Research on the Mechanism of Oxygen-Induced Embrittlement Fracturing in Industrial Electrolytic Nickel
Abstract
1. Introduction
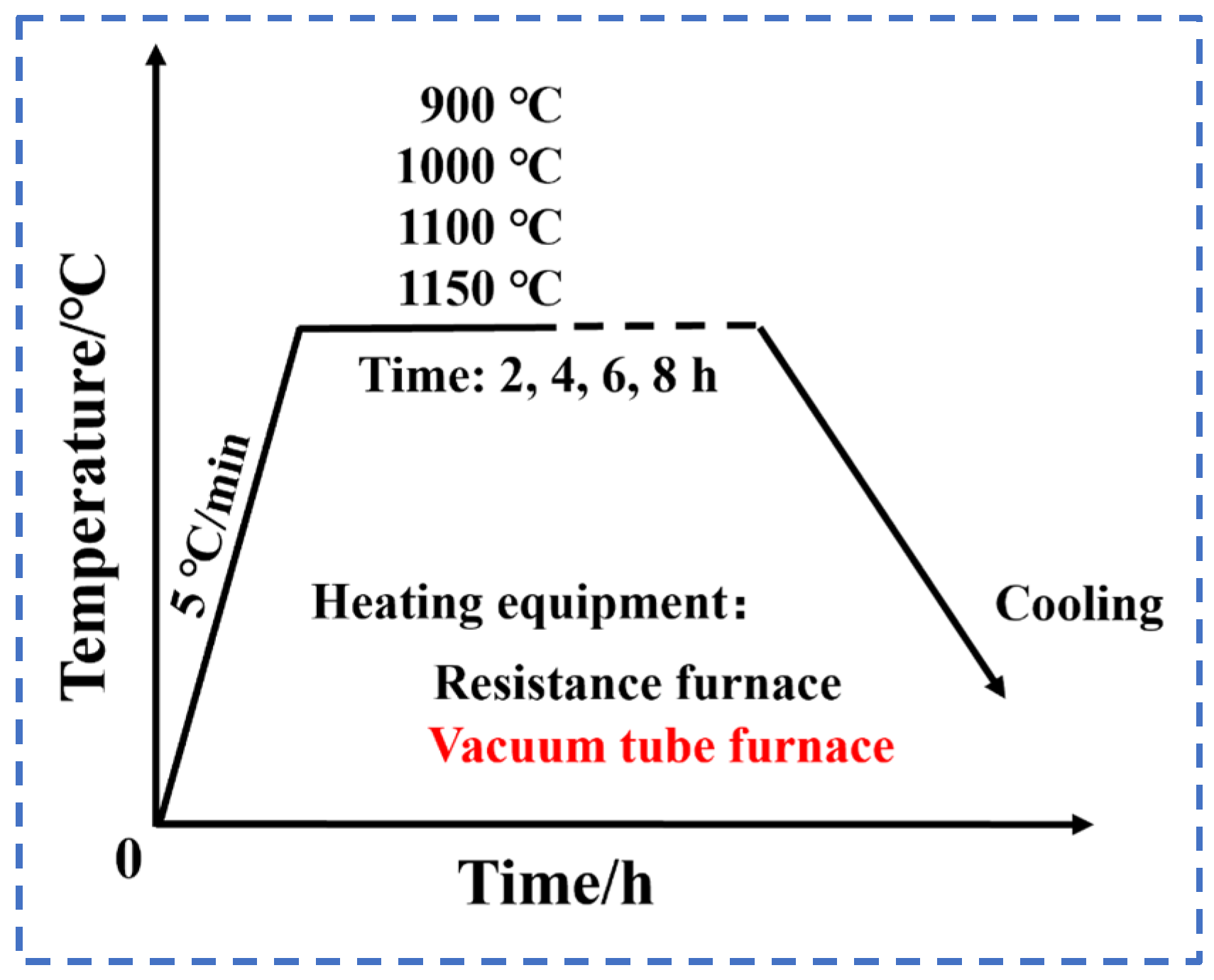
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Microstructure of Electrolytic Nickel
3.2. Microstructure of Electrolytic Nickel after High-Temperature Heat Treatment
3.2.1. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Electrolytic Nickel after Heat Treatment in Atmospheric Conditions
3.2.2. Microstructure of Electrolytic Nickel under Vacuum Heat Treatment
3.3. Cracking Analysis during Hot-Rolling Process
3.3.1. Macroscopic Defects of Electrolytic Nickel Hot Rolling
3.3.2. Impurities and Residual Gas Elements in Hot-Rolling Cracks
3.3.3. Microstructure of Electrolytic Nickel Hot Rolling
3.3.4. Hot-Rolled Crack Fracture Morphology
3.3.5. TEM Observation of Electrolytic Nickel Hot Rolling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Q.; Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, M.; Lim, S. Preparation of high-purity nickel by floating zone refining under a hydrogen atmosphere. Vacuum 2023, 217, 112557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, D.; Krivobokov, V. Angular thickness distribution and target utilization for hot Ni target magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2019, 160, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wen, M.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y. Formation of thin films via cold-rolled/annealed nickel sputtering targets. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2023, 41, 063401–063405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuth, T.; Theile, R.; Krivtsova, O. New Technological Approach in Fabrication of High Purity Nickel Wire. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 892, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, J. Microstructures characterization of micro/nanocrystalline electrolytic nickel plates by cold rolling deformation. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2019, 48, 1975–1981. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. Research on Industrial Electrolytic Nickel Plate by Large Area EBSD Method. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2021, 50, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar]
- Nia, N.; Creus, J.; Feaugas, X.; Savall, C. The effect of tungsten addition on metallurgical state and solute content in nanocrystalline electrodeposited nickel. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 609, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnik, E.; Wojnicki, M.; Włoch, G. Effect of gluconate addition on the electrodeposition of nickel from acidic baths. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 207, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenatchi, B.; Renuga, V.; Manikandan, A. Electrodeposition of Nickel on Glassy Carbon Electrode from Protic Ionic Liquids with Imidazolium Cation. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 2016, 26, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, B. The effect of valine on the process of nickel electrocrystallization on glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 796, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L. Effect of Thiourea Containing Composite Additives on Nickel Electrodeposition in Ammoniacal Solution. Crystals 2021, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, N.; Hadianfard, M. Exploring the potential of nickel-chloride bath for electroforming of pure nickel and nickel composites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhao, W. Comparison for microstructure and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nickel and rolled nickel. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3133–3140. [Google Scholar]
- Bricknell, R.; Woodford, D. The embrittlement of nickel following high temperature air exposure. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, D.; Bricknell, R. Environmental embrittlement of high temperature alloys by oxygen. Treatise Mater. Sci. Technol. 1983, 25, 157–199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Du, J.; Deng, Q. The influence of oxygen partial pressure on the crack propagation of superalloy under fatigue-creep-environment interaction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 140903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, W.; Digges, T. Effect of temperature on the tensile prorerties of high-purity nickel. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1952, 48, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Chellali, R.; Schlesiger, R.; Baither, D.; Schmitz, G. Intermediate temperature embrittlement in high-purity Ni and binary Ni(Bi) alloy. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricknell, R.; Woodford, D. The mechanism of cavity formation during high temperature oxidation of nickel. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, D.; Hussey, R.; Sproule, G.; Graham, M. Effect of carbon on cavity formation during the high-temperature oxidation of Ni. Oxid. Met. 1980, 14, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, D.; Bricknell, R. Grain boundary penetration of oxygen in nickel and the effect of boron additions. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12A, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodford, D. Gas phase embrittlement and time dependent cracking of nickel based superalloys. Energy Mater. 2006, 1, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yang, X.; Gong, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. Interactions between dislocations and threedimensional annealing twins in face centered cubic metals. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2019, 161, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, B. An analysis of carbon/oxygen gas bubble formation in some nickel alloys. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.; Chen, C.; Ho, C. Synergistic effects of additives on impurity residues in high-speed copper electrodeposition and voiding propensity in solder joints. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2024, 156, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brongersma, S.; Kerr, E.; Vervoort, I.; Saerens, A.; Maex, K. Grain growth, stress, and impurities in electroplated copper. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, M.; Dittel, V.; Acker, J.; Hoffmann, V.; Gruner, W.; Strehle, S.; Wetzig, K. Investigation of organic impurities adsorbed on and incorporated into electroplated copper layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 252, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangl, M.; Acker, J.; Oswald, S.; Uhlemann, M.; Gemming, T.; Baunack, S.; Wetzig, K. Incorporation of sulfur, chlorine, and carbon into electroplated Cu thin films. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, I.; Ohte, R.; Omura, N.; Takigawa, Y. Thermal embrittlement and microstructure change in electrodeposited Ni. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 745, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yu, H.; Lin, M.; Ortiz, M.; Xiao, S.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Hydrogen trapping and diffusion in polycrystalline nickel: The spectrum of grain boundary segregation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 173, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Q.; He, M.; Li, J.; Wang, S. The hydrogen embrittlement of pure Ni fabricated by additive manufacturing. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 16910–16922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perusin, S.; Viguier, B.; Monceau, D.; Andrieu, E. Experimental study of the interactions between oxidation and structural defects. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 461–464, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, P.; Gopal, P.; Srinivasan, S. First-principles study of diffusion and interactions of hydrogen with silicon, phosphorus, and sulfur impurities in nickel. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 125104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Gao, Q.; Li, Z. Effects of additives on morphology and hydrogen evolution activities of nickel films prepared by electrodepositing. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 8823–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T6516-2010; Electrolytic Nickel. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Dai, Z.; Su, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, X. Study on intermediate temperature brittleness mechanism of Inconel 625 deposited metal. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, K.; Brouzoulis, J.; Ekh, M. A fully coupled chemo-mechanical cohesive zone model for oxygen embrittlement of nickel-based superalloys. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 164, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, C. Intermediate-temperature mechanical properties of Ni–Si alloys. Intermetallics 2002, 10, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaendtner, J.; McMahon, J. Oxygen-induced intergranular cracking of a Ni-base alloy at elevated temperatures—An example of dynamic embrittlement. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 3369–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Ni | Co | C | Si | P | S | Fe | Cu | Al | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >99.90 | 0.02410 | 0.01200 | 0.02980 | <0.0003 | <0.0003 | 0.00819 | 0.00332 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| C% | S% | P% | O% | N% | H% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.0052 | 0.0005 | 0.0004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Sang, C.; Miao, C.; Xu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Xia, T. Research on the Mechanism of Oxygen-Induced Embrittlement Fracturing in Industrial Electrolytic Nickel. Materials 2024, 17, 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174428
Zhang H, Sang C, Miao C, Xu Y, Qiao J, Xia T. Research on the Mechanism of Oxygen-Induced Embrittlement Fracturing in Industrial Electrolytic Nickel. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174428
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Han, Chen Sang, Chengpeng Miao, Yangtao Xu, Jisen Qiao, and Tiandong Xia. 2024. "Research on the Mechanism of Oxygen-Induced Embrittlement Fracturing in Industrial Electrolytic Nickel" Materials 17, no. 17: 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174428
APA StyleZhang, H., Sang, C., Miao, C., Xu, Y., Qiao, J., & Xia, T. (2024). Research on the Mechanism of Oxygen-Induced Embrittlement Fracturing in Industrial Electrolytic Nickel. Materials, 17(17), 4428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174428





