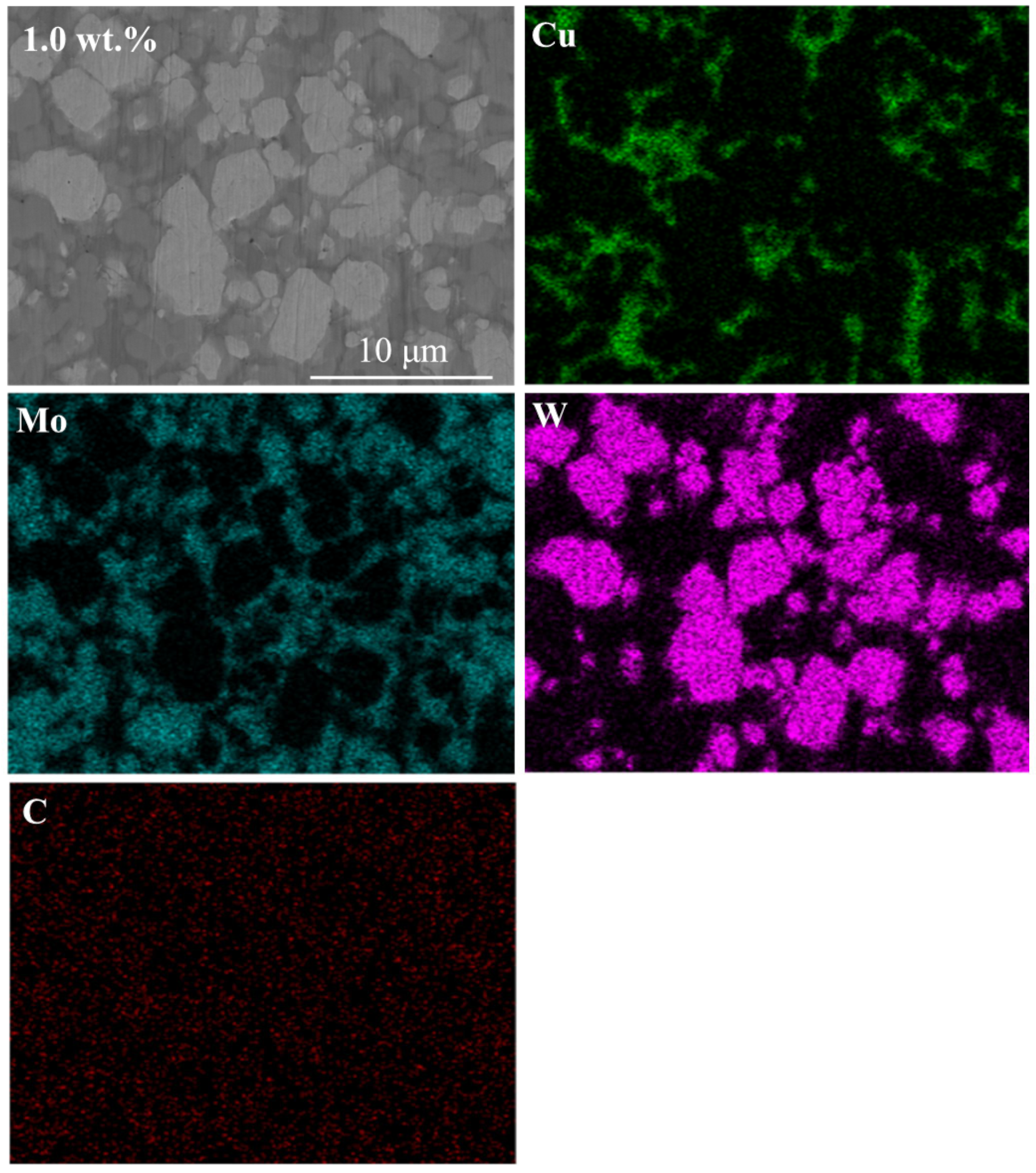
3.1.1. Phases and Microstructures of W-Mo-Cu Composites with Different Cu@Gr Contents
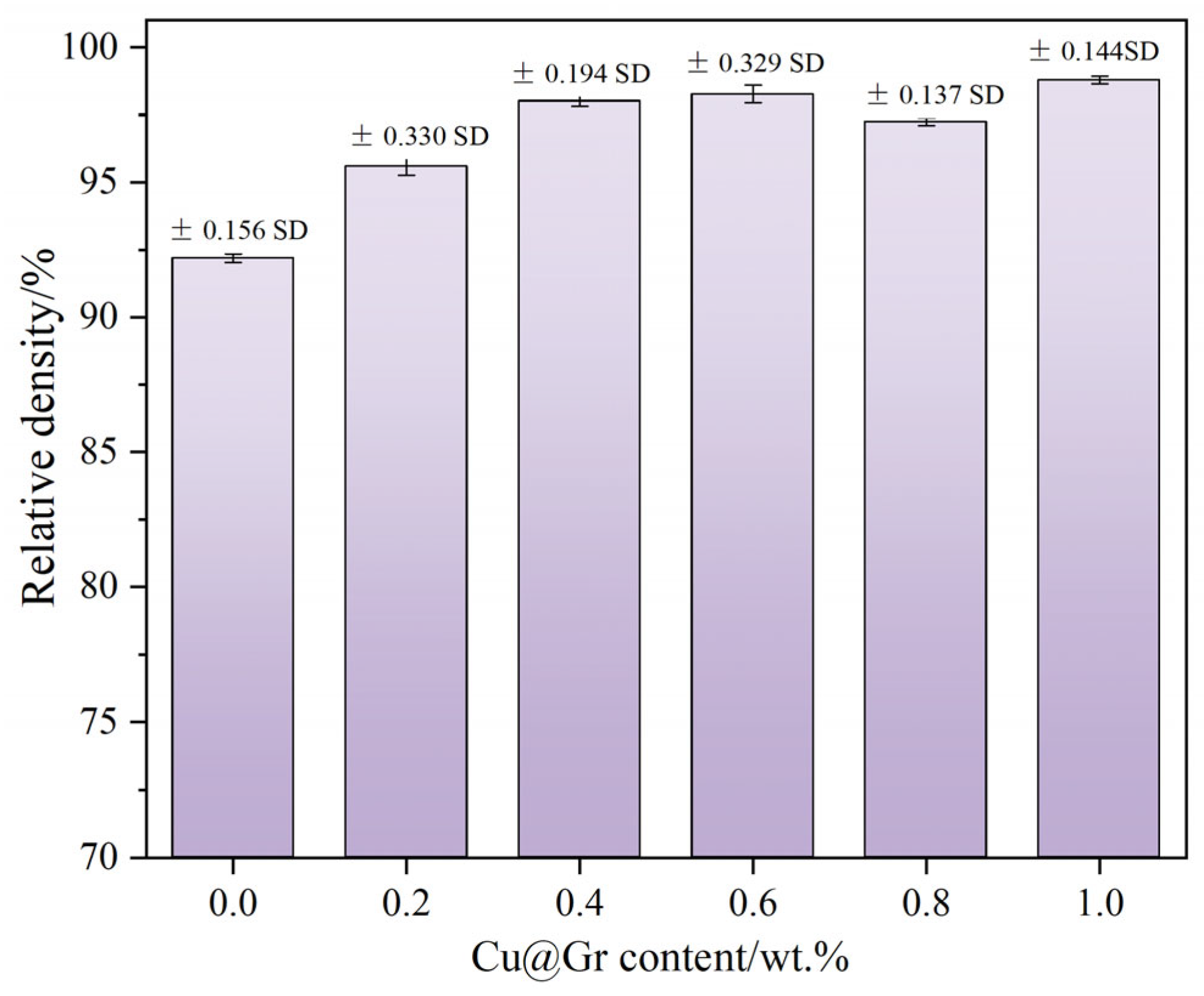
3.1.2. Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites with Different Cu@Gr Contents
3.2. Influence of W-Mo Green Compact Relative Density on the Microstructure and Properties of Cu@Gr/W-Mo-Cu Composites
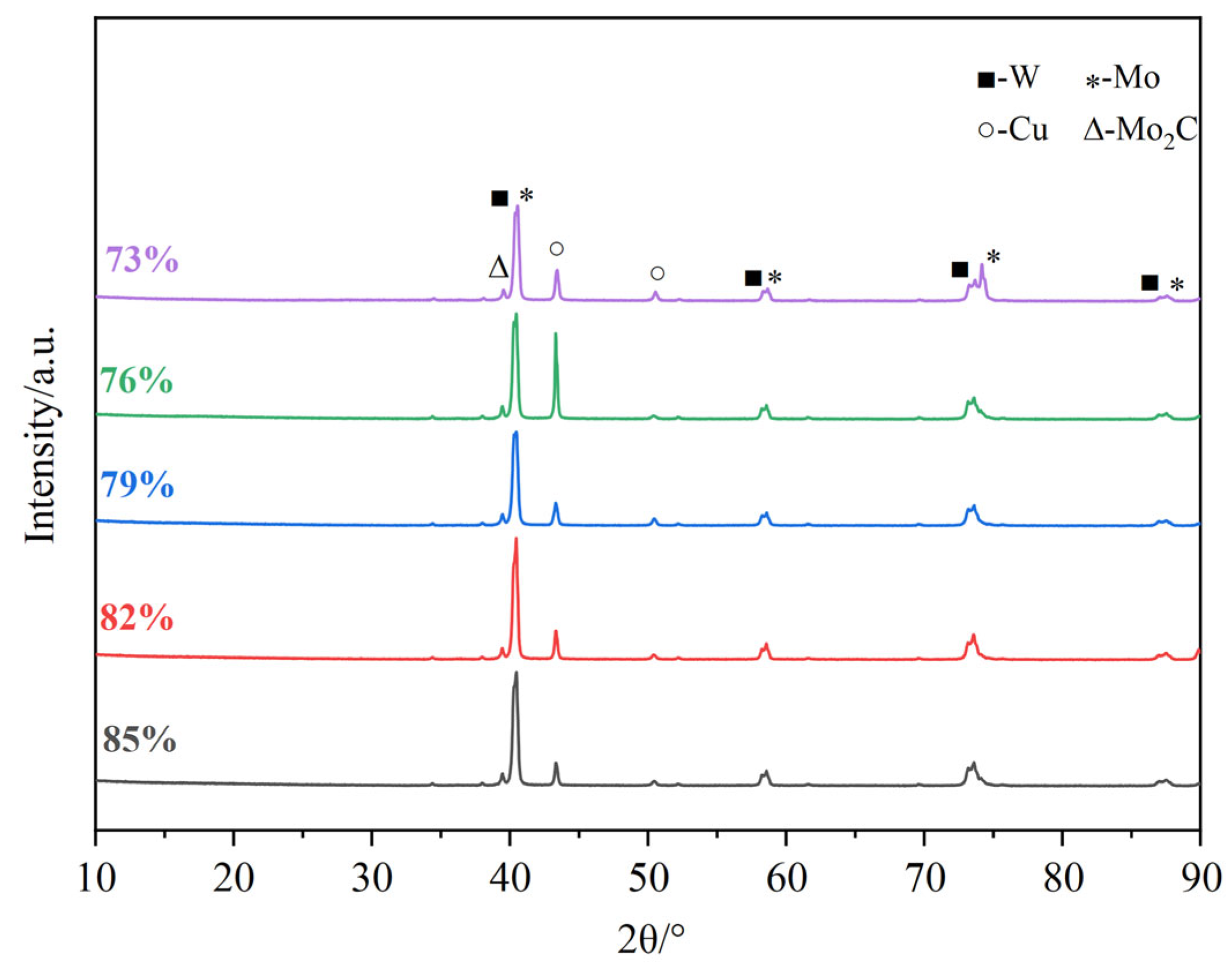
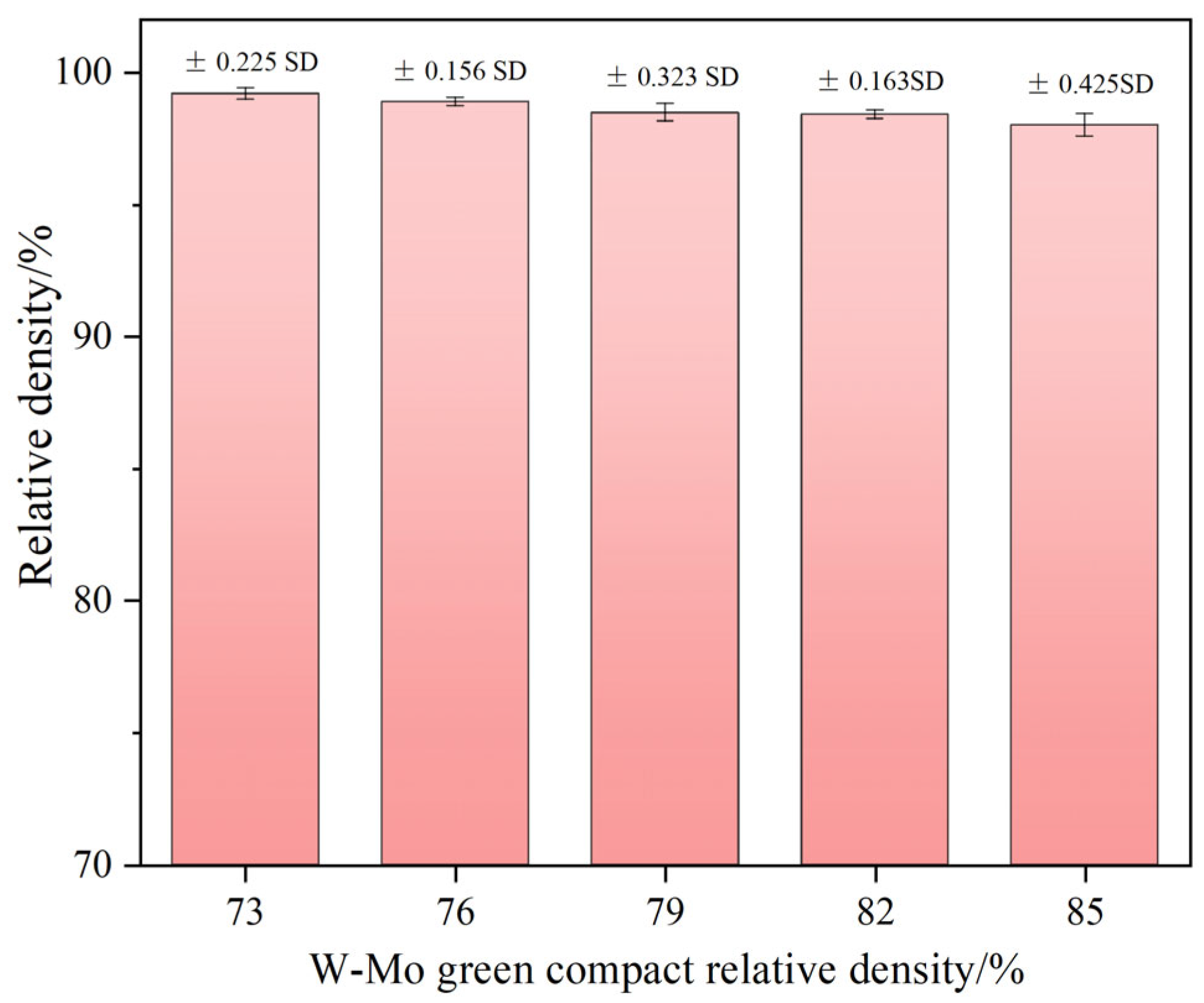
3.2.1. Phases and Microstructures of W-Mo-Cu Composites with Varying Relative Densities of W-Mo Green Compacts
3.2.2. Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites with Varying Relative Densities of W-Mo Green Compacts
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Without Cu@Gr, the composite contains W, Mo, and Cu phases. Upon adding 0.4 wt.% Cu@Gr, a small amount of Mo2C emerges, and its content increases with rising Cu@Gr content. Furthermore, the addition of Cu@Gr significantly enhances densification, reduces pores, enables uniform component distribution, and forms a Cu network between W and Mo. Moreover, composites can still maintain high densification when the Cu@Gr content exceeds 0.4 wt.%.
- (2)
- The addition of Cu@Gr substantially improves the properties of the W-Mo-Cu composites. As the Cu@Gr content increases, both thermal and electrical conductivities and hardness significantly improve. The thermal and electrical conductivities peak at a 0.6 wt.% addition, exhibiting increases of approximately 64% and 73%, respectively, compared to the non-added case. Hardness reaches its maximum at 1 wt.%, showing a roughly 25% increase relative to the non-added state.
- (3)
- Variations in the relative density of the W-Mo green compact have minimal effect on the phases of the composite and do not hinder the pivotal role of Cu@Gr in promoting sintering densification; composites prepared under varying relative densities remain highly dense. However, this parameter significantly influences the properties of the composite. As the relative density of the W-Mo green compact increases, the thermal and electrical conductivities of the composite decrease while its hardness increases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, G.; Wang, K.; Song, C.; Zhang, G. A low-cost, efficient, and industrially feasible pathway for large scale preparation of tungsten nanopowders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 78, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, G. Influence of Ti addition on the microstructure and comprehensive properties of Mo–Cu alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 2833–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Hou, C.; Tang, F.; Liang, S.; Luan, J.; Jiao, Z.; Liu, C.; Song, X.; Nie, Z. Thermal stability and high-temperature mechanical performance of nanostructured W–Cu–Cr–ZrC composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 208, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Li, S.; Zhang, H. Effect of copper content on the dynamic compressive properties of fine-grained tungsten copper alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 727, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Feng, K.; Liu, Y. Densification, microstructure, and properties of W-Mo-Cu alloys prepared with nano-sized Cu powders via large electric current sintering. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, K.; Zhou, H.; Chen, S. Microstructure and phases investigations of W-Mo-Cu alloy prepared by large current electric field sintering. Intermetallics 2022, 143, 107488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Xue, X. Effect of the distribution state of transition phase on the mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of W-Mo-Cu alloy by tuning elements content. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 827, 154333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, Y. W–Cu composites with homogenous Cu–network structure prepared by spark plasma sintering using core–shell powders. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 82, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jin, H.; Ding, F.; Bai, L.; Yuan, F. Fabrication of homogeneous Mo-Cu composites using spherical molybdenum powders prepared by thermal plasma spheroidization process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2018, 73, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.; Feng, K.; Zhou, H.; Shui, Y. Phase evolution of Mo-W-Cu alloy rapid prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Feng, K.; Ke, S.; Liu, Y. Study on the microwave sintering of the novel Mo-W-Cu alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 881, 160584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.; Kang, W.; Ding, Y.; Liang, S. Preparation and properties of W-Mo-Cu composite using solution combustion synthesized W-Mo solid solution nanopowder. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 111, 106064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Feng, K.; Liu, Y. Effects of electro-thermal cycles on the densification and properties of W-Mo-Cu alloys prepared via large current electric field sintering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 281, 125887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, J.; He, C.; Li, S.; Hao, Z.; Xue, X. Enhanced ductility of W-Mo-Cu alloy through the formation of nanometer-to-micrometer-thick dual-phase transition phase layer. Mater. Des. 2019, 164, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, K.; Feng, J.; Xing, J.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of WMoCu alloy doped with different sized Mo particles. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2024, 119, 106565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangarkani, M.; Borji, S.; Abbaszadeh, H.; Rahmani, A.A.; Zangeneh-madar, K. The effect of additive and sintering mechanism on the microstructural characteristics of W-40Cu composites. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2012, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, Y.; Hua, X.; Din, R.U.; Ye, Z. Effect of Fe on the sintering and thermal properties of Mo-Cu composites. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, A.G.; Arabi, H.; Rastegari, S. Tungsten-copper composite production by activated sintering and infiltration. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2011, 29, 538–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Feng, K.; Liu, Y. Studies towards activation of cobalt in W-Mo-Cu alloy sintered via large current electric field. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 117, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Nian, Q.; Chen, Y.; Nagaumi, H. Large scale production of graphene aluminum composites by stir casting: Process, microstructure and properties. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Bai, P.; Du, W.; Guan, R.; Tie, D.; Naik, N.; Huang, M.; Guo, Z. AZ91 alloy nanocomposites reinforced with Mg-coated graphene: Phases distribution, interfacial microstructure, and property analysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 902, 163484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Mei, Q.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Wan, L.; Zhang, G.; Mei, X.; Chen, Z.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y. Fabrication of graphene/copper nanocomposites via in-situ delamination of graphite in copper by accumulative roll-compositing. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 216, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Pei, J.; Du, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Bai, P.; Tie, D. Fabrication of magnesium-coated graphene and its effect on the microstructure of reinforced AZ91 magnesium-matrix composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Du, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, S. Ultra-high strengthening efficiency of graphene nanoplatelets reinforced magnesium matrix composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, S.F.; Paras, J.; Rafiee, M.A.; Rafiee, J.; Lee, S.; Kapoor, D.; Koratkar, N. Graphene–aluminum nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7933–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Wei, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, T.; Kardani, A.; Lin, Z.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Interface optimization by introducing Ti for strengthening graphene network/copper composites: New insight from MD simulations. Carbon 2025, 236, 120109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhan, Z. Preparation of graphene nanoplatelets-copper composites by a modified semi-powder method and their mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Tan, X.; Venkataraman, M.; Militky, J.; Xiong, W.; Mahendran, A.R.; Lammer, H.; Kejzlar, P. Effects of ultrasonic-assisted nickel pretreatment method on electroless copper plating over graphene. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Feng, K. Effect of Surface-Modified Graphene Addition on In Situ Synthesized Iron-Based Friction Materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, J.; Mi, X.; Gullapalli, H.; Thomas, A.V.; Yavari, F.; Shi, Y.; Ajayan, P.M.; Koratkar, N.A. Wetting transparency of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chen, W.; Zheng, C.; Deng, N. Microstructure and properties characterization of tungsten–copper composite materials doped with graphene. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Pan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, J. Compaction behavior and densification mechanisms of Cu-W composite powders. Powder Technol. 2021, 382, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Meng, L.; Zou, J.; Luo, L.; Wu, Y. Microstructure and properties of silver-added W-Cu prepared by infiltration sintering. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 108, 105947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Luo, G.; Shen, Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, L. Thermal and electrical properties of W–Cu composite produced by activated sintering. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, V.; Kumar, V.; Bansal, S.A. Mechanical properties of aluminium-graphene/carbon nanotubes (CNTs) metal matrix composites: Advancement, opportunities and perspective. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 138, 111224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, H.; Ghomashchi, R. Effect of graphene dispersion and interfacial bonding on the mechanical properties of metal matrix composites: An overview. FlatChem 2019, 16, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Brezovsky, J.J.; German, R.M. Effects of tungsten particle size and copper content on densification of liquid-phase-sintered W-Cu. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Chemical Reagents | Content (g/L) |
|---|---|
| SnCl2·2H2O | 20.0 |
| PdCl2 | 0.5 |
| HCl | 71.4 |
| Chemical Reagents | Content (g/L) |
|---|---|
| CuSO4·5H2O | 10.0 |
| Na2CO3 | 40.0 |
| Na2EDTA | 20.0 |
| KNaC4H4O6·4H2O | 40.0 |
| C10H8N2 | 4.0 |
| HCHO | 17.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, J.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, K.; Zhou, H. Tailoring Microstructure and Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites Fabricated via Infiltration Sintering: Effects of Graphene Addition and Skeleton Relative Density. Materials 2025, 18, 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112539
Cai J, Jiang Q, Feng K, Zhou H. Tailoring Microstructure and Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites Fabricated via Infiltration Sintering: Effects of Graphene Addition and Skeleton Relative Density. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112539
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Jinwen, Qiaoling Jiang, Keqin Feng, and Hongling Zhou. 2025. "Tailoring Microstructure and Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites Fabricated via Infiltration Sintering: Effects of Graphene Addition and Skeleton Relative Density" Materials 18, no. 11: 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112539
APA StyleCai, J., Jiang, Q., Feng, K., & Zhou, H. (2025). Tailoring Microstructure and Properties of W-Mo-Cu Composites Fabricated via Infiltration Sintering: Effects of Graphene Addition and Skeleton Relative Density. Materials, 18(11), 2539. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112539








