Abstract
In femtosecond laser fabrication, the laser-pulse train shows great promise in improving processing efficiency, quality, and precision. This research investigates the influence of pulse number, pulse interval, and pulse energy ratio on the lateral and longitudinal ultrafast melting process using an experiment and the molecular dynamics coupling two-temperature model (MD-TTM model), which incorporates temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters. The comparison of experimental and simulation results under single and double pulses proves the reliability of the MD-TTM model and indicates that as the pulse number increases, the melting threshold at the edge region of the laser spot decreases, resulting in a larger diameter of the melting region in the 2D lateral melting results. Using the same model, the lateral melting results of five pulses are simulated. Moreover, the longitudinal melting results are also predicted, and an increasing pulse number leads to a greater early-stage melting depth in the melting process. In the case of double femtosecond laser pulses, the pulse interval and pulse energy ratio also affect the early-stage melting depth, with the best enhancement observed with a 2 ps interval and a 3:7 energy ratio. However, pulse number, pulse energy ratio, and pulse interval do not affect the final melting depth with the same total energies. The findings mean that the phenomena of melting region can be flexibly manipulated through the laser-pulse train, which is expected to be applied to improve the structural precision and boundary quality.
1. Introduction
Femtosecond lasers play an important role in micro- and nano-fabrication because of the advantages of high energy intensity and small collateral damage [1,2,3,4,5]. The interaction between femtosecond lasers and metallic materials can be divided into two stages [1,6,7]. Firstly, upon femtosecond laser irradiation, the electron sub-system absorbs laser energy as a result of a sharp electron temperature increment. The lattice sub-system remains at a low temperature, resulting in thermal nonequilibrium between the electron sub-system and the lattice sub-system [8,9,10,11]. Secondly, this nonequilibrium drives electron-phonon coupling energy transport. The whole relaxation process between the two sub-systems lasts several picoseconds and is accompanied by the combined effect of electron heat conduction and electron-phonon coupling [8,9]. Eventually, the increment of lattice temperature triggers photo-mechanical and photo-thermal effects, leading to an abrupt phase change [10,12,13,14].
By conducting further research on such nonequilibrium and nonlinear processes, it is possible to exert control over the corresponding phase-change phenomena to meet diverse processing requirements, these include reducing the heat-affected zone (HAZ) [1,2,7,12,15], minimizing the generation of microcracks [12,15,16] and recasts [15,17], facilitating nanoparticle sintering [5,15,18,19,20], and achieving highly localized material removal [12,21,22].
In recent decades, a novel melting phenomenon known as homogeneous melting has been discovered. Distinguished from the conventional melting process (heterogeneous melting [23]), when subjected to femtosecond laser irradiation, the metal undergoes rapid heating and reaches a highly superheated state. Subsequently, the liquid nucleation process takes place homogeneously, leading to complete melting within a few picoseconds [23,24].
Its mechanism has prompted extensive theoretical, experimental, and simulation investigations [4,8,24,25,26,27]. The transition from the solid phase to the liquid phase of Al was observed via ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) by Siwick et al. [25]. Rethfeld et al. proposed the theory of ultrafast thermal melting in laser-excited solids, specifically referring to the phenomenon of homogeneous nucleation [24]. The formation mechanism of the two melting phenomena was further analyzed by Ivanov and Zhigilei using the molecular dynamics coupling two-temperature model (MD-TTM model) [8]. The transition from heterogeneous to homogeneous melting at higher energy densities is visualized through UED by Mo et al. [4]. The influence of electron heat conduction and electron-phonon coupling on laser-metal interaction was elucidated by Ivanov et al., and the pulse duration and the laser fluence could affect the above processes [10]. In general, under femtosecond laser irradiation, the metals are heated to a sufficiently high temperature where heterogeneous nucleation is suppressed and homogeneous nucleation predominates. Consequently, the system undergoes catastrophic homogeneous nucleation and completes the phase change within a few picoseconds.
The aforementioned research demonstrates that the control of ultrafast melting processes encounters significant challenges attributed to the imperative requirement for achieving electron dynamic regulation. Fortunately, the electron dynamics control (EDC), by the shaping femtosecond laser-pulse train, can realize the effective control of femtosecond laser fabrication at the electron level [1]. Significant advancements have been made by precisely designing laser-pulse trains to modify thermophysical properties and subsequently alter the phase-change process [1,28]. Li et al. discovered that the pulse train can alter energy transport and associated phase change, enabling control over the size distribution of metal nanoparticles [15]. Povarnitsyn et al. unveiled two mechanisms for suppressing ablation irradiated by a double-pulses laser (DP) [29]. Förster and Lewis conducted a comprehensive analysis of the mechanisms active during the different stages of the ablation process induced by a DP [13]. Englert et al. controlled the ionization processes in high-band-gap materials via temporal asymmetric pulse shapes on intrinsic time and intensity scales [30]. The incubation phenomenon during laser ablation with bursts of femtosecond pulses was reported by Gsudiuso et al. [31]. Rong et al. found the advantages of femtosecond laser-pulse train processing in reducing thermal-mechanical damage compared to single-pulse (SP) processing [17].
Despite the wide range of potential applications for laser-pulse trains, current research on the spatiotemporal shaping femtosecond pulses primarily focuses on the ablation phenomenon. There is limited direct research on controlling the melting process with spatiotemporal-shaping femtosecond pulses, particularly with pulse numbers exceeding two. However, the melting process directly determines the quality, efficiency, and precision of the processing. Roy et al. investigated the influence of Cu nanoparticle size and morphology on sintering temperature and sintering quality. It was found that the sintered product of Cu nanoparticles exhibited outstanding mechanical strength and high electrical conductivity [32]. By employing ultrashort laser pulses in assisted powder-bed fusion, Ullsperger et al. discovered a more uniform melting pool shape, along with refined primary Si and eutectic structure during the powder-bed fusion process [33]. Furthermore, advancements in first-principles research have shown that the material properties affected by electron temperature in the MD-TTM model are not suitable to be expressed by classical constant or linear equations [17,34,35].
In this work, firstly, the laser pulse is divided 1:1 by the combination of beam splitter and mirrors. The response of Al to the time interval and energy at energies slightly below the ablation threshold is investigated by adjusting the time interval and total energy of the double pulses. Secondly, the thermophysical properties of Al obtained by different methods are compared and applied to the MD-TTM model. After the model validation, the significance of temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters in laser-material interactions during the ultrafast melting process is elucidated through comparative analysis. Subsequently, a simplified method, similar to that used in [22,36], was employed to combine the 1D results to obtain 2D results for both the SP and DP with a 2 ps interval, thereby replicating the observed diameter increase in the melting region in the experimental results and analyzing relevant phenomena. Next, based on the verification of SP and DP simulation, the 2D melting region in Al was predicted under five pulses (FP) by employing the same mode. Furthermore, we also simulated the early-stage melting depth of Al when irradiated by a DP. The influence of different pulse numbers, pulse intervals, and pulse energy ratios on the longitudinal melting (propagation direction) phenomena of Al, including differences in melting depth and melting velocity, was investigated, along with their potential mechanisms.
2. Experimental and Modeling
2.1. Experimental Setup
Figure 1 illustrates the schematic diagram of the experimental setup. The femtosecond laser source is a Ti: sapphire chirped pulse-amplification (CPA) system (Spectra-Physics Spitfire Ace, Spitfire Pro-35F1KXP, California, CA, USA), operating at a repetition frequency of , with a full width at half maximum (FWHM) of and a center wavelength of . The laser pulse is split into two equal-energy pulses using a beam splitter (Thorlabs, Inc., Newton, NJ, USA) in a 1:1 split ratio. These two pulses are combined to form a DP train through the application of mirrors and a beam splitter. The time interval between the double pulses is precisely controlled by a one-dimensional translation stage (the minimum linear displacement is , Zolix, Inc., Beijing, China). Subsequently, the pulses are focused onto the sample by a plano-convex lens (, Thorlabs, Inc., Newton, NJ, USA). The sample Al (, one side polished, orient <100>) is positioned on a hexapod six-axis positioning system (M-840.5DG, Physik Instrumente, Inc., Auburn, MA, USA). The microstructures are observed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Thermo Scientific Apreo 2C, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
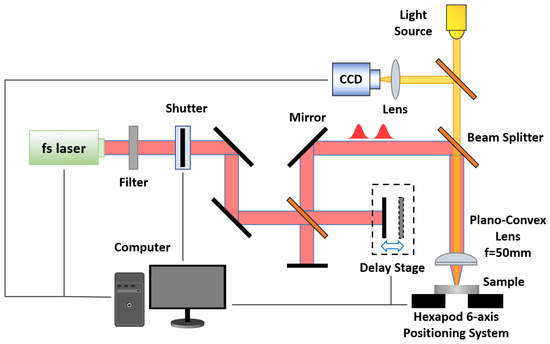
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the experimental setup of double-pulse laser processing.
To ensure that the experimental results are reliable, we obtained multiple data by keeping the shutter open and moving the sample along a straight line. The average value of these data was then taken as the experimental result. In addition, we imported SEM images into a MATLAB program and uniformly adjusted their contrast ratio. Through this program, we can obtain the SEM images after processing, which have a clear light-dark dividing line. The dividing line is used as the boundary of the melting region. Finally, the length of the major axis and the minor axis is obtained by fitting the elliptic equation according to the dividing line.
2.2. The MD-TTM Model
The Al melting process under femtosecond laser-pulse train irradiation is simulated by the MD-TTM model [34,35]. For the atomistic scale, the MD is used to provide a unique atomistic view of the laser-induced phase-change process.
where is the mass of atom with velocity , is the resultant force acting on atom , which is calculated from the EAM potential [37,38], and is the friction term, which directly relates to the electron-phonon coupling factor , where is the atom number density, is the Boltzmann constant, and is the random force from the Langevin dynamics.
where is the timestep and is a random vector. The sum of , and is in direct proportion to the energy transfer of electron-phonon coupling.
For the continuum scale, the TTM model is used to describe laser energy input, thermal diffusion, and temperature evolution. To establish the coupling between the MD model and the TTM model, the lattice sub-system in the classical TTM model is substituted with the aforementioned MD model.
where is the volumetric heat capacity, is the thermal conductivity, and is temperature. The subscripts and , represent electrons and lattices, respectively. is the electron-phonon coupling factor. In this work, the thermophysical parameters () of Al are determined by and , which are discussed in Section 3.2. The last term in the right hand of Equation (4a) is the laser source , which is a Gaussian beam that decays along the laser irradiation direction.
where is the pulse number of the current calculation, is the total pulse number, is the optical reflectivity (0.88 [37]), is the proportion of the th pulse to the total energy, is the total absorbed laser fluence, is the time of the current calculation, is the pulse duration, is the pulse interval between the ith and (i − 1)th sub-pulses, is the optical penetration depth, which equals the reciprocal of the optical absorption coefficient, is the ballistic transportation length (), and is the depth.
It should be emphasized that the above MD-TTM model is only applicable to thermal equilibrium conditions, and the solution of non-thermal equilibrium processes needs to use the hyperbolic two-temperature model (HTTM) proposed by Sobolev [39]. Nevertheless, the duration of the laser () in this work is much longer than the relaxation time of aluminum [40], in this case, the HTTM degenerates into the TTM [39]. Hence, it is justifiable to employ MD-TTM for analyzing the ultrafast melting phenomenon.
2.3. Simulation Details
2.3.1. Simplified Method and Computational Domain Settings
In the case of ablation simulations, the relatively large [41] lateral size (laser spot radius direction, the top surface region consists of million atoms) can present more abundant phenomena, such as surface melting, rapid resolidification, and generation of voids and a nanocrystalline layer in the sub-surface region [41,42], while smaller sizes cannot. It is well known that atomistic dimensions are in the length scale of Angstrom () [25]. Therefore, simulations to match the actual manufactured size in micrometers would require tens to millions of atoms, which requires huge computational resources. Therefore, an appropriate simplification method is a premise used to achieve the research goal of this work. Fortunately, this problem can be solved by the simplified method proposed by Kumar et al. [36] and applied to the MD-TTM model by Zhou et al. [22].
Figure 2 reveals the whole process by using this method to simplify the 3D manufacturing problem into a 1D computational domain. First of all, the laser energy and melting region have a full-scale axisymmetric feature. A 2D computational domain is directly simplified from the 3D computational domain. Next, the 2D computational domain is divided into a series of 1D computational domains. The position of the 1D computational domain in the 2D computational domain determines the total energy it can obtain. It must be noted that this division will indeed affect the calculations of lateral and longitudinal heat transfer, but at the nanoscale subdivision setting, the temperature difference between the 1D computational domain and the 2D computational domain is less than in Zhou et al.’s work [22].
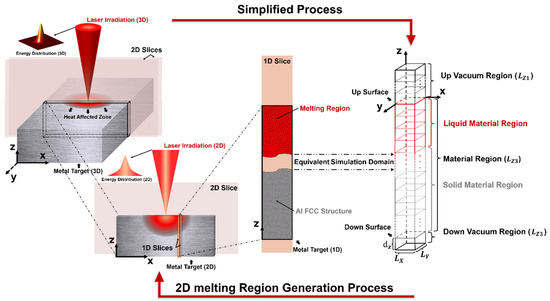
Figure 2.
Simplified dimensional schematic diagram of the Al melting process under laser irradiation and the design of 1D equivalent computational domain.
For the 1D computational domain, a similar method was used in our previous work [43]. The laser irradiated on the Al surface along the negative -direction. Two vacuum regions [27,43] were added to the up surface and down surface of the material region to ensure that atoms did not escape from the computational domain due to material expansion. The whole system was divided into grids with independent and . The temperature of the material was initially set to room temperature: . The size of the differential grid was . Furthermore, according to the findings in [11,44,45], it has been observed that when the film thickness exceeds , any further increase in thickness has a negligible impact on the surface laser-material interaction. This finding enabled us to accurately replicate the experimental results obtained from bulk samples () through the simulation of . The lattice sub-system was created using the classical MD method and equilibrated at for [43] in terms of the canonical ensemble (NVT) to complete the initialization and relaxation, which are seen in Figure 2. The grids are colored in red and grey to represent the liquid region and solid region, respectively. The colors also agree with the colors in the atomistic snapshots in Section 3. For the convenience of readers, all the parameters in this work are listed in the Nomenclature.
2.3.2. Computational Flowchart
Benefiting from previous works [34,35,46,47,48], the classical MD-TTM model has already been integrated into the Large-scale Atomic/Molecular Massively Parallel Simulator (LAMMPS) [49]. On this basis, two new modules were developed and integrated into the LAMMPS program. The details are illustrated in Figure 3. At the beginning of each loop, the program first runs the developed Module 1 named Physical Parameters Calculation. The kinetic energy of atoms was collected to calculate the of each grid through Equation (6) [49]
where is the total kinetic energy of atoms in the grid. Secondly, the new thermophysical parameters of each grid are updated by solving Equations (8)–(10). Eventually, all the thermophysical and optical parameters of Al involved in the MD-TTM model were updated and input into Module 2 (the MD-TTM model) to complete the whole loop. It should be emphasized that the electron temperature and lattice temperature shown in this work are obtained by simulation.
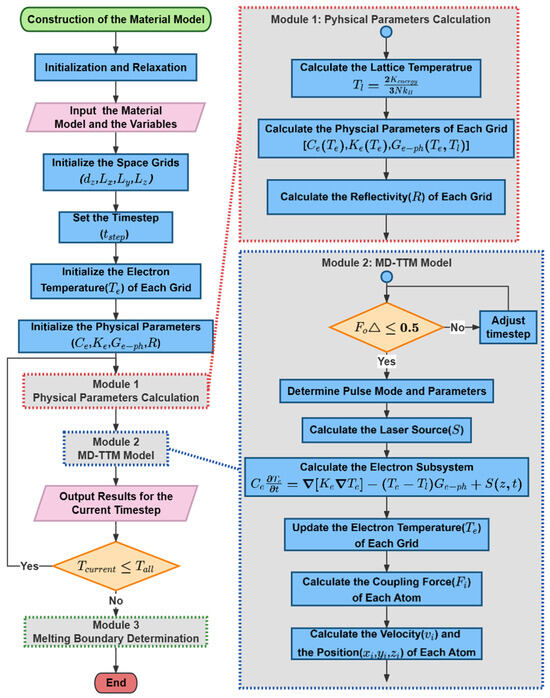
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the MD-TTM model incorporating dynamic thermophysical parameters.
Moreover, because the finite difference method (FDM) was utilized to solve the TTM model, it is necessary to meet the stability criterion.
where is the Fourier number, is the thermal diffusivity, and and , , represent timestep and spacesteps, respectively. If the conditions are not satisfied, the program will report an error.
2.3.3. Laser-Pulse Train
As shown in Figure 4, The spatiotemporal energy profiles throughout the overall femtosecond laser irradiation process are influenced by various factors, such as the pulse number, pulse interval, and energy ratio. When the simulation reaches the “Determine Pulse Mode and Parameters” process of “Module 2” in Figure 3, it will read the laser parameters and generate the desired spatiotemporal shaping laser-pulse train.
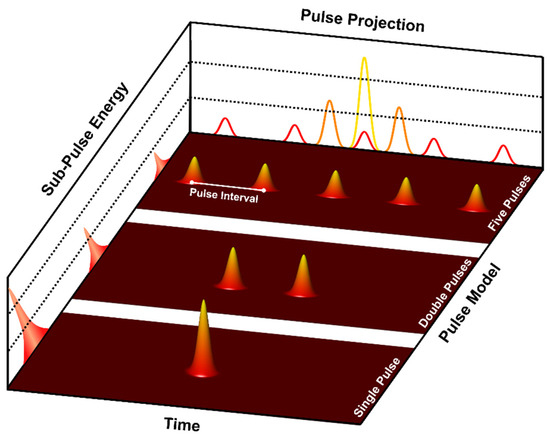
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of the laser-pulse train.
2.3.4. Judgement of Energy Conservation
In addition to the stability criterion, to meet the conservation of energy is essential. A series of additional 1D calculations with different aluminum film thicknesses and pulse settings are implemented. Table 1 shows the calculated results of . It should be noted that to facilitate the comparison, all temperatures are the overall average temperature at . As seen from Table 1, it can be found that the temperature difference of multiple pulse modes is within for the cases with the same energy and thickness. Even for the results with smaller , the error is within 2.5%. This is also shown in the standard deviation results. Therefore, the influence of the above errors on the simulation can be ignored.

Table 1.
The lattice temperature obtained by the simulation results with different thicknesses and pulse numbers.
3. Results and Discussion
Firstly, the response of Al to the time intervals and energies strictly below the ablation threshold is explored by adjusting the time interval and the total energy of the double pulses (Section 3.1). Secondly, multiple sets of thermophysical parameters obtained from different experiments and simulations are collected and compared. The impact of the laser-pulse number on the early stage of the melting process (first ) is conclusively demonstrated by the MD-TTM model incorporating temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters (Section 3.2). Thirdly, the 1D simulation results are assembled to obtain 2D results for an SP and a DP with a interval by a simplified method proposed by Kumar et al., enabling an analysis of the lateral differences in the melting phenomenon [36]. Additionally, the same method is employed to predict the results for FP (Section 3.3). Finally, the investigation explores the impact of pulse interval and pulse energy ratio on the longitudinal melting phenomenon in Al by the same model (Section 3.4).
3.1. Experimental Results of Al Response to Pulse Interval and Energy
The sample Al is irradiated by an SP and DPs with , , and intervals, respectively, and varying energies. In the case of the DP, the initial laser-pulse energy is divided into two pulses of equal energy.
Figure 5 illustrates SEM images of Al irradiated by SPs with varying energies. The size of the melting region increases as the pulse energy increases.
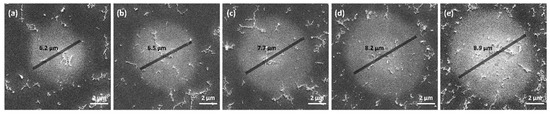
Figure 5.
SEM images of melting region for SPs at fluences (a) , (b) , (c) , (d) , and (e) .
Figure 6 shows the SEM images of the melting region of four settings of an SP and DPs with , , and intervals at a total fluence of . In terms of the size of the melting region, both DPs with and intervals demonstrate larger melting compared to the SP (SP: , the DP with a interval: , the DP with a interval: ,). Interestingly, the melting region diameter is the smallest for the DP with a interval (). This phenomenon may be attributed to electron excitation, as reported in [50,51,52]. Although these factors may result in reduced energy absorption and subsequently a smaller melting diameter, SEM results for the SP and DPs with and intervals confirm that multiple pulses enhance melting diameter, even when employing the same or lower laser energy. In addition, when comparing Figure 6c,d, the melting region is smaller for a DP with a interval than for a DP with a interval.
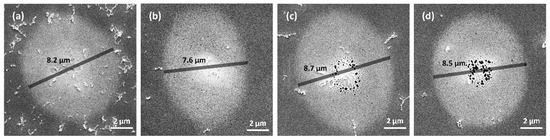
Figure 6.
SEM images of melting region for (a) an SP and DPs with pulse intervals of (b) , (c) , and (d) , at a total fluence of .
In terms of the morphology of the melting region, the melting regions for an SP and a DP with a interval exhibit high surface smoothness. Voids appear near the center of the melting region for DPs with and intervals. Specifically, the DP with a interval shows more concentrated voids. In addition, in multiple pulse experiments, the areas of melting exhibit an elliptical shape, with the long axis corresponding to the polarization direction. Moreover, as the number of pulses increases, the long axis becomes relatively longer compared to the short axis. This phenomenon is widely seen in other multi-pulse studies [50,53], and to avoid the influence of polarization, we choose the short axis as the melting diameter.
In conclusion, the interval of the DPs affects the diameters and the surface morphology of the melting region. The diameter of the melting region generated by a DP with a interval is the biggest with the largest void region. This will be discussed in detail in Section 3.3 and Section 3.4.
3.2. Comparison of the Temperature-Dependent Thermophysical Parameters and the Effect of Pulse Number on Simulation Results
Figure 7 presents the thermophysical parameters of Al obtained through various methods. The solid, dashed, and dotted lines represent the results obtained from the full-run quantum treatment (Jiang et al. [54]), classical simplified expression (Ideal Electron Gas and Simplified Expression [55]), empirical formula (Chen et al. [46]), and ab initio QM (Zhigilei et al. [56], Rong et al. [17], and Bevillon et al. [57]), respectively. It is evident that is influenced by in Figure 7a. As increases, exhibits initial linear growth and then tends to approach a constant value. Figure 7b illustrates the different . In contrast to the previous parameter, is affected by the lattice temperature, which decreases as the lattice temperature increases. Regarding , shown in Figure 7c, it is worth noting that the precise determination of remains an unresolved issue. Based on the current findings, it can be confirmed that the of Al exhibits an increasing trend with rising electron temperature.
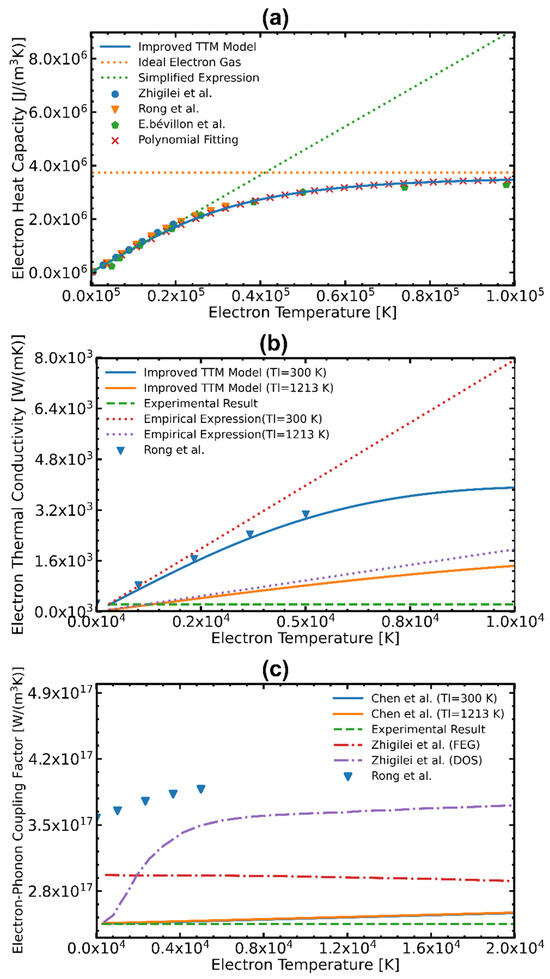
Figure 7.
Temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters of Al. Comparison of (a) electron heat capacity , (b) electron thermal conductivity , and (c) the electron-phonon coupling factor obtained by different calculation methods [17,46,54,55,56,57].
In summary, in this study, the temperature-dependent is determined through the polynomial fitting. By taking into account with the empirical formula, the temperature-dependent and are derived. The detailed expression is shown below:
- 1.
- For
- 2.
- For ke
- 3.
- For Ge–ph
Figure 8 shows the melting process of the first from the surface of Al after irradiation with different laser-pulse settings, with a total fluence of . Figure 8a–c represents the classical thermophysical parameters group, while Figure 8d–f corresponds to the temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters groups. During the melting process in both groups, Al’s surface undergoes a relatively rapid melting stage. Subsequently, from to , the melting region expands at a velocity lower than the speed of sound, while a clear melting region boundary appears. This two-stage process exhibits similarities to the phenomenon observed in our previous work [43]. The appearance of obvious melting is delayed with the increase in the number of pulses. This delay is attributed to the longer thermal time of Al and the lower energy carried by individual laser pulses in the multi-pulse mode. Taking FP as an example, the total time required for the laser energy to be absorbed equals the sum of the total pulse intervals () and the time for a Gaussian beam () to be fully absorbed, as shown in Figure 4—that is, . Interestingly, the more obvious differences are evident in the visible liquid-phase region boundaries at (black dot lines). In the case of the left group in Figure 8a–c, the impact of the change in pulse number is considered negligible. The variation in pulse numbers has minimal impact on the position of the melting region boundaries and the distribution of the liquidus point. However, for the temperature-dependent thermophysical parameter group in Figure 8d–f, more energy is transferred to a deeper position. Moreover, after the appearance of the boundary of the liquid phase region, there are still a large number of nucleation points below it, with liquid atoms comprising over of the total number of atoms in some grids.
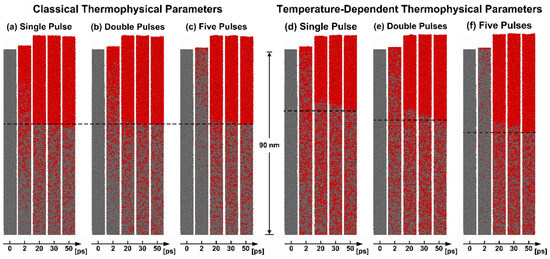
Figure 8.
Atomic snapshots of the melting process on the Al surface region of , the left is the classical thermophysical parameters group for (a) SP, (b) DP, and (c) FP, while the right is the temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters group for (d) SP, (e) DP, and (f) FP. The black dotted line represents the boundaries between the solid and liquid phases.
The spatial distribution of electron and lattice temperatures at different time points is illustrated in Figure 9. In each sub-figure, the solid lines in the temperature-dependent parameter group exhibit a smoother lattice temperature change with increasing depth compared to the dashed lines in the classical parameter group. This distinction arises from the increased electron thermal conductivity and electron-phonon coupling factor at higher electron temperatures, resulting in enhanced energy transfer towards the deeper region. For electron temperature in Figure 9a–c, as the pulse number increases, the peak time of electron temperature is delayed (SP, DP—, FP—), and the peak temperature of the surface is significantly reduced (classical parameters: SP—, DP, FP, temperature-dependent parameters: SP—, DP, FP). Regarding the lattice temperature in Figure 9d–f, an increment in pulse number leads to a higher lattice temperature. It is worth noting that the application of temperature-dependent parameters will increase the lattice temperature at a depth greater than , which is consistent with previous results [17,43]. This phenomenon is also the reason for the observed enlargement of the melting region shown in Figure 8.
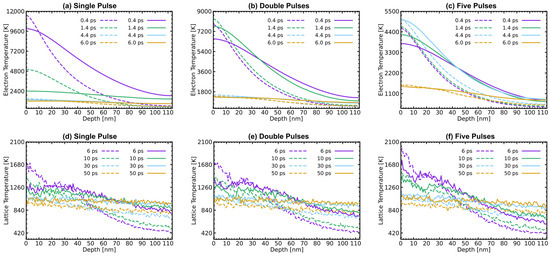
Figure 9.
Spatial distributions of (a–c) electron temperature , and (d–f) lattice temperature at different pulse numbers for (a,d) SP, (b,e) DP, and (c,f) FP. Dashed lines represent the classical thermophysical parameters group results and the solid lines represent the temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters group results.
In conclusion, the introduction of temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters can effectively reflect the phenomenon that multiple pulses increase the melting depth (first ). The increase in pulse number can significantly reduce the surface electron temperature. This causes the lattice sub-system to obtain more energy, thus increasing the lattice temperature. It is worth emphasizing that the enhancement effect of multiple pulses only occurs when the pulse energy is far below the ablation threshold (). When the pulse energy approaches the ablation threshold, the melting depth will be affected by the material size, surface expansion, and ablation phenomena and shows no increase or even a decrease [13,59]. Furthermore, the mentioned enhancement effect only occurs in the early stage. Nevertheless, the current results are sufficient to demonstrate that the MD-TTM model incorporating temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters can effectively achieve the control mechanism of Al’s thermophysical properties by pulse train.
3.3. The Influence of Multi-Pulse on the Phenomenon of Lateral Melting
Figure 10a,b depicts the morphology of the 2D melting region of the Al surface at , under the same laser energy, for both the SP and DP with a interval, respectively. Among them, the left is the simulation results, and the right is the experimental results. To facilitate a direct comparison between the simulated results and the experimental results presented in Section 3.1, the laser energy at the center of the simulation is set to , which is below the ablation threshold ( [37,38]).
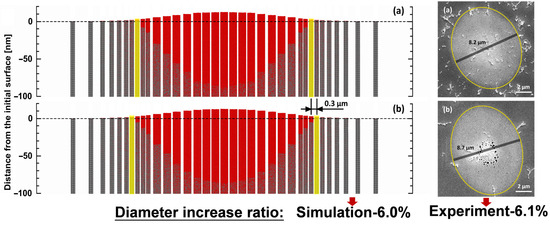
Figure 10.
The morphology of the 2D melting region () of the Al surface at (a) SP and (b) DP with a interval, the left is the simulation results, and the right is the experimental results.
In the results of the SP, it is observed that melting occurs within of the farthest position from the center of the laser spot, and the fluence at the position is , representing the melting threshold for the SP. In the results of the DPs, this position expands to , with a fluence of . Combining the results from Section 3.2, it is found that DPs can reduce the melting threshold compared to the SP, thereby enlarging the diameter of the melting region.
According to the above results, we speculate the cause of the void. During the subsequent development of the melting process, the atoms with more kinetic energy in the central region flow toward the lower liquid level in the edge region. As the liquid melting region resolidifies into a solid state, the surface expansion decreases, resulting in the formation of irregular voids. The larger diameters of the melting region observed for the DP indicate a higher kinetic energy of Al at the surface during liquefaction. This phenomenon may be the cause of the generation of irregular voids near the center for a DP with a interval, as discussed in Section 3.1. Combining this with the conclusion in Section 3.4 (that the early-stage melting depth is larger for a DP with a interval compared to a interval), the phenomenon of a more concentrated distribution of voids in the SEM image of the DP with a interval in Figure 6d may be caused by the lower kinetic energy of liquid atoms in the melting region.
Figure 11 presents the predicted results for FP under the same conditions discussed in this section. The results of FP exhibit larger melting diameters and depths, consistent with the previous discussions (Section 3.2).
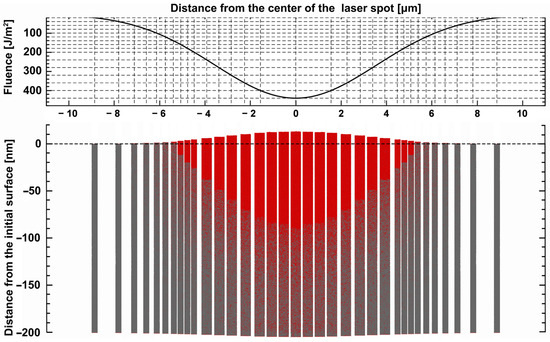
Figure 11.
The morphology of the 2D melting region () of the Al surface at FP with a interval.
Such results mean that it is possible to achieve an adjustment of the melting phenomenon through reasonable pulse design (pulse number, total pulse energy, pulse interval, and pulse energy ratio).
3.4. The Influence of Pulse Interval and Pulse Energy Ratio on the Longitudinal Melting Phenomenon
Due to the lack of experimental observation methods for longitudinal melting phenomena, this section exclusively relies on simulation to predict and analyze the results of longitudinal ultrafast melting. Figure 12 illustrates the longitudinal evolution of the melting region during the first irradiated by both the SP and DPs with varying pulse intervals. Consistent with the description in Section 3.2, Al mainly undergoes a rapid melting stage dominated by homogeneous melting and a slow melting stage dominated by heterogeneous melting [43]. MD snapshots at in Figure 12a and in Figure 12b are presented to describe the evolution of melting depth at different melting stages. Furthermore, the average velocities for the five stages are plotted in Figure 12c.
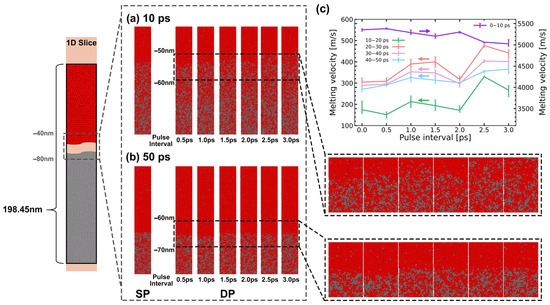
Figure 12.
The longitudinal evolution of the melting region during the first under both SP and DPs with varying pulse intervals. (a) atomic snapshots at , (b) atomic snapshots at , and (c) melting speed in different stages.
During the initial , the melting velocities for all pulse intervals and pulse numbers are significantly higher compared to subsequent stages, necessitating the use of the right y-axis for distinction, as shown in Figure 12c. At , there is little difference in melting depth between the SP and DPs, whereas the influence of pulse intervals becomes more pronounced. The maximum melting velocity is observed at the DP with a interval (). As the pulse interval increases, there is an overall decreasing trend in the average velocity during the rapid melting stage. Surprisingly, at a pulse interval, the melting velocity is higher than at a pulse interval. As the melting process further evolves, between and , the melting velocities decrease to below the speed of sound. The depth differences resulting from pulse intervals gradually decrease.
To provide a more detailed analysis of the mechanisms underlying the variations in melting velocity, Figure 13 shows contour plots of the evolution of electron temperature and lattice temperature with different pulse settings: SP, DP with a interval, and DP with a interval.
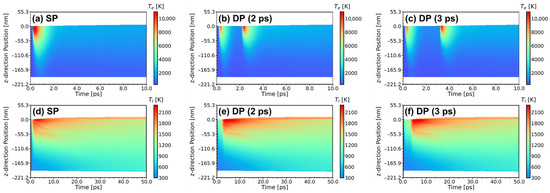
Figure 13.
Evolution of electron temperature and lattice temperature under different pulse settings (a,d) SP, (b,e) DP with a interval, (c,f) DP with a interval.
For the SP, the electron temperature at the Al surface easily reaches peak value (). However, due to the faster electron heat conduction compared to the lattice heat conduction, thermal rapidly diffuses from the surface “hot” electron region to the deep “cold” electron region, reducing the electron temperature, as seen in Figure 13a. Consequently, the thermalization time of the lattice is limited, leading to a smaller range of high lattice temperature regions, indicated by the red color in Figure 13d.
For the DP with a interval, although the peak electron temperature generated by the first laser pulse decreases compared to the SP (), due to the irradiation from the second laser pulse, the electron keeps a high temperature during the initial , as shown in Figure 13b. This increases the lattice thermalization time. The lattice sub-system gains more energy, forming a larger range of high-temperature regions, indicated by the red and orange colors in Figure 13e.
For the DP with a interval, the increasing pulse interval between the two sub-pulses allows for sufficient relaxation between the hot electron sub-system and the cold lattice sub-system. When the time the second sub-pulse arrives, the electron temperature reduces to , and the thermophysical parameter changes caused by the first sub-pulse have less effect on the absorption of the second sub-pulse. In other words, as the pulse interval continues to increase, the melting phenomena of the two sub-pulses become more independent, leading to a decreasing trend in the surface melting phenomenon.
Furthermore, as indicated in Section 3.2, electron thermal conductivity and the electron-phonon coupling factor are positively correlated with electron temperature. Combining the conclusions of [60], the effects of electron thermal conductivity and electron-phonon coupling factor are contradictory on lattice heating. The increase in electron thermal conductivity weakens the lattice heating, and a smaller melting depth is obtained. At the same time, the increase in the electron-phonon coupling factor enhances the lattice heating, and a larger melting depth is obtained. The peak velocity at implies that the influence of changes in the electron-phonon coupling factor on lattice thermalization is greater than that of electron thermal conductivity. This facilitates the energy absorption of the lattice sub-system from the second sub-pulse, resulting in a greater melting velocity and melting depth. However, when the pulse interval is greater than , during the irradiation of the second pulse, both the electron and lattice have sufficient time to relax and conduct heat deeper into the Al, leading to a “cooler” electron temperature at the surface. Consequently, the melting velocity decreases again, as shown in Figure 13c,f.
Figure 14 illustrates the impact of the pulse energy ratio of sub-pulses for DPs on the melting process. During the initial of the rapid melting stage, compared to the 1:1 and decreasing energy train, an increasing energy train results in a greater amplification of melting velocities, particularly evident at a interval with a 3:7 energy ratio configuration.
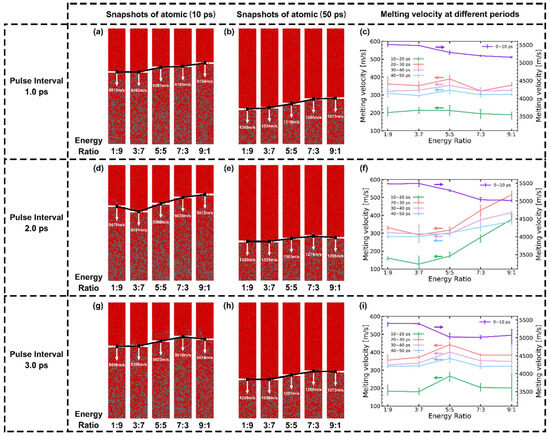
Figure 14.
The impact of sub-pulses energy ratio of DP on the melting process. Sub-figures for DPs with (a–c) , (d–f) , and (g–i) intervals, respectively. The first and second columns are atomic snapshots of and . The third column represents the melting speed vs. energy ratio at different stages.
The simulation results in this section can be summarized as follows: (i) For the rapid melting stage (), the melting depth is influenced by the pulse interval and pulse energy ratio. A DP with a interval and a pulse energy ratio of 3:7 exhibits the maximum melting depth. (ii) For the whole process of melting, it is observed that as the simulation time increases, the differences in melting depth gradually decrease. Predictably, due to the consistent total input energy, the final melting depth is independent of the pulse interval and energy ratio. This corresponds to the results presented in [13,59,61].
4. Conclusions
This study uses the femtosecond laser-pulse train melting experiment and the molecular dynamics coupling two-temperature model (MD-TTM model) incorporating temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters to investigate ultrafast melting processes of Al irradiated by different laser-pulse settings. The investigation encompasses variations in pulse number, pulse interval, and pulse energy ratio to explore both lateral and longitudinal melting processes. The research findings indicate that: (i) the MD-TTM model with temperature-dependent property parameters can effectively reflect the changes in Al’s thermophysical properties irradiated by the femtosecond laser train. This model provides theoretical support for the results of femtosecond laser multi-pulse experiments. (ii) As the pulse number increases, the melting threshold at the edge region of the laser spot decreases, resulting in an increase in the melting region diameter. (iii) At the same laser energy (much less than the ablation threshold), the melting depth of Al in the early stage increases with the increase in pulse number. Specifically, melting depth and melting velocity in the early stage reach the maximum for a DP with an increasing energy ratio (3:7) and a pulse interval. The pulse number, pulse interval, and energy ratio only influence melting depth and melting velocity in the early stage. This confirms that the independent control of melting phenomena can be achieved through pulse train. This will contribute to the improvement of processing quality in additive and subtractive manufacturing applications using femtosecond laser technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L.; methodology, Y.M. and J.G.; software, Y.M. and J.G.; validation, Y.M., A.G., Z.C., Q.W., J.G., Z.L. and J.L.; investigation, Y.M.; resources, Z.C.; data curation, A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.M.; writing—review and editing, A.G. and Z.C.; visualization, A.G.; supervision, Z.C., Q.W. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science and Technology Major Project Grant number 2019-VII-0009-0149 and the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number grant No. U2037205.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Please contact the corresponding author for data related to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Nomenclature
| Material constant for Al, | |
| Material constant for Al, | |
| Electron heat capacity, | |
| Lattice heat capacity, | |
| Absorb laser fluence, | |
| Total force exerted on atom , | |
| Fourier number, | |
| Random force, | |
| Initial electron-phonon coupling factor, | |
| Electron-phonon coupling factor, | |
| Pulse number of the current calculation, | |
| Total kinetic energy in the grid, | |
| Boltzmann constant, | |
| Electron thermal conductivity, | |
| Lattice thermal conductivity, | |
| Ballistic transportation length, | |
| Optical penetration depth, | |
| Mass of atom , | |
| Atom density, | |
| Total pulse number, | |
| Reflectivity, | |
| Laser source term, | |
| Electron temperature, | |
| Lattice temperature, | |
| Time of the current calculation, | |
| Pulse interval between the ith and (i − 1)th sub-pulses, | |
| Laser-pulse duration, | |
| Velocity of atom , | |
| Random vector, | |
| Depth of the laser irradiation, |
Greek symbols
| Thermal diffusivity, | |
| Friction term of atom , | |
| Timestep, | |
| , | Spacesteps, |
| Proportion of the th pulse to the total energy, | |
| Standard deviation, | |
| Electron relaxation time, |
References
- Jiang, L.; Wang, A.-D.; Li, B.; Cui, T.-H.; Lu, Y.-F. Electrons dynamics control by shaping femtosecond laser pulses in micro/nanofabrication: Modeling, method, measurement and application. Light Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 17134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugioka, K. Progress in ultrafast laser processing and future prospects. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 393–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinauskas, M.; Žukauskas, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Hayasaki, Y.; Mizeikis, V.; Buividas, R.; Juodkazis, S. Ultrafast laser processing of materials: From science to industry. Light Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, M.Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.K.; Dunning, M.; Witte, B.B.L.; Baldwin, J.K.; Fletcher, L.B.; Kim, J.B.; Ng, A.; Redmer, R.; et al. Heterogeneous to homogeneous melting transition visualized with ultrafast electron diffraction. Science 2018, 360, 1451–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.-Y.; Shugaev, M.V.; Wu, C.; Zhigilei, L.V. The effect of pulse duration on nanoparticle generation in pulsed laser ablation in liquids: Insights from large-scale atomistic simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 7077–7099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethfeld, B.; Ivanov, D.S.; Garcia, M.E.; Anisimov, S.I. Modelling ultrafast laser ablation. J. Phys. D 2017, 50, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhao, X. Numerical study of material decomposition in ultrafast laser interaction with metals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 463, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Combined atomistic-continuum modeling of short-pulse laser melting and disintegration of metal films. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 064114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Combined atomistic-continuum model for simulation of laser interaction with metals: Application in the calculation of melting thresholds in Ni targets of varying thickness. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Rethfeld, B. The effect of pulse duration on the interplay of electron heat conduction and electron–phonon interaction: Photo-mechanical versus photo-thermal damage of metal targets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9724–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Jiang, L.; Ji, P. The effect of enhanced heat transfer across metal–nonmetal interfaces subject to femtosecond laser irradiation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 19853–19867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X. Molecular dynamics studies of ultrafast laser-induced phase and structural change in crystalline silicon. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2012, 55, 6060–6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förster, G.D.; Lewis, L.J. Numerical study of double-pulse laser ablation of Al. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 224301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Y.; Jiang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y. Ultrafast quasi-three-dimensional imaging. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2023, 5, 045601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Tsai, H.-L. Phase change mechanisms during femtosecond laser pulse train ablation of nickel thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 064906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghilou, A.; He, M.; Schubert, J.S.; Zhigilei, L.V.; Kautek, W. Femtosecond laser generation of microbumps and nanojets on single and bilayer Cu/Ag thin films. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 11846–11860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Ji, P.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y. Multiscale Investigation of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Processing Aluminum in Burst Mode. Nanoscale Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 2018, 22, 324–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ji, P.; Jiang, L.; Lin, G.; Meng, Y. Femtosecond laser sintering Al nanoparticles: A multiscale investigation of combined molecular dynamics simulation and two-temperature model. Powder Technol. 2022, 407, 117682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L. Size distribution control of metal nanoparticles using femtosecond laser pulse train: A molecular dynamics simulation. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 109, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, S.; Hermann, J. Reducing nanoparticles in metal ablation plumes produced by two delayed short laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 053120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Qiu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Shaped femtosecond laser-regulated deposition sites of galvanic replacement for simple preparation of large-area controllable noble metal nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 579, 152123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Luo, G.; Hu, Y.; Qin, Y. Efficient modeling of metal ablation irradiated by femtosecond laser via simplified two-temperature model coupling molecular dynamics. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 77, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D.S.; Zhigilei, L.V. Kinetic Limit of Heterogeneous Melting in Metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 195701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethfeld, B.; Sokolowski-Tinten, K.; von der Linde, D.; Anisimov, S.I. Ultrafast thermal melting of laser-excited solids by homogeneous nucleation. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 092103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwick, B.J.; Dwyer, J.R.; Jordan, R.E.; Miller, R.J.D. An Atomic-Level View of Melting Using Femtosecond Electron Diffraction. Science 2003, 302, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, M.; Murphy, S.; Chen, Z.; Fossati, P.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Glenzer, S. Visualization of ultrafast melting initiated from radiation-driven defects in solids. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw0392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de With, G. Melting Is Well-Known, but Is It Also Well-Understood? Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 13713–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Tsai, H.-L. Modeling of ultrashort laser pulse-train processing of metal thin films. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2007, 50, 3461–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povarnitsyn, M.E.; Fokin, V.B.; Levashov, P.R.; Itina, T.E. Molecular dynamics simulation of subpicosecond double-pulse laser ablation of metals. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 92, 174104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englert, L.; Rethfeld, B.; Haag, L.; Wollenhaupt, M.; Sarpe-Tudoran, C.; Baumert, T. Control of ionization processes in high band gap materials via tailored femtosecond pulses. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 17855–17862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudiuso, C.; Giannuzzi, G.; Volpe, A.; Lugarà, P.M.; Choquet, I.; Ancona, A. Incubation during laser ablation with bursts of femtosecond pulses with picosecond delays. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3801–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.K.; Foong, C.S.; Cullinan, M.A. Effect of size, morphology, and synthesis method on the thermal and sintering properties of copper nanoparticles for use in microscale additive manufacturing processes. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 21, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullsperger, T.; Liu, D.; Yürekli, B.; Matthäus, G.; Schade, L.; Seyfarth, B.; Kohl, H.; Ramm, R.; Rettenmayr, M.; Nolte, S. Ultra-short pulsed laser powder bed fusion of Al-Si alloys: Impact of pulse duration and energy in comparison to continuous wave excitation. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, G.E.; Starikov, S.V.; Stegailov, V.V.; Saitov, I.M.; Zhilyaev, P.A. Atomistic Modeling of Warm Dense Matter in the Two-Temperature State. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2013, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarev, V.V.; Starikov, S.V. Atomistic simulation of ion track formation in UO2. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2014, 26, 475401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Kumar, K.; Samuel, G.L.; Shunmugam, M.S. Theoretical and experimental investigations of ultra-short pulse laser interaction on Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 263, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakhovskii, V.V.; Inogamov, N.A.; Petrov, Y.V.; Ashitkov, S.I.; Nishihara, K. Molecular dynamics simulation of femtosecond ablation and spallation with different interatomic potentials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9592–9596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, S.I.; Inogamov, N.A.; Petrov, Y.V.; Khokhlov, V.A.; Zhakhovskii, V.V.; Nishihara, K.; Agranat, M.B.; Ashitkov, S.I.; Komarov, P.S. Interaction of short laser pulses with metals at moderate intensities. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 92, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolev, S.L. Nonlocal two-temperature model: Application to heat transport in metals irradiated by ultrashort laser pulses. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2016, 94, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recoules, V.; Renaudin, P.; Clérouin, J.; Noiret, P.; Zérah, G. Electrical conductivity of hot expanded aluminum: Experimental measurements and ab initio calculations. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 66, 056412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Christensen, M.S.; Savolainen, J.-M.; Balling, P.; Zhigilei, L.V. Generation of subsurface voids and a nanocrystalline surface layer in femtosecond laser irradiation of a single-crystal Ag target. Phys. Rev. B 2015, 91, 035413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhigilei, L.V. Microscopic mechanisms of laser spallation and ablation of metal targets from large-scale molecular dynamics simulations. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Ji, P.; Jiang, L.; Lin, G.; Guo, J. Spatiotemporal insights into the femtosecond laser homogeneous and heterogeneous melting aluminum by atomistic-continuum modeling. Appl. Phys. A 2022, 128, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlinomaz, K.; Levy, Y.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Bulgakova, N.M. Modeling thermal response of Mo thin films upon single femtosecond laser irradiation: Dynamics of film melting and substrate softening. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2022, 196, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeaby, C.D.; Aditi, R. Two-temperature model for ultrafast melting of Au-based bimetallic films interacting with single-pulse femtosecond laser: Theoretical study of damage threshold. Phys. Rev. B 2023, 107, 195402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.K.; Tzou, D.Y.; Beraun, J.E. A semiclassical two-temperature model for ultrafast laser heating. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2006, 49, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.M.; Rutherford, A.M. Including the effects of electronic stopping and electron–ion interactions in radiation damage simulations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 016207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, A.M.; Duffy, D.M. The effect of electron–ion interactions on radiation damage simulations. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 496201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plimpton, S. Fast Parallel Algorithms for Short-Range Molecular Dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, L.; Lian, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.; Sun, J. Enhancement of ablation and ultrafast electron dynamics observation of nickel-based superalloy under double-pulse ultrashort laser irradiation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 4253–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shank, C.V.; Yen, R.; Hirlimann, C. Time-Resolved Reflectivity Measurements of Femtosecond-Optical-Pulse-Induced Phase Transitions in Silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-L.; Lu, S.-Y.; Yeh, J.-W.; Hsu, W.-K. Thermal expansion and enhanced heat transfer in high-entropy alloys. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2013, 46, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryashov, S.I.; Ionin, A.A. Multi-scale fluence-dependent dynamics of front-side femtosecond laser heating, melting and ablation of thin supported aluminum film. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 2016, 99, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tsai, H.-L. Improved Two-Temperature Model and Its Application in Ultrashort Laser Heating of Metal Films. J. Heat Transfer 2005, 127, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.Y.; Asta, M.; Hoyt, J.J. Kinetic coefficient of Ni solid-liquid interfaces from molecular-dynamics simulations. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 69, 024108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhigilei, L.V.; Celli, V. Electron-phonon coupling and electron heat capacity of metals under conditions of strong electron-phonon nonequilibrium. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 075133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bévillon, E.; Colombier, J.P.; Recoules, V.; Stoian, R. Free-electron properties of metals under ultrafast laser-induced electron-phonon nonequilibrium: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 115117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostetler, J.L.; Smith, A.N.; Czajkowsky, D.M.; Norris, P.M. Measurement of the electron-phonon coupling factor dependence on film thickness and grain size in Au, Cr, and Al. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 3614–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Krauß, A.; Lotze, J.; Trebin, H.-R. Simulation of laser ablation in aluminum: The effectivity of double pulses. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, Y. Ablation enhancement of metal in ultrashort double-pulse experiments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 261906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, C.M.; Srisungsitthisunti, P.; Weiner, A.M.; Xu, X. Enhanced machining of steel using femtosecond pulse pairs. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).