Quality of Machined Surface and Cutting Force When Milling NiTi Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Analysis of the Results
Surface Roughness
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dash, B.; Das, M.; Mahapatra, T.R.; Mishra, D. A concise review on machinability of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 5141–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M. Cutting force prediction in ball-end milling of Ni-Ti alloy. Proc. SPIE 2019, 1176, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd, J.J.; Leary, M.; Subic, A.; Gibson, M.A. A Review of Shape memory Alloy Research, Applications and Opportunities. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 1078–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlallah, A.; El-Bagoury, N.; Gad El-Rab, S.M.F.; Ahmed, R.A.; El-Ousamii, G. An overview of NiTi shape memory alloy: Corrosion resistance and antibacterial inhibition for dental application. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoud, B.F.; Korkmaz, M.E. A Review on Machinability of Shape Memory Alloys Through Traditional and Non-Traditional Machining Processes: A Review. Manuf. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinert, K.; Petzoldt, V. Machining of NiTi based Shape Memory Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2004, 378, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, E.; Gokkay, H.; Ozkan, D. Investigation of the Effects of Machining Parameters on Tool Life and Surface Roughness During the Face Milling of the NiTi Shape Memory Alloy with Uncoated Tools. Preprints 2020, 1, 2020080383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Kaya, I. Tool wear progression of PCD and PCBN cutting tools in high speed machining of NiTi shape memory alloy under various cutting speeds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 105, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shizuka, H.; Sakai, K.; Yang, H.; Sonoda, K.; Nagare, T.; Kurebayashi, Y.; Hayakawa, K. Difficult cutting property of NiTi alloy and its mechanism. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 4, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, E.; Altin Karatas, M.; Gokkaya, H.; Akinay, Y. Surface Integrity of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy in Milling with Cryogenic Heat Treated Cutting Tools under Different Cutting Conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 9426–9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M. Analysis of Cutting Forces and Geometric Surface Structures in the Milling of NiTi Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, E.; Erkan, O.; Ozkan, D.; Gokkaya, H. Optimization of Cutting Conditions, Parameters, and Cryogenic Heat Treatment for Surface Roughness in Milling of NiTi Shape Memory Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 7315–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altas, E.; Gokkaya, H.; Karatas, M.A.; Ozkan, D. Analysis of surface roughness and flank wear using the Taguchi method in milling of NiTi shape memory alloy with uncoated tools. Coatings 2020, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Kaya, İ. The effect of cutting tool and cutting speed on the surface integrity and functional properties in milling of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Fac. Eng. Arch. 2023, 38, 2375–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, B.; Niu, J. Influence of cutting parameters on surface roughness and strain hardening during milling NiTi shape memory alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Huo, H.; Wang, G.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z. Residual height of surface topography in milling nickel-titanium shape memory alloy using a small-diameter cutter. Mater. Lett. 2024, 361, 136105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, Z.A.; Mativenga, P.T. Machinability of nickel-titanium shape memory alloys under dry and chilled air cutting conditions. Int. J Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 126, 4675–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Song, Q. A novel dealloying assisted machining method to improve the machinability of NiTi alloy as a typical high toughness difficult-to-machine material. Mater. Des. 2023, 236, 112496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J. Effects of dealloying surface modification on machinability improvement of NiTi alloy during micro-machining process. Tribol. Int. 2024, 195, 109608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Manchiraju, S.; Jawahir, I.S. Modeling and simulation of machining-induced surface integrity characteristics of NiTi alloy. Proc. CIRP 2015, 31, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Kaya, I. A review on machining of NiTi shape memory alloys: The process and post process perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 2045–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Feng, J.; Zhang, W.H.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.C. Working mechanism of helix angle on peak cutting forces together with its design theory for peripheral milling tools. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 249, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, G.; Motorcu, A.R.; Nohutçu, S. Single and multi-objective optimization for cutting force and surface roughness in peripheral milling of Ti6Al4V using fixed and variable helix angle tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 80, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, D.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Duc, T.D. Influence of Different Cutter Helix Angle and Cutting Condition on Surface Roughness During End-Milling of C45 Steel. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Plodzien, M.; Burek, J.; Zylka, L.; Sulkowicz, P. The influence of end mill helix angle on high performance milling process. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Cao, P. The researches concern the influence of the helix angle on the composite machining process. Comp. Adv. Mater. 2021, 30, 263498332199837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórski, I.; Szczepaniak, A.; Kulisz, M.; Korpysa, J. Influence of the Tool Cutting Edge Helix Angle on the Surface Roughness after Finish Milling of Magnesium Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.N.; Bolar, G. Influence of End Mill Geometry on Milling Force and Surface Integrity While Machining Low Rigidity Parts. J. Inst. Eng. 2021, 102, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knápek, T.; Dvořáčková, Š.; Váňa, M. The Effect of Clearance Angle on Tool Life, Cutting Forces, Surface Roughness, and Delamination during Carbon-Fiber-Reinforced Plastic Milling. Materials 2023, 16, 5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Song, Q.; Cai, Y. Recent progress of machinability and surface integrity for mechanical machining Inconel 718: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 109, 215–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Li, C.; Don, L.; Bai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Jia, D.; Li, R.; Liu, Z. Effects of Physicochemical Properties of Different Base Oils on Friction Coefficient and Surface Roughness in MQL Milling AISI 1045. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2021, 8, 1629–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, K.; Li, J.; Sun, J. Investigation on machinability of NiTi shape memory alloys under different cooling conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, B.; Blagojevic, J.; Babic, M.; Velickovic, S.; Miladinovic, S. Optimization of hybrid aluminum composites wear using Taguchi method and artificial neural network. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2017, 69, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, K.; Kayacan, M.C. Cutting force modeling and accurate measurement in milling of flexible workpieces. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 133, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducroux, E.; Fromentin, G.; Viprey, F.; Prat, D.; D’Acunto, A. New mechanistic cutting force model for milling additive manufactured Inconel 718 considering effects of tool wear evolution and actual tool geometry. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M. Application of Taguchi method to optimization of surface roughness during precise turning of NiTi shape memory alloy. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10445, 1608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, L.; Grossi, N.; Scippa, A.; Campatelli, G. Surface error shape identification for 3-axis milling operations. Procedia CIRP 2021, 101, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, Y.; Huang, B.; Karaca, E.H.; Jawahir, S.I. Surface Characteristics of Machined NiTi Shape Memory Alloy, The Effects of Cryogenic Cooling and Preheating Conditions. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 3597–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
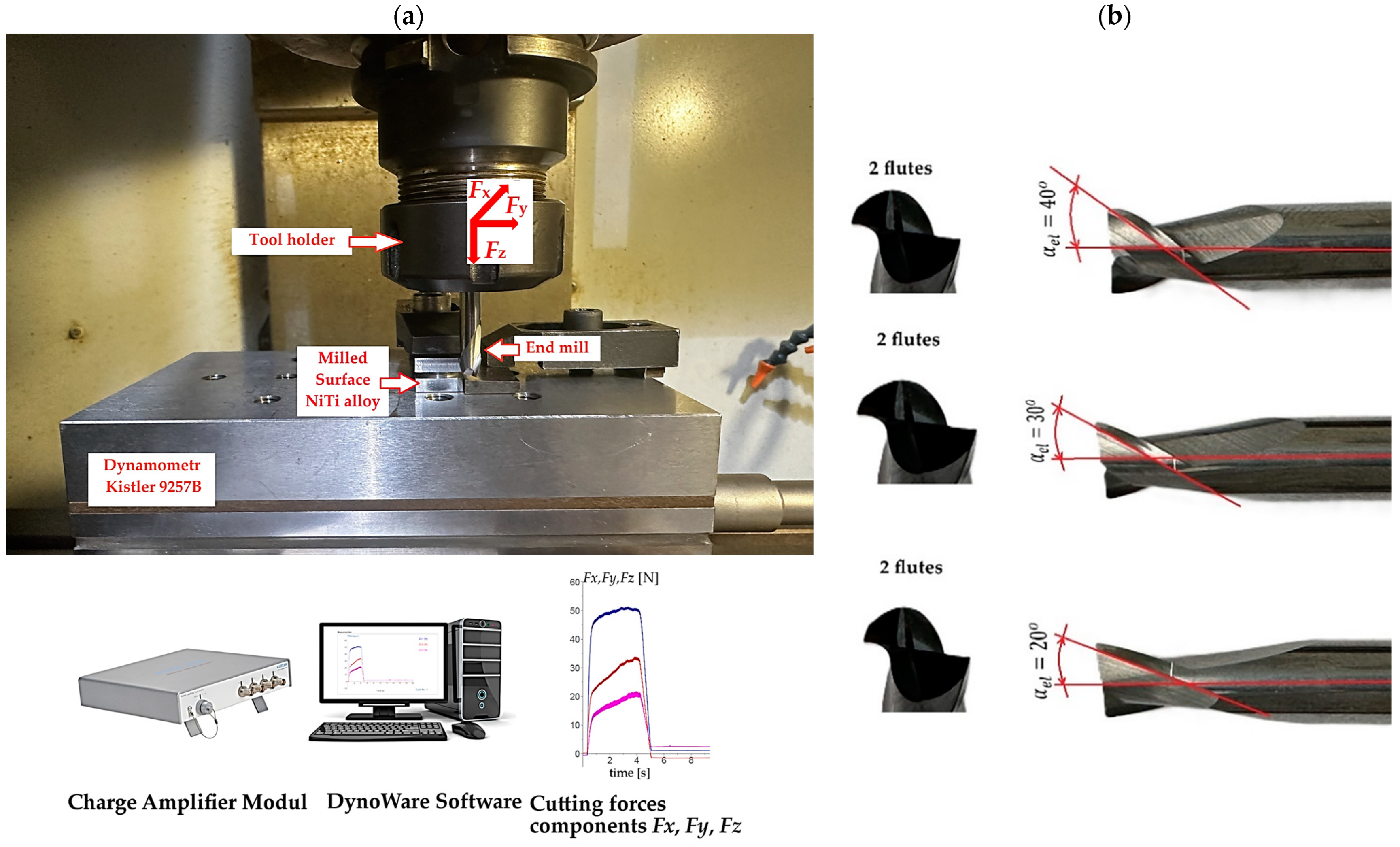
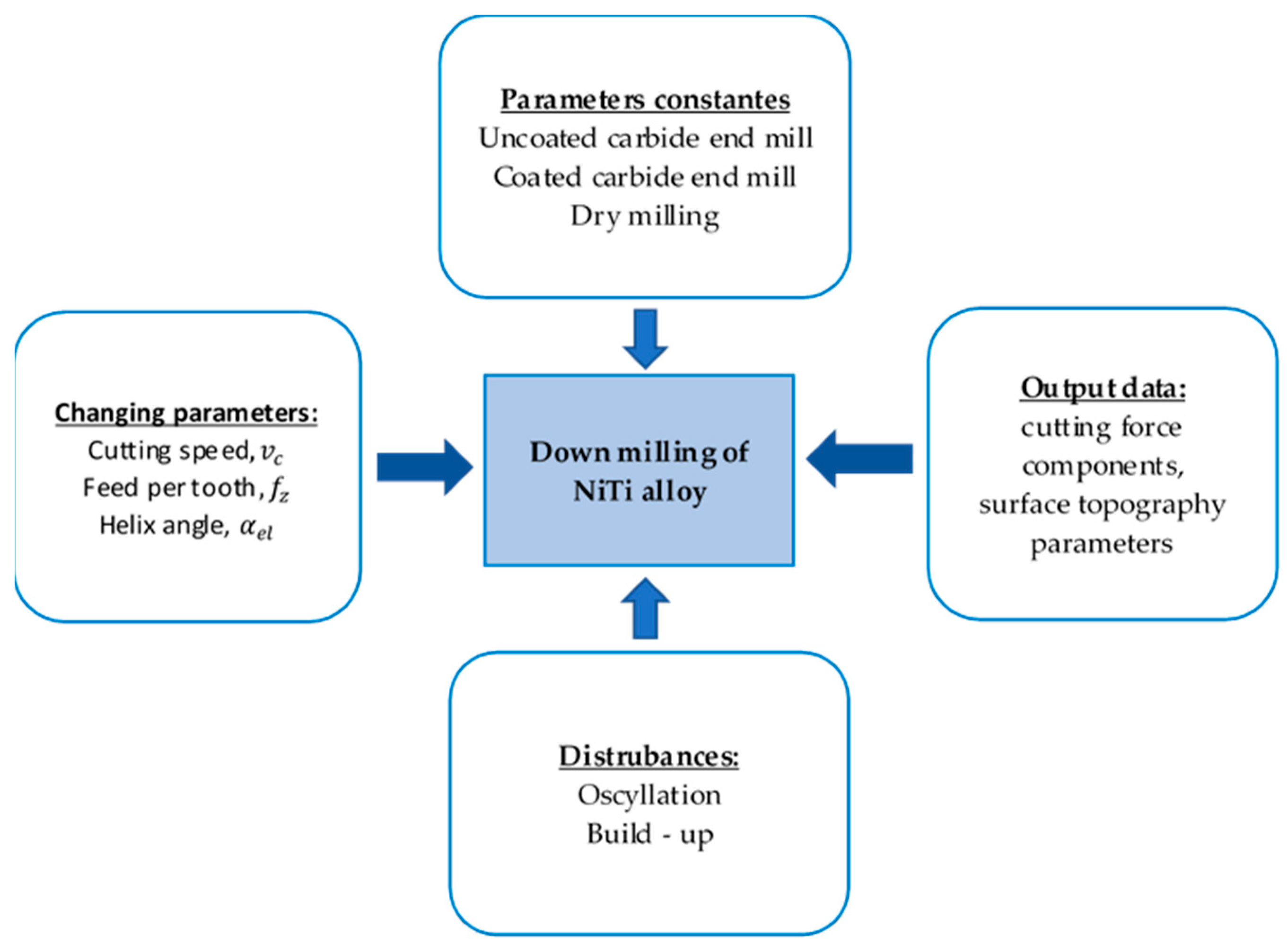

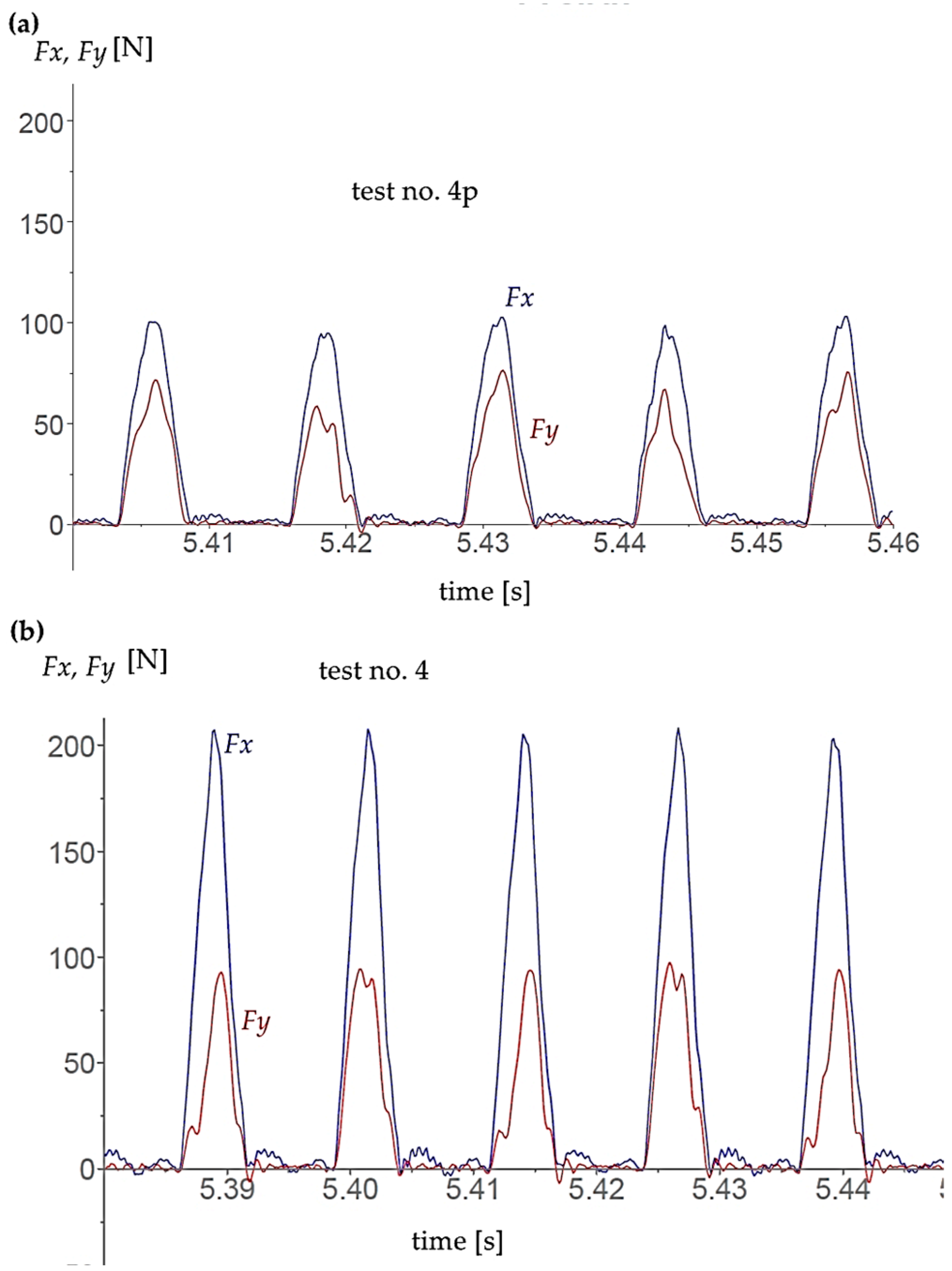
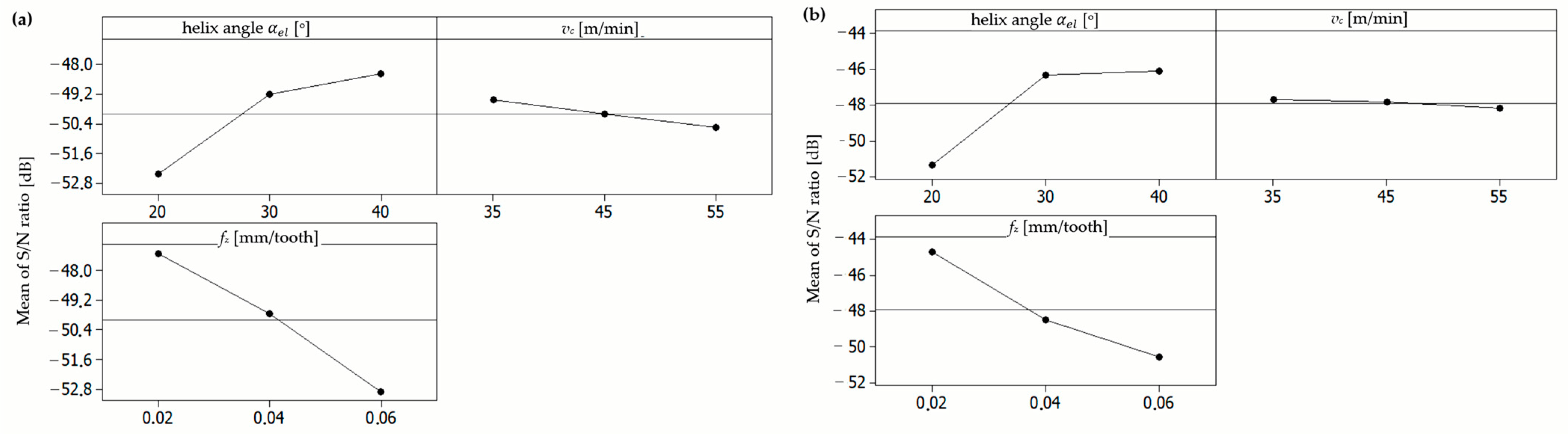
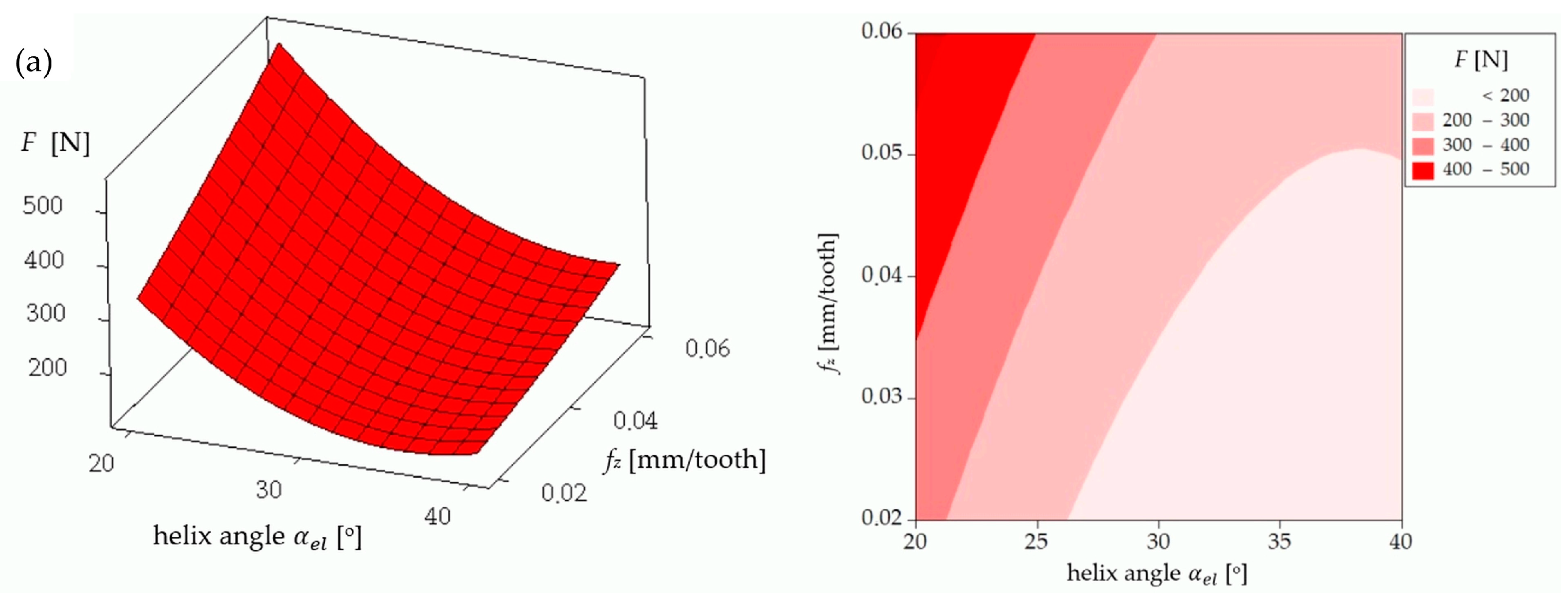
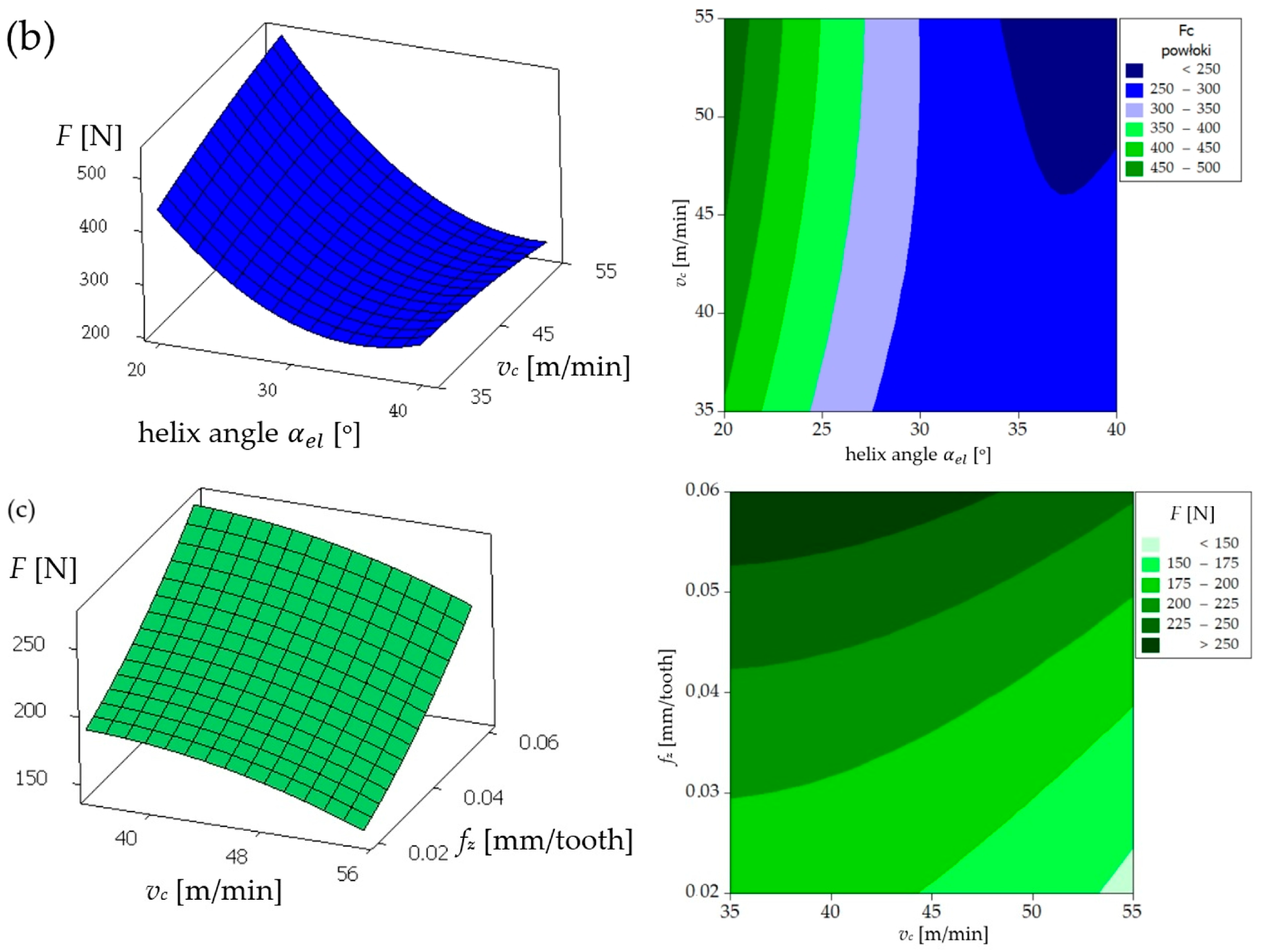
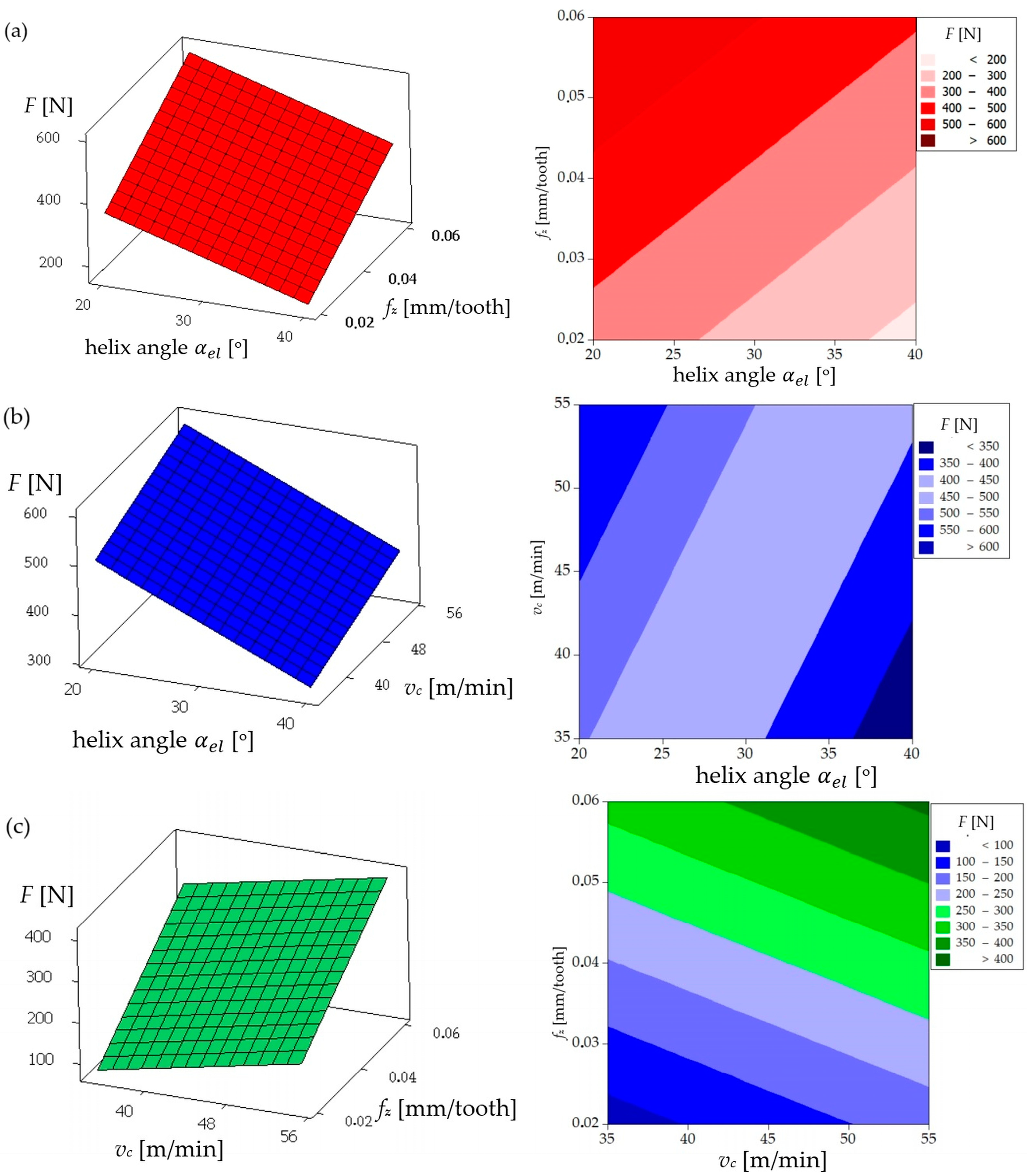

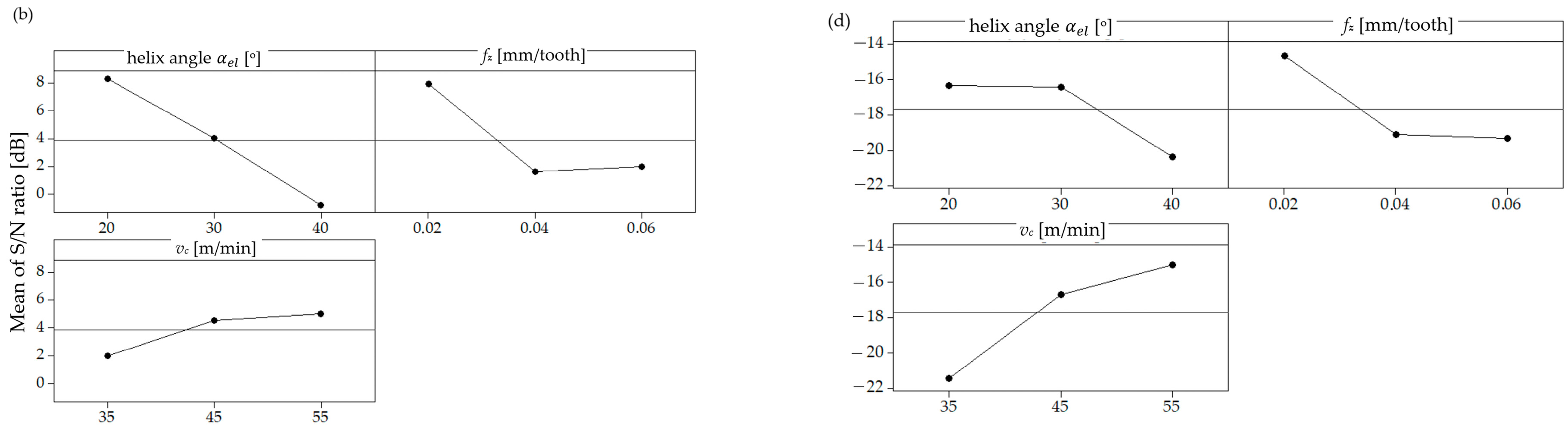
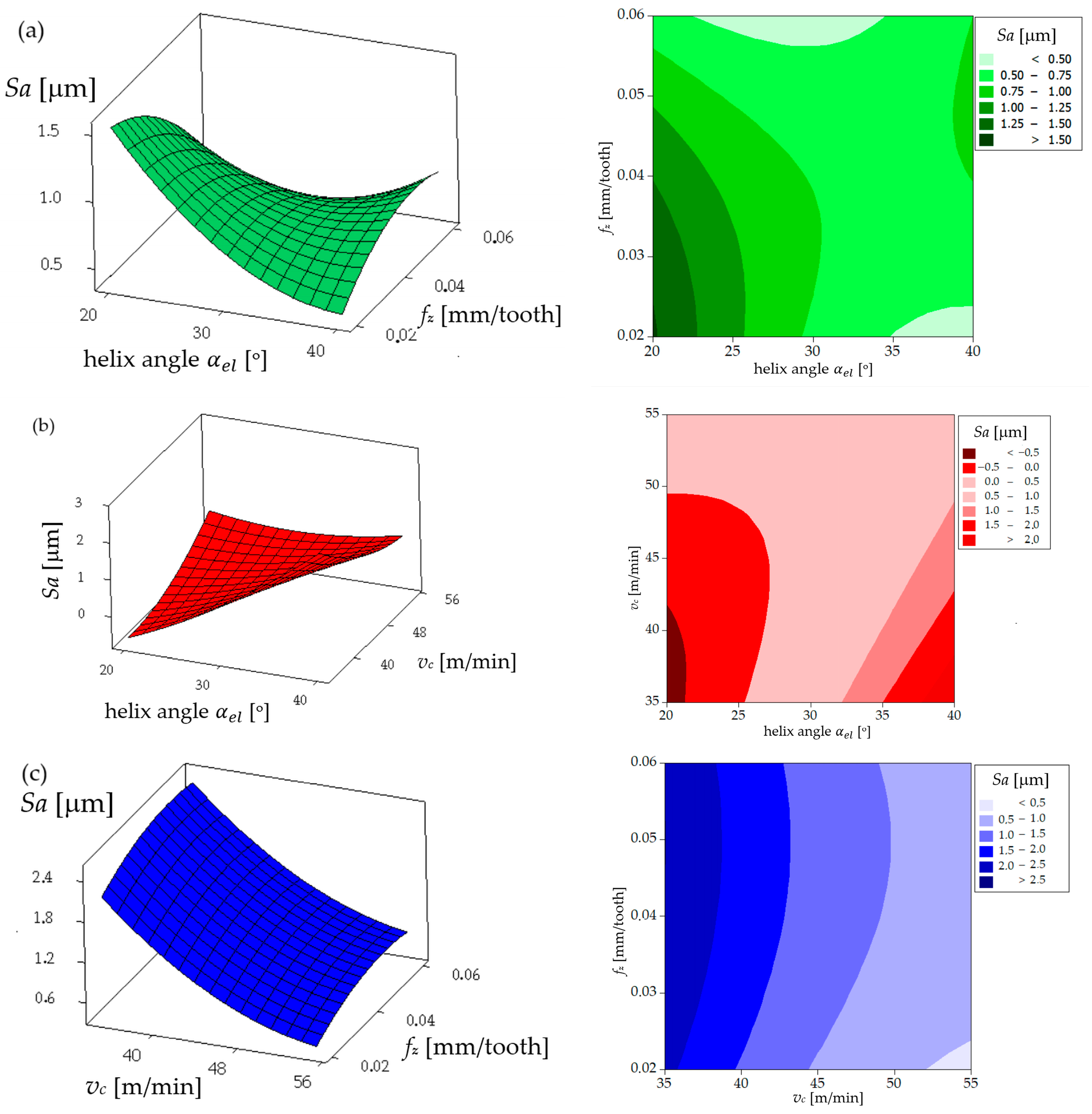
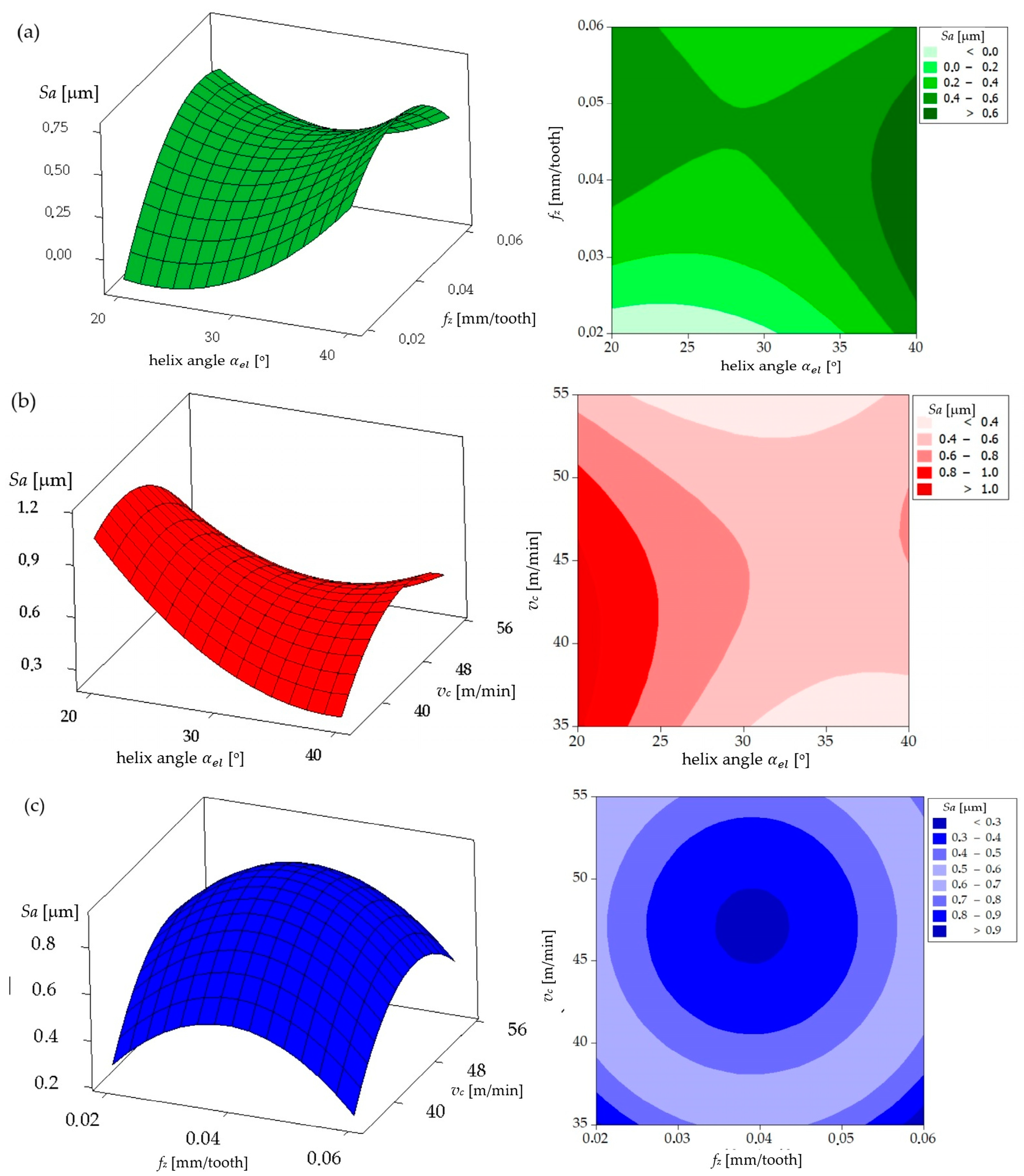
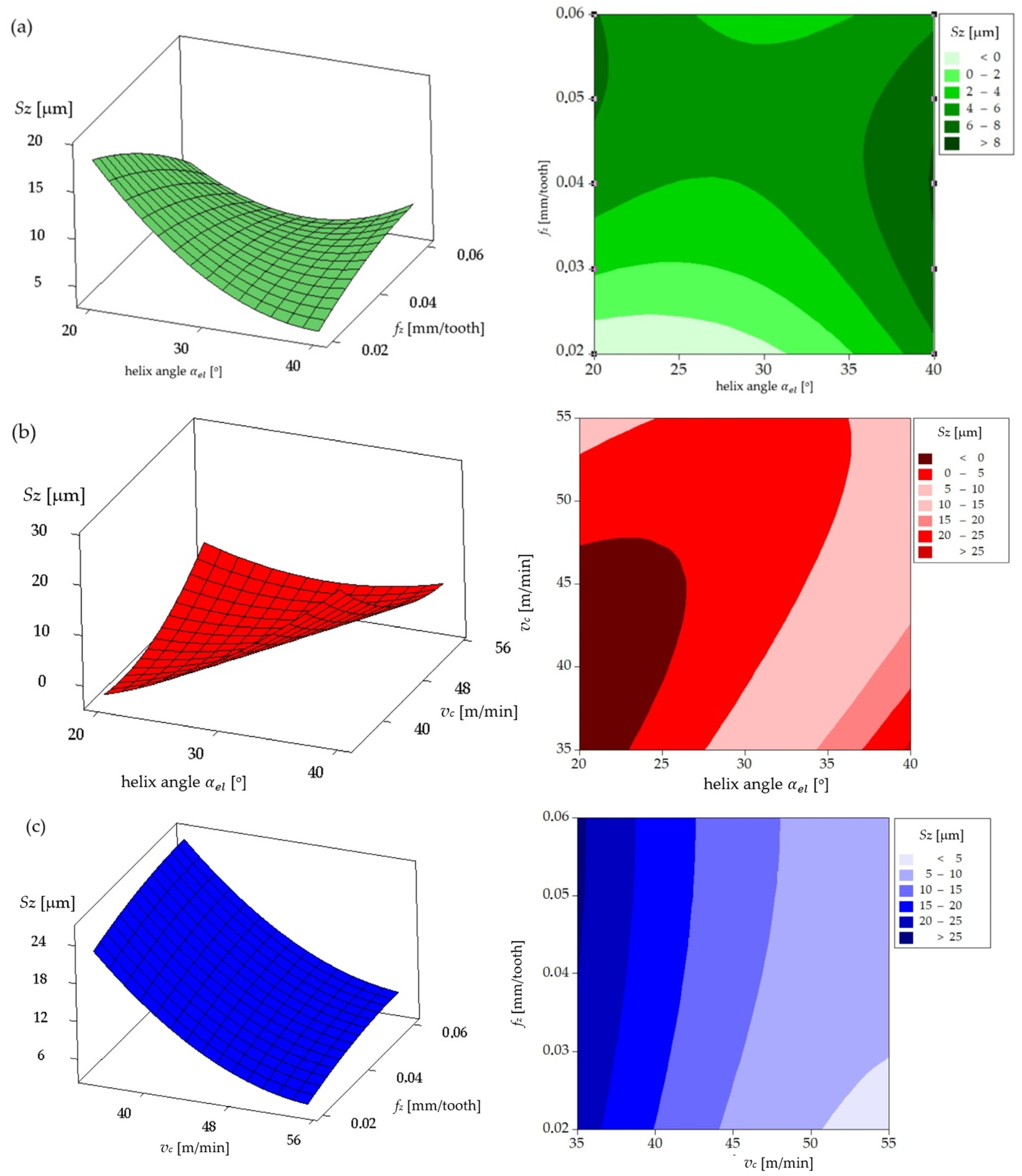

| Parameters | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| Helix angles (°) | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| Feed per tooth (mm/tooth) | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.06 |
| Cutting speed (m/min) | 35 | 45 | 55 |
| No. | (°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 0.02 | 35 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.04 | 45 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.06 | 55 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.02 | 45 |
| 5 | 30 | 0.04 | 55 |
| 6 | 30 | 0.06 | 35 |
| 7 | 40 | 0.02 | 55 |
| 8 | 40 | 0.04 | 35 |
| 9 | 40 | 0.06 | 45 |
| No. | (°) | Uncoated Carbide End Mills | Coated Carbide End Mills | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ff max (N) | Fr max (N) | Ft max (N) | F (N) | F_S/N (db) | Ff max (N) | Fr max (N) | Ft max (N) | F (N) | F_S/N (db) | ||||
| 1 | 20 | 0.02 | 35 | 120.9 | 23.4 | 188.3 | 255.4 | −48.14 | 124.9 | 19.9 | 201.2 | 237.7 | −49.15 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.04 | 45 | 220.0 | 62.9 | 310.8 | 397.4 | −51.98 | 221.2 | 61.7 | 314.9 | 389.7 | −52.18 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.06 | 55 | 405.3 | 110.5 | 580.9 | 716.8 | −57.11 | 310.9 | 93.8 | 431.5 | 540.0 | −55.90 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.02 | 45 | 94.9 | 35.6 | 221.4 | 243.5 | −47.73 | 75.4 | 44.2 | 119.9 | 148.4 | −46.52 |
| 5 | 30 | 0.04 | 55 | 138.2 | 83.3 | 212.1 | 266.5 | −48.51 | 115.1 | 71.1 | 170.7 | 217.8 | −49.52 |
| 6 | 30 | 0.06 | 35 | 188.6 | 111.0 | 298.8 | 370.4 | −51.37 | 151.7 | 99.6 | 204.0 | 273.0 | −51.57 |
| 7 | 40 | 0.02 | 55 | 86.9 | 100.0 | 149.6 | 199.8 | −46.01 | 71.6 | 80.0 | 95.4 | 143.6 | −46.21 |
| 8 | 40 | 0.04 | 35 | 133.6 | 150.0 | 186.2 | 273.9 | −48.75 | 120.3 | 131.8 | 128.9 | 220.1 | −47.54 |
| 9 | 40 | 0.06 | 45 | 142.2 | 163.7 | 244.6 | 326.9 | −50.29 | 144.5 | 157.4 | 144.9 | 258.2 | −51.29 |
| No. | (°) | Uncoated Carbide End Mills | Coated Carbide End Mills | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sz (μm) | Sa (μm) | Sa_S/N (dB) | Sz_S/N (dB) | Sz (μm) | Sa (μm) | Sa_S/N (dB) | Sz_S/N (dB) | ||||
| 1 | 20 | 0.02 | 35 | 7.93 | 0.308 | 10.2290 | −17.9855 | 5.12 | 0.374 | 8.5426 | −14.1854 |
| 2 | 20 | 0.04 | 45 | 4.61 | 0.311 | 10.1448 | −13.2740 | 11.50 | 0.983 | 0.1489 | −21.2140 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.06 | 55 | 7.66 | 0.592 | 4.5536 | −17.6846 | 6.17 | 0.523 | 5.6300 | −15.8057 |
| 4 | 30 | 0.02 | 45 | 5.51 | 0.514 | 5.7807 | −14.8230 | 3.41 | 0.301 | 10.4287 | −10.6551 |
| 5 | 30 | 0.04 | 55 | 6.38 | 0.738 | 2.6389 | −16.0964 | 4.17 | 0.393 | 8.1121 | −12.4027 |
| 6 | 30 | 0.06 | 35 | 8.24 | 0.656 | 3.6619 | −18.3185 | 5.09 | 0.415 | 7.6390 | −14.1344 |
| 7 | 40 | 0.02 | 55 | 3.63 | 0.406 | 7.8295 | −11.1981 | 5.40 | 0.505 | 5.9342 | −14.6479 |
| 8 | 40 | 0.04 | 35 | 25.10 | 2.470 | −7.8539 | −27.9935 | 4.50 | 0.529 | 5.5309 | −13.0643 |
| 9 | 40 | 0.06 | 45 | 12.50 | 1.290 | −2.2118 | −21.9382 | 6.85 | 0.602 | 4.4081 | −16.7138 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kowalczyk, M.; Tomczyk, K. Quality of Machined Surface and Cutting Force When Milling NiTi Alloys. Materials 2024, 17, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246122
Kowalczyk M, Tomczyk K. Quality of Machined Surface and Cutting Force When Milling NiTi Alloys. Materials. 2024; 17(24):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246122
Chicago/Turabian StyleKowalczyk, Małgorzata, and Krzysztof Tomczyk. 2024. "Quality of Machined Surface and Cutting Force When Milling NiTi Alloys" Materials 17, no. 24: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246122
APA StyleKowalczyk, M., & Tomczyk, K. (2024). Quality of Machined Surface and Cutting Force When Milling NiTi Alloys. Materials, 17(24), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246122







