Influence of Coarse Cement Particle Content on Intrinsic Self-Healing of Mortar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Specimen Preparation
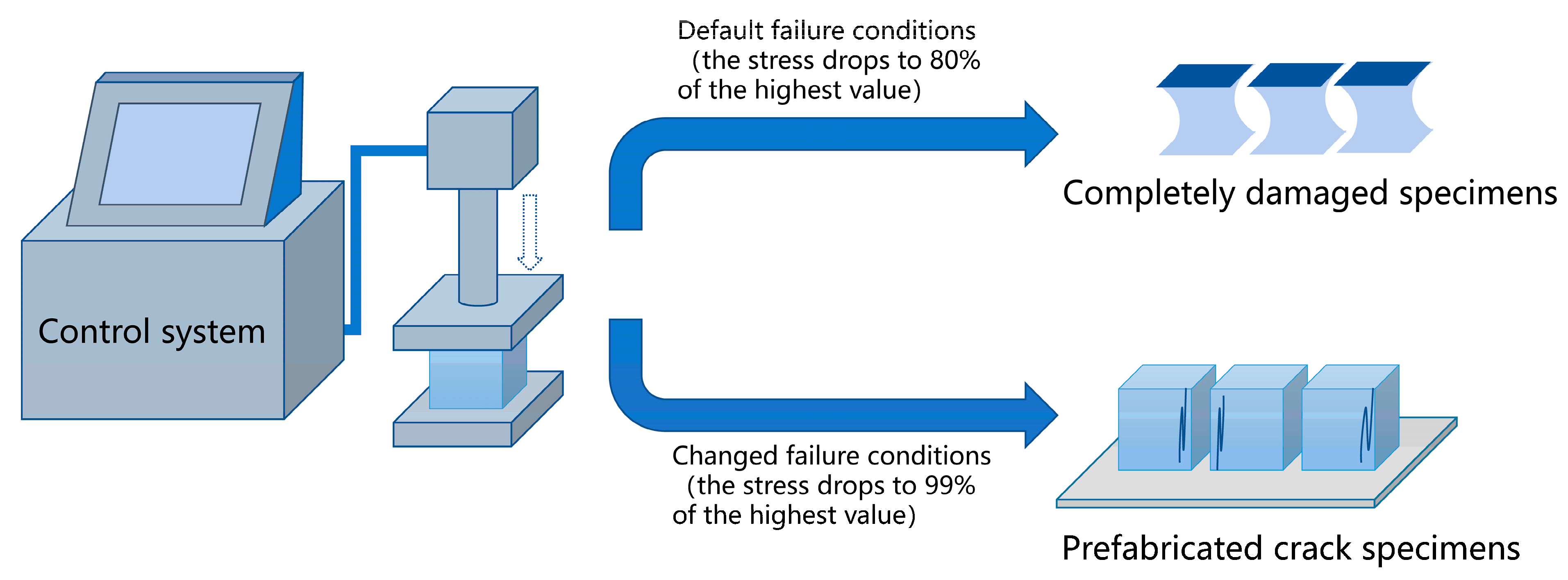
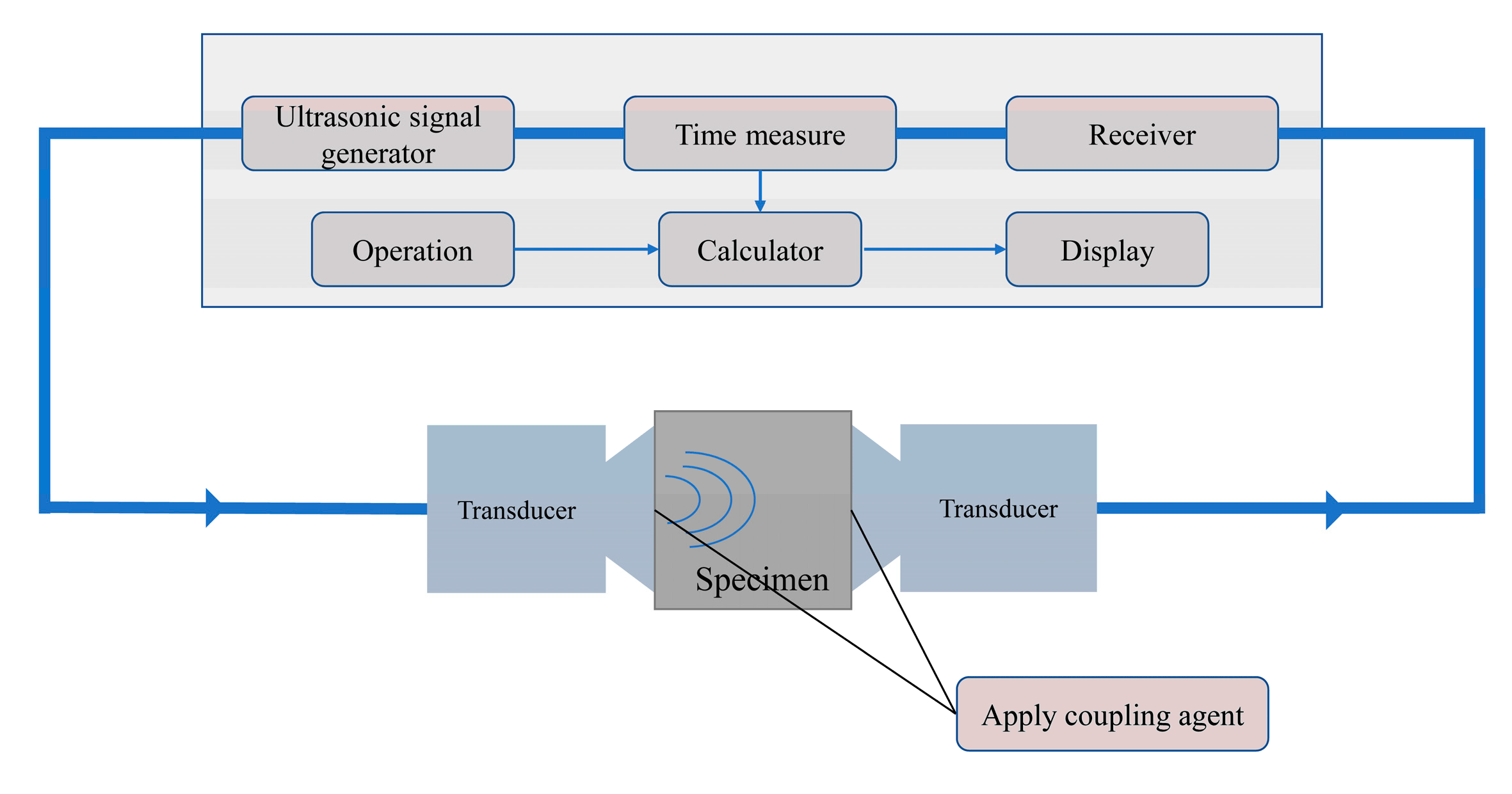
2.3. Testing
3. Results and Discussion
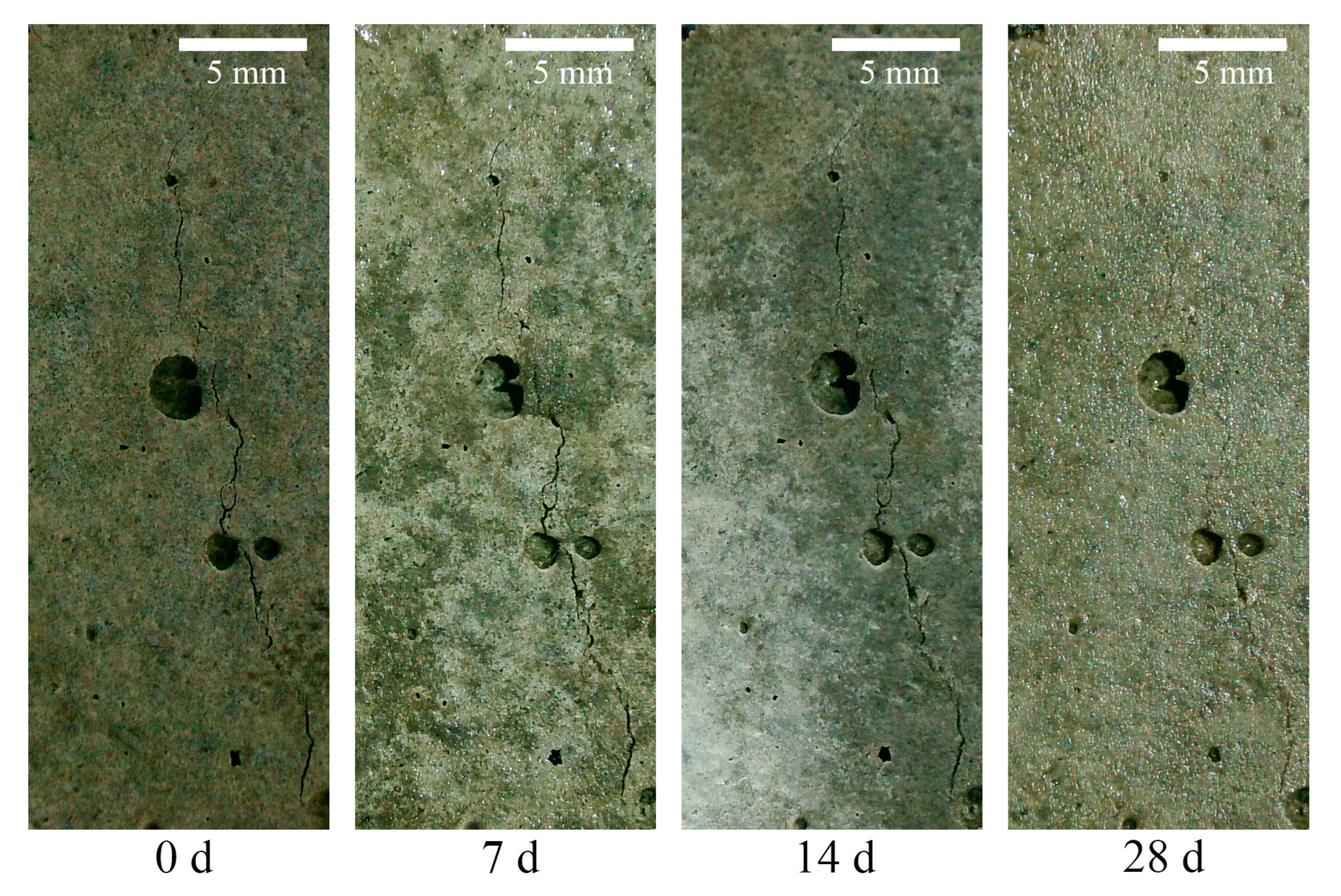
3.1. Crack Recovery
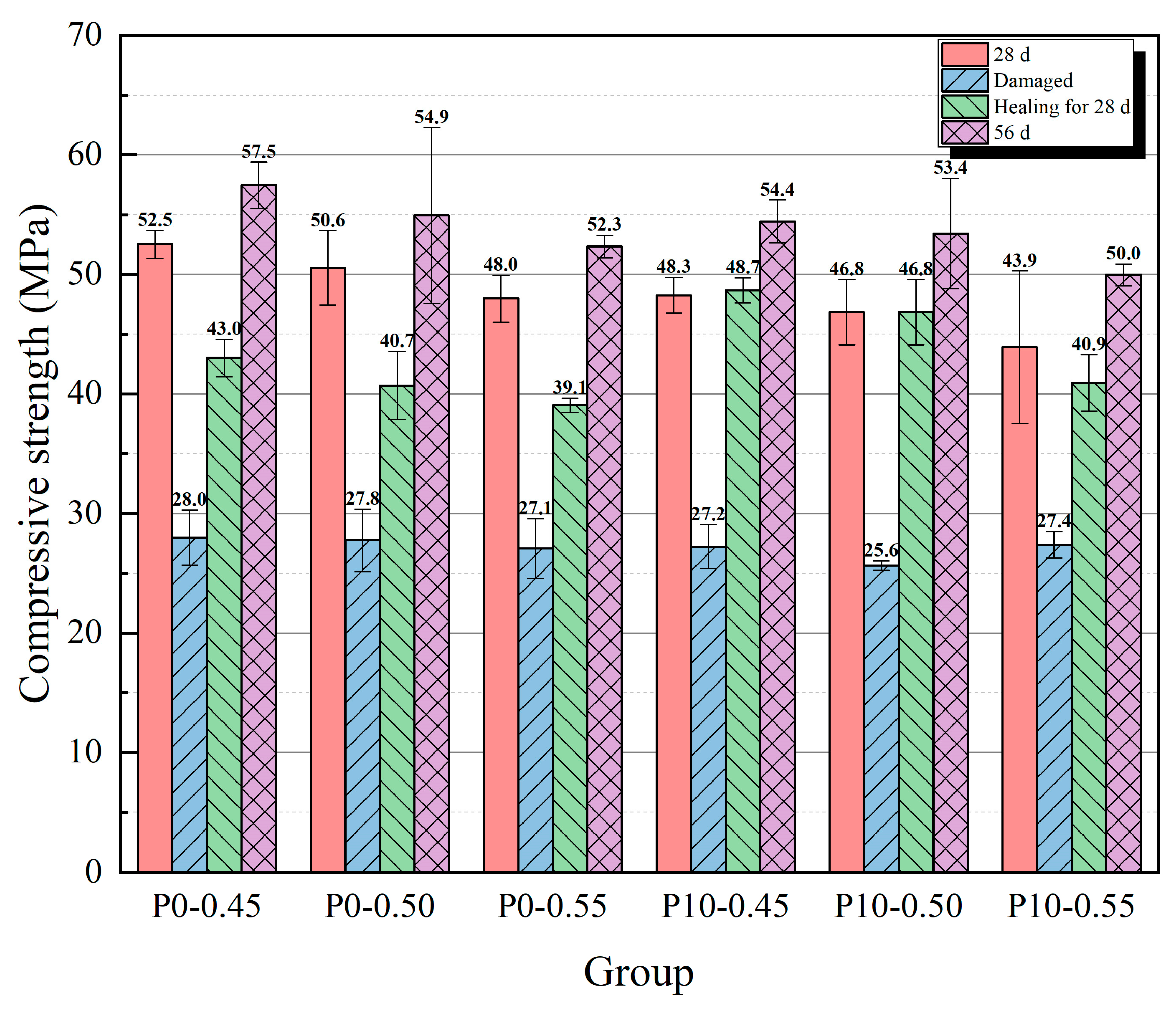
3.2. Compressive Strength
3.3. Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity
3.4. Theoretical Analysis and Calculation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muhammad, N.Z.; Shafaghat, A.; Keyvanfar, A.; Majid, M.Z.A.; Ghoshal, S.K.; Mohammadyan Yasouj, S.E.; Ganiyu, A.A.; Samadi Kouchaksaraei, M.; Kamyab, H.; Taheri, M.M.; et al. Tests and Methods of Evaluating the Self-Healing Efficiency of Concrete: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeer, C.M.; Rossi, E.; Tamis, J.; Jonkers, H.M.; Kleerebezem, R. From Waste to Self-Healing Concrete: A Proof-of-Concept of a New Application for Polyhydroxyalkanoate. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.; Khushnood, R.A.; Khaliq, W.; Murtaza, H.; Iqbal, R.; Khan, M.H. Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Immobilized Nano/Micro Inert and Reactive Additives for Feasibility Investigation in Self-Healing Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Jia, G.; Jiang, C.; Li, Z. Sugar-Coated Expanded Perlite as a Bacterial Carrier for Crack-Healing Concrete Applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.; Kanwal, H.; Hao, W.; Tang, C.; Liu, R. Study on Compressive Properties of Self-Healing Cement Paste Using Acoustic Emission and Digital Image Correlation. J. Test. Eval. 2022, 50, 2732–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Wu, R.; Song, X.; Zhang, P.; Wu, J. Mechanical Behavior and Self-Healing Mechanism of Polyurea-Based Double-Walled Microcapsule/Epoxy Composite Films. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 157, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ge, Y.; Yan, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, P. GO-Modified Double-Walled Polyurea Microcapsules/Epoxy Composites for Marine Anticorrosive Self-Healing Coating. Mater. Des. 2020, 189, 108547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Q. Influencing Factors of Self-Healing Performance of Concrete. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao/J. Build. Mater. 2018, 21, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dry, C.M. Three Designs for the Internal Release of Sealants, Adhesives, and Waterproofing Chemicals into Concrete to Reduce Permeability. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahy, Y.I.; Youssef, M.A. Flexural Behaviour of Superelastic Shape Memory Alloy Reinforced Concrete Beams during Loading and Unloading Stages. Eng. Struct. 2019, 181, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhu, S. Seismic Behavior of Self-Centering Reinforced Concrete Wall Enabled by Superelastic Shape Memory Alloy Bars. Bull Earthq. Eng 2018, 16, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Dong, Y. Performance-Based Assessment of Bridges with Steel-SMA Reinforced Piers in a Life-Cycle Context by Numerical Approach. Bull Earthq. Eng 2019, 17, 1667–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahmaran, M.; Keskin, S.B.; Ozerkan, G.; Yaman, I.O. Self-Healing of Mechanically-Loaded Self Consolidating Concretes with High Volumes of Fly Ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tittelboom, K.; Gruyaert, E.; Rahier, H.; De Belie, N. Influence of Mix Composition on the Extent of Autogenous Crack Healing by Continued Hydration or Calcium Carbonate Formation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 37, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Zhou, J.; De Rooij, M.R.; Schlangen, E.; Ye, G.; Van Breugel, K. Self-Healing Behavior of Strain Hardening Cementitious Composites Incorporating Local Waste Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmaran, M.; Yildirim, G.; Erdem, T.K. Self-Healing Capability of Cementitious Composites Incorporating Different Supplementary Cementitious Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 35, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, N. Self-Sealing, Autogenous Healing and Continued Hydration: What Is the Difference? Mat. Struct. 1998, 31, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, M.; Schlangen, E.; Joseph, C. Self-Healing Phenomena in Cement-Based Materials: State-of-the-Art Report of RILEM Technical Committee 221-SHC: Self-Healing Phenomena in Cement-Based Materials; De Rooij, M., Van Tittelboom, K., De Belie, N., Schlangen, E., Eds.; RILEM State-of-the-Art Reports; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; ISBN 978-94-007-6623-5. [Google Scholar]
- Self-Healing Materials: An Alternative Approach to 20 Centuries of Materials Science. Chem. Int.-Newsmag. IUPAC 2008, 30, 20–21. [CrossRef]
- Nishiwaki, T.; Kwon, S.; Homma, D.; Yamada, M.; Mihashi, H. Self-Healing Capability of Fiber-Reinforced Cementitious Composites for Recovery of Watertightness and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2014, 7, 2141–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termkhajornkit, P.; Nawa, T.; Yamashiro, Y.; Saito, T. Self-Healing Ability of Fly Ash–Cement Systems. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2009, 31, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, A.R.; Nehdi, M.L. Effect of Environmental Exposure on Autogenous Self-Healing of Cracked Cement-Based Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 111, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, K.; Jakubowski, J. The Effects of Age, Cement Content, and Healing Time on the Self-Healing Ability of High-Strength Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Marchand, J.; Boisvert, L. Effect of Cracking and Healing on Chloride Transport in OPC Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, C.-M.; Song, W.-J.; Popovics, J.S.; Shah, S.P. Extent of Healing of Cracked Normal Strength Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2000, 12, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, H.; Bazrgar, H. Effect of Coarse Cement Particles on the Self-Healing of Dense Concretes. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Du, P.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, Z. Research on the Improvement of Concrete Autogenous Self-Healing Based on the Regulation of Cement Particle Size Distribution (PSD). Materials 2019, 12, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Chen, H. Modeling of Self-Healing Efficiency for Cracks Due to Unhydrated Cement Nuclei in Hardened Cement Paste. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Chen, H. Modeling Self-Healing Efficiency on Cracks Due to Unhydrated Cement Nuclei in Cementitious Materials: Splitting Crack Mode. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2012, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Chen, H. Self-Healing Efficiency of Unhydrated Cement Nuclei for Dome-like Crack Mode in Cementitious Materials. Mater Struct 2013, 46, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, D.; Yu, J. Influence of Cement Coarse Particle on the Self-Healing Ability of Concrete Based on Ultrasonic Method. Adv. Mat. Res. 2010, 177, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Johannesson, B.; Geiker, M. A Review: Self-Healing in Cementitious Materials and Engineered Cementitious Composite as a Self-Healing Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-Y.; Yao, W.; Zheng, X.-F.; Wu, J.-P. Experimental Study on Self-Healing Performance of Concrete. J. Build. Mater. 2005, 8, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China (SAC). Method of Testing Cements—Determination of Strength (ISO Method). China Standards Press: Beijing, China, 2021.
- ASTM C597-22; American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM). Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Wang, J.; Wu, M. A Preliminary Study on an Effective and Simplistic Self-Healing Concept for Cement Using Coarse Clinker Particles as the Healing Agent. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 193, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Yu, L.; Liu, S.; Geng, D.; Yuan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, X.; Du, P. Improvement of Intrinsic Self-Healing Ability of Concrete by Adjusting Aggregate Gradation and Sand Ratio. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 124959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstulović, R.; Dabić, P. A Conceptual Model of the Cement Hydration Process. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Jin, N. Research on Kinetics Model of Cement Hydration Based on Microstructure Information. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao/J. Build. Mater. 2014, 17, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

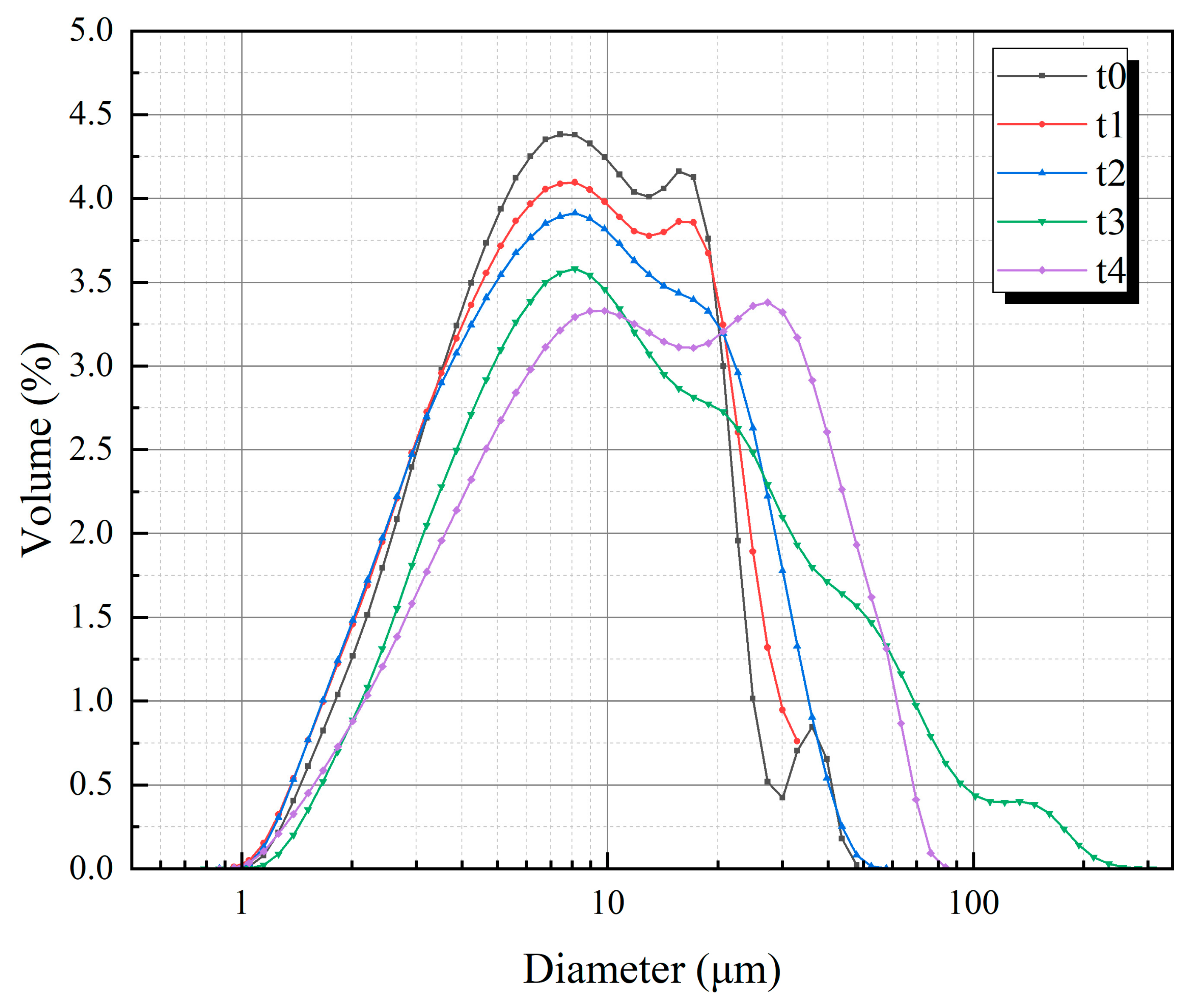
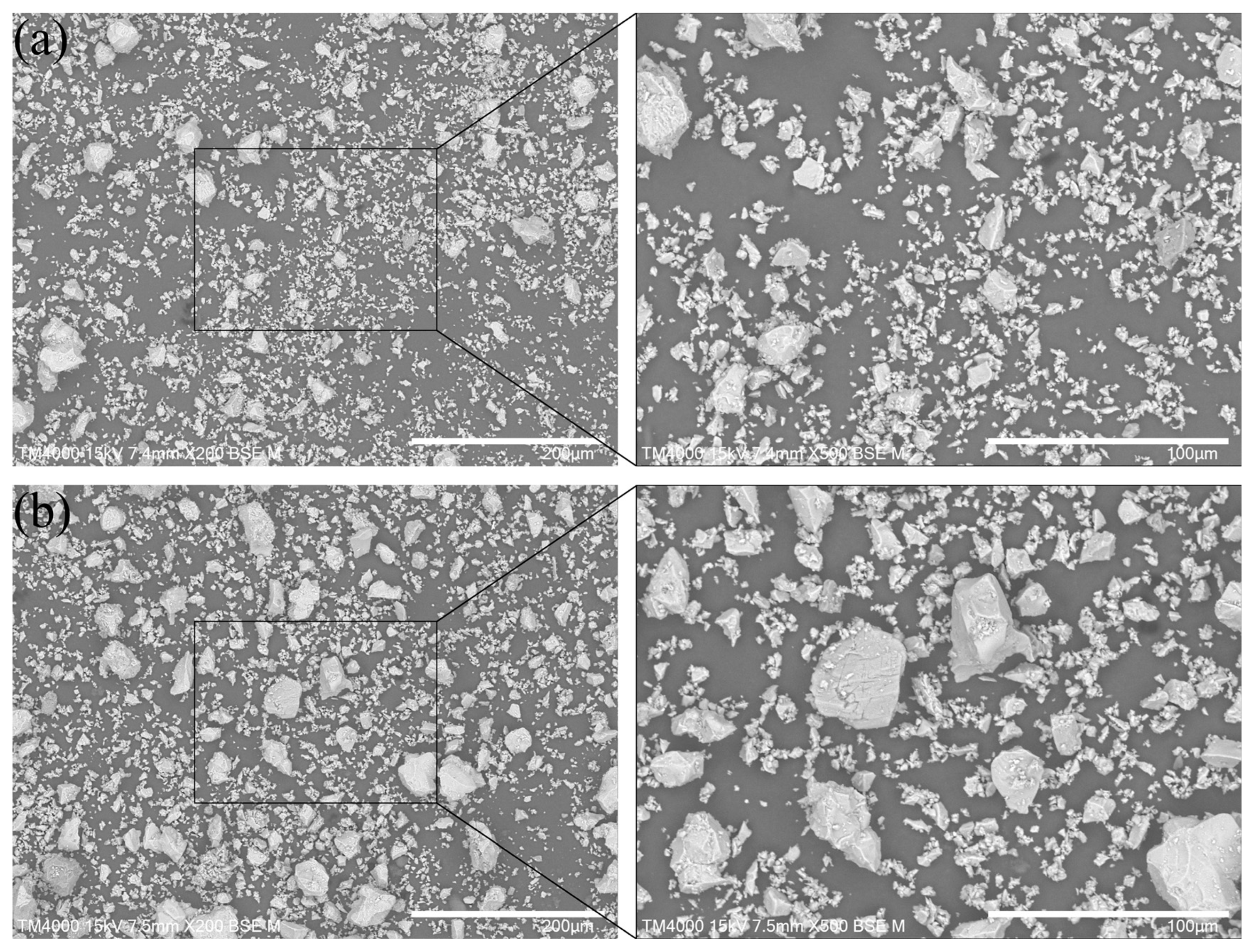
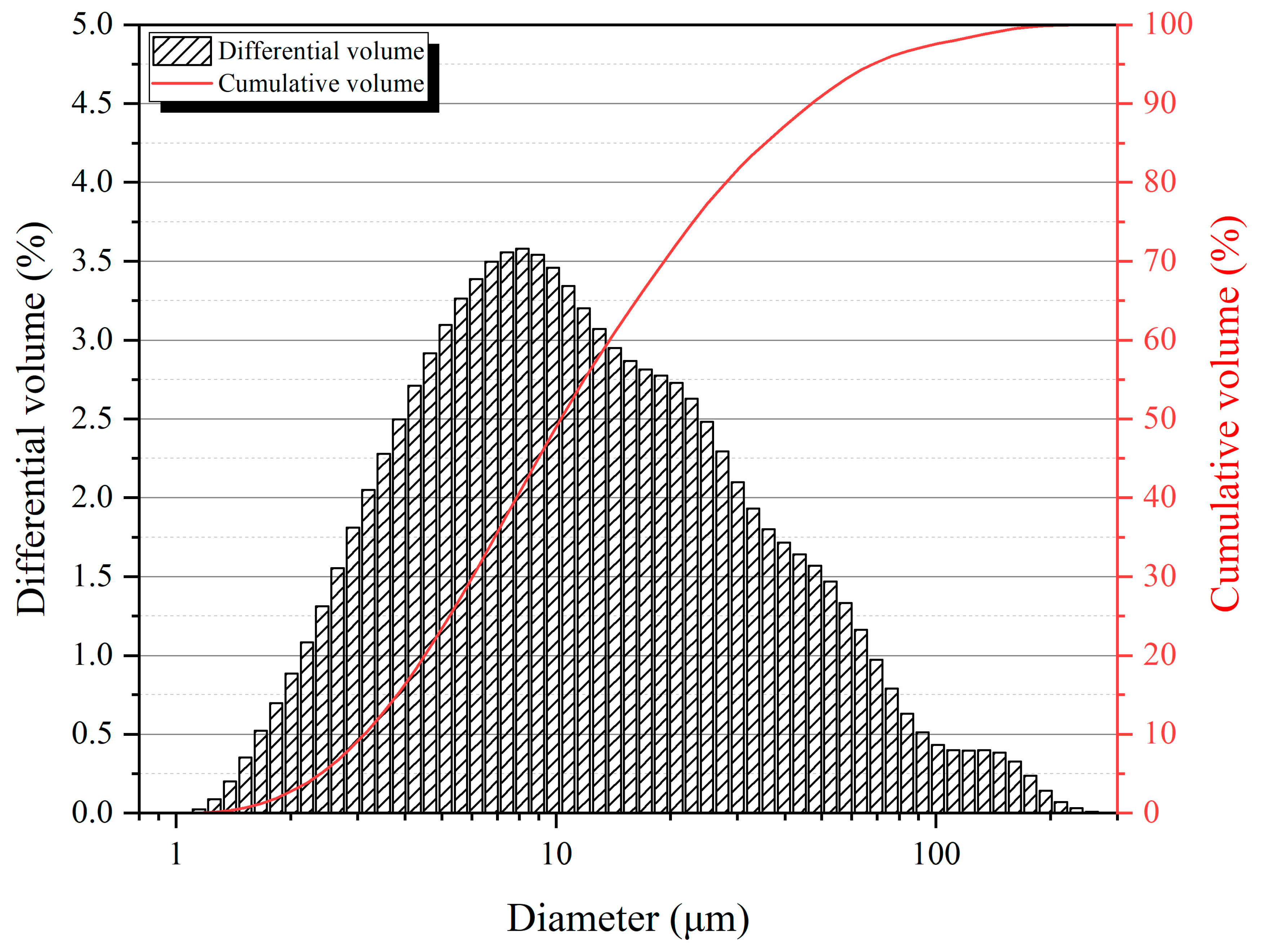
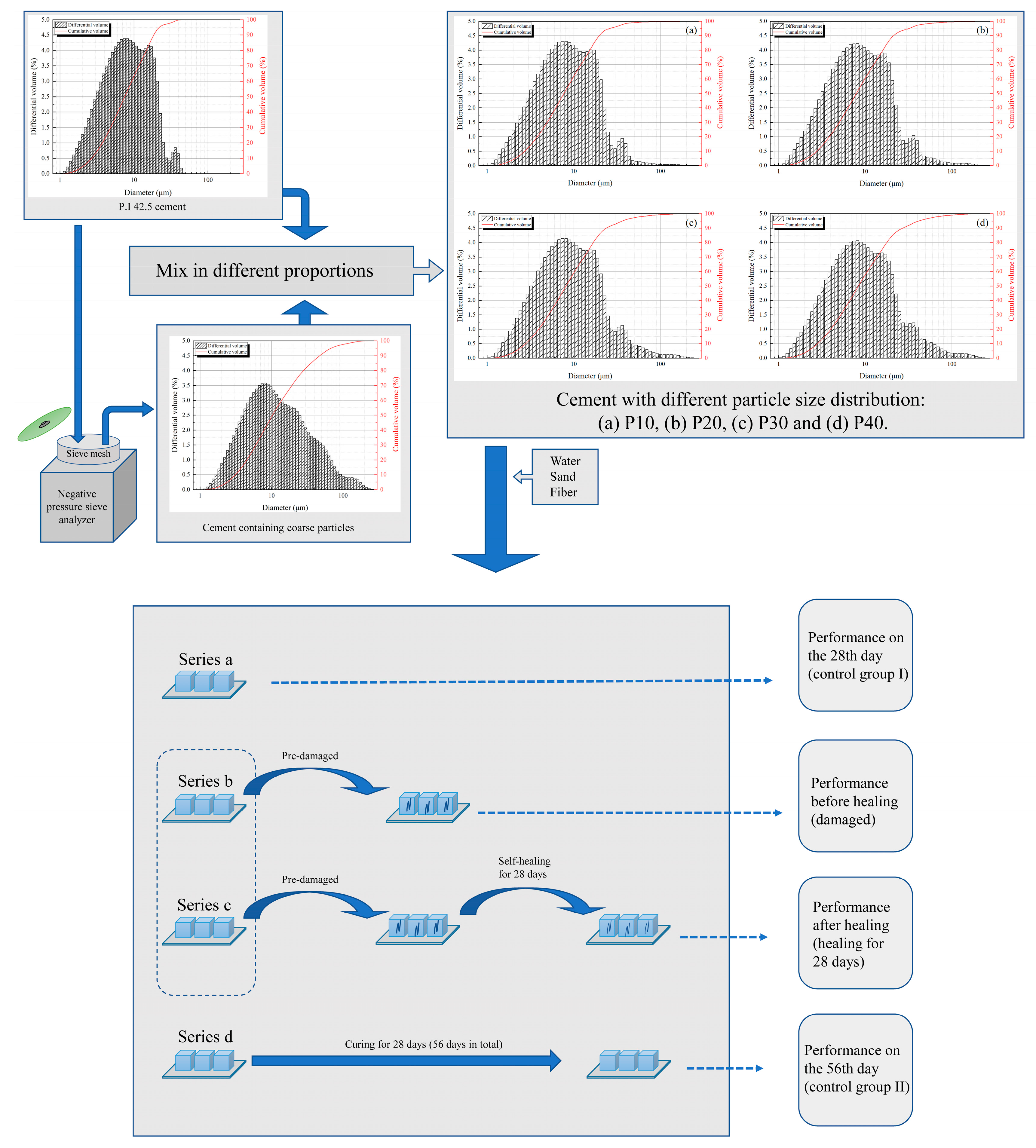

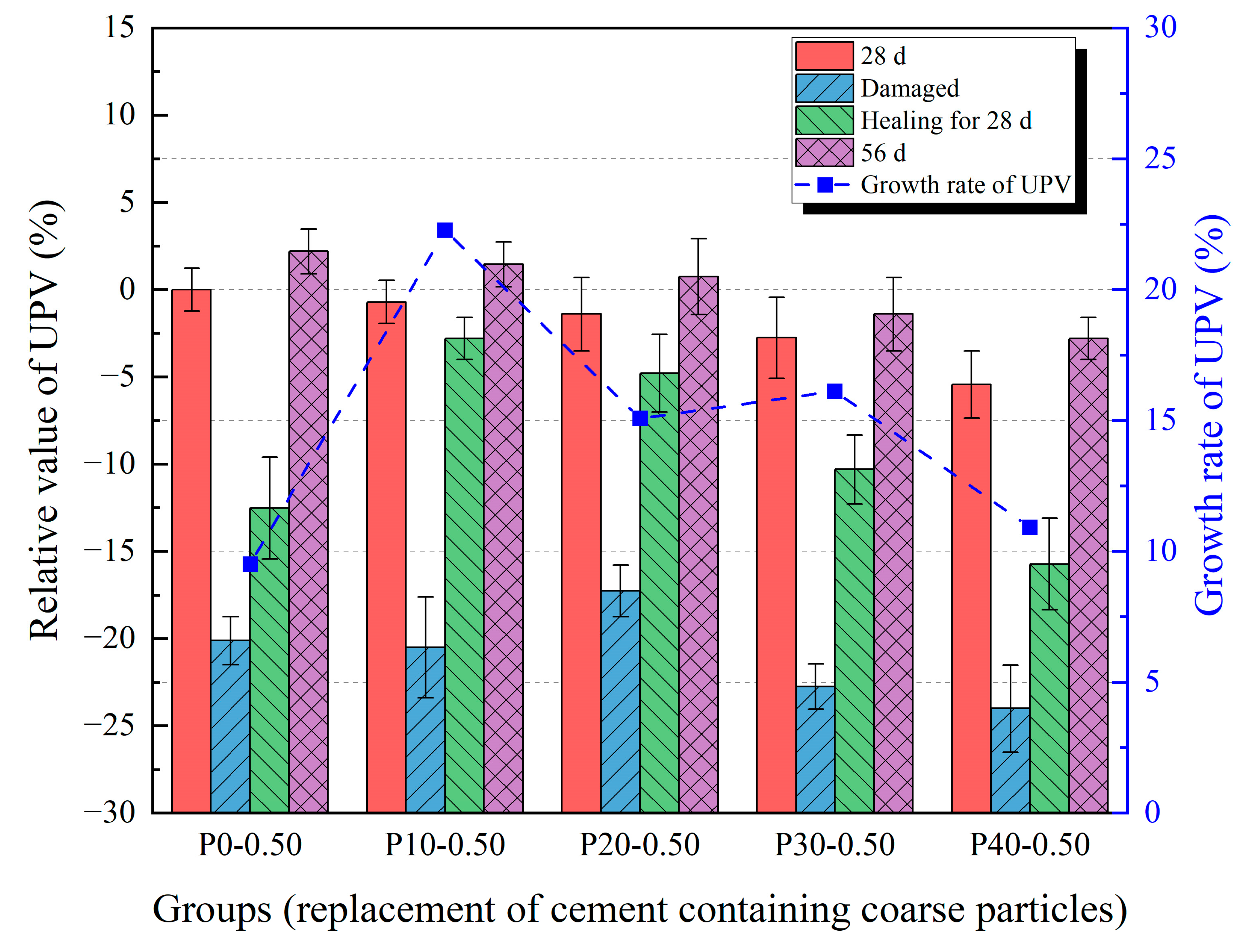
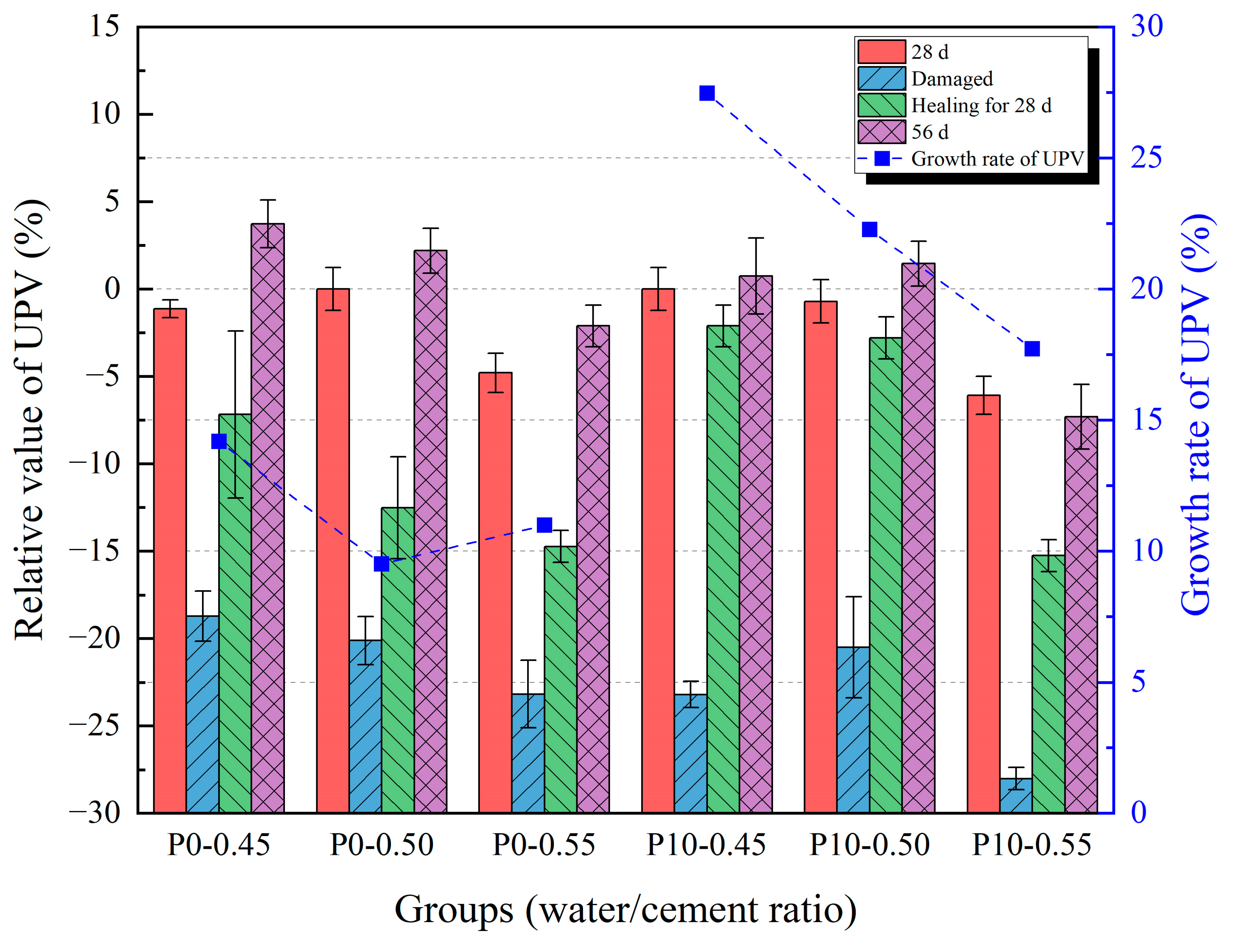
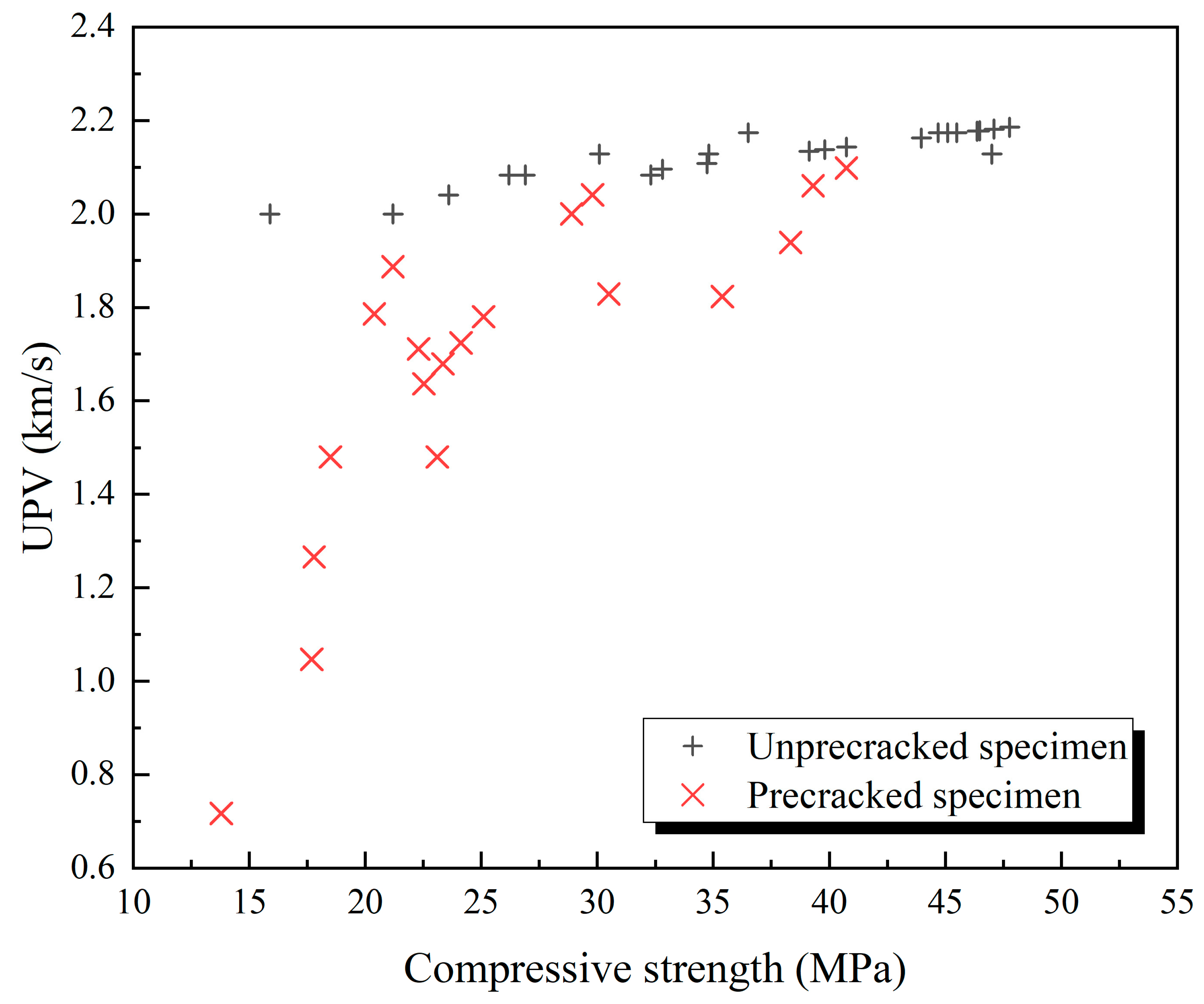
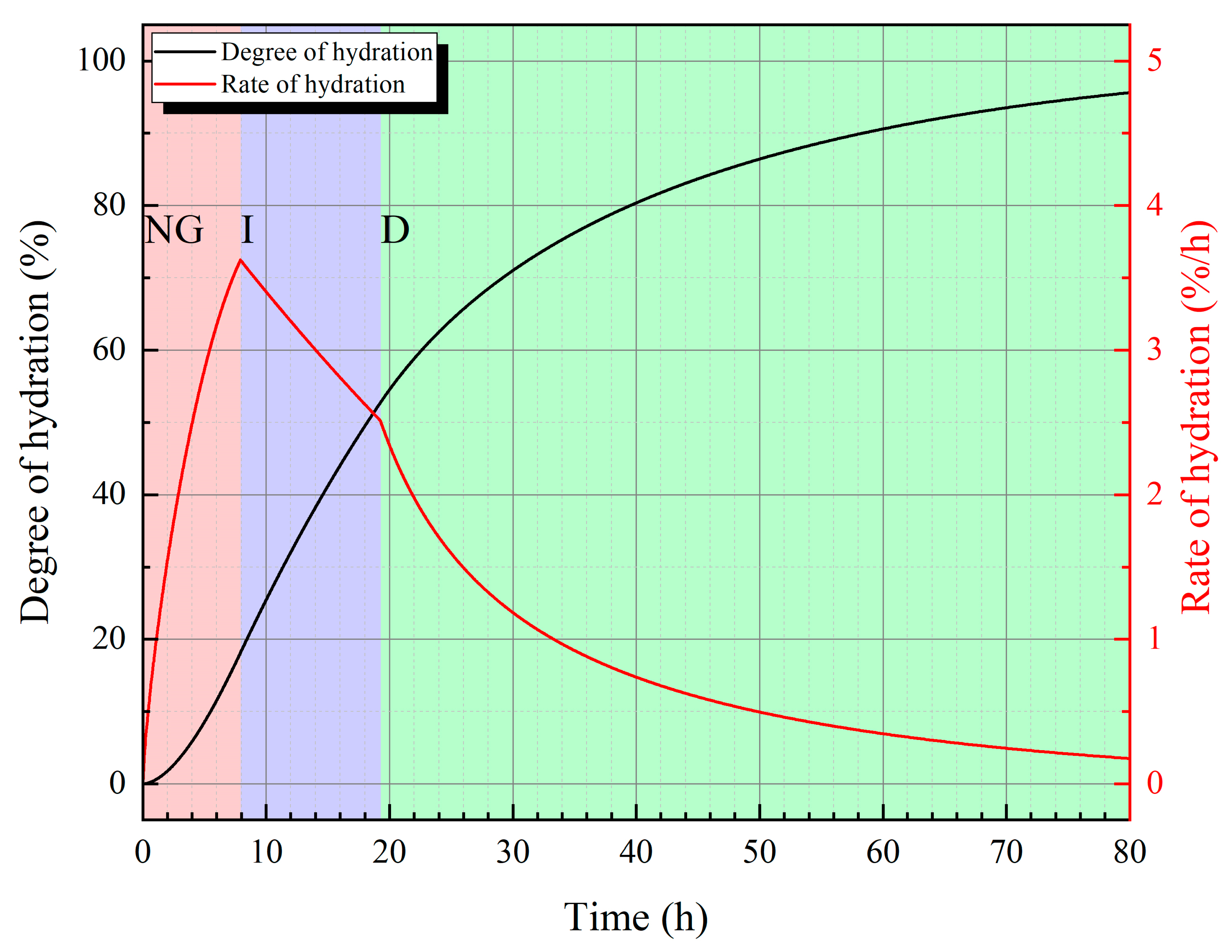
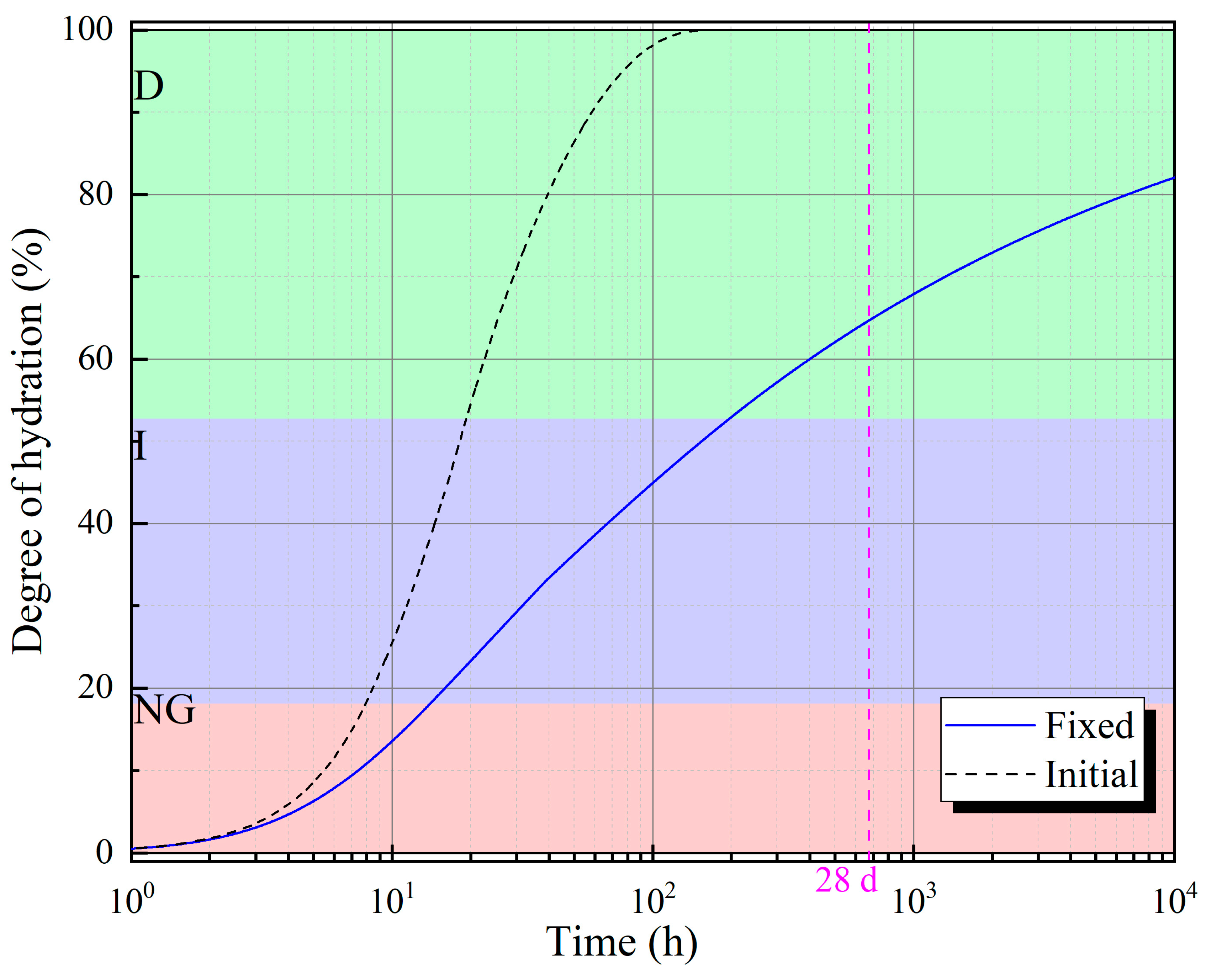
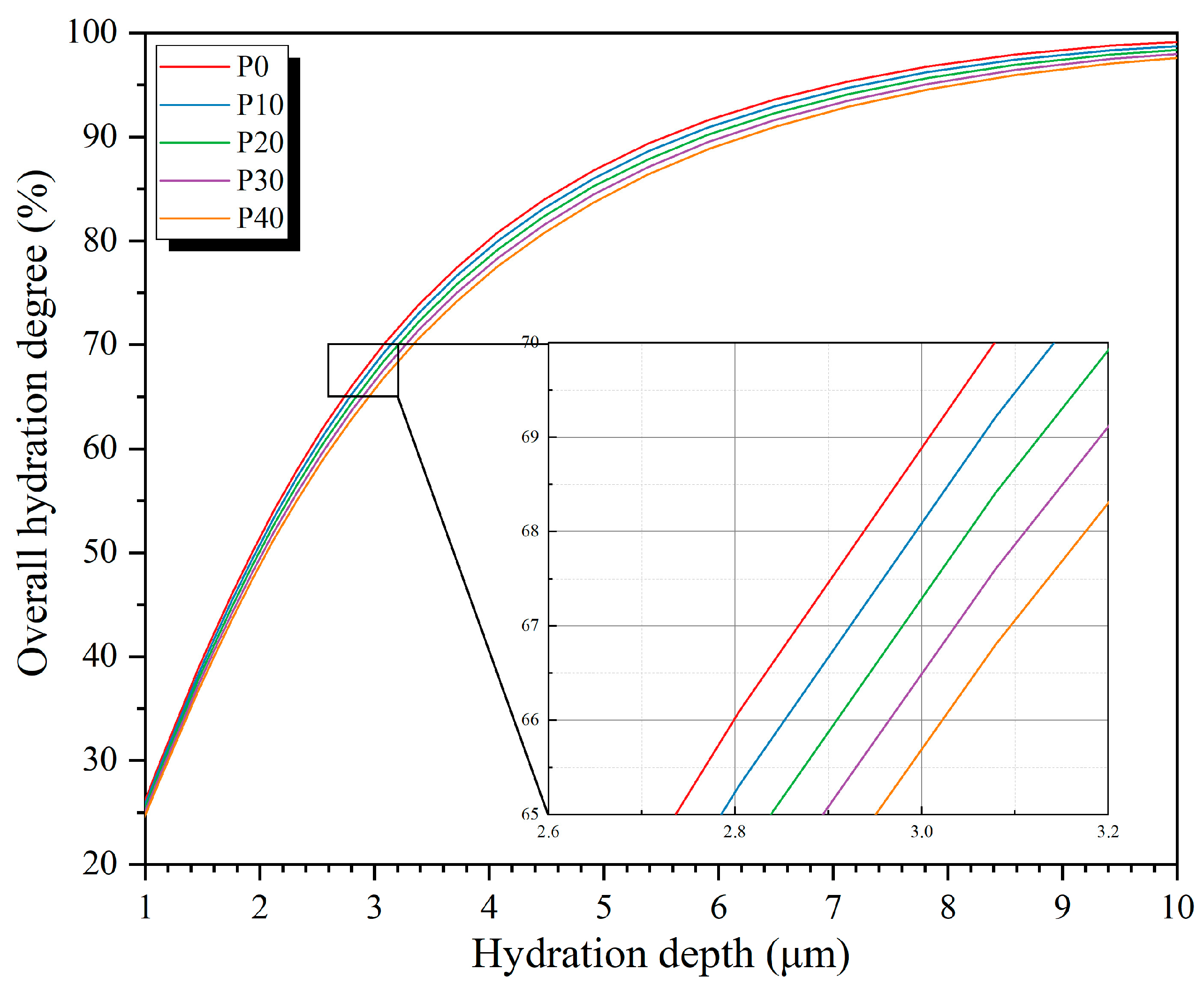
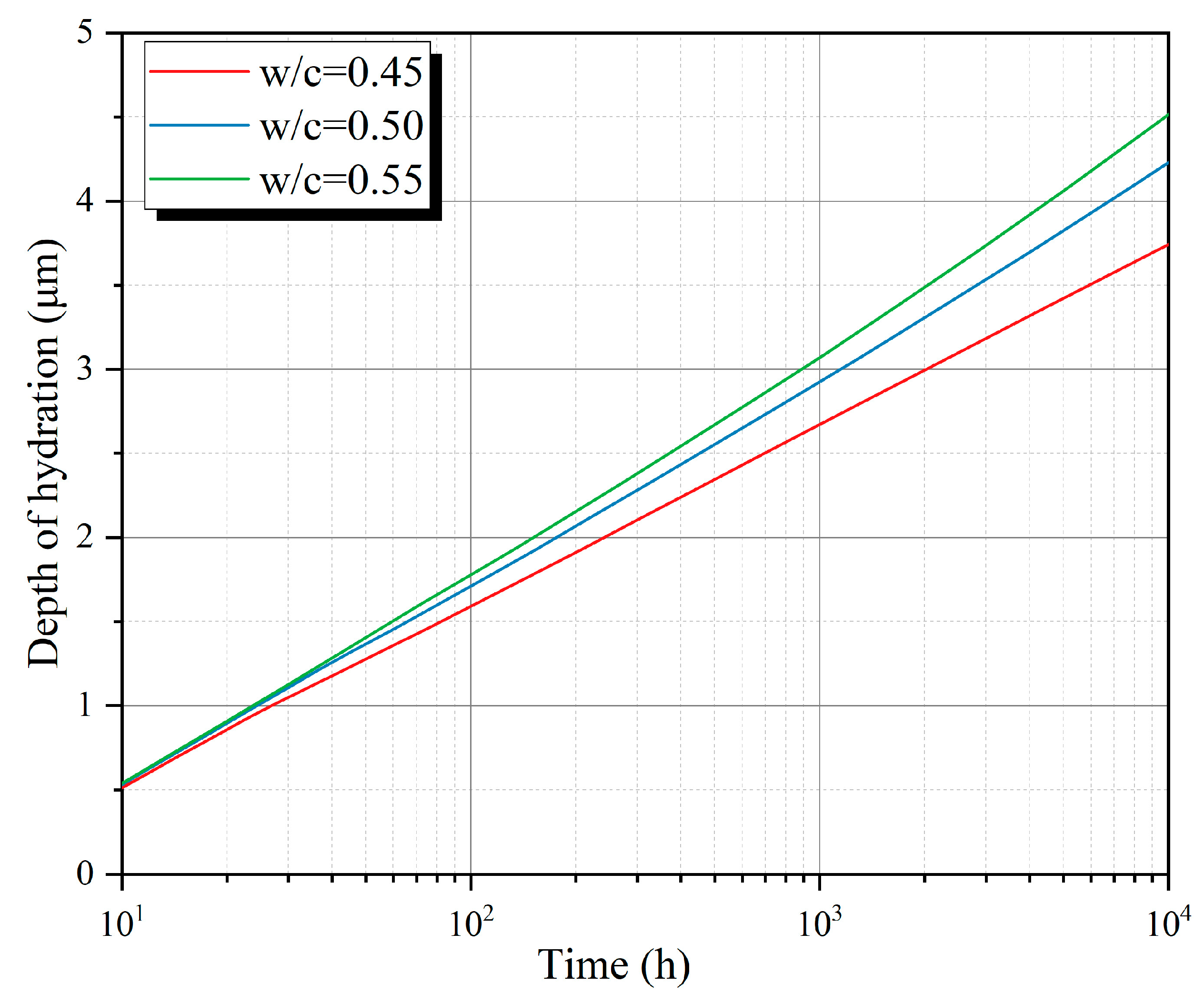


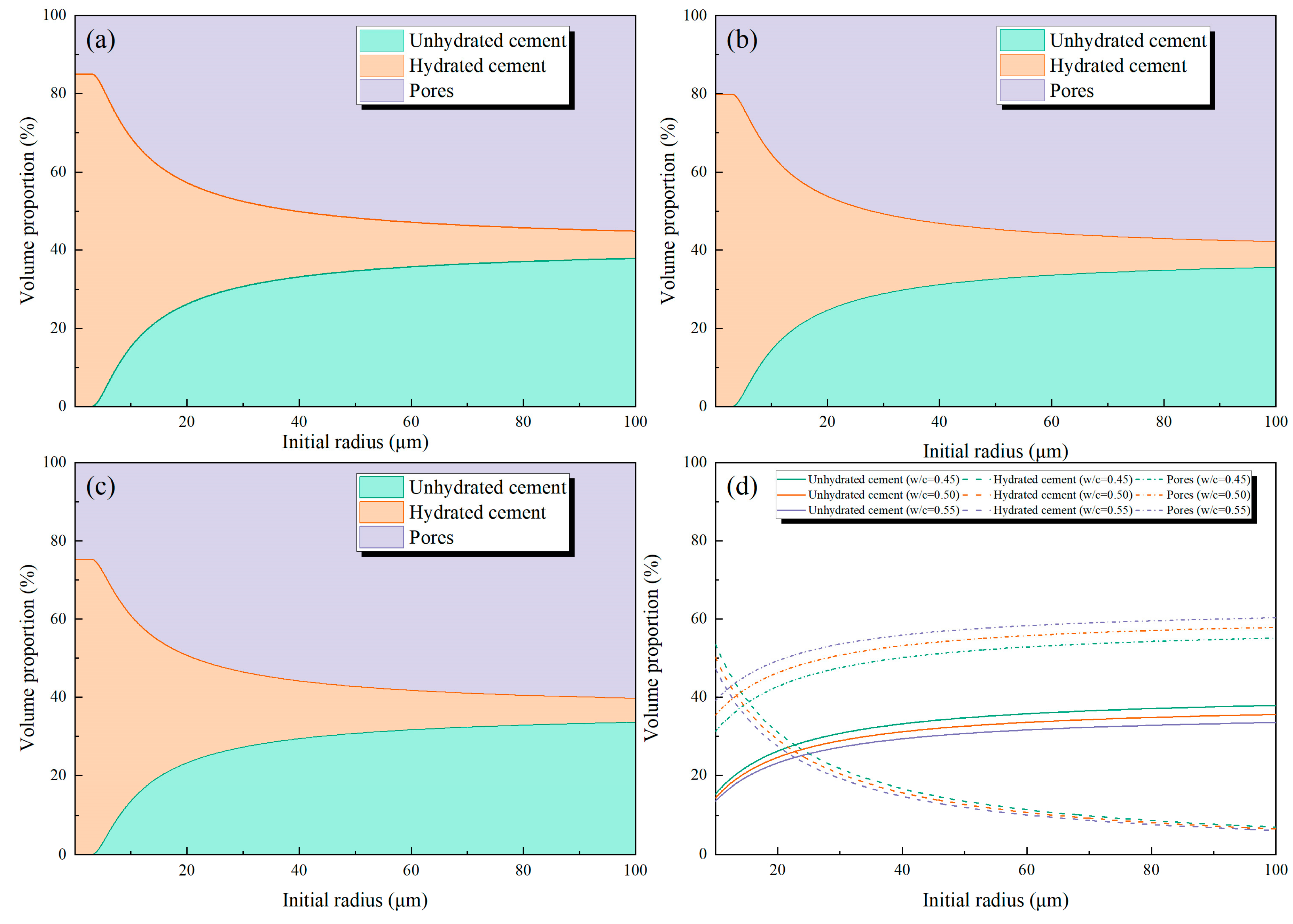

| Groups | t0 | t1 | t2 | t3 | t4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Screening time/s | 0 | 60 | 90 | 120 | 180 |
| Median diameter/μm | 8.25 | 8.28 | 8.56 | 11.67 | 12.79 |
| Groups | Initial Cement/g | Addition of Coarse Particles/g | Sand/g | Water/g | w/c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P0-0.50 | 450.0 | 0 | 1350.0 | 225.0 | 0.50 |
| P10-0.50 | 405.0 | 45.0 | 1350.0 | 225.0 | 0.50 |
| P20-0.50 | 360.0 | 90.0 | 1350.0 | 225.0 | 0.50 |
| P30-0.50 | 315.0 | 135.0 | 1350.0 | 225.0 | 0.50 |
| P40-0.50 | 270.0 | 180.0 | 1350.0 | 225.0 | 0.50 |
| P0-0.45 | 450.0 | 0 | 1350.0 | 202.5 | 0.45 |
| P0-0.55 | 450.0 | 0 | 1350.0 | 247.5 | 0.55 |
| P10-0.45 | 405.0 | 45.0 | 1350.0 | 202.5 | 0.45 |
| P10-0.55 | 405.0 | 45.0 | 1350.0 | 247.5 | 0.55 |
| Groups | Compressive Strength Recovery Rate/% |
|---|---|
| P0-0.50 | 74.11 |
| P10-0.50 | 87.66 |
| P20-0.50 | 83.44 |
| P30-0.50 | 82.67 |
| P40-0.50 | 76.63 |
| P0-0.45 | 74.85 |
| P0-0.55 | 74.63 |
| P10-0.45 | 89.44 |
| P10-0.55 | 81.91 |
| Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P.I. 42.5 cement | 0.0504 | 0.0138 | 0.0061 | 1.7510 |
| Groups | Percentage of >40 μm Particles |
|---|---|
| P0-0.50 | 0.21 |
| P10-0.50 | 1.49 |
| P20-0.50 | 2.77 |
| P30-0.50 | 4.05 |
| P40-0.50 | 5.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Yao, W.; She, A.; Wei, Y. Influence of Coarse Cement Particle Content on Intrinsic Self-Healing of Mortar. Materials 2025, 18, 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102216
Ma X, Yao W, She A, Wei Y. Influence of Coarse Cement Particle Content on Intrinsic Self-Healing of Mortar. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102216
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xingkong, Wu Yao, Anming She, and Yongqi Wei. 2025. "Influence of Coarse Cement Particle Content on Intrinsic Self-Healing of Mortar" Materials 18, no. 10: 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102216
APA StyleMa, X., Yao, W., She, A., & Wei, Y. (2025). Influence of Coarse Cement Particle Content on Intrinsic Self-Healing of Mortar. Materials, 18(10), 2216. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102216






