Effects of Quartz Sand on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Cementitious Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
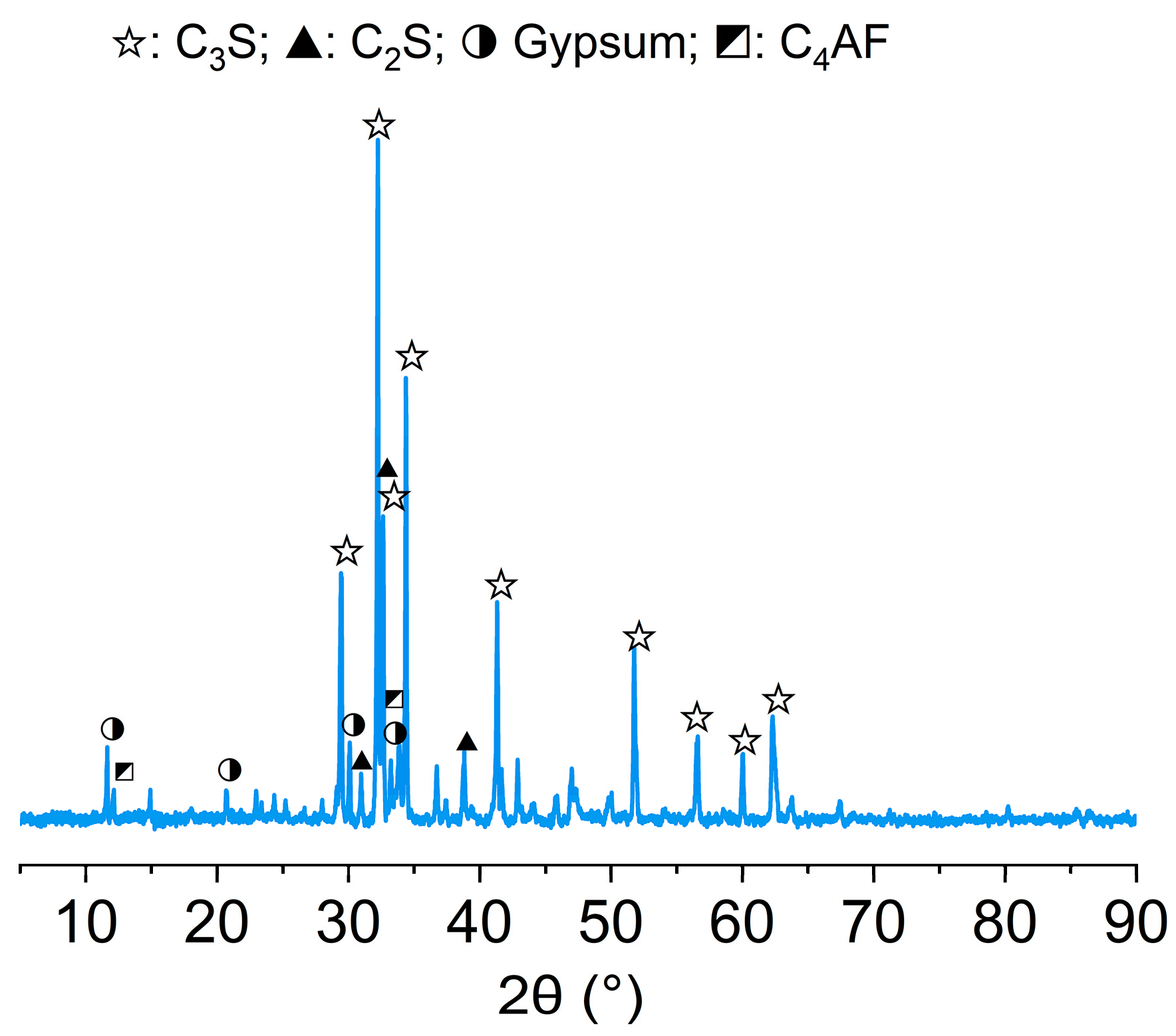
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Methods
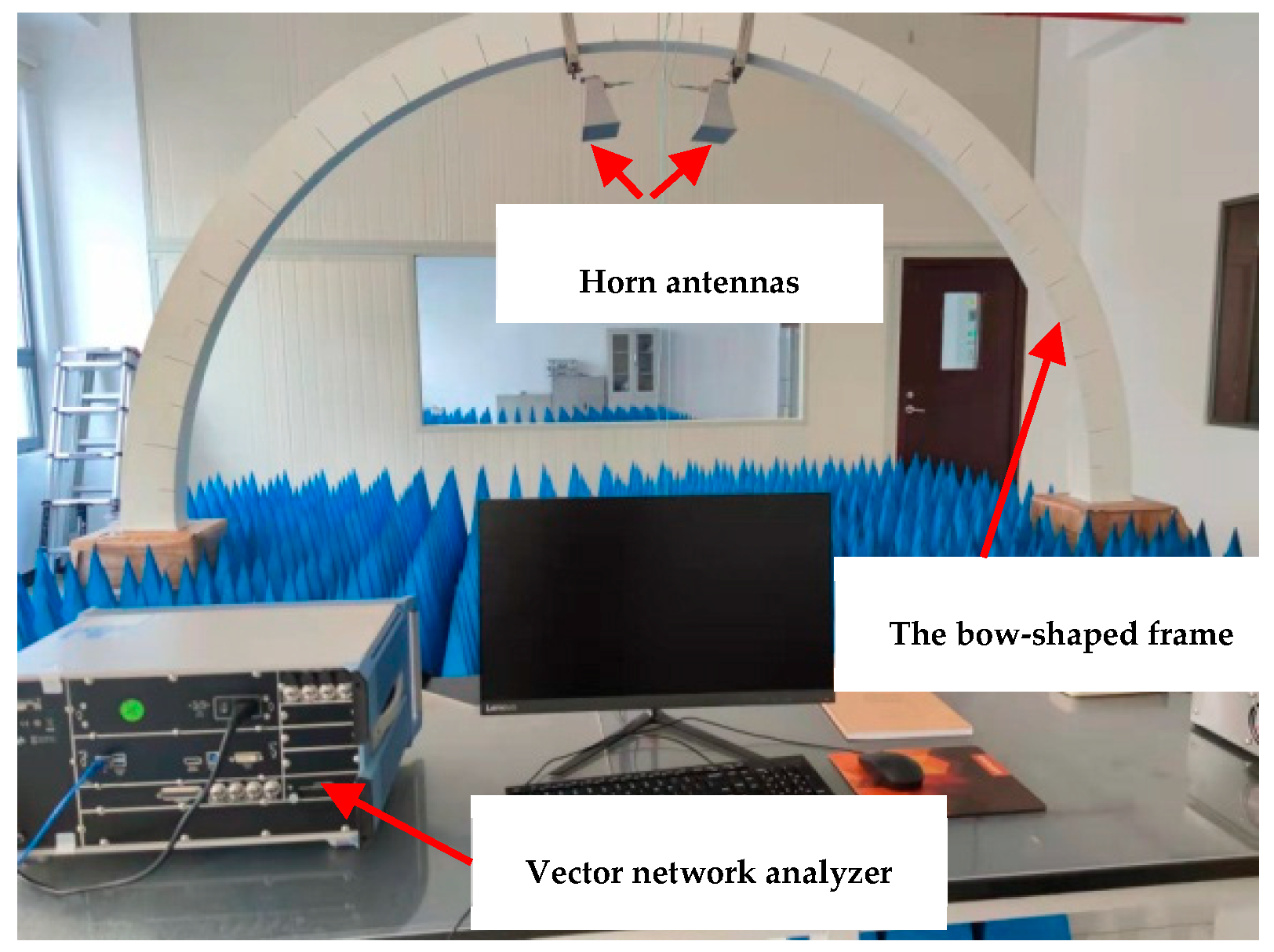
2.2.1. EMWs Reflection Loss (RL) Performance
2.2.2. Measurement and Simulation of Electromagnetic Parameters
- (1)
- Measurement
- (2)
- Simulation of RL curves
2.2.3. Oven-Dry Porosity
3. Results
3.1. Electromagnetic Reflection Loss
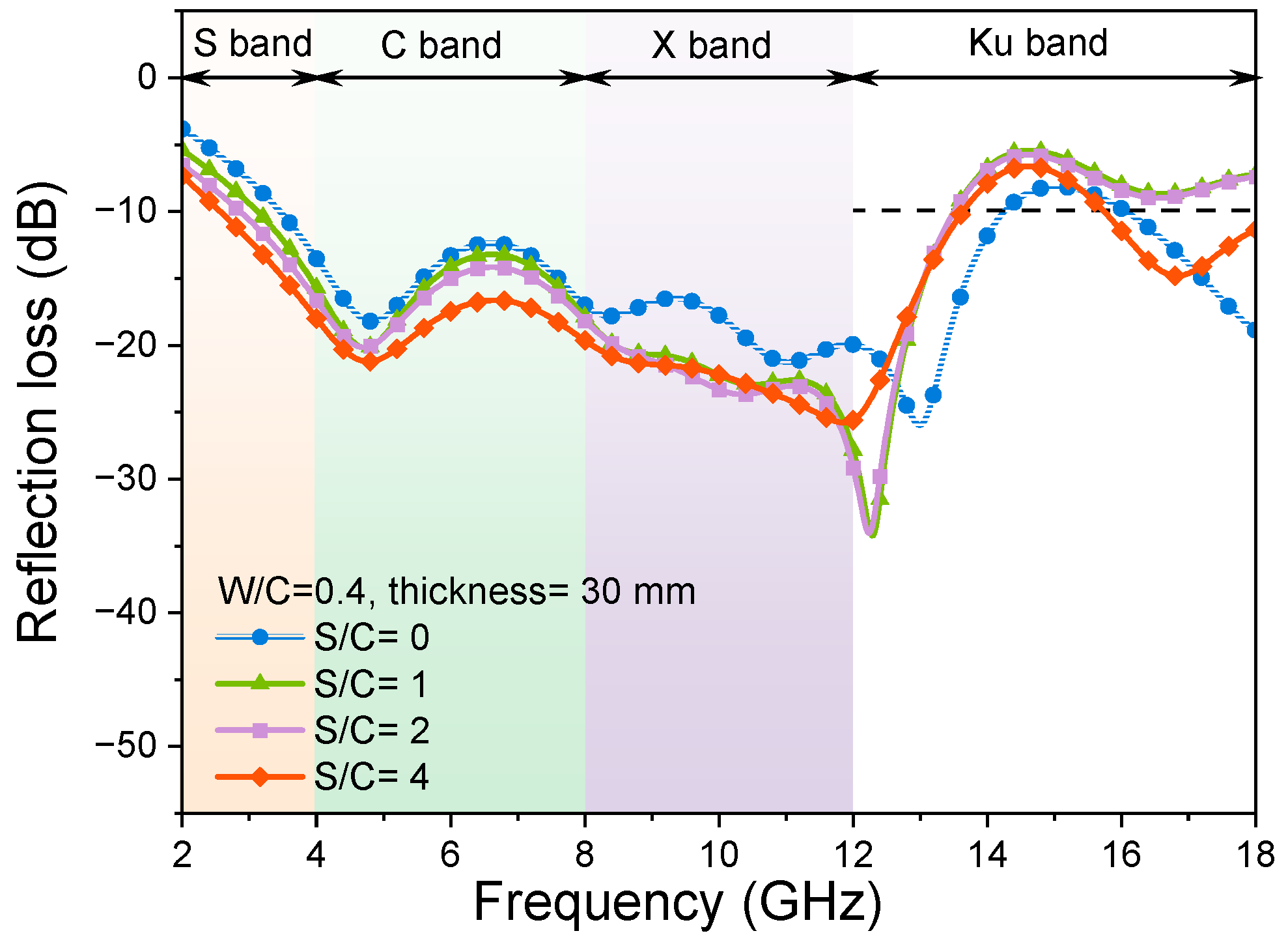
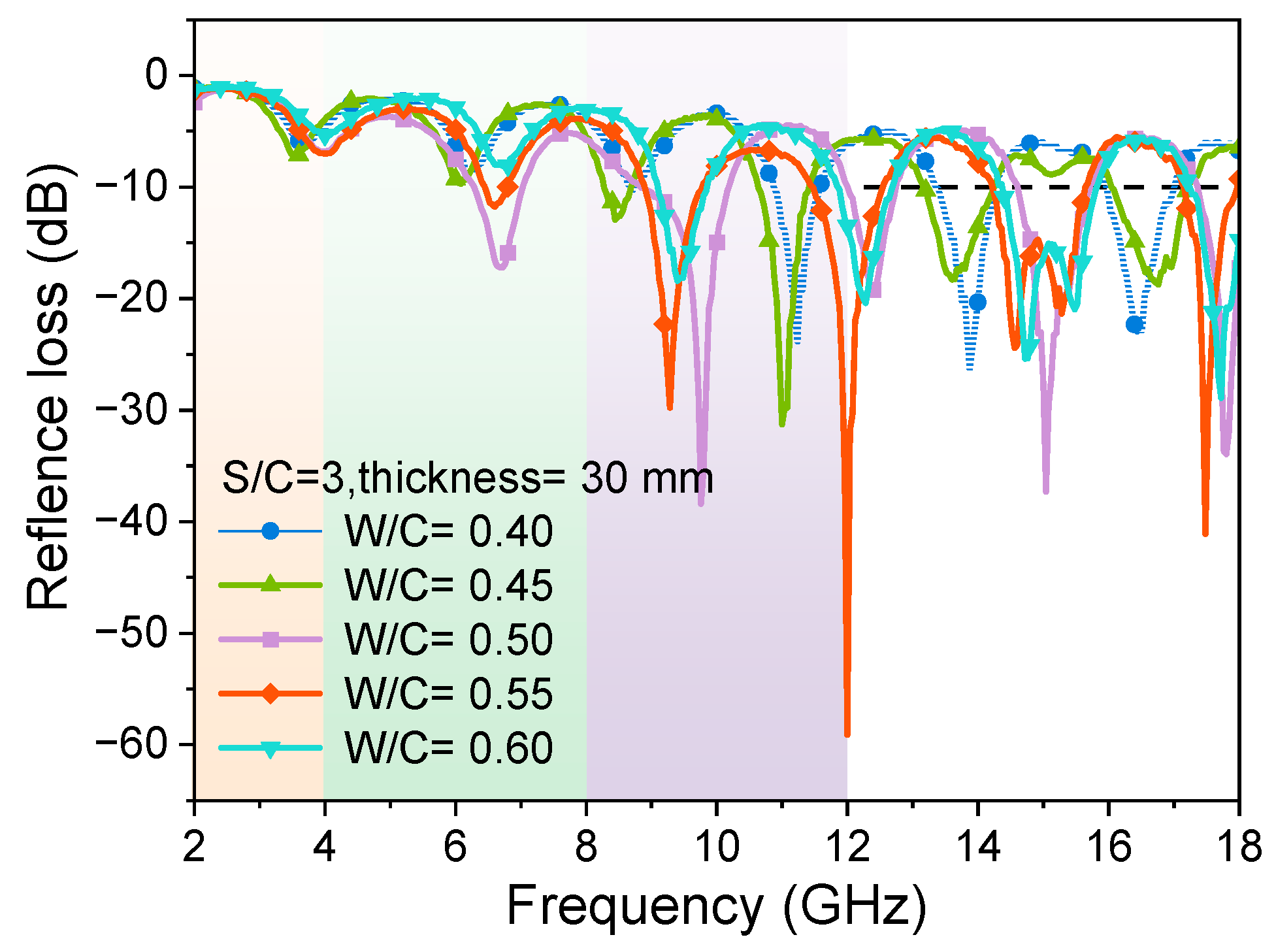
3.1.1. Effects of Sand-to-Cement Ratios
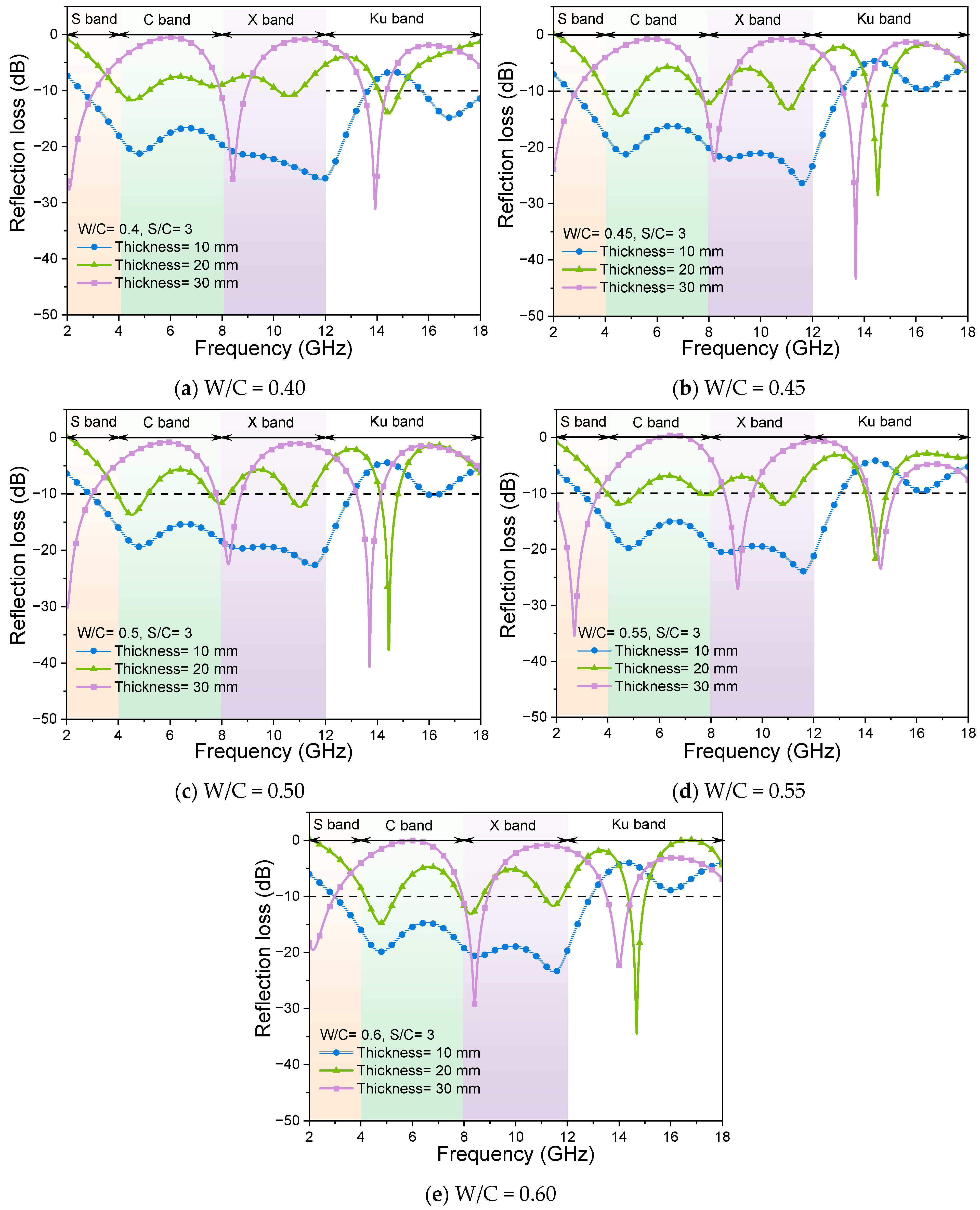
3.1.2. Effects of the Thickness of the Samples
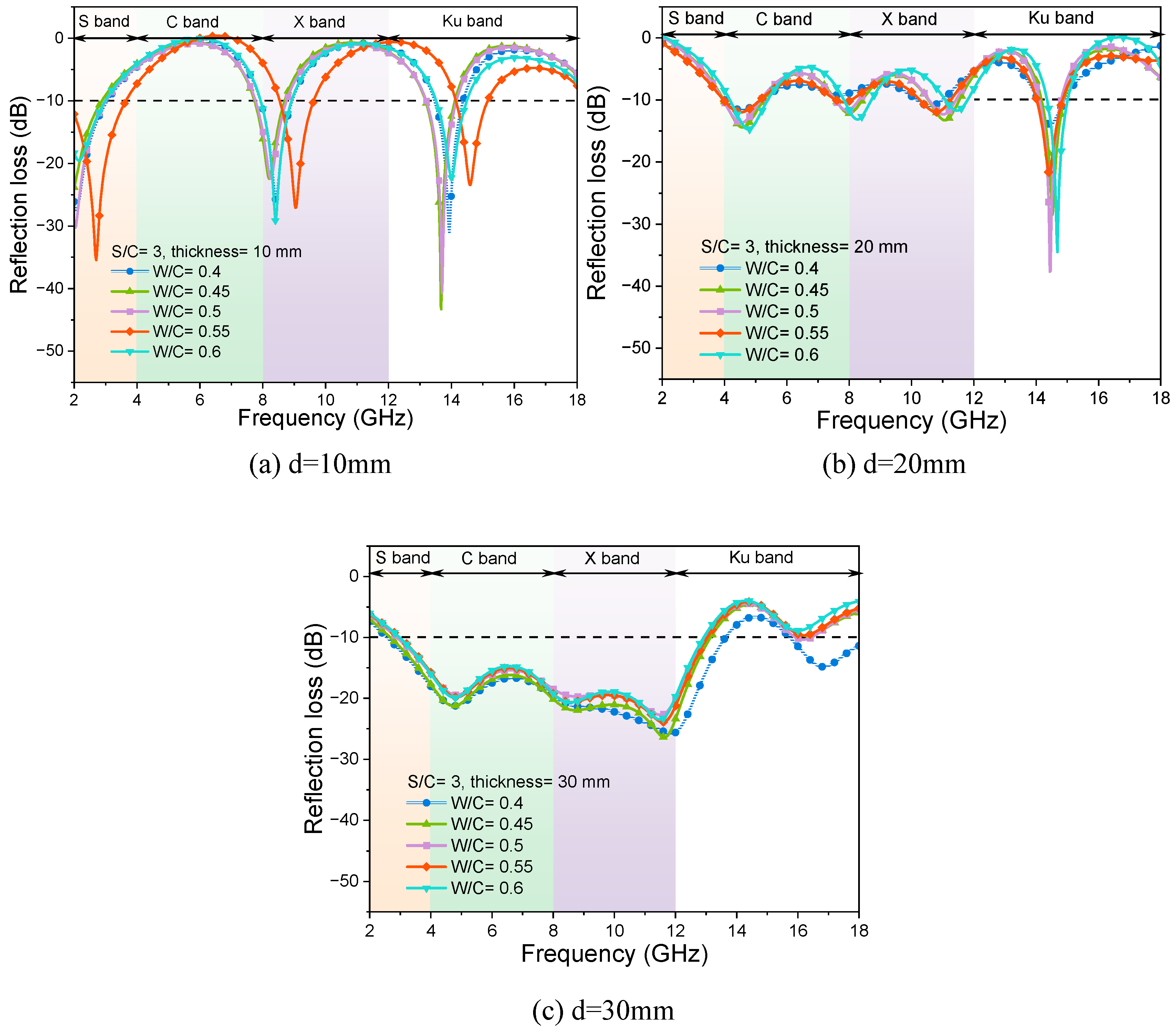
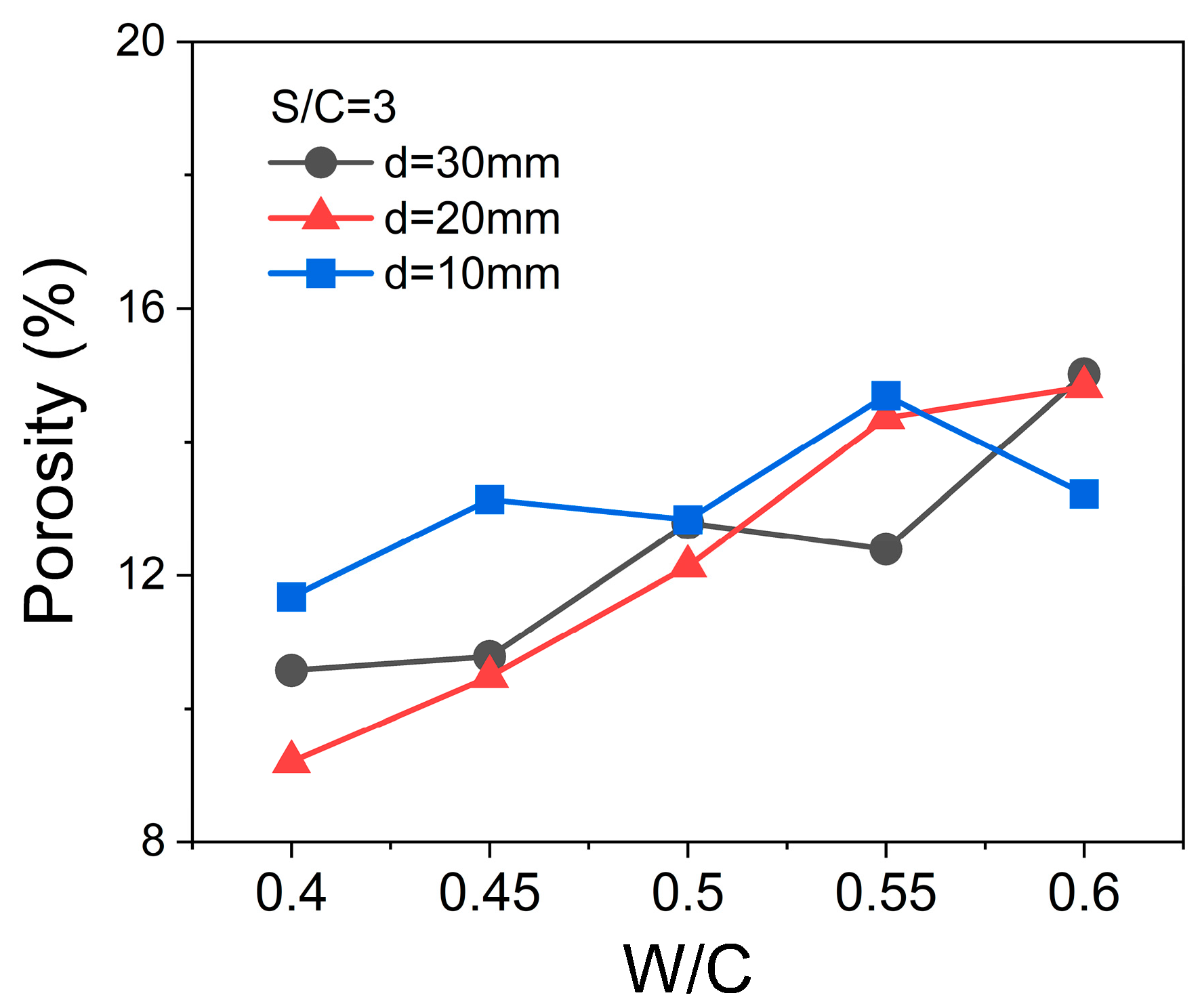
3.1.3. Effects of Water-to-Cement Ratios
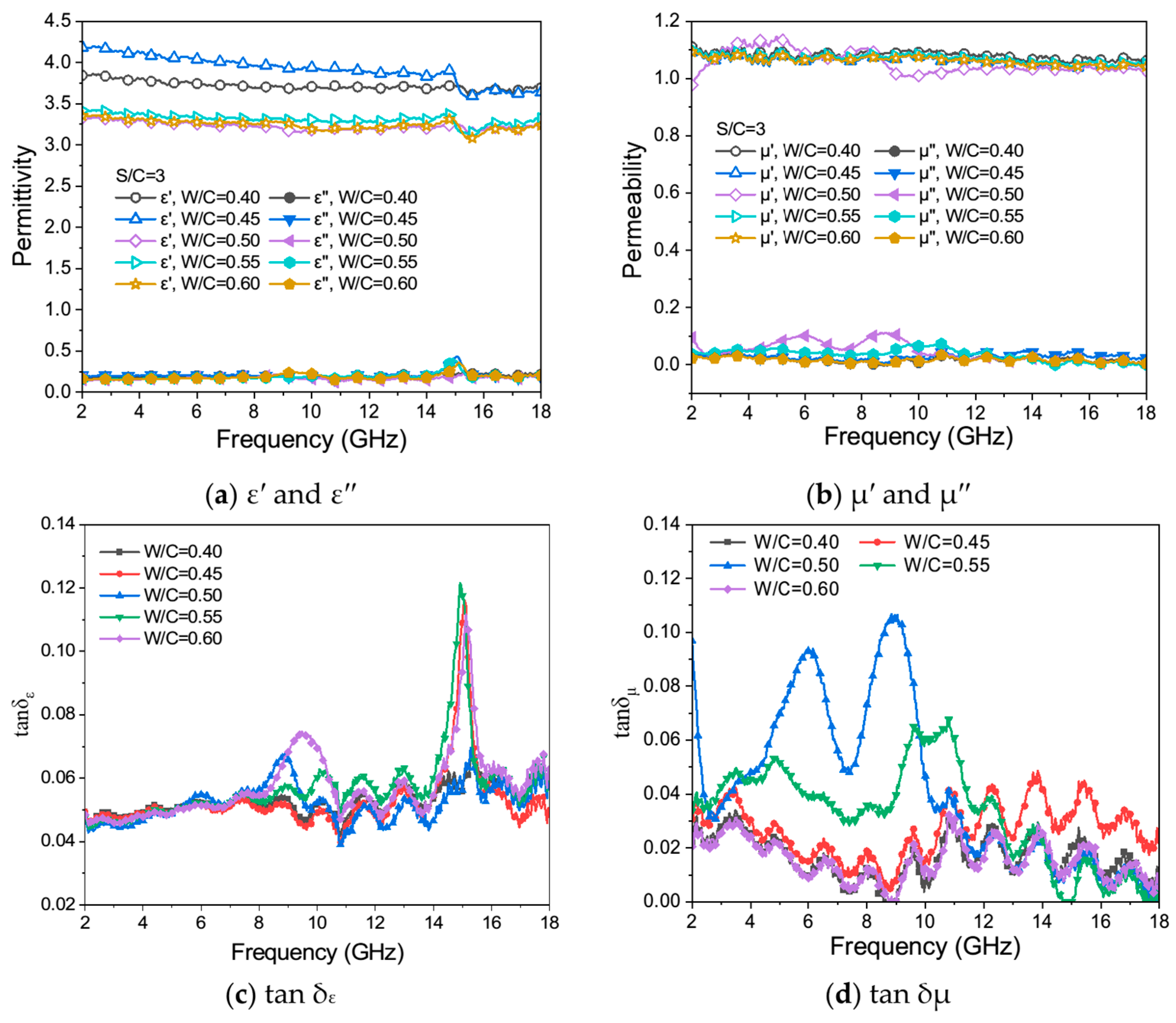
3.2. Electromagnetic Parameters
3.2.1. Samples with Different Sand-to-Cement Ratios
3.2.2. Samples with Different Water-to-Cement Ratios
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
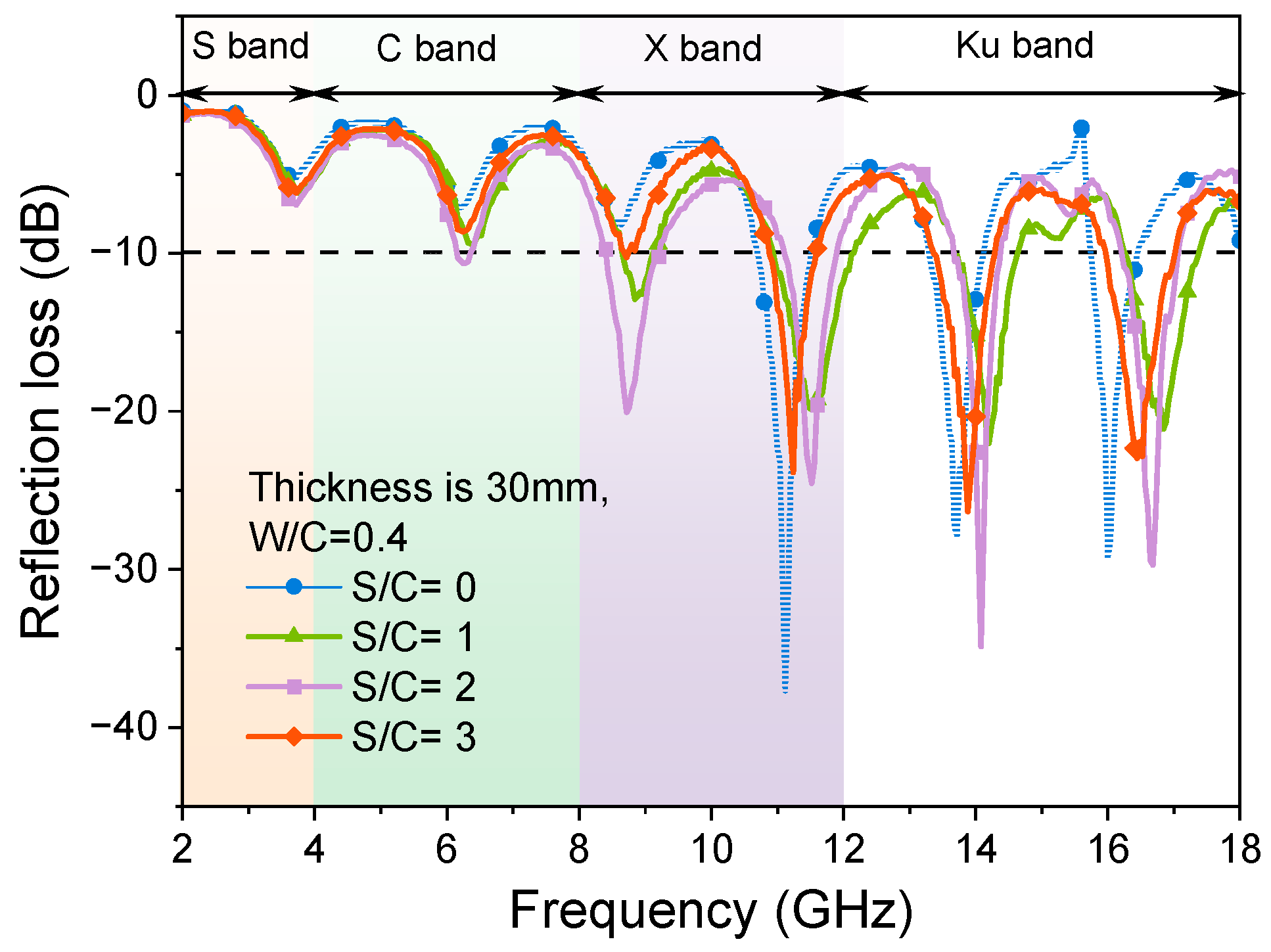
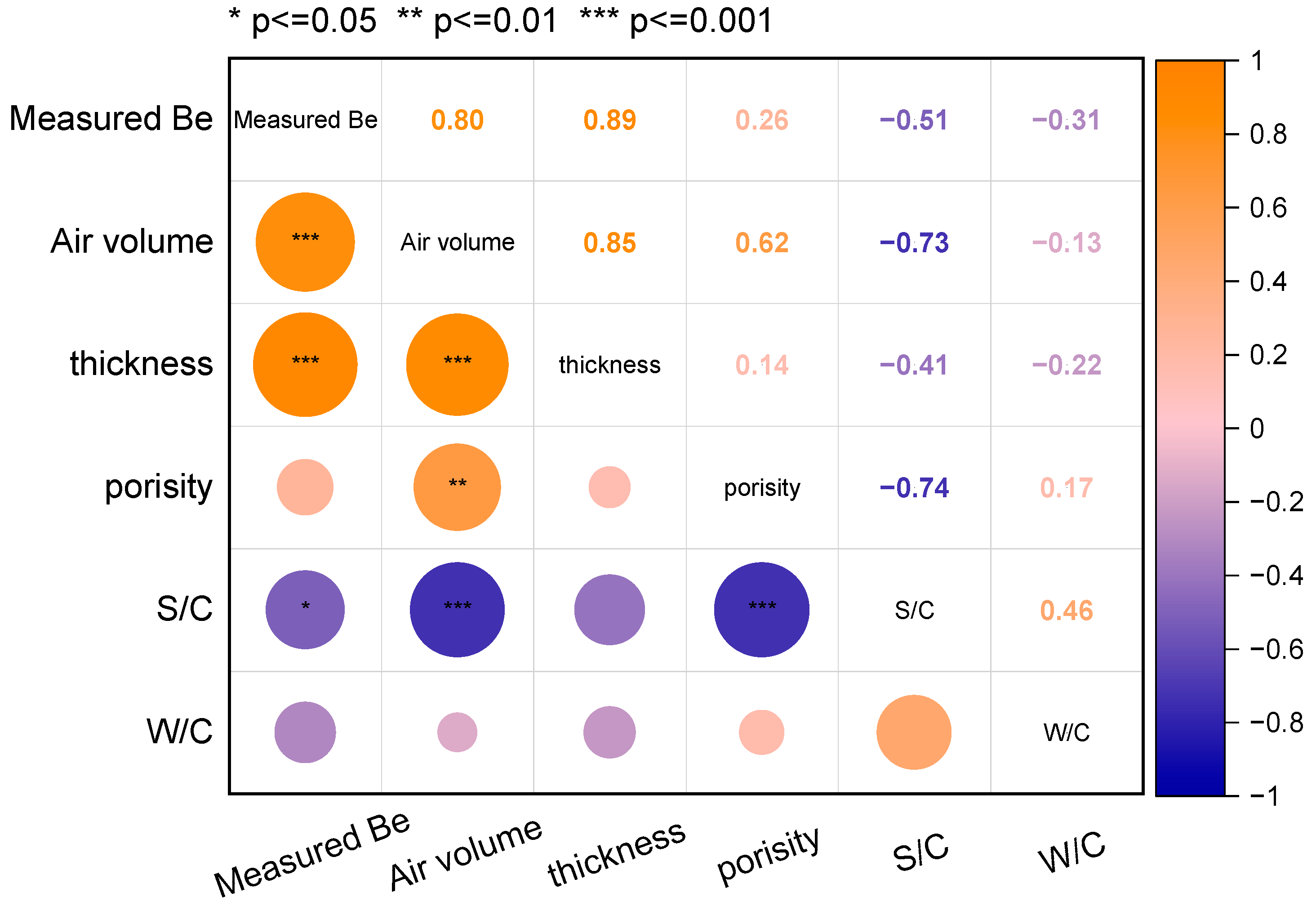
- The content variation of quartz sand in mortar samples with a constant W/C ratio significantly affects the EMW-absorption effective bandwidth values. The presence of quartz sand in the hardened cement-based materials regulates the oven-dry porosity values of samples, resulting in the change in air volumes in the matrix and the impedance-matching behaviours between cementitious materials and the EMW transparent phases (sand and air in the pores). The threshold of the S/C ratio of mortar is 3; that is, when the S/C ratio is larger than 3, the absorption of EMWs in the high-frequency band decreases sharply.
- The thicknesses of the mortar with the same S/C ratio and W/C ratios significantly influence the absorption performance of EMWs because of the changing of actual air volumes in the mortar. It was found that a mortar sample with a thickness of 30 mm obtained good EMW absorption with a larger effective absorption bandwidth. This indicates that the optimization of sample thickness is an essential factor in improving the absorption performance when designing EMW-absorbing materials.
- When the S/C ratio of a mortar sample is fixed, the change in W/C ratios will have little influence over the EMW-absorption performance of the mortar samples with the same thickness values. The variation in actual air volume values induced by higher W/C ratios in this work is not as much as that induced by the quartz sand contents in the mortar samples.
- The air within the porous structure and the sand in the solid skeleton of the mortar samples influence the EMW effective bandwidth in a coordinated way. The calculated electromagnetic parameters of mortar powder samples can qualitatively describe the effects of solid matrix variation caused by S/C and W/C ratios on EMW-absorption performance. The effective bandwidth of EMW absorption of a mortar sample is positively linearly related with the S/C ratios and the thicknesses of the sample. Therefore, the calculated EMW RL curves can hardly precisely describe the real EMW-absorption performance of mortar samples.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, J.; Cao, J.; Guo, M.; Yang, S.; Yao, H.; Lei, M.; Hao, Y.; Bi, K. Metamaterial Mechanical Antenna for Very Low Frequency Wireless Communication. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taishi, B.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, S. Dual-Band 3D Electrically Small Antenna Based on Split Ring Resonators. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zheng, L.; Aouraghe, M.A.; Xu, F. Ultra-Light-Weight Kevlar/Polyimide 3D Woven Spacer Multifunctional Composites for High-Gain Microstrip Antenna. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chung, D.D.L. Coke Powder as an Admixture in Cement for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding. Carbon N. Y. 2003, 41, 2433–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wen, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Bi, K. Extremely-Low Frequency Mechanical Antenna Based on Vibrating Permanent Magnet. Eng. Sci. 2021, 16, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Ali, T.; Manohara Pai, M.M. Highly Isolated Ultrawideband Multiple Input and Multiple Output Antenna for Wireless Applications. Eng. Sci. 2022, 17, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Sharan, T.; Singh, A.K. Enhancing the Axial Ratio Bandwidth of Circularly Polarized Open Ground Slot Coplanar Waveguide-Fed Antenna for Multiband Wireless Communications. Eng. Sci. 2022, 17, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilli, R.; Ravi Chandra, M.L.; Jordhana, D. Ultra-Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output Technologies for 6G Wireless Networks. Eng. Sci. 2021, 16, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Liu, S.; Duan, Y.; Cheng, J. Cement Based Electromagnetic Shielding and Absorbing Building Materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zhrani, S.; Bedaiwi, N.M.; El-Ramli, I.F.; Barasheed, A.Z.; Abduldaiem, A.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Umar, A. Underwater Optical Communications: A Brief Overview and Recent Developments. Eng. Sci. 2021, 16, 146–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.E.; Kang, Y.M. Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Properties of Ni-Zn Ferrite Powder–Epoxy Composites in GHz Range. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 513, 167075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasinghe, D.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Electromagnetic Shielding Properties of Carbon Fibre Reinforced Cementitious Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, S.; Liu, X. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Multifunctional Cementitious Composites Incorporating Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Fibers and Fly Ash: Effects of Microstructure and Hydration. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 143, 106389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.N.; Jang, D.; Lee, H.K.; Nam, I.W. Influence of Carbon Fiber Additions on the Electromagnetic Wave Shielding Characteristics of CNT-Cement Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Yuan, J.; Yang, C.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Effects of Graphite on the Mechanical and Microwave Absorption Properties of Geopolymer Based Composites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, B.; Tang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hao, L. Dual Gradient Direct Ink Writing of Functional Geopolymer-Based Carbonyl-Iron/Graphene Composites for Adjustable Broadband Microwave Absorption. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9277–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Ji, Z.; Ma, C.; Si, T.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Three-Dimensional Hexagonal Periodic Structured Absorber for Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 3115–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Wang, J. Three-Dimensional Periodic Structured Absorber for Broadband Electromagnetic Radiation Absorption. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2020, 16, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, J.S.; Alrowaili, Z.A.; Saleh, H.H.; Hammoud, A.; Alomairy, S.; Sriwunkum, C.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Synthesis, Physical and Nuclear Shielding Properties of Novel Pb–Al Alloys. Prog. Nucl. Energy 2021, 142, 103992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.T.; Hegler, S.; Liebscher, M.; Navarro de Sosa, I.; Li, H.; Plettemeier, D.; Drossel, W.G.; Mechtcherine, V. Dielectric Material Characterization of Concrete in GHz Range in Dependence on Pore Volume and Water Content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 311, 125234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukwa, M.; Brodwin, M.; Christo, S.; Chang, J.; Shah, S.P. The Influence of the Hydration Process upon Microwave Properties of Cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 1991, 21, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Mahmoud, A.E.R.; Parashar, S.K.S. Enhancement of Electromagnetic Shielding and Piezoelectric Properties of White Portland Cement by Hydration Time. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houbi, A.; Aldashevich, Z.A.; Atassi, Y.; Bagasharova Telmanovna, Z.; Saule, M.; Kubanych, K. Microwave Absorbing Properties of Ferrites and Their Composites: A Review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 529, 167839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.F.; Howell, J.R. Measurements of Thermal Conductivity and Optical Properties of Porous Partially Stabilized Zirconia. Exp. Heat Transf. 1992, 5, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taishi, B.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, S. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Cement-Based Composites Filled with Porous Materials. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3017–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Liu, S.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, Y. Investigation of the Electromagnetic Characteristics of Cement Based Composites Filled with EPS. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Duan, Y.; Chen, G. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties of Cement-Based Composites Filled with Graphene Nano-Platelets and Hollow Glass Microspheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Effects of Air-Entraining Agents and Glass Powder on the Electromagnetic Wave Transmission and Mechanical Performances of Sulfoaluminate Cement. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, S.; Ji, Z.; Wu, Z.; Si, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Properties of Pyramidal Engineered Cement Mortar Containing Carbon Black. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, D.; Sobótka, M.; Jarczewska, K.; Logoń, D.; Majcher, K.; Musiał, M.; Niewiadomski, P.; Pakos, W.; Różański, A.; Trapko, T. Microstructure Properties of Cementitious Mortars with Selected Additives for Electromagnetic Waves Absorbing Applications. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 134, 104732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L. Investigation on Electromagnetic and Microwave Absorption Properties of Copper Slag-Filled Cement Mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 74, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.N.; Fang, Y.H.; Zhang, D.D.; Wang, B.; Zhuo, F.Y.; Huang, B.T. Microwave Absorption and Electromagnetic Properties of Ultra-High-Strength Cementitious Materials: Influence of Basalt Powder and Underlying Mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, H.; Xiong, D.; Cao, Z. Hollow Polyaniline/Fe3O4 Microsphere Composites: Preparation, Characterization, and Applications in Microwave Absorption. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Aslani, F.; Liu, M. Electromagnetic and Microwave Absorbing Properties of Cementitious Composite for 3D Printing Containing Waste Copper Solids. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 94, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, Y.; Yue, L.; Yang, T. Lightweight and Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Foamed Cement-Based Composites Incorporated with Hybrid Dielectric Fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, P.; Yu, Q.; Zhan, B.; Gao, P.; Guo, B.; Hong, L.; Yang, Y.; Han, A. Enhancing Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Flexural Properties in Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Foamed Cement-Based Composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 415, 134989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, C.; Zhang, J. Preparation of Black Titanium Monoxide Nanoparticles and Their Potential in Electromagnetic Wave Absorption. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 3458–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, W.; Kong, D.; Wei, S.; Li, W.; Chen, S. A Novel Core/Shell Cuprous Oxide-Based Structure with Improved Microwave Absorbing and Antibacterial Performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Peng, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F. Constructing a Two-Layer Oblique Honeycomb Sandwich Structure by LCD 3D Printing for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing. Compos. Struct. 2023, 305, 116449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.H.; Xie, B.; Li, H.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Q.H. Mechanical Properties and Electromagnetic Absorption Characteristics of Foam Cement-Based Absorbing Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 330, 127221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Matori, K.A.; Abbas, Z.; Zulkimi, M.M.M.; Idris, F.M.; Zaid, M.H.M.; Rahim, N.; Hasan, I.H.; Song, W.H. Single- and Double-Layer Microwave Absorbers of Cobalt Ferrite and Graphite Composite at Gigahertz Frequency. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2019, 32, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, W. Microwave Absorbing Properties of Double-Layer Cementitious Composites Containing Mn-Zn Ferrite. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, F.; Deng, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Xiang, Z.; Lu, W. Mace-like Carbon Fiber/ZnO Nanorod Composite Derived from Typha Orientalis for Lightweight and High-Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorber. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 1002–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, G.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Liu, X. Flexible Multilayered MXene/Thermoplastic Polyurethane Films with Excellent Electromagnetic Interference Shielding, Thermal Conductivity, and Management Performances. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2021, 4, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Du, Z.; Liu, C.; Shen, C.; Wang, Y. Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Enhancement of Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Carbonaceous Nanocomposites by Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-Assisted Segregated Structure: A Comparative Study of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Nanoplatelets. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Performance of Magnesium Phosphate Cement Functionalized by Nano-Fe3O4 Magnetic Fluid and Hollow Glass Microspheres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Properties of a Double-Layer EMW-Absorbing Structure Containing a Graded Nano-Sized Absorbent Combing Extruded and Sprayed 3D Printing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Aslani, F.; Ma, G. Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Performance of 3D Printed Wave-Shape Copper Solid Cementitious Element. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Effects of the Absorber, Thickness and Surface Roughness on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Characteristics of Magnesium Phosphate Cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Duan, Y.; Liu, S. The Electromagnetic Characteristics of Fly Ash and Absorbing Properties of Cement-Based Composites Using Fly Ash as Cement Replacement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 27, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Bai, E.; Xu, J.; Chen, J. Research on Electromagnetic Properties and Microwave Deicing Performance of Carbon Fiber Modified Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, Y.; Deng, G.; Yang, T. Broadband Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Performance by Designing the Foam Structure and Double-Layer for Cement-Based Composites Containing MWCNTs. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 131, 104595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, Y. Effect of Basalt Fiber on Electromagnetic Properties of Sulphoaluminate Cement. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2024, 48, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Guan, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Electromagnetic Absorption Properties of Composite Mortar with Graphene and Manganese-Zinc Ferrite. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 97, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monasterio, M.; Gaitero, J.J.; Erkizia, E.; Guerrero Bustos, A.M.; Miccio, L.A.; Dolado, J.S.; Cerveny, S. Effect of Addition of Silica- and Amine Functionalized Silica-Nanoparticles on the Microstructure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate (C-S-H) Gel. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; He, J.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Xue, H. Laminated Magnetic Graphene with Enhanced Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2012, 1, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zheng, J.; Liang, L.; Sun, K.; Song, Y.; Zhao, S. Effect of Zn Substitution on the Electromagnetic and Microwave Absorbing Properties of BaCo2 Hexaferrite. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 9970–9976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Qing, Y.; Luo, F.; Zhu, D. Effect of Carbon Black on Dielectric and Microwave Absorption Properties of Carbon Black/Cordierite Plasma-Sprayed Coatings. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2015, 24, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wei, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, F.; Liu, F. Design and Optimization of Double-Layer Structure for Improved Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Characteristic of Single-Layer Foam Cement-Based Materials Containing Carbon Black. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 89, 109319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Li, T.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J.; Qi, Q.; Meng, F. Structure–Activity Relationship in Microstructure Design for Electromagnetic Wave Absorption Applications. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Reference | W/C | S/C | Thicknesses (mm) | Be (GHz) | RLmin (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [13] | 0.30 | 0.24 | 20 | 1.28 | −19.47 |
| [29] | 0.33 | 1.5 | 20 | 2.31 | −13.70 |
| [30] | 0.30 | 1.5 | 25 | 1.54 | −14.47 |
| [31] | 0.50 | 3 | 10 | - | −7.70 |
| [32] | 0.20 | 1 | 20 | 4.25 | −23.07 |
| Components | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | SO3 | Cl | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Others |
| Content | 0.80 | 4.52 | 5.31 | 21.01 | 0.17 | 3.67 | 0.15 | 1.18 | 58.90 | 0.28 | 3.81 | 0.22 |
| Group | W/C | S/C | Thicknesses (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ref-0.40-10 | 0.4 | 3 | 10 |
| Ref-0.40-20 | 0.4 | 3 | 20 |
| Ref-0.40-30 | 0.4 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.45-10 | 0.45 | 3 | 10 |
| Ref-0.45-20 | 0.45 | 3 | 20 |
| Ref-0.45-30 | 0.45 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.50-10 | 0.5 | 3 | 10 |
| Ref-0.50-20 | 0.5 | 3 | 20 |
| Ref-0.50-30 | 0.5 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.55-10 | 0.55 | 3 | 10 |
| Ref-0.55-20 | 0.55 | 3 | 20 |
| Ref-0.55-30 | 0.55 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.60-10 | 0.6 | 3 | 10 |
| Ref-0.60-20 | 0.6 | 3 | 20 |
| Ref-0.60-30 | 0.6 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.40-30 | 0.4 | 3 | 30 |
| Ref-0.40-30 | 0.4 | 2 | 30 |
| Ref-0.40-30 | 0.4 | 1 | 30 |
| Ref-0.40-30 | 0.4 | 0 | 30 |
| Group | S/C | W/C | Thickness (mm) | Be (GHz) | RLmin (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref-0.40-0-30 | 0 | 0.40 | 30 | 2.35 | −37.69 |
| Ref-0.40-1-30 | 1 | 0.40 | 30 | 3.71 | −22.04 |
| Ref-0.40-2-30 | 2 | 0.40 | 30 | 3.35 | −34.89 |
| Ref-0.40-3-30 | 3 | 0.40 | 30 | 2.75 | −26.34 |
| Ref-0.45-3-30 | 3 | 0.45 | 30 | 3.47 | −31.26 |
| Ref-0.50-3-30 | 3 | 0.50 | 30 | 4.51 | −38.38 |
| Ref-0.55-3-30 | 3 | 0.55 | 30 | 4.55 | −59.12 |
| Ref-0.60-3-30 | 3 | 0.60 | 30 | 3.79 | −28.92 |
| Ref-0.40-3-10 | 3 | 0.40 | 10 | 0 | −5.80 |
| Ref-0.40-3-20 | 3 | 0.40 | 20 | 1.96 | −20.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Shi, W.; Huang, L.; Xie, A. Effects of Quartz Sand on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Cementitious Materials. Materials 2024, 17, 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235795
Li C, Wang Z, Shi W, Huang L, Xie A. Effects of Quartz Sand on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Cementitious Materials. Materials. 2024; 17(23):5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235795
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chaoqun, Zixiao Wang, Weizheng Shi, Ling Huang, and Aming Xie. 2024. "Effects of Quartz Sand on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Cementitious Materials" Materials 17, no. 23: 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235795
APA StyleLi, C., Wang, Z., Shi, W., Huang, L., & Xie, A. (2024). Effects of Quartz Sand on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption of Cementitious Materials. Materials, 17(23), 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17235795






