Comparative Study of Stress–Strain Behavior and Microstructure of Three Solid-Waste-Powder-Modified Lateritic Clays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Lateritic Clay
2.1.2. Solid Waste Powder
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Specimen Preparation
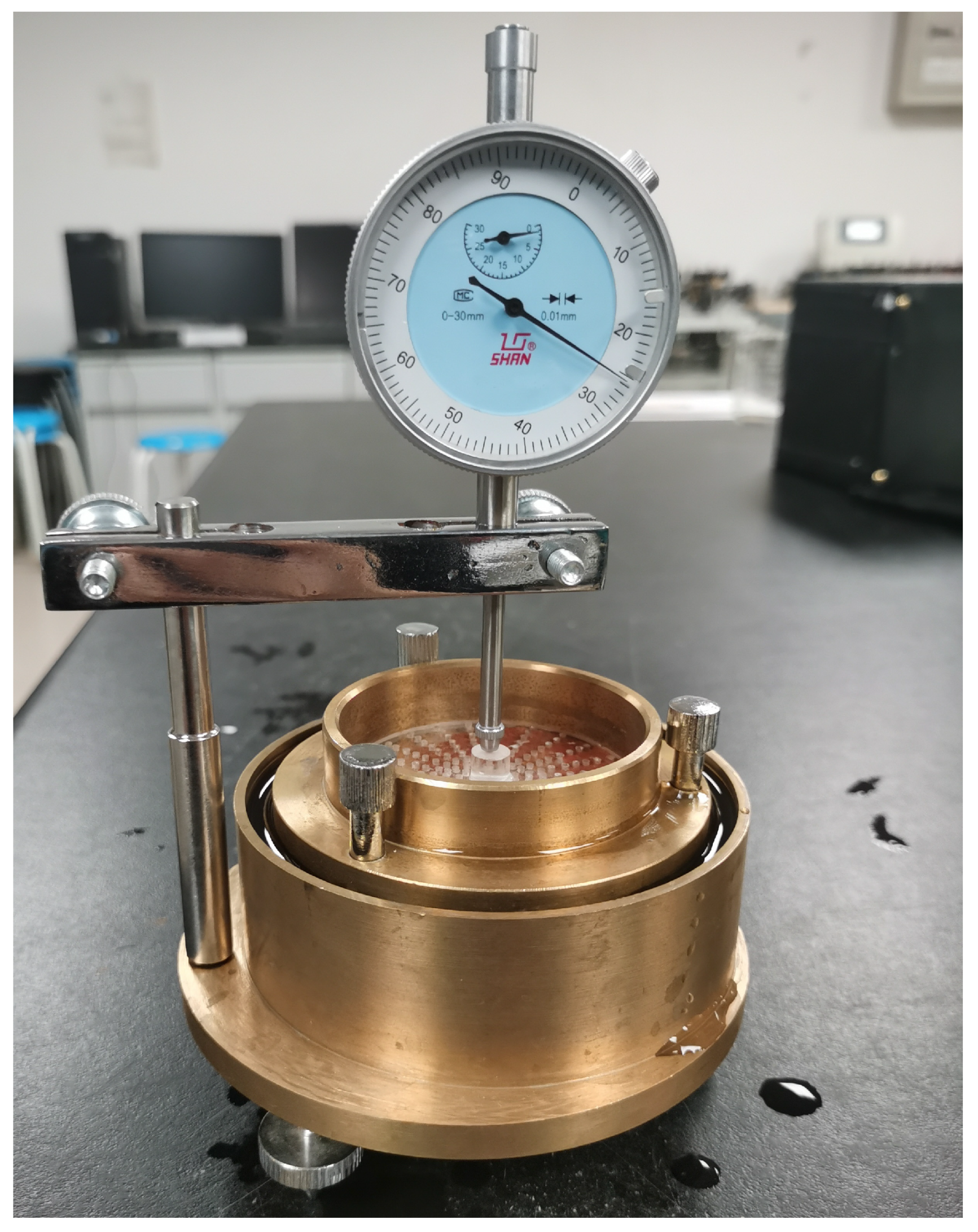
2.2.2. Uniaxial Compression Test
2.2.3. Direct Shear Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Stress–Strain Behavior
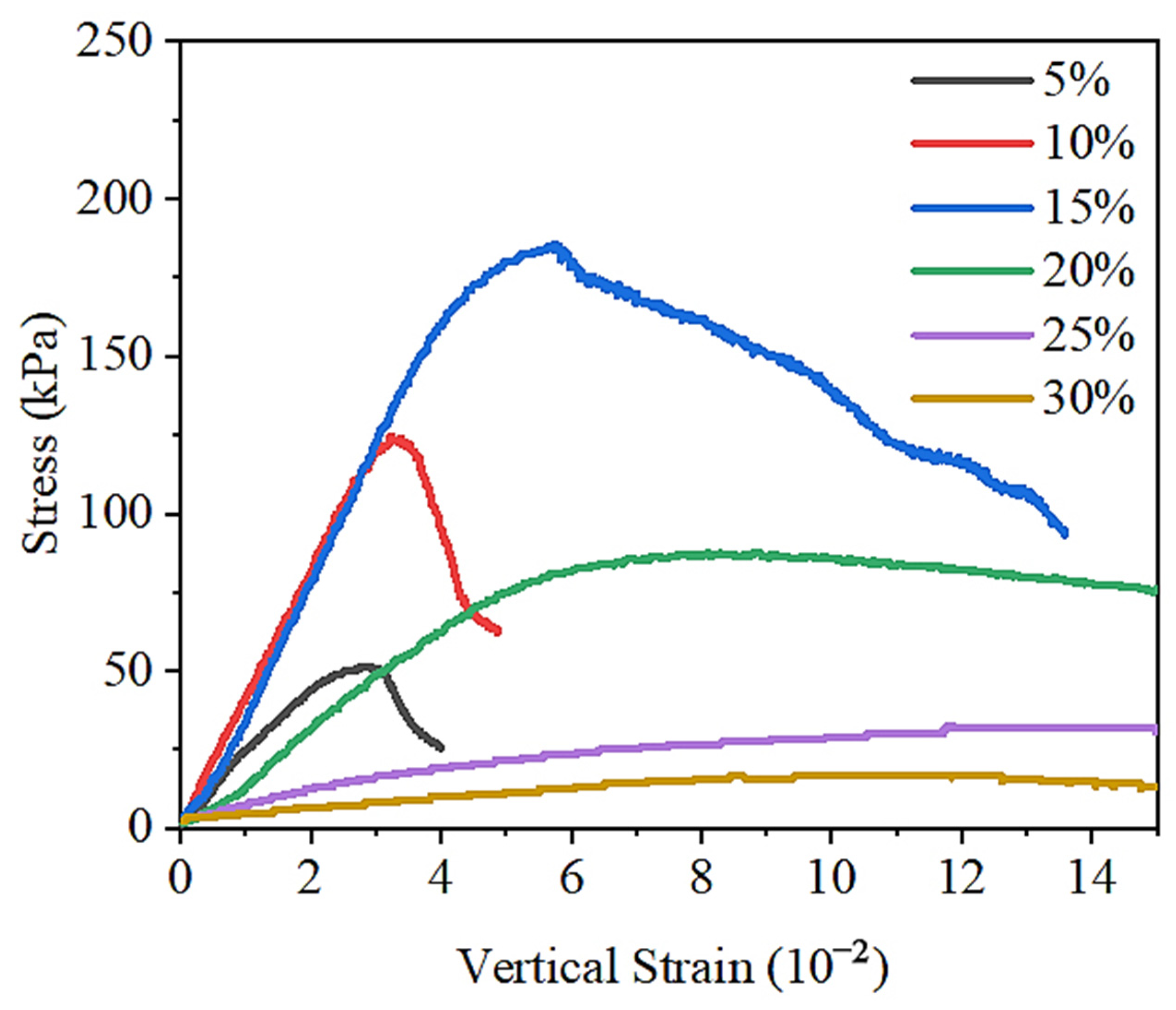
3.1.1. Stress–Strain Behavior of Lateritic Clay with Different Water Contents
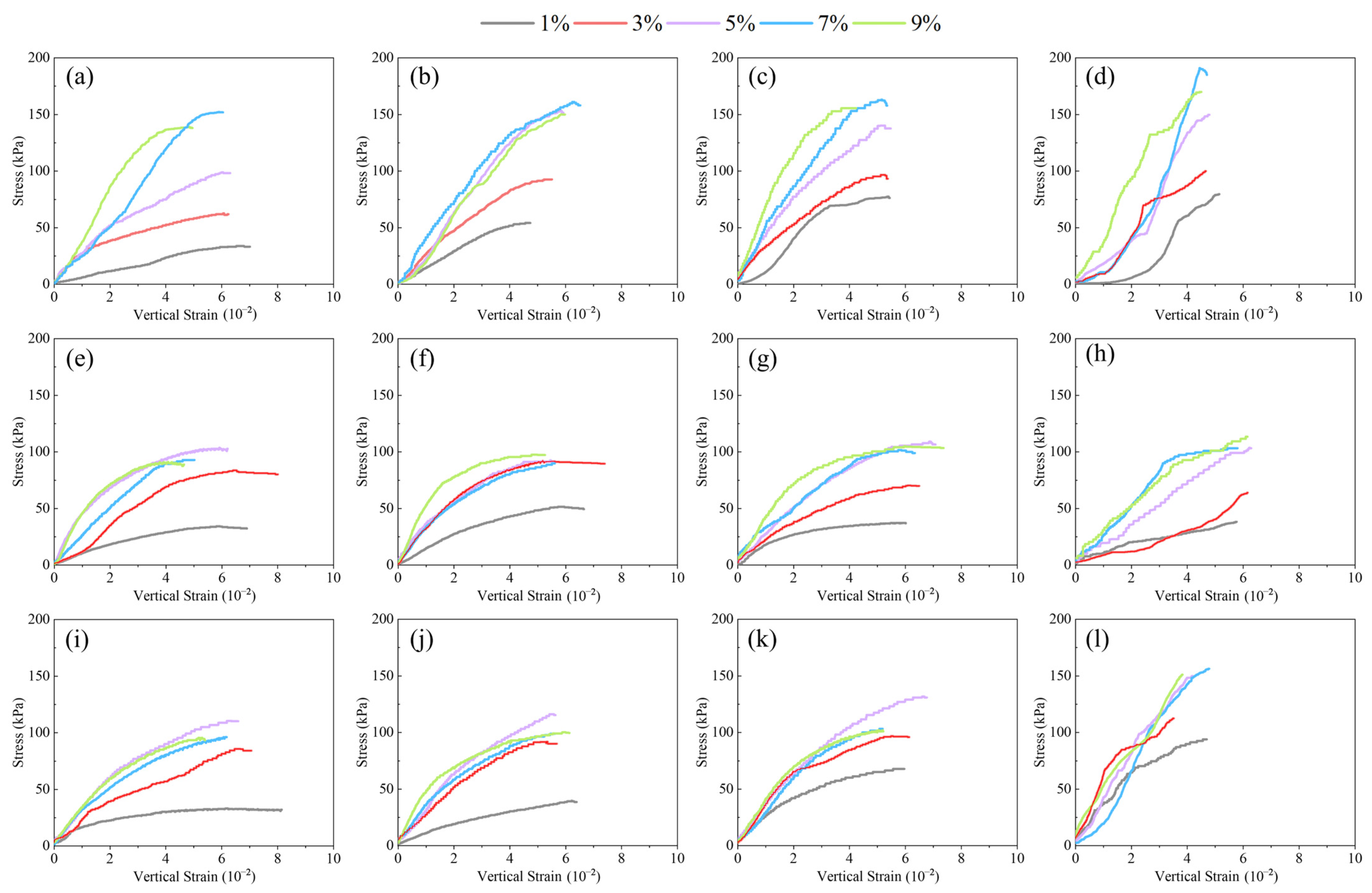
3.1.2. Stress–Strain Behavior of Lateritic Clay Modified by Different Kinds of Solid Waste
3.2. Shear Strength
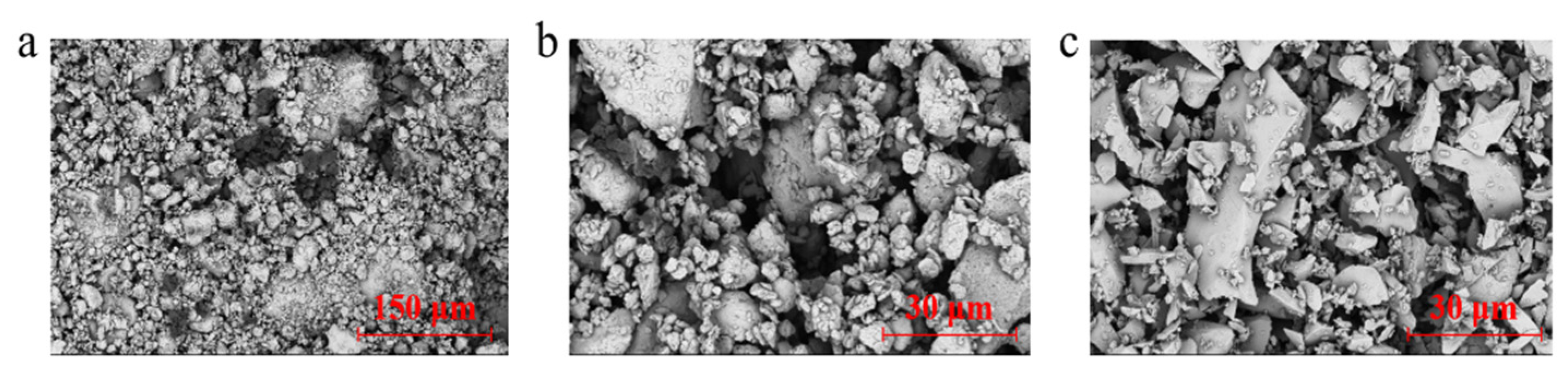
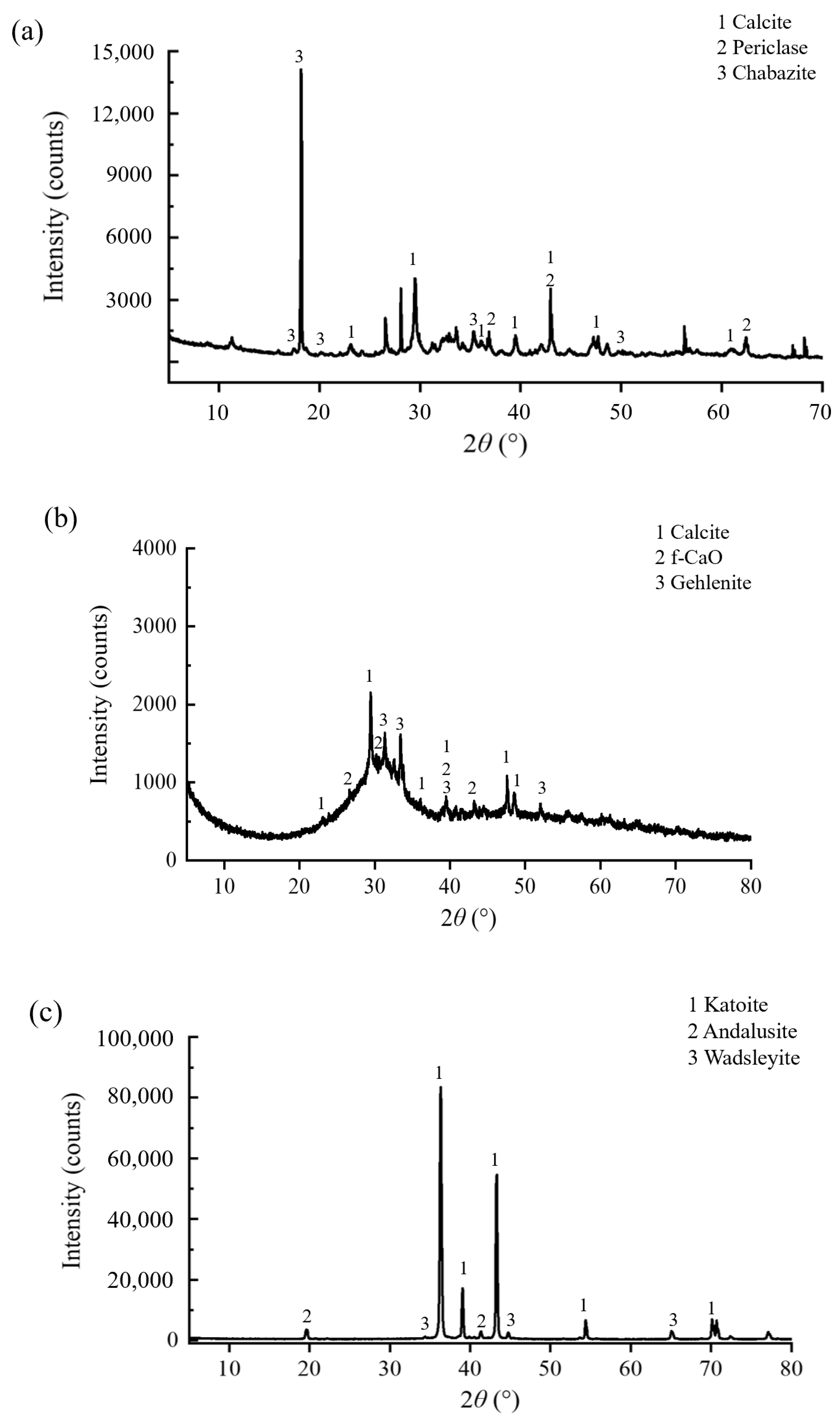
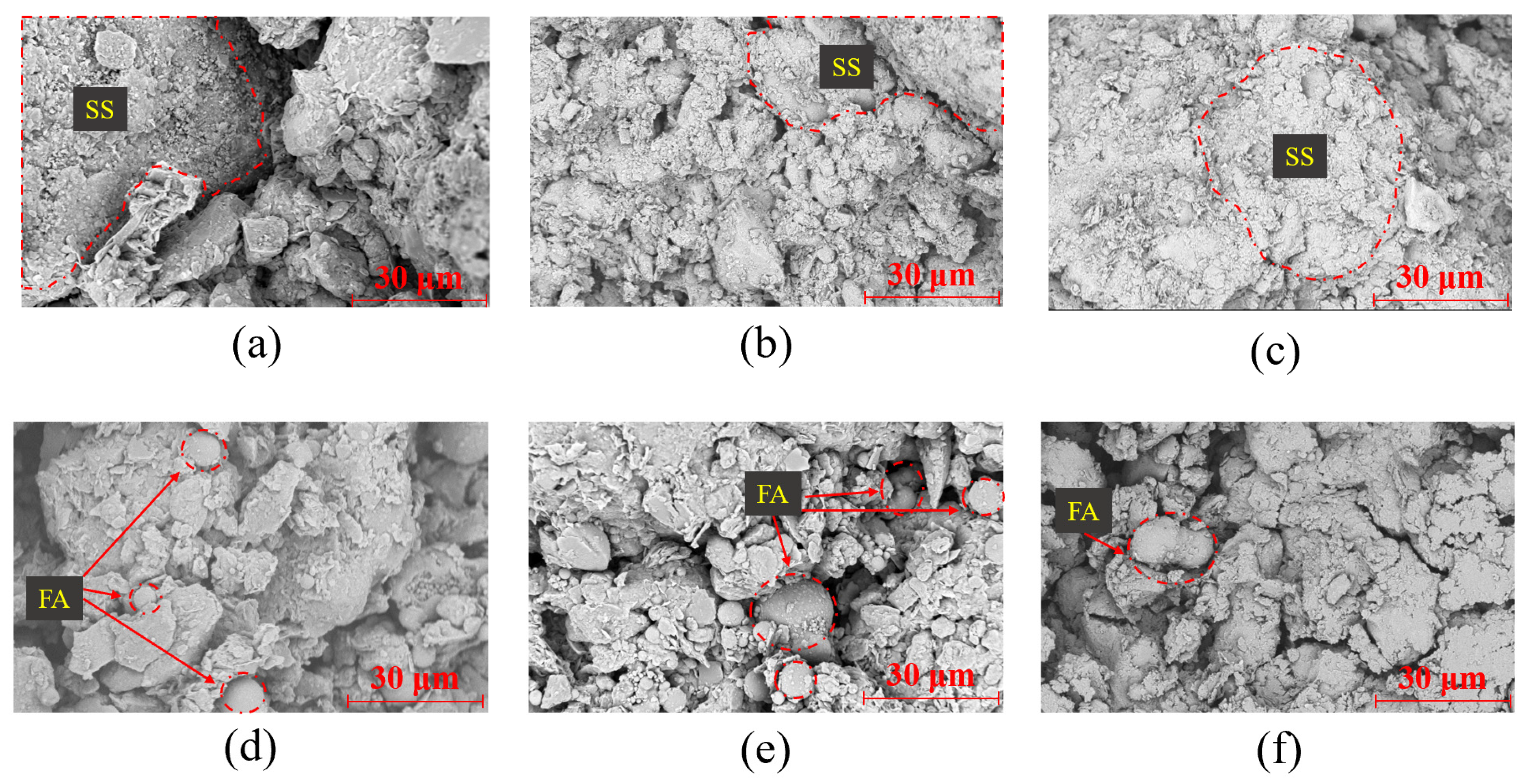
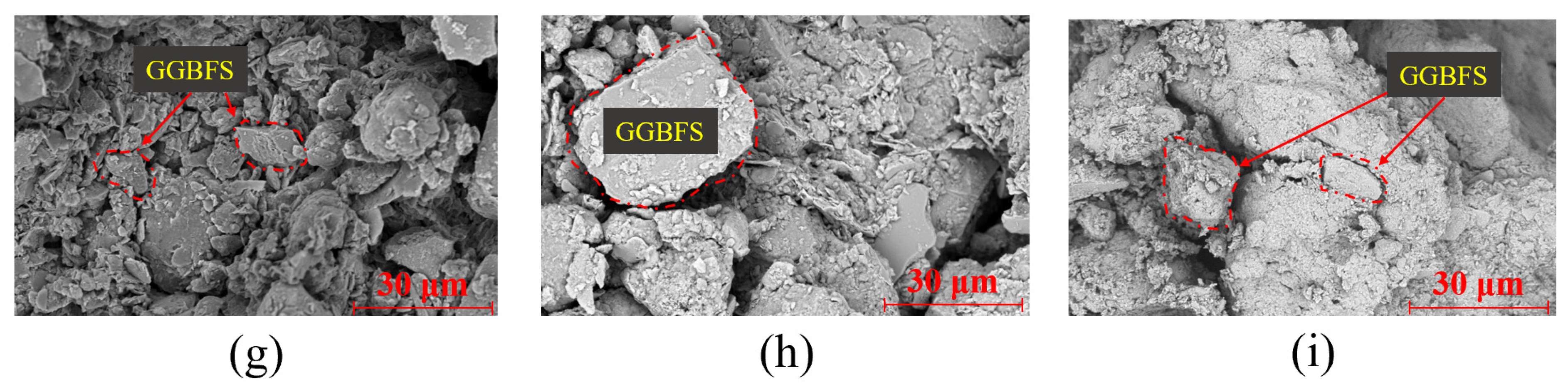
3.3. Relationship Between the Microstructure and Stress–Strain Behavior of Modified Lateritic Clay
3.4. Volumetric Stability of Modified Lateritic Clay
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attoh-Okine, N. Application of Genetic-Based Neural Network to Lateritic Soil Strength Modeling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2004, 18, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, M.G.; Bonder, B.H. Soil-Water Characteristic Curves Obtained for a Colluvial and Lateritic Soil Profile Considering the Macro and Micro Porosity. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2012, 30, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Bentil, O.; Zhou, C. Small Strain Shear Modulus and Damping Ratio of Two Unsaturated Lateritic Sandy Clays. Can. Geotech. J. 2021, 58, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; He, Y.; Liu, J. Construction of Weak Expansive Red Clay on Dongxin Expressway in Hunan Province, China. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2016, 30, C4015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, A.; Jayadeva, M.S. Double-Layer Theory and Compressibility of Clays. Geotechnique 1982, 32, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.R.; Sun, S.R.; Li, K. Study on Influence of Moisture Content on Strength and Brittle-Plastic Failure Characteristics of Xiashu Loess. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2023, 2023, 5919325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malizia, J.P.; Shakoor, A. Effect of Water Content and Density on Strength and Deformation Behavior of Clay Soils. Eng. Geol. 2018, 244, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horpibulsuk, S.; Suddeepong, A.; Chamket, P.; Chinkulkijniwat, A. Compaction Behavior of Fine-Grained Soils, Lateritic Soils and Crushed Rocks. Soils Found. 2013, 53, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecomte-Nana, G.; Goure-Doubi, H.; Smith, A.; Wattiaux, A.; Lecomte, G. Effect of Iron Phase on the Strengthening of Lateritic-Based “Geomimetic” Materials. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 70, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.; Akinniyi, D.; Zhou, C.; Chiu, C. Comparisons of Weathered Lateritic, Granitic and Volcanic Soils: Compressibility and Shear Strength. Eng. Geol. 2019, 249, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Qian, Z.Z. Influence of Five Additives on No Loading Swelling Potential of Red Clay. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, L.; Glasser, F.P.; Imbabi, M.S. A New, Carbon-Negative Precipitated Calcium Carbonate Admixture (PCC-A) for Low Carbon Portland Cements. Materials 2019, 12, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, B.; Wang, J.; He, P.; Zhou, C.; Huo, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, G.; Ding, Q. Cement Industry of China: Driving Force, Environment Impact and Sustainable Development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 75, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, S.; Paul, B.; Kumar, M. Sustainable Approaches for LD Slag Waste Management in Steel Industries: A Review. Metallurgist 2016, 60, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gong, X.; Nie, Z.; Cui, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, W. Environmental Impact Analysis of Blast Furnace Slag Applied to Ordinary Portland Cement Production. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 120, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.T.; Ji, X.S.; Sarker, P.K.; Tang, J.H.; Ge, L.Q.; Xia, M.S.; Xi, Y.Q. A Comprehensive Review on the Applications of Coal Fly Ash. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 141, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.; Pandian, P.K. Industrial Wastes as Auxiliary Additives to Cement/Lime Stabilization of Soils. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1267391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.R.; Qin, W.Z. Performance Characteristics of Soil-Cement from Industry Waste Binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2003, 15, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, N.P.; Mahendran, K.; Arunachelam, N. Effects of Industrial and Agricultural Wastes on Mud Blocks Using Geopolymer. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1054176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Jin, X.; Zhao, T.; Li, H.; Zhou, L. Study on the Strength Mechanism of Red Clay Improved by Waste Tire Rubber Powder. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaramaiah, A.; Shankar, A.U.R.; Singh, A.; Pammar, K.H. Utilization of Lateritic Soil Stabilized with Alkali Solution and Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag as a Base Course in Flexible Pavement Construction. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2020, 13, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R. Utilization of Waste Materials and By-Products in Producing Controlled Low-Strength Materials. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, G.; Ding, Y.; Wu, T.; Ding, S.; Shi, M.; Fan, H. Engineering Properties Optimization of Dispersive Soil by Calcium Silicate Waste—The Role of Steel-Making Slag. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimar, Z.; Pooni, J.; Robert, D.; Giustozzi, F.; Zhou, A.; Setunge, S.; Kodikara, J. Performance of Industrial Fly Ash Based Stabilized Mine Haul Roads Under Seasonal Moisture Changes. Transp. Geotech. 2024, 48, 101295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Wu, X.; Sun, T.; Yang, F.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhu, J. Replacing Cement with GGBS to Stabilize Phosphogypsum-Soil Mixture in Road Materials: A Comprehensive Assessment of Mechanical Property, Water Stability and Environmental Performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Han, Q.; Song, X.; Liu, Z. Study on the Cyclic Shear Performance of Waste Steel Slag Mixed Soil. Buildings 2023, 13, 3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guan, W.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Xie, M.; Zhang, X. Innovative Fly-Ash-Based Soil Crust Rehabilitation: Enhancing Wind Erosion Resistance in Gravel-Layered Desert Mining Areas. Land 2025, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darsi, B.P.; Molugaram, K.; Madiraju, S.V.H. Subgrade Black Cotton Soil Stabilization Using Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag (GGBS) and Lime, an Inorganic Mineral. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2021, 6, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, M.; Xia, L.; Zhan, L.; Wang, Y. Recognition of Changes in Air and Soil Temperatures at a Station Typical of China’s Subtropical Monsoon Region (1961–2018). Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2487-11; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011.
- ASTM D4318-17; Standard Test Methods for Liquid Limit, Plastic Limit, and Plasticity Index of Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D4832-16; Standard Test Method for Preparation and Testing of Controlled Low Strength Material (CLSM) Test Cylinders. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2016.
- Yu, C.; He, C.-B.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.-A.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-Q. Disintegration characteristics and mechanism of red clay improved by steel slag powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 444, 137873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, H. Experimental study and strength formulation of soil-based controlled low-strength material containing stainless steel reducing slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. The Ball Effect and Lubricity Contrast Analysis of Concrete Mixed with Fly Ash. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 154–158. [Google Scholar]






| Different Kinds of Pulp | pH Value |
|---|---|
| SS | 12.80 |
| FA | 8.18 |
| GGBFS | 9.50 |
| Lateritic clay | 6.69 |
| Oxides | Composition (wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lateritic Clay | SS | FA | GGBS | |
| Calcium oxide (CaO) | 0.74 | 41.22 | 3.60 | 59.31 |
| Silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 52.99 | 6.32 | 35.71 | 16.31 |
| Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) | 18.78 | 2.88 | 37.34 | 10.24 |
| Ferric oxide (Fe2O3) | 13.48 | 22.44 | 9.86 | 1.46 |
| Magnesium oxide (MgO) | 1.04 | 5.68 | 0.46 | 5.63 |
| Additive | Test Group | Dry Mass Ratio of Solid Waste to Lateritic Clay | Curing Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 1-1 | 0.01 | 3, 7, 14 |
| 1-2 | 0.03 | ||
| 1-3 | 0.05 | ||
| 1-4 | 0.07 | ||
| 1-5 | 0.09 | ||
| FA | 2-1 | 0.01 | 3, 7, 14 |
| 2-2 | 0.03 | ||
| 2-3 | 0.05 | ||
| 2-4 | 0.07 | ||
| 2-5 | 0.09 | ||
| GGBFS | 3-1 | 0.01 | 3, 7, 14 |
| 3-2 | 0.03 | ||
| 3-3 | 0.05 | ||
| 3-4 | 0.07 | ||
| 3-5 | 0.09 |
| Specimen | Cohesive Force (kPa) | Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|
| Unmodified lateritic clay | 3 | 21 |
| SS-modified lateritic clay | 28 | 19 |
| FA-modified lateritic clay | 26 | 12 |
| GGBFS-modified lateritic clay | 23 | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, W.; Dai, K.; Lin, D.; Yue, B.; Su, B.; Lin, Z.; Chen, M.; Zheng, H.; Luo, Z. Comparative Study of Stress–Strain Behavior and Microstructure of Three Solid-Waste-Powder-Modified Lateritic Clays. Materials 2025, 18, 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102377
Qiao W, Dai K, Lin D, Yue B, Su B, Lin Z, Chen M, Zheng H, Luo Z. Comparative Study of Stress–Strain Behavior and Microstructure of Three Solid-Waste-Powder-Modified Lateritic Clays. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102377
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Wei, Kuncheng Dai, Daming Lin, Bing Yue, Bidi Su, Zhiping Lin, Mingyou Chen, Haofeng Zheng, and Zhihua Luo. 2025. "Comparative Study of Stress–Strain Behavior and Microstructure of Three Solid-Waste-Powder-Modified Lateritic Clays" Materials 18, no. 10: 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102377
APA StyleQiao, W., Dai, K., Lin, D., Yue, B., Su, B., Lin, Z., Chen, M., Zheng, H., & Luo, Z. (2025). Comparative Study of Stress–Strain Behavior and Microstructure of Three Solid-Waste-Powder-Modified Lateritic Clays. Materials, 18(10), 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102377






