Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of Ni60/TiC and NbC Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding
Abstract
1. Introduction
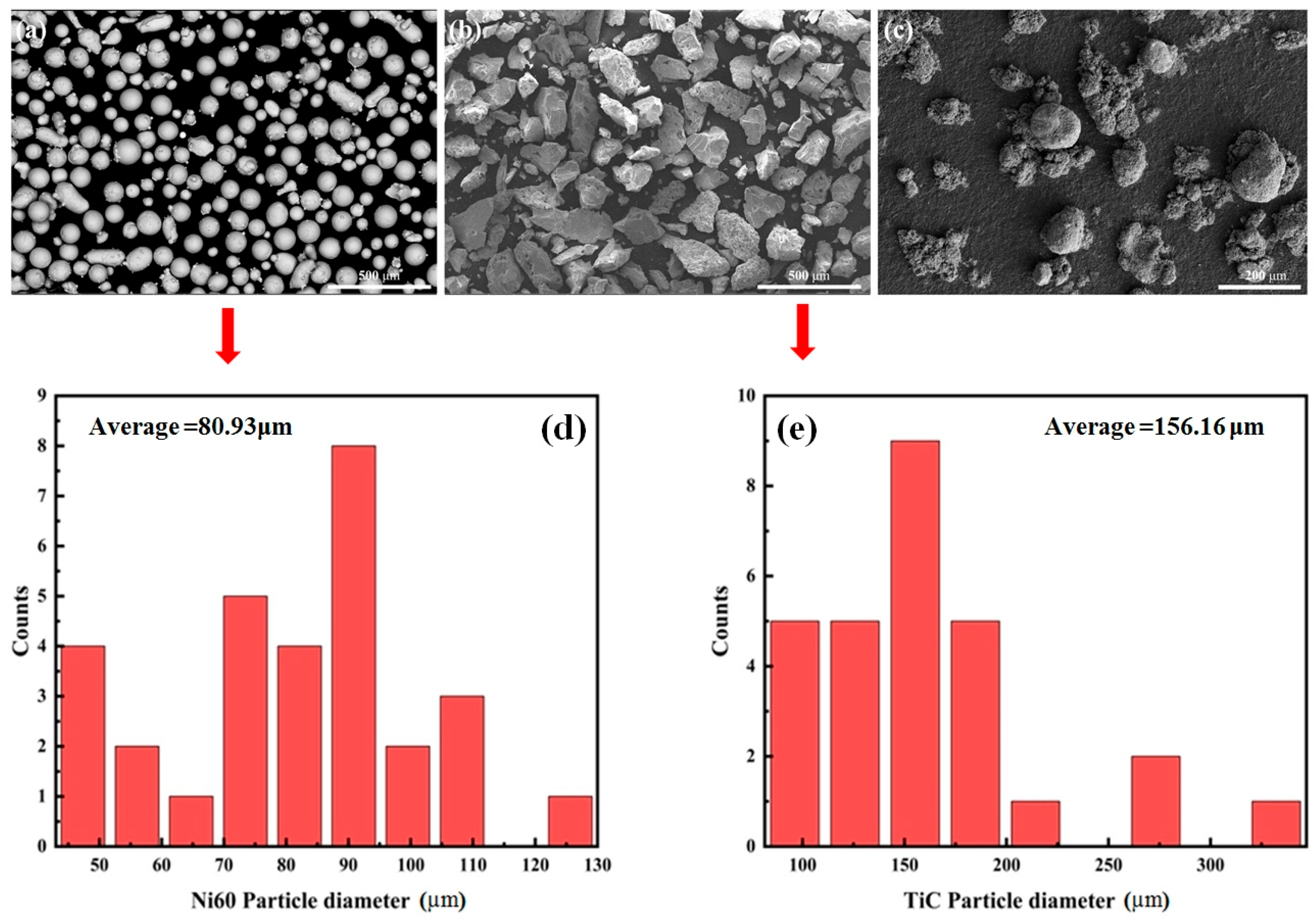
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. Metallographic Analysis
3.2. Microscopic Morphology
3.3. Micro-Hardness
3.4. Wear Resistance
3.5. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of TiC and NbC significantly altered the phase composition and microstructure of the coatings. S1 contained residual TiC particles and Cr7C3 carbides, while S2 formed Ni3C, Nb2C, and fine carbides. S3 exhibited partial dissolution of NbC, leading to the formation of Fe3Nb3C and Nb2C phases.
- (2)
- Lattice distortion induced by NbC was more pronounced than that by TiC, as evidenced by XRD peak shifts, contributing to refined grain structures and enhanced mechanical properties.
- (3)
- Due to the synergistic effect of uniform carbide distribution and severe lattice distortion, the average microhardness measured for the S2 coating is 1045 HV, slightly higher than 881 HV for S1 and 981 HV for S3, but all are significantly higher than the hardness of Ni60 (672.8 HV).
- (4)
- Wear resistance followed the order S2 > S3 > S1, with S2 showing the lowest wear rate attributed to its superior hardness and carbide reinforcement. Abrasive wear dominated in all coatings, with fatigue cracks observed in worn surfaces.
- (5)
- Electrochemical tests revealed that S3 exhibited the best corrosion resistance in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution, characterized by the highest corrosion potential and the lowest corrosion current density. This was attributed to the formation of a dense and stable passivation film promoted by NbC.
- (6)
- The combination of TiC and NbC in S2 optimized hardness and wear resistance through carbide dispersion strengthening and grain refinement. However, the increased cathode area from carbide phases slightly reduced its corrosion resistance compared to S3.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Lu, H.; Qi, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Ning, J.; Dun, Y.; Xue, P.; Xu, P.; et al. Investigation on synergism between additive and subtractive manufacturing for curved thin-walled structure. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2022, 17, 220–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Ning, J.; Dun, Y.; Meng, G.; Xue, P.; Xu, P.; Xin, B. Effects of ultrasound on multilayer forming mechanism of Inconel 718 in directed energy deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 48, 102462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, I.A.; Murr, L.E.; Terrazas, C.A.; Bermudez, D.; Mireles, J.; Injeti, V.S.V.; Li, K.; Yu, B.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wicker, R.B. Grain boundary and microstructure engineering of Inconel 690 cladding on stainless-steel 316L using electron-beam powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhu, L.; Ning, J.; Xin, B.; Dun, Y.; Yan, W. Manipulating molten pool dynamics during metal 3D printing by ultrasound. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 021416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ning, J.; Zhu, L.; Yang, Z.; Yan, W.; Dun, Y.; Xue, P.; Xu, P.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Role of porosity defects in metal 3D printing: Formation mechanisms, impacts on properties and mitigation strategies. Mater. Today 2022, 59, 133–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.B.; Meng, Q.D.; Li, C.C.; Li, Z.X.; Wu, D.Z. Effects of tilt angle between laser nozzle and substrate on bead morphology in multi-axis laser cladding. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 43, 311–322A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Li, T.; Shi, B.W.; Wang, D.; Adnan, M.; Lu, H.T. The influence of substrate tilt angle on the morphology of laser cladding layer. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 391, 125706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.F.; Zhang, G. Study on process optimization of WC-Co50 cermet composite coating by laser cladding. Int. J. Refract. Metal. Hard Mater. 2020, 87, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, S.; Pan, H.; Yuan, C.; Chen, X. Research on remanufacturing strategy for 45 steel gear using H13 steel powder based on laser cladding technology. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 49, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.F.; Dai, X.Q. Laser induction hybrid rapid cladding of WC particles reinforced NiCrBSi composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4708–4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; She, J.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Latest research advances on magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide. J. Magnes Alloys 2020, 8, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulkhair, N.T.; Simonelli, M.; Parry, L.; Ashcroft, I.; Tuck, C.; Hague, R. 3D printing of aluminium alloys: Additive manufacturing of aluminium alloys using selective laser melting. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Dubey, A.K. Recent trends in laser cladding and surface alloying. Opt. Laser. Technol. 2021, 134, 106619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Du, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Bai, H.L.; Jiang, E.Y. Influence of WC particle behavior on the wear resistance properties of Ni–WC composite coatings. Wear 2004, 257, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.P.; Mishra, S.K.; Tiwari, P.; Kukreja, L.M. Solid-Particle Erosion Behaviour of WC/Ni Composite Clad layers with Different Contents of WC Particles. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 50, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, D.P.; Muvvala, G.; Nath, A.K. High-temperature abrasive wear characteristics of H13 steel modified by laser remelting and cladded with Stellite 6 and Stellite 6/30% WC. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 422, 127498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Liu, F.L.; Miao, X.H.; Yang, F. Influence of laser cladding process on the magnetic properties of WC-FeNiCr metal-matrix composite coatings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1862–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasobane, P.; Madindwa Peter, M.; Masina, B.N. Effects of energy density on the microstructure evolution of TiC/Ti-6Al-4V-ELI metal composite fabricated with laser metal deposition. MATEC Web Conf. 2022, 370, 08004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, H.; Sarkari Khorrami, M.; Geranmayeh, A.; Sohi, M.H. In-situ synthesis of TiC/Ti alloyed layer via pulsed Nd: YAG laser melting of Ti-6Al-4V titanium with preplaced carbon-based powder. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 172, 107864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.R.A.S.; Hussein, A.H.A.; Nofal, A.; Hassab Elnaby, S.I.; Elgazzar, H. A contribution to laser cladding of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Metall. Res. Technol. 2019, 116, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Al-Sayed, S.R.; Hassab Elnaby, S.I.; Nofal, A.; Elgazzar, H. Prominent achievements of laser surface treatment of martensitic stainless steel and alpha-beta 6/4 titanium alloy. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 786, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, R.N.; Elshazli, A.M.; Hussein, A.H.A.; Al-Sayed, S.R. Impact of laser process parameters in direct energy deposition on microstructure, layer characteristics, and microhardness of TC21 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 121, 5139–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhen, J.Y. Microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding WCreinforced Ni based composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy. Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 2022, 51, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Wu, M.; Ma, Y.; Cui, C. Effect of TiC content on microstructure and properties of laser clad layer on TC4 alloy. Heat. Treat. Met. 2020, 45, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Yi, D.H.; Yang, X.H.; Zhang, W.D.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Bai, P.K. Influence of NbC particles on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Wang, J.M.; Wei, C.B.; Zhang, Q.; Su, C.J.; Sui, H.M. Wear properties of spark plasma-sintered AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy with NbC additions. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 36, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.Z.; Ren, W.B.; Zuo, W.H.; Wang, Y.J. Comparative study on the reinforcement effects of WC and TiC in the laser cladding layer of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 134, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.T. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of laser cladding iron-based coatings with two types of NbC reinforcement. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 479, 130558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, J. Microstructure evolution, corrosion and corrosive wear properties of NBC-reinforced FeNiCoCr-based high entropy alloys coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 171, 109352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.d.C.; Beneduce, F.; Magnabosco, R.; da Silva, A.L.N. Effect of TiC content on the carbide particle growth of NbC–Ni cemented carbide. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 105, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.-Y.; Zhang, J.-W. The influence of laser power on the microstructure and friction performance of laser-prepared TiC-NbC composite coatings on stainless steel surfaces. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, L.; Sun, R.; Zhang, T.; Yang, X. Research and progress of laser cladding on engineering alloys: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 66, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Shi, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J. Wear behavior and corrosion resistance of laser-clad Ni60-1% carbon nanotubes coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 482, 130686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Shi, W.Q.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Huang, J. Wear behavior of single-layer graphene oxide reinforced CoCrFeNiMn HEA coating by laser cladding. Intermetallics 2024, 175, 108512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Shi, W.Q.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Huang, J. Corrosion resistance and wear behavior of CoCrFeNiMn@Gr high entropy alloy-based composite coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 3769–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Shi, W.Q.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Huang, J. Analysis of the wear behavior and corrosion resistance of CoCrFeNiMn-2% CNTs laser cladding composite coating. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 6910–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Shi, W.Q.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Huang, J. Microstructure and properties analysis of AlCoCrFeNi high-entropy alloy/iron-based amorphous composite coatings prepared by laser cladding. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2024, 624, 122732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xi, S.Q.; Sun, C.F. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding and CoCr2.5FeNi2Tix high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Fu, H.G.; Ma, T.J.; Wang, K.M.; Yang, X.J.; Lin, J. Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNi-WC/TiC composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 194, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Vaclav, O.; Kornel, C.; Jeffthm, D. Microstructure and Phase Formation in a Rapidly Solidified Laser-Deposited Ni-Cr-B-Si-C Hardfacing Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 45A, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M. Mechanism and control of the nick-based alloy WC laser cladded layer microstructure. Appl. Laser 2006, 5, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sreeramagiri, P.; Babuska, T.; Krick, B.; Ray, P.K.; Balasubramanian, G. Lattice distortion as an estimator of solid solution strengthening in high-entropy alloys. Mater. Charact. 2021, 172, 110877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.Y.; Yang, T.C.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, Z.Y.; Huang, J. Effect of W Content on Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladding CoCrFeNi HEA Coating. Coatings 2023, 13, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ma, S.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Pan, S.; Wei, F. Quality enhancement of crack-free laser-cladded NiCrSiBC-WC coating by in-situ temperature field assistance (ITFA) and post-laser remelting (PLR). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 484, 130873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Luo, F.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, W.Q. Preparation of AlCoCrFeNi/W-TiC HEA composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and rubbing of flat surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1953, 24, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangtong, P.; Rodchanarowan, A.; Chaysuwan, D.; Chanlek, N.; Goodall, R. The corrosion behaviour of CoCrFeNix (x = Cu, Al, Sn) high entropy alloy systems in chloride solution. Corros. Sci. 2020, 172, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriari, A.; Ghaffari, M.; Khaksar, L.; Nasiri, A.; Hadadzadeh, A.; Amirkhiz, B.S.; Mohammadi, M. Corrosion resistance of 13wt% Cr martensitic stainless steels: Additively manufactured CX versus wrought ni-containing AISI 420. Corros. Sci. 2021, 184, 109362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Kong, D.C.; Wang, L.; Li, R.X.; Ni, X.Q.; Cheng, M.; Dong, C.F.; Engelberg, D. Pit growth kinetics of additively manufactured MoNi over-alloyed type 316L stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 7532–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Liu, Z.D.; Ma, H.R.; Liu, Q.B.; Mao, J.; Zhang, J.; Kong, Y. Comparative study on the corrosion behaviour of 1.4529 super austenitic stainless steel and laser-cladding 1.4529 coating in simulated desulfurized flue gas condensates. Corros. Sci. 2022, 209, 110794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.C.; Tsou, T.W. Ideal capacitive behavior of hydrous manganese oxide prepared by anodic deposition. Electrochem. Commun. 2002, 4, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Dai, C.; Luo, H.; Li, D.; Du, C.; Li, X. The corrosion behavior and film properties of Al-containing high-entropy alloys in acidic solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 560, 0169–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.D.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, N.; Xiao, G.C.; Zhang, H. High-temperature oxidation behavior and corrosion resistance of in-situ TiC and Mo reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10151–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, G.S.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, X.T.; Gao, L.; Song, X.J. Effect of niobium content on microstructure and wear and corrosion resistance of laser-clad FeCo0. 5CrNi1. 5B0. 5Nbx coatings on ductile iron. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ma, Q.C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.M.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.M. Effect of Nb content on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Inconel 625 coating formed by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 458, 129311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material | Chemical Composition (Mass. %) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Si | Mn | Fe | Cr | Ni | B | |
| Q235B | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.38 | Bal. | - | - | - |
| Ni60 | 0.8 | 4 | - | 15 | 15.5 | Bal. | 3.5 |
| Name of Coatings | Mass Fractions/(Mass.%) |
|---|---|
| S1 | Ni60 + 20%TiC |
| S2 | Ni60 + 10%TiC + 10%NbC |
| S3 | Ni60 + 20%NbC |
| Parameter | Ecorr (V) | Icorr (A/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||
| S1 | −0.806 | 1.055 × 10−5 | |
| S2 | −0.783 | 2.737 × 10−6 | |
| S3 | −0.657 | 1.732 × 10−6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, Q.; Luo, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Liu, C. Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of Ni60/TiC and NbC Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials 2025, 18, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112459
Zhan Q, Luo F, Huang J, Wang Z, Ma B, Liu C. Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of Ni60/TiC and NbC Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112459
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Qiang, Fangyan Luo, Jiang Huang, Zhanshan Wang, Bin Ma, and Chengpu Liu. 2025. "Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of Ni60/TiC and NbC Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding" Materials 18, no. 11: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112459
APA StyleZhan, Q., Luo, F., Huang, J., Wang, Z., Ma, B., & Liu, C. (2025). Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of Ni60/TiC and NbC Composite Coatings Prepared by Laser Cladding. Materials, 18(11), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112459







