Creation of Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions N-Butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide, Resistant to Recrystallization Caused by Exposure to Moisture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Generation of SD/ASD GML-3
2.2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.3. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
2.2.4. Dissolution Test
2.2.5. Accelerated Aging Stability Tests
3. Results
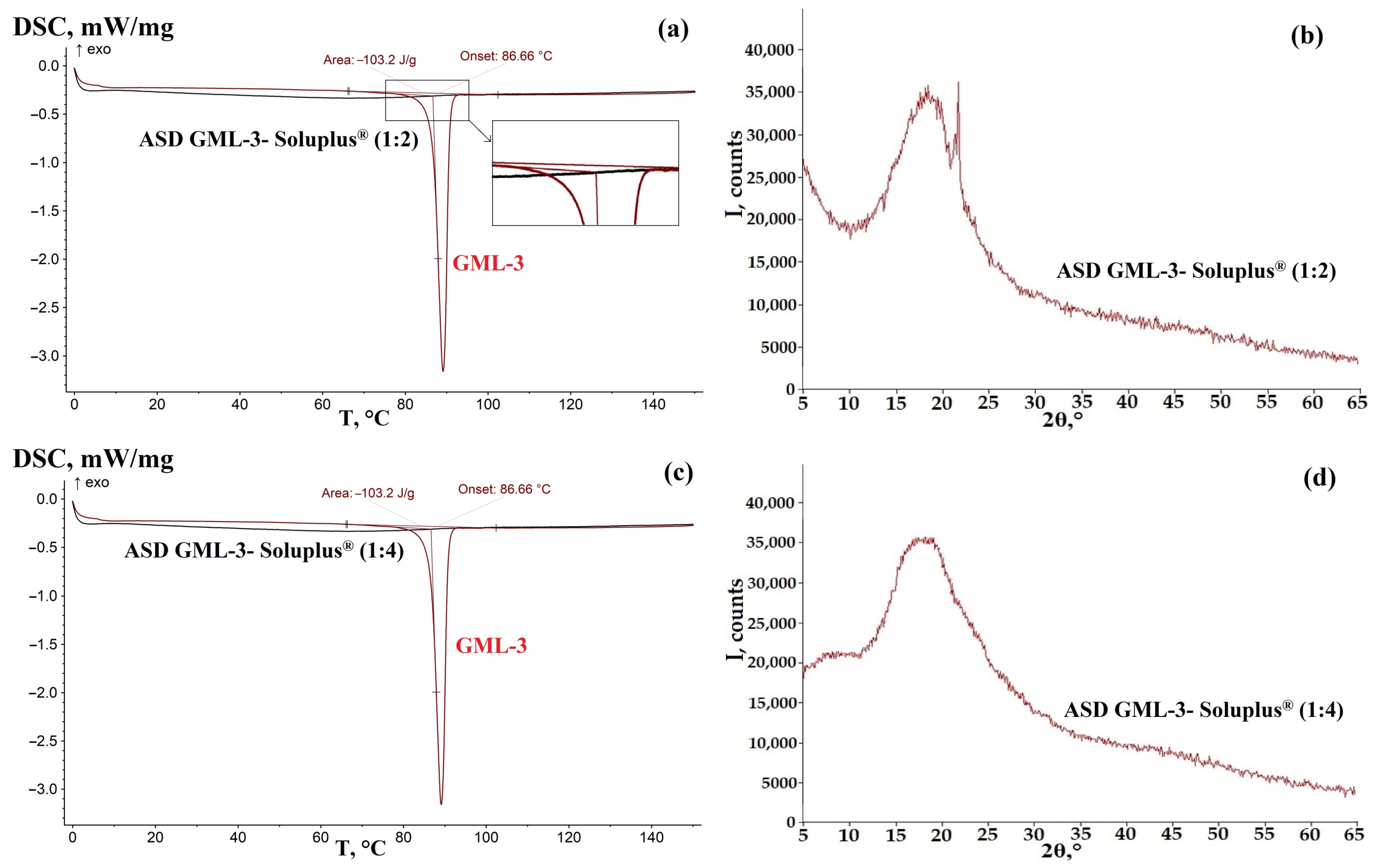
3.1. ASD GML-3 Crystallization Analysis with Soluplus®
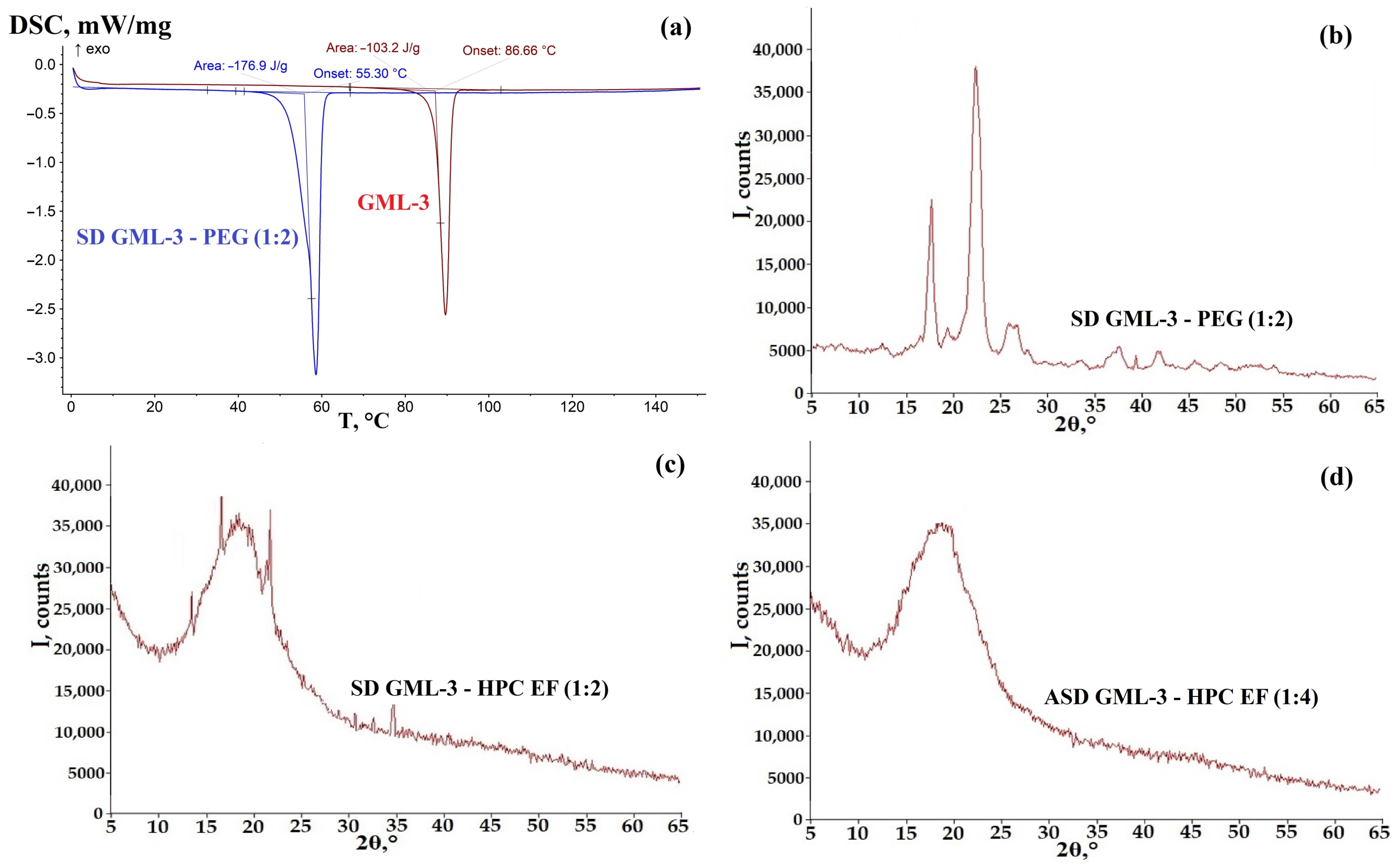
3.2. Analysis of the Crystallinity of SD GML-3 with PEG
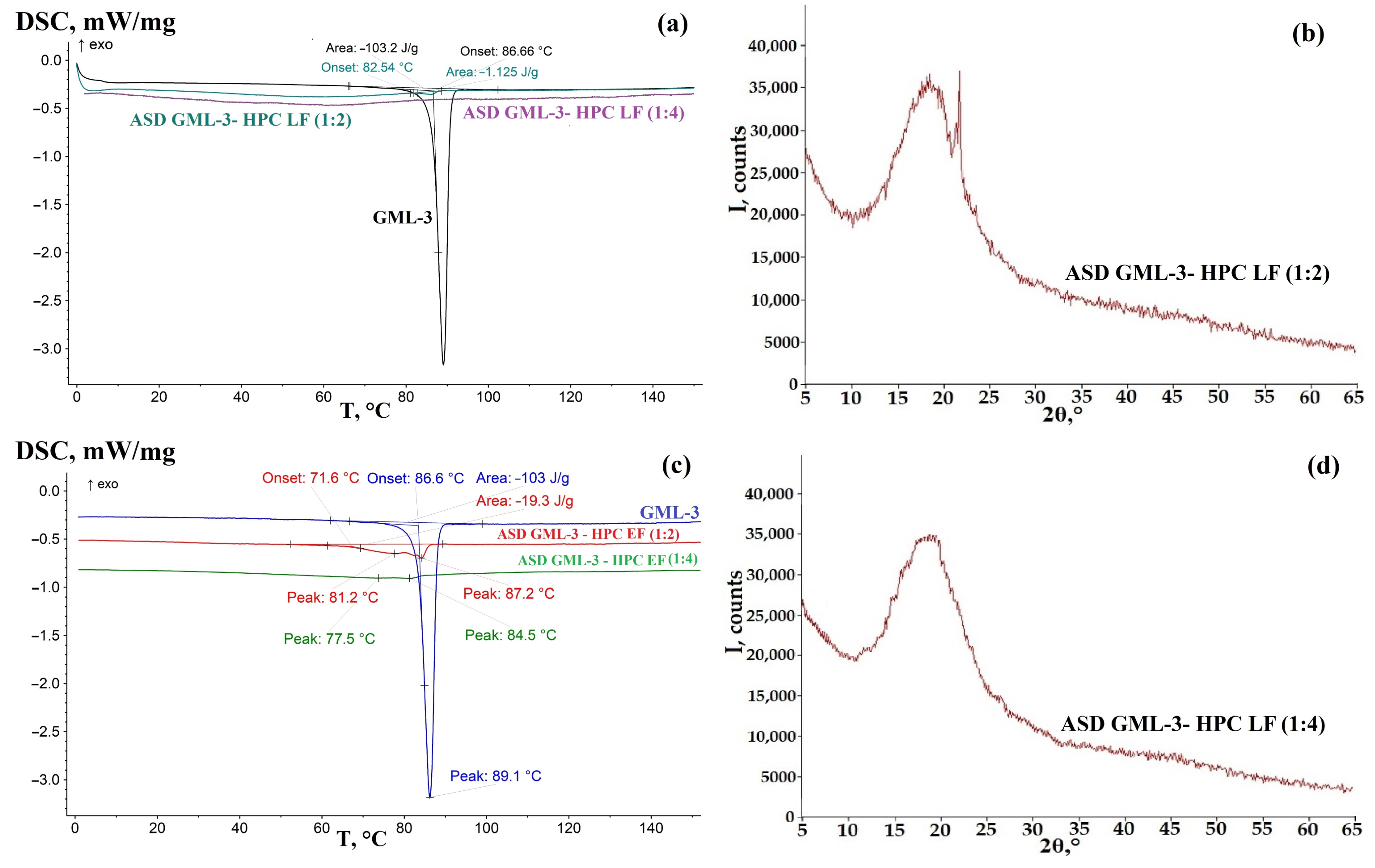
3.3. Analysis of the Crystallinity of ASD GML-3 Using HPC
3.4. Evaluation of the Effect of Humidity on the Crystallinity of GML-3 in ASD
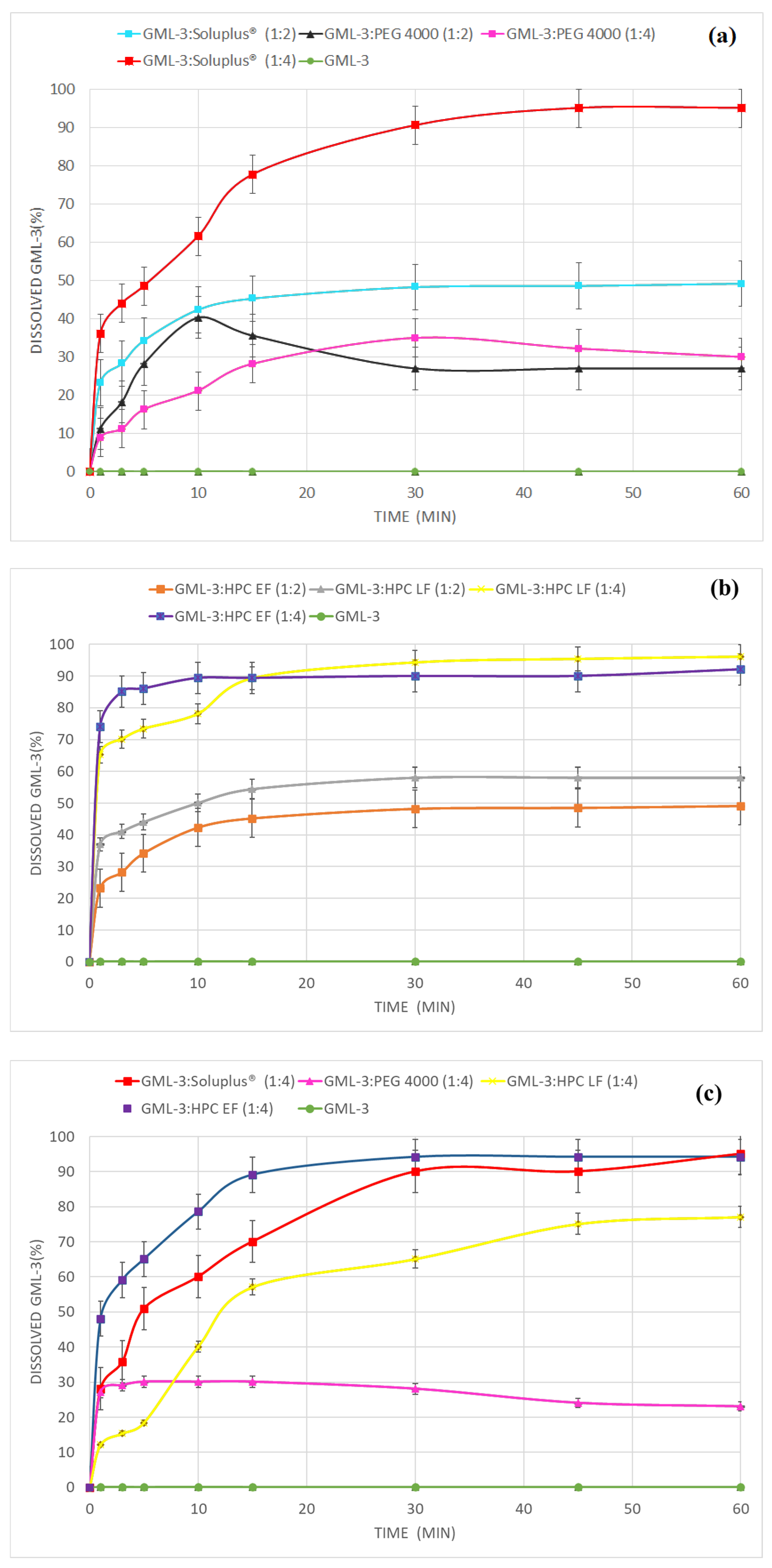
3.5. Comparative Dissolution Kinetics of SD GML-3:PEG, ASD GML-3:Soluplus® and ASD GML-3:HPC
3.6. Comparative Dissolution Kinetics of SD GML-3:PEG, ASD GML-3:Soluplus® and ASD GML-3:HPC After Storage Under High Humidity Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saberi, A.; Kouhjani, M.; Yari, D.; Jahani, A.; Asare-Addo, K.; Kamali, H.; Nokhodchi, A. Development, recent advances, and updates in binary, ternary co-amorphous systems, and ternary solid dispersions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Mitra, B.; Jain, U.; Gong, Y.; Agrawa, A.; Karki, S.; Taylor, L.S.; Kumar, S.; Zhou, Q. Pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersion: A review of manufacturing strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2505–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AL-Japairai, K.; Almurisi, S.H.; Mahmood, S.; Madheswaran, T.; Chatterjee, B.; Sri, P.; Ahmad Mazlan, N.A.B.; Hagbani, T.A.; Alheibshy, F. Strategies to improve the stability of amorphous solid dispersions in view of the hot melt extrusion (HME) method. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 647, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, A.S.-C.; Waterman, K.C.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Cai, T.; Zhang, X. Accelerated stability modeling of recrystallization from amorphous solid Dispersions: A Griseofulvin/HPMC-AS case study. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulkarim, V.; Sharma, P.K.; Gumbleton, M. Self-emulsifying drug delivery system: Mucus permeation and innovative quantification technologies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 142, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaan, I.; Frenning, G. A new modelling approach for dissolution of polydisperse powders. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 633, 122626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.A.; Williams, R.O., III. Specific mechanical energy—An essential parameter in the processing of amorphous solid dispersions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaujia, P.; Poovizhi, P.; Ng, W.K.; Tan, R.B.H. Amorphous formulations for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement of poorly soluble APIs. Powder Technol. 2015, 285, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Pang, Z.; Qian, S.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Heng, W. Gelation Elimination and Crystallization Inhibition by Co-Amorphous Strategy for Amorphous Curcumin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Mechanistic insight into gel formation of co-amorphous resveratrol and piperine during dissolution process. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 634, 122644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cai, L.; Xue, F.; Chen, H.; Gong, J.; Du, S. Polymer-mediated and ultrasound-assisted crystallization of ropivacaine: Crystal growth and morphology modulation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 97, 106475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yan, A.; Sun, T.; Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Pan, B. Self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion: A promising platform for oral drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2024, 241, 114057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhan, J.; Ma, R.; Tian, Y. Simultaneous improvement of the physical and biological properties of starch films by incorporating steviol glycoside-based solid dispersion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 311, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, A.; Zhu, W.; Kesisoglou, F. Physiologically Based Absorption Modeling for Amorphous Solid Dispersion Formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3206–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Hao, G.; Liu, M.; Zeng, Z. Recent Progress on Crystal Nucleation of Amorphous Solid Dispersion. Cryst. Growth Des. 2024, 24, 8655–8666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Cape, J.L.; Mankani, B.R.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Shepard, K.B.; Morgen, M.M.; Taylor, L.S. Water-Induced Phase Separation of Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 4004–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Yamazoe, C.; Yasuda, Y.; Higashi, K.; Kawakami, K.; Moribe, K. Mechanism of Enhanced Nifedipine Dissolution by Polymer-Blended Solid Dispersion through Molecular-Level Characterization. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4099–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, J.A.; Nichols, B.L.B.; Mosquera-Giraldo, L.I.; Yazdi, S.T.; Taylor, L.S.; Edgar, K.J. 6-Carboxycellulose Acetate Butyrate: Effectiveness as an Amorphous Solid Dispersion Polymer. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 4589–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Harris, M.T.; Taylor, L.S. Time-Resolved SAXS/WAXS Study of the Phase Behavior and Microstructural Evolution of Drug/PEG Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Taylor, L.S.; Harris, M.T. Evaluation of the Microstructure of Semicrystalline Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Harris, M.T.; Taylor, L.S. Modification of Crystallization Behavior in Drug/Polyethylene Glycol Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, S.; Oguchi, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Yamamoto, K. Improved dissolution of ofloxacin via solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 156, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBoyace, K.; Wildfong, P.L.D. The Application of Modeling and Prediction to the Formation and Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaval, M.; Dudhat, K.; Soniwala, M.; Dudhrejiya, A.; Sunny, S.; Prajapati, B. A review on stabilization mechanism of amorphous form based drug delivery system. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107411. [Google Scholar]
- Takano, R.; Maurer, R.; Jacob, L.; Stowasser, F.; Stillhart, C.; Page, S. Formulating Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Impact of Inorganic Salts on Drug Release from Tablets Containing Itraconazole-HPMC Extrudate. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, L.; Peng, D.; Tian, B. Supersaturation and phase behavior during dissolution of amorphous solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 631, 122524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajracharya, R.; Lee, S.H.; Song, J.G.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.; Han, H.-K. Development of a Ternary Solid Dispersion Formulation of LW6 to Improve the In Vivo Activity as a BCRP Inhibitor: Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Gala, U.; Chauhan, H. Classification of solid dispersions: Correlation to (i) stability and solubility (ii) preparation and characterization techniques. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.S.; Matzger, A.J. Effect of Polymer Hydrophobicity on the Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions and Supersaturated Solutions of a Hydrophobic Pharmaceutical. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, C.; Guan, X.; Yuan, D. The solid dispersion of resveratrol with enhanced dissolution and good system physical stability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 84, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of Temperature and Moisture on the Physical Stability of Binary and Ternary Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Celecoxib. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrov, G.V.; Deeva, O.A.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Yarkov, S.A.; Yarkova, M.A.; Seredenin, S.B. Design, synthesis and anxiolytic-like activity of 1-arylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3368–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarkov, S.A.; Mokrov, G.V.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Yarkova, M.A.; Seredenin, S.B. Pharmacological study of new compounds acting as regulators of 18-kDa translocator protein ligands. Eksp. Klin. Farmakol. 2016, 79, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yarkova, M.A.; Mokrov, G.V.; Gudasheva, T.A.; Seredenin, S.B. Anxiolytic activity of original pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine derivatives (TSPO ligands) depends on neurosteroid biosynthesis. Pharm. Chem. J. 2016, 50, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markeev, V.B.; Blynskaya, E.V.; Tishkov, S.V.; Alekseev, K.V.; Marakhova, A.I.; Vetcher, A.A.; Shishonin, A.Y. Composites of N-butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide with Polymers: Effect of Crystallinity on Solubility and Stability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.G.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Moisture sorption by polymeric excipients commonly used in amorphous solid dispersion and its effect on glass transition temperature: I. Polyvinylpyrrolidone and related copolymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, V.; Hu, Y.; Tajber, L.; Erxleben, A.; Corrigan, O.I.; McArdle, P.; Healy, A.M. Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Sulfonamide/Soluplus® and Sulfonamide/PVP Prepared by Ball Milling. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E794-06; Standard Test Method for Melting And Crystallization Temperatures by Thermal Analysis. ASTM International: Barr Harbor Drive, PA, USA, 2018.
- ISO 11357-1; Plastics—Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). International Organization for Standardization, ISO Central Secretariat: Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markeev, V.B.; Tishkov, S.V.; Vorobei, A.M.; Parenago, O.O.; Blynskaya, E.V.; Alekseev, K.V.; Marakhova, A.I.; Vetcher, A.A. Modeling of the Aqueous Solubility of N-butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide: From Micronization to Creation of Amorphous–Crystalline Composites with a Polymer. Polymers 2023, 15, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Khanh, H.P.; Haimhoffer, Á.; Nemes, D.; Józsa, L.; Vasvári, G.; Budai, I.; Bényei, A.; Ujhelyi, Z.; Fehér, P.; Bácskay, I. Effect of Molecular Weight on the Dissolution Profiles of PEG Solid Dispersions Containing Ketoprofen. Polymers 2023, 15, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hecke, E.; Benali, M. Solid dispersions of quercetin-PEG matrices: Miscibility prediction, preparation and characterization. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bley, H.; Fussnegger, B.; Bodmeier, R. Characterization and stability of solid dispersions based on PEG/polymer blends. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 390, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.G.; Banella, S.; Serajuddin, A.T.M. Moisture Sorption by Polymeric Excipients Commonly Used in Amorphous Solid Dispersions and its Effect on Glass Transition Temperature: II. Cellulosic Polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 3114–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbert, C.; Stoyanov, E.; Sadowski, G. Phase behavior of ASDs based on hydroxypropyl cellulose. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseson, D.E.; Tran, T.B.; Karunakaran, B.; Ambardekar, R.; Hiew, T.N. Trends in amorphous solid dispersion drug products approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration between 2012 and 2023. Int. J. Pharm. X 2024, 7, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkov, V.; Vinarov, Z.; Tcholakova, S. Mechanisms of dissolution and crystallization of amorphous glibenclamide. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, R.; Kim, D.W.; Ud Din, F.; Mustapha, O.; Yousaf, A.M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.-G. Effect of hydroxypropylcellulose and Tween 80 on physicochemical properties and bioavailability of ezetimibe-loaded solid dispersion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Prezotti, F.; Araujo, F.; Lopes, C.; Loureiro, A.; Marques, S.; Sarmento, B. Third-generation solid dispersion combining Soluplus and poloxamer 407 enhances the oral bioavailability of resveratrol. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 595, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, S.; Djuris, J.; Dapcevic, A.; Medarevic, D.; Ibric, S.; Zizovic, I. Soluplus®, Eudragit®, HPMC-AS foams and solid dispersions for enhancement of Carvedilol dissolution rate prepared by a supercritical CO2 process. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Rehman, I.U.; Darr, J.A. Characterization and drug release investigation of amorphous drug–hydroxypropyl methylcellulose composites made via supercritical carbon dioxide assisted impregnation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| SD | k (min−n) | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GML-3:Soluplus® (1:4) | 0.358 | 0.253 | 0.998 |
| GML-3:HPC LF (1:4) | 0.627 | 0.111 | 0.980 |
| GML-3:HPC EF (1:4) | 0.842 | 0.205 | 0.995 |
| GML-3:Soluplus® (1:4) after 3 weeks (40 °C and 75%RH) | 0.350 | 0.253 | 0.998 |
| GML-3:HPC LF (1:4) after 3 weeks (40 °C and 75%RH) | 0.155 | 0.406 | 0.995 |
| GML-3:HPC EF (1:4) after 3 weeks (40 °C and 75%RH) | 0.576 | 0.131 | 0.962 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markeev, V.B.; Blynskaya, E.V.; Alekseev, K.V.; Dorofeev, V.L.; Marakhova, A.I.; Vetcher, A.A. Creation of Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions N-Butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide, Resistant to Recrystallization Caused by Exposure to Moisture. Materials 2025, 18, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010203
Markeev VB, Blynskaya EV, Alekseev KV, Dorofeev VL, Marakhova AI, Vetcher AA. Creation of Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions N-Butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide, Resistant to Recrystallization Caused by Exposure to Moisture. Materials. 2025; 18(1):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010203
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkeev, Vladimir B., Evgenia V. Blynskaya, Konstantin V. Alekseev, Vladimir L. Dorofeev, Anna I. Marakhova, and Alexandre A. Vetcher. 2025. "Creation of Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions N-Butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide, Resistant to Recrystallization Caused by Exposure to Moisture" Materials 18, no. 1: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010203
APA StyleMarkeev, V. B., Blynskaya, E. V., Alekseev, K. V., Dorofeev, V. L., Marakhova, A. I., & Vetcher, A. A. (2025). Creation of Long-Term Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions N-Butyl-N-methyl-1-phenylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-3-carboxamide, Resistant to Recrystallization Caused by Exposure to Moisture. Materials, 18(1), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010203







