Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Electrodes for High-Performance Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nafion/EMImBF4 Membrane
2.3. Fabrication of Actuators
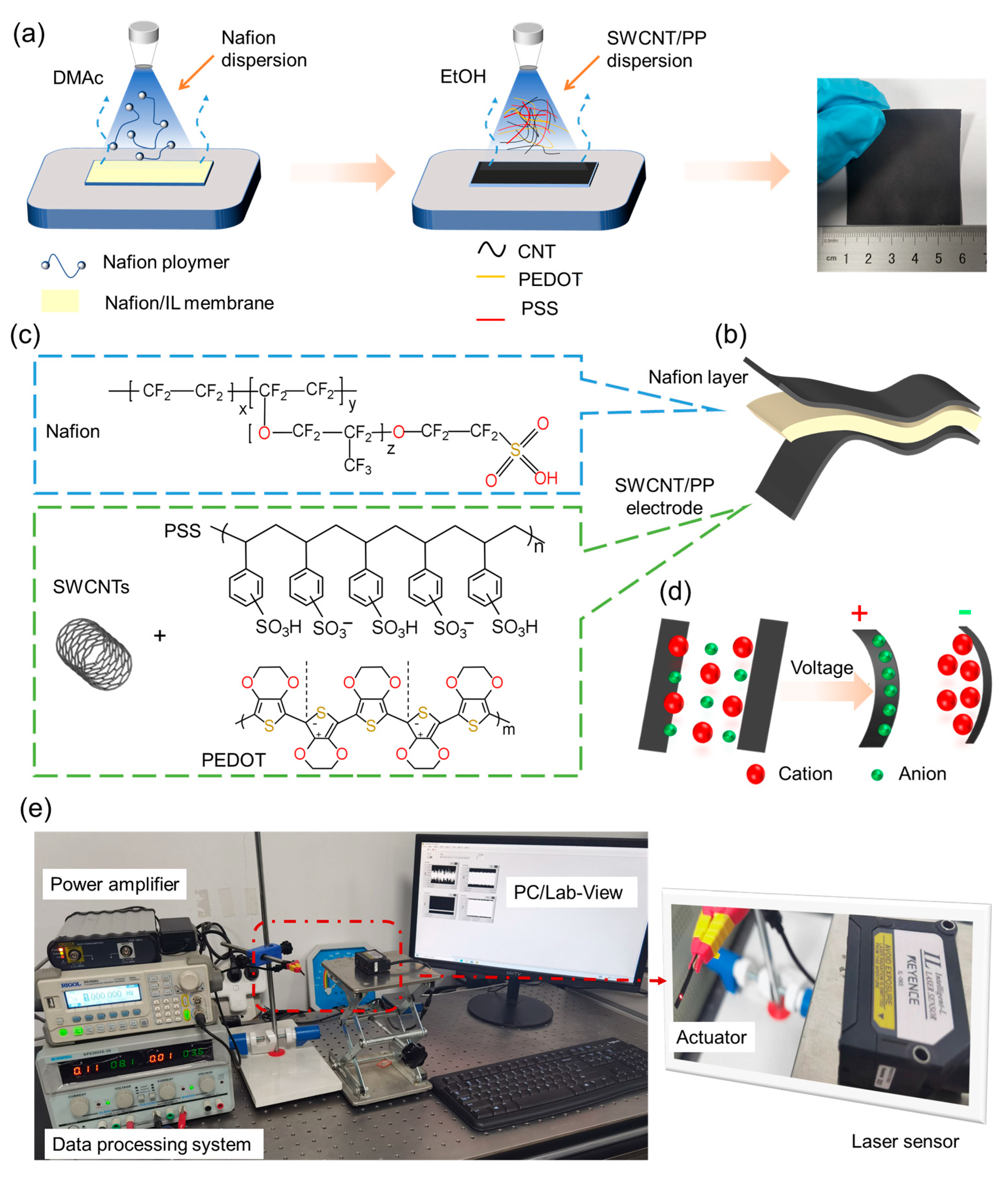
- (a)
- Preparation of spraying solutions: An amount of 0.08 g of SWCNTs was dispersed into 16 mL of EtOH by sonicating in an ice-water bath for 45 min to prepare SWCNT/EtOH dispersion. An amount of 0.55 g of PP solution (1.1 wt% in water) was dissolved into 12 mL of EtOH and stirred for 2 h to obtain the PP/EtOH solution. Then, 6 mL of SWCNT/EtOH dispersion and 6 mL of PP/EtOH solution were mixed and stirred for 2 h to prepare the SWCNT/PP/EtOH solution.
- (b)
- Preparation of actuators: First, a 2 cm × 1.5 cm sized Nafion/EMImBF4 membrane was fixed on a heating platform. Second, 0.1 mL of the casting solution was sprayed onto the membrane surface using a spray gun. The platform was heated to 120 °C to completely remove DMAc and other solvents. After that, 12 mL of the SWCNTs/PP/EtOH solution was put into the spray gun and sprayed onto the membrane surface. The membrane was then heated to 80 °C to remove EtOH and to form a conductive surface, which works as an electrode while the actuator is working. After that, the above steps were repeated to prepare the electrode on the other side of the Nafion/EMImBF4 membrane. Finally, actuators with SWCNT/PP electrodes on both sides of the Nafion/EMImBF4 membrane were successfully obtained, which are named SWCNT/PP actuators. To be compared, actuators with PP electrodes were also prepared by utilizing the same method and named PP actuators. The actuators were cut into 20 mm × 2 mm × (95 ± 5) μm (length × width × thickness) sized specimens for characterization.
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Observation
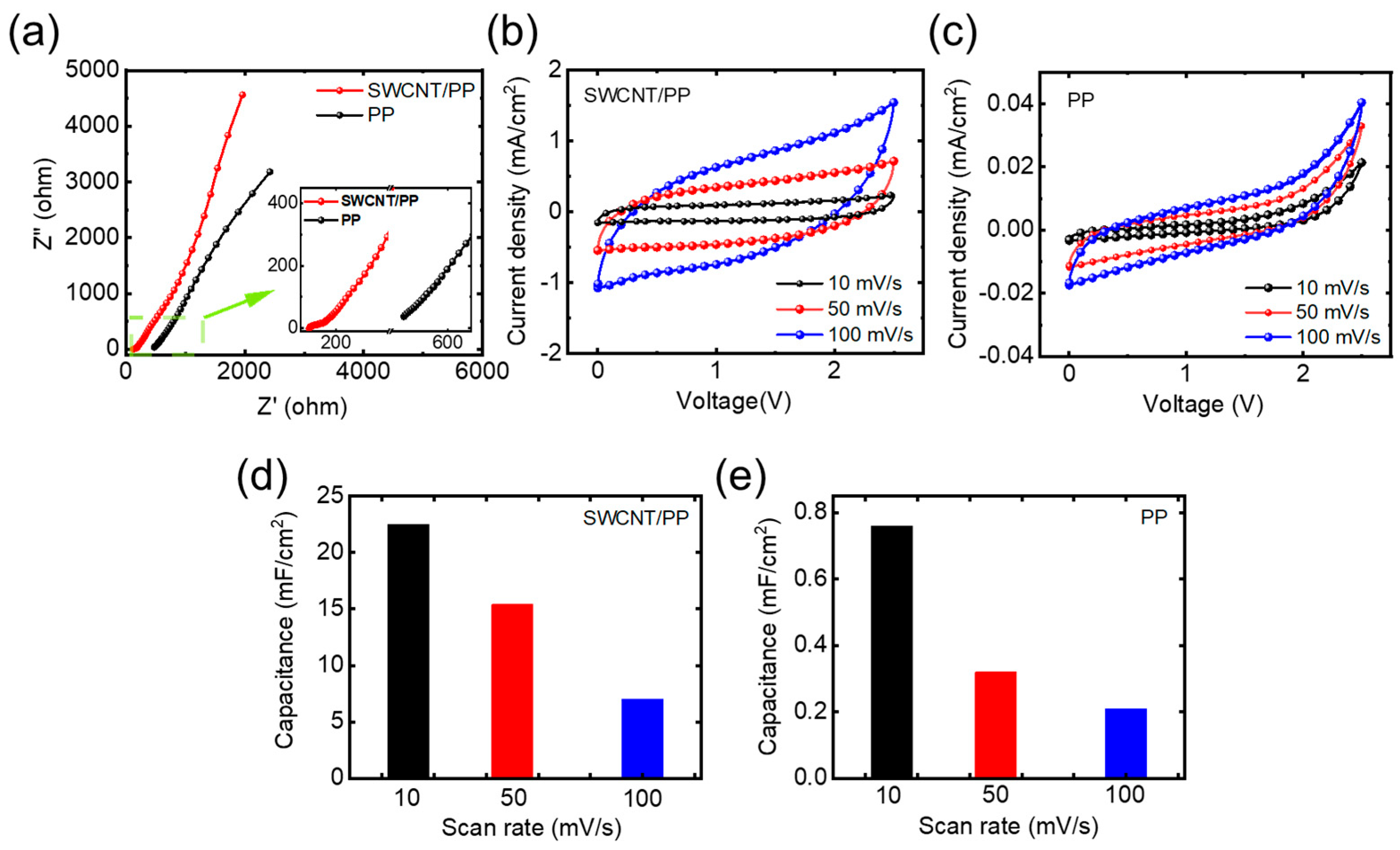
3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations
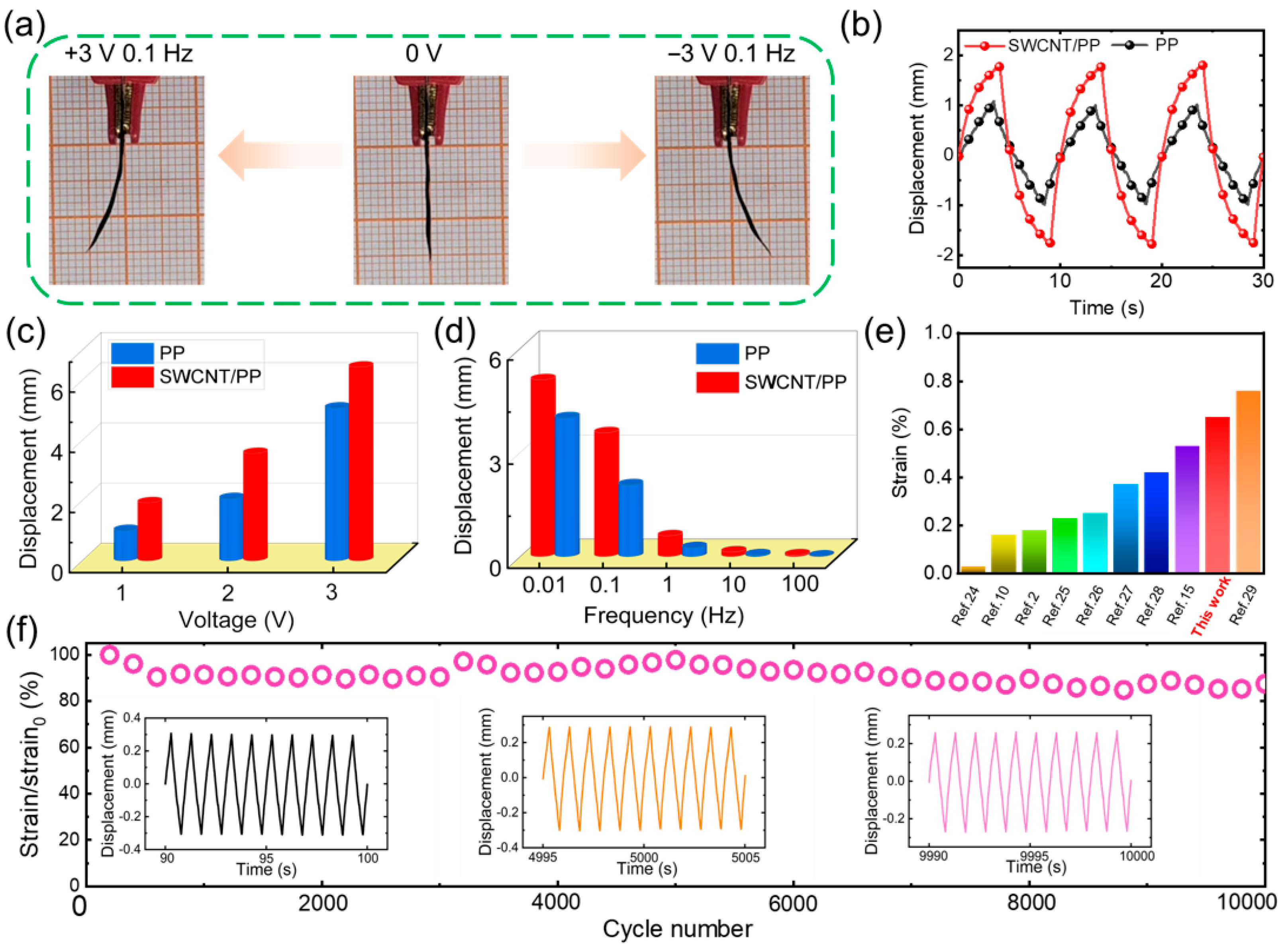
3.3. Electromechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ma, S.; Liang, Y.; Ren, L.; Ren, L. Low-voltage driven ionic polymer-metal composite actuators: Structures, materials, and applications. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 202206135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Ghosh, T.K. Bioinspired Structures for Soft Actuators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 202101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G.; Ru, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, C.F.; Li, L.; Zhu, D. Ionic Flexible Sensors: Mechanisms, Materials, Structures, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Yeatman, E.M. A comparative review of artificial muscles for microsystem applications. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y. Fabrication and characterization of a novel smart-polymer actuator with nanodispersed CNT/Pd composite interfacial electrodes. Polymers 2022, 14, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Bian, C.; Luo, B.; Li, D. A moisture and electric coupling stimulated ionic polymer-metal composite actuator with controllable deformation behavior. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 02LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Asaka, K.; Kiyohara, K.; Sugino, T.; Takeuchi, I.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T. High performance fully plastic actuator based on ionic-liquid-based bucky gel. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5555–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Chen, W. Carbon Nanotube and Graphene-based Bioinspired Electrochemical Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Li, H.; Ma, T.; Yang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Jiang, P. A review of soft actuator motion: Actuation, design, manufacturing and applications. Actuators 2022, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, D.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Yan, B.; Wu, Z.; Park, S. Highly electro-responsive ionic soft actuator based on graphene nanoplatelets-mediated functional carboxylated cellulose nanofibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 231, 109845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Asaka, K.; Sugino, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Takeuchi, I.; Terasawa, N.; Futaba, D.N.; Hata, K.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T. Highly Conductive sheets from millimeter-long single-walled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquids: Application to fast-moving, low-voltage electromechanical actuators operable in air. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 1582–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmre, V.; Lust, E.; Jänes, A.; Koel, M.; Peikolainen, A.-L.; Torop, J.; Johanson, U.; Aabloo, A. Electroactive polymer actuators with carbon aerogel electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi-Najafabadi, A.; Yasuda, S.; Kobashi, K.; Yamada, T.; Futaba, D.N.; Hatori, H.; Yumura, M.; Iijima, S.; Hata, K. Extracting the full potential of single-walled carbon nanotubes as durable supercapacitor electrodes operable at 4 v with high power and energy density. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, E235–E241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ma, W.; Song, L.; Niu, Z.; Cai, L.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, W.; et al. Superfast-response and ultrahigh-power-density electromechanical actuators based on hierarchal carbon nanotube electrodes and chitosan. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 4636–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Bian, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Horiuchi, T.; Sugino, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Asaka, K. Controllable and durable ionic electroactive polymer actuator based on nanoporous carbon nanotube film electrode. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 085032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassian, R.; Kim, J.; Nguyen, V.H.; Kotal, M.; Oh, I. Functionally Antagonistic Hybrid Electrode with Hollow Tubular Graphene Mesh and Nitrogen-Doped Crumpled Graphene for High-Performance Ionic Soft Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Minamikawa, H.; Nakazumi, T.; Hara, Y. Actuation properties of paper actuators fabricated using PEDOT/PSS electrode films. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.-W.P.; Cottinet, P.-J.; Tsai, S.-Y.; Foster, B.; Liang, R.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C. Improved performance of carbon nanotube buckypaper and ionic-liquid-in-Nafion actuators for rapid response and high durability in the open air. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 171–172, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, N.; Asaka, K. High performance polymer actuators based on single-walled carbon nanotube gel using ionic liquid with quaternary ammonium or phosphonium cations and with electrochemical window of 6V. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Niu, L.; Dong, S.; Ivaska, A. Electrochemical functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes in large quantities at a room-temperature ionic liquid supported three-dimensional network electrode. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4797–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.H.; Cui, C.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Barisci, J.N.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Mazzoldi, A.; De Rossi, D.; Rinzler, A.G.; et al. Carbon nanotube actuators. Science 1999, 284, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, J.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, D. Preparation and characterization of water-soluble carbon nanotube reinforced Nafion membranes and so-based ionic polymer metal composite actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, D. Tunable actuation behavior of ionic polymer metal composite utilizing carboxylated carbon nanotube-doped Nafion matrix. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 3090–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Sridhar, V.; Oh, I.-K. Electro-active graphene–Nafion actuators. Carbon 2011, 49, 1279–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Ru, J.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, B.; Chen, H. A three-electrode structured ionic polymer carbon-composite actuator with improved electromechanical performance. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 085017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, H.; Wang, F. High-performance hot-pressed ionic soft actuator based on ultrathin self-standing PEDOT:PSS electrodes and Nafion membrane. MRS Commun. 2023, 13, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bae, S.; Kotal, M.; Stalbaum, T.; Kim, K.J.; Oh, I. Soft but Powerful Artificial Muscles Based on 3D Graphene–CNT–Ni Heteronanostructures. Small 2017, 13, 1701314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, B.; Bian, C.; Wang, Y. Printing single-walled carbon nanotube/Nafion composites by direct writing techniques. Mater. Des. 2018, 155, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Yoo, Y.-T. Preparation and performance of IPMC actuators with electrospun Nafion®–MWNT composite electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Outer Diameter | Purity | Length | Surface Area | Electric Conductivity | Ig/Id |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 nm | >95 wt% | 5–30 µm | > 490 m2/g | >100 S/cm | >20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, H.; Hu, G.; Lu, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ru, J. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Electrodes for High-Performance Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuator. Materials 2024, 17, 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102469
Tao H, Hu G, Lu S, Li B, Zhang Y, Ru J. Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Electrodes for High-Performance Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuator. Materials. 2024; 17(10):2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102469
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Haoxiang, Guangyao Hu, Shun Lu, Bing Li, Yongxing Zhang, and Jie Ru. 2024. "Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Electrodes for High-Performance Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuator" Materials 17, no. 10: 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102469
APA StyleTao, H., Hu, G., Lu, S., Li, B., Zhang, Y., & Ru, J. (2024). Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced PEDOT: PSS Hybrid Electrodes for High-Performance Ionic Electroactive Polymer Actuator. Materials, 17(10), 2469. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102469








