Evaluation of the Microstructure and Properties of As-Cast Magnesium Alloys with 9% Al and 9% Zn Additions
Abstract
1. Introduction
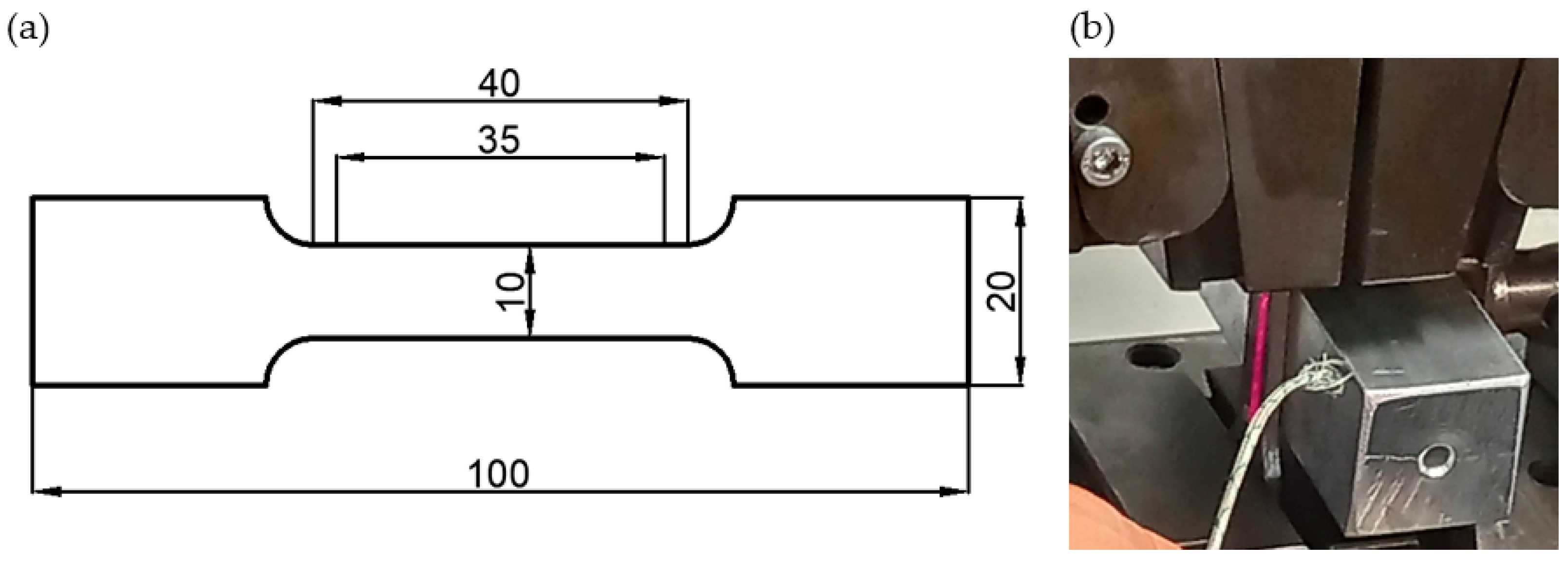
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
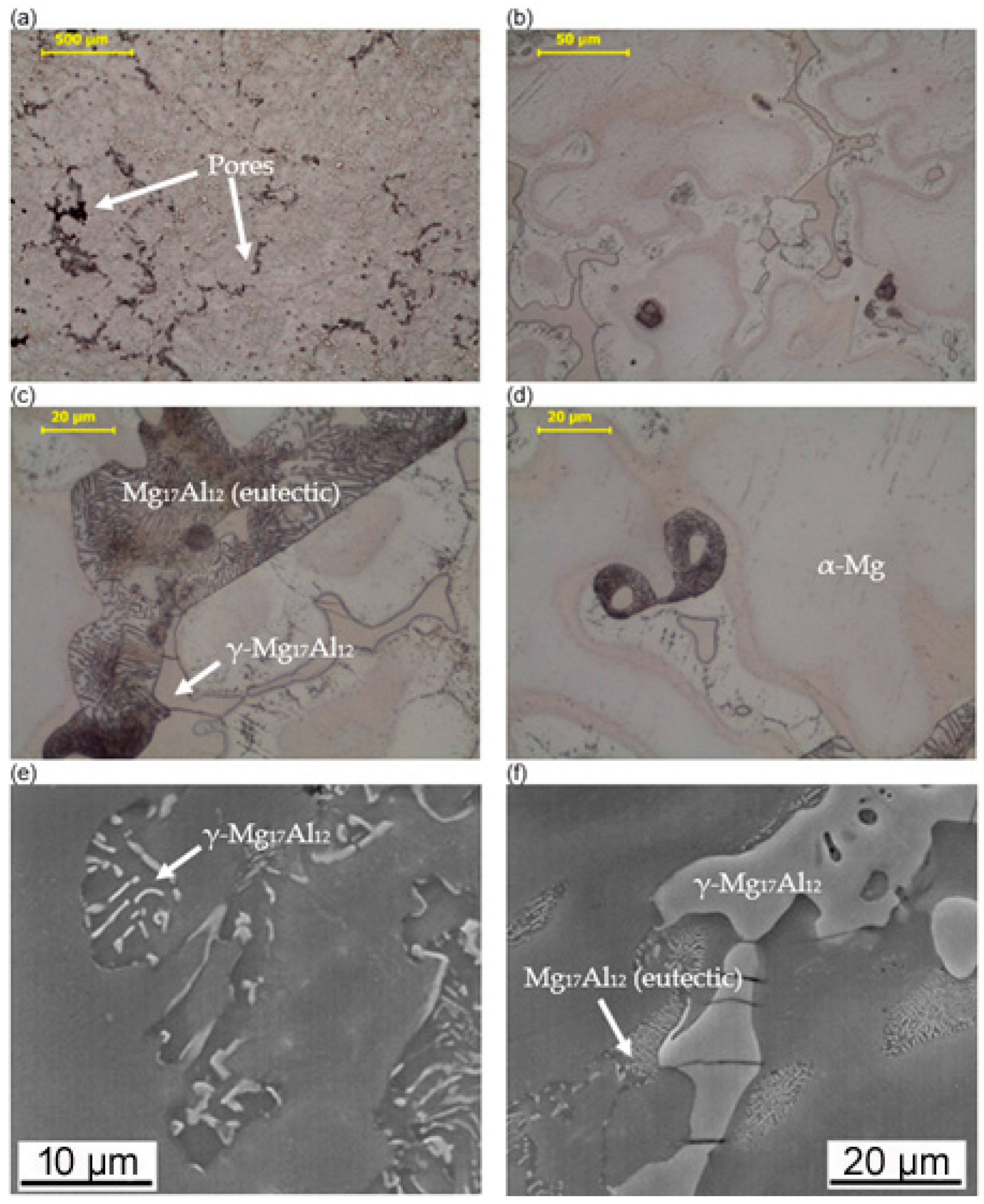
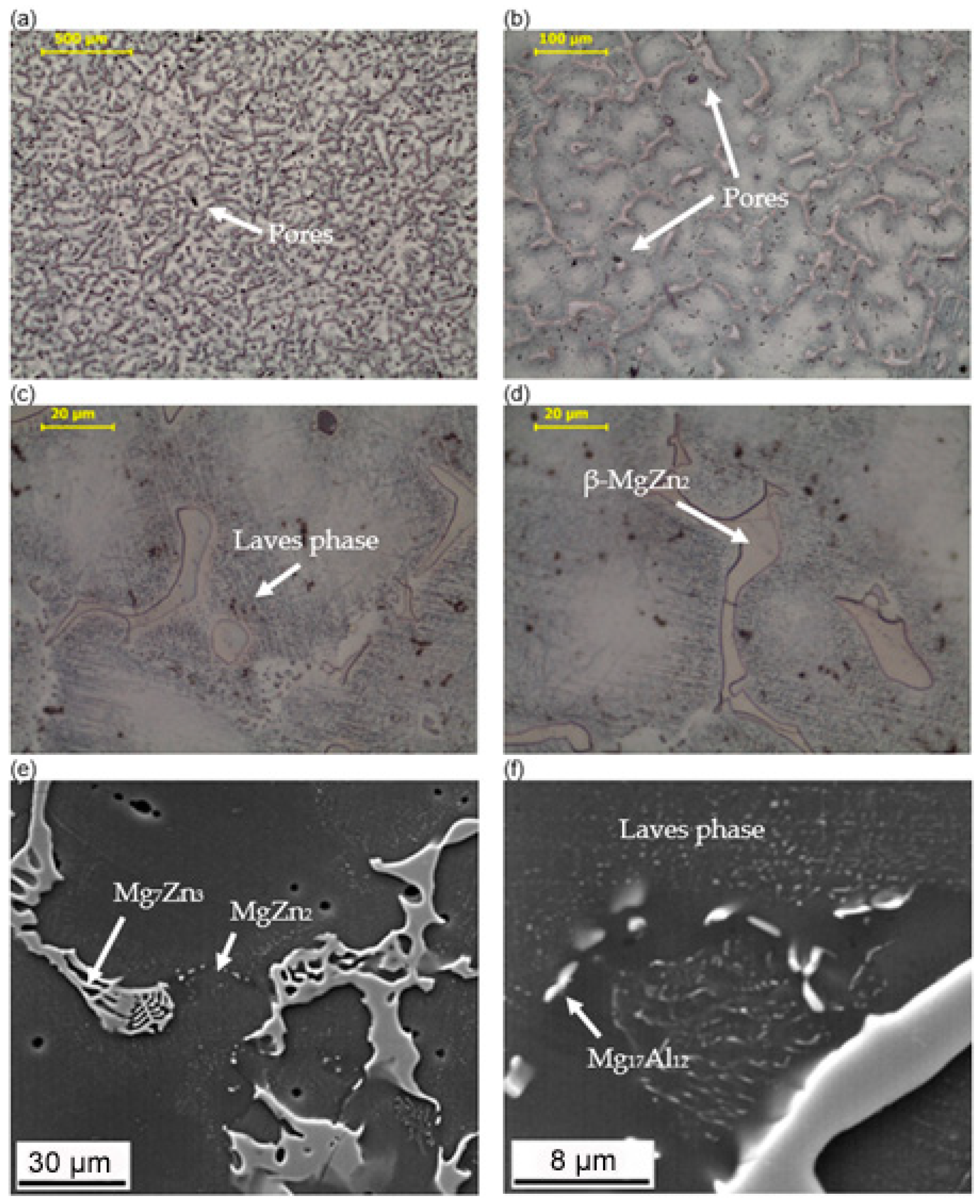
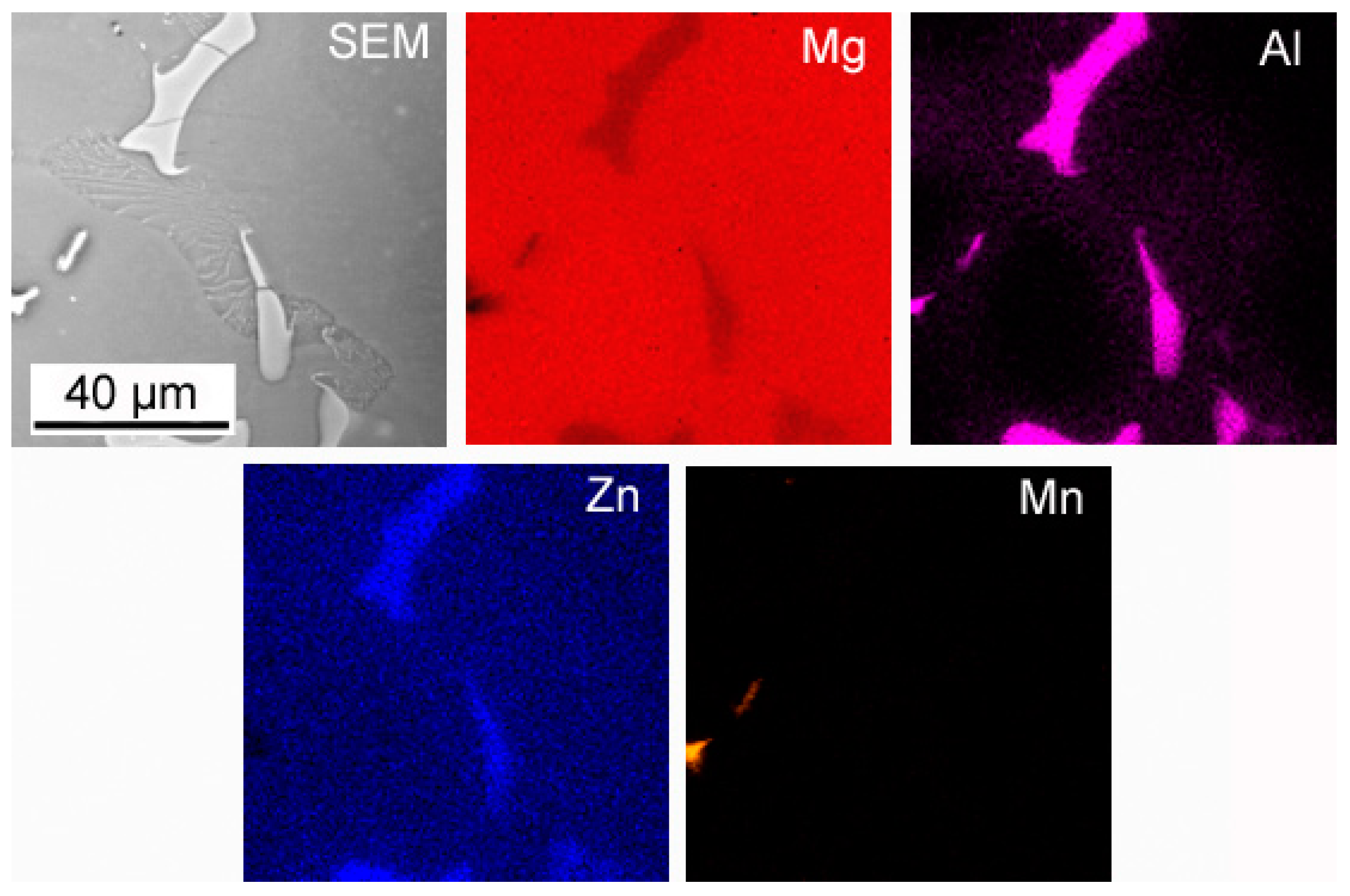
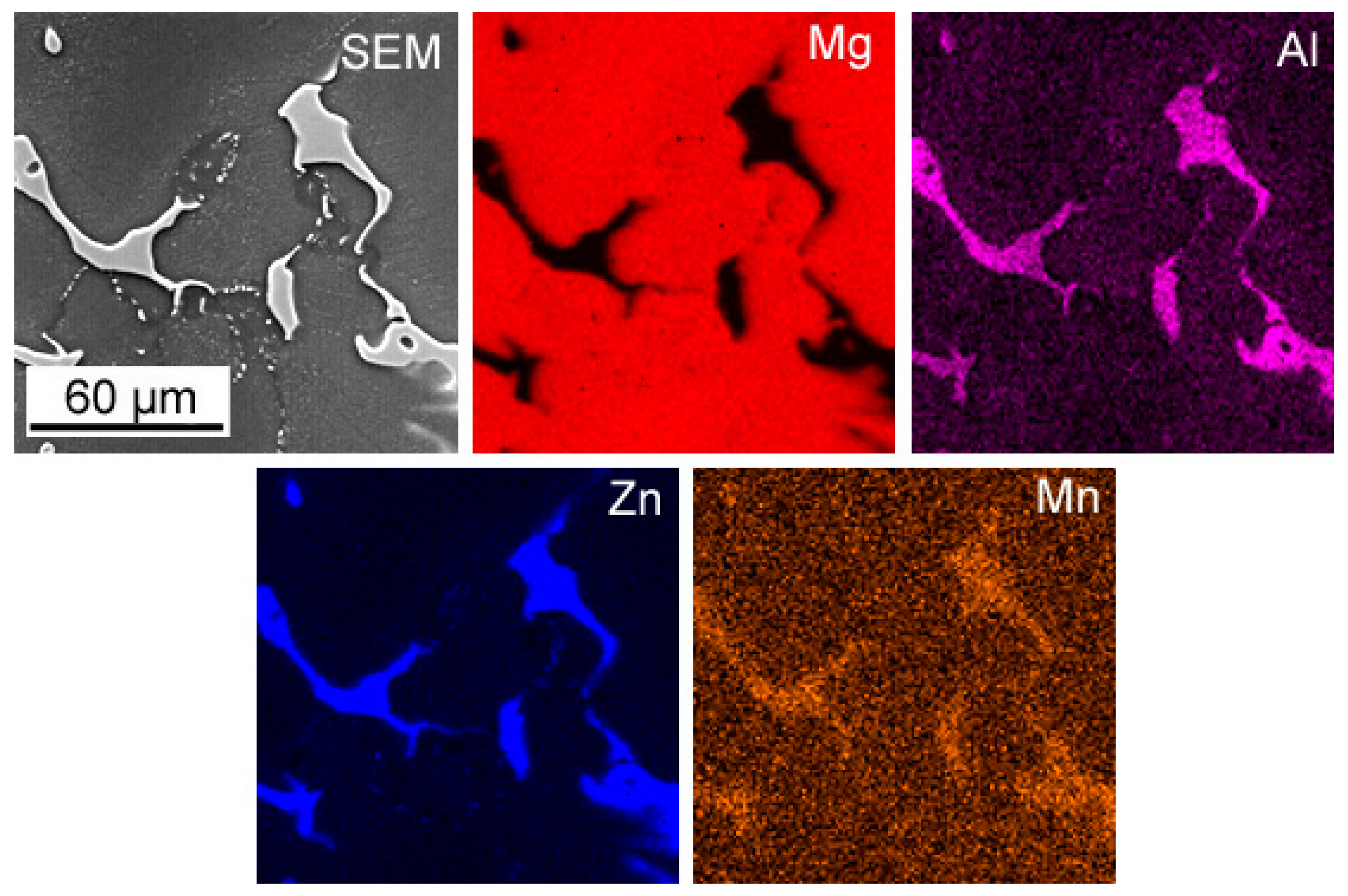
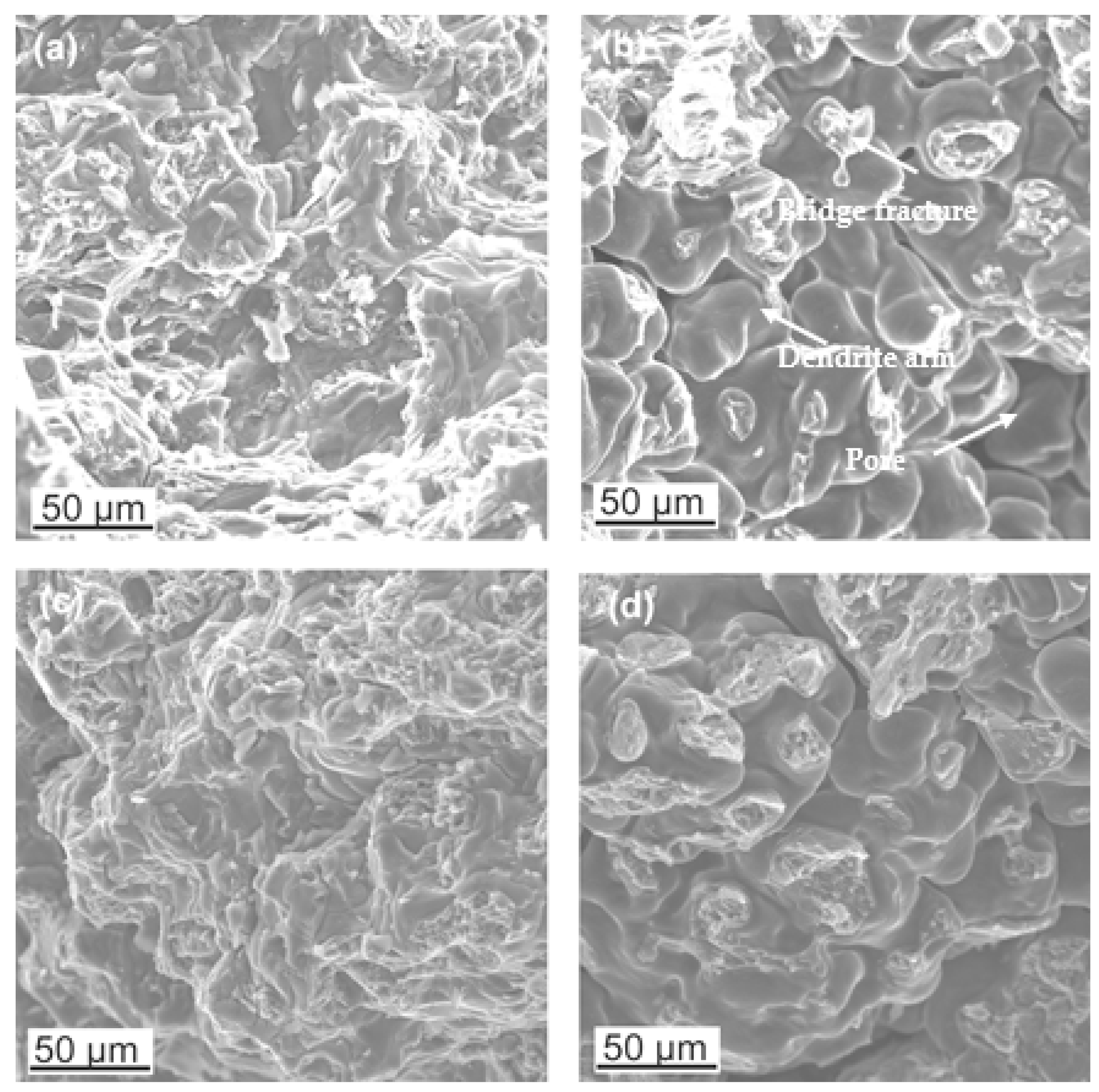
3.1. Microstructure Analysis
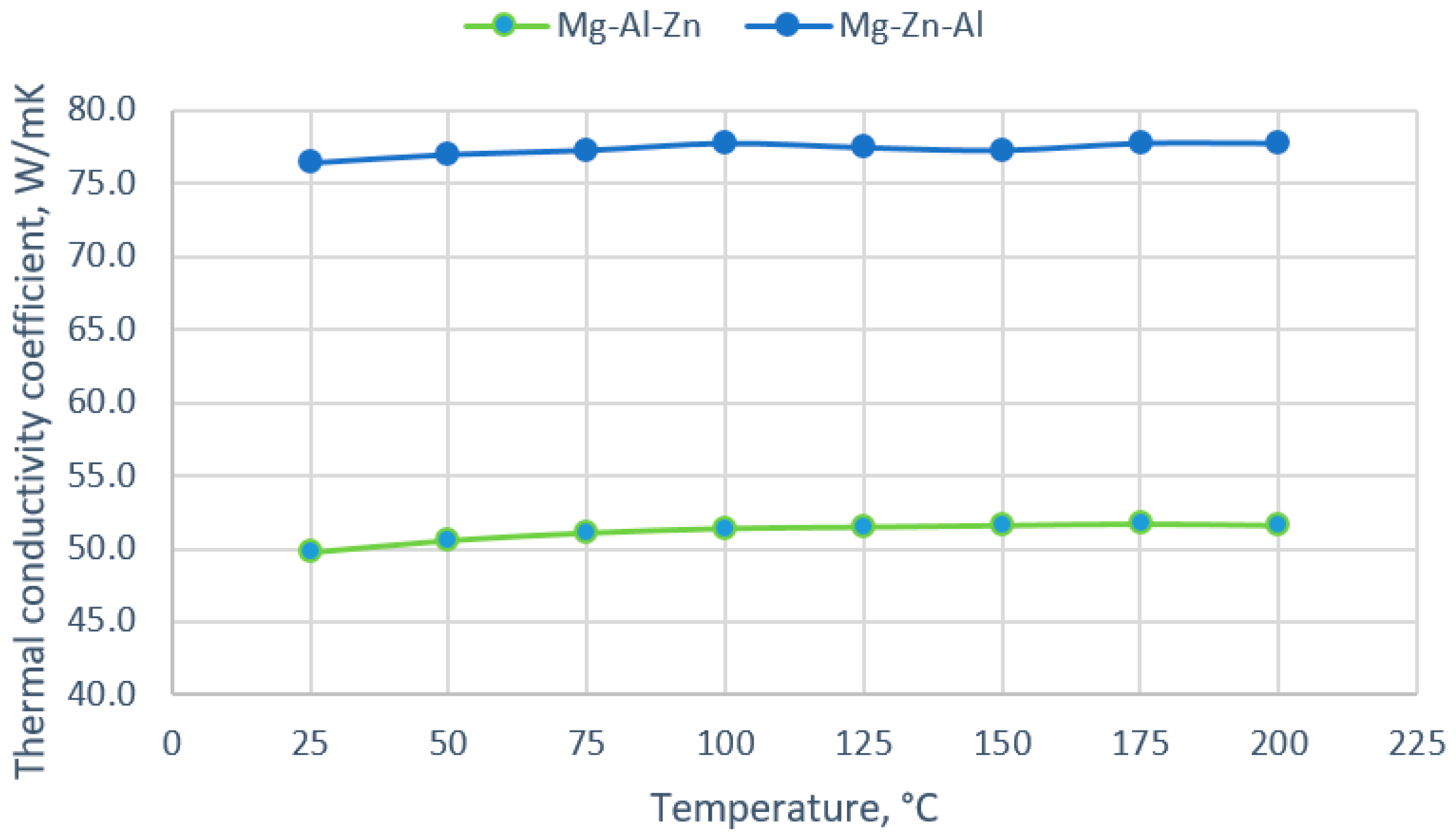
3.2. Thermal Conductivity Coefficient
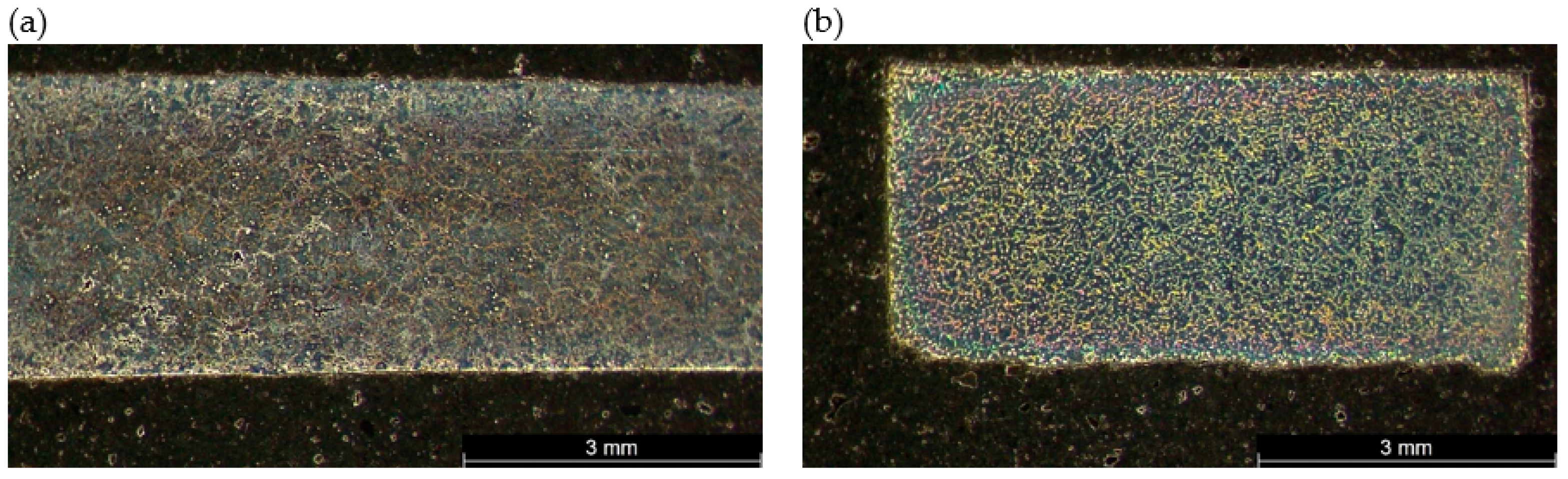
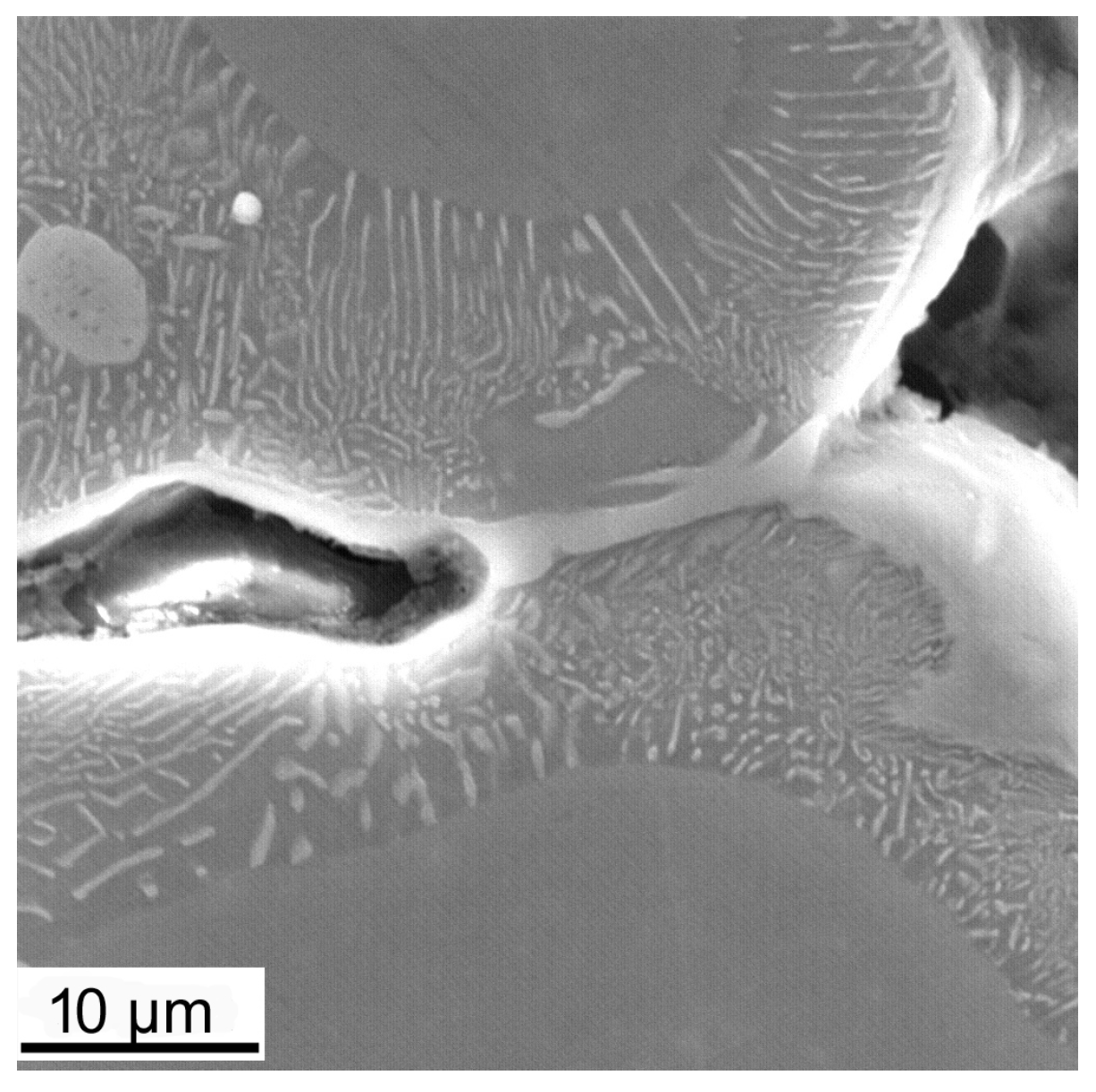
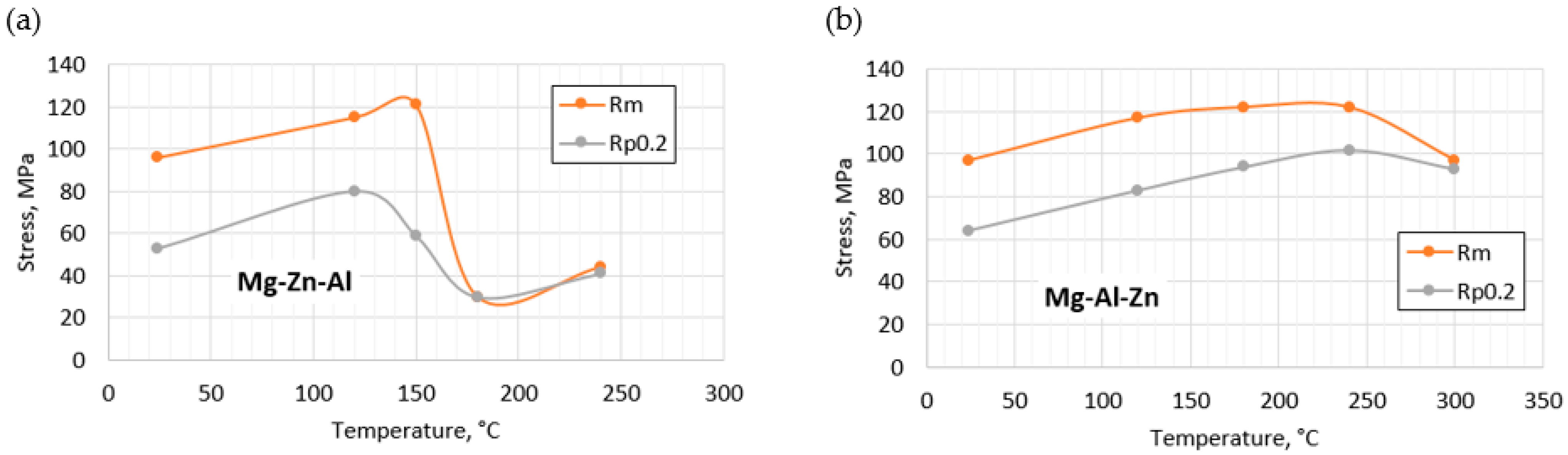
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Both alloy castings, with the addition of 9% Al and 9% Zn, have a dendritic structure, where the alloying components occur mainly in the interdendritic areas. In the interdendritic areas, mainly the γ-Mg17Al12 phase and the Laves β-MgZn2 phase occur. The presence of impurities in the alloy also promotes the formation of other intermetallic phases of a dispersive nature, which can be found both in the matrix and in the interdendritic areas. The presence of low-melting phases increases the hot-cracking susceptibility of both alloys. To avoid hot cracking it is necessary to use the preheating and low cooling rate. The preheating temperature should be in the range of the highest mechanical properties range.
- (2)
- With increasing temperature to 200 °C, the thermal conductivity coefficient does not change significantly and is approximately 50 W/mK for the Mg-9Al-1Zn alloy and 77 W/mK for the Mg-9Zn-1Al alloy.
- (3)
- With an increase in temperature, the initial tensile strength increases to 120 MPa at 150 °C for 9% Zn and 180–240 °C for 9% Al. A further increase in temperature causes a gradual decrease in the yield and tensile strength. The relatively low tensile strength of the Mg alloy with 9% Al is due to the presence of internal discontinuities in the material too.
- (4)
- The Mg alloy with 9% Al is characterized by a higher hardness (83 HV10) in the as-cast state compared to the alloy with 9% Zn (46 HV10). The difference in hardness is the effect of the structure of the alloy, where aluminum, in addition to occurring in intermetallic and eutectic phases, also causes the strengthening of the matrix, and zinc forms finely dispersed precipitates.
6. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, X.; Yi, S. Deformation Mechanisms of Magnesium Alloys with Rare-Earth and Zinc Additions under Plane Strain Compression. Materials 2024, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z. Prediction of Mechanical Properties of Rare-Earth Magnesium Alloys Based on Convolutional Neural Networks. Materials 2024, 17, 4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Gajević, S.; Sharma, L.K.; Pradhan, R.; Miladinović, S.; Ašonja, A.; Stojanović, B. Magnesium-Titanium Alloys: A Promising Solution for Biodegradable Biomedical Implants. Materials 2024, 17, 5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Lü, S.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Guo, G.; Guo, W.; Wu, S. Effects of Mg17Al12 phase on microstructure evolution and ductility in the AZ91 magnesium alloy during the continuous rheo-squeeze casting-extrusion process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 191, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashoufi, K.; Garmroodi, P.; Mirzakhani, A.; Assempour, A. Cyclic contraction-expansion extrusion (CCEE): An innovate severe plastic deformation method for tailoring the microstructure and mechanical properties of magnesium AZ91 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 8541–8554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Ma, Z.; Han, X.; Hu, X.; Chang, Z.; Zhou, J. Effect of strain rates on mechanical behavior, microstructure evolution and failure mechanism of extruded-annealed AZ91 magnesium alloy under room-temperature tension. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 4644–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yan, F.; Sun, J.; Xing, W.; Li, S. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Extruded AZ80 Magnesium Alloy during Room Temperature Multidirectional Forging Based on Twin Deformation Mode. Materials 2024, 17, 5055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, R.; Hossain, I.; Mohanavel, V.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Alharbi, S.A.; Al Obaid, S. Analysis and optimization of machining parameters of AZ91 alloy nanocomposite with the Influences of nano ZrO2 through vacuum diecast process. Heliyon 2024, 10, e34931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, T.O.; Sudin, I.; Alsakkaf, A.; Idris, J.; Fadil, N.A. Effect of homogenization heat treatment on the microstructure of AZ91 magnesium alloy at different temperatures and ageing times. J. Eng. Res. 2023, 11, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Chaubey, A.; Sahoo, R.; Kushwaha, A.; Basu, A.; Majhi, J.; Gupta, M. Influence of ultrasonic shot peening on the microstructure and impression creep performance of squeeze-cast AZ91 alloy reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 938, 168640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, S.; Bohlen, J.; Dieringa, H. Influence of recycled carbon fiber addition on the microstructure and creep response of extruded AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 2518–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavallian, P.; Rabiee, S.M.; Aval, H.J. Effect of solution treatment of AZ91 alloy on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of friction stir back extruded AZ91/bioactive glass composite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 6992–7007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.-X.; Hu, M.-L.; Ji, Z.-S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, H.-Y. Effect of La/Nd ratio on microstructure and tensile properties of AZ91-RE alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2024, 34, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, B.; Chen, X.; Zheng, K.; Pan, F. Influence of Ti particle sizes on microstructure and mechanical behaviors of AZ91-Ti composites under different loading paths. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 886, 145723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, M.; Aval, H.J. Effect of friction stir back extrusion rotational speed on microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion behaviour of AZ91-Ca alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 4441–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motavallian, P.; Rabiee, S.M.; Aval, H.J. Investigation of microstructure and corrosion behavior of AZ91/64SiO2-31CaO-5P2O5 composite wire fabricated by friction stir back extrusion. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 464, 129451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Marodkar, A.; Ghosh, A.; Borkar, H. Effect of Ca addition on the microstructure and creep behaviour of AZ91 Mg alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Xiao, M.; Liu, F.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hybrid hexagonal BN nanotube and nanoplatelet reinforced AZ91 Mg matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Gao, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Gupta, M. Improving wear and corrosion resistances of Mg2Si/AZ91 composites via tailoring microstructure and intrinsic properties of Mg2Si induced by Sb modification. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, S.; Branislav, H.; Martina, J.; Jana, P. Microstructure evolution and corrosion mechanism of AZ91 magnesium alloy in chloride environments for commercial purposes prepared by Ohno continuous casting. Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 74, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabestari, S.G.; Ghaniabadi, E. Effect of Ca and rotation speed on microstructure and solidification parameters of AZ91 magnesium alloy produced by semi-solid casting through rotating container process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2023, 33, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, X.; Huang, G.; Zheng, K.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Microstructures and the improved mechanical properties of AZ91 alloy by incorporating Ti-6Al-4V particles. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 7340–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, T.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X. Effect of hard-plate rolling and annealing treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of NbB2 particle-reinforced AZ91 composite. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-L.; Deng, K.-K.; Nie, K.-B.; Wang, C.-J.; Xu, C.; Shi, Q.-X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of freeze-casted in-situ ABOw@Al2O3/AZ91 composites. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 42015–42025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.-Q.; Deng, K.-K.; Nie, K.-B.; Wang, C.-J.; Xu, C.; Shi, Q.-X. Preparation, microstructure, and mechanical properties of SiCp/AZ91 magnesium matrix laminar material. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 891, 145977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojanová, Z.; Gärtnerová, V.; Jäger, A.; Námešný, A.; Chalupová, M.; Palček, P.; Lukáč, P. Mechanical and fracture properties of an AZ91 Magnesium alloy reinforced by Si and SiC particles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Shen, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy fabricated by multi-layer and multi-pass CMT based WAAM technique. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Bharath, R.R.; Atrens, A.; Srinivasan, P.B. Microstructure and mechanical properties of welds of AZ31B magnesium alloy produced by different gas tungsten arc welding variants. Def. Technol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braszczyńska-Malik, K.; Mróz, M. Gas-tungsten arc welding of AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 9951–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, B.R.; Reddy, G.P.K.; Mounika, A.; Sree, P.N.; Pinneswari, P.R.; Ambica, I.; Babu, R.A.; Amarnadh, P. Joining of AZ31 and AZ91 Mg alloys by friction stir welding. J. Magnes. Alloys 2015, 3, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Vigneshwar, M.; Selvamani, S.; Prakash, A.; Hariprasath, P. The Comparative Analysis on Friction Stir Welded and Gas Tungsten Arc Welded AZ91 Grade Magnesium Alloy Butt Joints. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 6688–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuz, L.; Kołodziejczak, P.; Kolasa, A. Structure of butt joint of as-cast magnesium alloys. Weld. Int. 2015, 30, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, A.; Delavar, H.; Sedighi, M. Microstructure and surface integrity of machined AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha Chowdary, V.; Ravikumar, D.; Anand Kumar, S.; Kondaiah, V.V.; Ratna Sunil, B. Influence of heat treatment on the machinability and corrosion behavior of AZ91 Mg alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marakini, V.; Srinivasa Pai, P.; D’Mello, G. Effect of liquid nitrogen assisted milling on AZ91 magnesium alloy. Results Eng. 2024, 22, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marodkar, A.S.; Patil, H.; Chavhan, J.; Borkar, H. Effect of gravity die casting, squeeze casting and extrusion on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, W.; Zeng, X.; Zhu, Y. Fracture behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Lett. 2000, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovík, J.; Kajánek, D.; Pastorek, F.; Štrbák, M.; Florková, Z.; Jambor, M.; Hadzima, B. The Effect of Mechanical Pretreatment on the Electrochemical Characteristics of PEO Coatings Prepared on Magnesium Alloy AZ80. Materials 2023, 16, 5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM E1461-13; Standard Test Method for Thermal Diffusivity by the Flash Method. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- Alrasheedi, N.H.; Ataya, S.; Seleman, M.M.E.-S.; Ahmed, M.M.Z. Tensile Deformation and Fracture of Unreinforced AZ91 and Reinforced AZ91-C at Temperatures up to 300 °C. Materials 2023, 16, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Sheng, D.; Fang, Y.; Xiong, K.; Song, Y. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Tensile and Failure Response of Multiple-Hole-Fiber-Reinforced Magnesium Alloy Laminates under Various Temperature Environments. Materials 2023, 16, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Alloy | Al | Zn | Mn | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-Zn | 8.62 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0.36 |
| Mg-Zn-Al | 0.87 | 9.24 | 0.34 | 0.42 |
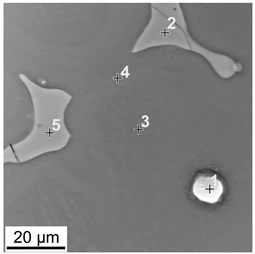 | No. | Zn | Al | Mn |
| 1 | 0.7 | 32.8 | 50.3 | |
| 2 | 3.3 | 35.2 | 0.01 | |
| 3 | 0.3 | 2.9 | 0.05 | |
| 4 | 0.6 | 6.6 | 0.01 | |
| 5 | 0.8 | 36.7 | 0.02 |
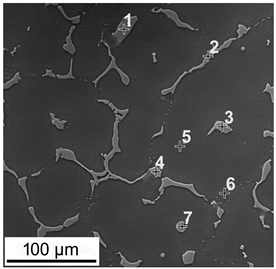 | No. | Zn | Al | Mn |
| 1 | 64.1 | 13.4 | 0.02 | |
| 2 | 55.9 | 11.1 | 0.25 | |
| 3 | 63.1 | 8.8 | 0.08 | |
| 4 | 64.8 | 8.0 | 0.00 | |
| 5 | 5.4 | 1.3 | 0.05 | |
| 6 | 5.9 | 1.6 | 0.01 | |
| 7 | 47.3 | 4.9 | 0.03 |
| Temperature, °C | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast Mg-Al-Zn | 49.8 | 50.6 | 51.1 | 51.4 | 51.5 | 51.6 | 51.7 | 51.6 |
| As-cast Mg-Zn-Al | 76.4 | 77.0 | 77.3 | 77.8 | 77.5 | 77.3 | 77.8 | 77.8 |
| Temperature, °C | Mg-Zn-Al | Mg-Al-Zn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No | Rp0.2, MPa | Rm, MPa | A, % | Sample No | Rp0.2, MPa | Rm, MPa | A, % | |
| 24 | L2 | 53 | 96 | 0.20 | 92 | 64 | 97 | 1.15 |
| 120 | L3 | 80 | 115 | 0.38 | 93 | 83 | 117 | 0.98 |
| 150 | L6 | 59 | 121 | 0.48 | 94 | 94 | 122 | 0.94 |
| 180 | L4 | 30 | 31 | 2.10 | 95 | 102 | 122 | 0.79 |
| 240 | L5 | 41 | 44 | 1.67 | 96 | 93 | 97 | 0.38 |
| Alloy | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-Zn | 82 | 84 | 83 | 82 | 83 | 83 |
| Mg-Zn-Al | 44 | 46 | 46 | 47 | 45 | 46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuz, L.; Novák, V.; Tatíček, F. Evaluation of the Microstructure and Properties of As-Cast Magnesium Alloys with 9% Al and 9% Zn Additions. Materials 2025, 18, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010010
Tuz L, Novák V, Tatíček F. Evaluation of the Microstructure and Properties of As-Cast Magnesium Alloys with 9% Al and 9% Zn Additions. Materials. 2025; 18(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuz, Lechosław, Vít Novák, and František Tatíček. 2025. "Evaluation of the Microstructure and Properties of As-Cast Magnesium Alloys with 9% Al and 9% Zn Additions" Materials 18, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010010
APA StyleTuz, L., Novák, V., & Tatíček, F. (2025). Evaluation of the Microstructure and Properties of As-Cast Magnesium Alloys with 9% Al and 9% Zn Additions. Materials, 18(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010010






