Investigations on Cavitation Erosion and Wear Resistance of High-Alloy WC Coatings Manufactured by Electric Arc Spraying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
- -
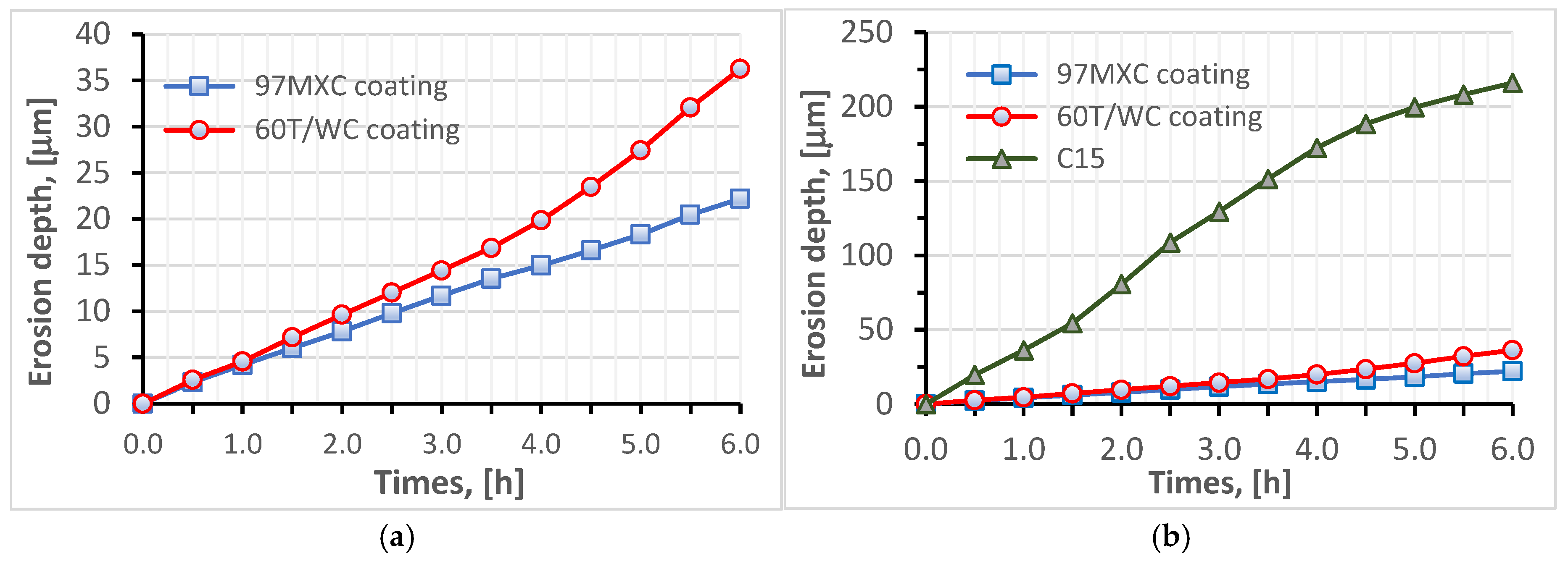
- The 60T/WC coating presented a resistance to EC less than 1.67 times that of the resistance to EC of the 97MXC layer (see Table 4);
- -
- After 1.5 h of testing, the 60T/WC coating had a stable erosion rate (approximately 4.8 µm/h);
- -
- After 6 h of testing, the 60T/WC layer had an MDE of 1.6 times higher than that of 97MXC;
- -
- Both coatings presented an average erosion depth at least six times lower than of the C15 steel sample.
4. Conclusions
- -
- The 60T/WC coatings presented an erosion by cavitation resistance 7.2 times lower than that of the C15 carbon steel sample, close to that of the 97MXC coatings, which offered a higher erosion by cavitation resistance;
- -
- Both types of coatings presented relatively stable erosion rates, as well as similar values of average erosion depth (MDE), six times higher than the C15 steel sample;
- -
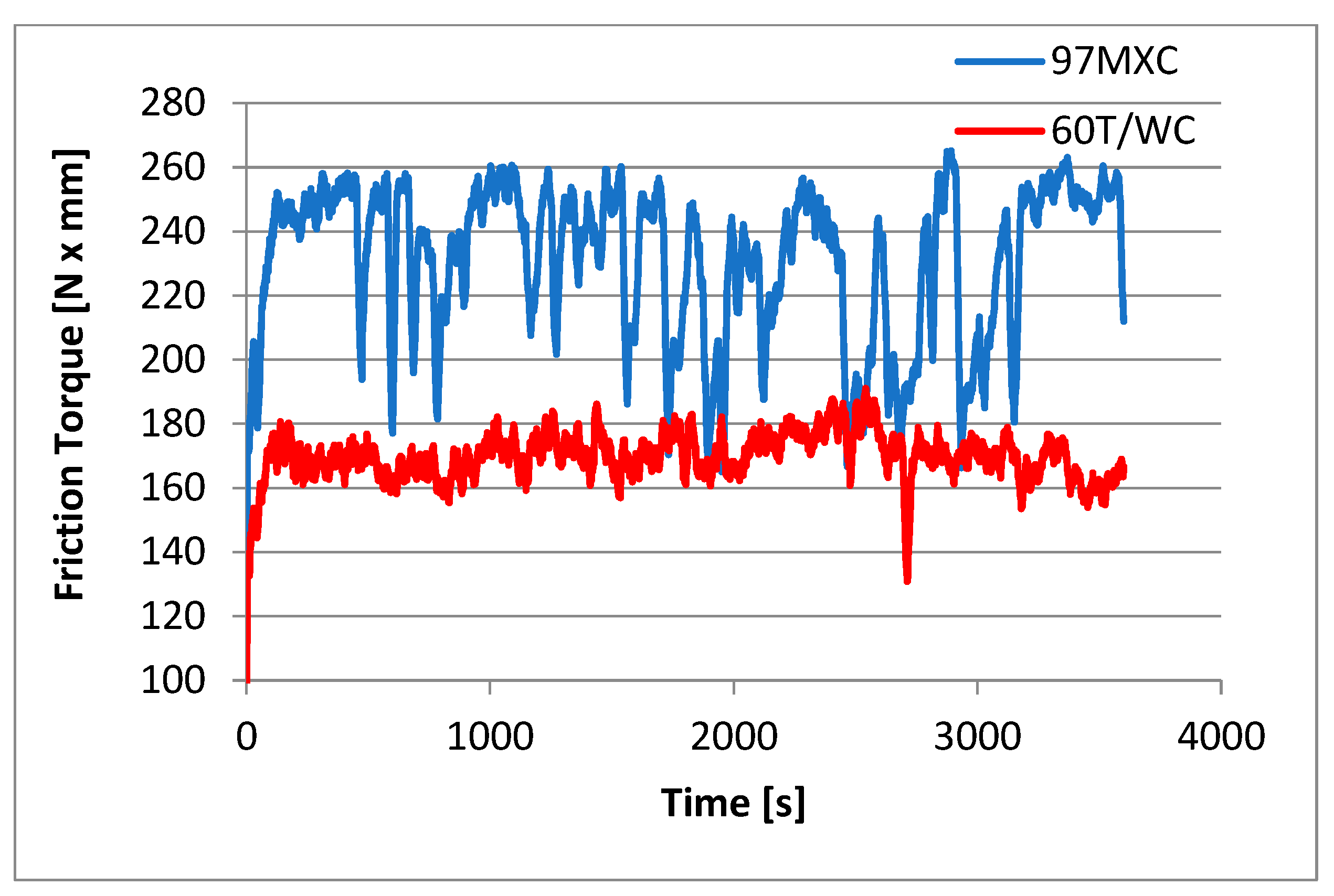
- The wear resistance tests by dry friction demonstrated that, although the CoF of the 60T/WC coatings was more stable and presented values approximately 10% lower than the CoF of the 97MXC, the wear of the 60T/WC layers—recorded for 40N loads—was over 200% higher than the wear of the 97MXC coatings. This aspect demonstrates that the 97MXC coatings presented a better behaviour in response to dry friction than 60T/WC;
- -
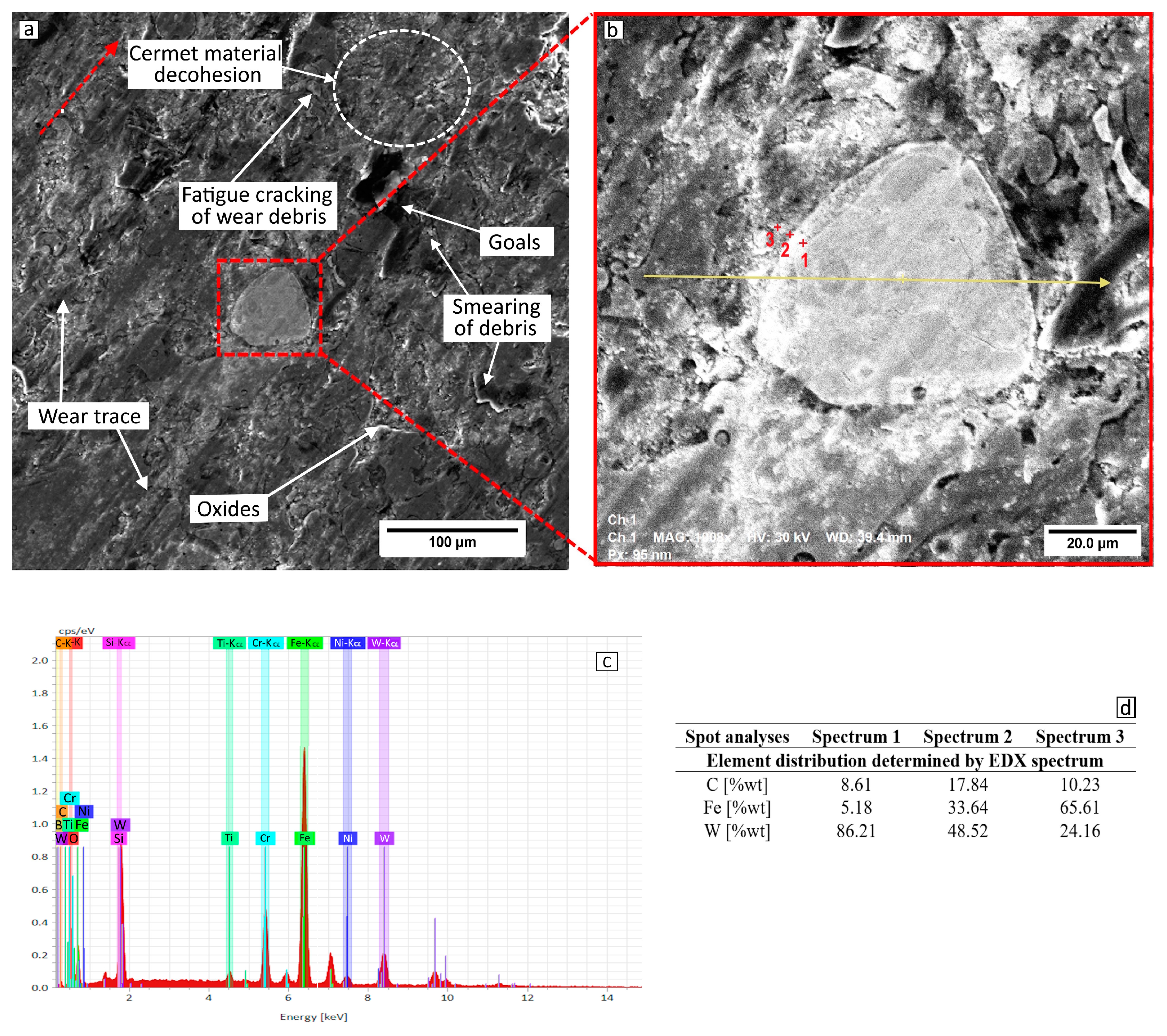
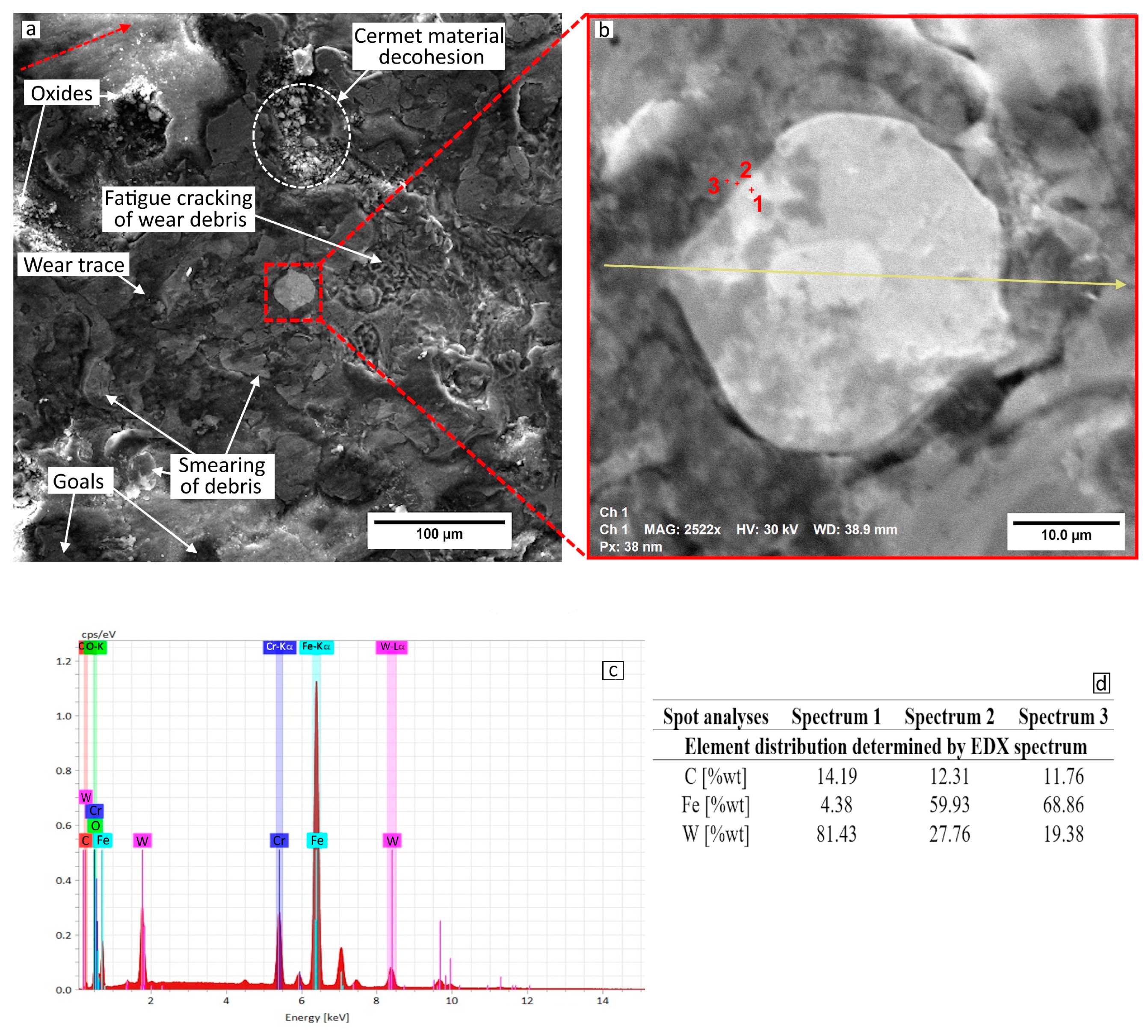
- The dominant wear mechanism was abrasive wear, followed by fatigue. Both phenomena were determined by the cohesion of the layer material and the weakening of the WC particles. The wear products formed a tribofilm subjected to plastic deformation and detached from the wear track. The wolfram carbides in the 97MXC coating were embedded in the metal matrix through an intermediate layer of ferrite alloyed with wolfram, which increased the wear resistance of the coating.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlton, J.S. Marine Propellers and Propulsion, 1st ed.; Butterworth Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1994; p. 199. ISBN 9780080971230. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.K.; Vinay, G.; Ang, A.S.; Mahajan, D.K.; Singh, H. Cavitation erosion mechanisms of HVOF-sprayed Ni-based cermet coatings in 3.5% NaCl environment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 434, 128194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Xiong, T.; Zheng, Y. Cavitation Erosion and Jet Impingement Erosion Behavior of the NiTi Coating Produced by Air Plasma Spraying. Coatings 2018, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ružić, J.; Stašić, J.; Božić, D.; Dojčinović, M.; Volkov-Husović, T. Influence of the fabrication process of copper matrix composites on cavitation erosion resistance. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2017, 23, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, S.; Cruma, A. Handbook of Acoustics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Brennen, C.E. Cavitation and Bubble Dynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1995; ISBN 0-19-509409-3. [Google Scholar]
- Abouel-Kasem, A.; El-Deen, A.; Emara, K.M.; Ahmed, S.M. Investigation Into Cavitation Erosion Pits. J. Tribol. 2009, 131, 031605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preece, C.M.; Hansson, I.L.H. A Metallurgical Approach to Cavitation Erosion. In Advances in the Mechanics and Physics of Surfaces; Harwood Academic Publishers: London, UK, 1981; Volume 1, pp. 199–253. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hokkirigawa, K.; Oba, R.; Kikuchi, K. SEM Observation of Vibratory Cavitation Fracture–Mode During the Incubation Period and the Small Roughness Effect. JSME Int. J. 1991, 34, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hokkirigawa, K.; Oba, R. Fatigue Failure of SUS 304 Caused by Vibratory Cavitation Erosion. Wear 1994, 177, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brijesh, V.; Inge, L.H.H. The cavitation erosion-corrosion of stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 1990, 30, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.T.; Cheng, F.T.; Man, H.C. Synergistic effect of cavitation erosion and corrosion of various engineering alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 290, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouel-Kasem, A.; Ahmed, S.M. Cavitation Erosion Mechanism Based on Analysis of Erosion Particles. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 031601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huen, W.Y.; Lee, H.; Vimonsatit, V.; Mendis, P.; Lee, H.S. Transversely isotropic elastic-plastic properties in thermal arc sprayed Al–Zn coating: A microporomechanics approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réquiz, R.; Camero, S.; Rivas, A.L. Characterization of the hydrogen damage in an API 5L X52 steel by scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Microanal. 2005, 11, 1992–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, M.A.; Dann, M.; Salama, M.M. Influence of grade on the reliability of corroding pipelines. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Liu, Y.; Qin, J.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, S. Electrochemical Study of Carbon Steel and 304 Stainless Steel Erosion Behavior in Sand-Containing Water. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 8375–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-P.; Kim, W.-S.; Kho, Y.-T. Fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth properties of the base metal and weld metal of a type 304 stainless steel pipeline for LNG transmission. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Vessel. Pip. 2001, 78, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimiciuc, S.-A.; Saviuc, A.; Tudose-Sandu-Ville, F.; Toma, S.; Nedeff, F.; Rusu, C.M.; Agop, M. Non-Linear Behaviors of Transient Periodic Plasma Dynamics in a Multifractal Paradigm. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.K. Erosion–corrosion interactions and their effect on marine and offshore materials. Wear 2006, 261, 1012–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang; Wang, J.; Zammit, A.; Buhagiar, J.; Cassar, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J. Investigation on the failure mechanism of graphite-like carbon coatings under cavitation erosion in distilled water. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 467, 129686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Vinay, G.; Anupam, A.; Ang, A.S.M.; Mahajan, D.K.; Singh, H. Effect of prolonged immersion on corrosion and cavitation resistance of HVOF-sprayed WC-NiCr and WC-Hastelloy cermet coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 494 Pt. B, 131384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hong, S.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, W.; Kang, M.; Fu, X. Cavitation erosion resistance in NaCl medium of HVOF sprayed WC-based cermet coatings at various flow velocities: A comparative study on the effect of Ni and CoCr binder phases. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 94, 105407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, F.; Lin, J.; Kang, M.; Ndumia, J.N.; Liu, J. Microstructure and Tribological Properties of Fe-Based-Al2O3-B4C Composite Coatings Prepared by High-Velocity Arc Spraying. Coatings 2022, 12, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Hagen, L.; Kokalj, D. Embedment of eutectic tungsten carbides in arc sprayed steel coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 331, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purba, R.H.; Shimizu, K.; Kusumoto, K.; Todaka, T.; Shirai, M.; Hara, H.; Ito, J. Erosive wear characteristics of high-chromium based multi-component white cast irons. Tribol. Int. 2021, 159, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, E.; Song, R.; Cai, C. Study of the three-body impact abrasive wear behaviour of a low alloy steel reinforced with niobium. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 46, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazac, A.M.; Bejinariu, C.; Baciu, C.; Toma, S.L.; Florea, C.D. Experimental Determination of Force and Deformation Stress in Nanostructuring Aluminum by Multiaxial Forging Method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 657, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krella, A.; Zakrzewska, D.E.; Marchewicz, A. The resistance of S235JR steel to cavitation erosion. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szala, M.; Walczak, M.; Świetlicki, A. Effect of Microstructure and Hardness on Cavitation Erosion and Dry Sliding Wear of HVOF Deposited CoNiCrAlY, NiCoCrAlY and NiCrMoNbTa Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, S.L.; Savin, G.; Toma, B.F.; Bejinariu, C.; Ionita, I.; Vizureanu, P.; Badaru, G.; Sandu, A.V.; Cazac, A.; Burduhos, N.D. System of Concentric Nozzles for Metal Spraying Guns for Drawable Metallic Materials, Has Conical Stiffening Shoulder That Is Provided on Conical Nozzle. RO134208-A2, 16 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Haraga, R.A.; Chicet, D.L.; Cimpoiesu, N.; Toma, S.L.; Bejinariu, C. Influence of the Stand-off Distance and of the Layers Thickness on the Adhesion and Porosity of the 97MXC Deposits Obtained by Arc Spraying Process. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 877, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haraga, R.; Chicet, D.; Toma, S.; Carlescu, V.; Bejinariu, C. Microhardness and Elastic Properties Evaluation of WC-TiC Coatings Obtained by Arc Spraying Process. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2024, 69, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 21920-3:2021 (en); Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile—Part 3: Specification Operators. International Organization for Standardization, ISO Central Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- ASTM E 2109-01; Standard Test Methods for Determining Area Percentage Porosity in Thermal Sprayed Coatings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Panturu, M.; Chicet, D.; Paulin, C.; Lupescu, S.; Munteanu, C. Microstructural aspects of TBC’s deposited on internal combustion engine valve materials. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 907, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łatka, L.; Michalak, M.; Szala, M.; Walczak, M.; Sokołowski, P.; Ambroziak, A. Influence of 13 Wt% TiO2 content in alumina-titania powders on microstructure, sliding wear and cavitation erosion resistance of APS sprayed coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 410, 126979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Leng, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chen, R.; Lu, G. Diffusion characteristics of surface treatment emulsion in aged asphalt mortar of porous asphalt mixture through SEM/EDS analysis. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2024, 25, 2290093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G32-16(2021) e1; Standard Test Method for Cavitation Erosion Using Vibratory Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Calin, M.; Curteza, A.; Toma, S.A.M. Morphological properties of polyamide 6-cnt nanofibers obtained by electrospinning method. Metal. Int. 2013, 18, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM B962-17; Standard Test Methods for Density of Compacted or Sintered Powder Metallurgy (PM) Products Using Archimedes’ Principle. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ISO 6507-1:2018; Metallic materials—Vickers hardness test, Part 1: Test method. International Organization for Standardization. ISO Central Secretariat: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Niranatlumpong, P.; Koiprasert, H. Phase transformation of NiCrBSi–WC and NiBSi–WC arc sprayed coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, B.; Yu, Z. Corrosion and wear resistance of TiN/TiO2 composite ceramic coatings deposited by supersonic arc spraying. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 18655–18666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C633-13 (Reapproved 2021); Standard Test Method for Adhesion or Cohesion Strength of Thermal Spray Coatings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Dorner-Reisel, A.; Reisel, G.; Seeger, J.; Svoboda, S.; Akhtar, W.A.A. Thermally sprayed coatings for protection of integrated sensor systems on tribological loaded Surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 424, 127619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Wu, Y.; Gao, W.; Wang, B.; Guo, W.; Lin, J. Microstructural characterization and microhardness distribution of HVOFsprayed WC–10Co–4Cr coating. Surf. Eng. 2014, 30, 5–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Fu, B.; Jiang, J.L.X. Microstructure and wear performance of arc sprayed Fe-FeB-WC coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2008, 17, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E384-22; Standard Test Method for Microindentation Hardness of Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Jonda, E.; Szala, M.; Sroka, M.; Łatka, L.; Walczak, M. Investigations of cavitation erosion and wear resistance of cermet coatings manufactured by HVOF spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 608, 155071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamana, M.S.; Pukasiewicz, G.M.A.; Sampath, S. Influence of cobalt content and HVOF deposition process on the cavitation erosion resistance of WC-Co coatings. Wear 2017, 398–399, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://kermetico.com/applications/hvaf-equipment-cavitation-erosion-protection-hydro-turbine-coating# (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Ozkavak, H.V.; Sahin, S.; Sarac, M.F.; Alkan, Z. Wear properties of WC–Co and WC–CoCr coatings applied by HVOF technique on different steel substrates. Mater. Test. 2020, 62, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myalska, H.; Lusvarghi, L.; Bolelli, G.; Sassatelli, P.; Moskal, G. Tribological behavior of WC-Co HVAF-sprayed composite coatings modified by nano-sized TiC addition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 371, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Shuvho, B.A.; Hossain, N.; Hassan, M.; Debnath, U.K.; Mia, S. Friction and wear characteristics of ceramics composite under multidirectional motions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. 2021, 236, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rukhande, S.W.; Rathoda, W.S.; Bhosale, D. Sliding Wear Investigation of Ni-based Coating at Elevated Temperatures. Tribol. Ind. 2021, 43, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matikainen, V.; Bolelli, G.; Koivuluoto, H.; Sassatelli, P.; Lusvarghi, L.; Vuoristo, P. Sliding wear behaviour of HVOF and HVAF sprayed Cr₃C₂-based coatings. Wear 2017, 388–389, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekes, D.; Psyllaki, P.; Vardavoulias, M. Wear Micro-Mechanisms of Composite WC-Co/Cr-NiCrFeBSiC Coatings. Part I: Dry Sliding. Tribol. Ind. 2014, 36, 361–374. [Google Scholar]
- Muntean, R.; Pascal, D.-T.; Kazamer, N.; Mărginean, G.; Șerban, V.-A. Sliding Wear Behavior of High-Temperature Vacuum-Brazed WC-Co-NiP Functional Composite Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymański, Ł.; Olejnik, E.; Sobczak, J.J.; Szala, M.; Kurtyka, P.; Tokarski, T.; Janas, A. Dry sliding, slurry abrasion and cavitation erosion of composite layers reinforced by TiC fabricated in situ in cast steel and gray cast iron. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 308, 117688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Chen, T.; Yuan, C. Effects of cobalt content on the microstructure, mechanical properties and cavitation erosion resistance of HVOF sprayed coatings. Coatings 2019, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

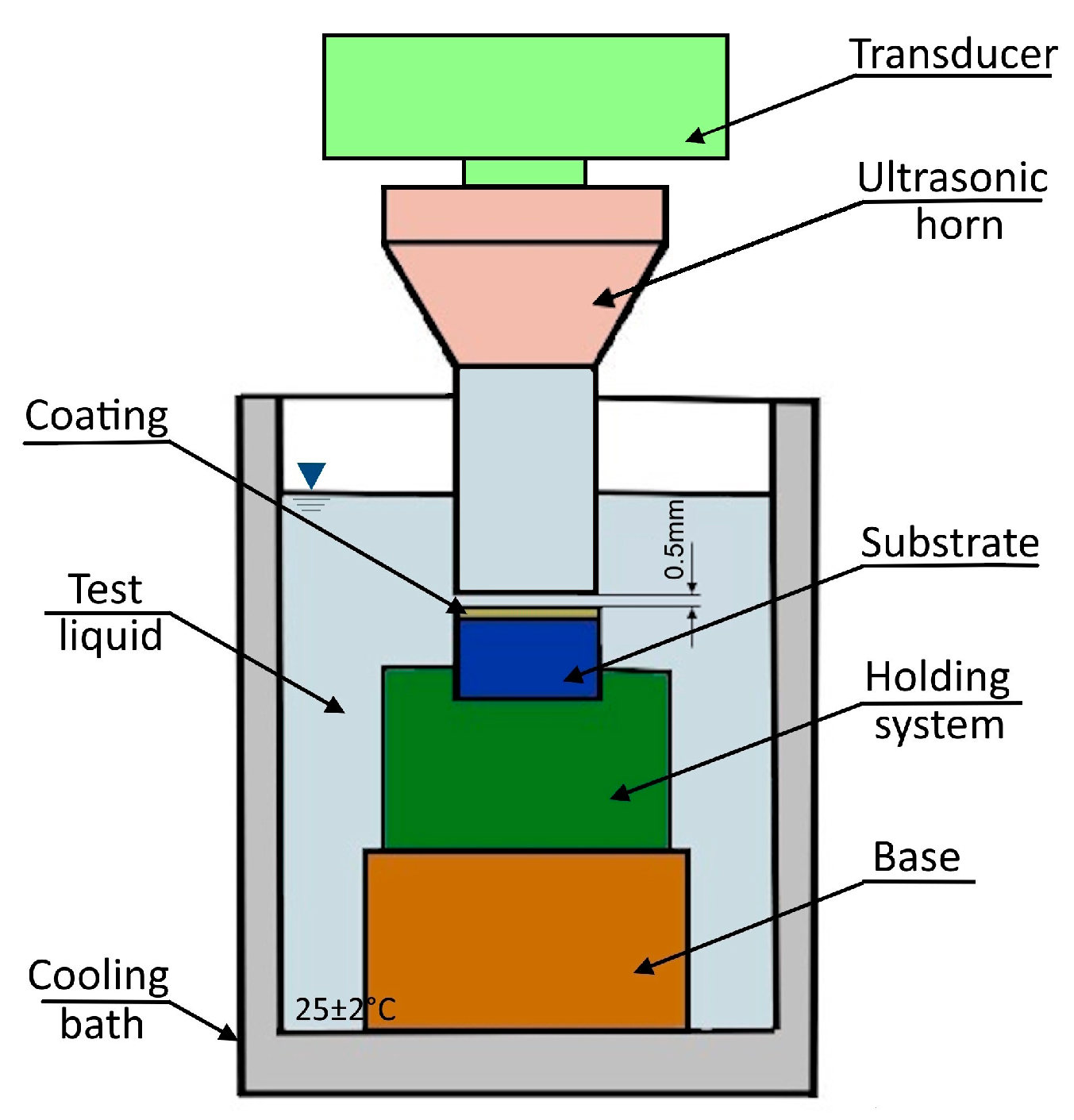
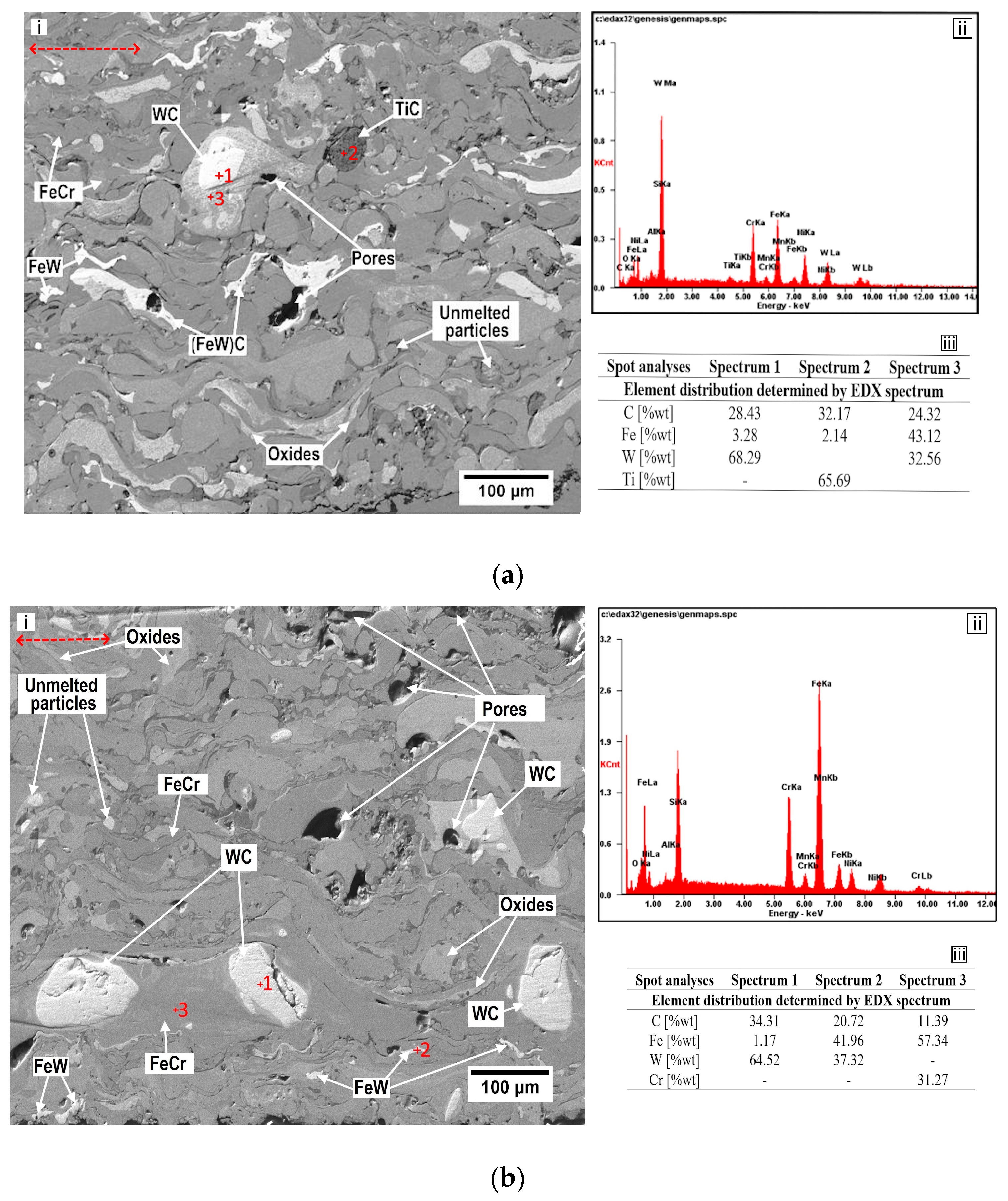
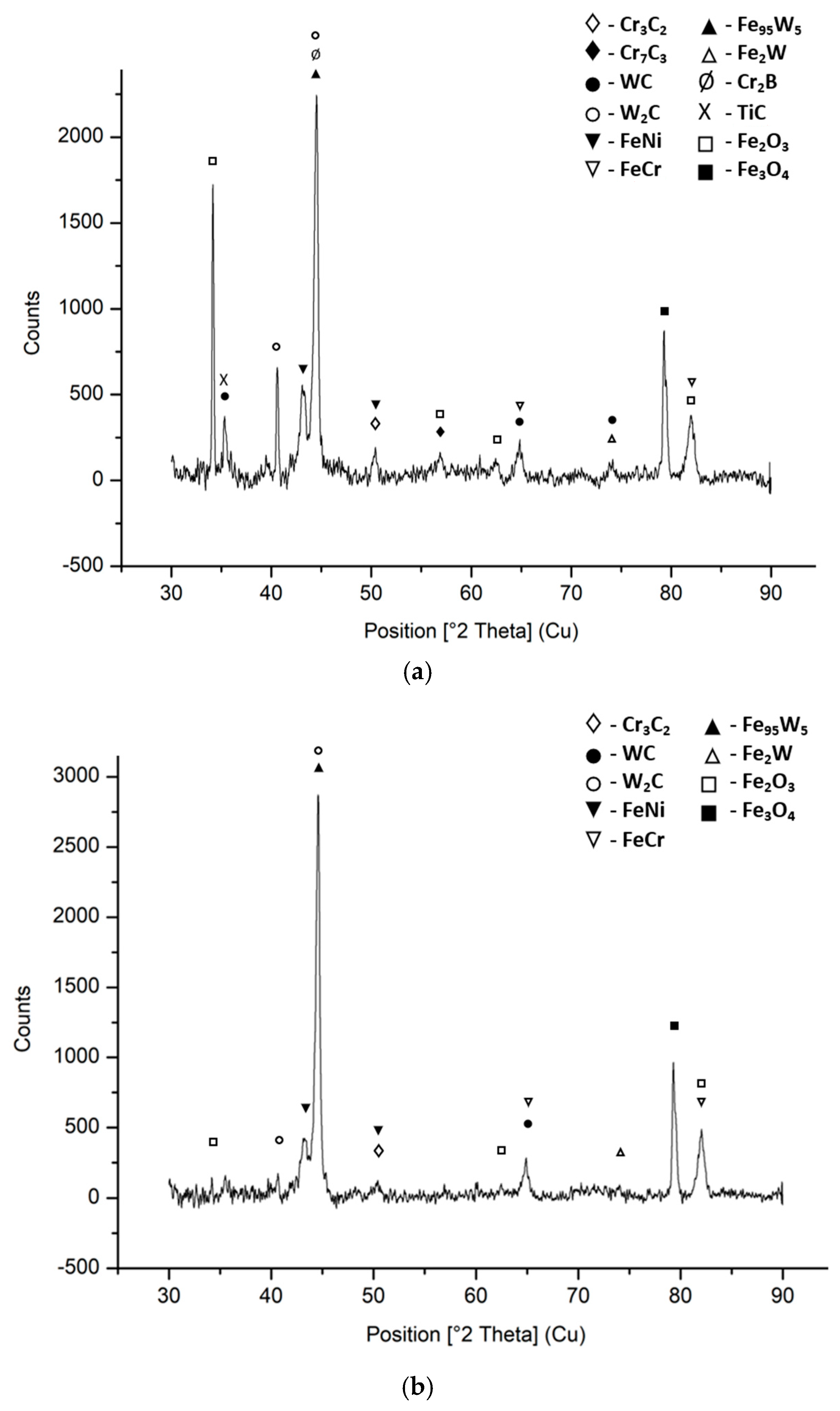

| Materials | Chemical Compositions (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Cr | B | Ni | Si | WC | P | S | TiC | Mn | Fe | |
| C15 | 0.12–0.18 | - | - | - | 0.4 | - | 0.045 | 0.045 | - | 0.3–0.6 | Balance |
| 97MXC | - | 13 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 26 | - | - | 6 | - | Balance |
| 60T | 0.3 | 13 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | Balance |
| Parameters | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| 97MXC | 60T/WC | |
| Current intensity (A) | 240 | 180 |
| Voltage (V) | 32 | 30 |
| Primary air pressure (bar) | 6 | 6 |
| Secondary air pressure—for WC training (bar) | - | 2 |
| Stand-off distance—SOD (mm) | 180 | 200 |
| Movement speed of the gun (m/s) | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| The number of passes | 3 | 3 |
| Coating | Porosity—According to ASTME 2109-01 [%] [35] | Adherence—According to ASTM C633-13 [MPa] [45] | HV300—According to ASTM E384 [49] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 97MXC | 11.42% ± 0.7 | 47.12 ± 4.1 | 823 ± 34 |
| 60T/WC | 13.26% ± 0.5 | 42.76 ± 3.8 | 656 ± 42 |
| Sample Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 97MXC | 60T/WC | C15 | |
| Total mass (mg) | 87.4 | 75.6 | 77.32 |
| Average erosion depth (μm) | 24.2 | 28.7 | 328 |
| Maximum erosion (μm/h) | 5.7 | 12.4 | 96.2 |
| Lost volume (mm3) | 6.3 | 10.5 | 76.4 |
| Parameters | Materials | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 97MXC | 60T/WC | |||
| Load [N] | 20 | 40 | 20 | 40 |
| CoF | 0.122 ± 0.011 | 0.238 ± 0.024 | 0.110 ± 0.028 | 0.215 ± 0.012 |
| Wear [g/h] | 0.002 ± 0.008 | 0.029 ± 0.015 | 0.043 ± 0.018 | 0.089 ± 0.021 |
| Initial mass [g] | 42.276 | 41.886 | 41.736 | 42.273 |
| Final mass [g] | 42.274 | 41.854 | 41.681 | 42.181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levărdă, E.; Cîrlan, D.-C.; Chicet, D.L.; Petcu, M.; Toma, S.L. Investigations on Cavitation Erosion and Wear Resistance of High-Alloy WC Coatings Manufactured by Electric Arc Spraying. Materials 2025, 18, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102259
Levărdă E, Cîrlan D-C, Chicet DL, Petcu M, Toma SL. Investigations on Cavitation Erosion and Wear Resistance of High-Alloy WC Coatings Manufactured by Electric Arc Spraying. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102259
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevărdă, Edmund, Dumitru-Codrin Cîrlan, Daniela Lucia Chicet, Marius Petcu, and Stefan Lucian Toma. 2025. "Investigations on Cavitation Erosion and Wear Resistance of High-Alloy WC Coatings Manufactured by Electric Arc Spraying" Materials 18, no. 10: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102259
APA StyleLevărdă, E., Cîrlan, D.-C., Chicet, D. L., Petcu, M., & Toma, S. L. (2025). Investigations on Cavitation Erosion and Wear Resistance of High-Alloy WC Coatings Manufactured by Electric Arc Spraying. Materials, 18(10), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102259











