The Effect of d10 Precious Elements on Structural, Magnetic and Elastic Properties of MnPt Alloy: A First-Principles Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Method
3. Results and Discussion
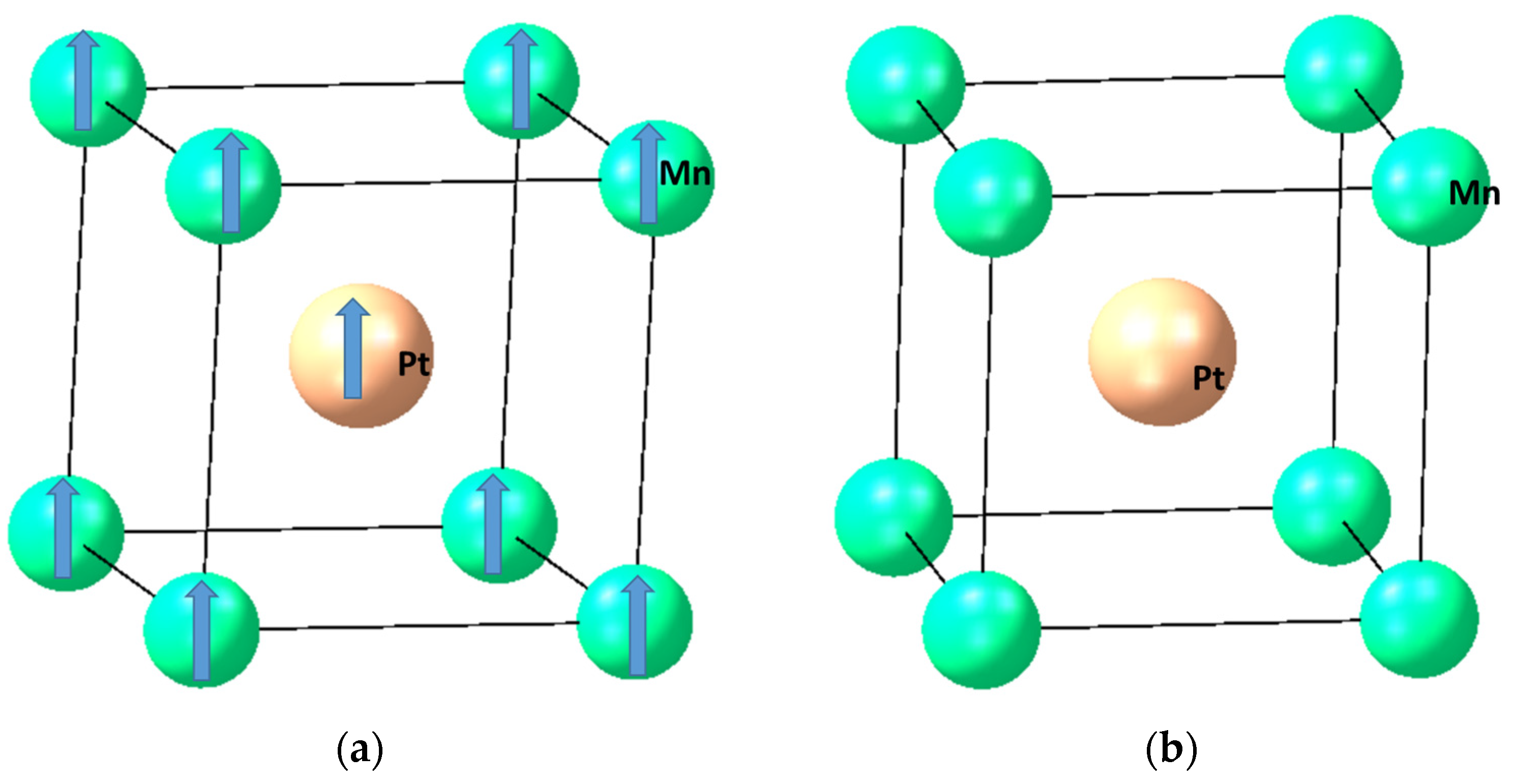
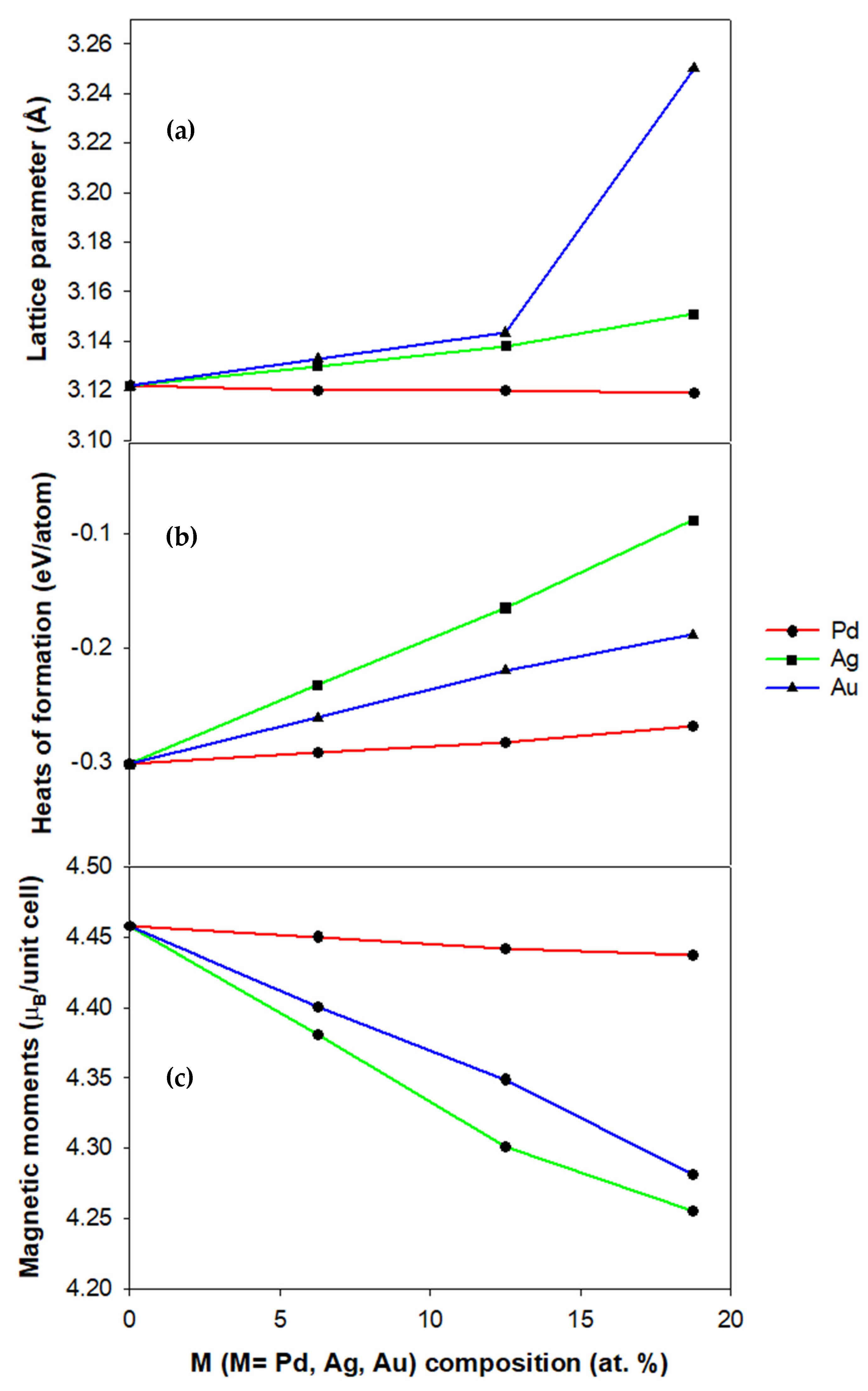
3.1. Structural and Magnetic Properties
3.2. Elastic Properties
3.2.1. Mn50Pt50−xPdx
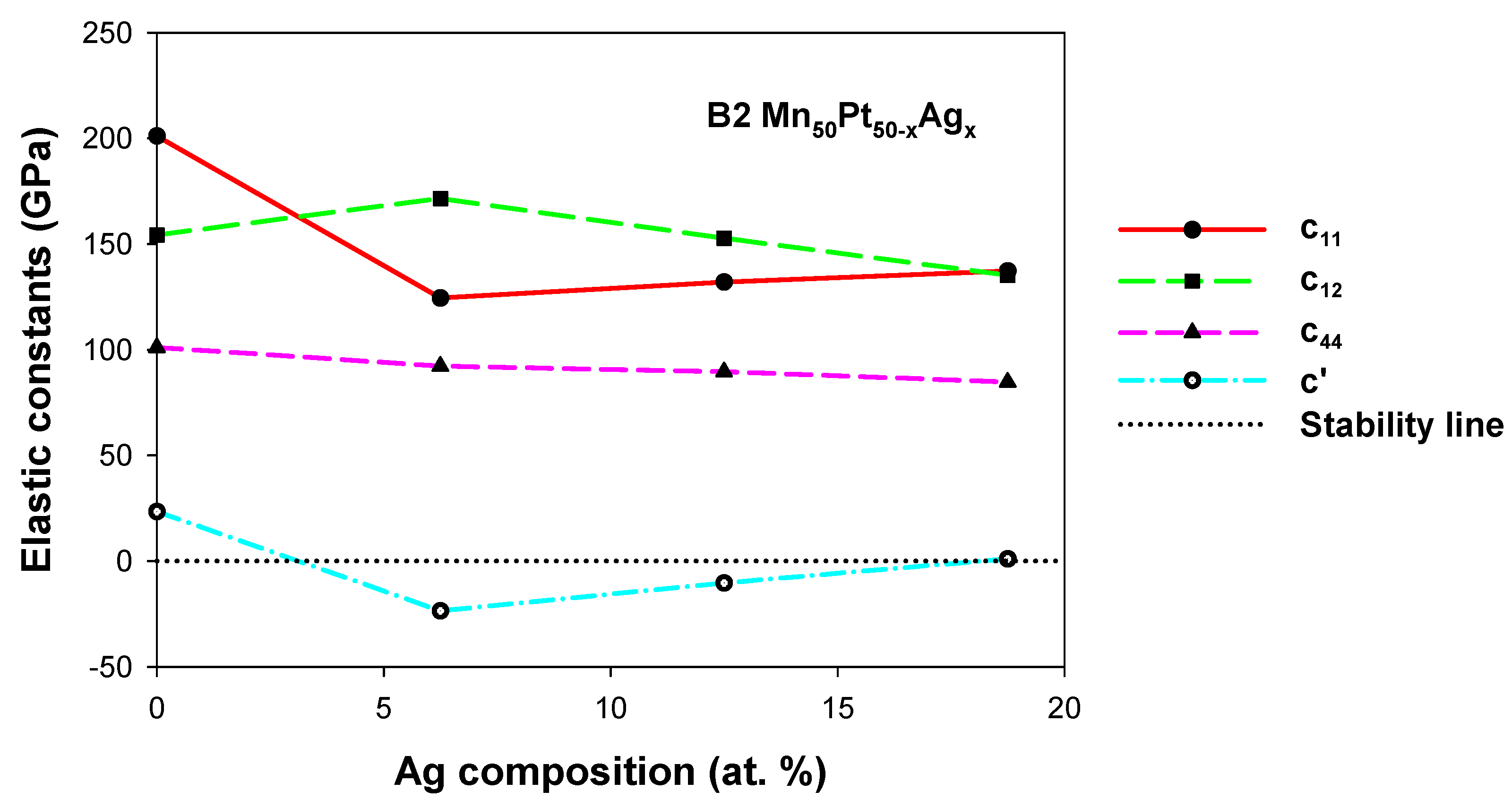
3.2.2. Mn50Pt50−xAgx
3.2.3. Mn50Pt50−xAux
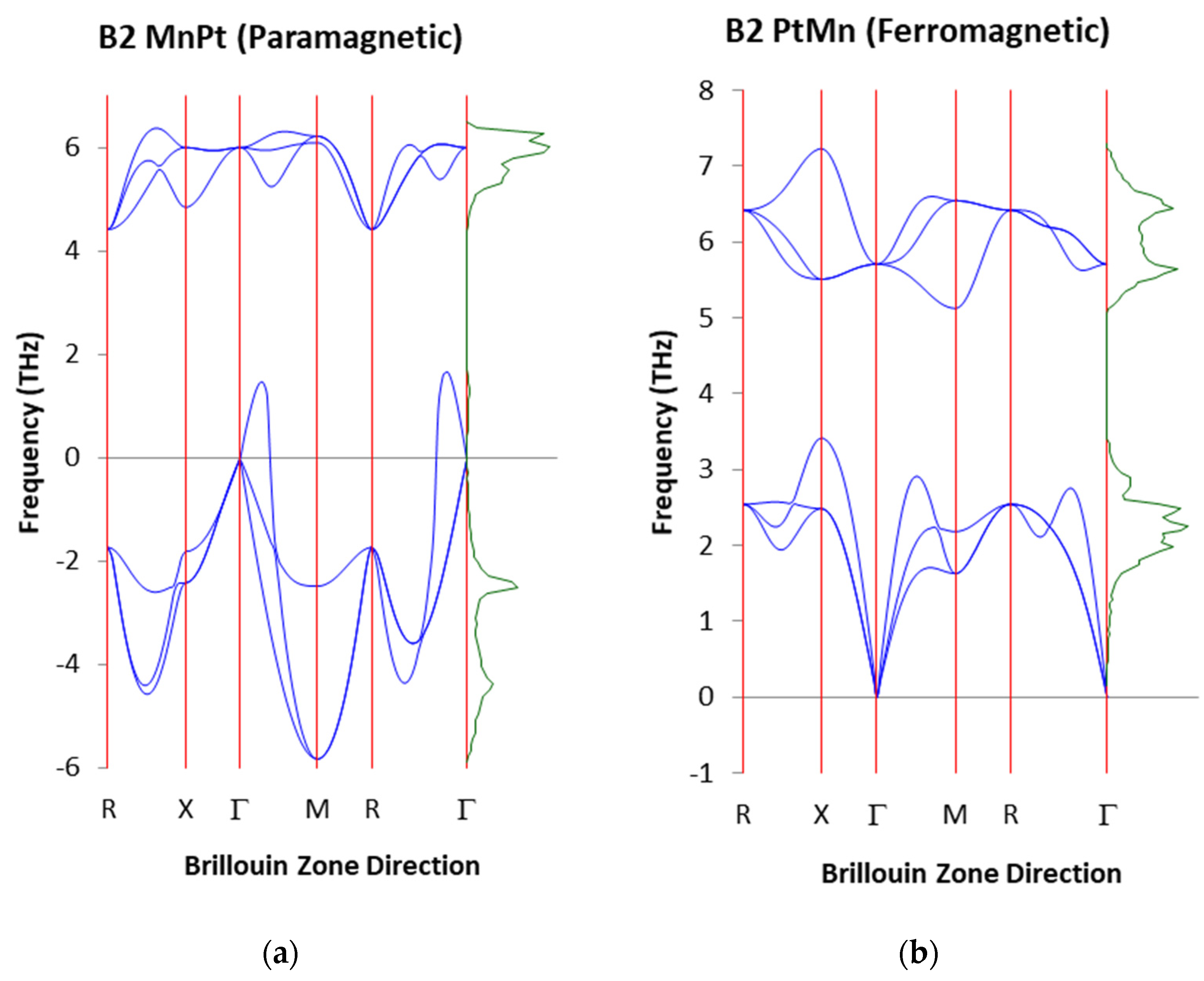
3.3. Vibrational Properties of PM and FM B2 MnPt Structures at 50 at. % Pt
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coey, J.M.D. Permanent magnets: Plugging the gap. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, R.Y.; Sakuma, A.; Fukamichi, K. Magnetic anisotropy energy of antiferromagnetic L10-type equiatomic Mn alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 052504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, A.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Fukamichi, K. Magnetic structures and their stability in Mn3Rh ordered and disordered alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 66, 014432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.J.; Lee, T.; Das, P.; Debnath, B.; Carman, G.P.; Lake, R.K. Strain control of the Néel vector in Mn-based antiferromagnets. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 142403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, S.; Chantrell, R.W.; Evans, R.F.L. Atomistic simulations of the magnetic properties of IrxMn1−x alloys. Phys. Rev. Mater. 2021, 5, 034406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, C.; Chen, M.M.; Yogi, T. Gigabit-density magnetic recording. Proc. IEEE 1993, 81, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puebla, J.; Kim, J.; Kondou, K.; Otani, Y. Spintronic devices for energy-efficient data storage and energy harvesting. Commun. Mater. 2020, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, R.F.C.; Marks, R.F.; Gider, S.; Marley, A.C.; Parkin, S.S.P.; Mauri, D. MnxPt1−x: A new exchange bias material for Permalloy. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 81, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Gorman, G.L.; Tsang, C. Antiferromagnetic and hard-magnetic stabilization schemes for magneto-resistive sensors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1996, 32, 3443. [Google Scholar]
- Kishi, H.; Kitade, Y.; Miyake, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Kobayashi, K. Study of exchange-coupled bias field in Ni-Fe/Pd-Pt-Mn thin films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1996, 32, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chepulskii, R.V.; Butler, W.H. First-principles study of magnetic properties of L10-ordered MnPt and FePt alloys. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 81, 094437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umetsu, R.Y.; Fukamichi, K.; Sakuma, A. Electrical and Magnetic Properties, and Electronic Structures of Pseudo-Gap-Type Antiferromagnetic L10-Type MnPt Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krén, E.; Kádár, G.; Pál, L.; Sólyom, J.; Szabó, P.; Tarnóczi, T. Magnetic Structures and Exchange Interactions in the Mn-Pt System. Phys. Rev. 1968, 171, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladwig, P.F.; Chang, Y.A. Paramagnetic to antiferromagnetic phase transformation in sputter deposited Pt–Mn thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaad, A.; Ahmad, A.A.; Obeidat, T.S. Structural, electronic and magnetic properties of the ordered binary FePt, MnPt, and CrPt3 alloys. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diale, R.; Ngoepe, P.; Moema, J.; Phasha, M.; Chauke, H. Thermodynamic and magnetic properties of Pt50Mn50-xMx (M= Cr, Fe) alloys: A first-principles study. MATEC Web of Conf. 2022, 370, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diale, R.G.; Ngoepe, P.E.; Moema, J.S.; Phasha, M.J.; Moller, H.; Chauke, H.R. A computational study of the thermodynamic and magnetic properties of Co-alloyed MnPt. MRS Adv. 2023, 8, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 58–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-Consistent Equations Including Exchange and Correlation Effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkhorst, H.J.; Pack, J.D. Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 13, 5188–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, W. Textbook of crystal physics. Ann. Phys. Chem. 1889, 274, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlinski, K.; Li, Z.Q.; Kawazoe, Y. First-Principles Determination of the Soft Mode in Cubic ZrO. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4063–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.D.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, Z. The structural, elastic, phonon, thermal and electronic properties of MnX (X=Ni, Pd and Pt) alloys: First-principles calculations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 333, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlangu, R.; Phasha, M.J.; Chauke, H.R.; Ngoepe, P.E. Structural, elastic and electronic properties of equiatomic PtTi as potential high temperature shape memory Alloy. Intermetallics 2013, 3, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, M.J.; Klein, B.M. First-principles calculation of elastic properties. In: Westbrook JH, Fleischer RL, editors. Intermetallic Compounds–Principles and Practice. Vol. 1. London: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd. Intermet. Compd. 1994, 1, 195–210. [Google Scholar]
- Frantsevich, I.N.; Voronov, S.A. Handbook on Elastic Constants and Moduli of Elasticity for Metals and Nonmetals; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1983; pp. 60–180. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, G.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Ning, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, M.; Liu, R. Mechanical, electronic and thermal properties of Cu5Zr and Cu5Hf by first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Composition | Mn | Pt | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn50Pt50 | 3.784 | 0.667 | |
| Mn50Pt50−xPdx | |||
| Mn50Pt43.75Pd6.25 | 3.788 | 0.407 | 0.360 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Pd12.5 | 3.792 | 0.398 | 0.365 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Pd18.75 | 3.797 | 0.404 | 0.356 |
| Mn50Pt50−xAgx | |||
| Mn50Pt43.75Ag6.25 | 3.773 | 0.411 | 0.062 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Ag12.5 | 3.756 | 0.374 | 0.060 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Ag18.75 | 3.758 | 0.355 | 0.056 |
| Mn50Pt50−xAux | |||
| Mn50Pt43.75Au6.25 | 3.783 | 0.401 | 0.114 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Au12.5 | 3.780 | 0.376 | 0.112 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Au18.75 | 3.765 | 0.362 | 0.096 |
| Elastic Constants, Cij (GPa) | PM-B2 Mn50Pt50 | PM-B2 Mn50Pt50 |
|---|---|---|
| C11 | 68 (68) | 201 |
| C12 | 330 (329) | 154 |
| C44 | 138 (134) | 101 |
| C′ | −131 (−131) | 23 |
| Structure | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Hardness (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn50Pt50 | 184.69 | 0.32 | 6.80 |
| Mn50Pt43.75Pd6.25 | 118.38 | 0.38 | 2.90 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Pd12.5 | 124.90 | 0.37 | 3.36 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Pd18.75 | 128.51 | 0.36 | 3.66 |
| Structure | Young’s (Gpa) | Poisson Ratio | Hardness (Gpa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn50Pt50 | 184.69 | 0.32 | 6.80 |
| Mn50Pt43.75Ag6.25 | 125.43 | 0.37 | 3.44 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Ag12.5 | 133.67 | 0.35 | 4.28 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Ag18.75 | 133.24 | 0.34 | 4.66 |
| Structure | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Hardness (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mn50Pt50 | 184.69 | 0.32 | 6.80 |
| Mn50Pt43.75Au6.25 | 123.00 | 0.37 | 3.23 |
| Mn50Pt37.5Au12.5 | 129.53 | 0.36 | 3.81 |
| Mn50Pt31.25Au18.75 | 150.42 | 0.33 | 5.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diale, R.; Ngoepe, P.; Chauke, H.; Moema, J.; Phasha, M. The Effect of d10 Precious Elements on Structural, Magnetic and Elastic Properties of MnPt Alloy: A First-Principles Study. Materials 2024, 17, 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030541
Diale R, Ngoepe P, Chauke H, Moema J, Phasha M. The Effect of d10 Precious Elements on Structural, Magnetic and Elastic Properties of MnPt Alloy: A First-Principles Study. Materials. 2024; 17(3):541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030541
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiale, Ramogohlo, Phuti Ngoepe, Hasani Chauke, Joseph Moema, and Maje Phasha. 2024. "The Effect of d10 Precious Elements on Structural, Magnetic and Elastic Properties of MnPt Alloy: A First-Principles Study" Materials 17, no. 3: 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030541
APA StyleDiale, R., Ngoepe, P., Chauke, H., Moema, J., & Phasha, M. (2024). The Effect of d10 Precious Elements on Structural, Magnetic and Elastic Properties of MnPt Alloy: A First-Principles Study. Materials, 17(3), 541. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17030541







