Thermal Insulation Based on NBR-Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Reinforced with Carbon Fibers: Mechanical and Ablation Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blending Technology of PR/NBR/CF Composite
2.3. Homogenization of the Propellant
2.4. Characterization of Materials
3. Results and Discussion
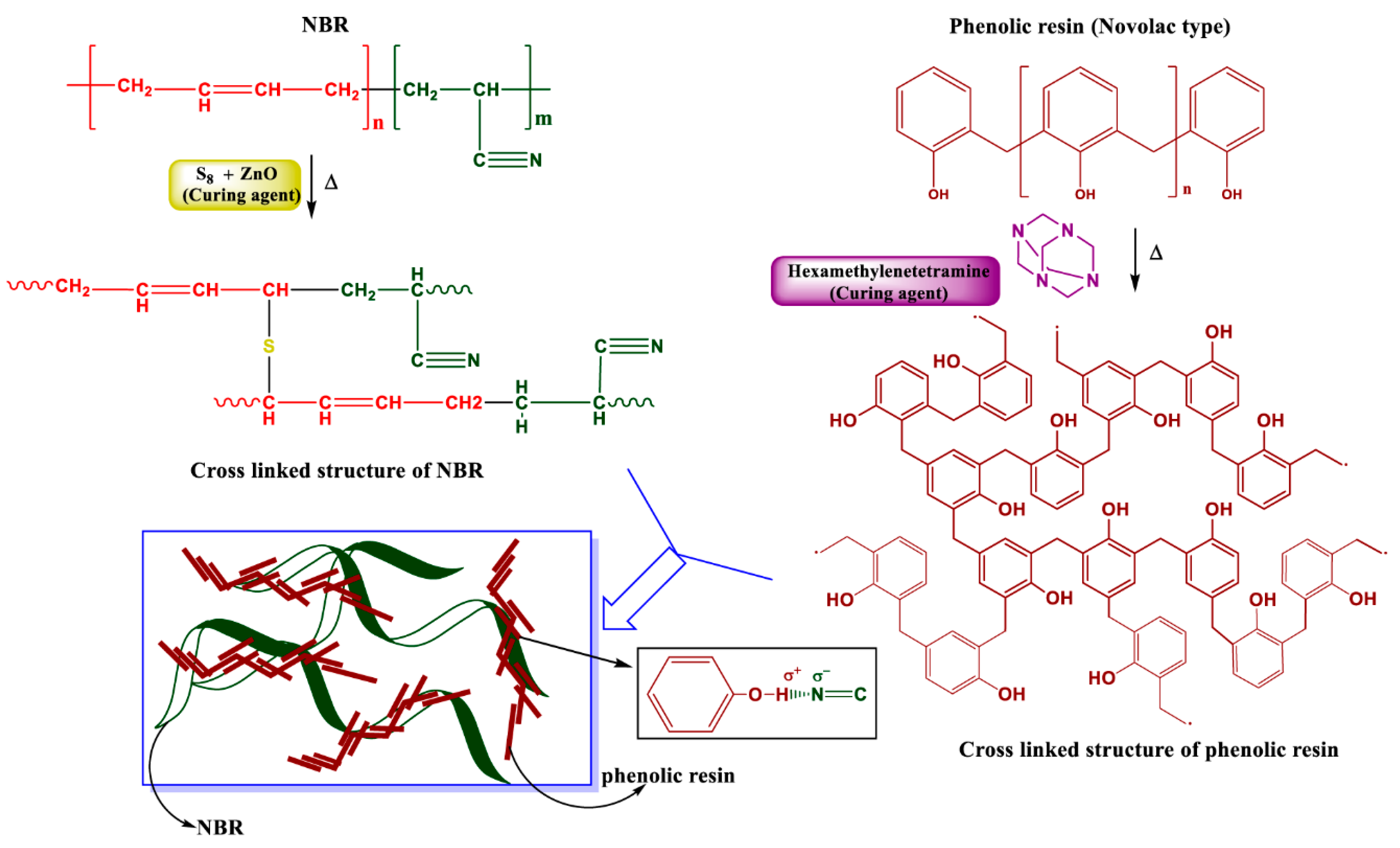
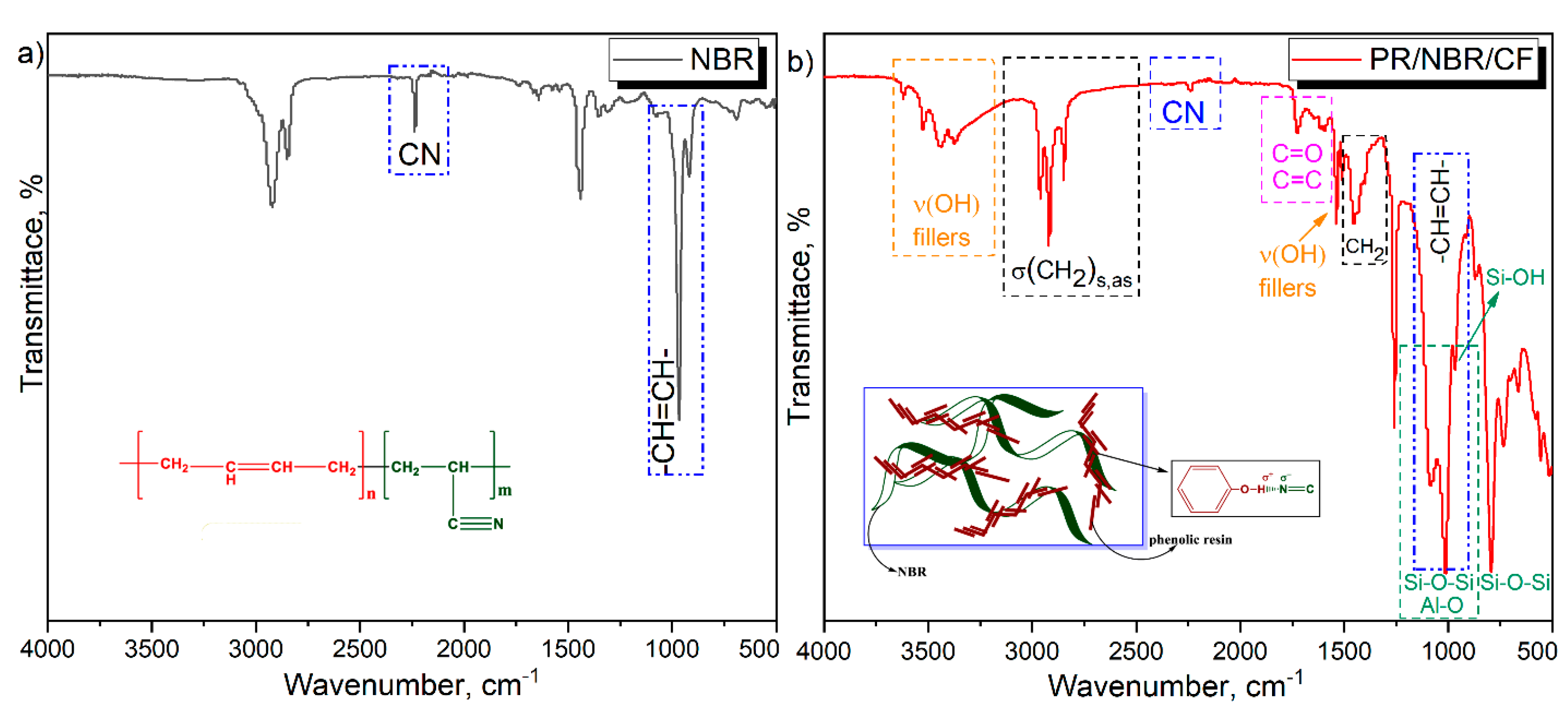
3.1. FTIR Analysis
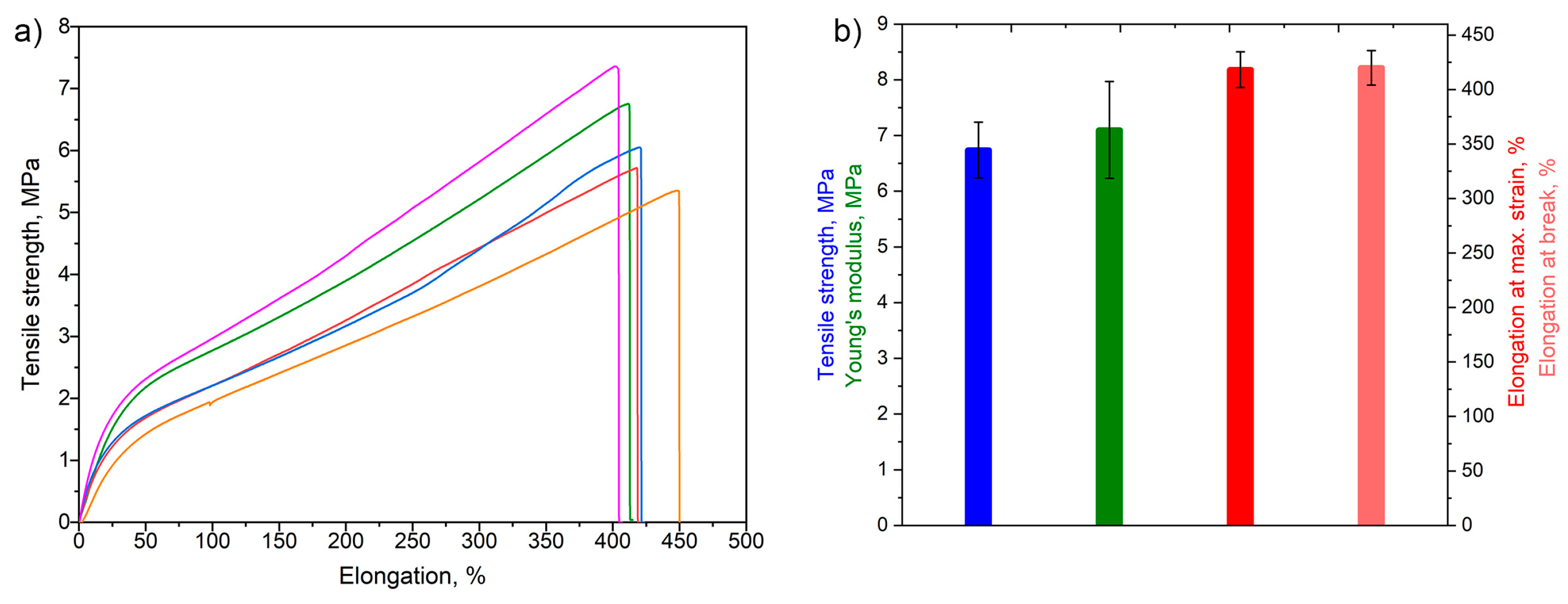
3.2. Mechanical Characterization and Bond Strength
Bond Strength Between PR/NBR/CF Composite and ACRP
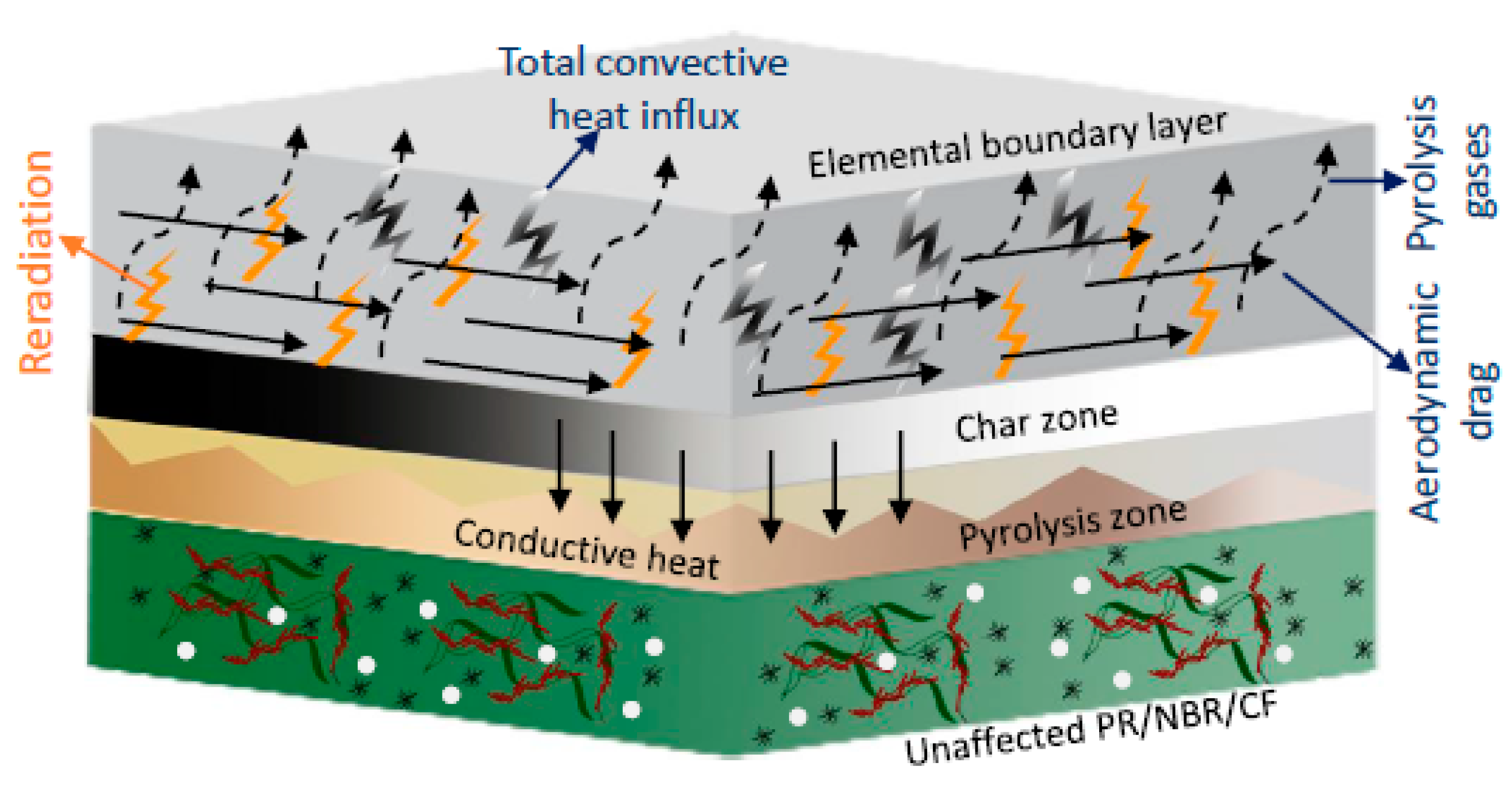
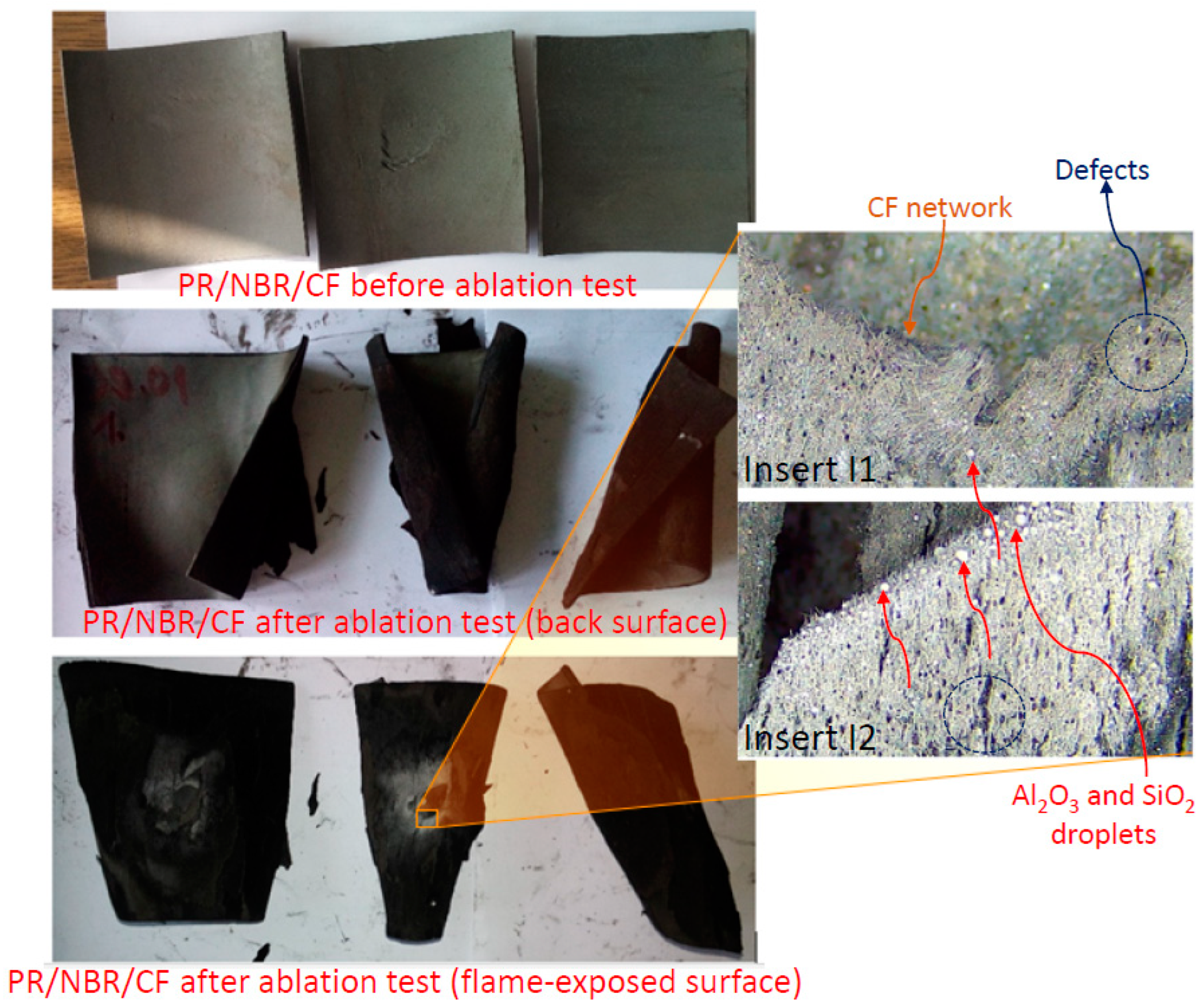
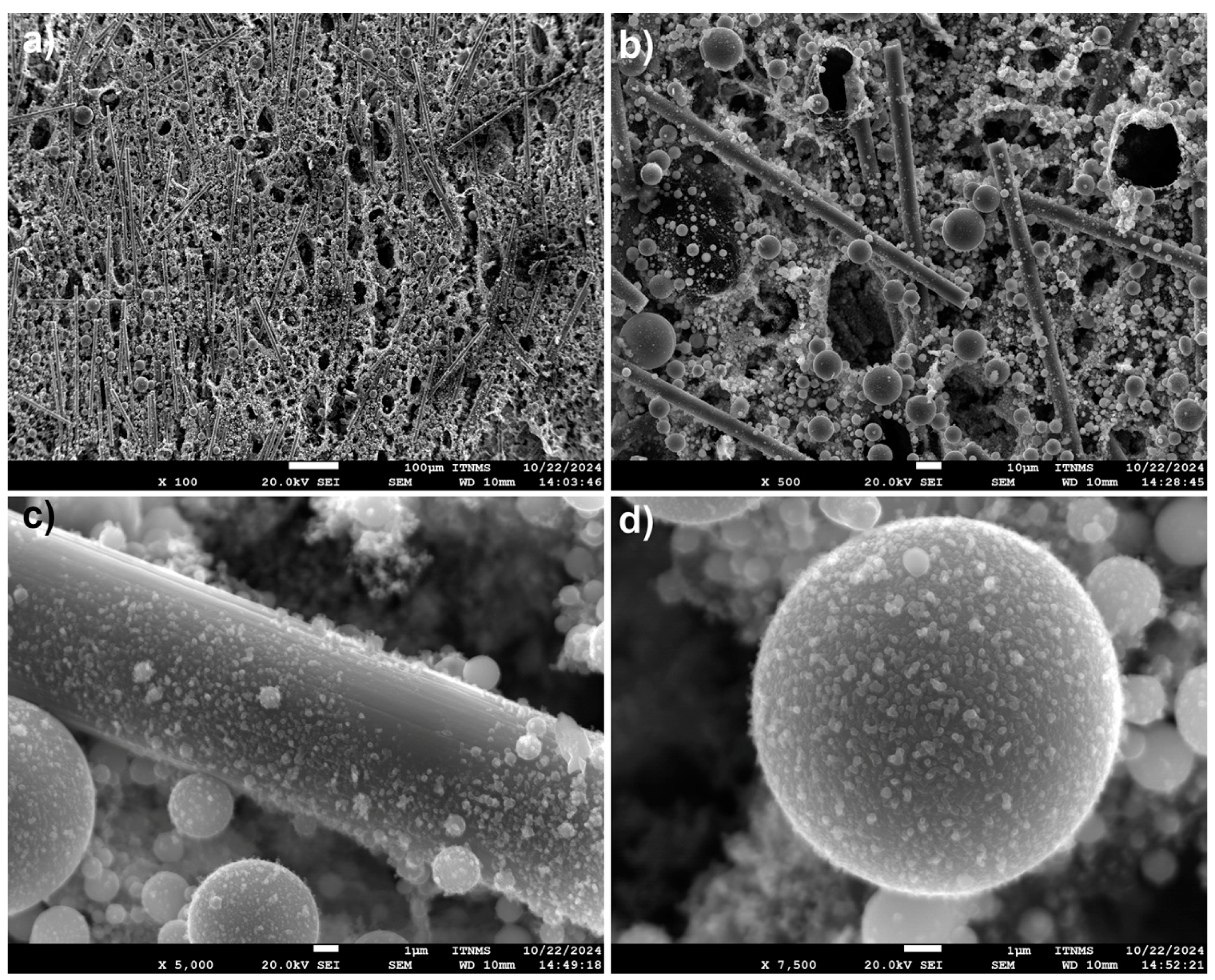
3.3. Ablation Resistance
3.4. Results of Firing of Solid Rocket Motor (SRM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TPM | Thermal protective material |
| PR | Phenolic resin |
| NBR | Acrylonitrile butadiene rubber |
| CFs | Carbon fibers |
| PR/NBR/CF | NBR elastomerized PR composite, reinforced with chopped carbon fibers |
| PBW | Parts by weight |
| ACRP | Aluminized composite rocket propellant |
| DOA | Dioctyl adipate |
| TETA | Triethylenetetramine |
| IPDI | Isophorone diisocyanate |
| AP | Ammonium perchlorate oxidizer |
References
- Koo, J.H.; Langston, J. Polymer Nanocomposite Ablative Technologies for Solid Rocket Motors; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128139080. [Google Scholar]
- Natali, M.; Kenny, J.M.; Torre, L. Science and technology of polymeric ablative materials for thermal protection systems and propulsion devices: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 192–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, M.; Torre, L. Composite Materials: Ablative. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Composites; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Enew, A.M.; Elfattah, M.A.; Fouda, S.R.; Hawash, S.A. Effect of aramid and carbon fibers with nano carbon particles on the mechanical properties of EPDM rubber thermal insulators for solid rocket motors application. Polym. Test. 2021, 103, 107341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, C.M.; Sureshkumar, M.S.; Kakade, S.D.; Gupta, M. Ethylene-propylene diene rubber as a futuristic elastomer for insulation of solid rocket motors. Def. Sci. J. 2006, 56, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali, M.; Puri, I.; Rallini, M.; Kenny, J.; Torre, L. Ablation modeling of state of the art EPDM based elastomeric heat shielding materials for solid rocket motors. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 111, 460–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, M.; Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, S.S.; Abdel-Hamid, S.M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Javaid, U.; Khan, M.B. Ablation and thermo-mechanical investigation of short carbon fiber impregnated elastomeric ablatives for ultrahigh temperature applications. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 110, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, G.S.; White, W.E. Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Ablative Insulation for Rocket Motors. WO 01/20966 A2, 29 March 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Gui, H.; Zhang, T.; Mou, J. The influence of phenolic resin modified by cardanol on improving the processability of PVC. J. Elastomers Plast. 2024, 56, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, K.; Panda, B.P.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent developments in elastomeric heat shielding materials for solid rocket motor casing application for future perspective. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Mechanical properties and microstructure of acrylonitrile–butadiene rubber vulcanizates reinforced by in situ polymerized phenolic resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 3853–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, N.; Iqbal, S.S.; Anwar, A.W.; Sarwar, A.; Jabeen, F.; Jabeen, S. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber/Phenolic Resin Blended Ablative Composites for High Temperature Applications. Int. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Sci. 2014, 2, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, R.; Rashid, N.; Ali, Z.; Khan, A.U.; Nazir, M.S.; Ul-Haq, N. 7Effects on Thermal and Ablative Properties of Phenolic Resin (Novolac) Blended Acrylonitrile Butadiene Rubber. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh Kumar, S.; Asseref, P.M.; Dhanasekaran, J.; Mohan, S.K. A new approach with prepregs for reinforcing nitrile rubber with phenolic and benzoxazine resins. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 12526–12533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Han, S.; Xia, L.; Li, C.; Wu, H.; Guo, S.; Yan, N.; Li, H.; Luan, T. Synergetic effect of aramid fiber and carbon fiber to enhance ablative resistance of EPDM-based insulators via constructing high-strength char layer. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 201, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Flambard, X. Heat resistance and flammability of high performance fibres: A review. Fire Mater. 2002, 26, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusmirović, J.; Galović, J.; Kluz, M.; Perković, S.; Brzić, S.; Bogosavljević, M.; Milojković, A.; Kovačević, T. Using potential of filament-wound carbon/glass polymeric composites as rocket motor thermal insulation. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, S1541–S1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodić, V. Case Bonded System for Composite Solid Propellants. Sci. Tech. Rev. 2007, LVII, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, N.; Sagar, S.; Khan, M.B.; Rafique, H.M. Ablation, thermal stability/transport and mechanical investigations of modified nanokaolinite impregnated acrylonitrile butadiene rubbercomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 48, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.V.; Gharde, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Polymer Composites as Ablative Materials. In Macromolecular Engineering: From Precise Synthesis to Macroscopic Materials and Applications; WILEY-VCH GmbH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Guo, Y. Silicone rubber ablative composites improved with zirconium carbide or zirconia. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 44, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, X.; Gao, R.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Peng, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, M. Research on the ablation resistance of Al2O3/PF composite coatings deposited by supersonic plasma spraying on resin matrix surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 491, 131140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients | PBW * | Wt.% ** | mass, kg |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBR rubber, 28% | 100 | 28.82 | 1.44 |
| Phenolic resin | 90 | 25.94 | 1.30 |
| Carbon fiber | 25 | 7.20 | 0.36 |
| Carbon black | 20 | 5.76 | 0.29 |
| SiO2 (fumed silica) | 45 | 12.97 | 0.65 |
| Al2O3 | 50 | 14.41 | 0.72 |
| Vulkacit H-30 | 8 | 2.31 | 0.12 |
| Stearic acid | 1 | 0.29 | 0.01 |
| Vulkacit DM | 1.5 | 1.44 | 0.07 |
| Sulfur | 1.5 | 0.43 | 0.02 |
| ZnO | 5.0 | 0.43 | 0.02 |
| Total | 347 | 100 | 5.0 |
| Tensile Test Results | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| σ, MPa | εmax, % | εbr, % | E, MPa | Reference | |
| PR/NBR/CF | 6.7 ± 0.5 | 418.3 ± 16.3 | 419.9 ± 15.9 | 7.1 ± 0.8 | This work |
| PR5PBW/NBR | 15.5 | 650.0 | / | / | [11] |
| PR10PBW/NBR | 19.5 | 575.0 | / | / | [11] |
| PR15PBW/NBR | 21.0 | 525.0 | / | / | [11] |
| PR20PBW/NBR | 18.2 | 495.0 | / | / | [11] |
| NBR-Ph * | 17.7 | / | 668.4 | / | [14] |
| T, °C | Load F, N | Strip Width, cm | Longitudal Load, N/cm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR/NBR/CF | 25 | 2.97 | 2.50 | 1.19 |
| Sample | I80, s/m | I180, s/m | E, m/s | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR/NBR/CF | 2262 | 4524 | 2.00 × 10−4 | This work |
| PR5PBW/NBR * | / | / | 2.25 × 10−4 ** | [13] |
| PR10PBW/NBR * | / | / | 2.00 × 10−4 | [13] |
| PR20PBW/NBR * | / | / | 1.17 × 10−4 | [13] |
| PR50PBW/NBR * | / | / | 1.00 × 10−4 | [13] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gržetić, J.; Brzić, S.; Mijatov, S.; Živković, S.; Živanović, V.; Galović, J.; Kovačević, T. Thermal Insulation Based on NBR-Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Reinforced with Carbon Fibers: Mechanical and Ablation Properties. Materials 2025, 18, 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102250
Gržetić J, Brzić S, Mijatov S, Živković S, Živanović V, Galović J, Kovačević T. Thermal Insulation Based on NBR-Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Reinforced with Carbon Fibers: Mechanical and Ablation Properties. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102250
Chicago/Turabian StyleGržetić, Jelena, Saša Brzić, Slavko Mijatov, Saša Živković, Veselin Živanović, Jela Galović, and Tihomir Kovačević. 2025. "Thermal Insulation Based on NBR-Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Reinforced with Carbon Fibers: Mechanical and Ablation Properties" Materials 18, no. 10: 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102250
APA StyleGržetić, J., Brzić, S., Mijatov, S., Živković, S., Živanović, V., Galović, J., & Kovačević, T. (2025). Thermal Insulation Based on NBR-Elastomerized Phenolic Resin Reinforced with Carbon Fibers: Mechanical and Ablation Properties. Materials, 18(10), 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102250







