Utilizing T1- and T2-Specific Contrast Agents as “Two Colors” MRI Correlation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Relaxation Time Determination
2.3. Data Analysis and Fitting
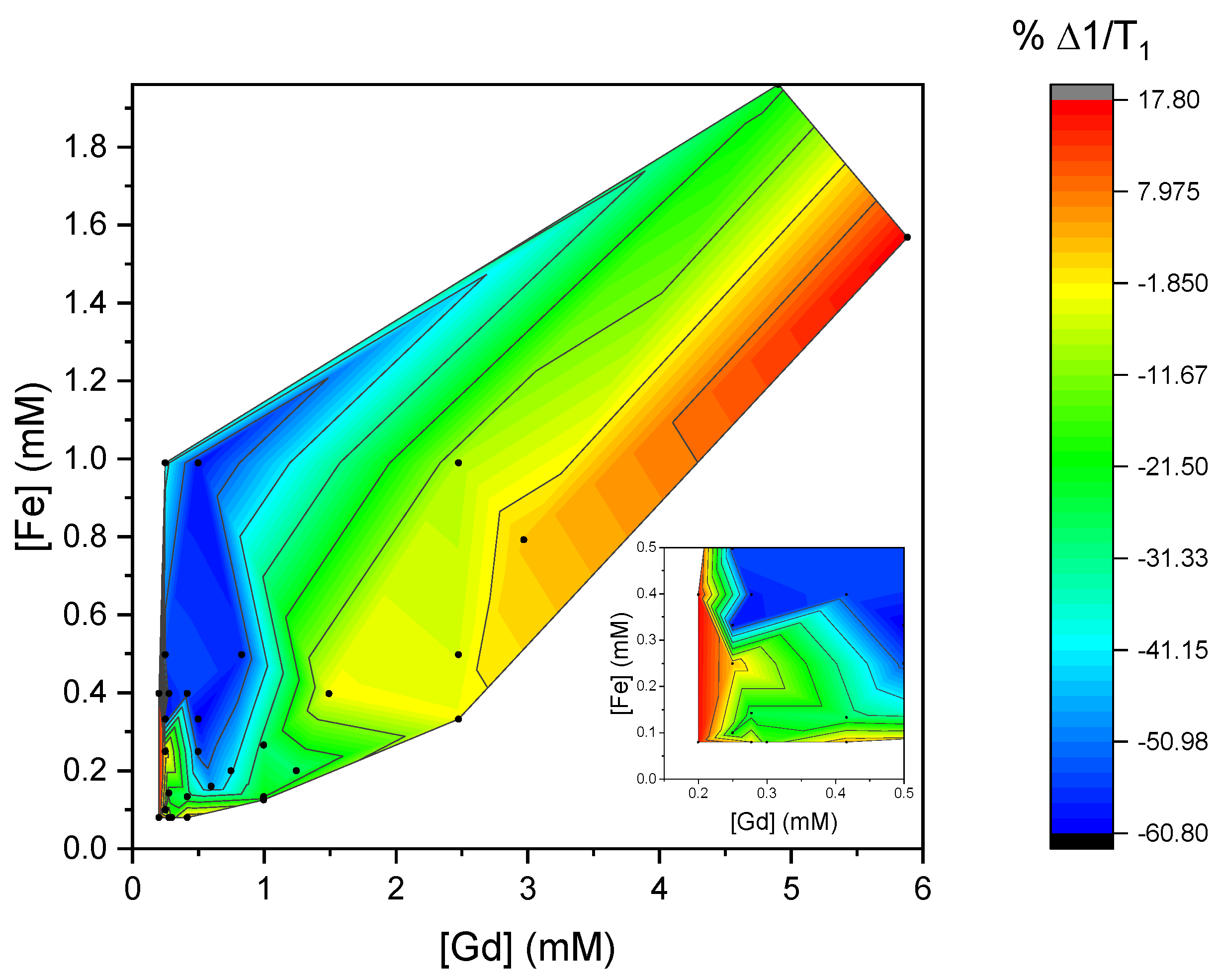
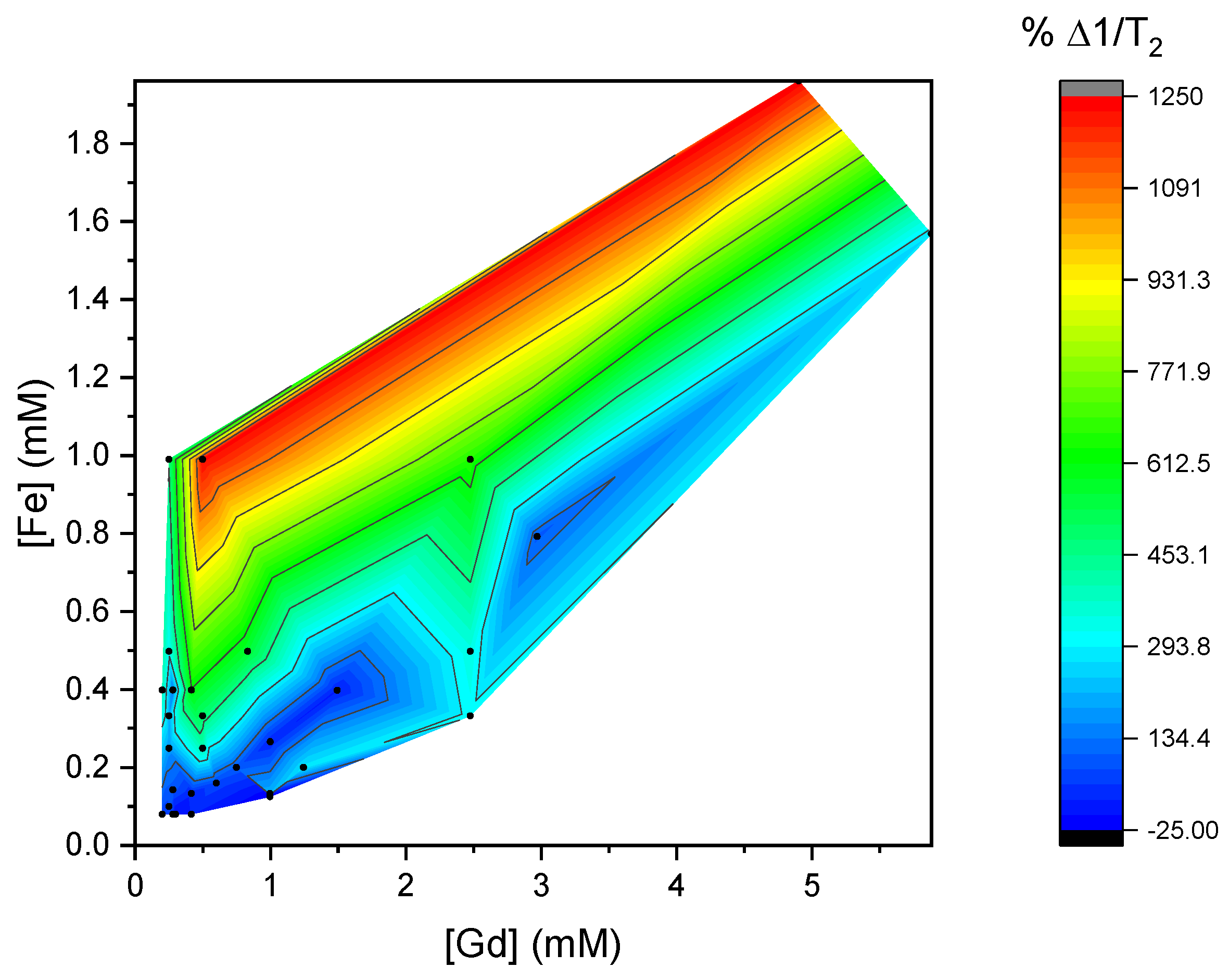
3. Results and Discussion
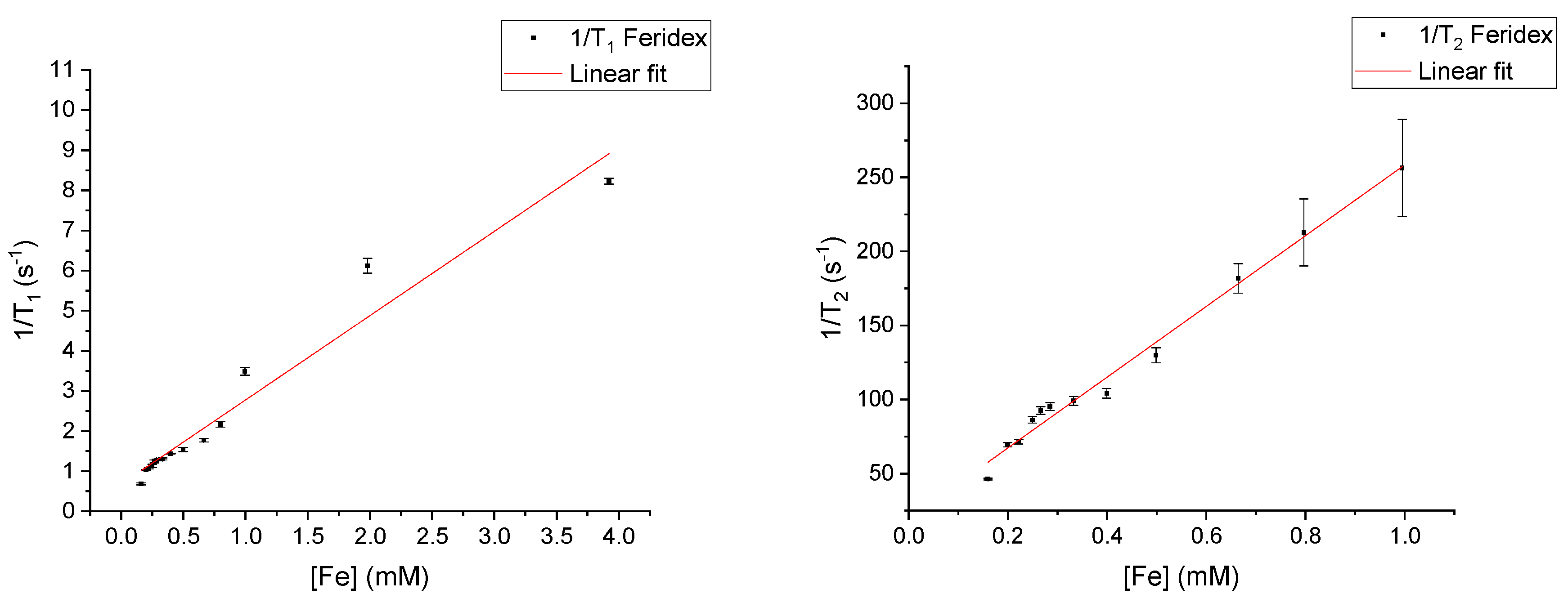
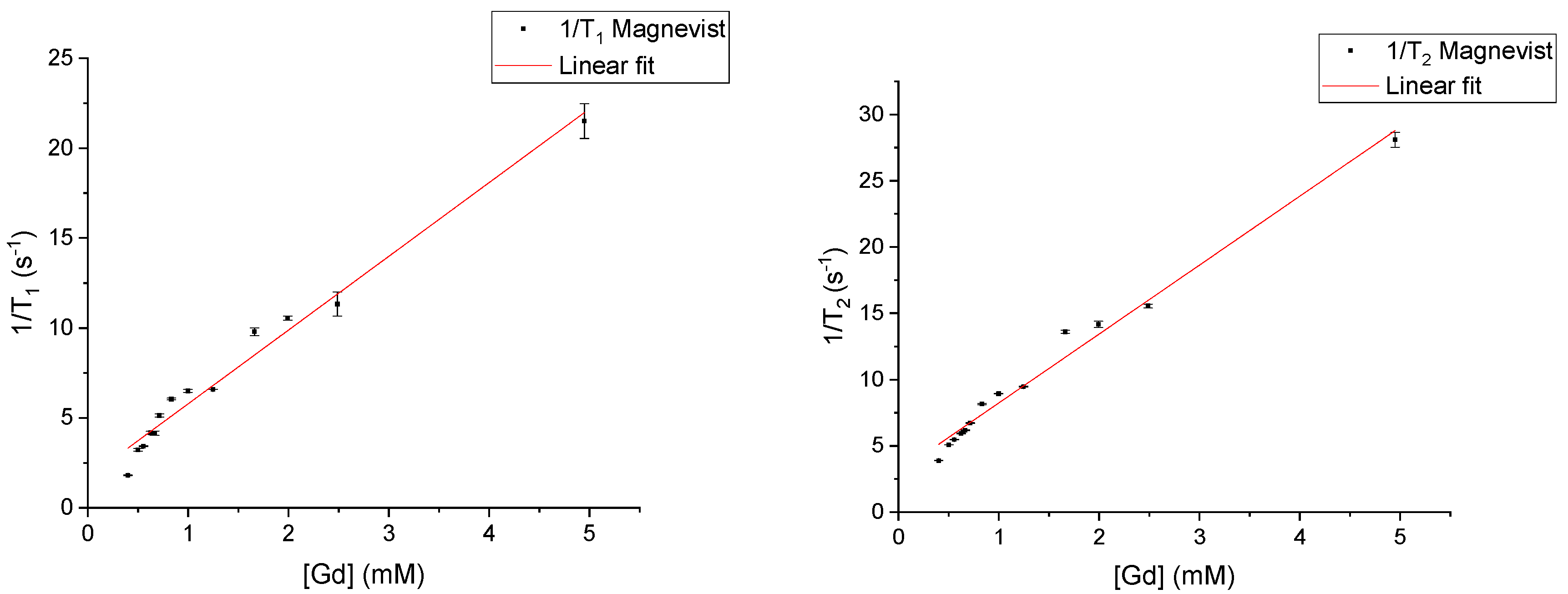
3.1. Relaxivities of Pure CAs
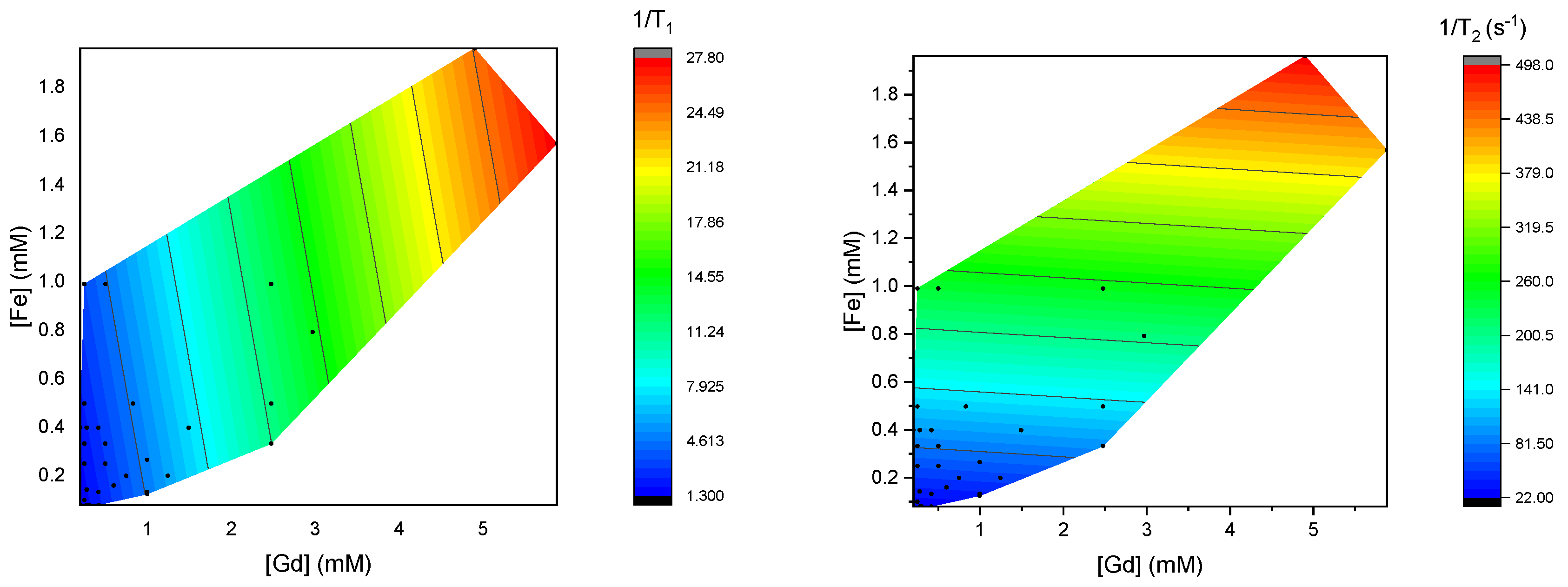
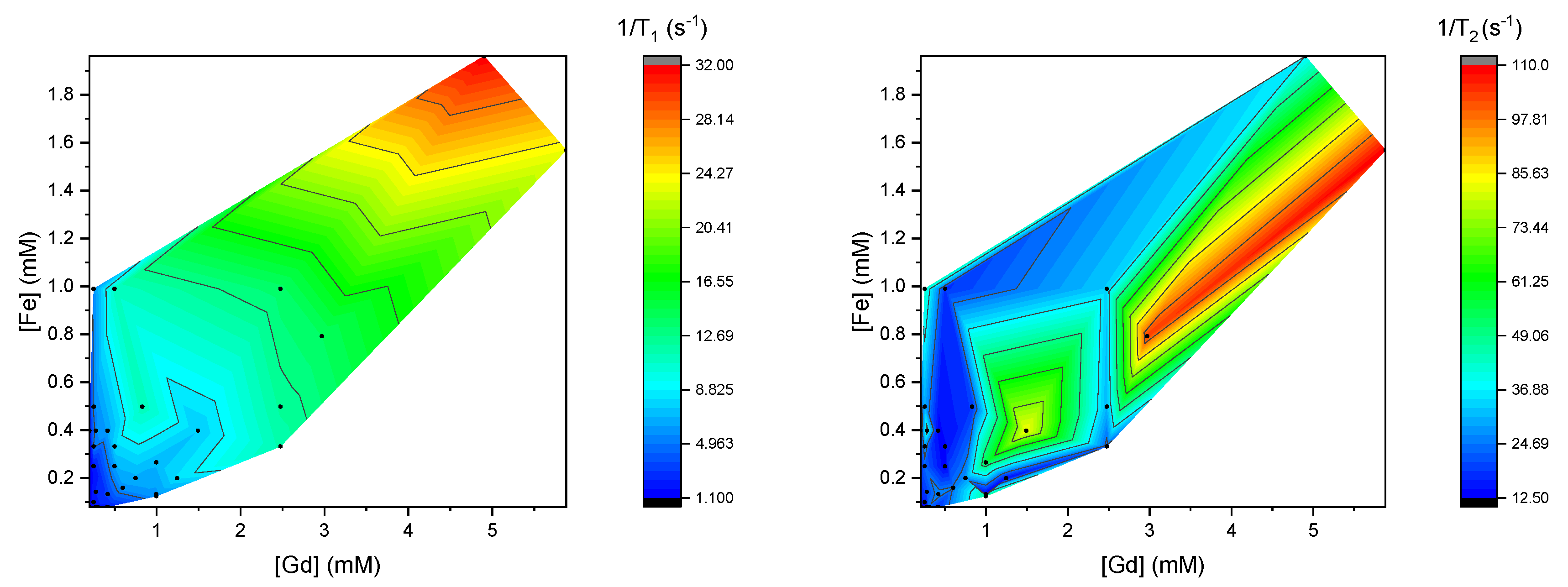
3.2. Relaxivities of Mixtures of CAs
3.3. Theoretical Insight
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blamire, A.M. The Technology of MRI—The next 10 Years? Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, 601–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewes, D.B.; Kucharczyk, W. Physics of MRI: A Primer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 35, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutt, B.K.; Lee, D.H. The Impact of Field Strength on Image Quality in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1996, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachha, B.; Huang, S.Y. MRI with Ultrahigh Field Strength and High-Performance Gradients: Challenges and Opportunities for Clinical Neuroimaging at 7 T and Beyond. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2021, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic Nanoparticles for MRI Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.-D.; Paudel, R.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Zhang, Z.-S.; Zhou, S.-K. MRI Contrast Agents: Classification and Application (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strijkers, G.J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; van Tilborg, G.A.F.; Nicolay, K. MRI Contrast Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRobbie, D.W.; Moore, E.A.; Graves, M.J.; Prince, M.R. MRI from Picture to Proton, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.J.J.; Oakden, W.; Stanisz, G.J.; Scott Prosser, R.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Size-Tunable, Ultrasmall NaGdF4 Nanoparticles: Insights into Their T1 MRI Contrast Enhancement. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3714–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.; Blasiak, B.; Tomanek, B.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Validation of Inner, Second, and Outer Sphere Contributions to T1 and T2 Relaxation in Gd3+-Based Nanoparticles Using Eu3+ Lifetime Decay as a Probe. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 11557–11569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.K.; Johnson, N.J.J.; Cramen, J.; Blasiak, B.; Latta, P.; Tomanek, B.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. NaDyF4 Nanoparticles as T2 Contrast Agents for Ultrahigh Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Blasiak, B.; Marenco, A.J.; Trudel, S.; Tomanek, B.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Design and Regulation of NaHoF4 and NaDyF4 Nanoparticles for High-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.C.; Marrett, S.; Torrescorzo, J.; Ku, S.; Collins, L. MRI-PET Correlation in Three Dimensions Using a Volume-of-Interest (VOI) Atlas. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1991, 11 (Suppl. S1), A69–A78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, L.; Nicolai, E.; Luongo, A.; Aiello, M.; Catalano, O.A.; Soricelli, A.; Salvatore, M. Comparison of Whole-Body PET/CT and PET/MRI in Breast Cancer Patients: Lesion Detection and Quantitation of 18F-Deoxyglucose Uptake in Lesions and in Normal Organ Tissues. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, N.L. Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. In Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 337–378. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S. Fluorescence Spectroscopy of Single Biomolecules. Science 1999, 283, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.E.; Donnola, S.B.; Jiang, Y.; Batesole, J.; Darrah, R.; Drumm, M.L.; Brady-Kalnay, S.M.; Steinmetz, N.F.; Yu, X.; Griswold, M.A.; et al. Dual Contrast—Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting (DC-MRF): A Platform for Simultaneous Quantification of Multiple MRI Contrast Agents. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.E.; Johansen, M.; Erokwu, B.O.; Hu, H.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kavran, M.; Vincent, J.; Drumm, M.L.; Griswold, M.A.; et al. Dynamic, Simultaneous Concentration Mapping of Multiple MRI Contrast Agents with Dual Contrast—Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marriott, A.; Bowen, C.; Rioux, J.; Brewer, K. Simultaneous Quantification of SPIO and Gadolinium Contrast Agents Using MR Fingerprinting. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 79, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Gulani, V.; Seiberlich, N.; Liu, K.; Sunshine, J.L.; Duerk, J.L.; Griswold, M.A. Magnetic Resonance Fingerprinting. Nature 2013, 495, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.H. From the Relaxivity of Gd (DTPA)2− to Everything Else. Magn. Reson. Med. 1991, 22, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, S.H.; Kellar, K.E. Theory of 1/T1 and 1/T2 NMRD Profiles of Solutions of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, F.; Janka, R.; Fellner, C.; Dobritz, M.; Lenz, M.; Lang, W.; Bautz, W. Gd-BOPTA: “The MRA Contrast Agent of Choice”? Rontgenpraxis 1999, 52, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer, M.; Bauer, H.; Mintorovitch, J.; Requardt, M.; Weinmann, H.-J. Comparison of Magnetic Properties of MRI Contrast Media Solutions at Different Magnetic Field Strengths. Investig. Radiol. 2005, 40, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panich, A.M.; Salti, M.; Goren, S.D.; Yudina, E.B.; Aleksenskii, A.E.; Vul’, A.Y.; Shames, A.I. Gd (III)-Grafted Detonation Nanodiamonds for MRI Contrast Enhancement. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korchinski, D.J.; Taha, M.; Yang, R.; Nathoo, N.; Dunn, J.F. Iron Oxide as an MRI Contrast Agent for Cell Tracking: Supplementary Issue. Magn. Reson. Insights 2015, 8, MRI.S23557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, J.M.; Chu, W.-J.; Lee, J.-H.; Reineke, T.M. A β-Cyclodextrin “Click Cluster” Decorated with Seven Paramagnetic Chelates Containing Two Water Exchange Sites. Bioconjugate Chem. 2008, 19, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravan, P. Protein-Targeted Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Contrast Agents: Design and Mechanism of Action. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N.; Morgan, L.O. Proton relaxation times in paramagnetic solutions. Effects of electron spin relaxation. J. Chem. Phys. 1961, 34, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.; Blasiak, B.; Tomanek, B.; Latta, P.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Target-Specific Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Human Prostate Adenocarcinoma Using NaDyF4–NaGdF4 Core–Shell Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24345–24355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, I.; Galas, O.; Luchinat, C.; Messori, L.; Parigi, G. A Theoretical Analysis of the 1H Nuclear Magnetic Relaxation Dispersion Profiles of Diferric Transferrin. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 14217–14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, I.; Kowalewski, J.; Luchinat, C.; Nilsson, T.; Parigi, G. Nuclear Spin Relaxation in Paramagnetic Complexes of S = 1: Electron Spin Relaxation Effects. J. Phys. Chem. 1999, 111, 5795–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, E.; Westlund, P.-O. 1H NMRD Profile and ESR Lineshape Calculation for an Isotropic Electron Spin System with S = 7/2. A Generalized Modified Solomon–Bloembergen–Morgan Theory for Nonextreme-Narrowing Conditions. J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 1996, 122, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewski, J.; Luchinat, C.; Nilsson, T.; Parigi, G. Nuclear Spin Relaxation in Paramagnetic Systems: Electron Spin Relaxation Effects under near-Redfield Limit Conditions and Beyond. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 7376–7382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Kowalewski, J. Nuclear Spin Relaxation in Solution of Paramagnetic Complexes with Large Transient Zero-Field Splitting. Mol. Phys. 2003, 101, 2861–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, D.; Kowalewski, J. General Treatment of Paramagnetic Relaxation Enhancement Associated with Translational Diffusion. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 174104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, M.E. High-Field-Strength Magnetic Resonance. Potential and Limits. Top. Magn. Reson. Imag. 2007, 18, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frencken, A.L.; Blasiak, B.; Tomanek, B.; Kruk, D.; van Veggel, F.C.J.M. Utilizing T1- and T2-Specific Contrast Agents as “Two Colors” MRI Correlation. Materials 2025, 18, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102290
Frencken AL, Blasiak B, Tomanek B, Kruk D, van Veggel FCJM. Utilizing T1- and T2-Specific Contrast Agents as “Two Colors” MRI Correlation. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102290
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrencken, Adriaan L., Barbara Blasiak, Boguslaw Tomanek, Danuta Kruk, and Frank C. J. M. van Veggel. 2025. "Utilizing T1- and T2-Specific Contrast Agents as “Two Colors” MRI Correlation" Materials 18, no. 10: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102290
APA StyleFrencken, A. L., Blasiak, B., Tomanek, B., Kruk, D., & van Veggel, F. C. J. M. (2025). Utilizing T1- and T2-Specific Contrast Agents as “Two Colors” MRI Correlation. Materials, 18(10), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102290





