Impact of Polymers on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics of Shale Oil-Produced Fluid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
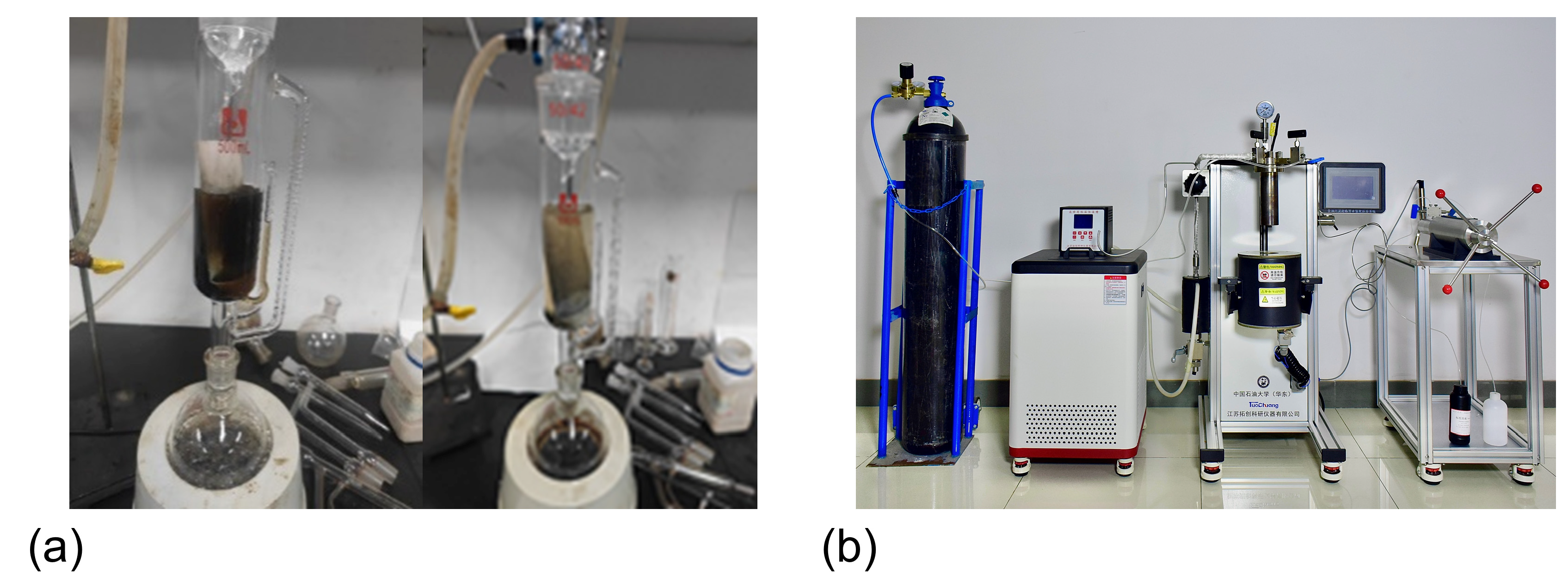
2.1. Experimental Setup
- (1)
- Temperature-controlled sand sedimentation experimental system
- (2)
- Sand sedimentation treatment system
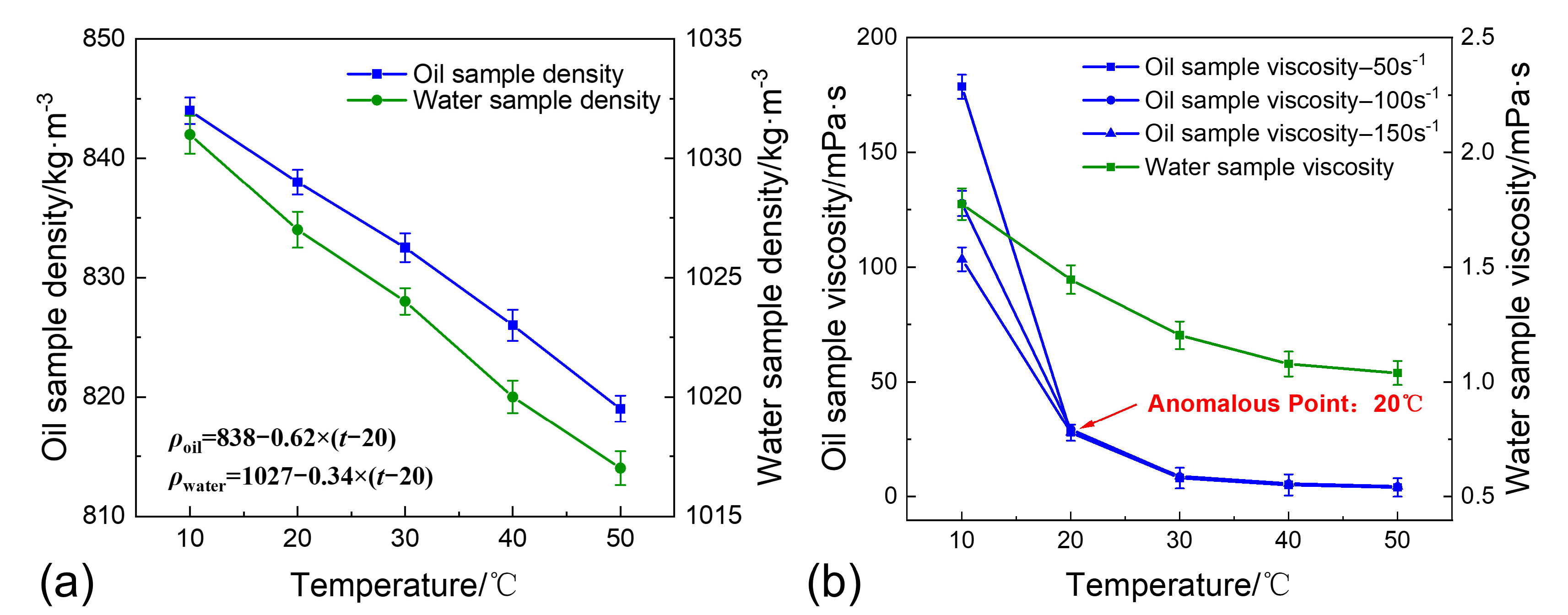
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Impact of the Water Content on the Sand Sedimentation Characteristics
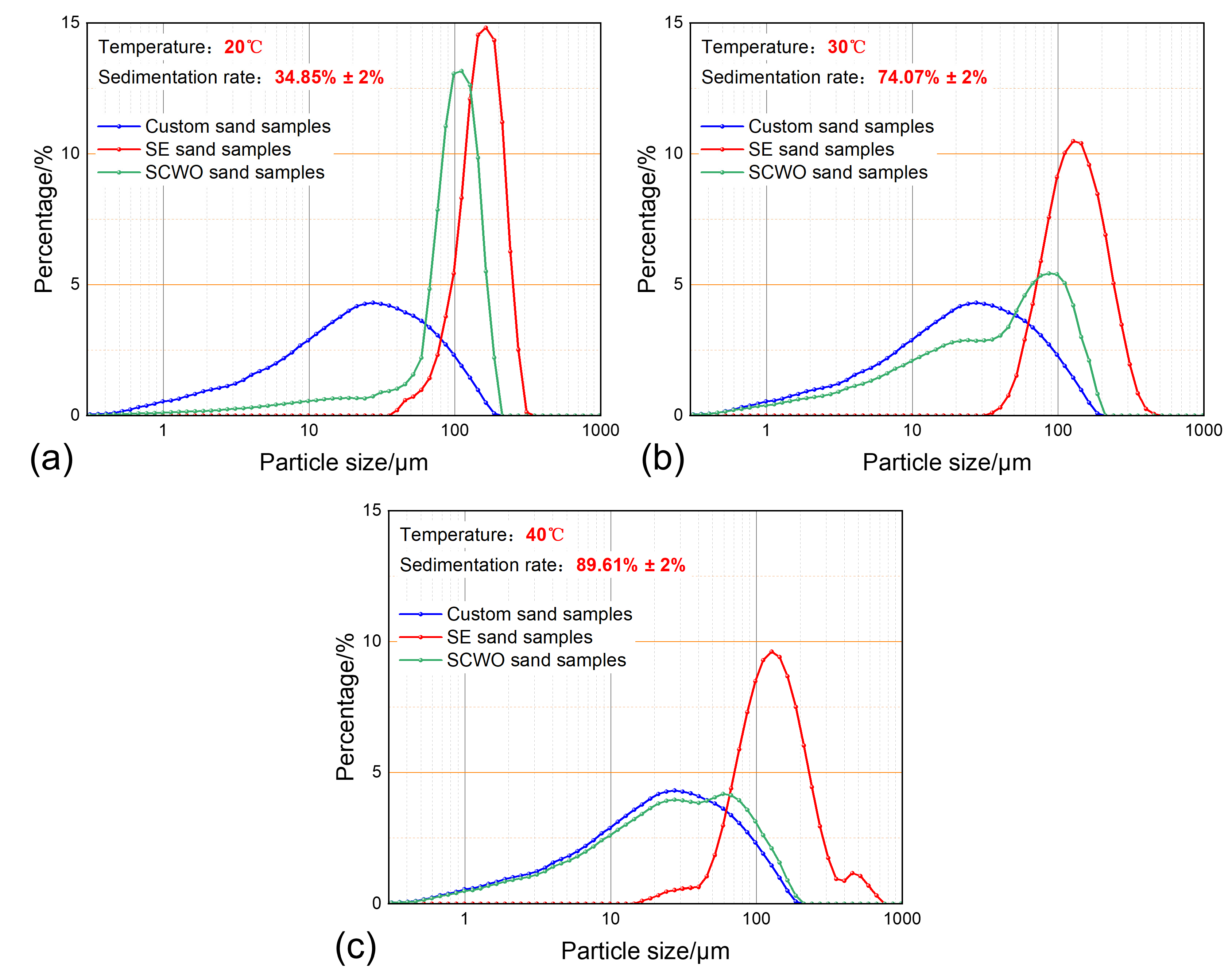
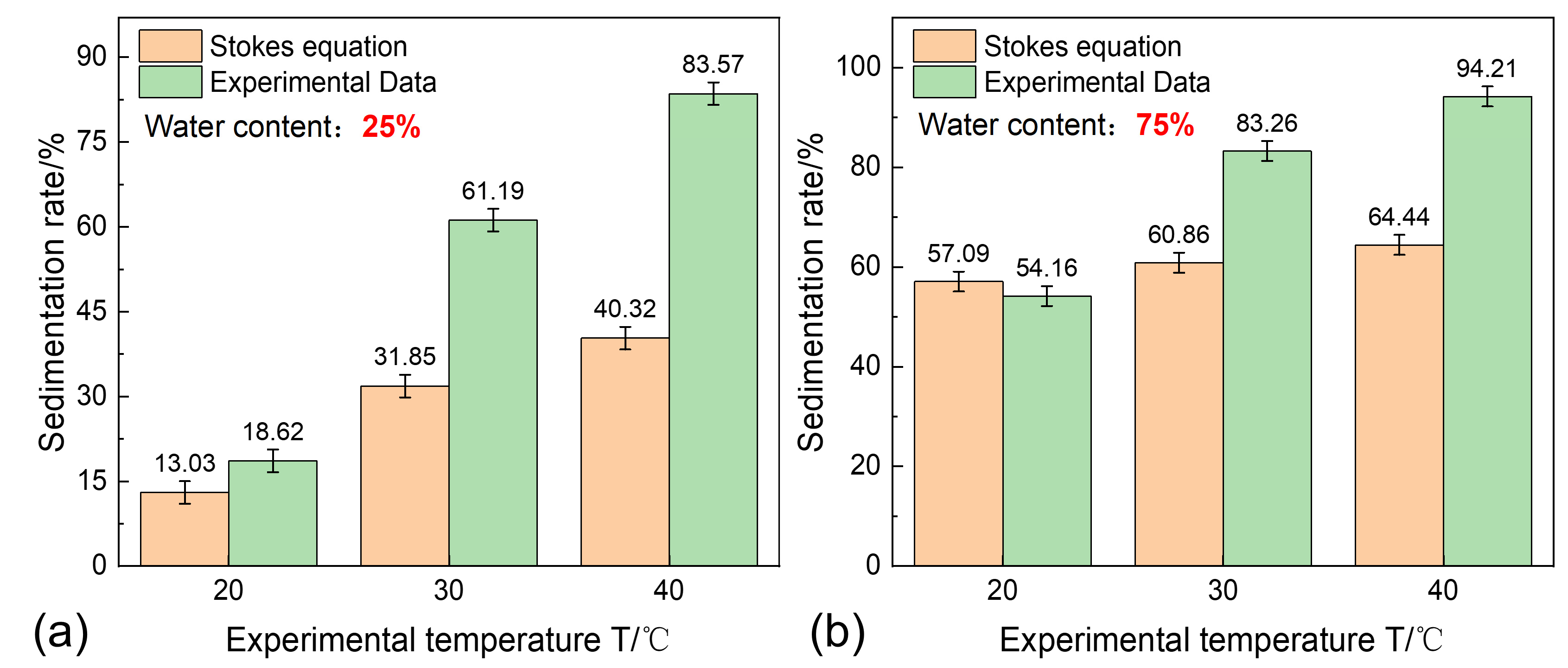
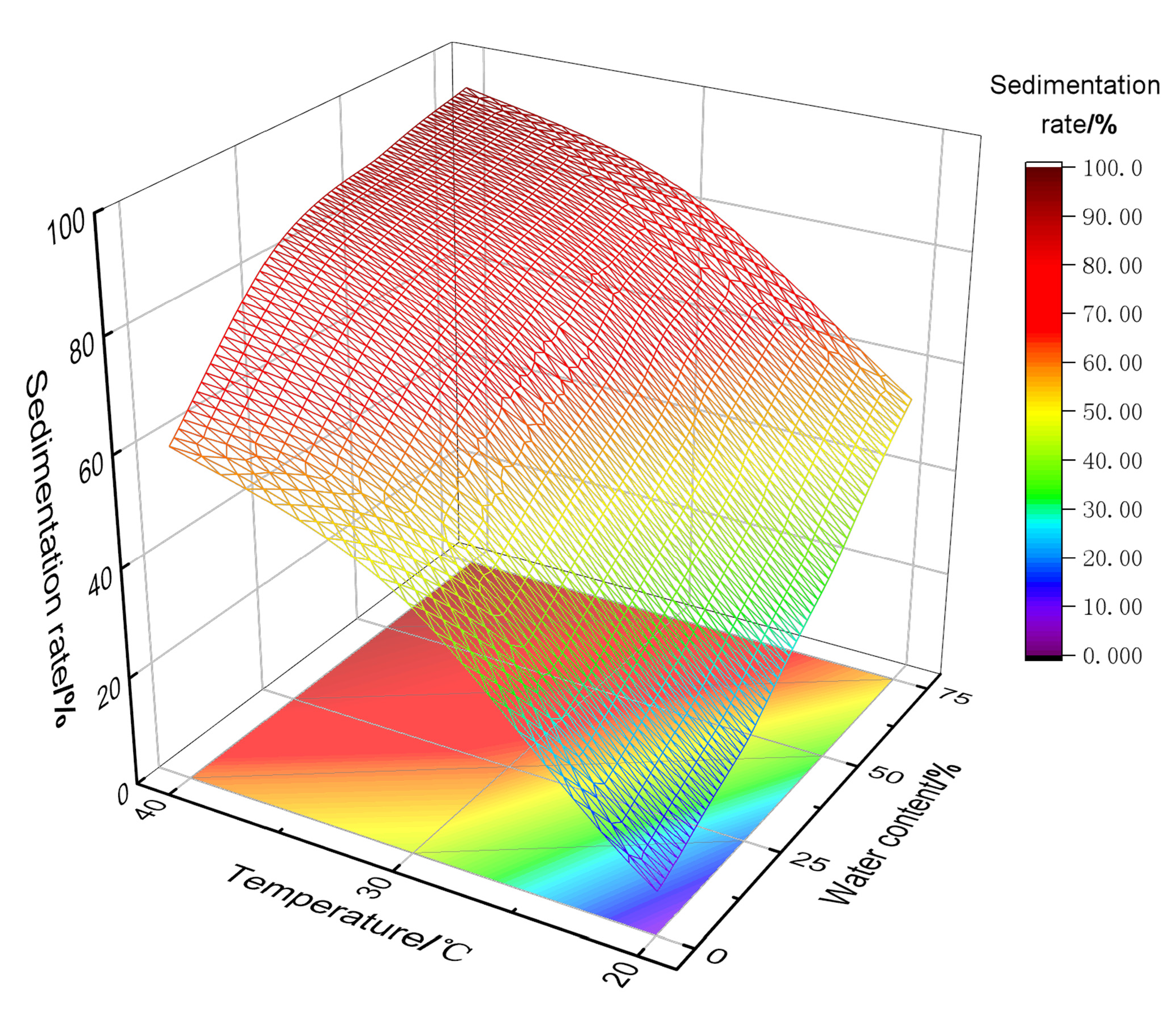
3.2. The Impact of Temperature on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics
3.3. The Impact of the Sand Concentration on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics
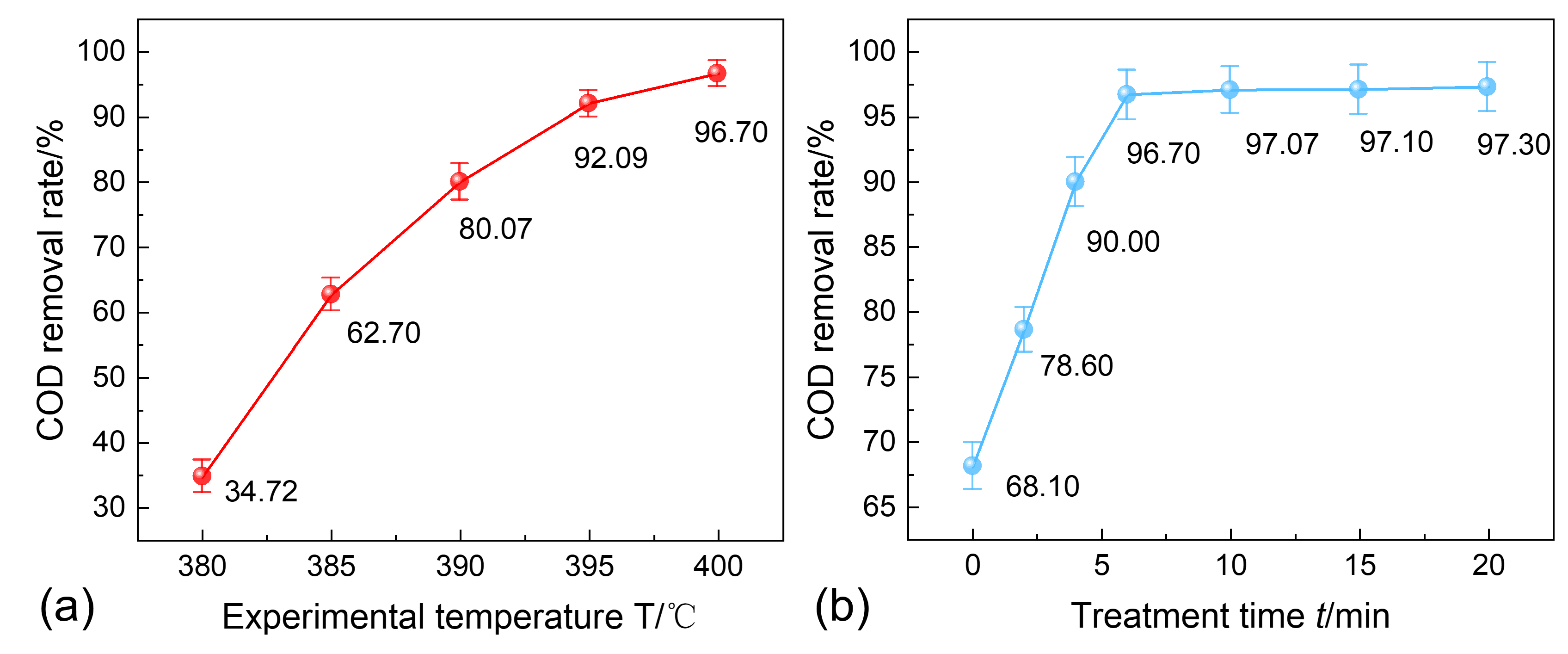
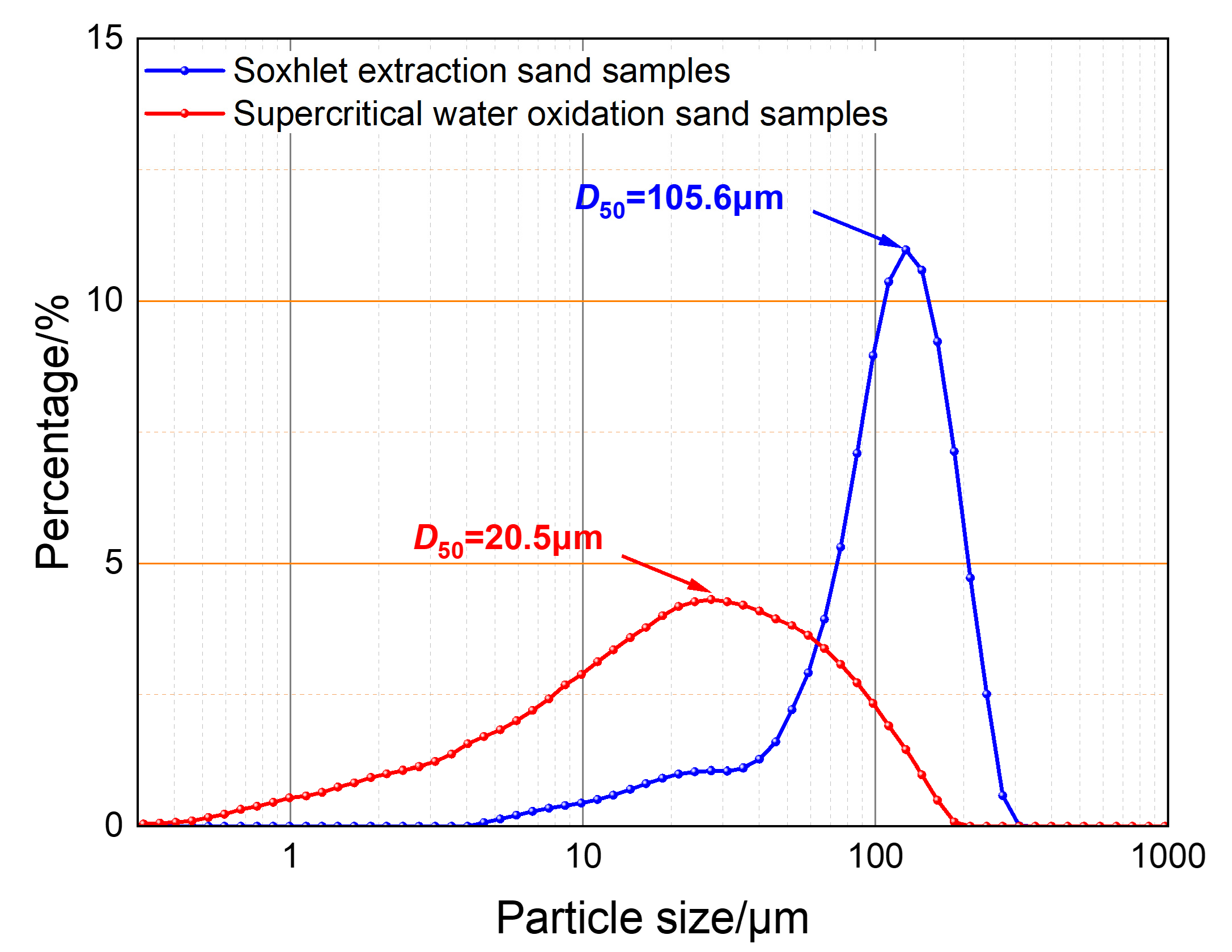
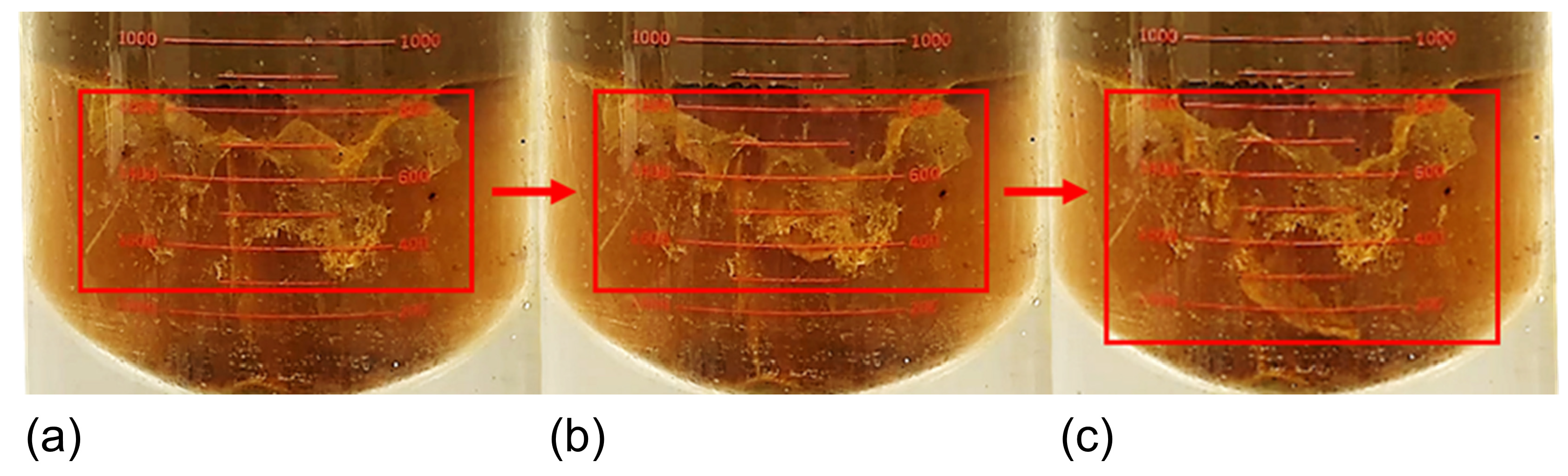
3.4. Water-Washing Effect Evaluation
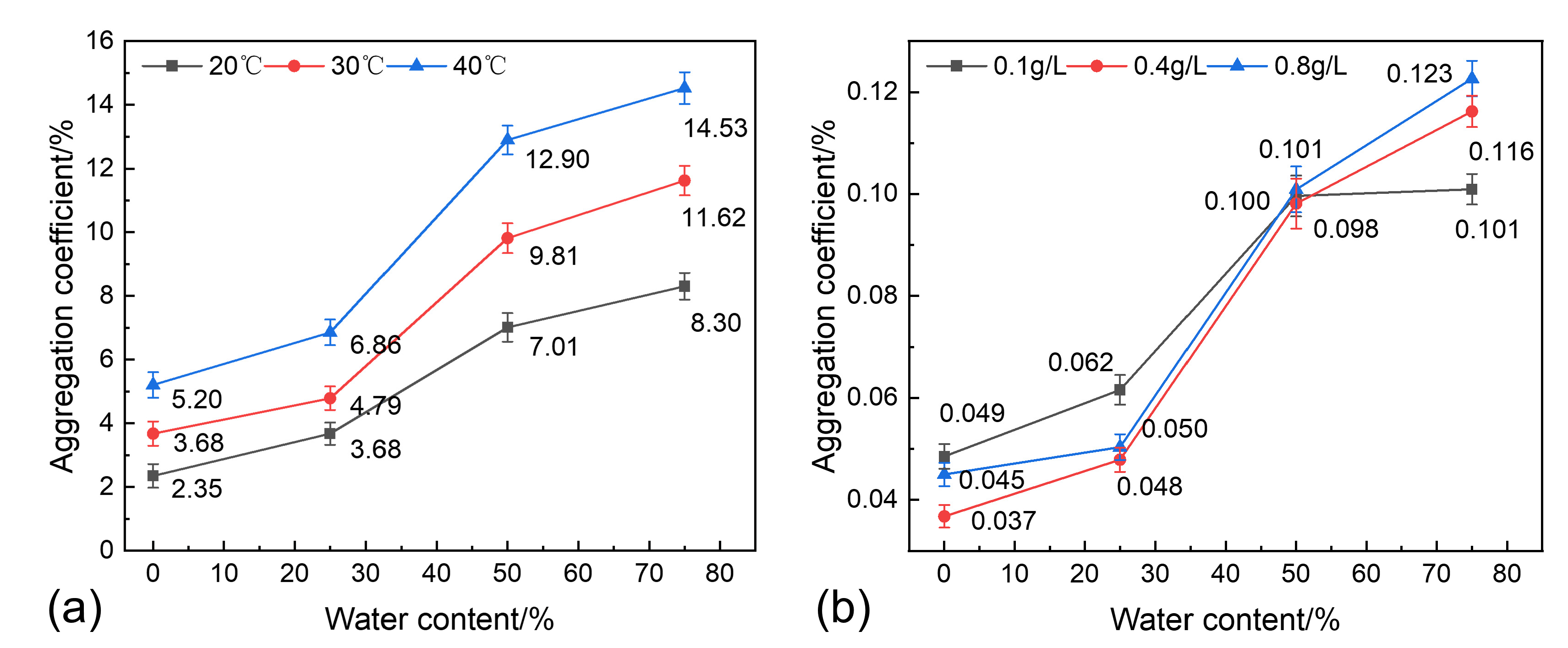
3.5. Analysis of Sand Sedimentation Mechanisms
- (1)
- Polymer flocculation–sedimentation mechanism
- (2)
- Synergistic sedimentation mechanism of the temperature and water content
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Water content is a key factor in regulating sand sedimentation characteristics. As the water content increases, sand particles are more easily transferred into the low-viscosity water phase during sedimentation, significantly reducing the viscous resistance to sedimentation. However, when the water content is too high, the polymers in the continuous water phase hinder sand sedimentation, weakening the water-washing effect. On the other hand, a high water content increases the polymer content in the produced fluid, significantly increasing the likelihood of polymer precipitation adhering to sand particles, enhancing the flocculation–sedimentation effect;
- (2)
- Temperature is the core governing factor in regulating sand sedimentation characteristics. Increasing the temperature significantly reduces the viscosity of shale oil, weakening the viscous resistance to sand particle sedimentation and enhancing single-particle gravity sedimentation. On the other hand, increasing the temperature disrupts polymer stability, promoting polymer precipitation, enhancing the flocculation–sedimentation effect, and strengthening multi-particle flocculation–sedimentation;
- (3)
- The sand concentration is a secondary influencing factor on sand sedimentation characteristics. The experiment shows that under 50% water content conditions, when the sand concentration increases by eight times, the sand sedimentation rate increases by only 15.09%, and the particle size distribution curves of Soxhlet extraction-treated sand and SCWO-treated sand show no significant correlation with the changes in the sand concentration. Therefore, it can be concluded that, with the sand sample particle size distribution remaining unchanged, the sand particle management and regulation in polymer-containing shale oil production fluids can to some extent ignore the risk of fluctuations in sand concentration;
- (4)
- The water-washing effect under pure water conditions shows that, under the same sedimentation conditions, the proportion of small particle-sized sand under pure water conditions is much smaller than that under produced water conditions, indicating that the polymer flocculation–sedimentation effect plays a more significant role in promoting the sedimentation of small particle-sized sand. Therefore, it can be concluded that achieving the sedimentation of small particle-sized sand is key to sand particle management and regulation of polymer-containing shale oil production fluids;
- (5)
- In summary, in regard to the sand removal conditions of a three-phase separator involving shale oil with polymer-containing produced liquid, it is advisable to appropriately increase the water-washing stage and increase the separation temperature to promote sand particle sedimentation. In regard to pipeline transportation conditions for shale oil with polymer-containing produced liquid, the water content should be minimized, and the transportation temperature should be reduced to maintain the suspension stability of the sand particles.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, H.; Xia, S.; Li, N.; Wang, T.; Zheng, W.; Yu, T.; Shu, Q.; Han, Y. Emulsifying Stability and Viscosity Reduction for Heavy Crude Oil in Surfactant-Polymer Composite System. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 362, 119713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Pang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Y.; Qi, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Z.; Zeng, H. Electric Field-Induced Deformation and Breakup of Water Droplets in Polymer-Flooding W/O Emulsions: A Simulation Study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Sun, D.; Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, T.; Li, Y. Demulsification and Bio-Souring Control of Alkaline-Surfactant-Polymer Flooding Produced Water by Gordonia Sp. TD-4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 263, 118359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; You, Y.; Yue, X.; Feng, S.; An, W.; Li, Q.; Liang, X. Impact of Fracturing Fluid Retention and Flowback on Development Effect after Large Scale Fracturing in Shale Oil Wells: A Case Study from the Shale Oil of Chang 7 Member, Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin. Unconv. Resour. 2024, 4, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; He, Y.; Guo, Q.; Dang, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, C. Technological Issues in Shale Oil Development Using Horizontal Wells in Ordos Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 8, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabirian, R.; Mohan, R.; Shoham, O.; Kouba, G. Critical Sand Deposition Velocity for Gas-Liquid Stratified Flow in Horizontal Pipes. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganat, T. Experimental Investigation of Viscous Oil–Water–Sand Flow in Horizontal Pipes: Flow Patterns and Pressure Gradient. Petroleum 2024, 10, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, R.; Mohan, R.S.; Shoham, O. Investigation of Critical Sand-Deposition Velocity in Horizontal Gas/Liquid Stratified Flow. SPE Prod. Oper. 2017, 32, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajemidupe, O.T.; Aliyu, A.M.; Baba, Y.D.; Archibong-Eso, A.; Yeung, H. Sand Minimum Transport Conditions in Gas–Solid–Liquid Three-Phase Stratified Flow in a Horizontal Pipe at Low Particle Concentrations. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 143, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, H.; Jafarpour, M.; Azadbakht, S.; Nouri, A.; Vaziri, H.; Chan, D.; Xiao, Y. Review of Sand Production Prediction Models. J. Pet. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibong-Eso, A.; Aliyu, A.M.; Yan, W.; Okeke, N.E.; Baba, Y.D.; Fajemidupe, O.; Yeung, H. Experimental Study on Sand Transport Characteristics in Horizontal and Inclined Two-Phase Solid-Liquid Pipe Flow. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2020, 11, 04019050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhamoorthy, P.Z.; Williams, B.; Sambath, K.; Subramani, H.J.; Cremaschi, S. An Integrated Framework for Sand Handling in Wellbore and Surface Facilities. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 239, 212947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, G.G. Mathematical and Physical Papers, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Qu, J. Study on the Settling Velocity of Drilling Cuttings in the Power Law Fluid. Powder Technol. 2020, 362, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Qu, J.-Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Q.-B. A Novel Predictive Model of Drag Coefficient and Settling Velocity of Drill Cuttings in Non-Newtonian Drilling Fluids. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-P.; Song, X.-Z.; Kuru, E.; Chen, H.-B.; Yu, B.-W.; Lin, Z.-C.; Sun, Y.-X. Settling Behavior of Spherical Particles in Eccentric Annulus Filled with Viscous Inelastic Fluid. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Yu, B.; Song, X.; Li, G.; Zhu, S.; Xu, Z.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z. A Unified Equation of Settling Velocity for Particles Settling in Cylinder, Annulus and Fracture. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 213, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Khalid, M.-S.-U.; Liu, M. Semi-Resolved CFD-DEM Simulation of Fine Particle Migration with Heat Transfer in Heterogeneous Porous Media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 197, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, B.; Sun, L.; Wang, J. Optimization of specifications and operation parameters of gravity setting tank in Laojunmiao united station. Contemp. Chem. Ind. 2017, 46, 864–866. [Google Scholar]
- Alajmi, A.F.; Algharaib, M.; Al-Hamad, K. Estimation of Sand Settling Time in Heavy Oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jing, J.; Qin, M.; Zhang, W.; Shan, Y.; Cheng, Y. Experimental Study and Models of the Settling of Sand in Heavy Oil. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 217, 110930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S. Study on Desanding Behavior of Emulsified Shale Oil with Sand. Fuel 2025, 394, 135100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jing, J.; Luo, M.; Qin, M.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, L. Experimental Study on Hydrocyclone Desanding of High-Viscosity Oil. Fuel 2023, 341, 127691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Mu, L.; Jiang, X. Study on the Performance of Downhole Axial Cyclone with Spiral Fins for Drainage and Sand Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 111032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Luo, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.; Jing, J.; Qin, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C. Experimental and Mechanistic Study of the Surfactant-Assisted Hydrocyclone Desanding of Heavy Oil. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 228, 212031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanou, P.S. Variable Entanglement Density Constitutive Rheological Model for Polymeric Fluids. Rheol. Acta 2024, 63, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolata, B.E.; Olmsted, P.D. A Thermodynamically Consistent Constitutive Equation Describing Polymer Disentanglement under Flow. J. Rheol. 2023, 67, 269–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Chu, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q. Treatment of Polyacrylamide-Containing Wastewater by Ionizing Radiation: Efficient Reduction of Viscosity and Degradation of Polyacrylamide. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2023, 202, 110547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, X.; Yan, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P.; He, L. An Experimental Study on the Coalescence Behavior of Oil Droplet in ASP Solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 203, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Huang, X.; Yan, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, P.; He, L. An Experimental Study on the Floating Motion of Oil Drop in ASP Solution. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process Intensif. 2018, 125, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Khan, N.; Pu, C. A New Method of Plugging the Fracture to Enhance Oil Production for Fractured Oil Reservoir Using Gel Particles and the HPAM/Cr3+ System. Polymers 2019, 11, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fu, H.; Bao, M.; Luo, C.; Han, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Lu, J. Emulsions Stabilized by Asphaltene-Polyacrylamide-Soil Three-Phase Components: Stabilization Mechanism and Concentration Effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, K.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, X. A Review of the Interfacial Stability Mechanism of Aging Oily Sludge: Heavy Components, Inorganic Particles, and Their Synergism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliabadian, E.; Kamkar, M.; Chen, Z.; Sundararaj, U. Prevention of Network Destruction of Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide (HPAM): Effects of Salt, Temperature, and Fumed Silica Nanoparticles. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31, 013104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.-W.; Li, C.-X.; Yang, F.; Yao, B.; Duan, Z.; Chen, X.-Y.; Sheng, F.-J. Co-Adsorption Behavior of Aggregated Asphaltenes and Silica Nanoparticles at Oil/Water Interface and Its Effect on Emulsion Stability. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, W.; Yan, B.; Zhang, L. Thermally Regulated Flocculation-Coalescence Process by Temperature-Responsive Cationic Polymeric Surfactant for Enhanced Crude Oil-Water Separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 481, 136491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Yan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Z.; Du, C. Preparation, Oil Removal and Flocculation Efficiency Evaluation of a PAC-P(AM-BA) Hybrid Polymer Flocculant Based on Response Surface Method. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Duan, M.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, S. The Effect of Polymer on the Floatation-Flocculation Performance of Flocculant for Treating Polymer Flooding Produced Water. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 677, 132345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, D.; Xu, F. Prediction of Compressive and Flexural Strength of Coal Gangue-Based Geopolymer Using Machine Learning Method. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 44, 112076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versaci, M.; Laganà, F.; Manin, L.; Angiulli, G. Soft Computing and Eddy Currents to Estimate and Classify Delaminations in Biomedical Device CFRP Plates. J. Electr. Eng. 2025, 76, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Hu, M.; Hu, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z. Reactor for Biomass Conversion and Waste Treatment in Supercritical Water: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 171, 113031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; He, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Q. Oily Sludge Treatment in Subcritical and Supercritical Water: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-kaabi, F.K.H. Supercritical Water Oxidation for the Treatment of Various Organic Wastes: A Review. Int. J. Rural Dev. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Xu, D.; Hao, B.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S. Chemical Reactions of Organic Compounds in Supercritical Water Gasification and Oxidation. Water Res. 2021, 190, 116634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Guo, S.; Li, L.; Jin, H.; Ge, Z.; Guo, L. Supercritical Water Gasification Mechanism of Polymer-Containing Oily Sludge. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 26834–26847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Wang, G.; Li, L.; Ge, H.; Jin, H.; Guo, L. Experimental Investigation on the Degradation of Polymer-Containing Oily Sludge in Sub-/Supercritical Water. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 1983–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yin, F.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; He, C.; Xu, Y. Supercritical Water Oxidation of Oil-Based Drill Cuttings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 332, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpagkou, R.; Pantokratoras, A. The Influence of Lamellar Settler in Sedimentation Tanks for Potable Water Treatment—A Computational Fluid Dynamic Study. Powder Technol. 2014, 268, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


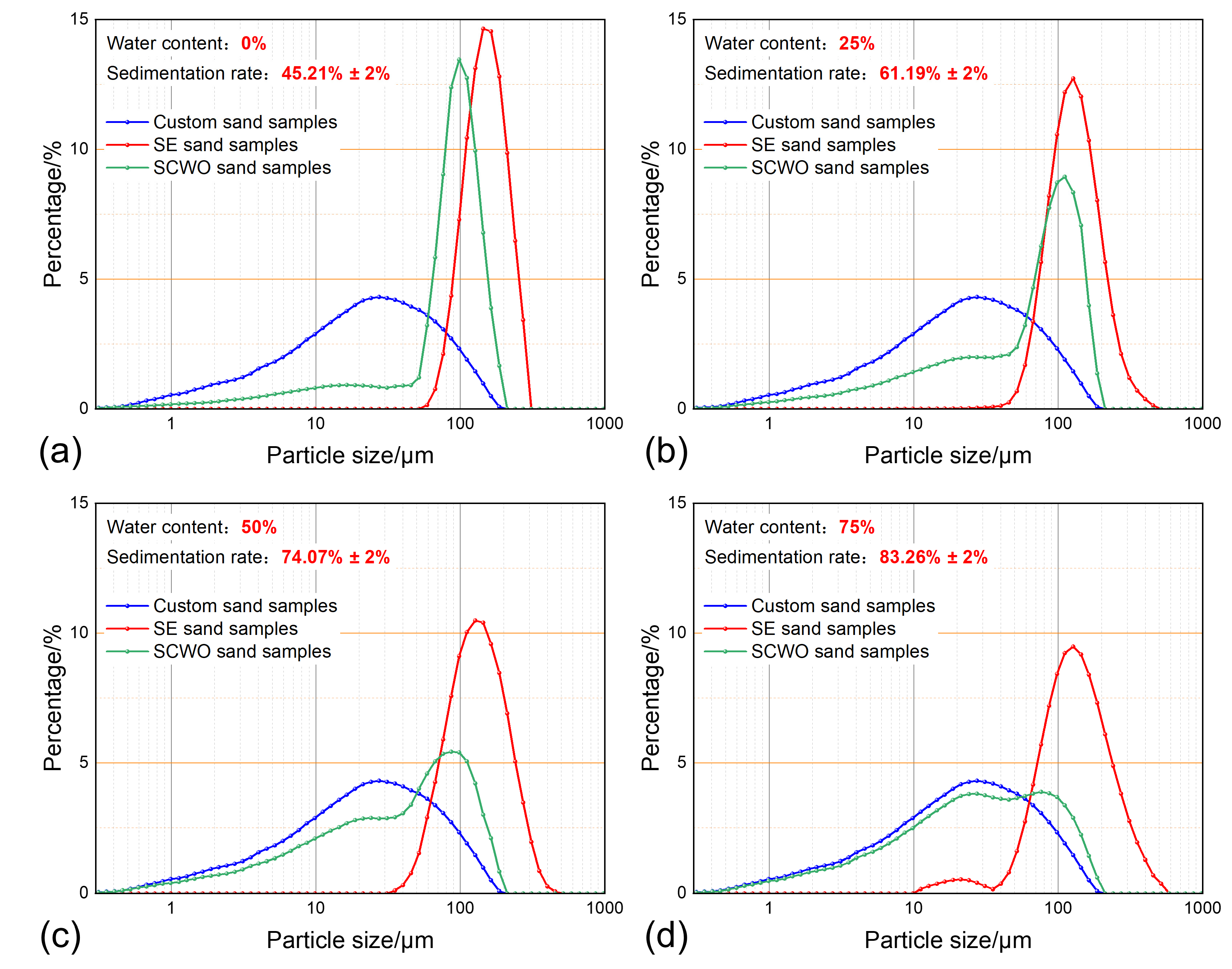


| Group Number | Water Content | Temperature | Sand Concentration | Sedimentation Time | Water Phase Property | Related Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0% | 30 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 7a |
| 2 | 25% | 30 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 7b |
| 3 | 50% | 30 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 7c |
| 4 | 75% | 30 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 7d |
| 5 | 50% | 20 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 9a |
| 6 | 50% | 40 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 9c |
| 7 | 50% | 30 °C | 0.1 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 10a |
| 8 | 50% | 30 °C | 0.8 g/L | 30 min | produced water | Figure 10c |
| 9 | 50% | 30 °C | 0.4 g/L | 30 min | pure water | Figure 11b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Gao, T.; Zhao, R.; Bai, L.; Luo, X. Impact of Polymers on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics of Shale Oil-Produced Fluid. Materials 2025, 18, 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102269
Shang Y, Zhang Q, Li W, Gao T, Zhao R, Bai L, Luo X. Impact of Polymers on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics of Shale Oil-Produced Fluid. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102269
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Yongbin, Qiaosheng Zhang, Wanrui Li, Tian Gao, Ruhao Zhao, Lan Bai, and Xiaoming Luo. 2025. "Impact of Polymers on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics of Shale Oil-Produced Fluid" Materials 18, no. 10: 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102269
APA StyleShang, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, W., Gao, T., Zhao, R., Bai, L., & Luo, X. (2025). Impact of Polymers on Sand Sedimentation Characteristics of Shale Oil-Produced Fluid. Materials, 18(10), 2269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102269






