Salt Crystallization in Limestone: Materials Decay and Chemomechanical Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benavente, D.; del Cura, M.A.G.; Fort, R.; Ordónez, S. Durability Estimation of Porous Building Stones from Pore Structure and Strength. Eng. Geol. 2004, 74, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torraca, G. Porous Building Materials Materials Science for Architectural Conservation, 3rd ed.; ICCROM, Ed.; ICCROM: Rome, Italy, 2005; ISBN 92-9077-198-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Oguchi, C.T. Role of Pore Size Distribution in Salt Uptake, Damage, and Predicting Salt Susceptibility of Eight Types of Japanese Building Stones. Eng. Geol. 2010, 115, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casnedi, L.; Cappai, M.; Cincotti, A.; Delogu, F.; Pia, G. Porosity Effects on Water Vapour Permeability in Earthen Materials: Experimental Evidence and Modelling Description. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 27, 100987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, M.; Pia, G. Thermal Conductivity of Porous Building Materials: An Exploration of New Challenges in Fractal Modeling Solutions. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2023, 8, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabat, Á.; Cano, M.; Tomás, R. Effect of Water Saturation on Strength and Deformability of Building Calcarenite Stones: Correlations with Their Physical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, R.; Borgatta, L.; Wendler, E. Investigation of the Deterioration Mechanisms Induced by Moisture and Soluble Salts in the Necropolis of Porta Nocera, Pompeii (Italy). Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striani, R.; Cappai, M.; Casnedi, L.; Esposito Corcione, C.; Pia, G. Coating’s Influence on Wind Erosion of Porous Stones Used in the Cultural Heritage of Southern Italy: Surface Characterisation and Resistance. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, M.; Casnedi, L.; Carcangiu, G.; Delogu, F.; Pozzi-Escot, D.; Pacheco, G.; Pia, G.; Meloni, P. Weathering of Earth-Painted Surfaces: Environmental Monitoring and Artificial Aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappai, M.; Delogu, F.; Pozzi-Escot, D.; Pacheco Neyra, G.; Meloni, P.; Pia, G. Degradation Phenomena of Templo Pintado Painted Plasters. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viles, H.A. Can Stone Decay Be Chaotic? Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2005, 390, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, Z.; Huang, X.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Z. Study on Deterioration Law and Mechanism of Gray Brick Due to Salt Crystallization. Materials 2022, 15, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappai, M.; Sanna, U.; Pia, G. A Fuzzy Model for Studying Kinetic Decay Phenomena in Genna Maria Nuraghe: Material Properties, Environmental Data, Accelerated Ageing, and Model Calculations. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rives, V.; García-Talegón, J. Decay and Conservation of Building Stones on Cultural Heritage Monuments. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 514–516, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardell, C.; Benavente, D.; Rodríguez-Gordillo, J. Weathering of Limestone Building Material by Mixed Sulfate Solutions. Characterization of Stone Microstructure, Reaction Products and Decay Forms. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinario, L.; Oguchi, C.T. Underground Salt Weathering of Heritage Stone: Lithological and Environmental Constraints on the Formation of Sulfate Efflorescences and Crusts. J. Cult. Herit. 2021, 49, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godts, S.; Orr, S.A.; Steiger, M.; Stahlbuhk, A.; De Kock, T.; Desarnaud, J.; De Clercq, H.; Cnudde, V. Salt Mixtures in Stone Weathering. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Hamilton, A.; McNall, M.; Whitaker, K.; Scherer, G.W. The Chemomechanics of Crystallization during Rewetting of Limestone Impregnated with Sodium Sulfate. J. Mater. Res. 2011, 26, 1472–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa Marzal, R.M.; Scherer, G.W. Crystallization of Sodium Sulfate Salts in Limestone. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Marzal, R.M.; Scherer, G.W. Mechanisms of Damage by Salt. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2010, 331, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.A.G.; De la Torre, A.G. Sulfoaluminate Cement. In Eco-Efficient Concrete; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Jalali, S., Labrincha, J., John, V.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 488–522. ISBN 9780857094247. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Arce, P.; Doehne, E. Kinetics of Sodium Sulfate Efflorescence as Observed by Humidity Cycling with ESEM. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Heritage, Weathering and Conservation (HWC 2006), Madrid, Spain, 21–24 June 2006; Volume 1, pp. 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Scrivano, S.; Gaggero, L. An Experimental Investigation into the Salt-Weathering Susceptibility of Building Limestones. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2020, 53, 5329–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, G.W. Stress from Crystallization of Salt. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-X.; Chen, W.-W.; Kuang, J.; Du, W.-F. Effect of Salts on Earthen Materials Deterioration after Humidity Cycling. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena da Fonseca, B.; Ferreira Pinto, A.P.; Rucha, M.; Alves, M.M.; Montemor, M.F. Damaging Effects of Salt Crystallization on a Porous Limestone after Consolidation Treatments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 374, 130967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Doehne, E. Salt Weathering: Influence of Evaporation Rate, Supersaturation and Crystallization Pattern. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Navarro, C.; Doehne, E.; Sebastian, E. How Does Sodium Sulfate Crystallize? Implications for the Decay and Testing of Building Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Caruso, F.; Sanchez, A.M.A.; Scherer, G.W. Chemo-Mechanics of Salt Damage in Stone. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, N.; Flatt, R.J.; Scherer, G.W. Crystallization Damage by Sodium Sulfate. J. Cult. Herit. 2003, 4, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradise, T.R. Petra Revisited: An Examination of Sandstone Weathering Research in Petra, Jordan. Spec. Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 2005, 390, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzner, B.; Heinrichs, K.; Bouchardiere, D. La Weathering Damage on Pharaonic Sandstone Monuments in Luxor-Egypt. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.E.; Carlos, A.; Beber, D.M. The Conservation of Wall Paintings. Proceedings of the a Symposium Organized by the Courtauld Institute of Art and the Getty Conservation Institute, London, UK, 13–16 July 1987; Cather, S., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; ISBN 089236162X. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji, S.; Jensen, A.D. Efflorescence and Breakdown of Building Materials; Nordic Concrete Federation: Stockholm, Sweden, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Zoghlami, K.; Martín-Martín, J.D.; Gómez-Gras, D.; Navarro, A.; Parcerisa, D.; Rosell, J.R. The Building Stone of the Roman City of Dougga (Tunisia): Provenance, Petrophysical Characterisation and Durability. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2017, 349, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassar, J. The Use of Limestone in a Historic Context—The Experience of Malta. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2010, 331, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegesmund, S.; Grimm, W.D.; Dürrast, H.; Ruedrich, J. Limestones in Germany Used as Building Stones: An Overview. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2010, 331, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, J.P.; Regueiro, M. Carbonate Rocks in the Mediterranean Region—From Classical to Innovative Uses of Building Stone. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2010, 331, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belfiore, C.M.; Calabrò, C.; Ruffolo, S.A.; Ricca, M.; Török; Pezzino, A.; La Russa, M.F. The Susceptibility to Degradation of Stone Materials Used in the Built Heritage of the Ortygia Island (Syracuse, Italy): A Laboratory Study. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2021, 146, 104877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomo, A.E.; Minervino Amodio, A.; Prosser, G.; Sileo, M.; Rizzo, G. Evaluation of Soft Limestone Degradation in the Sassi UNESCO Site (Matera, Southern Italy): Loss of Material Measurement and Classification. J. Cult. Herit. 2020, 42, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oggiano, G.; Funedda, A.; Carmignani, L.; Pasci, S. The Sardinia-Corsica Microplate and Its Role in the Northern Apennine Geodynamics: New Insights from the Tertiary Intraplate Strike-Slip Tectonics of Sardinia. Boll. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2009, 128, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L. Maud: A Rietveld Analysis Program Designed for the Internet and Experiment Integration. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Found. Crystallogr. 2000, 56, s54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, L. Quantitative Rietveld Analysis in Batch Mode with Maud. IUCr 2005, 32, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Steiger, M. Crystal Growth in Porous Materials - I: The Crystallization Pressure of Large Crystals. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 282, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, M.; Asmussen, S. Crystallization of Sodium Sulfate Phases in Porous Materials: The Phase Diagram Na2SO4-H2O and the Generation of Stress. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 4291–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
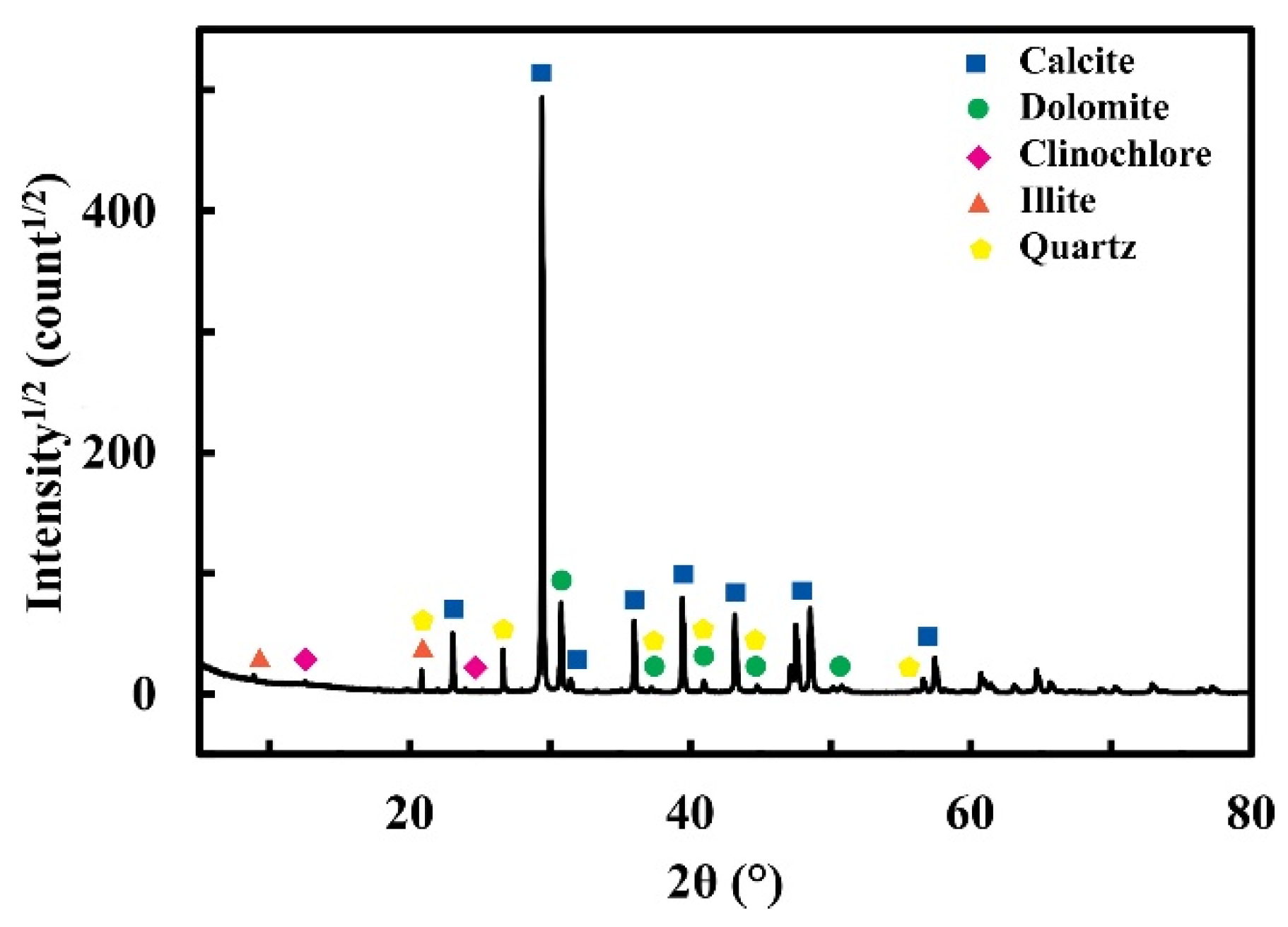
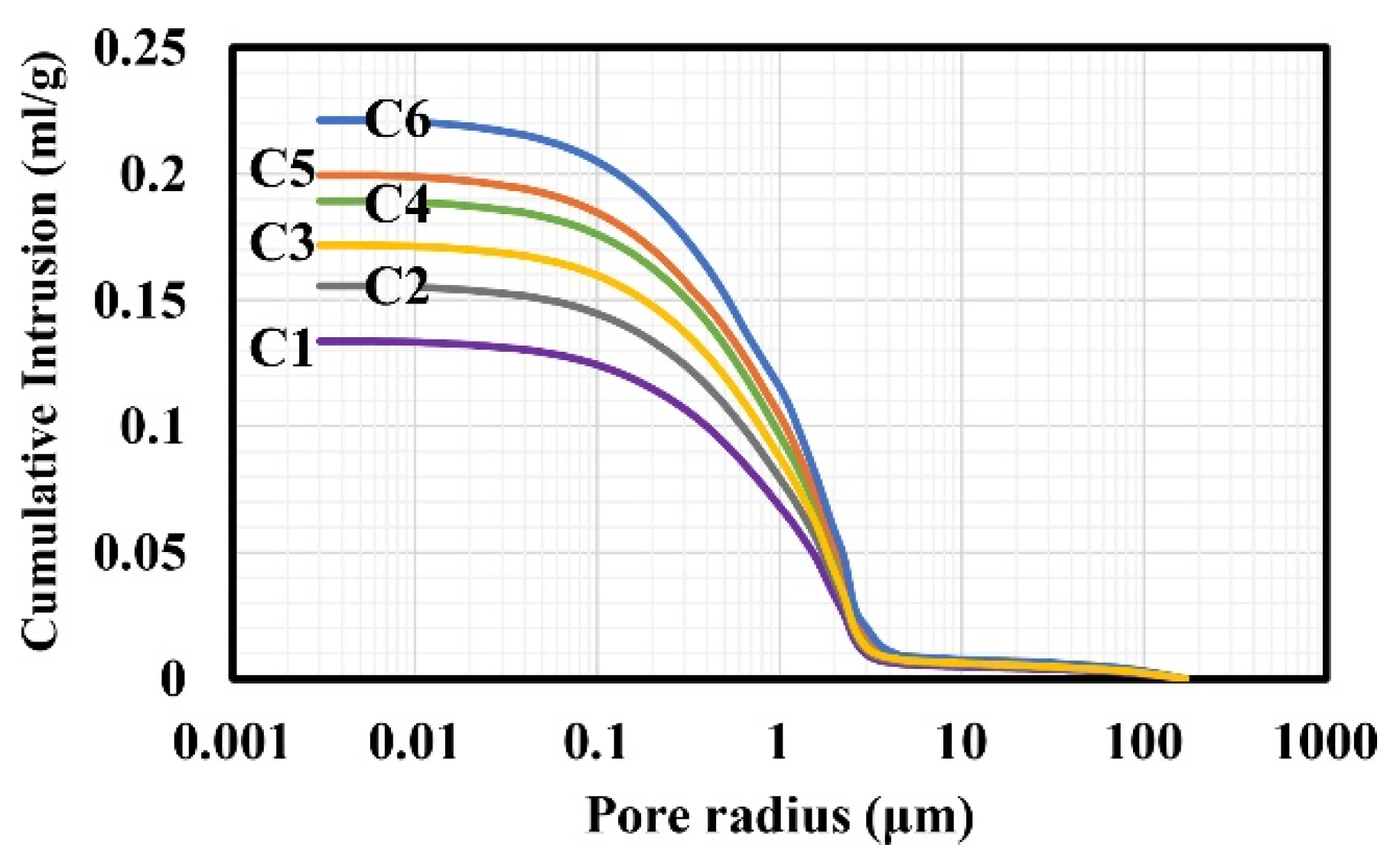
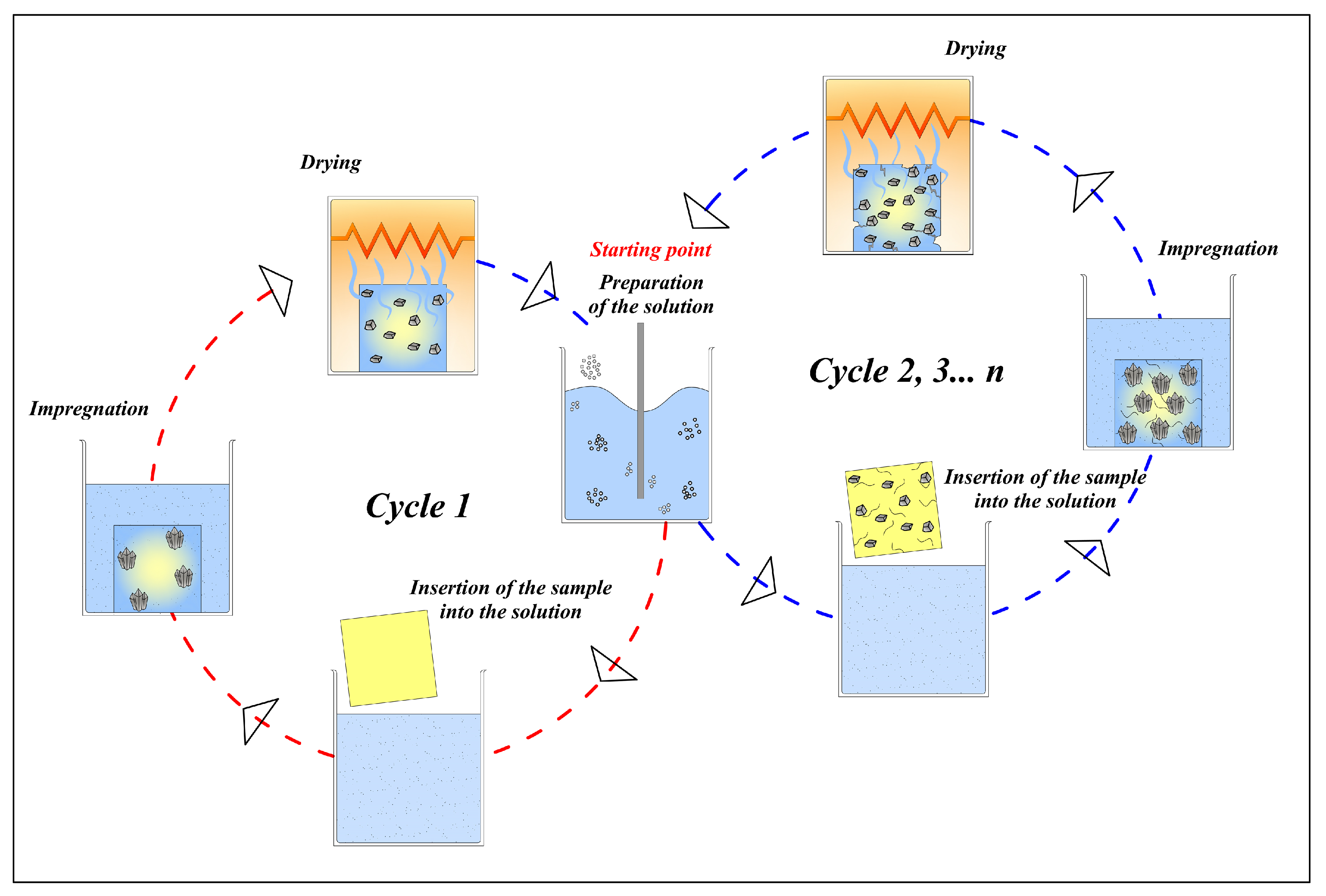
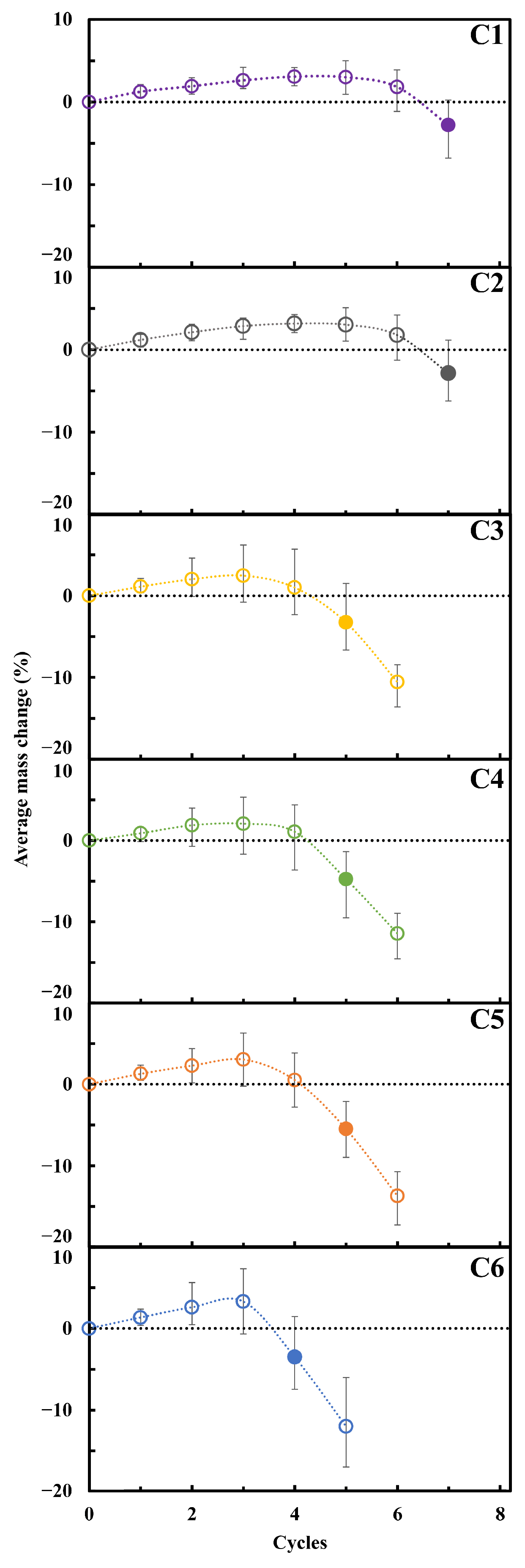
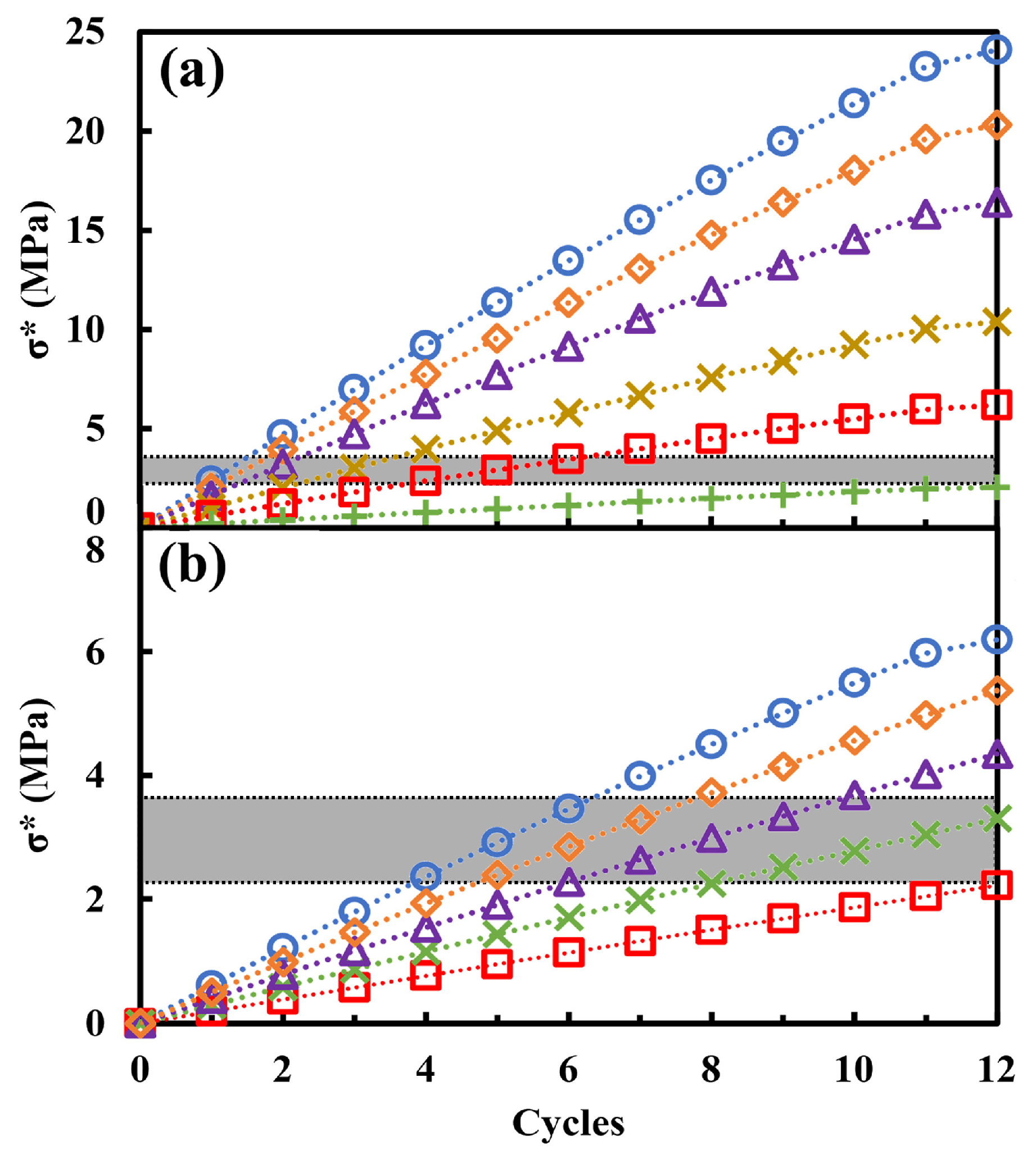
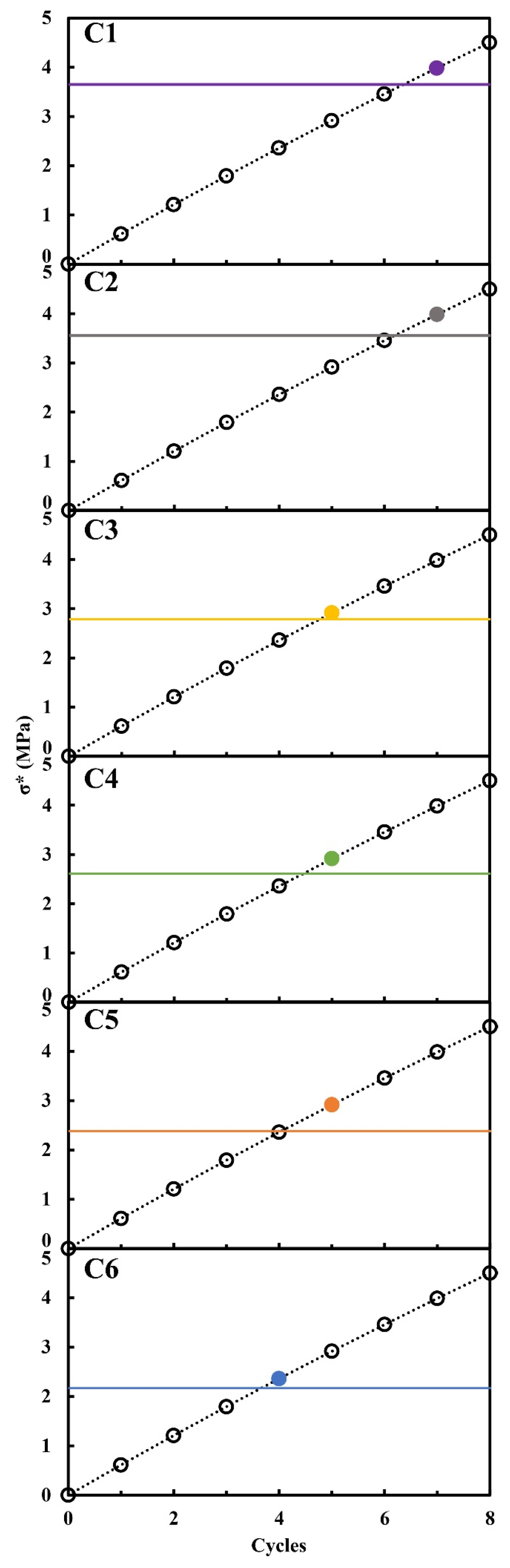
| Series | ε (%) | εr >1 µm (%) | ε1 < r < 0.05 µm (%) | εr < 0.05 µm (%) | APR (µm) | SSA (m2/g) | δ (g/cm3) | σT (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 26.00 ± 2.00 | 12.08 ± 0.80 | 12.55 ± 0.45 | 1.37 ± 0.75 | 0.263 ± 0.62 | 1.14 ± 0.96 | 1.96 ± 2.00 | 4.0 ± 0.2 |
| C2 | 30.26 ± 2.50 | 15.09 ± 0.73 | 13.95 ± 0.61 | 1.22 ± 1.16 | 0.275 ± 1.15 | 1.38 ± 1.08 | 1.95 ± 2.50 | 3.8 ± 0.3 |
| C3 | 33.41 ± 2.30 | 16.65 ± 0.92 | 15.41 ± 0.75 | 1.35 ± 0.63 | 0.322 ± 0.53 | 1.39 ± 0.68 | 1.83 ± 2.30 | 3.2 ± 0.2 |
| C4 | 36.81 ± 1.85 | 18.35 ± 0.83 | 16.97 ± 0.56 | 1.49 ± 0.46 | 0.321 ± 0.82 | 1.42 ± 0.94 | 1.76 ± 1.85 | 3.0 ± 0.4 |
| C5 | 39.10 ± 2.20 | 19.96 ± 0.59 | 17.45 ± 0.43 | 1.69 ± 1.18 | 0.185 ± 0.79 | 1.86 ± 1.12 | 1.71 ± 2.20 | 2.8 ± 0.3 |
| C6 | 43.38 ± 2.00 | 22.15 ± 0.74 | 19.36 ± 0.26 | 1.87 ± 1.00 | 0.213 ± 1.03 | 1.91 ± 0.94 | 1.58 ± 2.00 | 2.6 ± 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cappai, M.; Casti, M.; Pia, G. Salt Crystallization in Limestone: Materials Decay and Chemomechanical Approach. Materials 2024, 17, 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163986
Cappai M, Casti M, Pia G. Salt Crystallization in Limestone: Materials Decay and Chemomechanical Approach. Materials. 2024; 17(16):3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163986
Chicago/Turabian StyleCappai, Marta, Marta Casti, and Giorgio Pia. 2024. "Salt Crystallization in Limestone: Materials Decay and Chemomechanical Approach" Materials 17, no. 16: 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163986
APA StyleCappai, M., Casti, M., & Pia, G. (2024). Salt Crystallization in Limestone: Materials Decay and Chemomechanical Approach. Materials, 17(16), 3986. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163986







