The Biocompatibility and the Effect of Titanium and PEKK on the Osseointegration of Customized Facial Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Samples
- Titanium specimen preparation
- PEKK specimen preparation
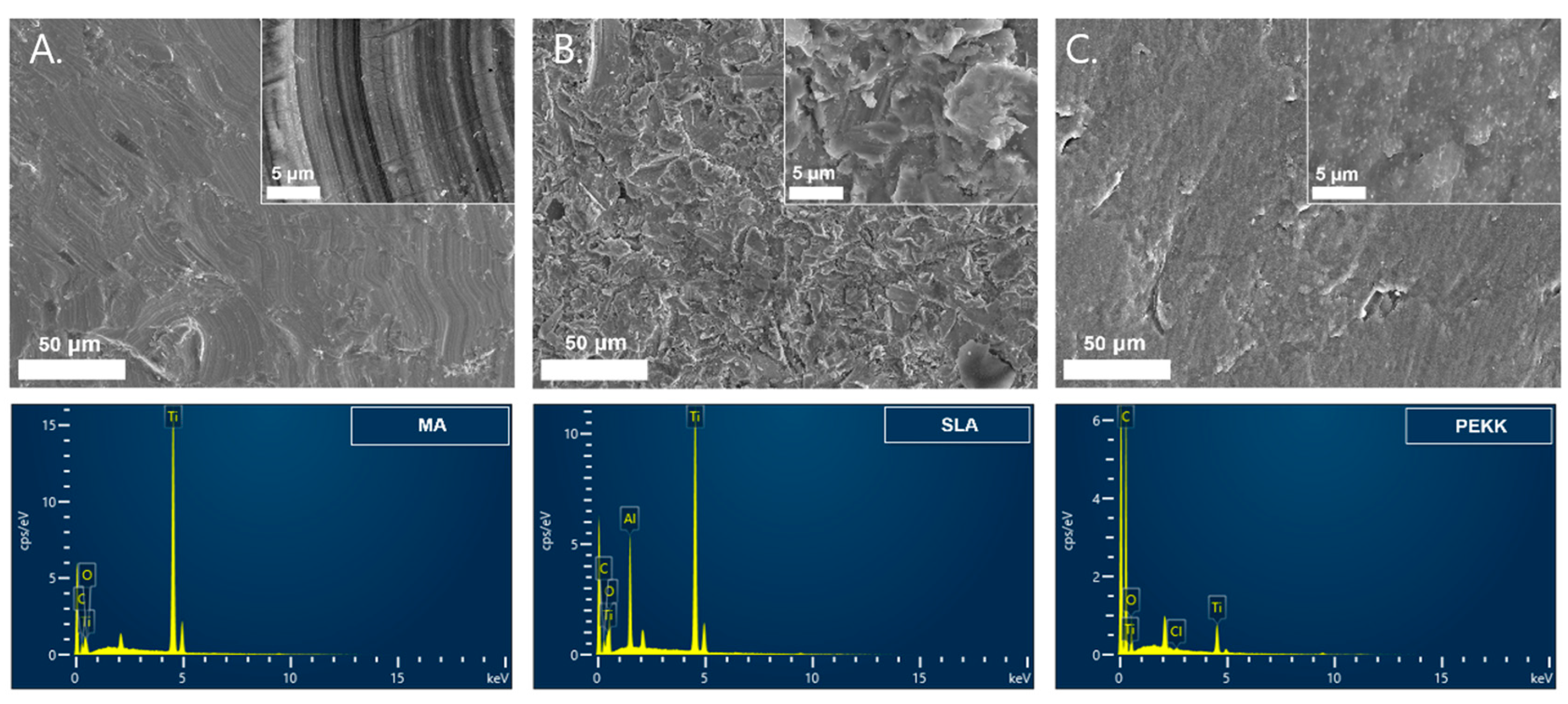
2.2. MA, SLA, and PEKK Implant Surface Analyses
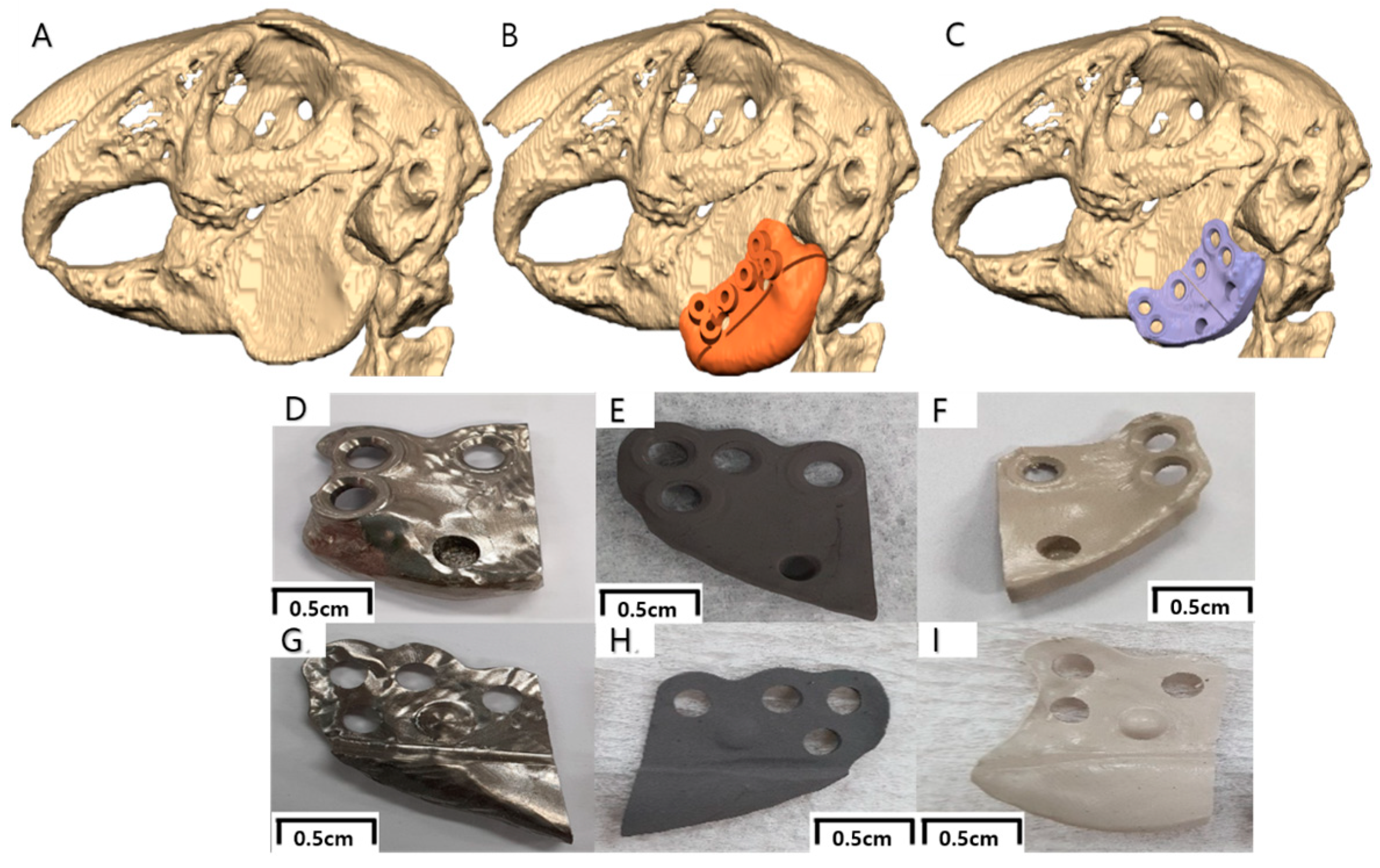
2.3. Virtual Surgical Planning and Computer-Aided Implant Design/Fabrication
2.4. In Vivo Studies
- Approval for animal experiment
- Animals and CT taking
- Surgical procedure
- Animal sacrifice and retrieval of specimens
2.5. Histological Preparation and Analysis
- Histological preparation
- Histological analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Implant Surface Analyses
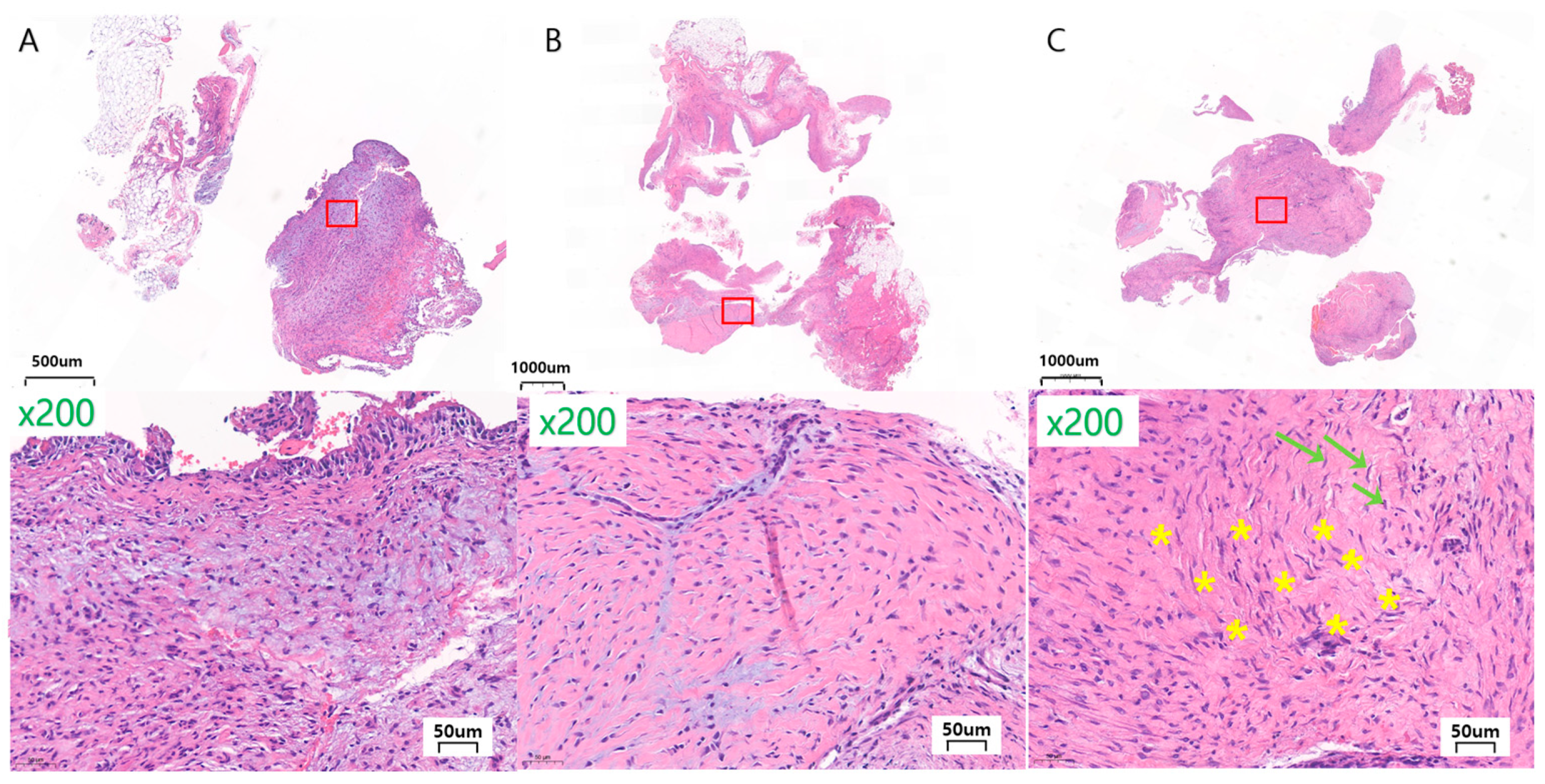
3.2. In Vivo Histological Observations and Analyses
- General finding
- Assessment of soft tissue reaction
- Inflammation percentage
- Field severity (minimal, mild, moderate, severe)
- Granulation tissue formation
- Fibrosis
- Other findings
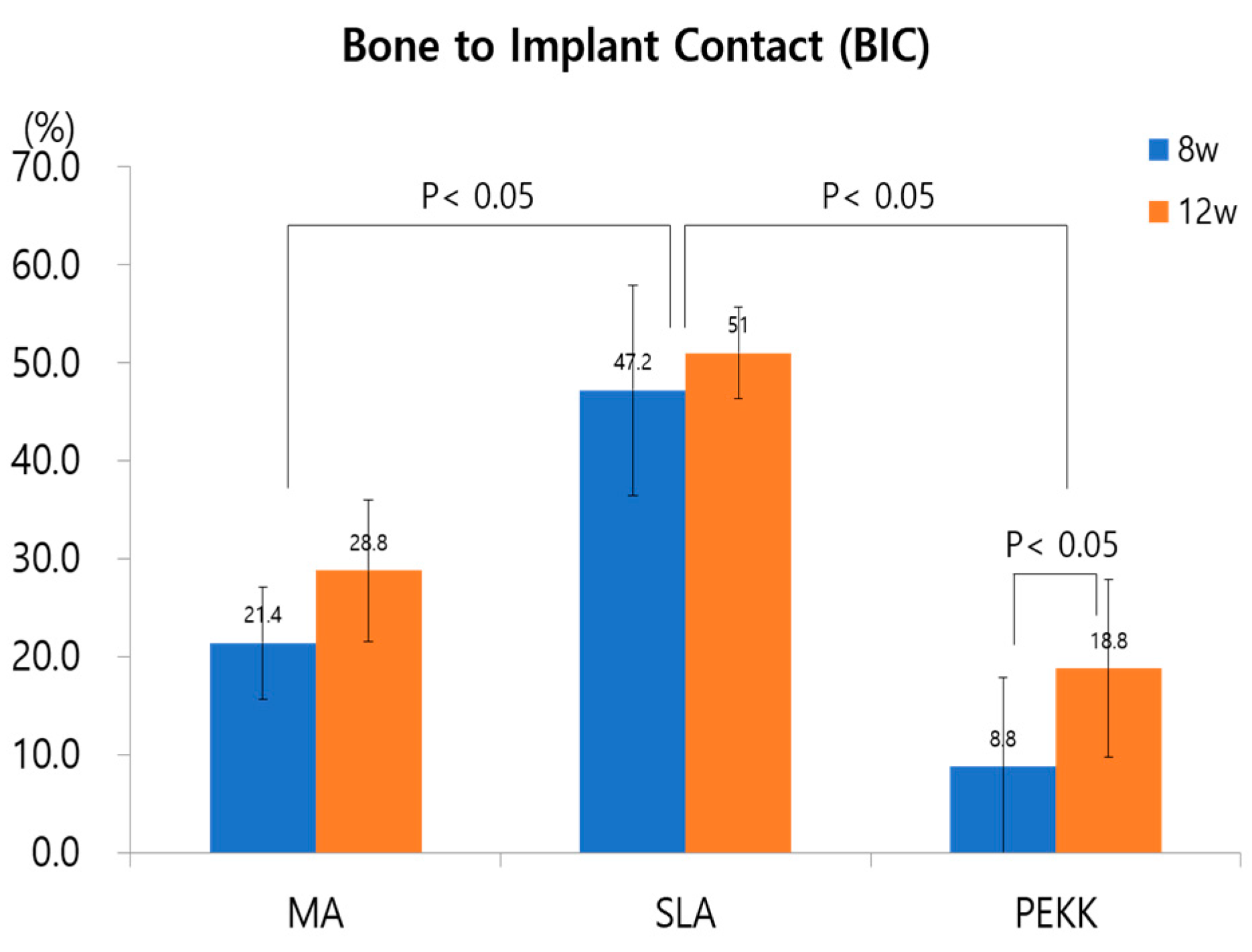
3.3. Assessment of Mandible Defect Repair and Implant Osseointegration
- Mandible defect and implant medial surface
- Implant lateral surface and periosteum
4. Discussion
4.1. Soft Tissue Reaction on Facial Implants
4.2. Hard Tissue Reaction on Facial Implants
- Ma, SLA, PEKK-surfaced implants, and bone
- Ma, SLA, PEKK-surfaced implants and the periosteum
- Limitations and recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cuzalina, L.A.; Hlavacek, M.R. Complications of facial implants. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 21, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.Y.; Dhir, K.; Binder, W.J.; Hilger, P.A. Alloplastic Facial Implants. Facial Plast. Surg. 2021, 37, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, E.; Mohammadi, M.; Alam, M.; Abbasi, K.; Gharibian Bajestani, S.; Khanmohammad, R.; Haseli, M.; Yazdanian, M.; Esmaeili Fard Barzegar, P.; Tebyaniyan, H. The current regenerative medicine approaches of craniofacial diseases: A narrative review. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedogni, A.; Bettini, G.; Bedogni, G.; Menapace, G.; Sandi, A.; Michelon, F.; Di Carlo, R.; Franco, P.; Saia, G. Safety of boneless reconstruction of the mandible with a CAD/CAM designed titanium device: The replica cohort study. Oral. Oncol. 2021, 112, 105073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashaba, M.M.; Shaheen, H.A.; Ibrahim, W.H.; AlDainy, D.G. Accuracy of patient-specific temporal implants using PEKK. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2021, 49, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Yan, S.; Qiao, C.; Qu, Y.; Gao, S.; Shangguan, W.; Wu, G. Endoscopic-Assisted Forehead Augmentation with Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Patient-Specific Implant (PSI) for Aesthetic Considerations. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024, 48, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvinen, S.; Suojanen, J.; Kormi, E.; Wilkman, T.; Kiukkonen, A.; Leikola, J.; Stoor, P. The use of patient specific polyetheretherketone implants for reconstruction of maxillofacial deformities. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiduddin, K.; Mian, S.H.; Umer, U.; Alkhalefah, H.; Ahmed, F.; Hashmi, F.H. Design, Analysis, and 3D Printing of a Patient-Specific Polyetheretherketone Implant for the Reconstruction of Zygomatic Deformities. Polymers 2023, 15, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Lee, T.C.; Koshy, P.; Abdullah, H.Z.; Idris, M.I. Evolution of anodised titanium for implant applications. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Galli, S.; Prgomet, Z.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Osseointegration and foreign body reaction: Titanium implants activate the immune system and suppress bone resorption during the first 4 weeks after implantation. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.A.; Thomsen, P.; Palmquist, A. Osseointegration and current interpretations of the bone-implant interface. Acta Biomater. 2019, 84, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneksomboonpol, P.; Mahardawi, B.; Nan, P.N.; Laoharungpisit, P.; Kumchai, T.; Wongsirichat, N.; Aimjirakul, N. Surface structure characteristics of dental implants and their potential changes following installation: A literature review. J. Korean Assoc. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 49, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayrak, M.; Kocak-Oztug, N.A.; Gulati, K.; Cintan, S.; Cifcibasi, E. Influence of Clinical Decontamination Techniques on the Surface Characteristics of SLA Titanium Implant. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Fan, X.; Bai, S.; Luo, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, X. In vitro application of drug-loaded hydrogel combined with 3D-printed porous scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 065019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollkommer, T.; Henningsen, A.; Friedrich, R.E.; Felthaus, O.H.; Eder, F.; Morsczeck, C.; Smeets, R.; Gehmert, S.; Gosau, M. Extent of Inflammation and Foreign Body Reaction to Porous Polyethylene In Vitro and In Vivo. In Vivo 2019, 33, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakides, T.R.; Kim, H.J.; Zheng, C.; Harkins, L.; Tao, W.; Deschenes, E. Foreign body response to synthetic polymer biomaterials and the role of adaptive immunity. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 022007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Komasa, S.; Kusumoto, T.; Kuwamoto, S.; Okunishi, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Sekino, T.; Okazaki, J. Immunomodulatory Properties and Osteogenic Activity of Polyetheretherketone Coated with Titanate Nanonetwork Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.D.; Eells, A.C.; Saba, E.S.; Boczar, D.; Restrepo, D.J.; Huayllani, M.T.; Sisti, A.; Hu, M.S.; Gould, D.J.; Forte, A.J. Alloplastic Facial Implants: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Outcomes and Uses in Aesthetic and Reconstructive Plastic Surgery. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2019, 43, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzig, T.; Mende, K.C.; Mohme, M.; Kniep, H.; Dreimann, M.; Stangenberg, M.; Westphal, M.; Gauer, T.; Eicker, S.O. Carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK versus titanium implants: An in vitro comparison of susceptibility artifacts in CT and MR imaging. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykaras, N.; Iacopino, A.M.; Marker, V.A.; Triplett, R.G.; Woody, R.D. Implant materials, designs, and surface topographies: Their effect on osseointegration. A literature review. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 675–690. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.W.; Chien, E.Y.; Chien, H.H. Dental implant bioactive surface modifications and their effects on osseointegration: A review. Biomark. Res. 2016, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civantos, A.; Domínguez, C.; Pino, R.J.; Setti, G.; Pavón, J.J.; Martínez-Campos, E.; Garcia, F.J.G.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Allain, J.P.; Torres, Y. Designing bioactive porous titanium interfaces to balance mechanical properties and in vitro cells behavior towards increased osseointegration. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 368, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.B.; Slosar, P.; Schwartz, Z.; Cohen, D.J.; Goodman, S.B.; Anderson, P.A.; Boyan, B.D. A Review of Biomimetic Topographies and Their Role in Promoting Bone Formation and Osseointegration: Implications for Clinical Use. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, D.L.; Schenk, R.K.; Lussi, A.; Higginbottom, F.L.; Buser, D. Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: A histometric study in the canine mandible. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zol, S.M.; Alauddin, M.S.; Said, Z.; Mohd Ghazali, M.I.; Hao-Ern, L.; Mohd Farid, D.A.; Zahari, N.A.H.; Al-Khadim, A.H.A.; Abdul Aziz, A.H. Description of Poly(aryl-ether-ketone) Materials (PAEKs), Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK) for Application as a Dental Material: A Materials Science Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqurashi, H.; Khurshid, Z.; Syed, A.U.Y.; Rashid Habib, S.; Rokaya, D.; Zafar, M.S. Polyetherketoneketone (PEKK): An emerging biomaterial for oral implants and dental prostheses. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 28, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlOtaibi, N.M.; Dunne, M.; Ayoub, A.F.; Naudi, K.B. A novel surgical model for the preclinical assessment of the osseointegration of dental implants: A surgical protocol and pilot study results. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Ortiz-García, I.; Jiménez-Guerra, A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Muñoz-Guzón, F.; Perez, R.A.; Gil, F.J. Comparison between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants: In Vivo Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Lee, H.S.; Chiueh, T.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, H.A.; Lin, Y.C.; Cha, T.L.; Meng, E. Histopathological assessment of inflammation and expression of inflammatory markers in patients with ketamine-induced cystitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anabtawi, M.; Thomas, M.; Lee, N.J. The Use of Interlocking Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Patient-Specific Facial Implants in the Treatment of Facial Deformities. A Retrospective Review of Ten Patients. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 1145.e1–1145.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S.; Ravindran, S.; Cooper, L.F. Topography-mediated immunomodulation in osseointegration; Ally or Enemy. Biomaterials 2022, 291, 121903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, N.; Eren, B.; Fedakar, R.; Akgoz, S. The significance of hemosiderin deposition in the lungs and organs of the mononucleated macrophage resorption system in infants and children. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, E.R.; Watkins, G.; Lam, N.V.; Tsuda, H.; Hermann, C.; Johal, J.; Liu, H. Objective pathological diagnosis of coal worker’s pneumoconiosis. JAMA 1981, 245, 1829–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential Causes of Titanium Particle and Ion Release in Implant Dentistry: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyaseer, A.A.A.; de Lima, M.H.S.; Braga, T.T. The Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition Process During the Fibrosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, N.; Stoddart, J.C.; van Arkel, R.J. The limit of tolerable micromotion for implant osseointegration: A systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.Y.; Shih, Y.H.; Hsia, S.M.; Wang, T.H.; Li, P.J.; Lin, D.J.; Sun, K.T.; Chiu, K.C.; Shieh, T.M. In Vitro Assessment of the Cell Metabolic Activity, Cytotoxicity, Cell Attachment, and Inflammatory Reaction of Human Oral Fibroblasts on Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Implant-Abutment. Polymers 2021, 13, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frodel, J.L.; Lee, S. The use of high-density polyethylene implants in facial deformities. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1998, 124, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Nehra, M.; Kedia, D.; Dilbaghi, N.; Tankeshwar, K.; Kim, K.H. Nanotechnology-based biomaterials for orthopaedic applications: Recent advances and future prospects. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 106, 110154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; Manero, J.M.; Ruperez, E.; Velasco-Ortega, E.; Jimenez-Guerra, A.; Ortiz-Garcia, I.; Monsalve-Guil, L. Mineralization of Titanium Surfaces: Biomimetic Implants. Materials 2021, 14, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.L.; Woodrow, K.A. Medical Applications of Porous Biomaterials: Features of Porosity and Tissue-Specific Implications for Biocompatibility. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, e2102087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, P.; Liu, S.; Attarilar, S.; Ma, R.L.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, L. Multi-Scale Surface Treatments of Titanium Implants for Rapid Osseointegration: A Review. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Alfonso-Rodriguez, C.A.; Monsalve-Guil, L.; Espana-Lopez, A.; Jimenez-Guerra, A.; Garzon, I.; Alaminos, M.; Gil, F.J. Relevant aspects in the surface properties in titanium dental implants for the cellular viability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apablaza, J.A.; Días, F.J.; Sánchez, K.G.; Navarro, P.; Venegas, C.; Fuentes, R. Analysis of the Chemical Composition and Morphological Characterization of Tissue Osseointegrated to a Dental Implant after 5 Years of Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Xu, X.; Ni, Y.F.; Sun, H.T.; Yu, R.Y.; Wei, S.C. In vivo study of liposome-modified polyetheretherketone implant on bacteriostasis and osseointegration. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban = J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2021, 53, 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Zeng, F.; Ren, T.; Guo, W. Efficacy of bone defect therapy involving various surface treatments of titanium alloy implants: An in vivo and in vitro study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, K.R.S.; Goyal, M.; Mittal, N.; George, J.S. Accuracy of freehand versus guided immediate implant placement: A randomized controlled trial. J. Dent. 2023, 136, 104620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsadon, O.; Wood, D.; Patrick, D.; Pollington, S. Fatigue behavior and damage modes of high performance poly-ether-ketone-ketone PEKK bilayered crowns. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 110, 103957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, R.; Zhu, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, K.; Song, Y.; Zhang, X. Comparison of osteointegration property between PEKK and PEEK: Effects of surface structure and chemistry. Biomaterials 2018, 170, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Postiglione, F.; Khater, A.G.A.; Al-Hamed, F.S.; Lorusso, F. A Novel Technique to Increase the Thickness of TiO(2) of Dental Implants by Nd: DPSS Q-sw Laser Treatment. Materials 2020, 13, 4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Umebayashi, M.; Abdallah, M.N.; Dong, G.; Roskies, M.G.; Zhao, Y.F.; Murshed, M.; Zhang, Z.; Tran, S.D. Combination of polyetherketoneketone scaffold and human mesenchymal stem cells from temporomandibular joint synovial fluid enhances bone regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Ramakrishnan, S.A.; Lopez, K.G.; Madhu, S.; Ramos, M.R.D.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Hallinan, J.; Nolan, C.P.; Benneker, L.M.; Vellayappan, B.A. Can Polyether Ether Ketone Dethrone Titanium as the Choice Implant Material for Metastatic Spine Tumor Surgery? World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.C.; Jaffee, S.; Averick, S.; Swink, I.; Horvath, S.; Zhukauskas, R. A comparative study of three biomaterials in an ovine bone defect model. Spine J. Off. J. N. Am. Spine Soc. 2020, 20, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Ueda, M. Effects of cortical bone perforation on periosteal distraction: An experimental study in the rabbit mandible. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, R.; Sendlbeck, C.; Wahabzada, H.; Tudor, C.; Prechtl, C.; Schlegel, K.A. Periosteal elevation induces supracortical peri-implant bone formation. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprio, S.; Fricia, M.; Maddalena, G.F.; Nataloni, A.; Tampieri, A. Osteointegration in cranial bone reconstruction: A goal to achieve. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, e470–e476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dec, P.; Modrzejewski, A.; Pawlik, A. Existing and Novel Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Guan, H.; Ivanovski, S.; Loo, Y.C.; Johnson, N.W.; Zhang, H. Effect of bone to implant contact percentage on bone remodelling surrounding a dental implant. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 39, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, E. Smart Porous Scaffold Promotes Peri-Implant Osteogenesis under the Periosteum. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 6321–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mabrey, J.D.; Agrawal, C.M. An interspecies comparison of bone fracture properties. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 1998, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shash, Y.H.; El-Wakad, M.T.; El-Dosoky, M.A.A.; Dohiem, M.M. Evaluation of stresses on mandible bone and prosthetic parts in fixed prosthesis by utilizing CFR-PEEK, PEKK and PEEK frameworks. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Kang, J.; Yang, C.; Zheng, J.; Su, Y.; Dong, E.; Liu, Y.; Yao, S.; Shi, C.; Pang, H.; et al. Additive manufactured polyether-ether-ketone implants for orthopaedic applications: A narrative review. Biomater. Transl. 2022, 3, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Takaneka, S.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Kaito, T. Impact of mechanical stability on the progress of bone ongrowth on the frame surfaces of a titanium-coated PEEK cage and a 3D porous titanium alloy cage: In vivo analysis using CT color mapping. Eur. Spine J. Off. Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deform. Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 2021, 30, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Ma | SLA | PEKK | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 w (n = 4) | 12 w (n = 4) | 8 w (n = 4) | 12 w (n = 4) | 8 w (n = 4) | 12 w (n = 4) | ||
| Inflammation in whole tissue (%) | Average | 20.63 | 25.63 | 14.25 | 12.63 | 5.88 | 15.75 |
| Field severity (n) | Minimal | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Mild | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Moderate | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Severe | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| Granulation tissue formation (n) | Absent | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| Present | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| Fibrosis in soft tissue (n) | Absent | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Loose, thin fiber | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |
| Thick collagen, focal | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
| Thick collagen, diffuse | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-O.; Pyo, J.-Y.; On, S.-W.; Seo, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-Y. The Biocompatibility and the Effect of Titanium and PEKK on the Osseointegration of Customized Facial Implants. Materials 2024, 17, 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174435
Hong S-O, Pyo J-Y, On S-W, Seo J-Y, Choi J-Y. The Biocompatibility and the Effect of Titanium and PEKK on the Osseointegration of Customized Facial Implants. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174435
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sung-Ok, Ju-Yeon Pyo, Sung-Woon On, Ja-Yeong Seo, and Jin-Young Choi. 2024. "The Biocompatibility and the Effect of Titanium and PEKK on the Osseointegration of Customized Facial Implants" Materials 17, no. 17: 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174435
APA StyleHong, S.-O., Pyo, J.-Y., On, S.-W., Seo, J.-Y., & Choi, J.-Y. (2024). The Biocompatibility and the Effect of Titanium and PEKK on the Osseointegration of Customized Facial Implants. Materials, 17(17), 4435. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174435






