Incorporation of Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles into Carbon Ceramic Composite: Electrode Material with Improved Electroanalytical Performance in 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Determination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the CCEs
2.3. Apparatus
2.4. Electrochemical Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
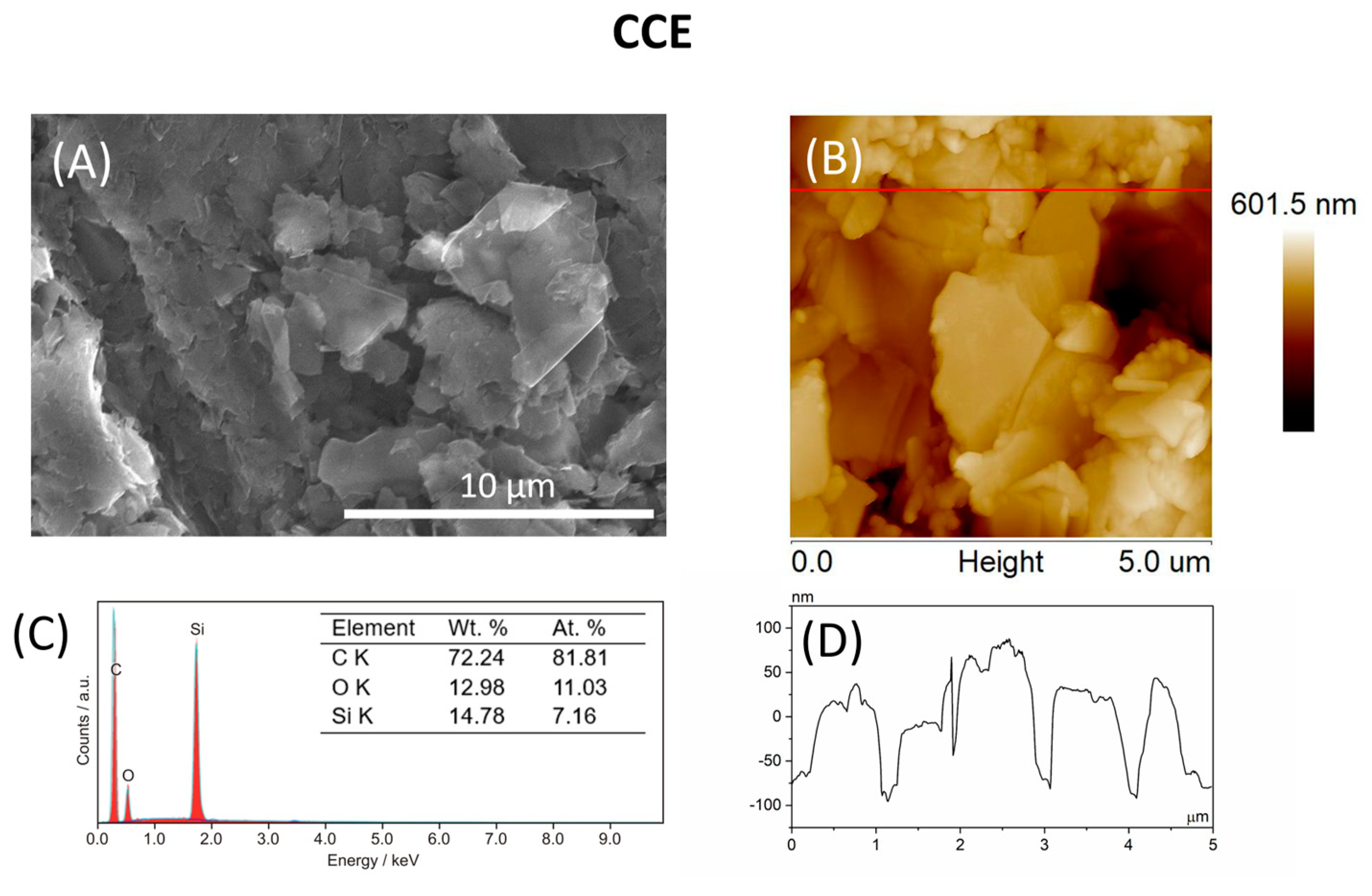
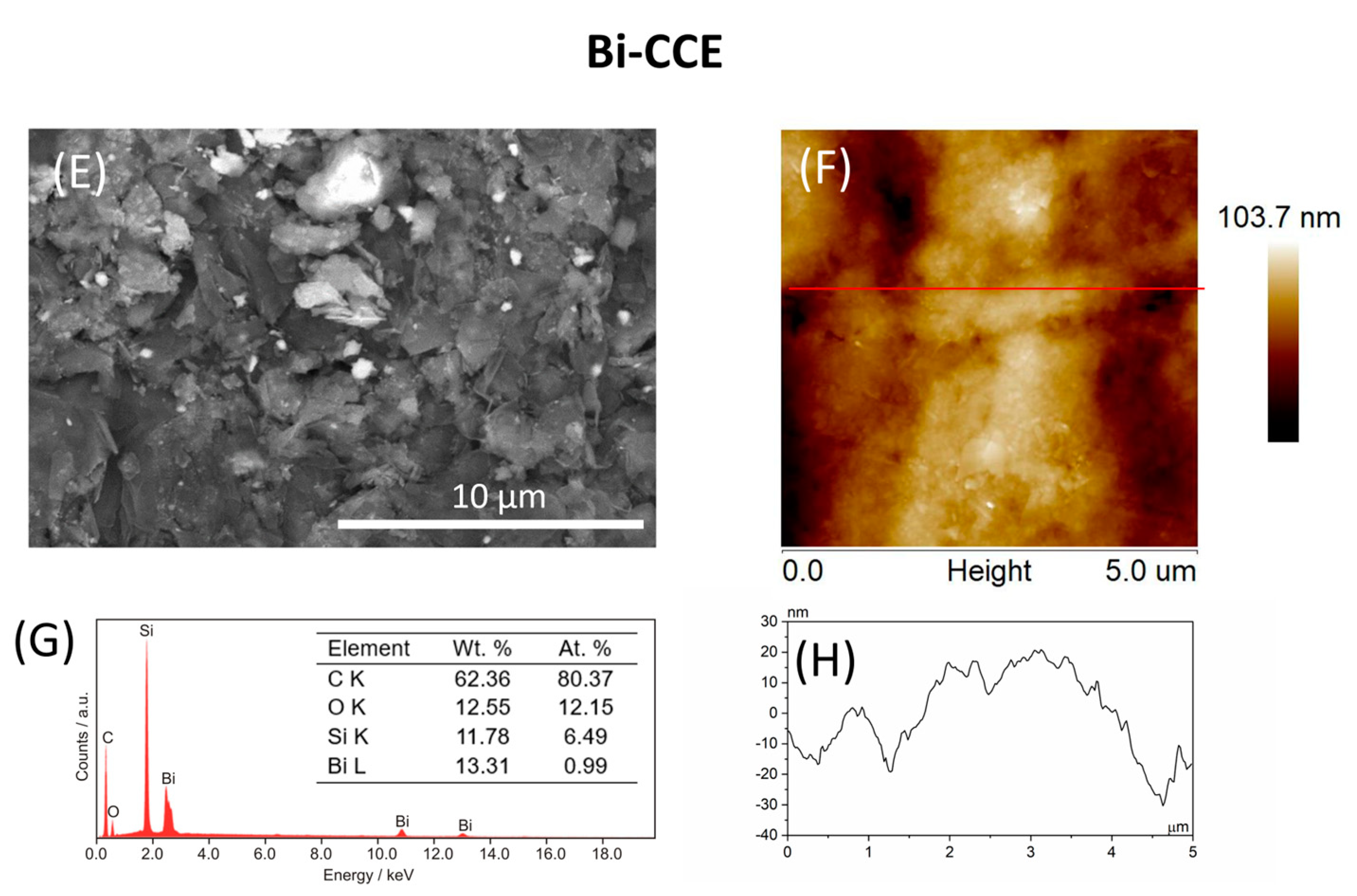
3.1. Surface Characterization of CCEs
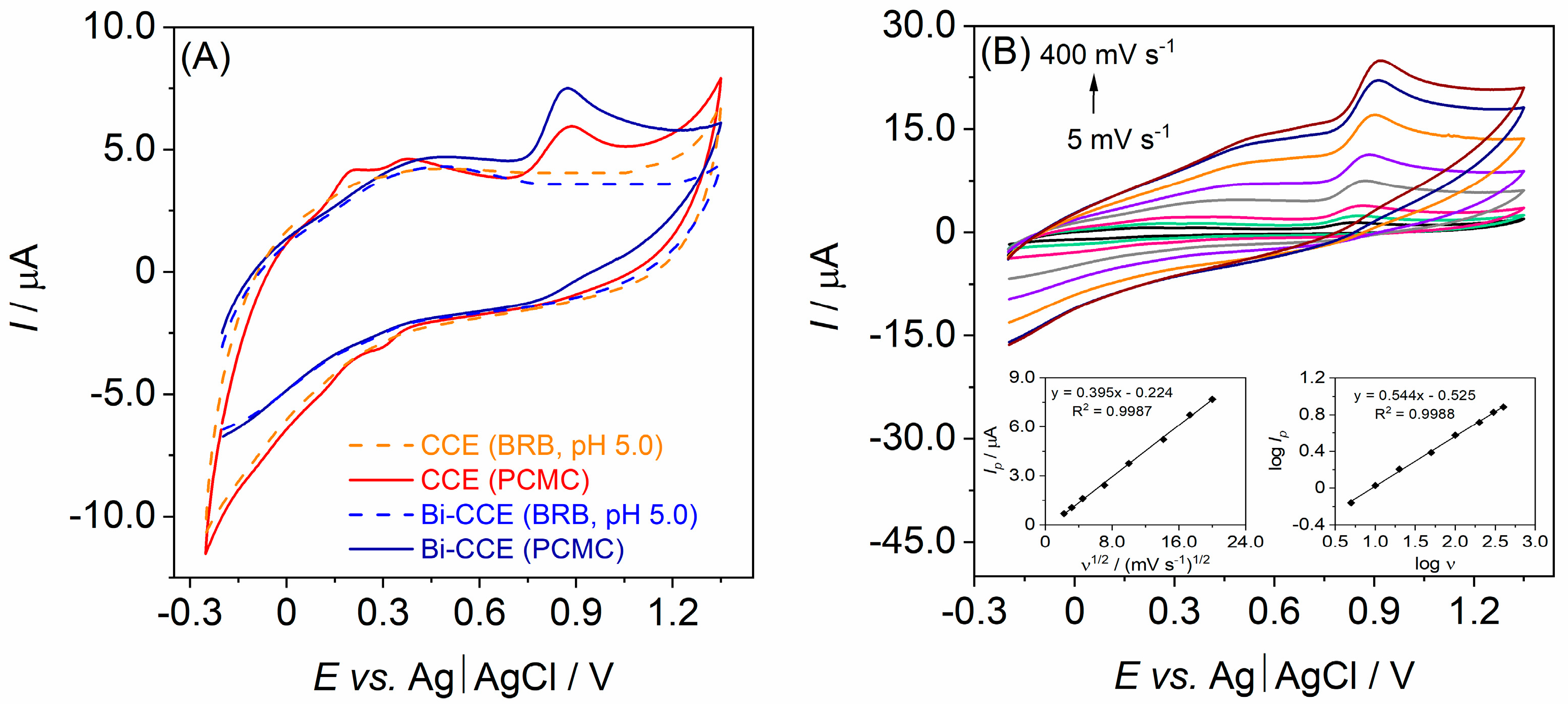
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of CCEs
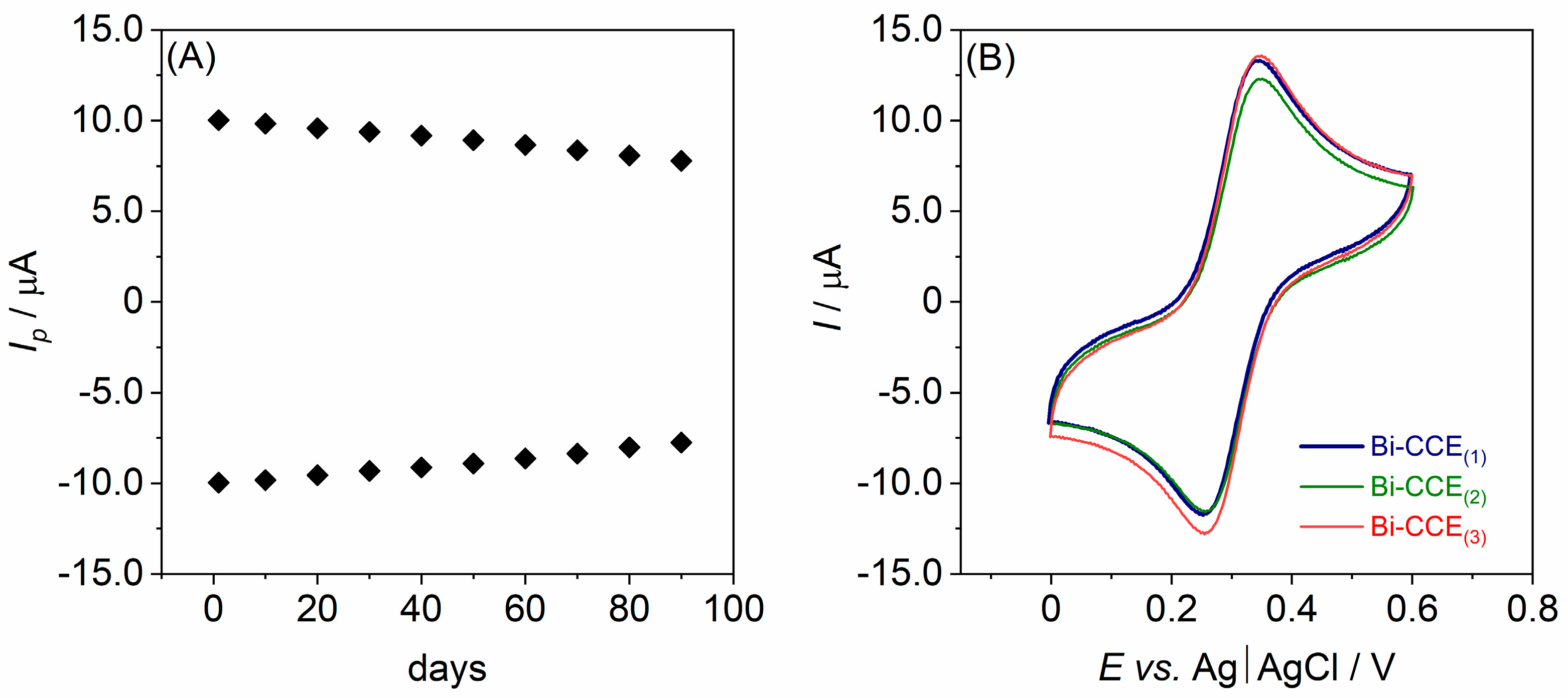
3.3. Long-Term Stability and Reproducibility Study of the Bi-CCE
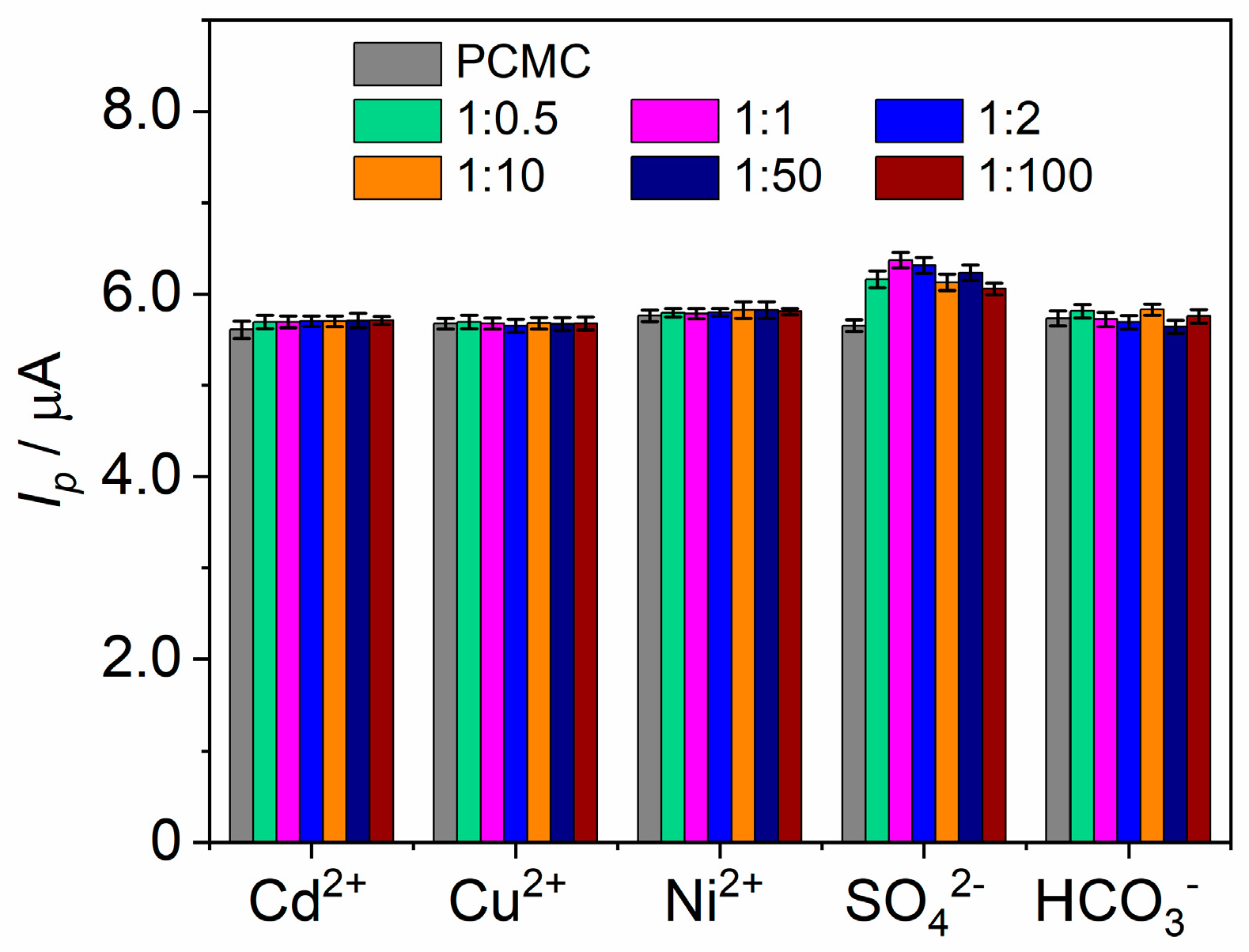
3.4. Electroanalytical Performance of the Bi-CCE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiwanti, P.K.; Wardhana, B.Y.; Sutanto, L.G.; Chanif, M.F. A Review on Carbon-Based Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensor of Quinolone Antibiotics. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202103997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghlimi, C.; Moutcine, A.; Chtaini, A.; Isaad, J.; Soufi, A.; Ziat, Y.; Amhamdi, H.; Belkhanchi, H. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors for Monitoring Drugs and Metabolites in Pharmaceutical and Biological Samples. ADMET DMPK 2023, 11, 151–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumya, W.; Taoufik, N.; Achak, M.; Barka, N. Chemically Modified Carbon-Based Electrodes for the Determination of Paracetamol in Drugs and Biological Samples. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasoň, S.; Daňhel, A.; Schwarzová-Pecková, K.; Fojta, M. Carbon Electrodes in Electrochemical Analysis of Biomolecules and Bioactive Substances: Roles of Surface Structures and Chemical Groups. In Nanotechnology and Biosensors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 51–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalkiewicz, S.; Skorupa, A.; Jakubczyk, M. Carbon Materials in Electroanalysis of Preservatives: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Siwal, S.S.; Chauhan, G.; Saini, A.K.; Kumari, A.; Thakur, V.K. Recent Advances in Electrochemical-Based Sensors Amplified with Carbon-Based Nanomaterials (CNMs) for Sensing Pharmaceutical and Food Pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Du, X. Electrochemical Sensors Based on Carbon Nanomaterial Used in Diagnosing Metabolic Disease. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R.; Lovric, M.; Bogeski, I.; Kappl, R.; Hoth, M. Square-Wave Voltammetry: A Review on the Recent Progress. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirceski, V.; Gulaboski, R. Recent Achievements in Square-Wave Voltammetry a Review. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tsionsky, M.; Gun, G.; Glezer, V.; Lev, O. Sol-Gel-Derived Ceramic-Carbon Composite Electrodes: Introduction and Scope of Applications. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 1747–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev, O.; Tsionsky, M.; Rabinovich, L.; Glezer, V.; Sampath, S.; Pankratov, I.; Gun, J. Organically Modified Sol-Gel Sensors. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 22A–30A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumya, W.; Charafi, S.; Achak, M.; Bessbousse, H.; Elhalil, A.; Abdennouri, M.; Barka, N. Modification Strategies of Sol–Gel Carbon Ceramic Electrodes and Their Electrochemical Applications. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Karimi, Z.; Amouzadeh Tabrizi, M. A Novel Electrochemical Cyanide Sensor Using Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Carbon Ceramic Electrode. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Sheng, Q.; Li, L.; Shen, Y. Bismuth Hexacyanoferrate-Modified Carbon Ceramic Electrodes Prepared by Electrochemical Deposition and Its Electrocatalytic Activity towards Oxidation of Hydrazine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 611, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, A.; Norouz-Sarvestani, F. High Electrocatalytic Effect of Au-Pd Alloy Nanoparticles Electrodeposited on Microwave Assisted Sol-Gel-Derived Carbon Ceramic Electrode for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehgan-Reyhan, S.; Najafi, M. Defective Mesoporous Carbon Ceramic Electrode Modified Graphene Quantum Dots as a Novel Surface-Renewable Electrode: The Application to Determination of Zolpidem. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 832, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Jahanbakhshi, M.; Pournaghi-Azar, M.H. Simultaneous Determination of Acetaminophen and Dopamine Using SWCNT Modified Carbon-Ceramic Electrode by Differential Pulse Voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Pournaghi-Azar, M.H. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine and Uric Acid by Use of a MWCNT Modified Carbon-Ceramic Electrode and Differential Pulse Voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5492–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Abazari, M.; Pournaghi-Azar, M.H. Simultaneous Determination of Codeine and Caffeine Using Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Modified Carbon-Ceramic Electrode. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2014, 114, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgiel, J.; Burnat, B.; Skrzypek, S. A Graphene Oxide Modified Carbon Ceramic Electrode for Voltammetric Determination of Gallic Acid. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 88, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnat, B.; Brycht, M.; Leniart, A.; Skrzypek, S. Carbon Black-Modified Carbon Ceramic Electrode—Its Fabrication, Characterization, and Electroanalytical Performance. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 130, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, J.; Burnat, B.; Kisielewska, A.; Fendrych, K.; Skrzypek, S. Fabrication and Application of Ferrierite–Modified Carbon Ceramic Electrode in Sensitive Determination of Estradiol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, B574–B580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, M.R.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K.; Gholizadeh, S. Nanobiocomposite Modified Carbon-Ceramic Electrode Based on Nano-TiO2-Plant Tissue and Its Application for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Dopamine. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1772–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, J.; Burnat, B.; Leniart, A.; Kisielewska, A.; Brycht, M.; Skrzypek, S. The Effect of Carbon Material on the Electroanalytical Determination of 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Using the Sol-Gel Derived Carbon Ceramic Electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Tian, C.; Zhai, J.; Yang, R. Sol-Gel Derived Carbon Nanotubes Ceramic Composite Electrodes for Electrochemical Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 125, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schebeliski, A.H.; Lima, D.; Marchesi, L.F.Q.P.; Calixto, C.M.F.; Pessôa, C.A. Preparation and Characterization of a Carbon Nanotube-Based Ceramic Electrode and Its Potential Application at Detecting Sulfonamide Drugs. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2018, 48, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, B.; Jahanbakhshi, M. Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Paracetamol and Phenylephrine: Carbon Nanotubes Ceramic Electrode as a Renewable Electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2015, 7, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Robak, J.; Węgiel, K.; Burnat, B.; Skrzypek, S. A Carbon Ceramic Electrode Modified with Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles for Determination of Syringic Acid by Stripping Voltammetry. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 4579–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, G. Renewable Three-Dimensional Prussian Blue Modified Carbon Ceramic Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 493, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teradal, N.L.; Seetharamappa, J. Bulk Modification of Carbon Paste Electrode with Bi2O3 Nanoparticles and Its Application as an Electrochemical Sensor for Selective Sensing of Anti-HIV Drug Nevirapine. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, S.; Wei, Q.; Sharel, P.E.; Zhu, R.; Cao, J.; Ma, L.; Zhou, K.C.; Meng, L. High-Sensitivity, Selective Determination of Dopamine Using Bimetallic Nanoparticles Modified Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode with Anodic Polarization Treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 4700–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisanci, F.B.; Yilmaz, B. Electrochemically Grown Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles on Gold as Sensor for Quantitication of Methimazole. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2018, 63, 941–952. [Google Scholar]
- Anku William, W.; Mamo Messai, A.; Govender Penny, P. Phenolic Compounds in Water: Sources, Reactivity, Toxicity and Treatment Methods. In Phenolic Compounds—Natural Sources, Importance and Applications; Soto-Hernández, M., Palma-Tenango, M., García-Mateos, R., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; pp. 419–443. ISBN 0000957720. [Google Scholar]
- Baranowska, I.; Bijak, K. Voltammetric Determination of Disinfectants at Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 68, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brycht, M.; Lochyński, P.; Barek, J.; Skrzypek, S.; Kuczewski, K.; Schwarzova-Peckova, K. Electrochemical Study of 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol on Anodically Pretreated Boron-Doped Diamond Electrode in the Absence and Presence of a Cationic Surfactant. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 771, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Xu, J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, X.; Lu, L.; Jia, H.; Xu, Q.; et al. Three-Dimensional PEDOT Composite Based Electrochemical Sensor for Sensitive Detection of Chlorophenol. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 837, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowska, I.; Bijak, K. Differential Pulse Voltammetry in Analysis of Disinfectants—2-Mercaptobenzothiazole, 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol, Triclosan, Chloramine-T. Cent. Eur. J. Chem. 2010, 8, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud-Macías, P.; López-Iglesias, D.; Sierra-Padilla, A.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; García-Guzmán, J.J. Bulk Modification of Sonogel–Carbon with Polyaniline: A Suitable Redox Mediator for Chlorophenols Detection. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Carramolino, G.; Petit-Dominguez, M.D. Application of New Sol-Gel Electrochemical Sensors to the Determination of Trace Mercury. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 614, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; ISBN 978-0-471-04372-0. [Google Scholar]
- Swartz, M.E.; Krull, I.S. Analytical Method Development and Validation; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 0-8247-0115-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nady, H.; El-Rabiei, M.M.; El-Hafez, G.M.A. Electrochemical Oxidation Behavior of Some Hazardous Phenolic Compounds in Acidic Solution. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuman, P. The Elucidation of Organic Electrode Processes; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1969; ISBN 978-1-4832-2725-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkan, S.A. (Ed.) Electroanalytical Methods in Pharmaceutical Analysis and Their Validation; HNB Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter | CCE | Bi-CCE |
|---|---|---|
| Linear range (μmol L−1) | 4.0–24.0 | 0.5–58.0 |
| Sensitivity (μA L μmol−1) | 0.0102 | 0.115 |
| LOD (a) (μmol L−1) | 0.73 | 0.17 |
| LOQ (a) (μmol L−1) | 2.21 | 0.50 |
| Precision (b) (%) | 2.6 | 0.8 |
| Accuracy (b) (%) | 86.3 | 101.2 |
| Electrode | Linear Range (µmol L−1) | LOD (µmol L−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| GCE | 21.0–210.4 | 9.3 | [37] |
| MWCNTs-GCE | 14.0–137.5 | 8.8 | [34] |
| UiO-66-NH2@PEDOT/GA-GCE | 0.6–18.0 | 0.20 | [36] |
| APT-BDDE (B/C = 2000 ppm) | 0.5–100.0 | 0.11 | [35] |
| SNG–C–PANI | 0.7–7.0 | 0.69 | [38] |
| MWCNTs-CCE | 3.0–32.0 | 0.71 | [24] |
| Bi-CCE | 0.5–58.0 | 0.17 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brycht, M.; Leniart, A.; Skrzypek, S.; Burnat, B. Incorporation of Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles into Carbon Ceramic Composite: Electrode Material with Improved Electroanalytical Performance in 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Determination. Materials 2024, 17, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030665
Brycht M, Leniart A, Skrzypek S, Burnat B. Incorporation of Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles into Carbon Ceramic Composite: Electrode Material with Improved Electroanalytical Performance in 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Determination. Materials. 2024; 17(3):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030665
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrycht, Mariola, Andrzej Leniart, Sławomira Skrzypek, and Barbara Burnat. 2024. "Incorporation of Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles into Carbon Ceramic Composite: Electrode Material with Improved Electroanalytical Performance in 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Determination" Materials 17, no. 3: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030665
APA StyleBrycht, M., Leniart, A., Skrzypek, S., & Burnat, B. (2024). Incorporation of Bismuth(III) Oxide Nanoparticles into Carbon Ceramic Composite: Electrode Material with Improved Electroanalytical Performance in 4-Chloro-3-Methylphenol Determination. Materials, 17(3), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030665










