Industrial-Scale Brownmillerite Formation in Oxygen-Blown Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag: A Novel Stabilization Approach for Sustainable Utilization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
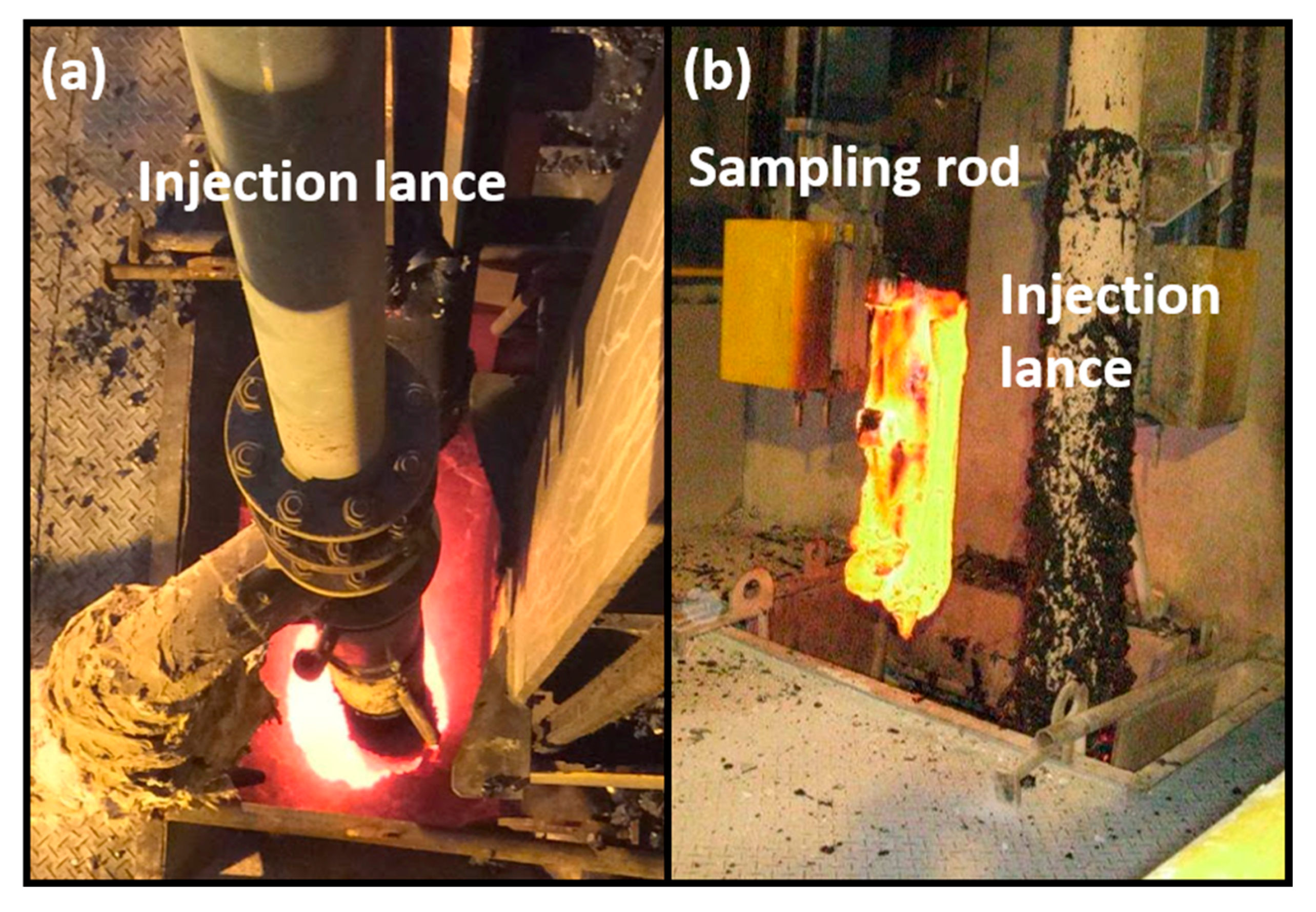
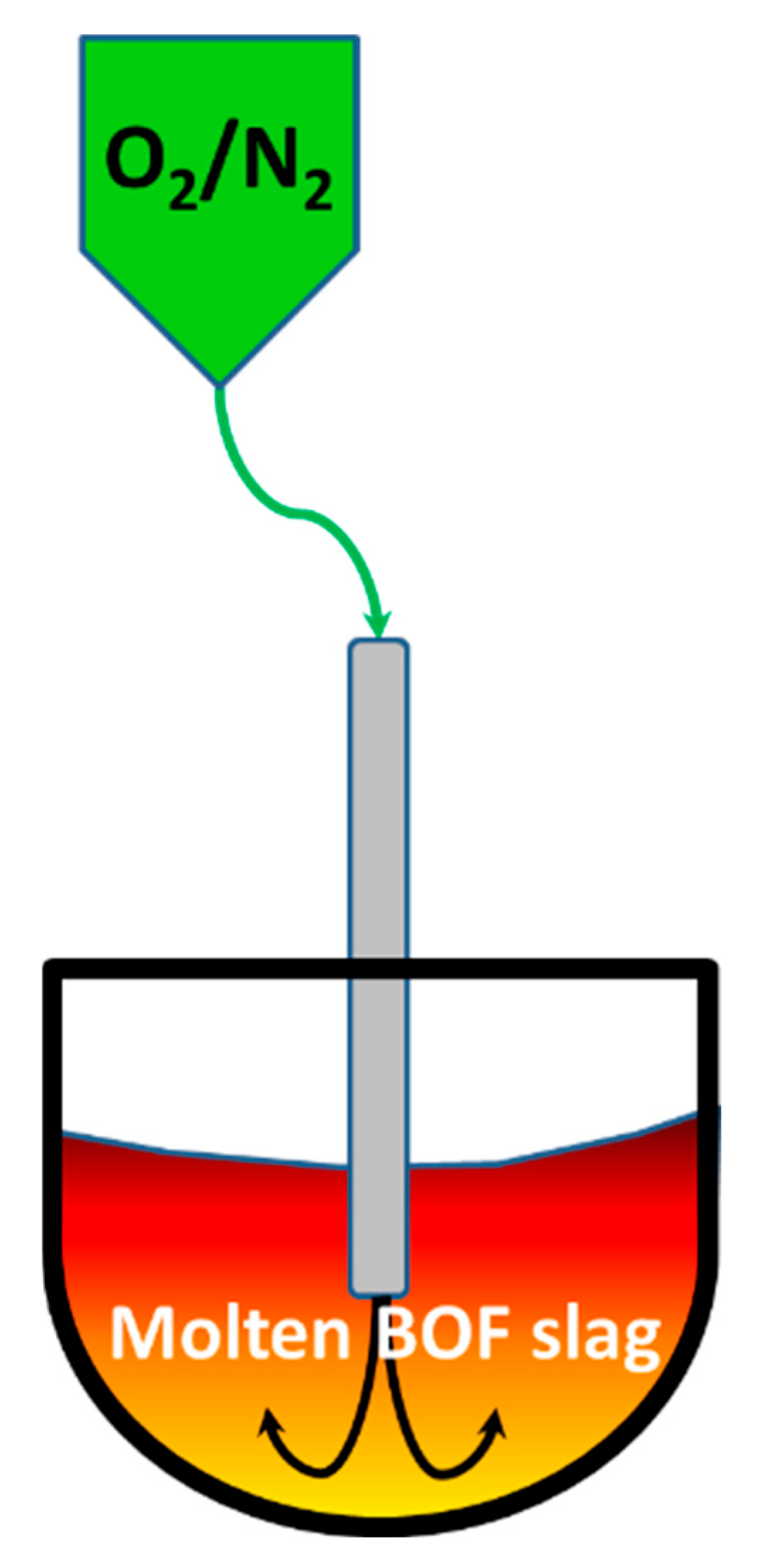
2.1. The Modification of Molten BOF Slag
2.2. Expansion Measurements of BOF Slag
- Vi: the volume of BOF slag before modification;
- Vf: the volume of BOF slag after modification.
2.3. XRD Measurements of BOF Slag
2.4. pH Measurements of BOF Slag
2.5. TCLP Tests of BOF Slag
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Principle of BOF Slag Stabilization
3.2. Mechanistic Study of BOF Slag Stabilization by Oxygen Blowing
3.3. Conditions for Stabilization of BOF Slag by Oxygen Blowing
- Ei: the expansion value of BOF slag before treatment
- Ef: the expansion value of BOF slag after treatment
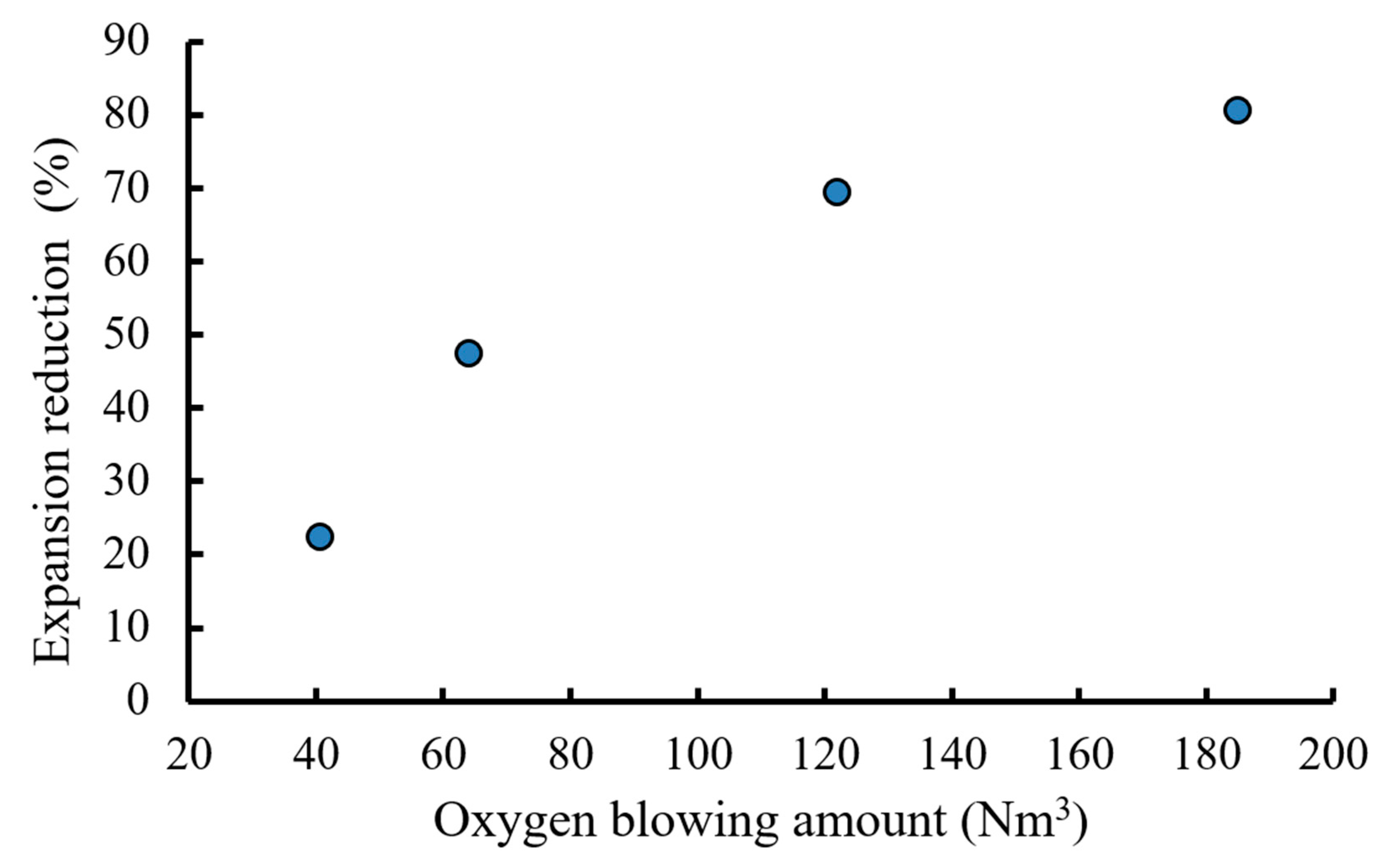
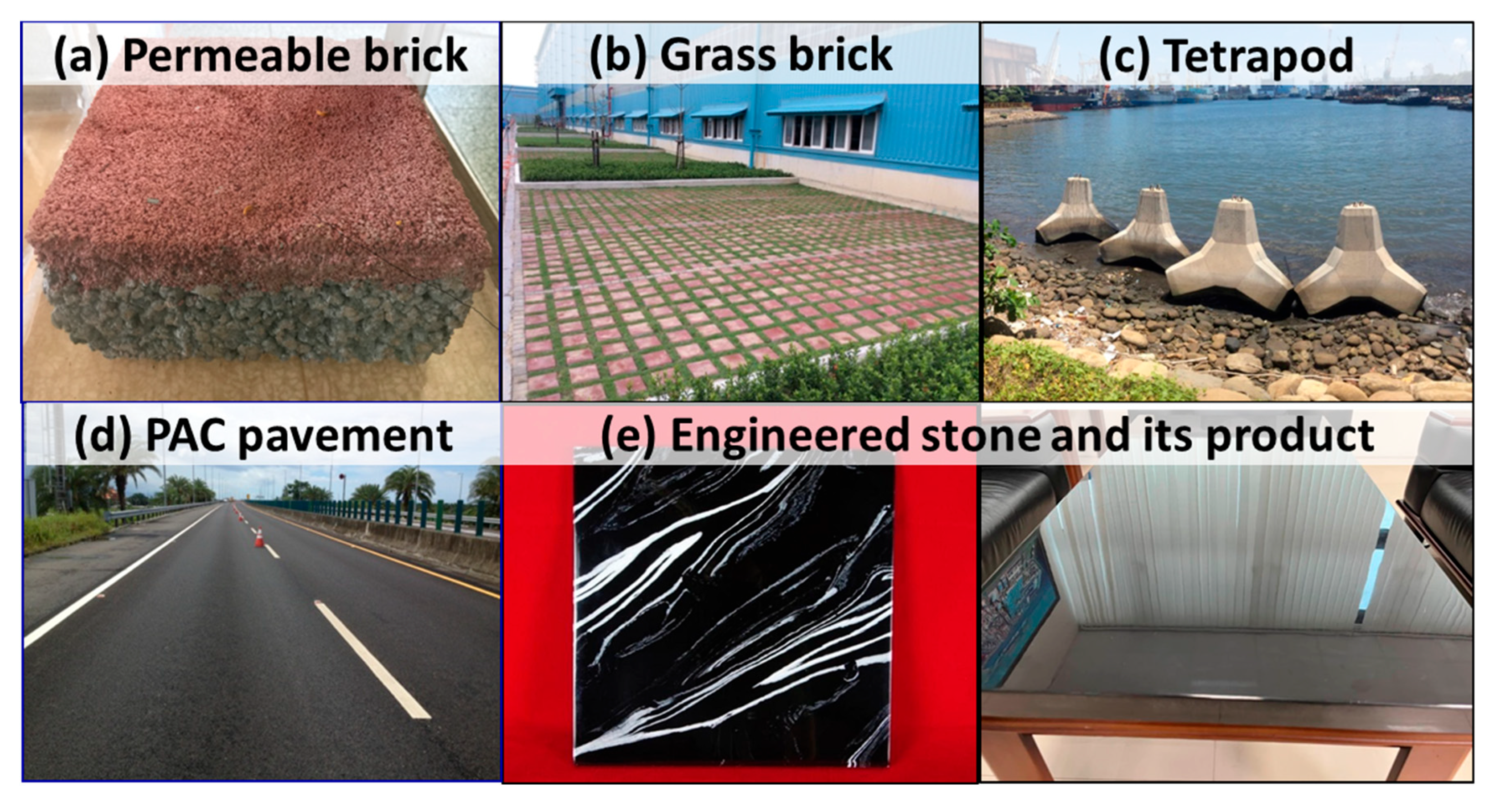
3.4. Properties of Modified BOF Slag and Its Applications
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasaki, T.; Takuji, H. Development of steam-aging process for steel slag. Nippon. Steel Tech. Rep. 2015, 109, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Application of the BSSF molten steel slag processing technology in POSCO. Baosteel Techn. Res. 2011, 5, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Kühn, M.; Drissen, P.; Schrey, H. Treatment of liquid steel slags. In Proceedings of the 2nd European slag conference, Düsseldorf, Germany, 9–11 October 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Engström, F.; Pontikes, Y.; Geysen, D.; Jones, P.T.; Björkman, B.; Blanpain, B. Hot stage engineering to improve slag valorisation options. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Slag Valorisation Symposium, Leuven, Belgium, 18–20 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Sheu, B.L. The application and breakthrough of BOF slag modification. China Steel Tech. Rep. 2015, 28, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Sheu, B.L. The application and breakthrough of BOF slag modification technique in CSC. In Proceedings of the 8th European Slag Conference, Linz, Austria, 21–23 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C. BOF Slag Hot-Stage Engineering Towards Iron Recovery and Use as Binders. Doctoral Thesis, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Huang, S.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. Optimization of mineralogy and microstructure of solidified basic oxygen furnace slag through SiO2 addition or atmosphere control during hot-stage slag treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaja, A.M.; Melzer, S.; Brouwers, H.J.H. On the optimization of BOF slag hydration kinetics. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 124, 104262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinohara, I.; Kase, N.; Maruoka, H.; Hirai, S.; Eba, H. Powder X-ray diffraction analysis of lime-phase solid solution in converter slag. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, T.; Du, C.M.; Koizumi, S.; Gao, X.; Ueda, S.; Kitamura, S. Extraction of phosphorus and recovery of phosphate from steelmaking slag by selective leaching. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, F.; Strandkvist, I.; Samuelsson, C.; Björkman, B. Influence of slag mineralogy on possibilities for use in alternative applications. In Proceedings of the 5th International Slag Valorisation Symposium, Leuven, Belgium, 3–5 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Strandkvist, I.; Sandström, Å.; Engström, F. Effect of FeO/MgO ratio on dissolution and leaching of magnesiowüstite. Steel Res. Int. 2017, 88, 1600322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Weng, T.T.; Lee, Y.C. Hot slag modification of BOF slag for preventing its disintegration to enhance slag utilization. China Steel Tech. Rep. 2019, 32, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Liao, K.S. Engineered stone made of modified BOF slag. In Proceedings of the 5th International Slag Valorisation Symposium, Leuven, Belgium, 3–5 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ulewicz, M.; Jura, J.; Zieliński, A.; Pietraszek, J. The application of converter sludge and slag to produce ecological cement mortars. Materials 2024, 17, 4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, Z.; Malekzadeh, A.; Poater, J. Brownmillerite calcium ferrite, a promising perovskite-related material in the degradation of a tight dye under ambient conditions. ChemistryOpen 2024, 13, e202300169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.H.P.; Ardisson, J.D.; Krohling, A.C.; Lago, R.M.; Júnior, W.G.; Tristão, J.C. Calcium ferrites for phosphate adsorption and recovery from wastewater. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
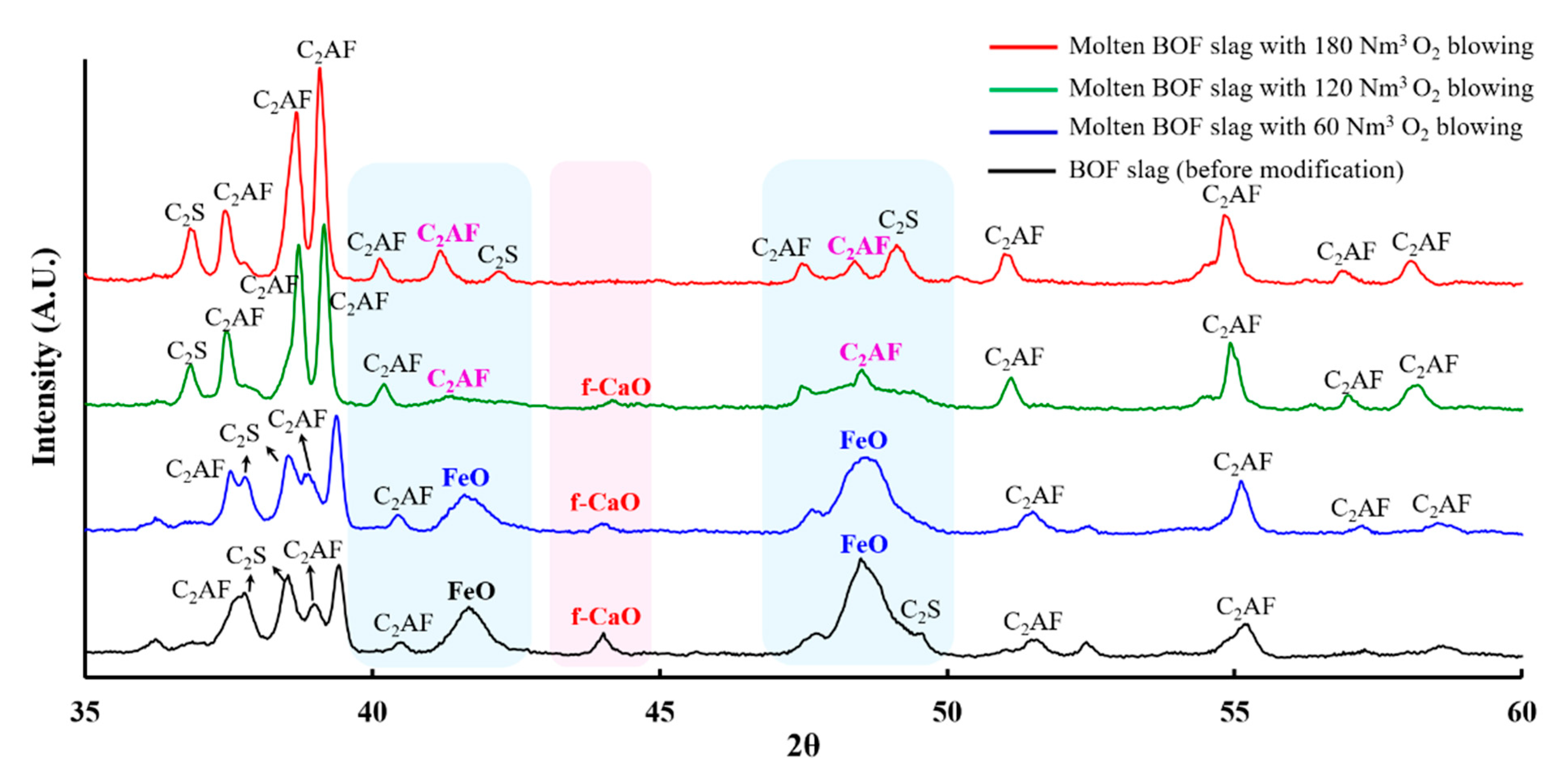
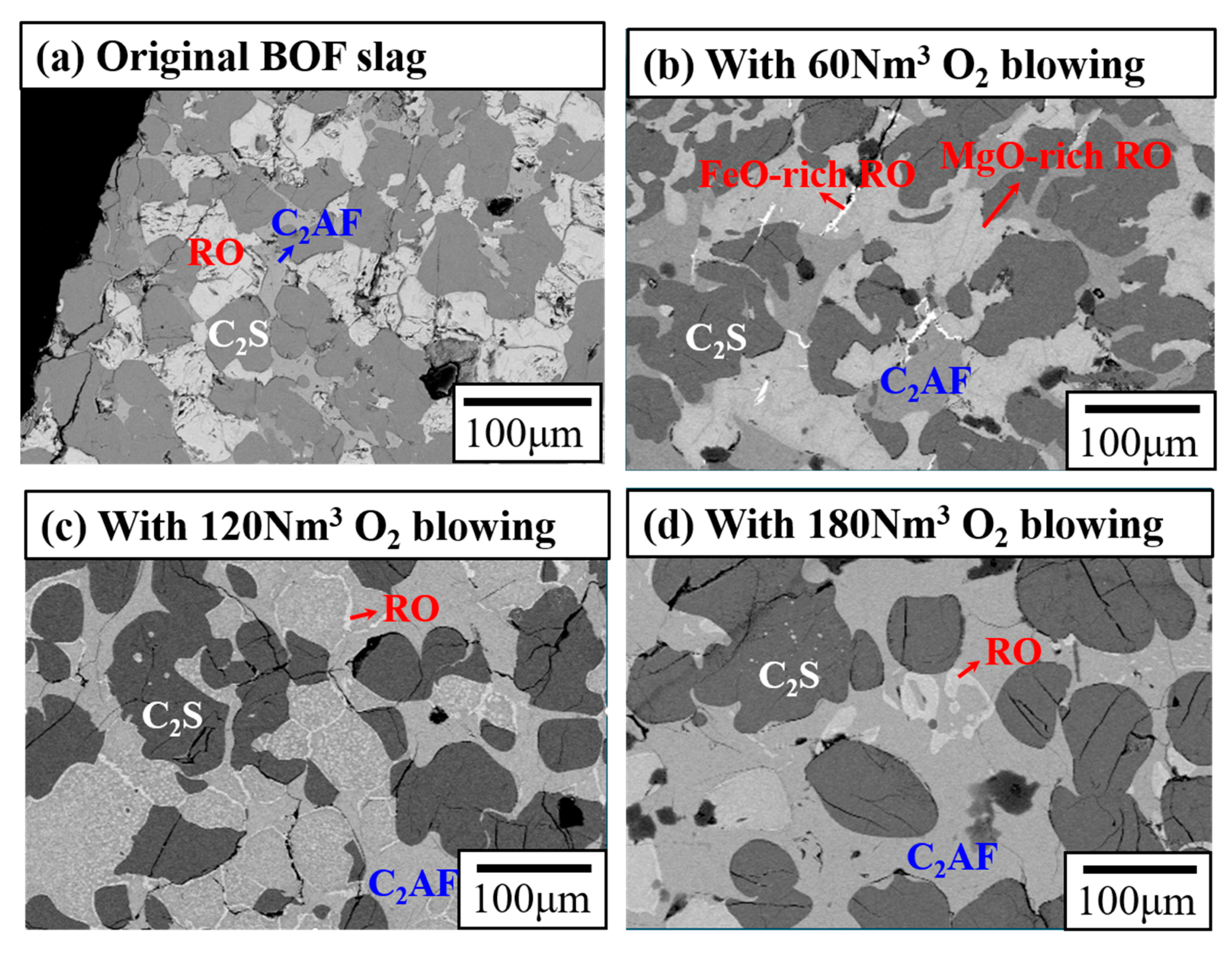
| Original BOF Slag | 60 Nm3 O2 Blowing | 120 Nm3 O2 Blowing | 180 Nm3 O2 Blowing | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2AF (Ca2AlxFe2−xO5) | 21.3% | 29.8% | 44.9% | 61.1% |
| C2S (2CaO·SiO2) | 41.7% | 36.8% | 34.7% | 35.1% |
| RO (FeO/MgO/MnO) | 34.1% | 32.9% | 21.2% | 3.8% |
| f-CaO | 2.9% | 0.5% | 0.2% | 0% |
| Characteristics | BOF Slag Without Oxygen Blowing | BOF Slag with Oxygen Blowing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal phase | C2S (2CaO·SiO2) | 42% | 35% |
| C2AF (Ca2AlxFe2−xO5) | 21% | 61% | |
| RO (FeO/MgO/MnO) | 34% | 4% | |
| f-CaO | 3% | 0% | |
| B2 (CaO/SiO2) | 3.8–4.7 | 3.8–4.7 | |
| Expansion rate (%) | 3–6 | <0.5 | |
| pH | 12.4 | 10.8 | |
| Elements | Methods | Standard (mg/L) | Modified BOF Slag (60 Nm3 O2 Blowing) (mg/L) | Modified BOF Slag (120 Nm3 O2 Blowing) (mg/L) | Modified BOF Slag (180 Nm3 O2 Blowing) (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | NIEA R317.11C | <5.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cd | NIEA R317.11C | <1.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cu | NIEA R317.11C | <15.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cr | NIEA R317.11C | <5.0 | <0.111 | <0.111 | <0.111 |
| As | NIEA R317.11C | <5.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Hg | NIEA R317.11C | <0.2 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Se | NIEA R317.11C | <1.0 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| Cr6+ | UV analysis | <2.5 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tseng, Y.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Tsai, M.-H. Industrial-Scale Brownmillerite Formation in Oxygen-Blown Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag: A Novel Stabilization Approach for Sustainable Utilization. Materials 2025, 18, 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102182
Tseng Y-H, Kuo Y-H, Tsai M-H. Industrial-Scale Brownmillerite Formation in Oxygen-Blown Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag: A Novel Stabilization Approach for Sustainable Utilization. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102182
Chicago/Turabian StyleTseng, Yao-Hung, Yu-Hsien Kuo, and Meng-Hsun Tsai. 2025. "Industrial-Scale Brownmillerite Formation in Oxygen-Blown Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag: A Novel Stabilization Approach for Sustainable Utilization" Materials 18, no. 10: 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102182
APA StyleTseng, Y.-H., Kuo, Y.-H., & Tsai, M.-H. (2025). Industrial-Scale Brownmillerite Formation in Oxygen-Blown Basic Oxygen Furnace Slag: A Novel Stabilization Approach for Sustainable Utilization. Materials, 18(10), 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102182





