Influence of Bonding Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31/Zn/Sn/5083 Diffusion Joint
Abstract
1. Introduction
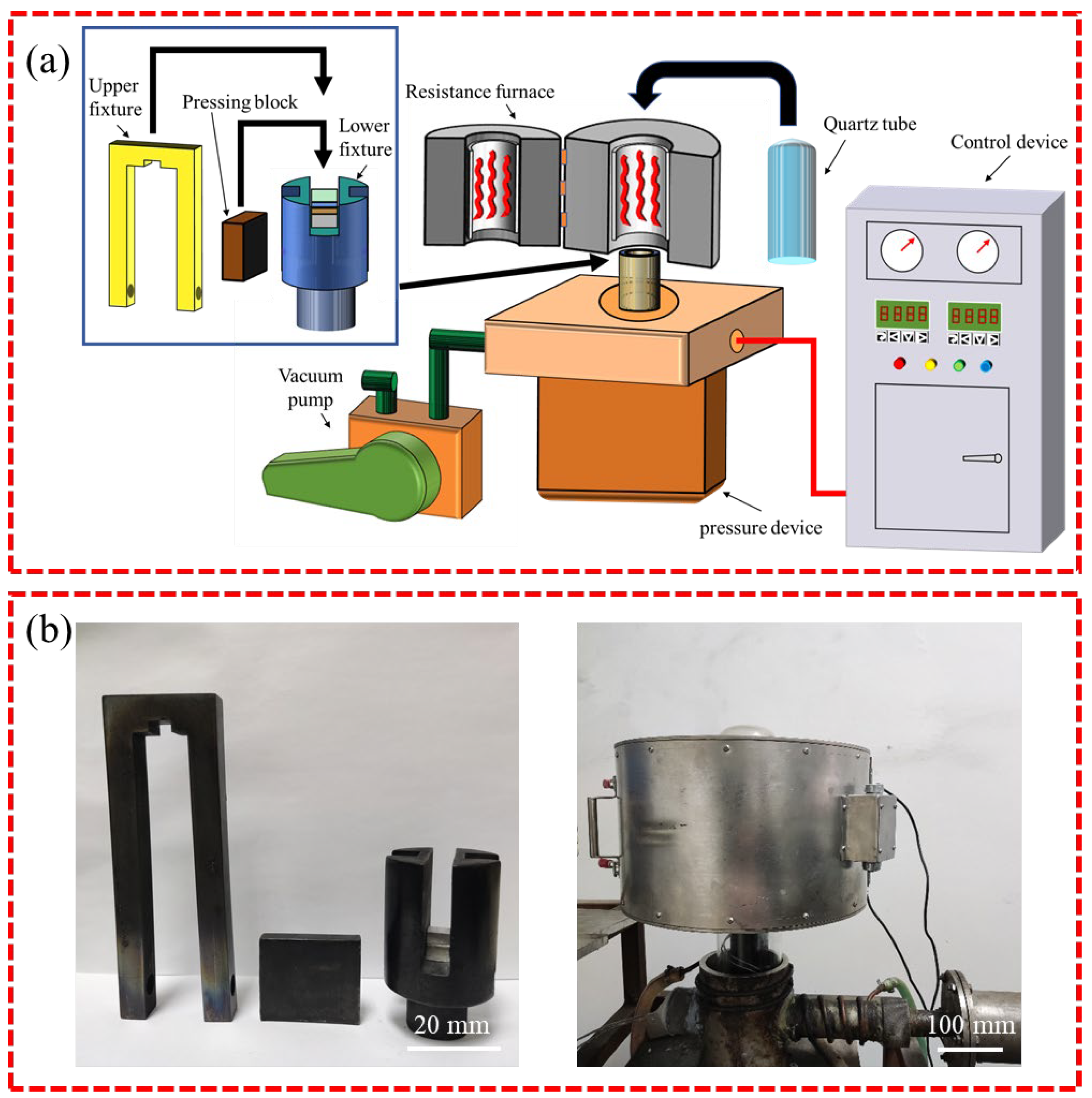
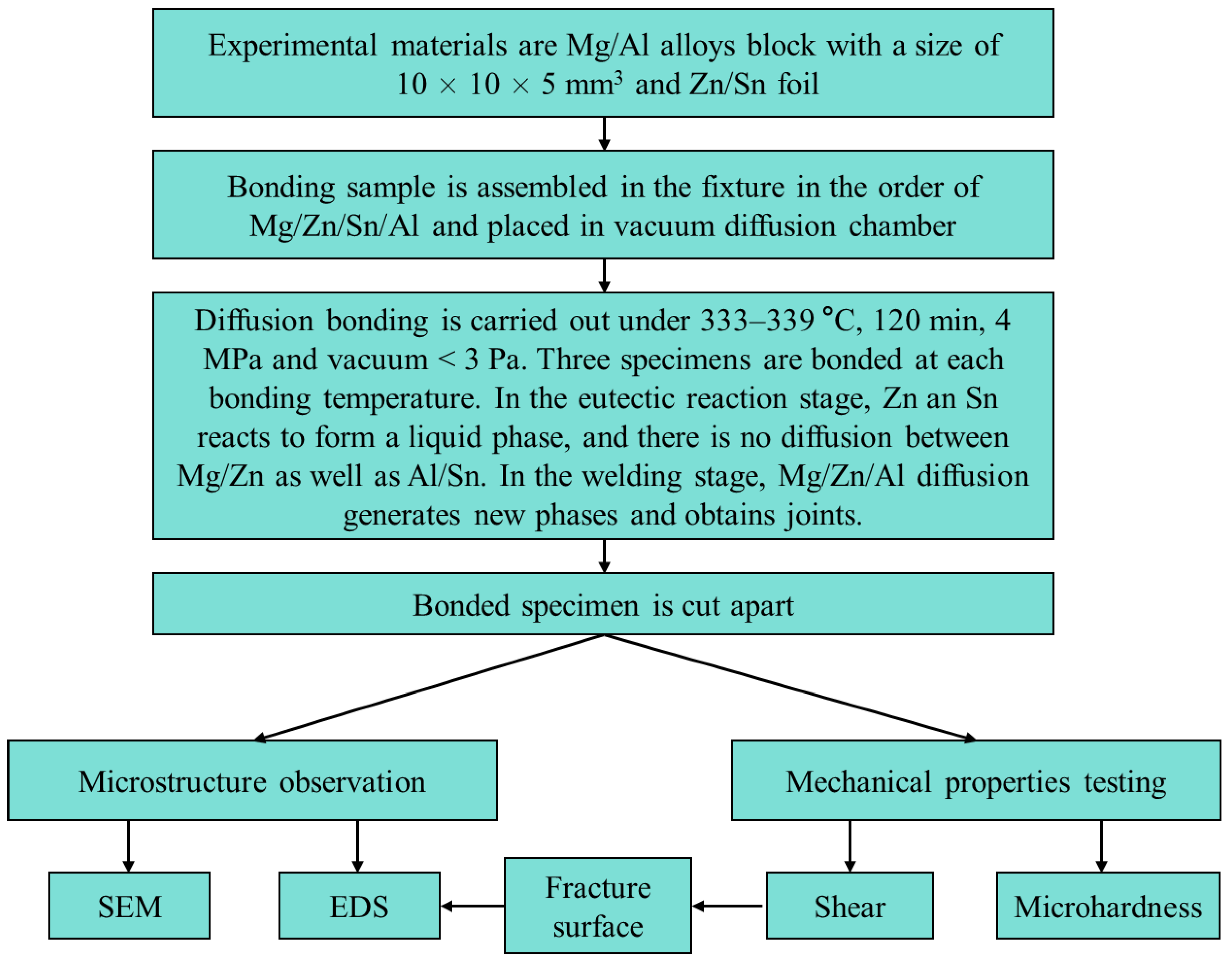
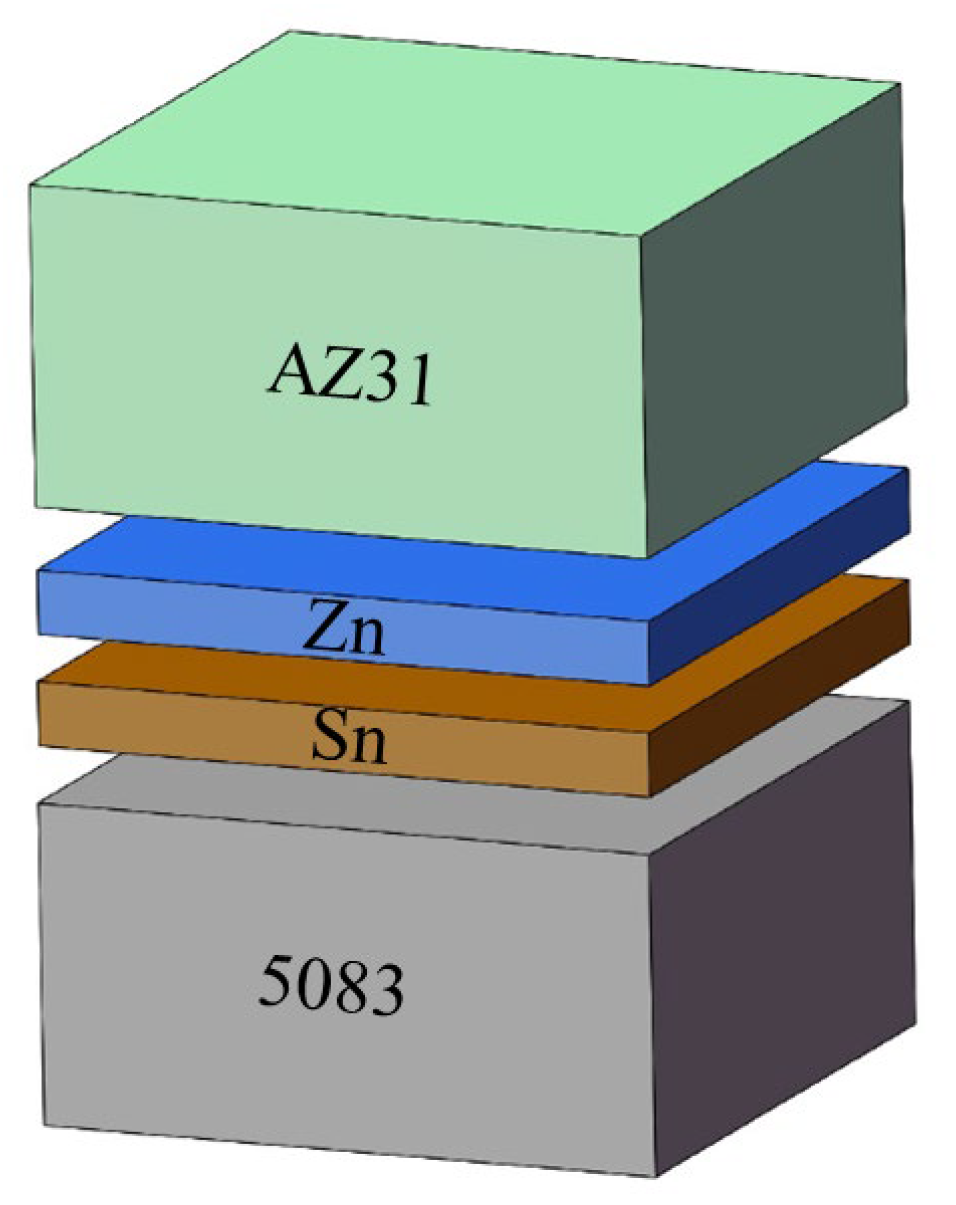
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the Joint Bonded at 333 °C
3.2. Microstructure of the Joint Bonded at 336 °C
3.3. Microstructure of Joint Bonded at 339 °C
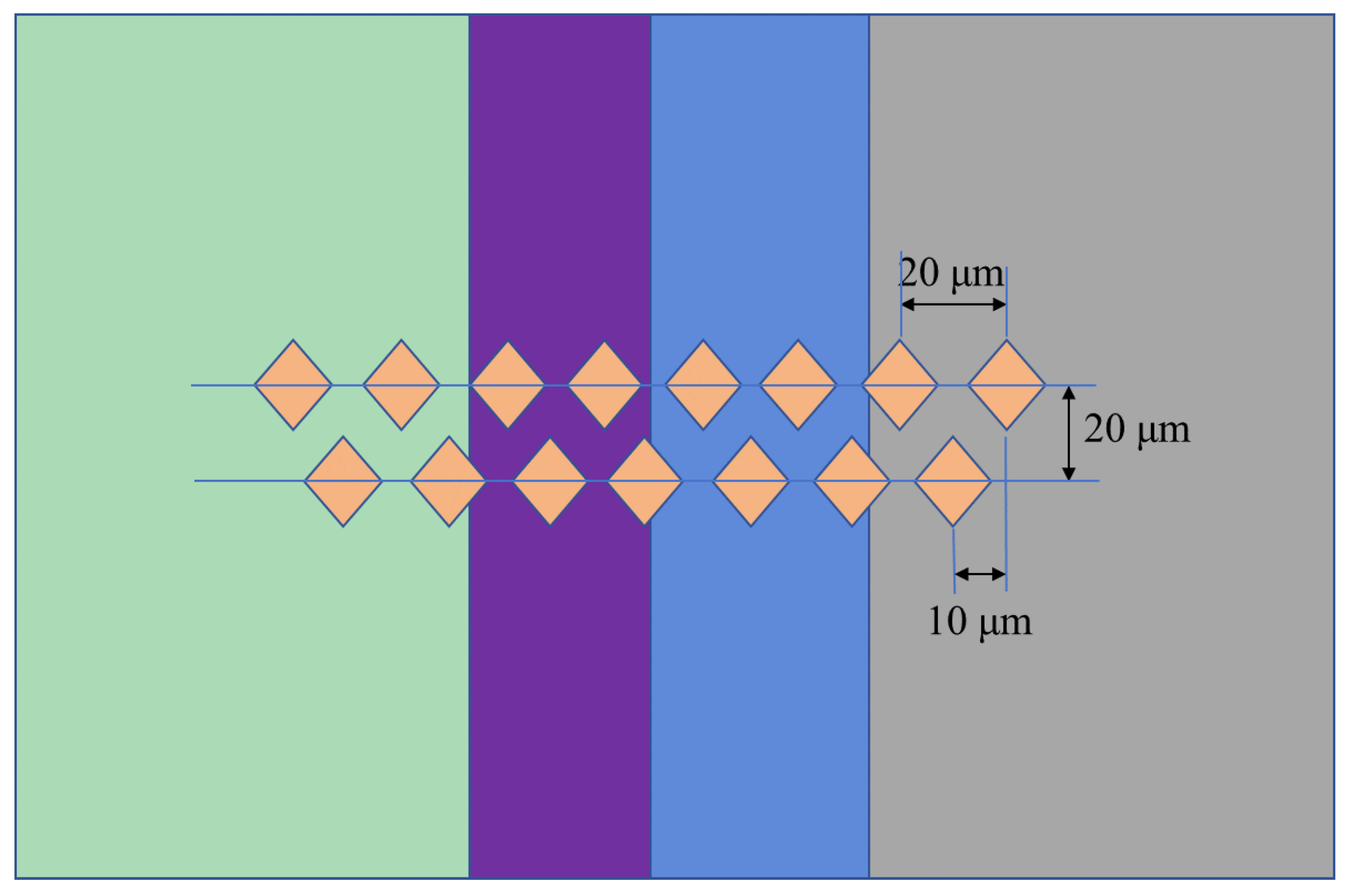
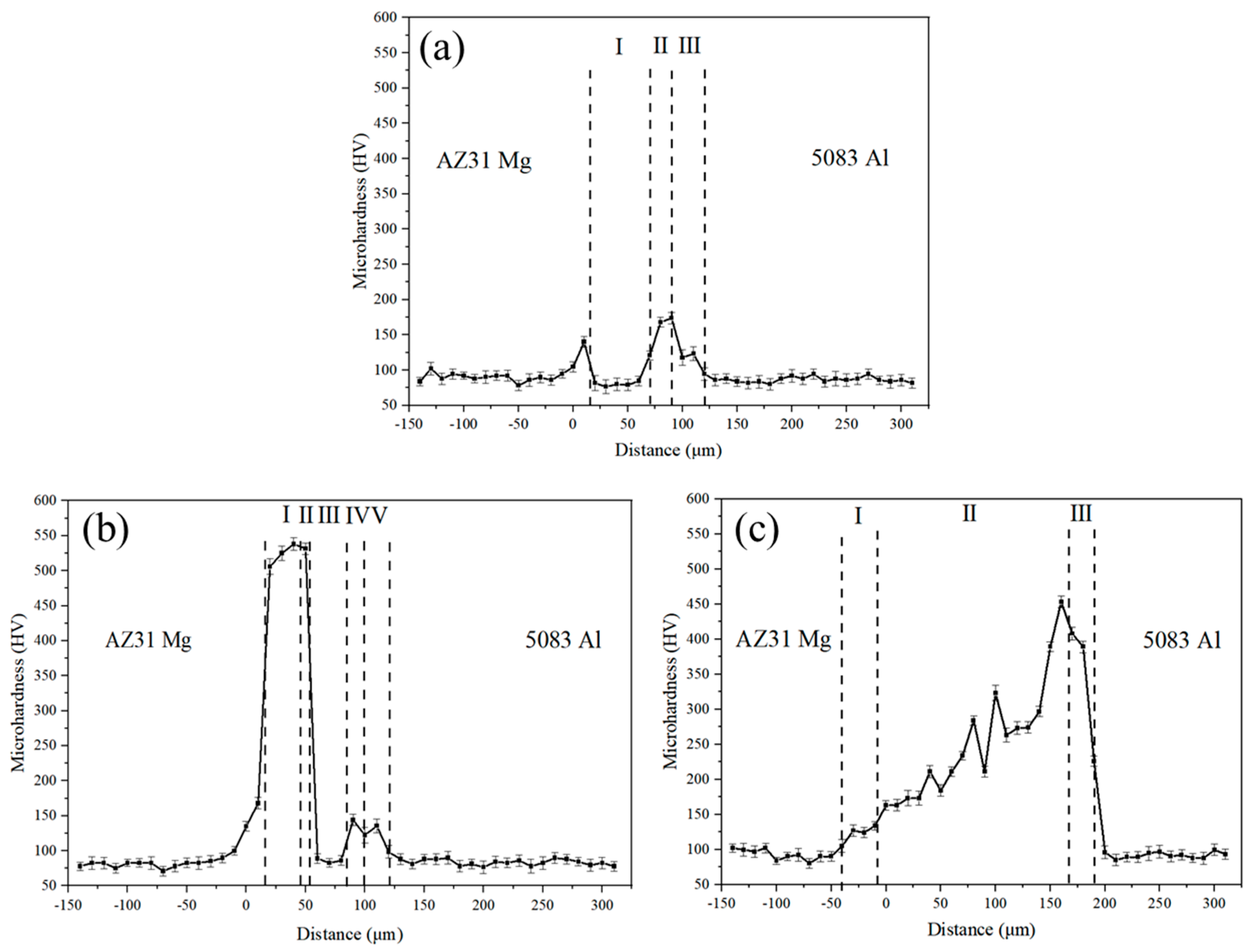
3.4. Microhardness of the Joints
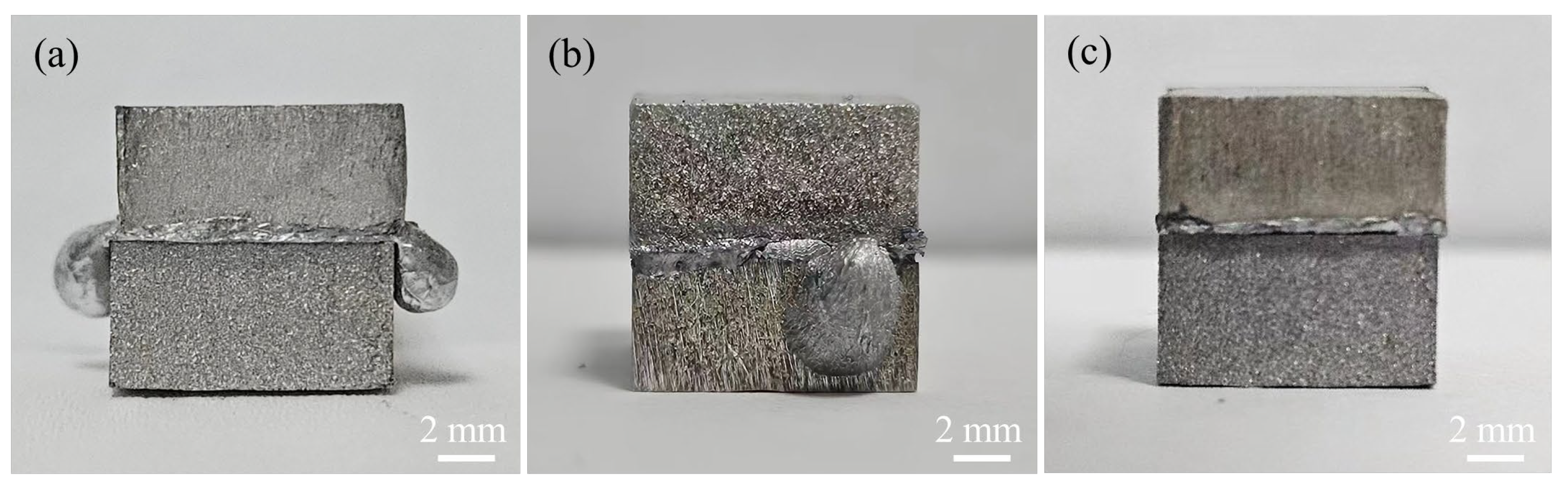
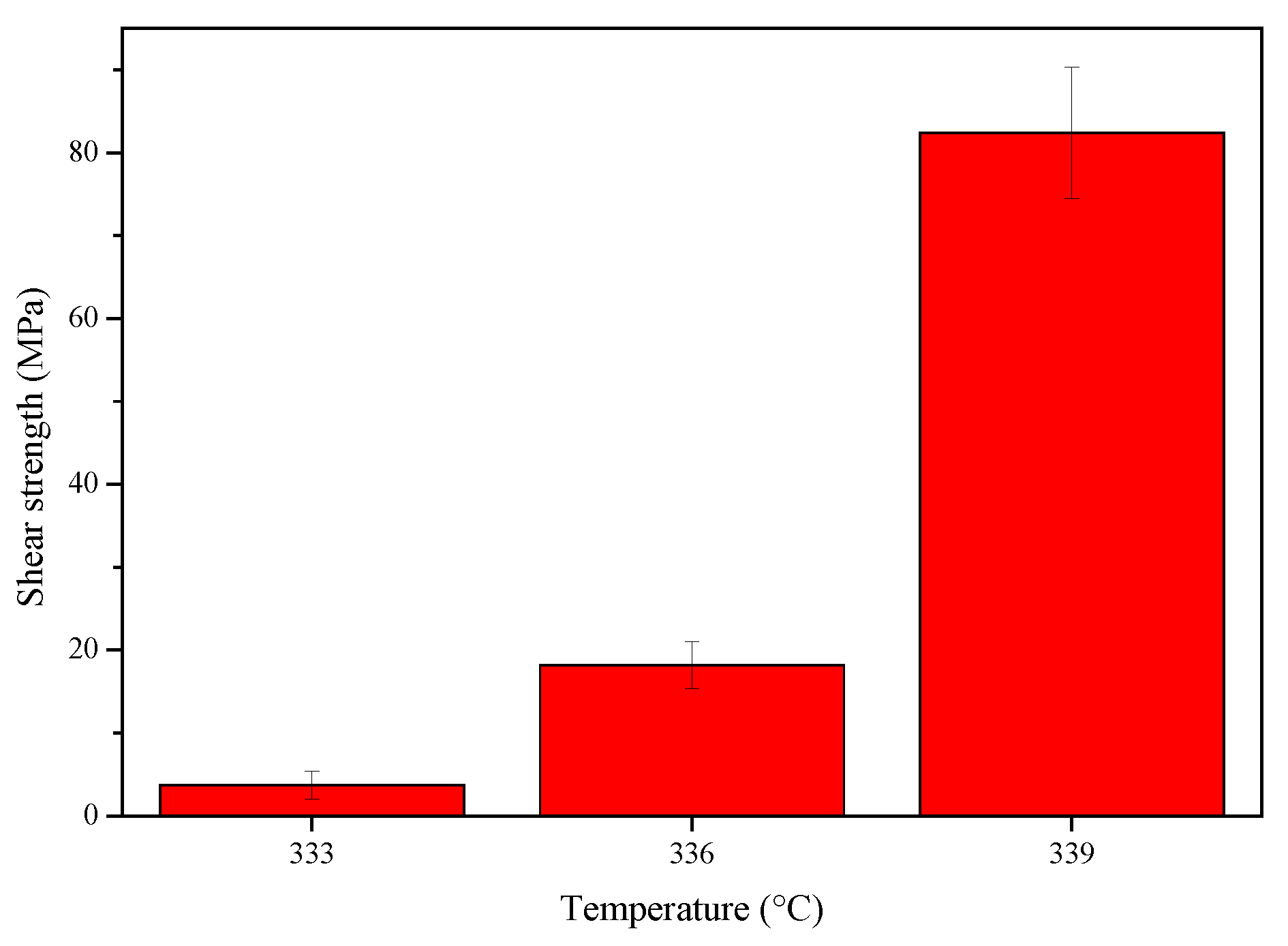
3.5. Shear Strength of the Joints
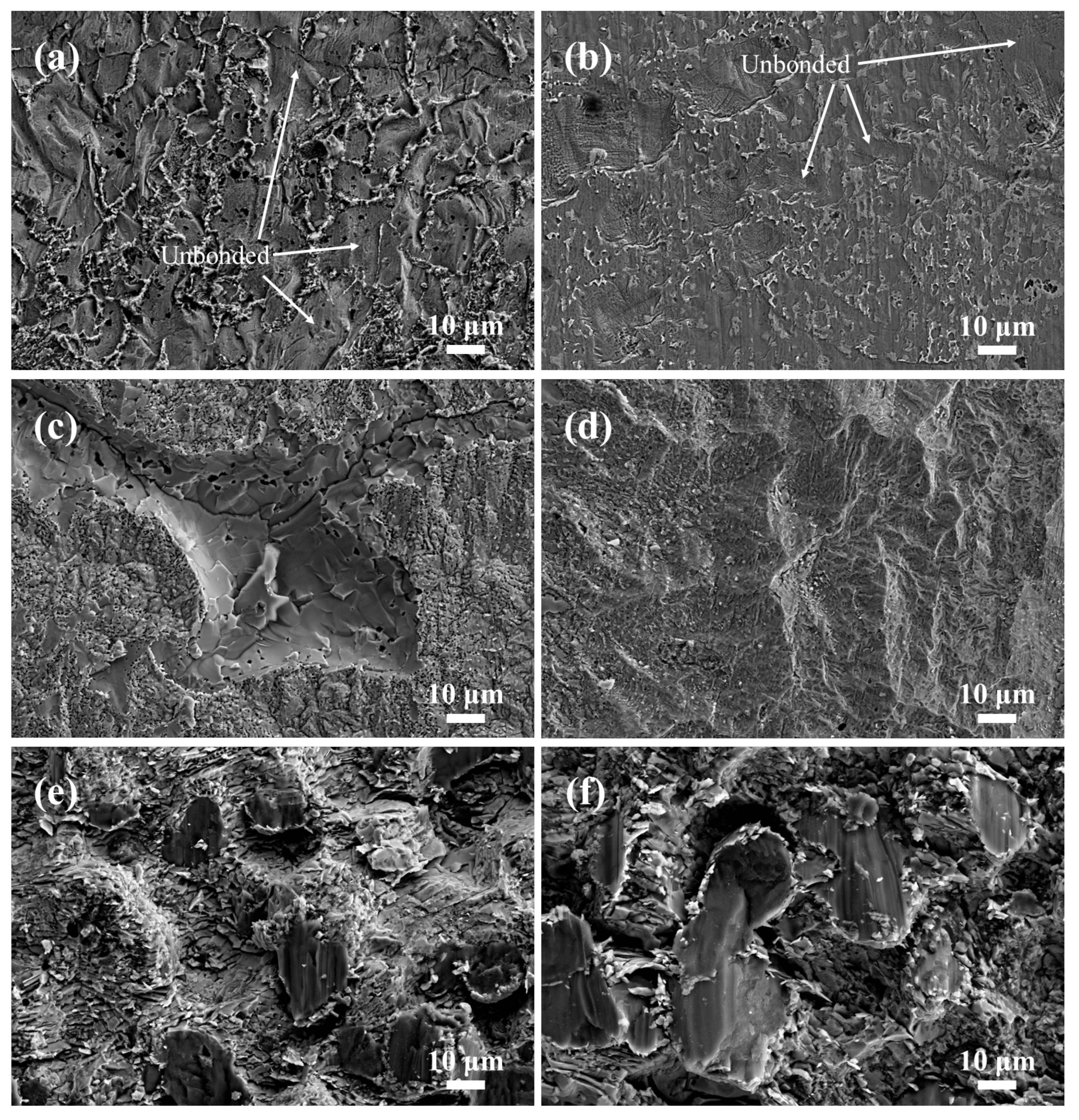
3.6. Shear Fracture Behavior of the Joints
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The bonding temperature varied, and the microstructure of the joints changed significantly. The bonding temperatures were 333 °C, 336 °C, and 339 °C, and the structures of the joints were AZ31/Zn/α + η/Al(Zn)/5083, AZ31/Mg(Zn)/MgZn2/Mg2Zn11/Zn/α + η/Al(Zn)/5083, and AZ31/Mg(Zn)/α-Mg + Mg7Zn3 + τ/Mg-Al-Zn solid solution/5083, respectively.
- (2)
- The maximum hardness value of the joints was 538 HV at the Mg-Zn IMC layer of the joint at 336 °C, and the highest shear strength of 78.3 MPa was achieved for the joint at 339 °C.
- (3)
- The shear fracture mode of all joints was brittle fracture. For the joints at 333 °C, 336 °C, and 339 °C, the shear fracture positions were located at the Mg/Zn interface, the Mg-Zn IMC layer, and the α-Mg + Mg7Zn3 + τ mixing region, respectively.
- (4)
- The formation of the Zn-Sn eutectic liquid phase reduced the Al/Zn bonding temperature, achieving a low-temperature diffusion bonding of AZ31/5083. However, limited by the diffusion and reaction of the Mg/Zn interface, the bonding temperature range was narrow, and a slight change in the bonding temperature had a significant effect on the joint structure. Therefore, the actual application requires the equipment to have a high control accuracy of temperature.
- (5)
- The structure and thickness of each layer had a significant impact on the strength of the joint. Therefore, further research is needed using collaborative adjustment of the eutectic reaction time and the bonding time to obtain greater strength of the joint.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.B.; Li, J.Z.; Sun, Q.J.; Jin, P.; Sun, Q.; Li, B.P.; Feng, J.C. Optimization of magnetic oscillation system and microstructural characteristics in arc welding of Al/Mg alloys. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 39, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrisutthekul, R.; Miyashita, Y.; Mutoh, Y. Dissimilar material laser welding between magnesium alloy AZ31B and aluminum alloy A5052-O. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.C.; Sun, L.Q.; Gao, W.L.; Li, G.Y.; Cui, J.J. The effect of temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al/Mg lap joints manufactured by magnetic pulse welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3270–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, E.; Shunmugasamy, V.C.; Mansoor, B. Dissimilar micro friction stir welding of ultra-thin Mg AZ31 to Al 6061 sheets. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Xing, Y.F.; Hu, J.Y.; Luo, J.D.; Zeng, S. Investigation on mechanism of ultrasonic welding AZ31B/5052 joint with laser texturing on mental surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 122, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, L.F.; Zhao, G.H.; Cai, Z.H.; Zhi, C.C. Effect of annealing temperature on tensile fracture behavior of AZ31/6061 explosive composite plate. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 4325–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.X.; Ma, Y.W.; Shan, H.; Niu, S.Z.; Li, Y.B. Friction self-piercing riveting (F-SPR) of aluminum alloy to magnesium alloy using a flat die. J. Magnes. Alloys 2022, 10, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.T.; He, P. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31B/AA7075 joints using non-equilibrium thermal compensation resistance welding. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 6315–6323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, M.; Khodabandeh, A.; Manafi, S. Evaluation of diffusion welding of 6061 aluminum and AZ31 magnesium alloys without using an interlayer. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.Q.; Wu, C.S.; Yang, C.L.; Padhy, G.K. Weld microstructure and mechanical properties in ultrasonic enhanced friction stir welding of Al alloy to Mg alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 254, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.X.; He, N.; Chen, C.L.; Gao, Z.H.; Gong, X.F.; Wang, R.Y.; He, L.L. Microstructural characterization of TLP bonded joints of Mar-M247 superalloys with Ni-Cr-B interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2023, 198, 112766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, M.; Prasad, M.J.N.V.; Narasimhan, K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy/interstitial free steel joint diffusion bonded with application of copper and nickel interlayers. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 6234–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Quan, G.F.; Ren, L.B.; Liu, B.S.; Ezzi, S.A.; Pan, H.H. Effect of Zn interlayer thickness on the microstructure and mechanical properties of two-step diffusion bonded joint of ZK60Mg and 5083Al. Vacuum 2019, 161, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.C.; Zhao, J.L.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Cao, Z.Q.; Li, T.J. Effect of Ni-based conversion coating and Ni-P electroless plating on the bonding process of pure Al and AZ31 alloy. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2014, 105, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.X.; Liu, C.C.; Zhang, Y.G.; Qin, Y.F.; Liu, N. Effect of Ni interlayer on characteristics of diffusion bonded Mg/Al joints. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Luo, G.Q.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Effect of silver interlayer on microstructure and mechanical properties of diffusion-bonded Mg-Al joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 541, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.M.; Zhao, L.M.; Xu, R.Z. Effect of interlayer composition on the microstructure and strength of diffusion bonded Mg/Al joint. Mater. Des. 2009, 30, 4548–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, H.; Mofid, M.A. Physical vapor deposition assisted diffusion bonding of Al alloy to Mg alloy using silver interlayer. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 4132–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habisch, S.; Bohme, M.; Peter, S.; Grung, T.; Mayr, P. The effect of interlayer materials on the joint properties of diffusion-bonded aluminium and magnesium. Metals 2018, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, G.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, L.M. Effect of Al thin film and Ni foil interlayer on diffusion bonded Mg-Al dissimilar joints. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 556, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Prangnell, P.B. Evaluation of Zn-rich coatings for IMC reaction control in aluminum-magnesium dissimilar welds. Mater. Charact. 2018, 139, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimal, R.J.G.R.; Sivakumar, M.; Raj, S.G.; Vendans, S.A.; Esakkimuthu, G. Microstructural, mechanical and metallurgical analysis of Al interlayer coating on Mg-Al alloy using diffusion bonding. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 5886–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, Z.W.; Leng, X.S.; Tong, A.Q.; Yan, J.C. Migrating behaviors of interfacial elements and oxide layers during diffusion bonding of 6063Al alloys using Zn interlayer in air. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 155, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Xiao, F.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, Y.B. Mechanism of improving strength and damping properties of powder-extruded Al/Zn composite after diffusion annealing. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2018, 28, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Murray, J.L.; Bennett, L.H.; Baker, H. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; American Society for Metals: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1986; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.P.; Qin, G.W.; Pei, W.L.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, H.D.; Li, H.X.; Jiang, M.; Hao, S.M. The α-Mg solvus and isothermal section of Mg-rich corner in the Mg-Zn-Al ternary system at 320 °C. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 481, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.X.; Pan, F.S.; Li, Z.S.; Luo, X.D. Effect of composition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Zn-Al alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Material | Mg | Zn | Cr | Mn | Ti | Ca | Al | Bi | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AZ31 | Bal | 1.03 | — | 0.22 | — | 0.04 | 2.99 | — | 0.08 |
| 5083 | 4.51 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.58 | 0.02 | — | Bal | — | 0.03 |
| Sn-Zn Eutectic Reaction | Diffusion Bonding | Vacuum Degree (Pa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) | |
| 200 | 60 | 4 | 333, 336, 339 | 120 | 4 | <3 × 10−1 |
| Point Number | Composition (at. %) | Phase Identity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mg | Zn | Sn | ||
| 1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 95.7 | 0 | Zn |
| 2 | 30.2 | 1.2 | 68.3 | 0.3 | α + η |
| 3 | 85.6 | 0.8 | 13.0 | 0.6 | Al(Zn) |
| Point Number | Composition (at. %) | Phase Identity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mg | Zn | Sn | ||
| 1 | 1.7 | 32.8 | 65.4 | 0.1 | MgZn2 |
| 2 | 1.3 | 16.0 | 82.6 | 0.1 | Mg2Zn11 |
| 3 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 97.3 | 0.1 | Zn |
| 4 | 41.6 | 2.1 | 56.3 | — | α + η |
| 5 | 86.8 | 0.3 | 12.8 | 0.1 | Al(Zn) |
| Point Number | Composition (at. %) | Phase Identity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mg | Zn | Sn | ||
| 1 | 2.5 | 94.5 | 3.0 | 0 | α-Mg |
| 2 | 2.6 | 93.9 | 3.1 | 0.4 | α-Mg |
| 3 | 15.2 | 44.8 | 40.0 | 0 | τ-Mg32(Al, Zn)49 |
| 4 | 16.3 | 43.8 | 39.8 | 0.1 | τ-Mg32(Al, Zn)49 |
| 5 | 39.0 | 39.8 | 21.2 | 0 | Al-Mg-Zn solid solution |
| 6 | 3.8 | 71.1 | 24.7 | 0.4 | Mg7Zn3 |
| 7 | 3.2 | 76.6 | 19.8 | 0.4 | Mg7Zn3 |
| 8 | 6.1 | 67.3 | 26.4 | 0.2 | Mg7Zn3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, T.; Guo, Y.; Chen, G.; Rong, Z.; Pan, H. Influence of Bonding Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31/Zn/Sn/5083 Diffusion Joint. Materials 2024, 17, 6110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246110
Tan T, Guo Y, Chen G, Rong Z, Pan H. Influence of Bonding Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31/Zn/Sn/5083 Diffusion Joint. Materials. 2024; 17(24):6110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246110
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Tianbao, Yangyang Guo, Gang Chen, Zijun Rong, and Houhong Pan. 2024. "Influence of Bonding Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31/Zn/Sn/5083 Diffusion Joint" Materials 17, no. 24: 6110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246110
APA StyleTan, T., Guo, Y., Chen, G., Rong, Z., & Pan, H. (2024). Influence of Bonding Temperature on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31/Zn/Sn/5083 Diffusion Joint. Materials, 17(24), 6110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246110






