Optimization Design of Submerged-Entry-Nozzle Structure Using NSGA-II Genetic Algorithm in Ultra-Large Beam-Blank Continuous-Casting Molds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of the SENs and CFD Models
2.1. Design of the SENs
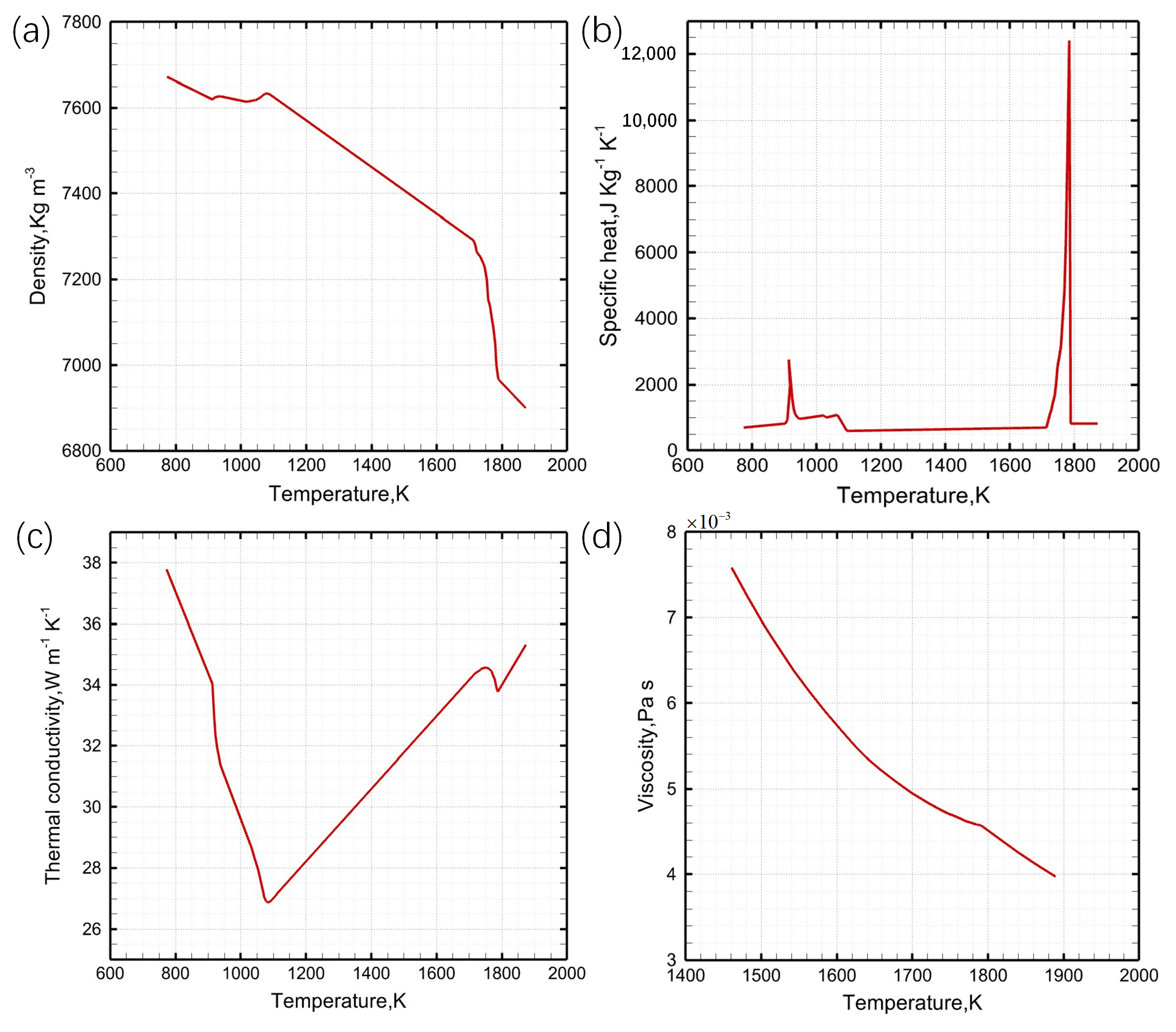
2.2. Basic Assumptions of the CFD Models
2.3. Governing Equations of the CFD Models
2.3.1. Fluid Flow Model
2.3.2. Heat Transfer and Solidification Model
2.4. Simulation Procedure of the CFD Models
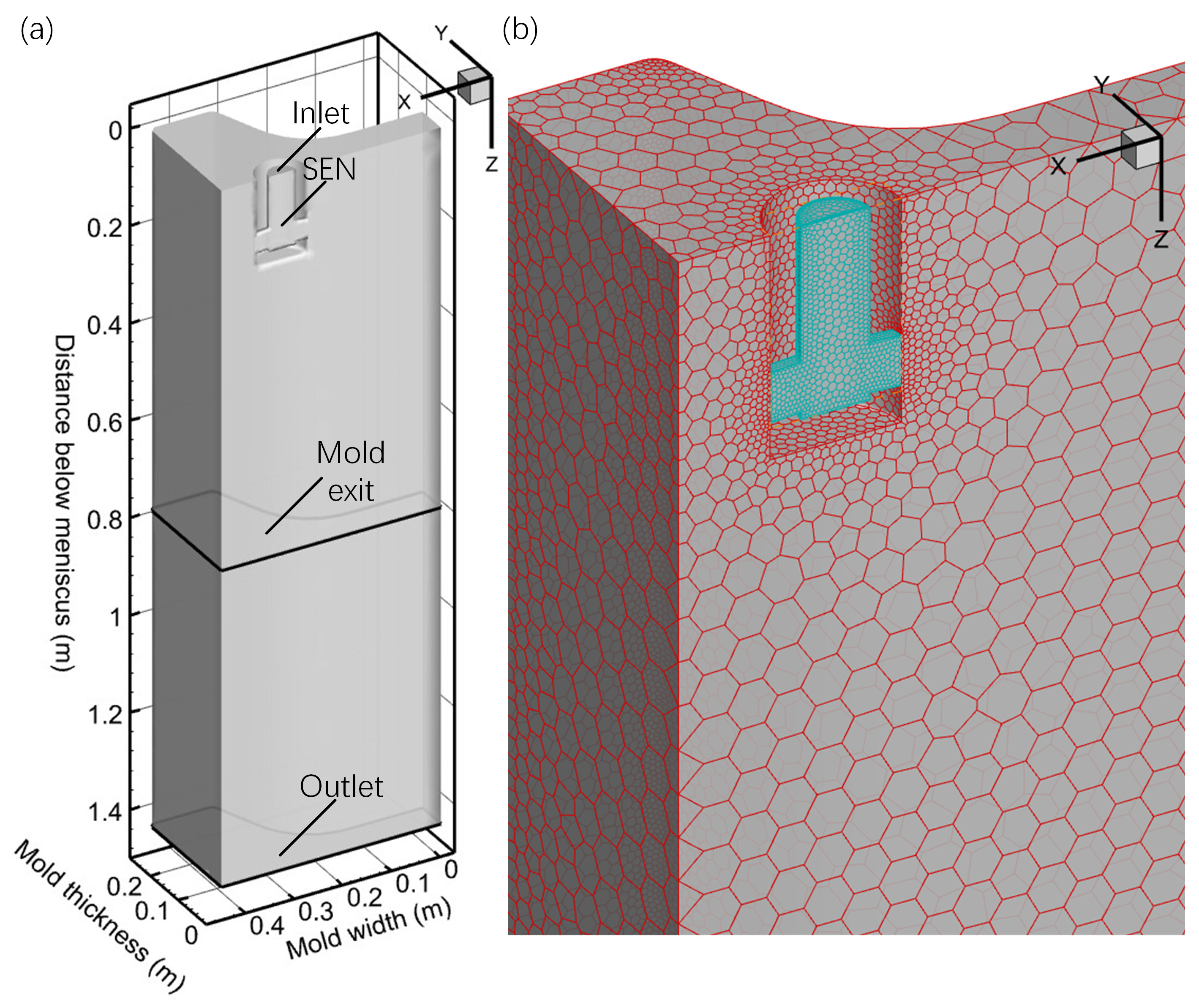
2.4.1. Simulation Models and Parameters
2.4.2. Boundary and Solution Method
3. Comparison of Fluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Solidification for Two-Port SEN and Three-Port SEN
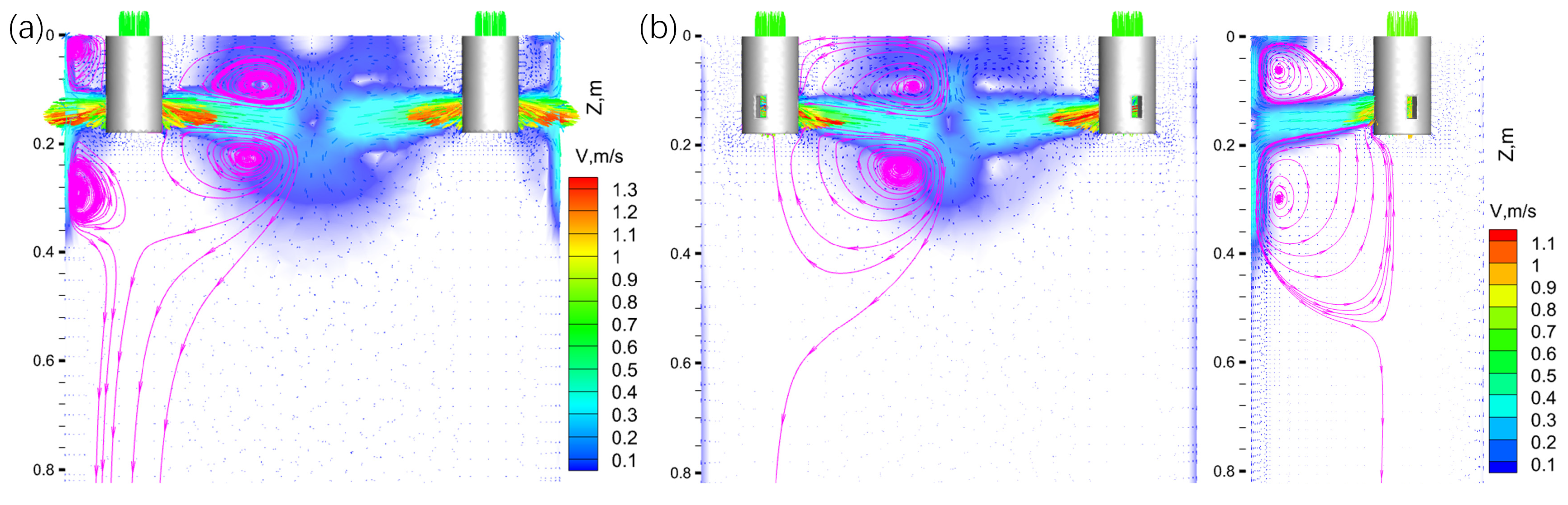
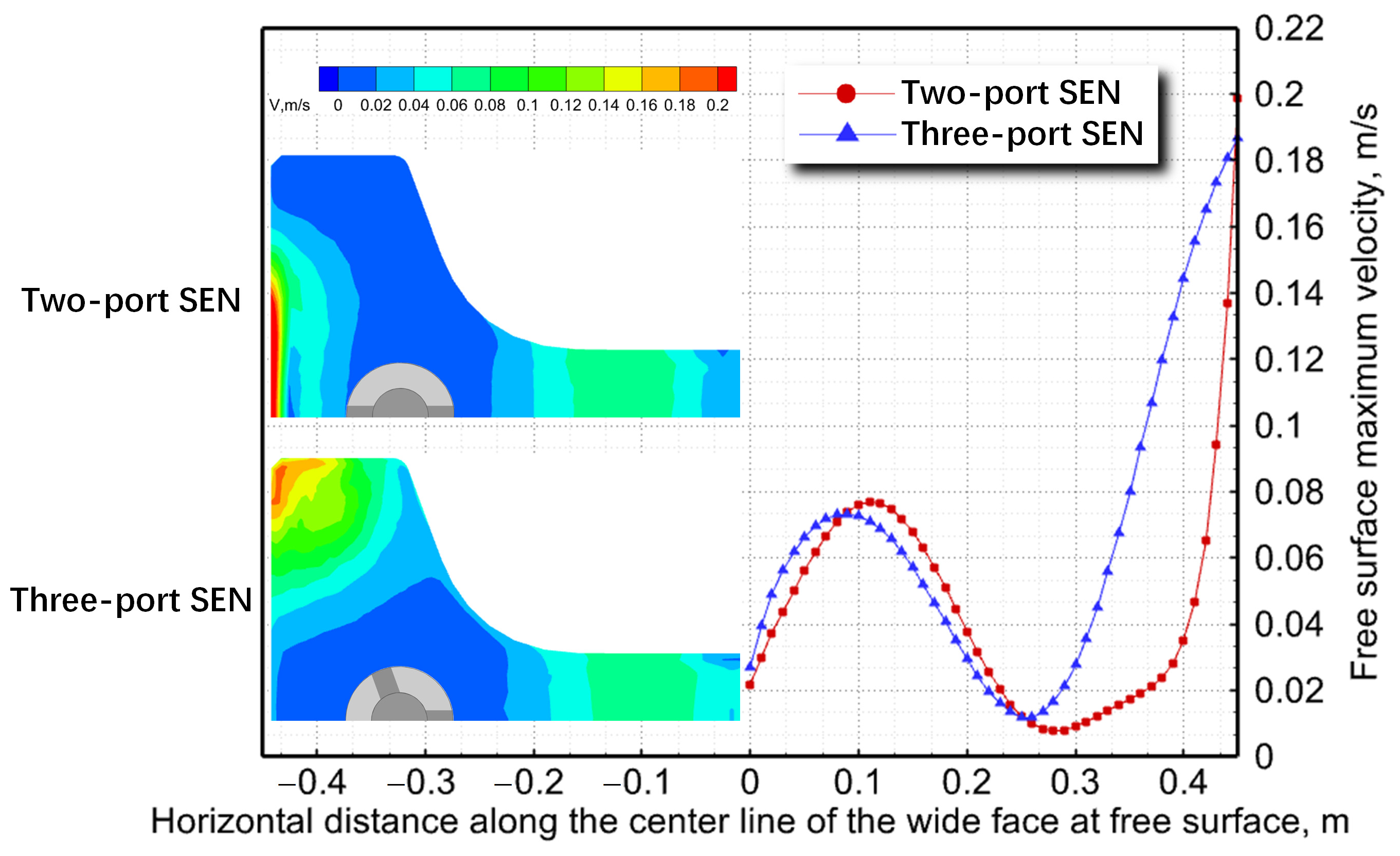
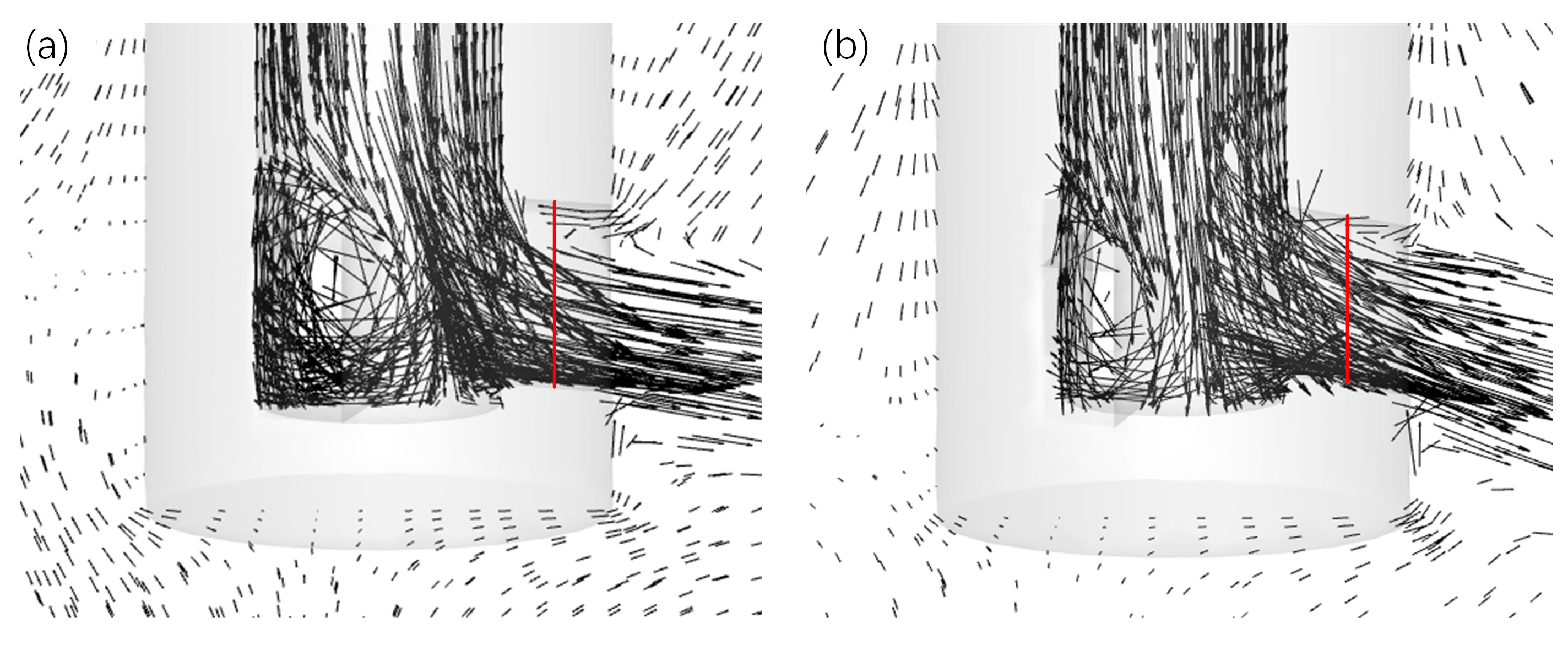
3.1. Fluid Flow
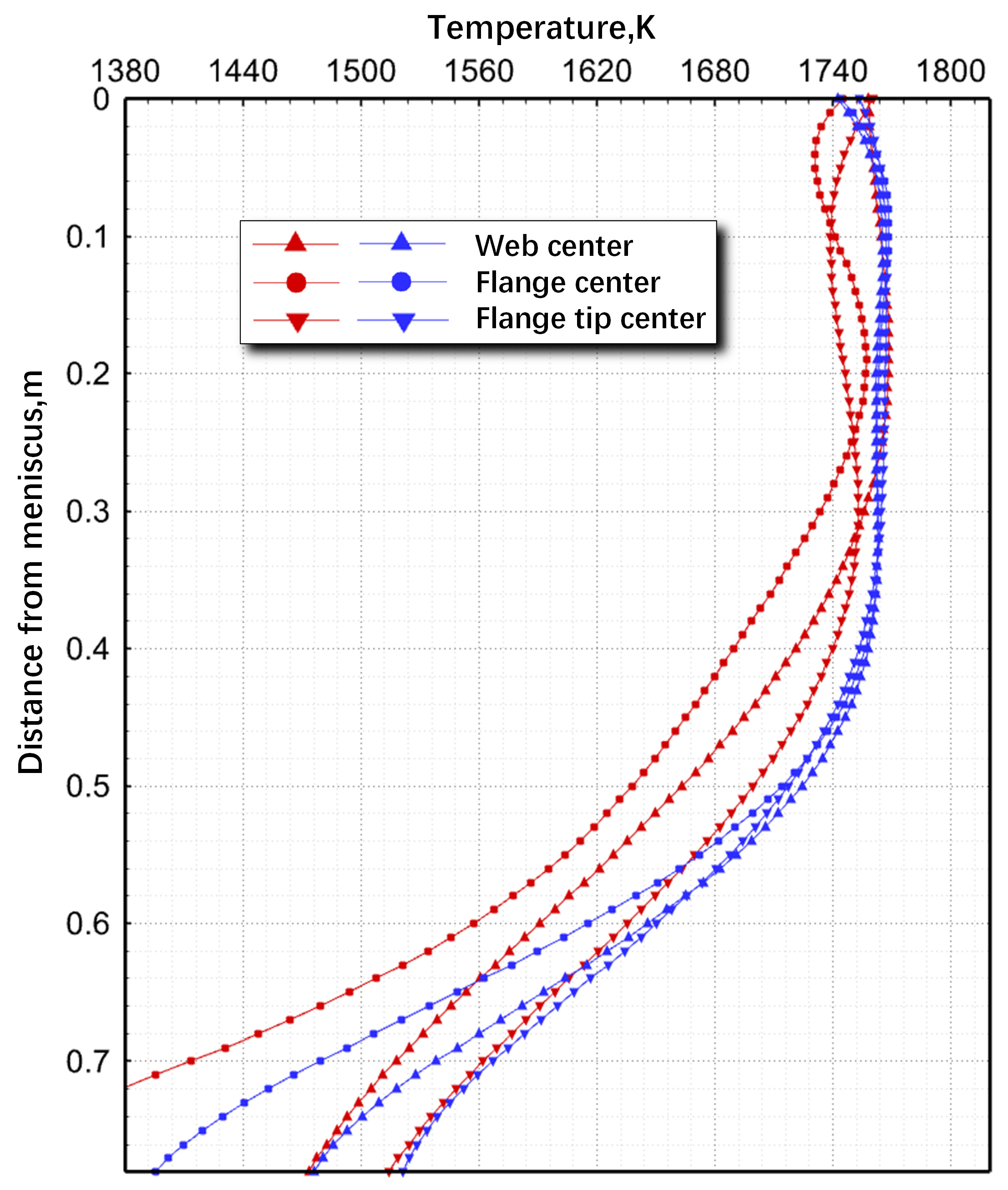
3.2. Temperature Field and Solidification
4. Multi-Objective Optimization Model for Three-Port SEN Structure
4.1. Knowledge Base Representation for Metallurgical Quality Control
4.2. Definition of the Optimization Issues
4.3. Surrogate Models and Error Metrics
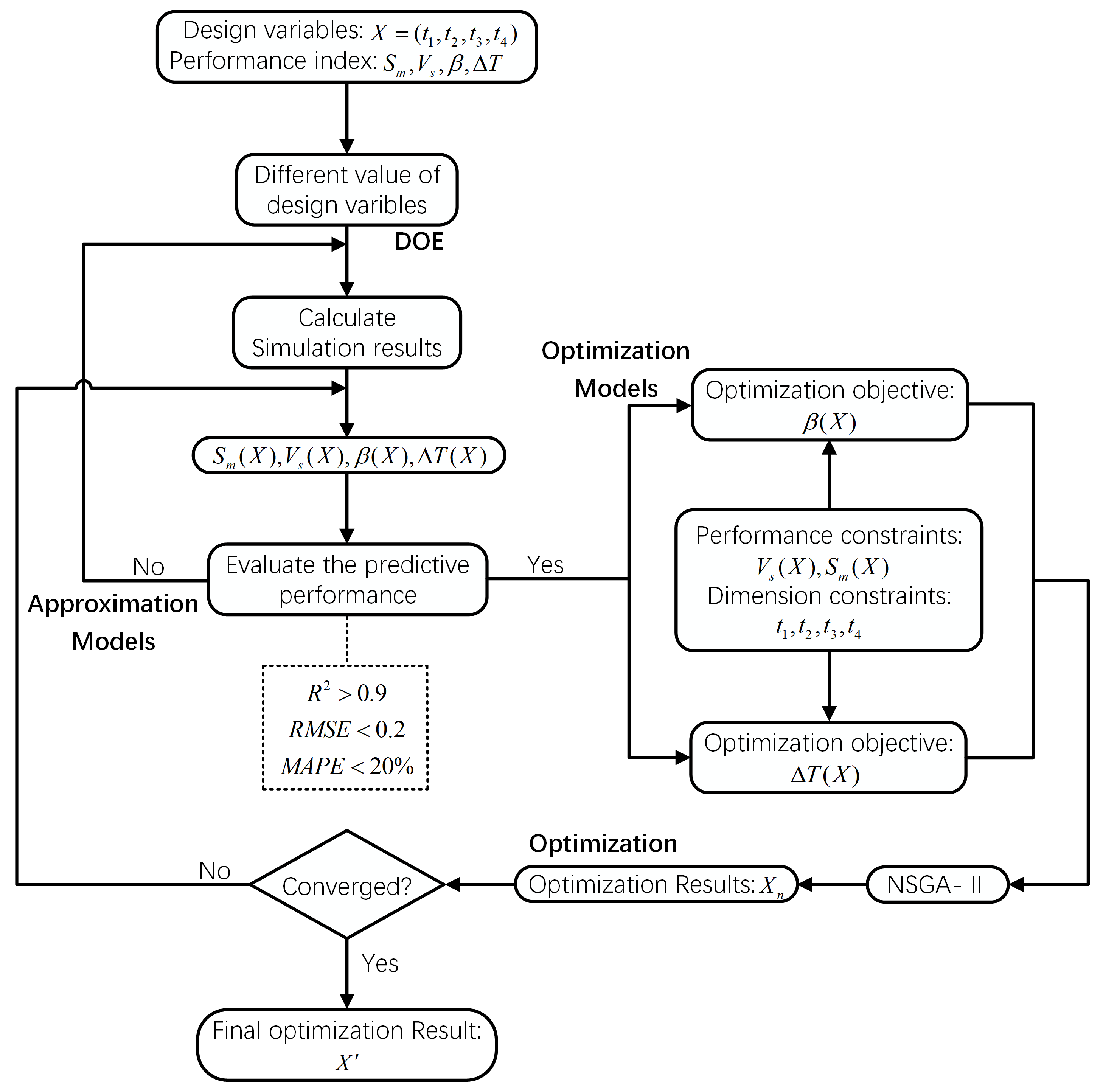
4.4. Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm and Procedure
5. Results and Discussion of Three-Port SEN Structure Optimization
5.1. Error Analysis of Surrogate Models
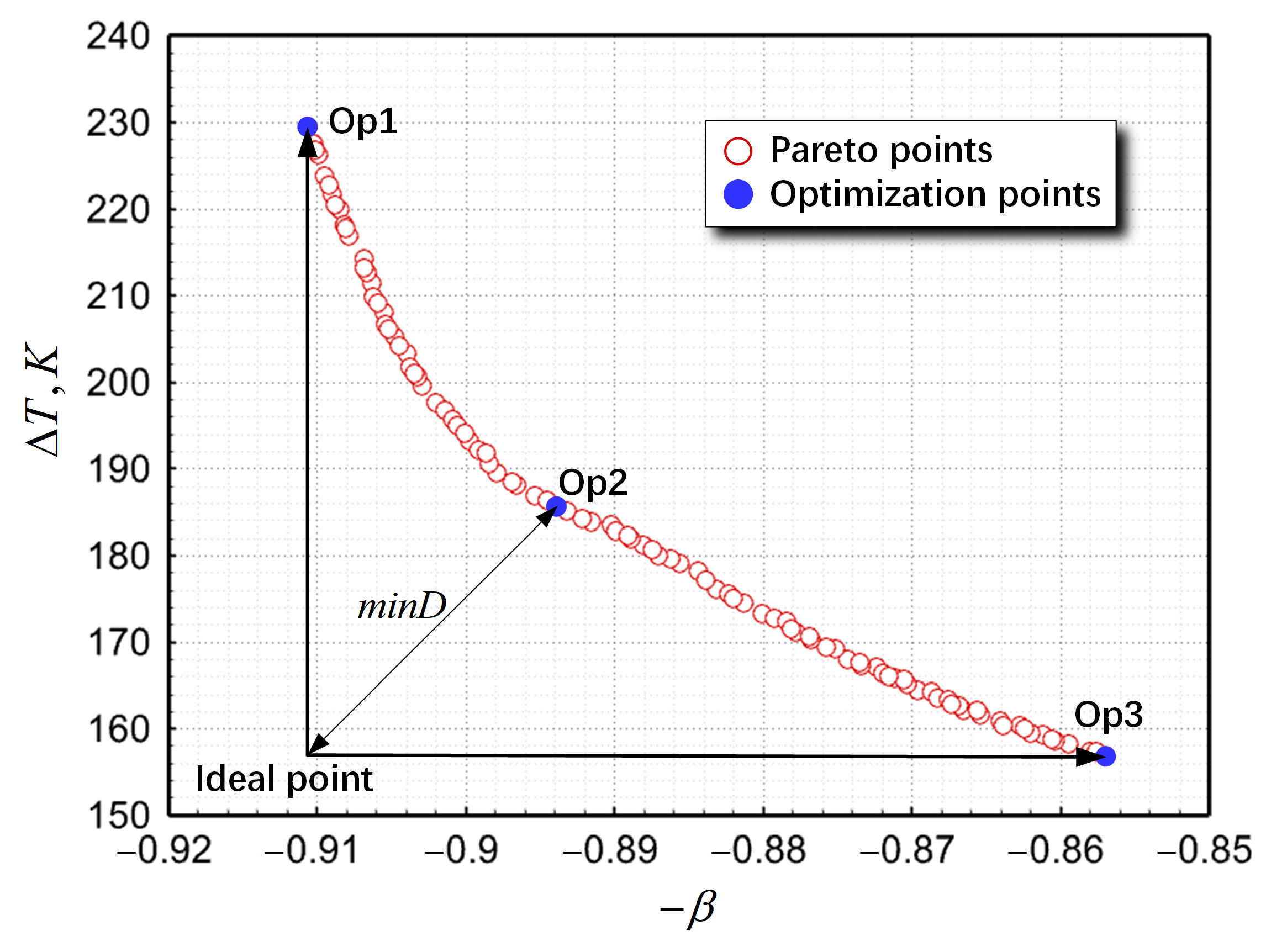
5.2. Multi-Objective Optimization Results
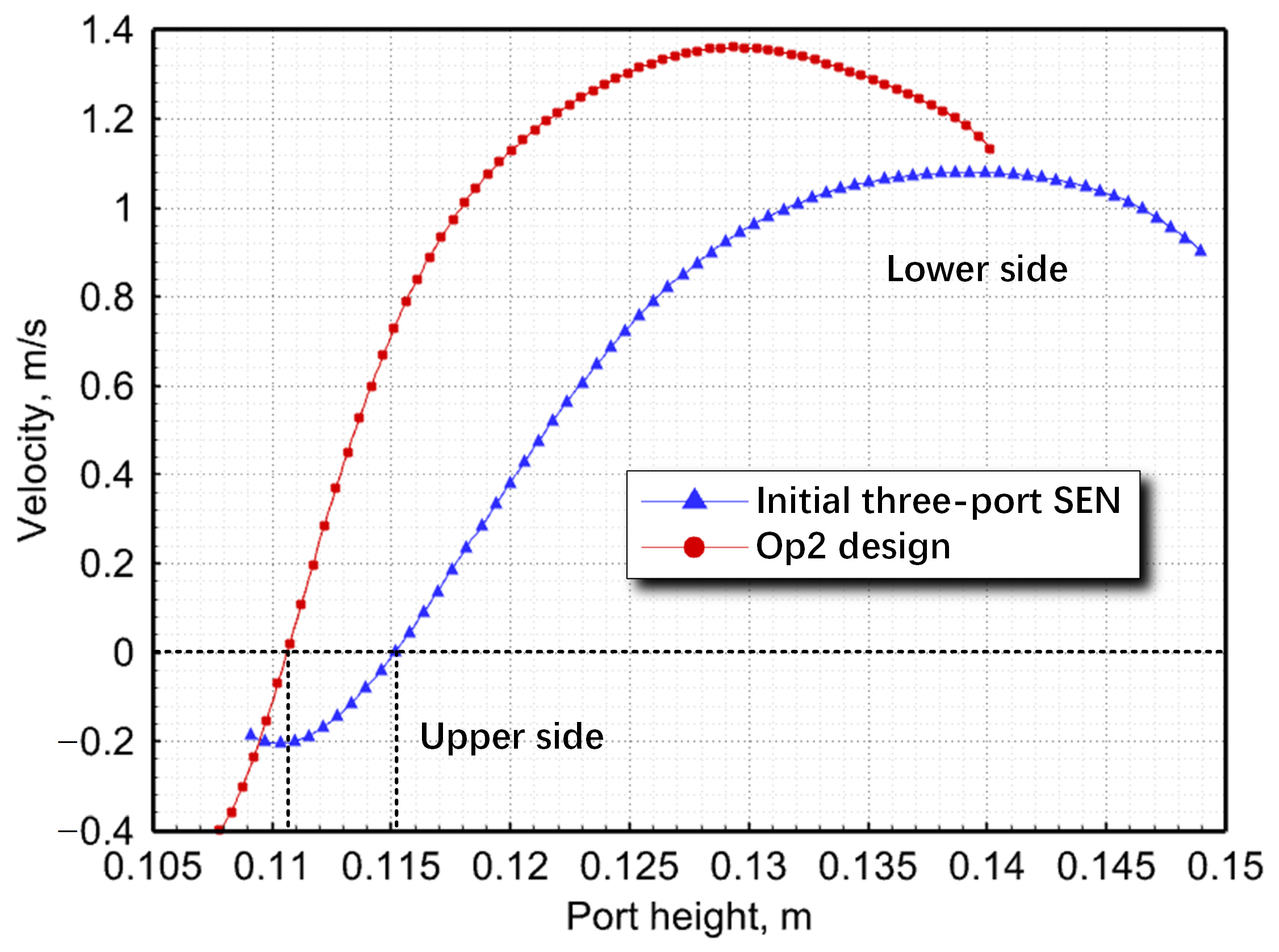
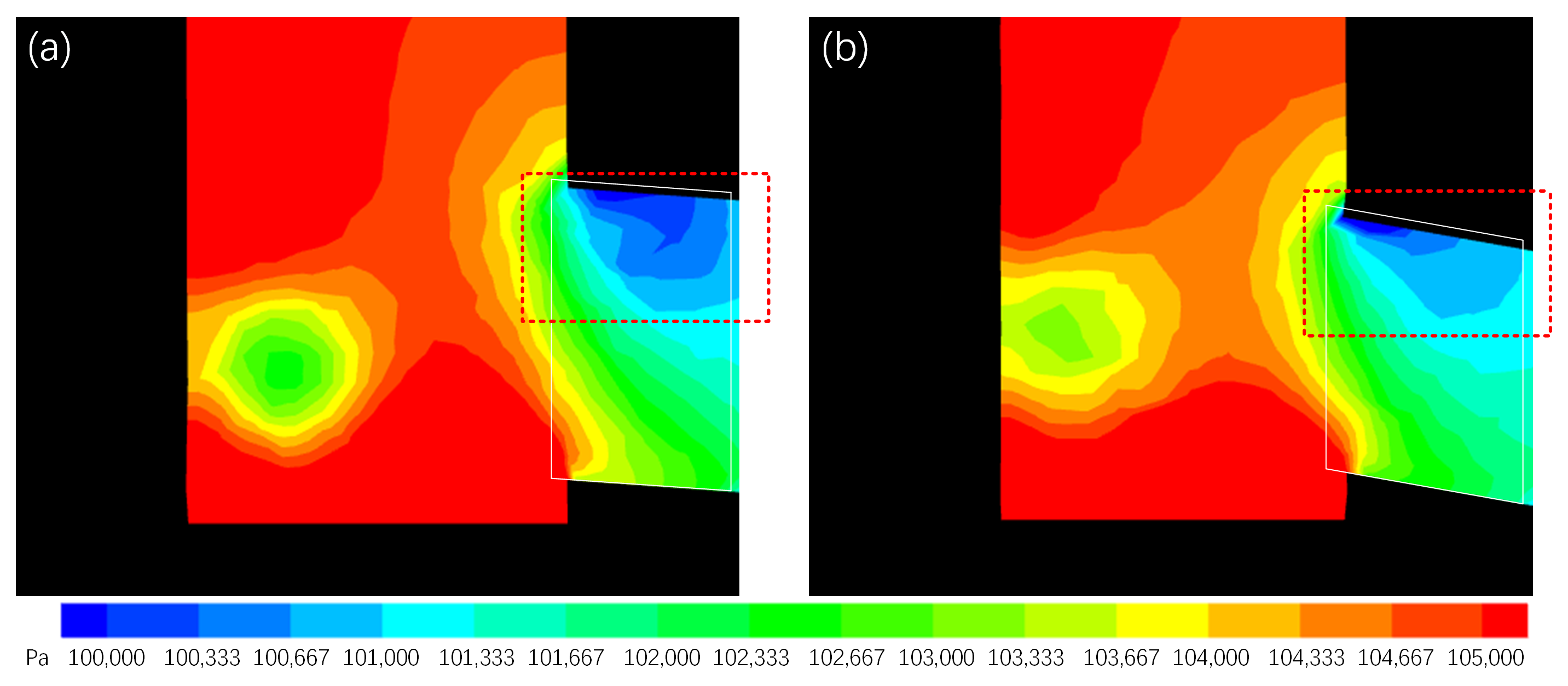
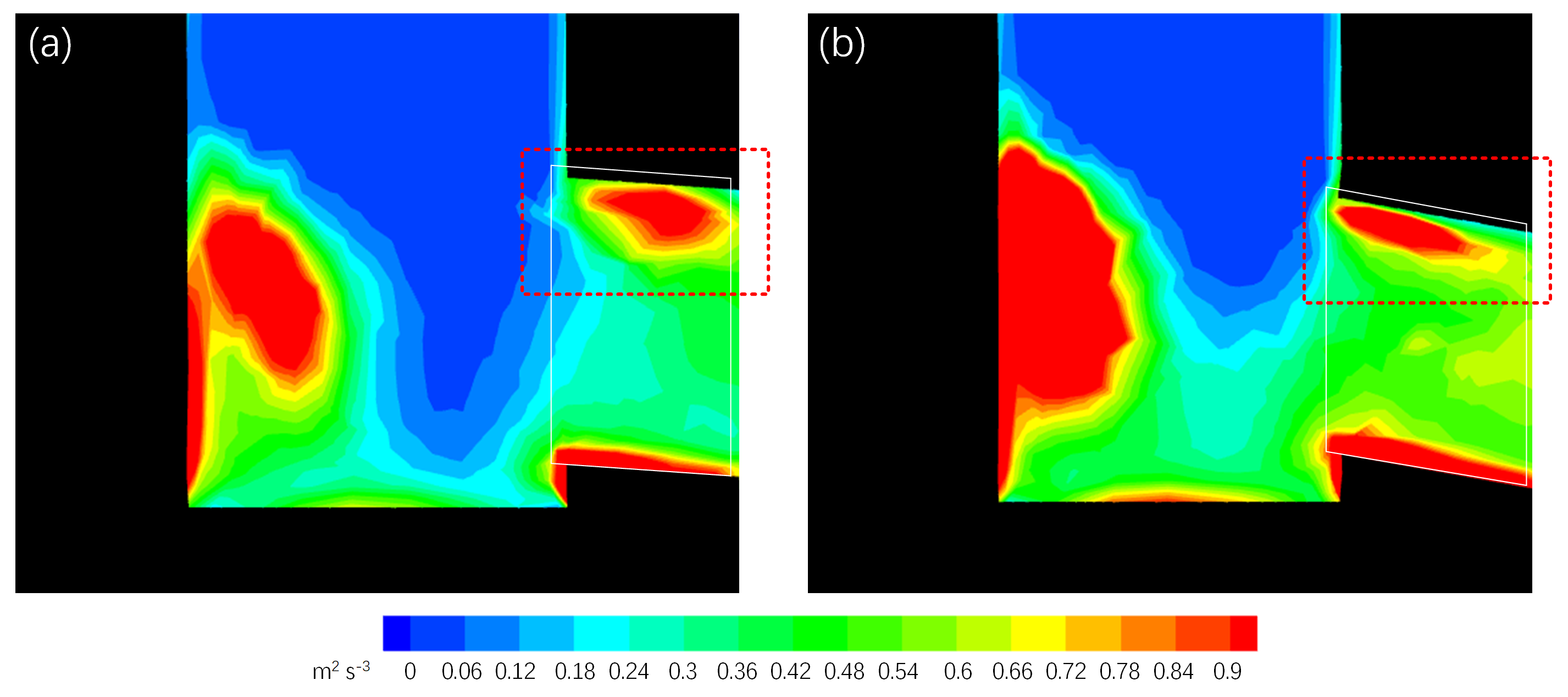
5.3. Discussion of the Three-Port SEN Structure Optimization
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.-E.; Yeo, T.-J.; Hwan OH, K.; Yoon, J.-K.; Yoon, U.-S. Prediction of cracks in continuously cast steel beam blank through fully coupled analysis of fluid flow, heat transfer, and deformation behavior of a solidifying shell. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 31, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, J.J.M.; Gabriel, W.V.; Ribeiro, L.Q.; Silva, C.A.d.; Silva, I.A.d.; Seshadri, V. Computational and physical simulation of fluid flow inside a beam blank continuous casting mold. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 233, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, C. Three-dimensional FEM study of fluid flow in mould for beam blank continuous casting: Influence of straight through conduit type SEN. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, C. Three-dimensional FEM study of fluid flow in mould for beam blank continuous casting: Influence of nozzle structure and parameters on fluid flow. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Long, M.; Chen, D. The influence of SEN structure on the flow and solidification phenomena in ultra-large-section beam blank mould. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 9463–9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, M.; Liu, K. Numerical Simulation of the Fluid Flow, Heat Transfer, and Solidification in Ultrahigh Speed Continuous Casting Billet Mold. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.G.; Zhang, L. Mathematical modeling of fluid flow in continuous casting. ISIJ Int. 2001, 41, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhou, Y.-z.; Chen, D.-f.; Long, M.-j.; Duan, H.-m. Optimization of submerged entry nozzle parameters for ultra-high casting speed continuous casting mold of billet. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, M. Transport phenomena in a beam-blank continuous casting mold with two types of submerged entry nozzle. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-w.; Du, Y.-p.; Shi, R.; Cui, X.-C.; Liu, C. Effect of SEN parameters on 3D flow field in mould of beam blank continuous caster. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2004, 11, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Long, M.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y. Hydraulic simulation of fluid flow in beam blank continuous casting mold with double nozzles. In Proceedings of the EPD Congress 2014, San Diego, CA, USA, 16–24 February 2014; pp. 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Hernandez, S.; Morales, R.D.; Barreto, J.d.J.; Morales-Higa, K. Numerical Optimization of Nozzle Ports to Improve the Fluidynamics by Controlling Backflow in a Continuous Casting Slab Mold. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 1794–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbeler, L.C.; Xu, K.; Thomas, B.G.; Koric, S.; Spangler, C. Thermomechanical modeling of beam blank casting. Iron Steel Technol. 2009, 6, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, N.; Kumar, K.S.; Roy, G. A heat transfer study of the continuous caster mold using a finite volume approach coupled with genetic algorithms. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2003, 12, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, N.; Kumar, R.; Jain, D. A study of the continuous casting mold using a pareto-converging genetic algorithm. Appl. Math. Model. 2001, 25, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, N.; Mukherjee, A. Optimisation of continuous casting mould parameters using genetic algorithms and other allied techniques. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2000, 27, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.A.; Cheung, N.; Garcia, A.; Spim, J.A. Application of a Solidification Mathematical Model and a Genetic Algorithm in the Optimization of Strand Thermal Profile Along the Continuous Casting of Steel. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2005, 20, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Deng, K.; Li, W.; Gan, Y.; Zhao, L. Mathematical simulation on coupled flow, heat, and solute transport in slab continuous casting process. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.P.; Launder, B. The prediction of laminarization with a two-equation model of turbulence. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1972, 15, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. Large eddy simulation on the fluid flow, solidification and entrapment of inclusions in the steel along the full continuous casting slab strand. JOM 2018, 70, 2968–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, L.; Nadalon, E.; Contini, A.; Barroso, R. Modeling of Solidification in Continuous Casting Round Billet with Mold Electromagnetic Stirring (M-EMS). Steel Res. Int. 2016, 88, 1600319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, A.D.; Voller, V.R.; Reid, K.J. Enthalpy-Porosity Technique for Modeling Convection-Diffusion Phase Change: Application to the Melting of a Pure Metal. Numer. Heat Transf. 1988, 13, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, W. Effect of Casting Parameters on the Flow Pattern in a Steel Continuous Casting Slab Mold: Numerical Simulation and Industrial Trials. Steel Res. Int. 2021, 93, 2100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Ni, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Song, X.; Liu, C. Influence of SEN on flow, solidification, and solute transport in bloom casting mold. JOM 2018, 70, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Ni, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Lv, Z. The Effects of a Submerged Entry Nozzle on Flow and Initial Solidification in a Continuous Casting Bloom Mold with Electromagnetic Stirring. Metals 2017, 7, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.L.; Chen, D.F.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Dong, Z.H.; Long, M.J.; Ruan, X.B. Influences of SEN structures on flow characters, temperature field and shell distribution in 420 mm continuous casting mould. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 40, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhu, L.G.; Lu, W.G.; Wang, B.X.; Ma, J.H. Thermo-mechanical simulation and parameters optimization for beam blank continuous casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 499, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Ji, C. Application of High Speed Continuous Casting on Low Carbon Conventional Slab in SGJT. Steel Res. Int. 2014, 85, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, S.; Cai, K.; Li, J.; Wan, X.; Thomas, B.G. Investigation of Fluid Flow and Steel Cleanliness in the Continuous Casting Strand. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 63–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-K. Applications of numerical simulation to continuous casting technology. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Najjar, F.M.; Thomas, B.G.; Hershey, D.E. Numerical study of steady turbulent flow through bifurcated nozzles in continuous casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1995, 26, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, D.F.; Long, M.J.; Shen, J.L.; Qin, R.S. Two-dimensional heat transfer model for secondary cooling of continuously cast beam blanks. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 41, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Wen, G.H.; Sun, W.; Wang, K.Z.; Yan, B. Analysis of Thermal Behavior for Beam Blank Continuous Casting Mold. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yang, C.; Peng, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, B. Crash performance and multi-objective optimization of a gradual energy-absorbing structure for subway vehicles. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 107, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, Q.; Liufu, K.; Deng, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, Q. Design of bionic-bamboo thin-walled structures for energy absorption. Thin-Walled Struct. 2019, 135, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Sun, G.; Li, G.; Gao, W.; Li, Q. Crashworthiness optimization of foam-filled tapered thin-walled structure using multiple surrogate models. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2012, 47, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, A.; Li, G. Design optimisation of composite bumper beam with variable cross-sections for automotive vehicle. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2016, 22, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, D.; Sofos, F.; Karakasidis, T.E. Artificial Intelligence in Physical Sciences: Symbolic Regression Trends and Perspectives. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 3845–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Latent heat of steel [] | 274,129 |
| Solidus of steel [] | 1715.65 |
| Liquidus of steel [] | 1785.47 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Population size | 100 |
| Number of function evolutions | 500 |
| Crossover probability | 0.7 |
| Mutation probability | 0.4 |
| Initialization mode | Random |
| Objective | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9215 | 0.9452 | 0.9502 | 0.9728 | |
| RMSE | 0.031 | 0.076 | 0.052 | 0.049 |
| MAPE (%) | 7.75 | 12.56 | 1.64 | 9.26 |
| Objective | Initial | Op1 Design | Op2 Design | Op3 Design | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| () | 55 | 45 | 45 | 46 | ||||||
| (°) | 4 | 11 | 10 | 9 | ||||||
| () | 110 | 110 | 110 | 111 | ||||||
| (°) | 110 | 114 | 114 | 112 | ||||||
| CFD | CFD | PRSM | RE (%) | CFD | PRSM | RE (%) | CFD | PRSM | RE (%) | |
| () | 9.26 | 12.47 | 12.24 | 1.87 | 12.08 | 12.14 | −0.49 | 11.09 | 11.71 | −5.29 |
| () | 0.1840 | 0.1999 | 0.1957 | 2.14 | 0.1972 | 0.1985 | −0.65 | 0.1808 | 0.1649 | 9.64 |
| 0.8535 | 0.9162 | 0.9106 | 0.61 | 0.9321 | 0.8940 | 4.26 | 0.8931 | 0.8570 | 4.21 | |
| Increase | 7.34% | 9.20% | 4.63% | |||||||
| () | 328.00 | 258.00 | 229.42 | 12.45 | 180.00 | 185.43 | −2.92 | 176.00 | 156.92 | 12.15 |
| Increase | −21.34% | −45.12% | −46.34% | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, N.; Duan, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, Q.; Deng, Y.; Ni, W. Optimization Design of Submerged-Entry-Nozzle Structure Using NSGA-II Genetic Algorithm in Ultra-Large Beam-Blank Continuous-Casting Molds. Materials 2024, 17, 4346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174346
Deng N, Duan J, Li Y, Gao Q, Deng Y, Ni W. Optimization Design of Submerged-Entry-Nozzle Structure Using NSGA-II Genetic Algorithm in Ultra-Large Beam-Blank Continuous-Casting Molds. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174346
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Nanzhou, Jintao Duan, Yibo Li, Qi Gao, Yulong Deng, and Weihua Ni. 2024. "Optimization Design of Submerged-Entry-Nozzle Structure Using NSGA-II Genetic Algorithm in Ultra-Large Beam-Blank Continuous-Casting Molds" Materials 17, no. 17: 4346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174346
APA StyleDeng, N., Duan, J., Li, Y., Gao, Q., Deng, Y., & Ni, W. (2024). Optimization Design of Submerged-Entry-Nozzle Structure Using NSGA-II Genetic Algorithm in Ultra-Large Beam-Blank Continuous-Casting Molds. Materials, 17(17), 4346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174346






