Rheological Behavior of SiO2 Ceramic Slurry in Stereolithography and Its Prediction Model Based on POA-DELM
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preparation and Rheological Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rheological Experiment
3. Rheological Results
4. Rheological Predicted Model
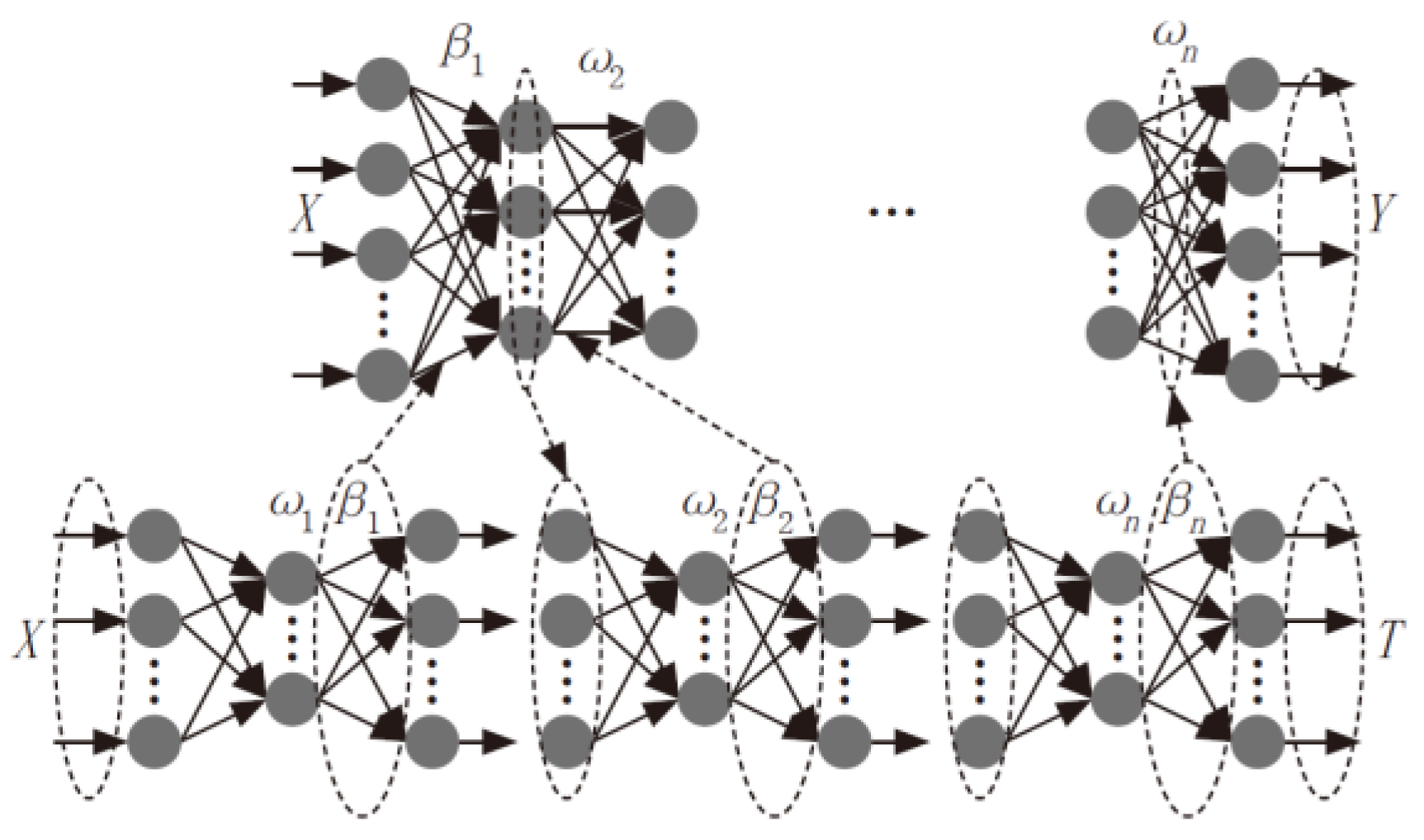
4.1. POA-DELM
4.1.1. Pelican Optimization Algorithm (POA)
4.1.2. Deep Extreme Learning Machine (DELM)
4.1.3. The Detailed Process of POA-DELM
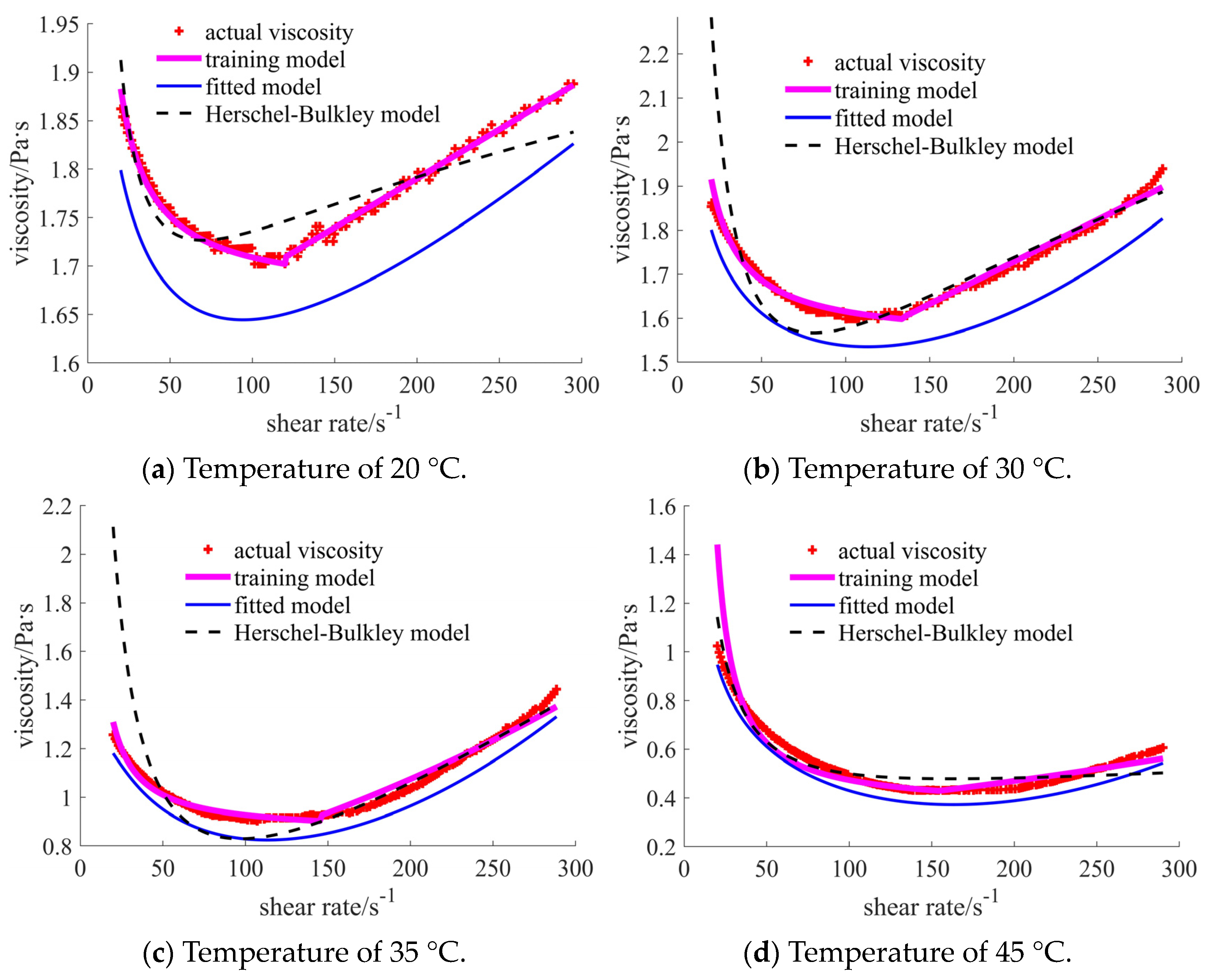
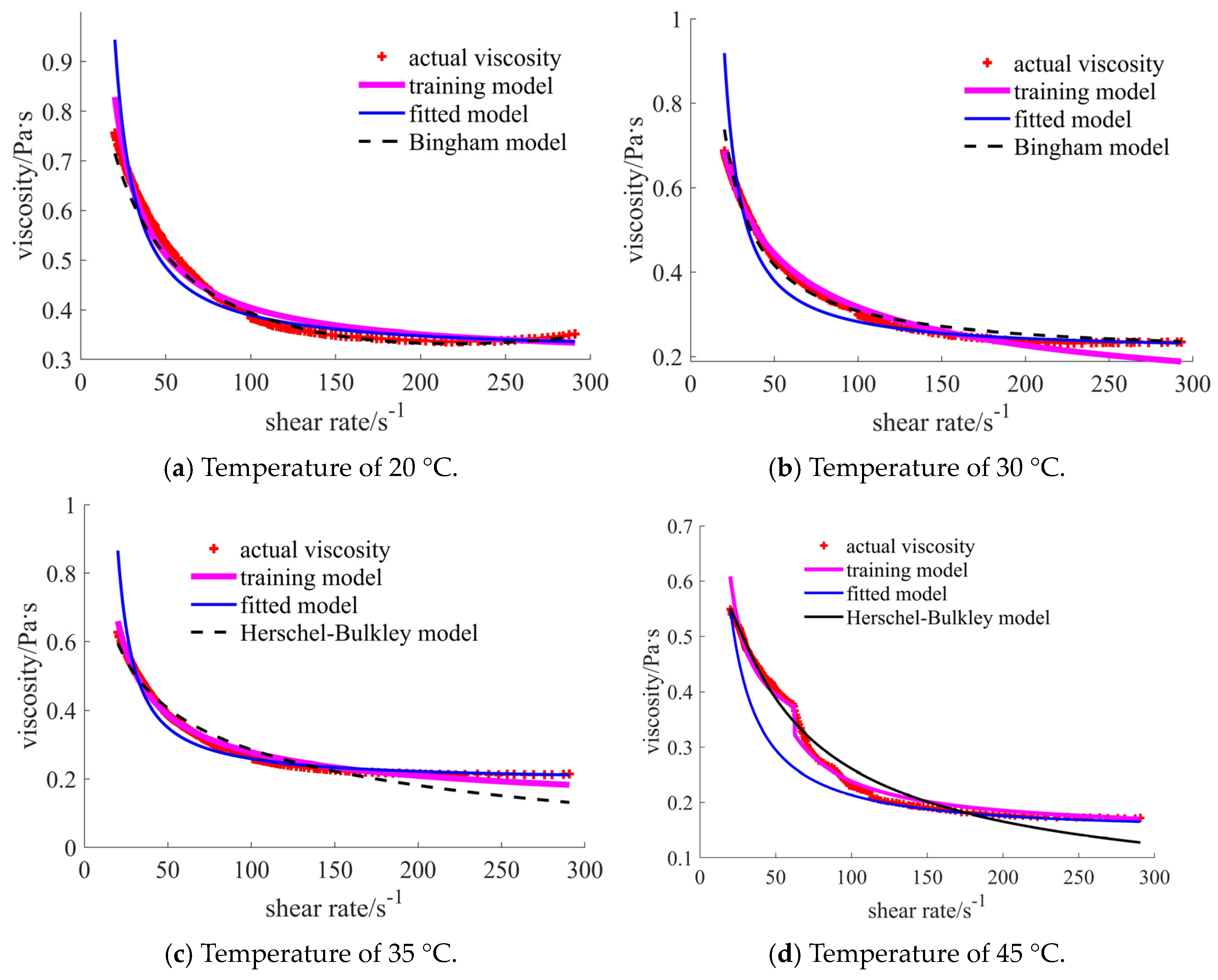
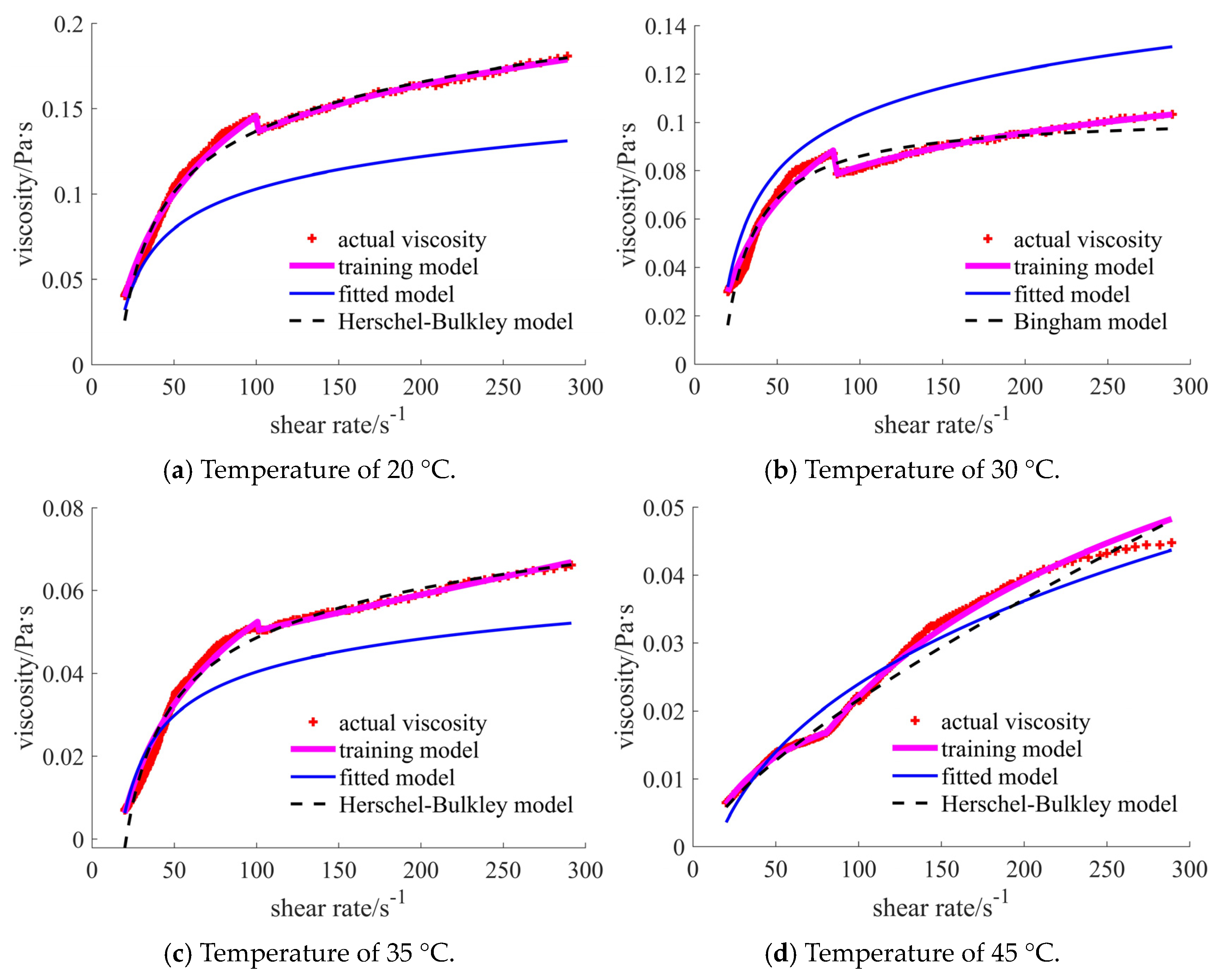
4.2. Training Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.L.; Lichade, K.; He, H.; Feinerman, A.; Pan, Y. Textured window design for continuous projection stereolithography process. Manuf. Lett. 2020, 24, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.G.; Chuang, S.I.; Son, J.H.; Jung, Y.; Jo, J.; Jeong, H. Functional prototype development: Inner visible multi-color prototype fabrication process using stereo lithography. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 130, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.N.; Kim, D. A study on effects of curing and machining conditions in post-processing of SLA additive manufactured polymer. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 119, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, J.W. Ceramic Stereolithography: Additive Manufacturing for Ceramics by Photopolymerization. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Tikhonov, A.; Dubinin, O.; Chugunov, S.; Shishkovsky, I. Piezoelectric properties of the 3D-printed lead-free ceramics. Ferroelectrics 2022, 601, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, H.J.; Dong, D.; Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Jiang, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Fan, G.; et al. Enhanced comprehensive properties of stereolithography 3D printed alumina ceramic cores with high porosities by a powder gradation design. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 131, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.J.; He, R.J.; Zhang, K.Q.; Xia, M.; Feng, C.; Fang, D. Dispersion and stability of SiC ceramic slurry for stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4720–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Q.; Xu, C.J.; Zhang, Z.M. Preparation and optimization of Si3N4 ceramic slurry for low-cost LCD mask stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 9400–9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chang, H.T.; Guo, X.T.; Liu, M.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y. Preparation of photosensitive SiO2/SiC ceramic slurry with high solid content for stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 30332–30337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Meng, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.Q.; Qu, Z.L.; Jing, S.K.; He, R.J. Roles of solid loading in stereolithography additive manufacturing of ZrO2 ceramic. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 99, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.H.; Zhao, Z. The effect of the surfactants on the formulation of UV-curable SLA alumina suspension. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 4761–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.Y.; Zou, B.; Lai, Q.G.; Huang, C.; Chen, Q.; Fu, X.; Shi, Z. Preparation and characterization of UV curable Al2O3 suspensions applying for stereolithography 3D printing ceramic microcomponent. Powder Technol. 2018, 338, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Zhang, J.X.; Duan, Y.S.; Liu, N.; Jiang, J.; Ma, R.; Xi, H.; Li, X. Rheology and Curability Characterization of Photosensitive Slurries for 3D Printing of Si3N4 Ceramics. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.W.; Deng, X.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. Investigation of Obstacles with Interactive Elements on the Flow in SiC Three-Dimensional Printing. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 10, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.W.; Deng, X.; Ding, S.; Zhu, L.; Wei, X.; Song, A. Effect mechanism of multiple obstacles on non-Newtonian flow in ceramic 3D printing (arcuate elements). Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 34554–34567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.W.; Deng, X.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.; Shi, B. Micro-flow investigation on laying process in Al2O3 stereolithography forming. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 033107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.X.; Liu, B.S.; Li, T.; Luo, G.; Li, S.; Duan, W.; Wang, G. Simulation and experimental analysis on the deformation rate on slender rod parts during the recoating process in high viscosity ceramic stereolithography. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 124, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Song, X. Supportability of a High-Yield-Stress Slurry in a New Stereolithography-Based Ceramic Fabrication Process. JOM 2018, 70, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.J.; Qin, X.B.; Bian, M.F.; Wang, Z. Study on liquid structure and viscosity of In-5%Cu alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2003, 32, 911–914. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Wu, S.S.; Lv, S.L.; Zeng, J.; An, P. Viscosity variation of hypereutectic Al-Si alloys with high iron contents around liquidus temperature. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2019, 32, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojovsky, P.; Dehghani, M. Pelican Optimization Algorithm: A Novel Nature-Inspired Algorithm for Engineering Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuma, P.D.; Dinimaharawati, A. Hybrid Pelican Komodo Algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2022, 13, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Lin, C.L.; Wen, J.; Yan, P.; Wang, Y. An Improved Pelican Optimization Algorithm Based on Chaos Mapping Factor. Eng. Lett. 2023, 31, EL31432. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Siew, C.K. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.B.; Zhou, H.M.; Ding, X.J.; Zhang, R. Extreme Learning Machine for Regression and Multiclass Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B-Cybern. 2012, 42, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Deng, C.W.; Huang, G.B.; Zhao, B. Compressed-Domain Ship Detection on Spaceborne Optical Image Using Deep Neural Network and Extreme Learning Machine. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Myttenaere, A.; Golden, B.; Le Grand, B.; Rossi, F. Mean absolute percentage error for regression models. Neurocomputing 2016, 192, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. Peerj Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, C.; Greco, A.; Montagna, F.; Licciulli, A.; Maffezzoli, A. Silica moulds built by stereolithography. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 4899–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, B.; Sameni, F.; Bianchi, F.; Zarezadeh, H.; Karmel, S.; Engstrøm, D.S.; Sabet, E. 3D printing ceramic cores for investment casting of turbine blades, using LCD screen printers: The mixture design and characterisation. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 42, 658–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H. Study on Rheology and Stability of Light Curing Silicon Oxide Ceramic Slurry. In Advances in Machinery, Materials Science and Engineering Application; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chartier, T.; Badev, A.; Abouliatim, Y.; Lebaudy, P.; Lecamp, L. Stereolithography process: Influence of the rheology of silica suspensions and of the medium on polymerization kinetics–cured depth and width. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
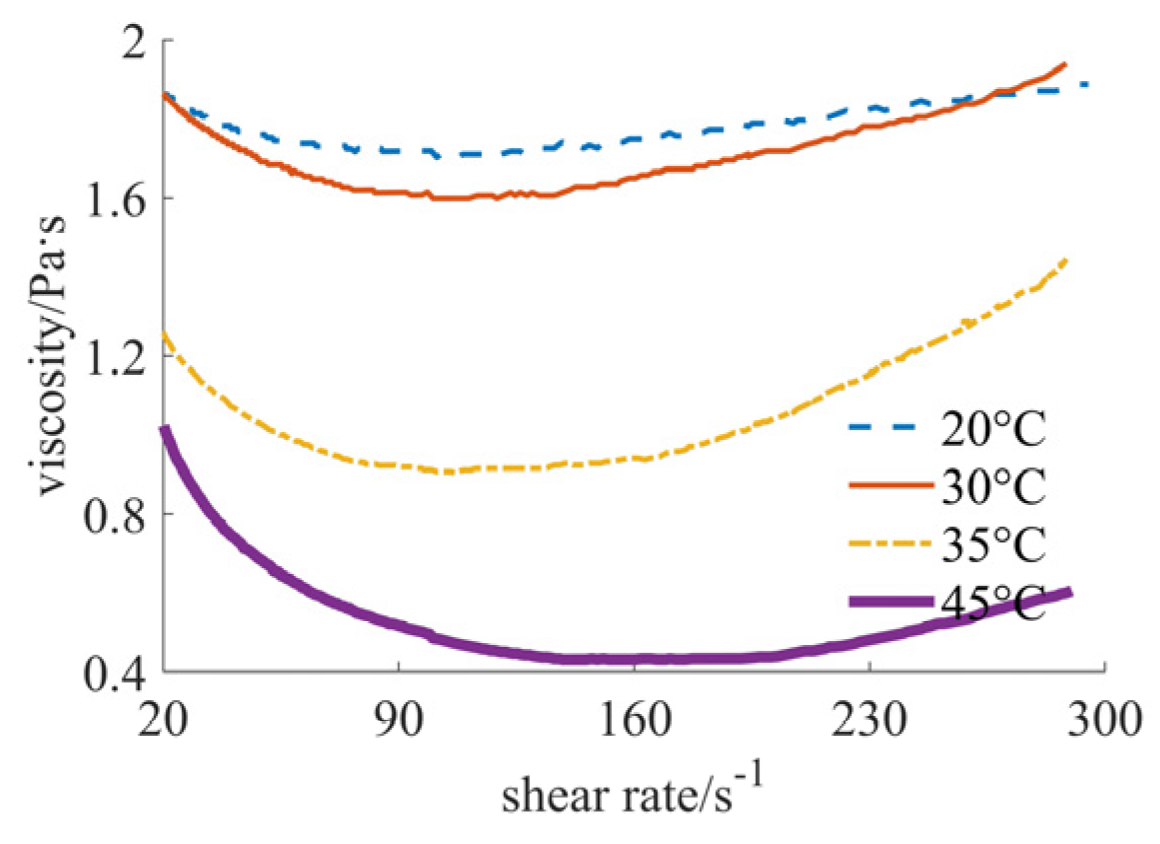
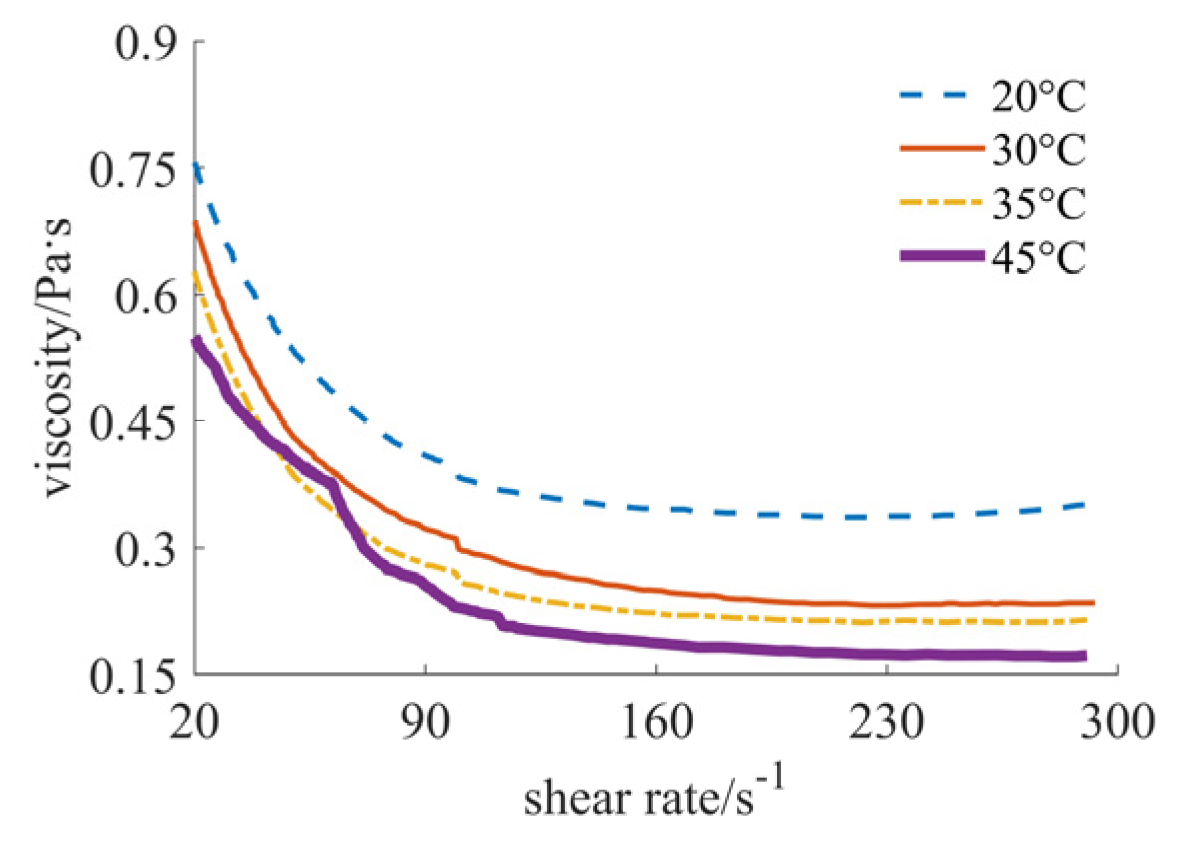
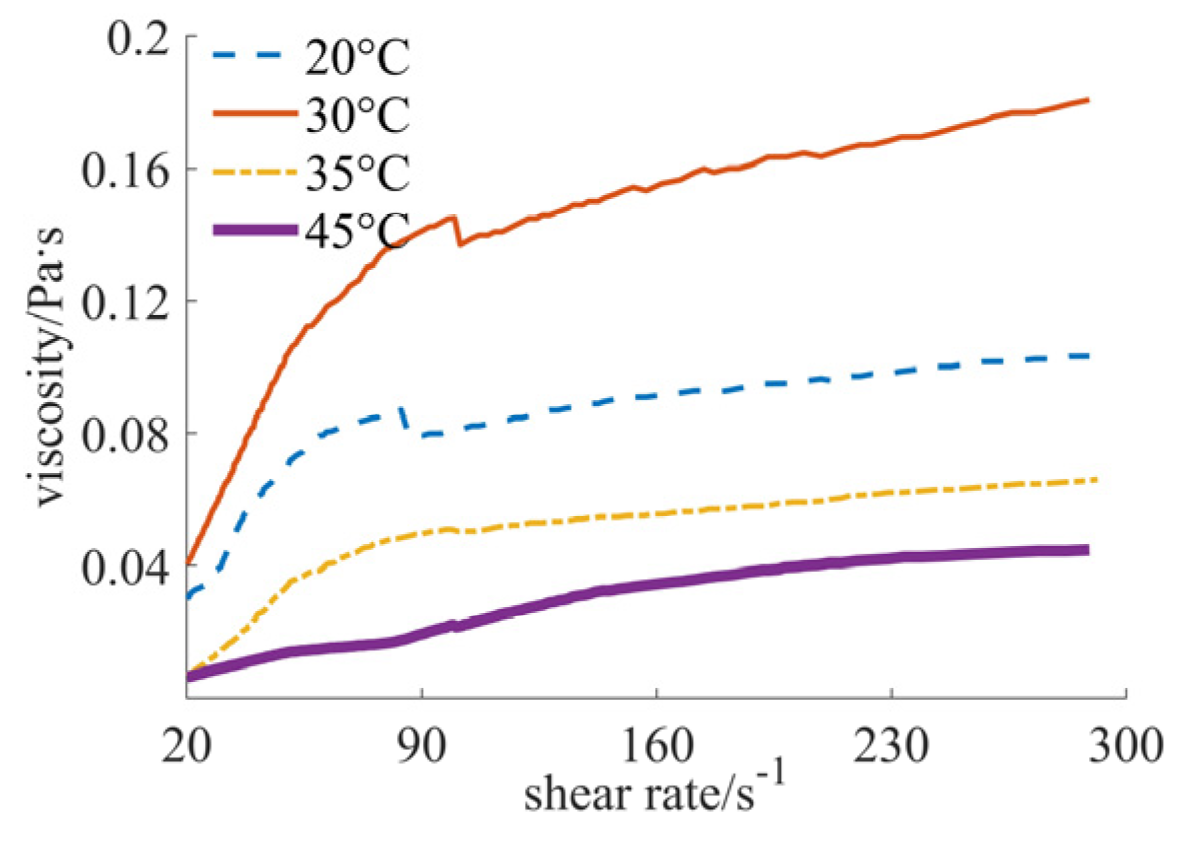


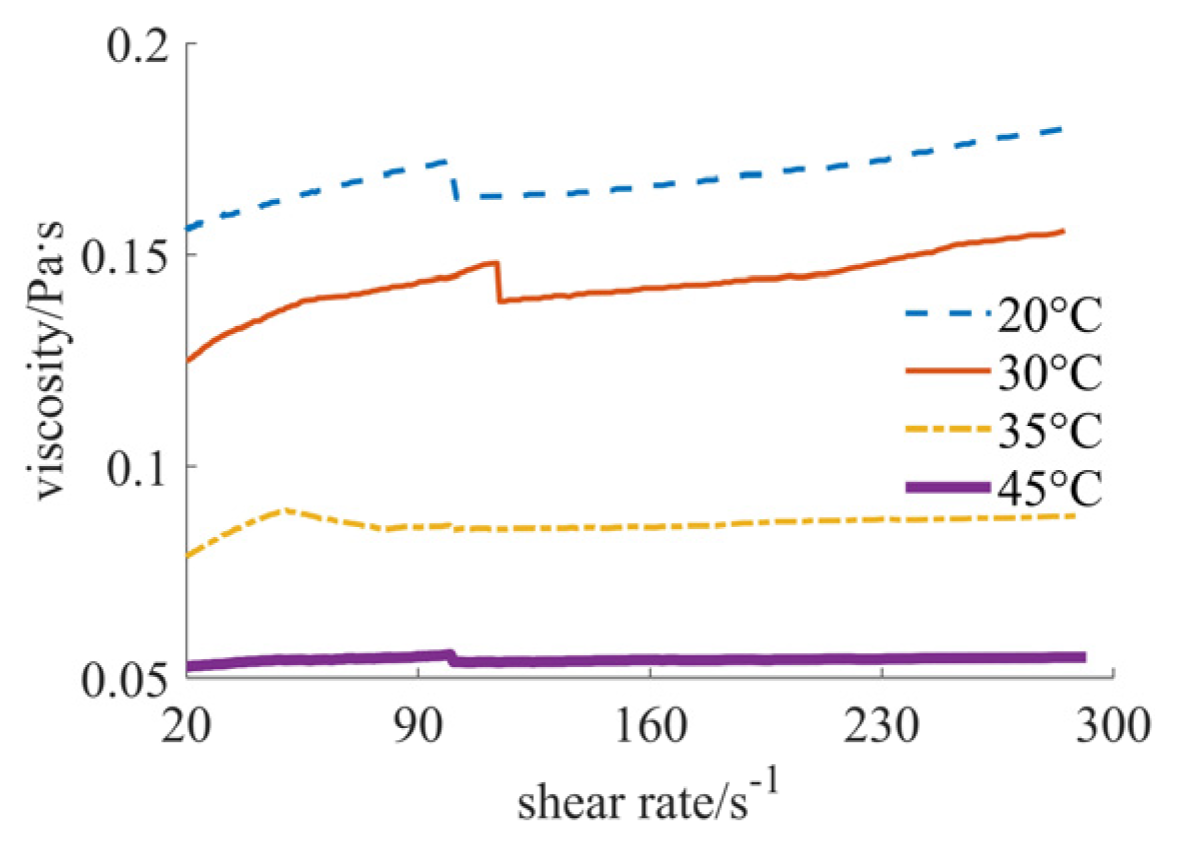
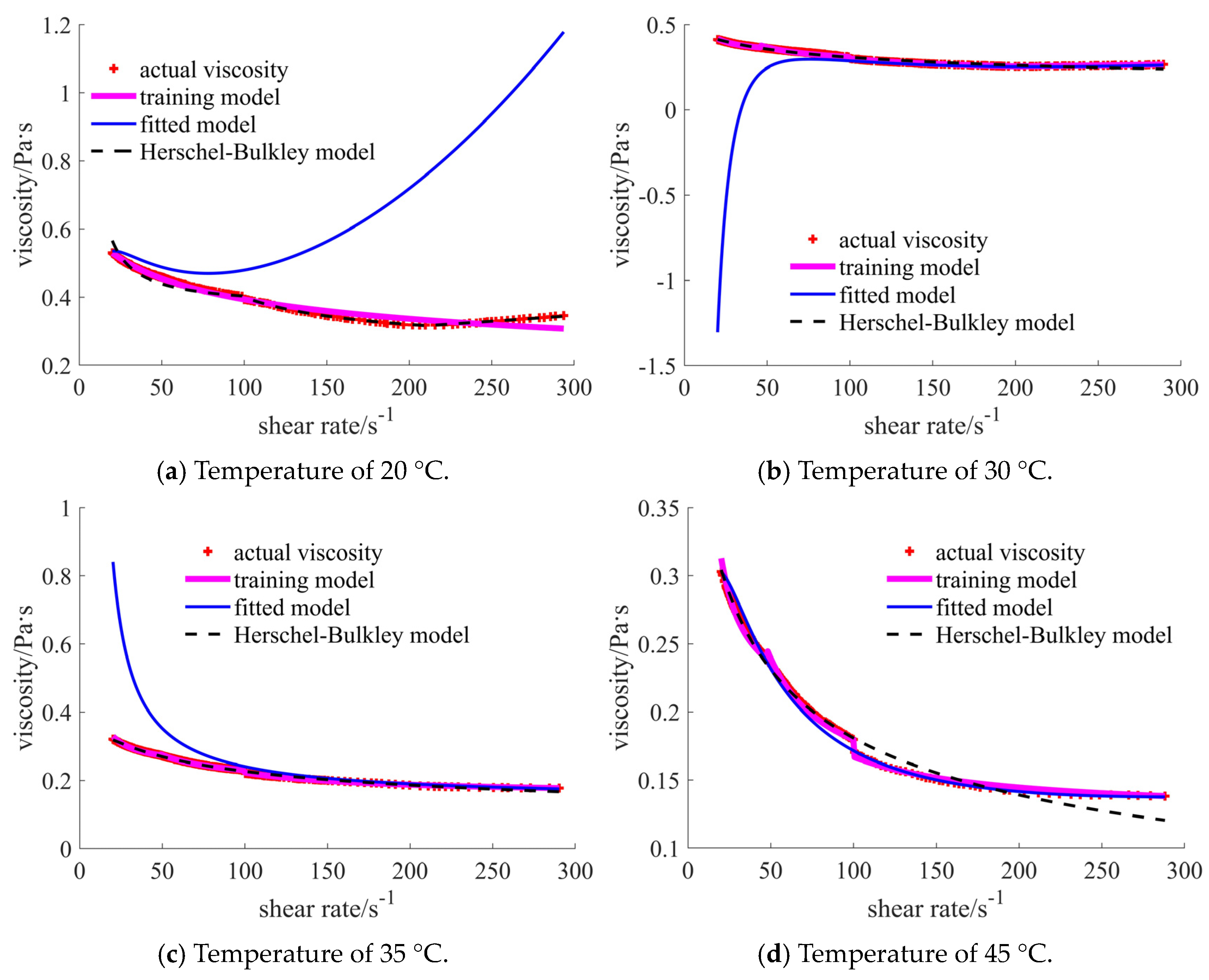
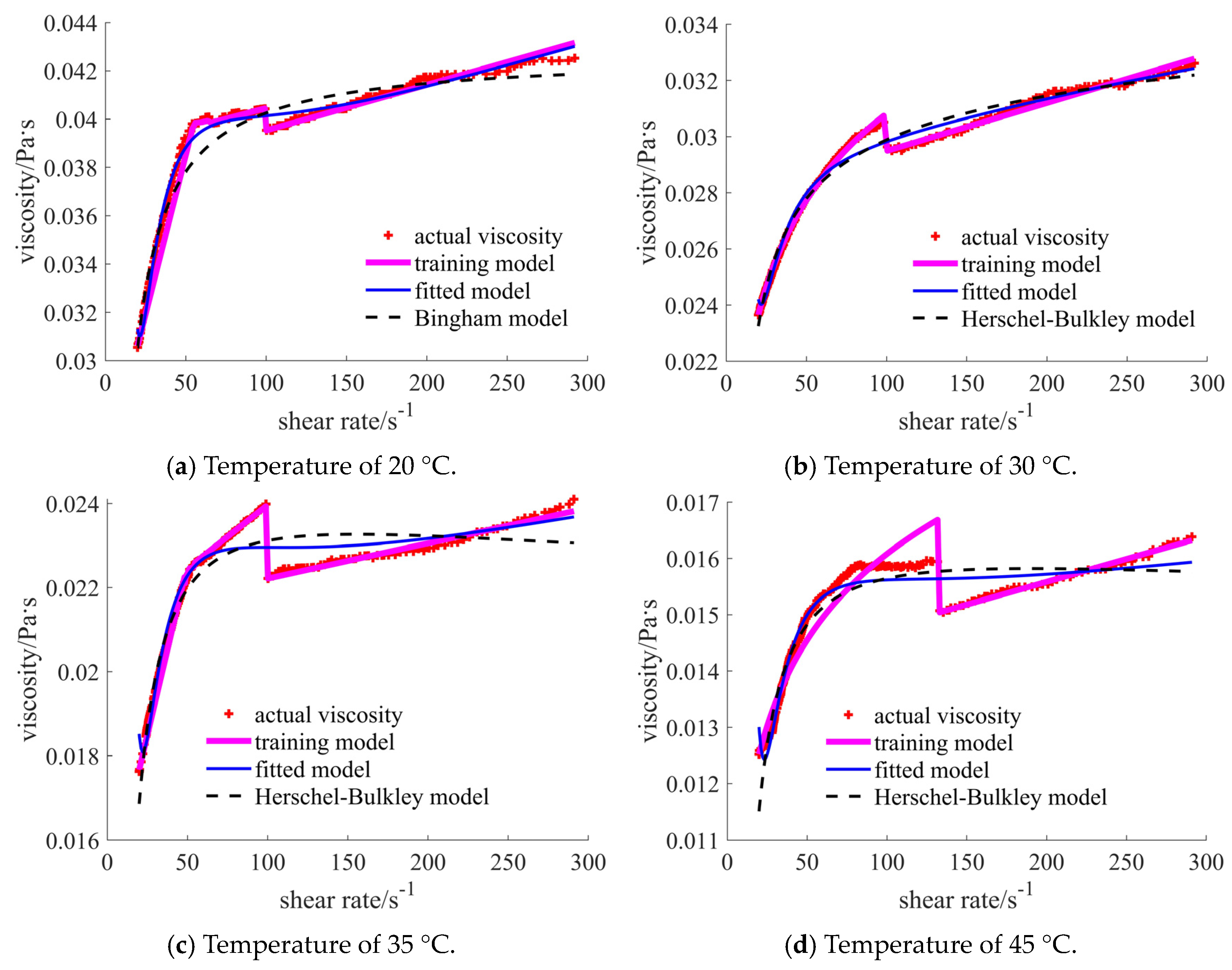
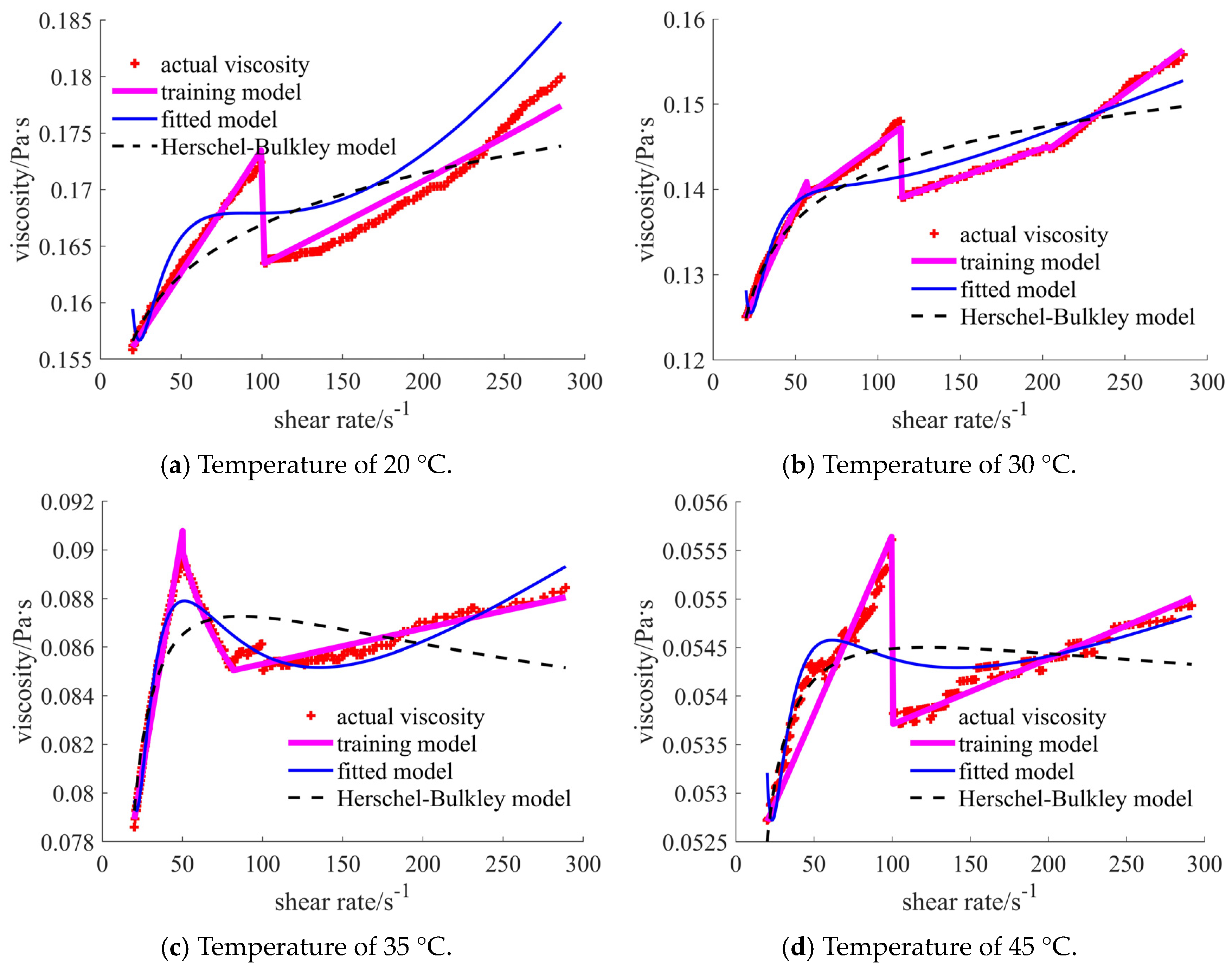
| Nano-Sized (Case 1) | Sub-Micron-Sized (Case 2) | Micron-Sized (Case 3) | 40% Nano-Sized and 5% Micron-Sized (Case 4) | 25% Nano-Sized and 20% Micron-Sized (Case 5) | 30% Nano-Sized and 15% Micron-Sized (Case 6) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 °C | [1.717, 1.888], shear thinning–thickening | [0.351, 0.756], shear thinning | [0.030, 0.103], shear thickening | [0.346, 0.530], shear thinning | [0.031, 0.043], shear thickening | [0.156, 0.180], shear thickening |
| 30 °C | [1.613, 1.939], shear thinning–thickening | [0.235, 0.687], shear thinning | [0.041, 0.181], shear thickening | [0.266, 0.411], shear thinning | [0.024, 0.033], shear thickening | [0.125, 0.156], shear thickening |
| 35 °C | [0.903, 1.445], shear thinning–thickening | [0.215, 0.628], shear thinning | [0.007, 0.066], shear thickening | [0.178, 0.321], shear thinning | [0.017, 0.024], shear thickening | [0.079, 0.088], shear thickening |
| 45 °C | [0.431, 1.024], shear thinning–thickening | [0.172, 0.550], shear thinning | [0.006, 0.045], shear thickening | [0.138, 0.303], shear thinning | [0.012, 0.016], shear thickening | [0.053, 0.055], shear thickening |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0057 | 0.0026 | 0.0047 | 0.987 | 1 | 0.0131 | 0.0058 | 0.0100 | 0.975 |
| 2 | 0.0736 | 0.0054 | 0.0733 | 0.754 | 2 | 0.0836 | 0.0481 | 0.0827 | 0.724 |
| 3 | 0.0217 | 0.0103 | 0.0184 | 0.809 | 3 | 0.0891 | 0.0316 | 0.0554 | 0.754 |
| 35 °C | 45 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0062 | 0.0184 | 0.0196 | 0.971 | 1 | 0.0580 | 0.0510 | 0.0323 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 0.0203 | 0.0746 | 0.0784 | 0.786 | 2 | 0.0612 | 0.1141 | 0.0610 | 0.769 |
| 3 | 0.0397 | 0.0693 | 0.0751 | 0.721 | 3 | 0.0405 | 0.0650 | 0.0347 | 0.859 |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0203 | 0.0347 | 0.0171 | 0.975 | 1 | 0.0129 | 0.0309 | 0.0095 | 0.993 |
| 2 | 0.0412 | 0.0533 | 0.0293 | 0.896 | 2 | 0.0576 | 0.0796 | 0.0393 | 0.852 |
| 3 | 0.0227 | 0.0312 | 0.0178 | 0.968 | 3 | 0.0170 | 0.0369 | 0.0148 | 0.987 |
| 35 °C | 45 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0104 | 0.0262 | 0.0082 | 0.992 | 1 | 0.0134 | 0.0304 | 0.0100 | 0.988 |
| 2 | 0.0439 | 0.0665 | 0.0282 | 0.865 | 2 | 0.0729 | 0.1502 | 0.0600 | 0.636 |
| 3 | 0.0240 | 0.0632 | 0.0189 | 0.960 | 3 | 0.0176 | 0.0537 | 0.0139 | 0.979 |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0034 | 0.0377 | 0.0028 | 0.994 | 1 | 0.0032 | 0.0514 | 0.0024 | 0.979 |
| 2 | 0.0262 | 0.1803 | 0.0212 | 0.604 | 2 | 0.0168 | 0.2536 | 0.0155 | 0.433 |
| 3 | 0.0045 | 0.0462 | 0.0036 | 0.988 | 3 | 0.0039 | 0.0602 | 0.0032 | 0.969 |
| 35 °C | 45 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0021 | 0.0800 | 0.0016 | 0.986 | 1 | 0.0006 | 0.0193 | 0.0004 | 0.997 |
| 2 | 0.0076 | 0.1857 | 0.0066 | 0.813 | 2 | 0.0021 | 0.0976 | 0.0018 | 0.963 |
| 3 | 0.0025 | 0.1009 | 0.0020 | 0.980 | 3 | 0.0018 | 0.0648 | 0.0014 | 0.972 |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0087 | 0.0146 | 0.0053 | 0.984 | 1 | 0.0034 | 0.0064 | 0.0022 | 0.996 |
| 2 | 0.2371 | 0.3770 | 0.1319 | 0.714 | 2 | 0.4359 | 0.5432 | 0.2118 | 0.358 |
| 3 | 0.0126 | 0.0205 | 0.0097 | 0.965 | 3 | 0.0081 | 0.0222 | 0.0064 | 0.976 |
| 35°C | 45°C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0016 | 0.0050 | 0.0013 | 0.998 | 1 | 0.0024 | 0.0090 | 0.0020 | 0.998 |
| 2 | 0.1432 | 0.3228 | 0.0928 | 0.675 | 2 | 0.0059 | 0.0216 | 0.0050 | 0.984 |
| 3 | 0.0026 | 0.0081 | 0.0018 | 0.996 | 3 | 0.0044 | 0.0160 | 0.0029 | 0.992 |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0003 | 0.0067 | 0.0002 | 0.989 | 1 | 0.0001 | 0.0031 | 0.0001 | 0.998 |
| 2 | 0.0005 | 0.0087 | 0.0003 | 0.968 | 2 | 0.0002 | 0.0075 | 0.0002 | 0.988 |
| 3 | 0.0006 | 0.0133 | 0.0005 | 0.954 | 3 | 0.0003 | 0.0092 | 0.0003 | 0.983 |
| 35 °C | 45 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0001 | 0.0056 | 0.0001 | 0.991 | 1 | 0.0002 | 0.0104 | 0.0001 | 0.963 |
| 2 | 0.0003 | 0.0126 | 0.0003 | 0.957 | 2 | 0.0003 | 0.0138 | 0.0002 | 0.940 |
| 3 | 0.0004 | 0.0169 | 0.0004 | 0.929 | 3 | 0.0003 | 0.0157 | 0.0002 | 0.926 |
| 20 °C | 30 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0009 | 0.0045 | 0.0008 | 0.976 | 1 | 0.0005 | 0.0029 | 0.0004 | 0.995 |
| 2 | 0.0030 | 0.0158 | 0.0027 | 0.744 | 2 | 0.0021 | 0.0121 | 0.0017 | 0.925 |
| 3 | 0.0027 | 0.0129 | 0.0022 | 0.784 | 3 | 0.0026 | 0.0140 | 0.0020 | 0.887 |
| 35 °C | 45 °C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | MAE | R2 | ||
| 1 | 0.0003 | 0.0034 | 0.0003 | 0.978 | 1 | 0.0002 | 0.0027 | 0.0001 | 0.883 |
| 2 | 0.0006 | 0.0057 | 0.0005 | 0.935 | 2 | 0.0003 | 0.0043 | 0.0002 | 0.715 |
| 3 | 0.0015 | 0.0152 | 0.0013 | 0.613 | 3 | 0.0004 | 0.0055 | 0.0003 | 0.602 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Min, B.-W.; Gu, H.; Wu, G.; Wu, W. Rheological Behavior of SiO2 Ceramic Slurry in Stereolithography and Its Prediction Model Based on POA-DELM. Materials 2024, 17, 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174270
Zhang J, Min B-W, Gu H, Wu G, Wu W. Rheological Behavior of SiO2 Ceramic Slurry in Stereolithography and Its Prediction Model Based on POA-DELM. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174270
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jie, Byung-Won Min, Hai Gu, Guoqing Wu, and Weiwei Wu. 2024. "Rheological Behavior of SiO2 Ceramic Slurry in Stereolithography and Its Prediction Model Based on POA-DELM" Materials 17, no. 17: 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174270
APA StyleZhang, J., Min, B.-W., Gu, H., Wu, G., & Wu, W. (2024). Rheological Behavior of SiO2 Ceramic Slurry in Stereolithography and Its Prediction Model Based on POA-DELM. Materials, 17(17), 4270. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174270




