Discharge Properties and Electrochemical Behaviors of Mg-Zn-xSr Magnesium Anodes for Mg–Air Batteries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
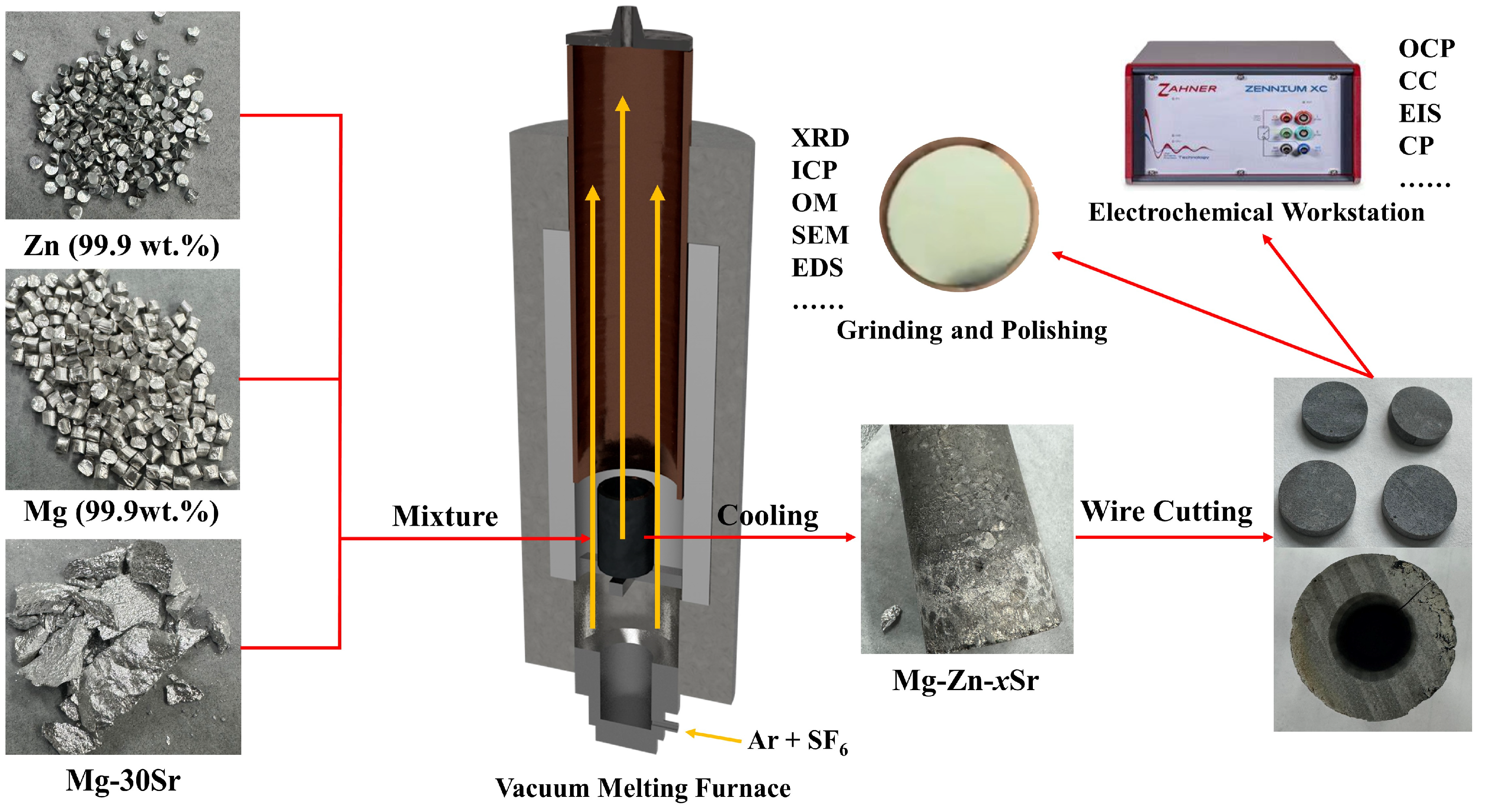
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Microscopic Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurement
2.4. Mg–Air Battery Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
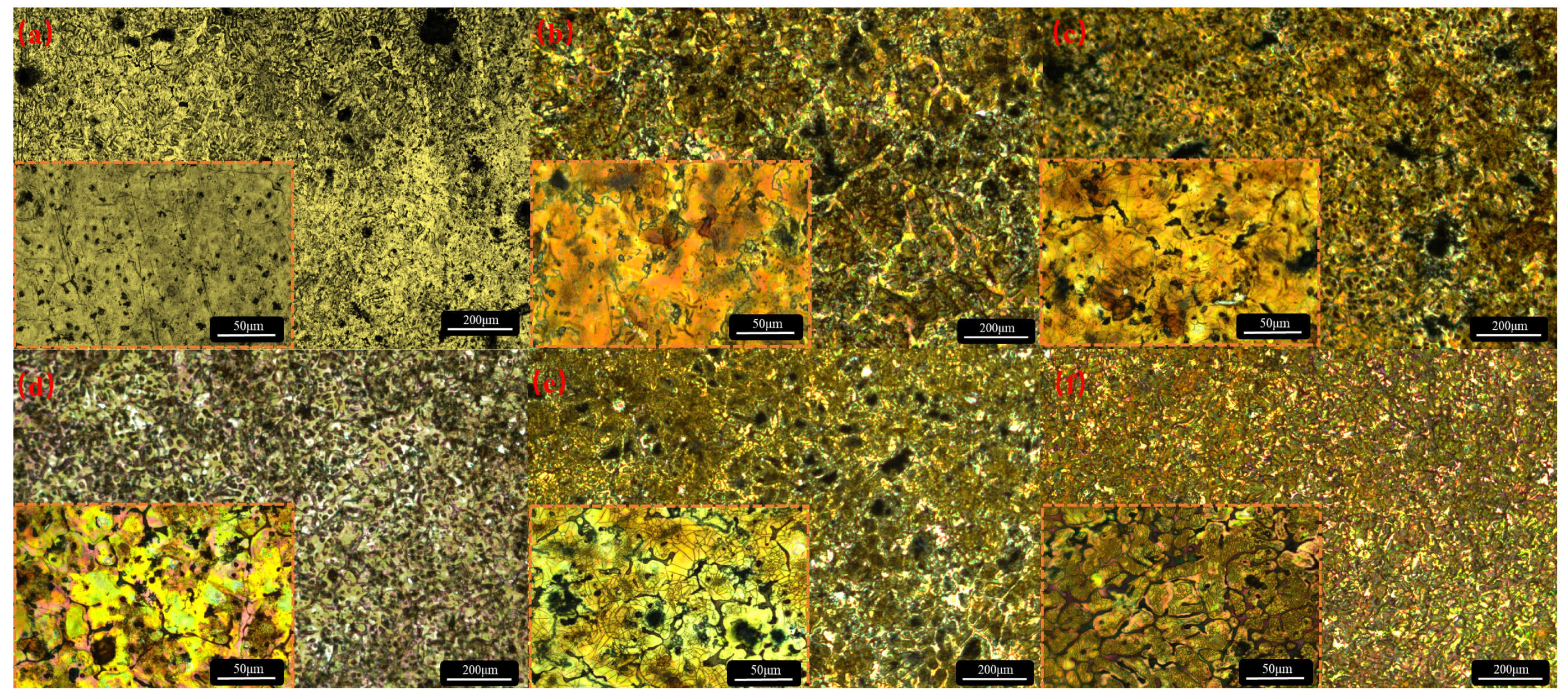
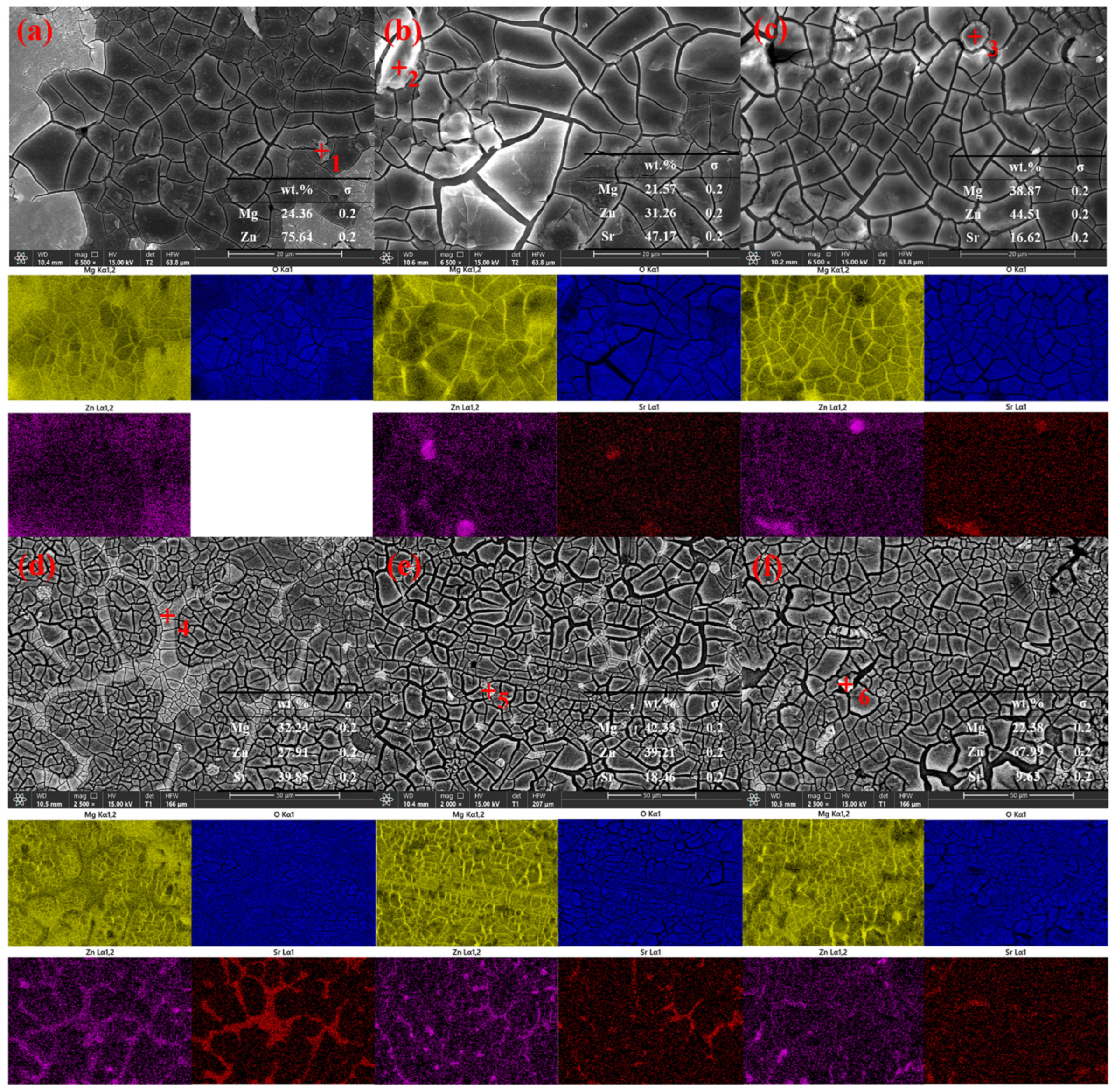
3.1. Microstructures of the Mg-Zn-xSr Alloys
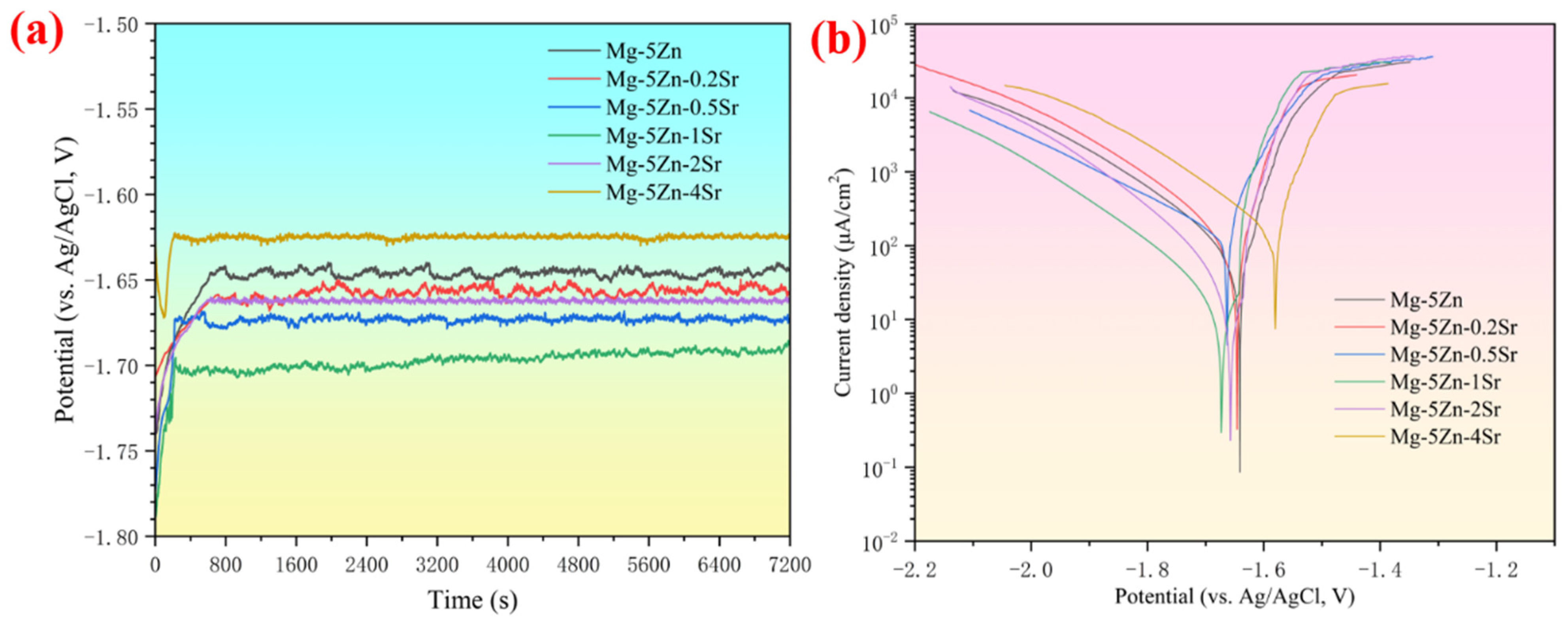
3.2. Electrochemical Analysis of Mg-Zn-xSr Alloys
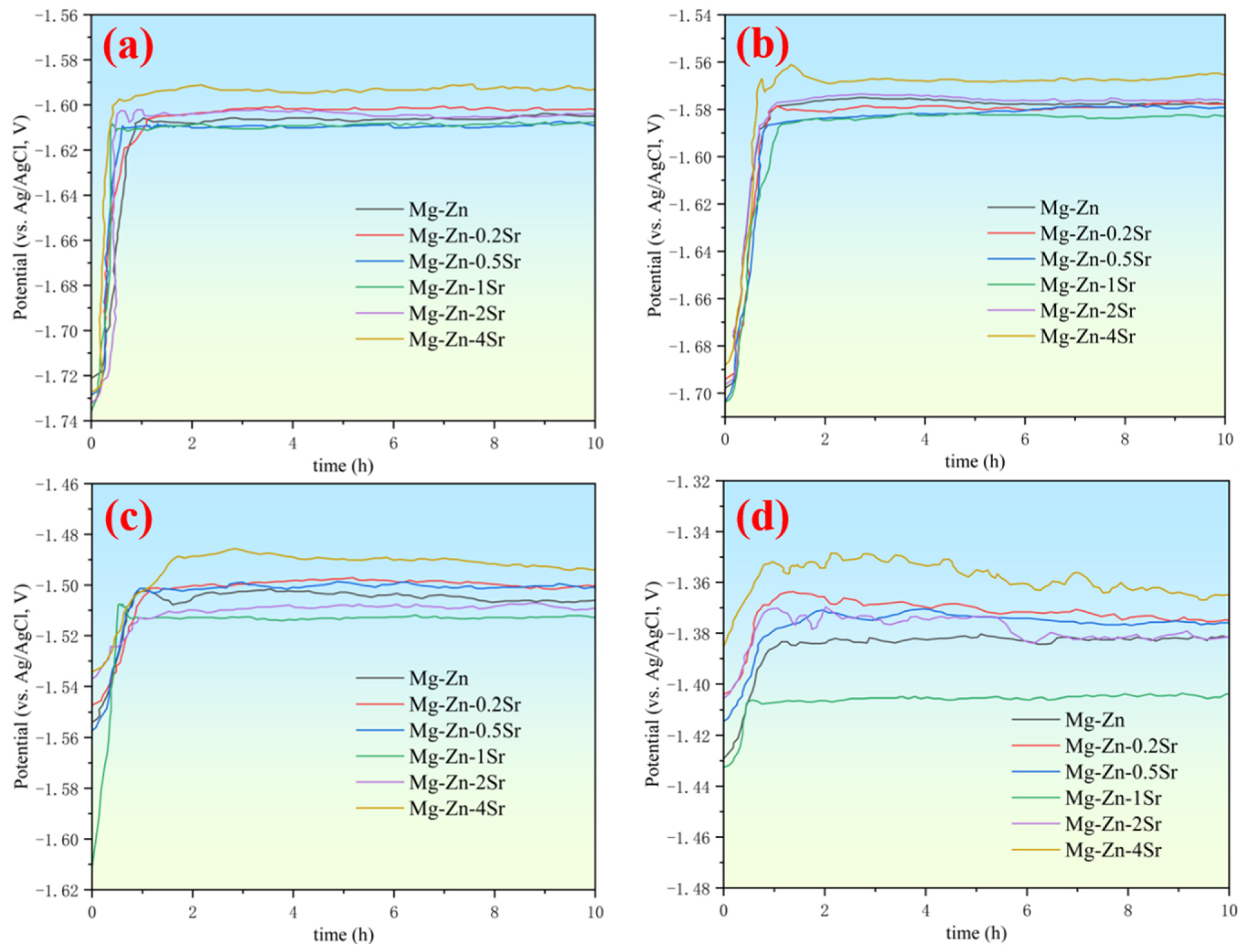
3.3. Discharge Properties of the Mg-Zn-xSr Alloys
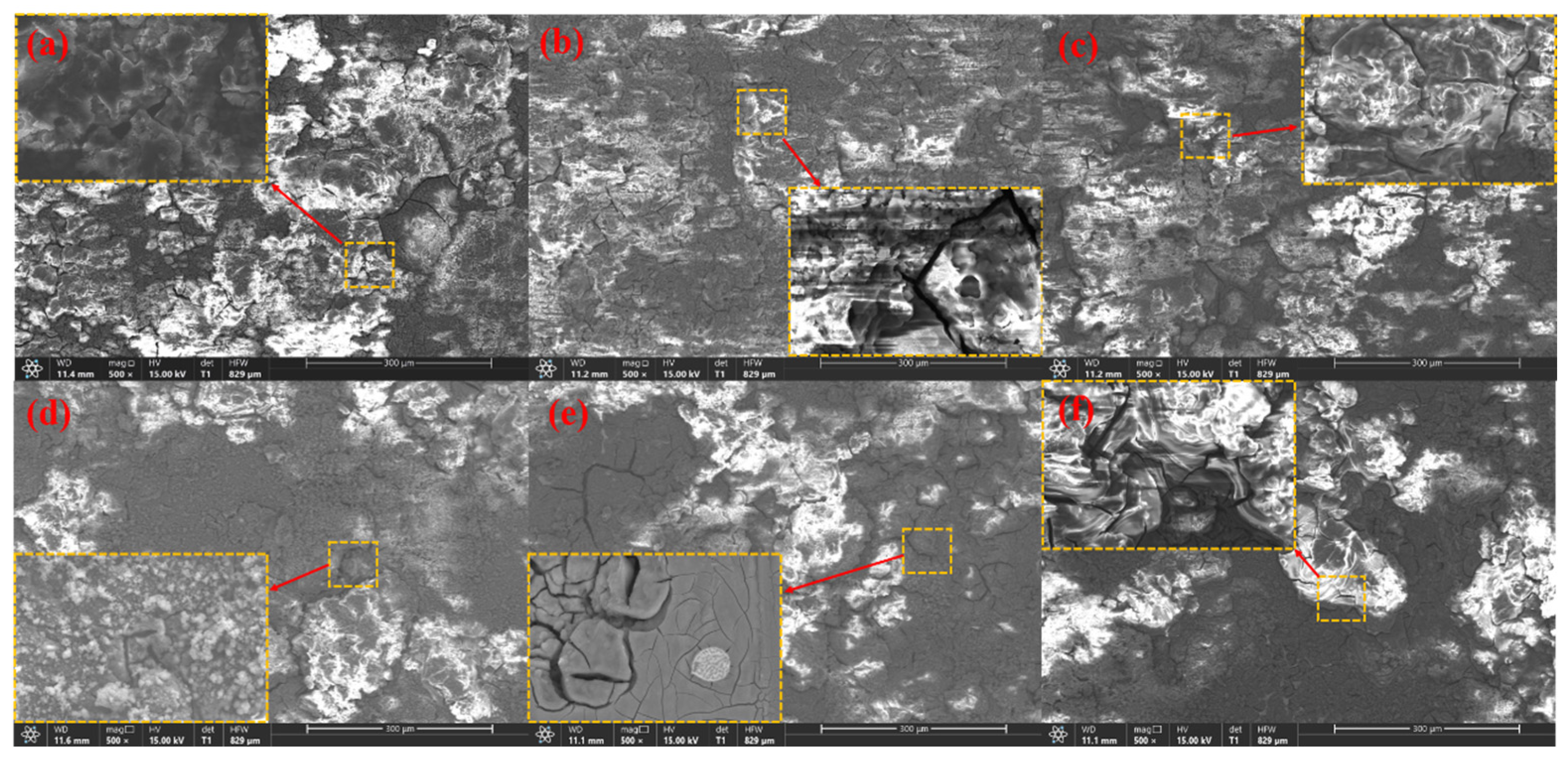
3.4. Surface Morphologies after Discharge
4. Conclusions
- The addition of Sr refined the grain size and improved the discharge performance of the Mg–Zn alloy. With the addition of Sr, the original point-like second phase gradually moved to the grain boundaries, and obvious grain boundaries formed when the Sr content reached 1 wt.%. As the Sr content continues to increase, the grain boundaries tend to crush, a large number of Sr-rich second phases begin to precipitate, the grain size becomes uneven, and the pitting points increase, resulting in the occurrence of galvanic corrosion.
- The addition of Sr can enhance the corrosion resistance of the matrix, which is due to the formation of a denser protective film and a network of grain boundary structures, hindering grain growth so that the grain size tends to be uniform. In alloys with high Sr contents, anodic dissolution is very uneven, resulting in many complex deep pits and layered protrusions, which is not conducive to the shedding of corrosion products and produces a ‘bulk effect’, which has a great influence on the electrochemical performance.
- The Mg-Zn-1Sr alloy exhibited the best discharge performance, with an open circuit potential of −1.689 V. In the Mg–air battery, the maximum energy density was 2046 mW h g−1 at a current density of 5 mA cm−2, and the maximum anode utilization rate was 61.86% at a current density of 10 mA cm−2, which is an excellent alternative material for Mg–air battery anode materials.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.S.; Sun, Y.; Gebert, F.; Chou, S.L. Current Progress on Rechargeable Magnesium-Air Battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.L.; Yao, Y. Designing modern aqueous batteries. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2023, 8, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.E.; Zhang, C.; Sawczyk, M.; Yuan, Q.H.; Chen, F.F.; Mendes, T.C.; Howlett, P.C.; Fu, C.K.; Kral, P.; Hawker, C.J.; et al. Ultrastable all-solid-state sodium metal batteries enabled by perfluoropolyether-based electrolytes. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.X.; Wang, J.J.; Song, Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Han, X.P.; Hu, W.B. In Situ Interfacial Passivation in Aqueous Electrolyte for Mg-Air Batteries with High Anode Utilization and Specific Capacity. Chemsuschem 2023, 16, e202202207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wang, X.M.; Li, H.F.; Feng, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, G.X.; Sun, S.H.; Zhang, Y.H. Approaches to construct high-performance Mg-air batteries: From mechanism to materials design. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 7924–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Dai, Q.W.; Xiang, Q.; Yang, N.; Zhang, G.P.; Shen, A.; Li, W.M. Microstructure design of advanced magnesium-air battery anodes. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 443–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Lu, Y.F.; Jia, H.X.; Ding, Z.; Wu, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Luo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.F.; et al. Magnesium-based energy materials: Progress, challenges, and perspectives. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 3896–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Chen, H.; He, E.; Wang, L.; Ye, T.T.; Lu, J.; Jiao, Y.D.; Wang, J.C.; Gao, R.; Peng, H.S.; et al. High-Energy-Density Magnesium-Air Battery Based on Dual-Layer Gel Electrolyte. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 15317–15322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, F.E.; Cheng, W.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Cui, Z.Q.; Yu, H.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, L.F.; Li, H.; Hou, H. Role of micro-Ca/In alloying in tailoring the microstructural characteristics and discharge performance of dilute Mg-Bi-Sn-based alloys as anodes for Mg-air batteries. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, T.A. Development of Aqueous Magnesium–Air Batteries: From structure to materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 988, 174262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.L.; Wei, S.H.; Chen, X.Z.; Gao, W. Magnesium alloys as anodes for neutral aqueous magnesium-air batteries. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1861–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Liu, X.; Le, Q.C.; Zhang, M.X.; Liu, M.; Atrens, A. A comprehensive review of the development of magnesium anodes for primary batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 12367–12399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; Zhang, T.A.; Xu, J.Z. Influence of temperature on the process of preparing homogenized magnesium-zinc alloy spherical powders using the relative vacuum method. Vacuum 2024, 225, 24A1503008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.L.; Chen, X.Z.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.H.; Gao, W. Hypoeutectic Mg-Zn binary alloys as anode materials for magnesium-air batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Cao, F.Y.; Ying, T.; Wang, Z.M.; Zheng, D.J.; Zhang, W.C.; Song, G.L. Achieving Ultrahigh Anodic Efficiency via Single-Phase Design of Mg-Zn Alloy Anode for Mg-Air Batteries. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 58737–58745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Xie, X.H.; Tang, H.Y.; Sun, H.; Qin, L.; Zheng, Y.F.; Gu, X.N.; Fan, Y.B. In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of Mg-2Sr-Ca and Mg-2Sr-Zn alloys. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Jiang, Z.T.; Zhu, S.J.; Guan, S.K. Effects of Sr addition on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of biodegradable Mg-Zn-Ca alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 838, 155611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.X.; Chen, J.H.; Yan, H.G.; Su, B.; Yu, Z.H.; Xia, W.J.; Gong, X.L. Effects of minor Sr addition on microstructure, mechanical and biocorrosion properties of the Mg-5Zn based alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, T.; Yari, M.; Sadreddini, S. Effect of Sr on the Microstructure and Properties of Mg-6Al Alloy. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2016, 52, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.W.; Jiang, H.T.; Zhang, Y. Discharge performance and behavior of Mg-xSr binary alloys as novel anodes for primary Mg-Air cells. J. Power Sources 2024, 602, 234269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Hudon, P.; Chartrand, P.; Jung, I.H.; Medraj, M. Experimental determination of the phase equilibria in the Mg-Zn-Sr ternary system. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7636–7646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.X.; Song, R.B.; Gao, F.; Cai, C.H.; Huang, L. Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Mg-Zn-Zr Alloys with Different Compositions. In Proceedings of the Chinese Materials Conference (CMC), Yinchuan, China, 6–12 July 2017; pp. 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Men, H.; Zhou, L. Effect of solutes on grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 123, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.C.; Wang, J.P.; Huang, Z.Q.; Zhang, T. Effects of Gd and Nd on microstructure, corrosion behavior, and electrochemical performance of Mg-Y-based anodes for magnesium air batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2022, 52, 1433–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Jia, Y.H.; Le, Q.C.; Wang, H.N.; Zhou, X.; Yu, F.X.; Atrens, A. Discharge properties and electrochemical behaviors of AZ80-La-Gd magnesium anode for Mg-air battery. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Sun, J.K.; Qiu, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Pu, Z.J.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Effects of alloying elements (Ca and Sr) on microstructure, mechanical property and in vitro corrosion behavior of biodegradable Zn-1.5Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 664, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.M.; Blawert, C.; Yang, H.; Wiese, B.; Feyerabend, F.; Bohlen, J.; Mei, D.; Deng, M.; Campos, M.S.; Scharnagl, N.; et al. Microstructure-corrosion behavior relationship of microalloyed Mg-0.5Zn alloy with the addition of Ca, Sr, Ag, In and Cu. Mater. Des. 2020, 195, 108980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xu, W.; Liu, C.B.; Cui, L.Y.; Zeng, R.C. Superior discharge performance of Mg-air battery: The influence of anodic intermetallic compounds Mg41Nd5 in Mg-4Li-3Nd-0.2Zn alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JmrT 2023, 25, 7024–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Fan, L.L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhou, M.Y.; Ren, L.B.; Yang, H.B.; Quan, G.F. Discharge performance of Mg-Y binary alloys as anodes for Mg-air batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 460, 142594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Y.; Cao, F.Y.; Ying, T.; Zheng, D.J.; Song, G.L. High-energy-capacity metal-air battery based on a magnetron-sputtered Mg-Al anode. J. Power Sources 2022, 520, 230874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.A.; Ma, M.L.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.J.; Shi, G.L.; Yuan, J.W.; Sun, Z.Q.; Zhao, G. The discharge and corrosion performances of as-cast Mg-Ga-Sn anodes for the primary magnesium-air battery. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 300, 127500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Su, D.B.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, M.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, L.F.; Pan, F.S. Micro-Alloyed Mg-Al-Mn-La Anode for Mg-Air Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 090526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Wang, L.Q.; Hoche, D.; Lamaka, S.V.; Jiang, P.L.; Snihirova, D.; Scharnagl, N.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Ca/In micro alloying as a novel strategy to simultaneously enhance power and energy density of primary Mg-air batteries from anode aspect. J. Power Sources 2020, 472, 228528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.P.; He, C.P.; Wang, J.G.; You, X.; Chen, Y.L.; Gou, Q.Y.; Yang, N.; Xie, G.; Hou, Y.Q. Inhibition of zinc dendrite growth in zinc-air batteries by alloying the anode with Ce and Yb. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 970, 172523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegani, Z.; Ebrahimi, S.A.S.; Hamawandi, B.; La Spada, L.; Batili, H.; Toprak, M.S. Targeted dielectric coating of silver nanoparticles with silica to manipulate optical properties for metasurface applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 287, 126250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Zou, Q.; Shi, Z.M.; Le, Q.C.; Zhang, M.X.; Atrens, A. The discharge performance of an as-extruded Mg-Zn-La-Ce anode for the primary Mg-air battery. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 404, 139763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.R.; Venezuela, J.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.Z.; Dargusch, M. Ultrahigh-purity Mg-Ge anodes enable a long-lasting, high energy-density Mg-air battery. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Hao, X.B.; Shangguan, F.E.; Chen, Y.H.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.F.; Cui, Z.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.C.; Wang, J.H.; et al. Electrochemical behavior and discharge performance of dilute Mg-Bibased alloy as an anode for primary Mg-air battery. Mater. Charact. 2024, 209, 113688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.C.; Huang, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Peng, C.; Pan, F.S. Performance of Mg-air Battery Based on AZ31 Mg Alloy Sheets with Different Grain Sizes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 8953–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Materials | Zn | Sr | Fe | Al | Mn | Si | Ni | Cu | Mg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-5Zn | 4.982 | - | 0.036 | 0.014 | 0.0124 | 0.0011 | 0.0002 | 0.0012 | Bal. |
| Mg-5Zn-0.2Sr | 4.836 | 0.195 | 0.012 | <0.01 | 0.0083 | 0.0121 | 0.0007 | 0.0016 | Bal. |
| Mg-5Zn-0.5Sr | 5.064 | 0.524 | 0.016 | <0.01 | 0.0034 | 0.0027 | 0.0006 | 0.0009 | Bal. |
| Mg-5Zn-1Sr | 4.921 | 1.064 | 0.021 | 0.016 | 0.0056 | 0.0020 | 0.0006 | 0.0021 | Bal. |
| Mg-5Zn-2Sr | 5.027 | 1.967 | 0.024 | 0.008 | 0.0021 | 0.0041 | 0.0009 | 0.0013 | Bal. |
| Mg-5Zn-4Sr | 5.133 | 4.126 | 0.007 | 0.021 | 0.0049 | 0.0016 | 0.0004 | 0.0008 | Bal. |
| Materials | Mg-Zn | Mg-Zn-0.2Sr | Mg-Zn-0.5Sr | Mg-Zn-1Sr | Mg-Zn-2Sr | Mg-Zn-4Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grain size (μm) | 176 ± 87 | 146 ± 88 | 97 ± 37 | 77 ± 26 | 68 ± 34 | 70 ± 54 |
| Refinement ratio | 0 | 17.04% | 44.88% | 56.25% | 61.36% | 60.23% |
| Material | Eoc (V vs. Ag/AgCl) | Ecorr (V vs. Ag/AgCl) | Icorr (μA cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-5Zn | −1.646 | −1.644 | 29.53 |
| Mg-5Zn-0.2Sr | −1.659 | −1.648 | 41.12 |
| Mg-5Zn-0.5Sr | −1.672 | −1.662 | 91.52 |
| Mg-5Zn-1Sr | −1.689 | −1.669 | 16.48 |
| Mg-5Zn-2Sr | −1.664 | −1.651 | 32.75 |
| Mg-5Zn-4Sr | −1.625 | −1.579 | 102.67 |
| Current (mA cm−2) | Mg-Zn | Mg-Zn-0.2Sr | Mg-Zn-0.5Sr | Mg-Zn-1Sr | Mg-Zn-2Sr | Mg-Zn-4Sr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge potential (vs. Ag/AgCl, V) | 0.5 | −1.605 | −1.602 | −1.608 | −1.607 | −1.605 | −1.594 |
| 2 | −1.576 | −1.577 | −1.579 | −1.582 | −1.574 | −1.565 | |
| 5 | −1.506 | −1.501 | −1.502 | −1.513 | −1.508 | −1.494 | |
| 10 | −1.382 | −1.375 | −1.377 | −1.405 | −1.381 | −1.365 | |
| Utilization efficiency (%) | 0.5 | 42.62 | 44.21 | 48.72 | 53.15 | 42.37 | 32.66 |
| 2 | 44.27 | 45.48 | 50.12 | 57.31 | 43.96 | 34.15 | |
| 5 | 48.64 | 47.83 | 51.69 | 59.46 | 48.71 | 36.85 | |
| 10 | 50.22 | 49.34 | 53.78 | 61.86 | 49.92 | 39.14 | |
| Specific capacity (mA h g−1) | 0.5 | 867 | 916 | 955 | 1007 | 849 | 671 |
| 2 | 1027 | 1133 | 1184 | 1218 | 994 | 749 | |
| 5 | 1143 | 1212 | 1263 | 1352 | 1102 | 811 | |
| 10 | 1218 | 1308 | 1348 | 1437 | 1196 | 872 | |
| Specific Energy (mW h g−1) | 0.5 | 1391 | 1467 | 1536 | 1618 | 1363 | 1069 |
| 2 | 1618 | 1787 | 1869 | 1927 | 1565 | 1172 | |
| 5 | 1721 | 1819 | 1897 | 2046 | 1662 | 1597 | |
| 10 | 1683 | 1798 | 1856 | 2019 | 1652 | 1190 |
| Mg-Zn-1Sr | AZ31 | AM10 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discharge potential (V) | −1.513 | −1.31 | −1.354 |
| Utilization efficiency (%) | 59.46 | 41.66 | 43.6 |
| Specific capacity (mA h g−1) | 1352 | 1243 | 1326 |
| Specific Energy (mW h g−1) | 2046 | 1628 | 1795 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J. Discharge Properties and Electrochemical Behaviors of Mg-Zn-xSr Magnesium Anodes for Mg–Air Batteries. Materials 2024, 17, 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174179
Liu H, Zhang T, Xu J. Discharge Properties and Electrochemical Behaviors of Mg-Zn-xSr Magnesium Anodes for Mg–Air Batteries. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174179
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongxuan, Tingan Zhang, and Jingzhong Xu. 2024. "Discharge Properties and Electrochemical Behaviors of Mg-Zn-xSr Magnesium Anodes for Mg–Air Batteries" Materials 17, no. 17: 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174179
APA StyleLiu, H., Zhang, T., & Xu, J. (2024). Discharge Properties and Electrochemical Behaviors of Mg-Zn-xSr Magnesium Anodes for Mg–Air Batteries. Materials, 17(17), 4179. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174179






