Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Zeolite Collection, Preparation, and Characterization
2.3. Laboratory-Scale Beer Filtration Experiments
2.4. Filtered Beer Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
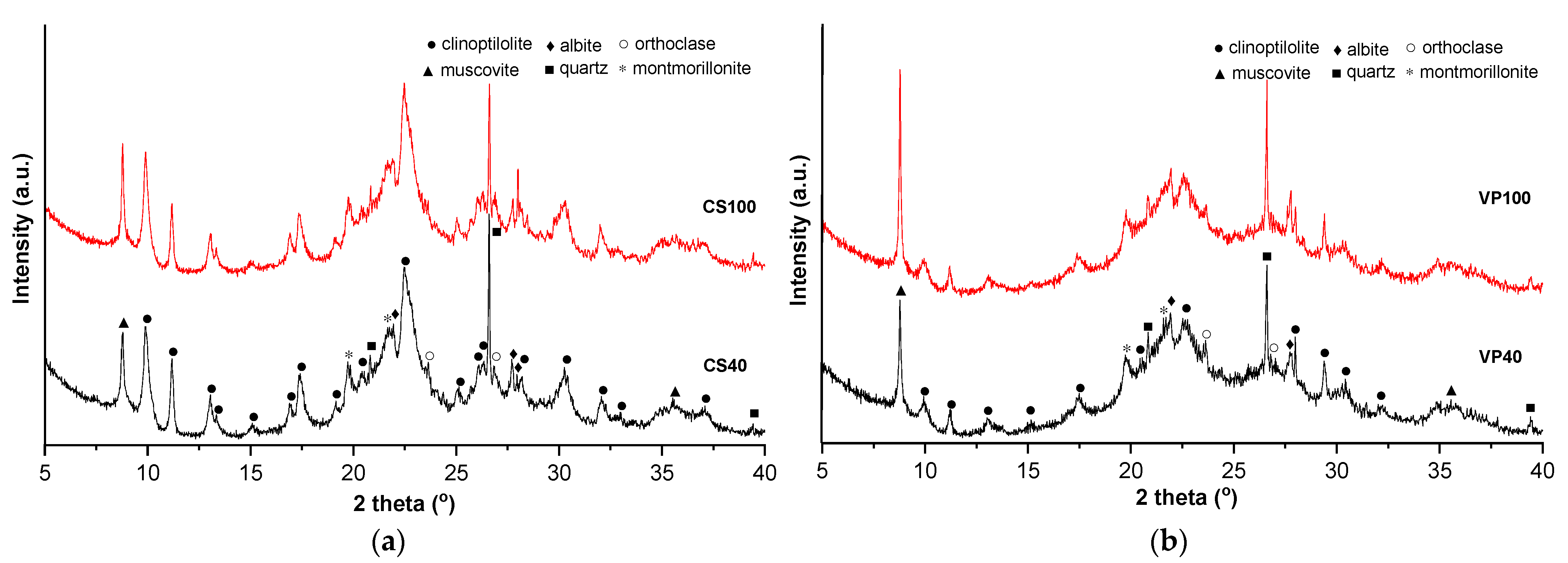
3.1. Zeolite Physicochemical Characteristics
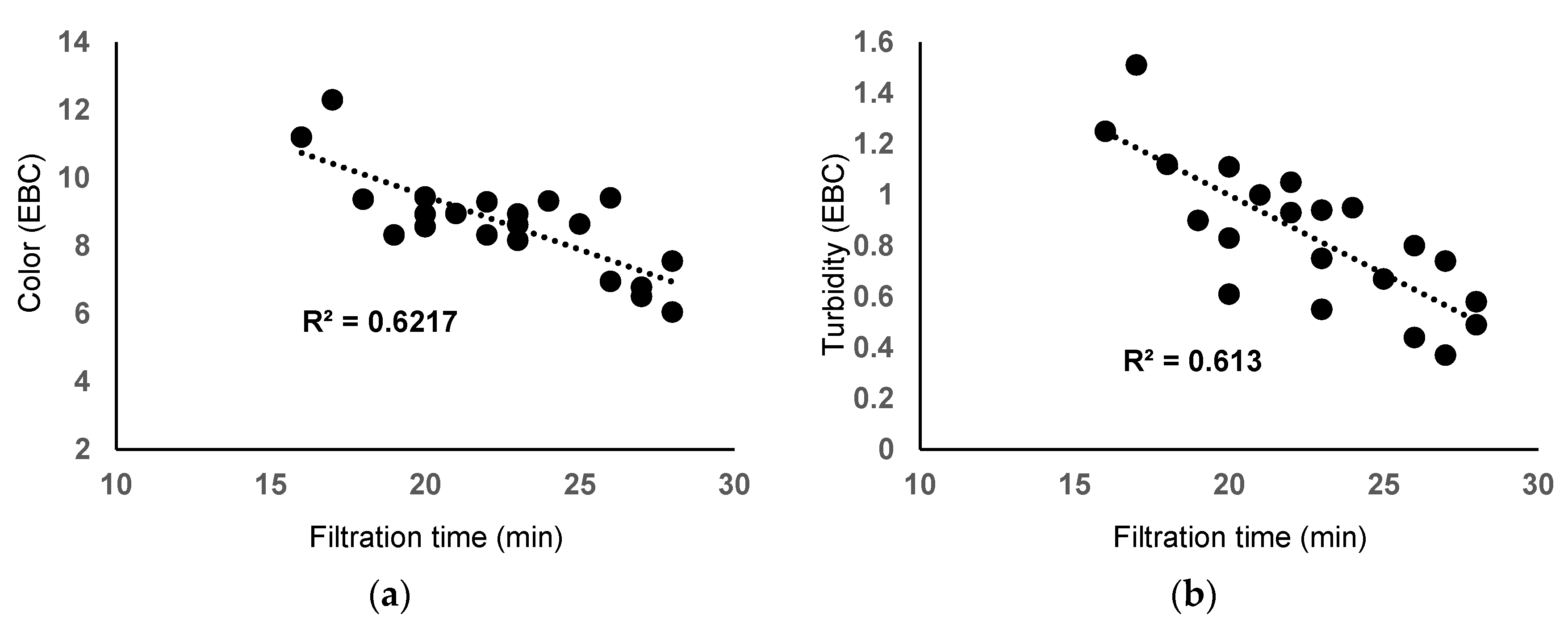
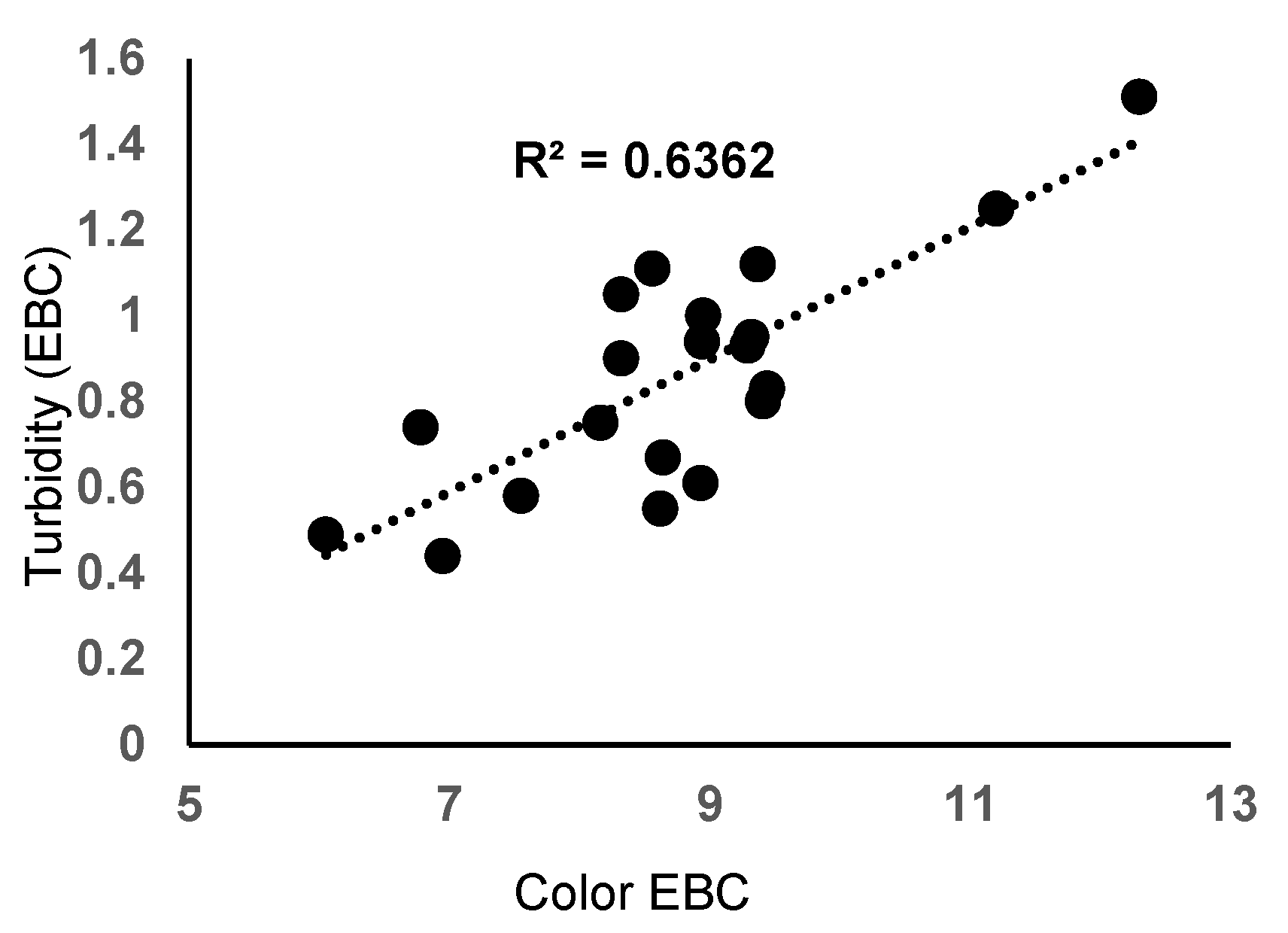
3.2. Main Physical-Chemical Characteristics of Filtered Beer from Laboratory Tests
3.3. Influence of Filtering Media on Metal Content in Filtered Beer
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iorizzo, M.; Coppola, F.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Sorrentino, E. Role of yeasts in the brewing process: Tradition and innovation. Processes 2021, 9, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciont, C.; Epuran, A.; Kerezsi, A.D.; Coldea, T.E.; Mudura, E.; Pasqualone, A.; Zhao, H.; Suharoschi, R.; Vriesekoop, F.; Pop, O.L. Beer safety: New challenges and future trends within craft and large-scale production. Foods 2022, 11, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, A.; Serra-Majem, L.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Pascual, V.; Tinahones, F.J.; Estruch, R. Moderate consumption of beer and its effects on cardiovascular and metabolic health: An updated review of recent scientific evidence. Nutrients 2021, 13, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimini, A.; Moresi, M. Towards a diatomaceous earth- and PVPP-free clarification and stabilization process of rough beer at room-temperature conditions. Int. J. Food Eng. 2018, 83, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, V.; Gonçalves, J.; Figueira, J.A.; Ornelas, L.P.; Branco, R.N.; Câmara, J.S.; Pereira, J.A. Beer volatile fingerprinting at different brewing steps. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafrai, A.V.; Permyakova, L.V.; Borodulin, D.M.; Sergeeva, I.Y. Modeling the physiological parameters of brewer’s yeast during storage with natural zeolite containing tuffs using artificial neural networks. Information 2022, 13, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slabý, M.; Štěrba, K.; Olšovská, J. Fitration of Beer—A Review Filtrace piva—Review. Kvasny Prum. 2018, 64, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frančáková, H.; Dráb, S.; Solgajová, M.; Tóth, Z.; Bojňanská, T. Effect of diatomaceous earth filtration on optical properties of beer, J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2013, 2, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar]
- Mastanjević, K.; Krstanović, V.; Lukinac, J.; Jukić, M.; Vulin, Z.; Mastanjević, K. Beer—The importance of colloidal stability (non-biological haze). Fermentation 2018, 4, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, F.; Hildebrand, N.; Wilkinson, S.; Back, W.; Krottenthalerm, M.; Becker, T. Large-scale study on beer filtration with combined filter aid additions to cellulose fibres. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemsch, K.; Heinrich, T. Raible-test for evaluation of filtration properties. Int. J. Food Eng. 2000, 106, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastanjević, K.; Krstanović, V.; Mastanjević, K.; Šarkanj, B. Malting and brewing industries encounter Fusarium spp. Related Problems. Fermentation 2018, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinovic, S.; Vlahovic, M.; Boljanac, T.; Pavlovic, L. Preparation of filter aids based on diatomites. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2006, 80, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Moresi, M. Novel cold sterilization and stabilization process applied to a pale lager. Int. J. Food Eng. 2015, 145, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devolli, A.; Kodra, M.; Shahinasi, E.; Stafasani, M.; Dara, F. Determination of optimal diatomaceous earth doses to improve beer filtration. In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Food Science and Technology, Durrës, Albania, 27–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editz, N.; Bentli, I.; Tatar, I. Improvement in filtration characteristics of diatomite by calcination. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 94, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroglu, N.; Emekci, M.; Athanassiou, C. Applications of natural zeolites on agriculture and food production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3487–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Reyes, C.A.; Reyes-Mendoza, G.A.; Henao-Martínez, J.A.; Williams, C.; Dyer, A. First report on the geologic occurrence of natural Na–A zeolite and associated minerals in cretaceous mudstones of the Paja formation of Vélez (Santander), Colombia. Crystals 2021, 11, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, O.; Senila, M.; Hoaghia, M.-A.; Scurtu, D.; Miu, I.; Levei, E.A. Effects of thermal treatment on natural clinoptilolite-rich zeolite behavior in simulated biological fluids. Molecules 2020, 25, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, M.P.M. Evaluation of a Substitute Filter Medium for Removal of Haze in Beer. Master’s Thesis, University of Adelaide, Department of Chemical Engineering, Adelaide, Australia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pandová, I.; Rimár, M.; Panda, A.; Valíček, J.; Kušnerová, M.; Harničárová, M. A Study of using natural sorbent to reduce iron cations from aqueous solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernat, D.C.; Brouwer, E.R.; Faber-Zirkzee, R.C.; Ottens, M. Flavour-improved alcohol-free beer—Quality traits, ageing and sensory perception. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 123, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernat, D.C.; Penning, M.M.; Swinkels, F.M.; Brouwer, E.R.; Ottens, M. Selective off-flavor reduction by adsorption: A case study in alcohol-free beer. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permyakova, L.V.; Pomozova, V.A.; Antipova, L.V. Improvement of brewer’s yeast viability by adjusting wort composition. Foods Raw Mater. 2017, 5, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasevic-Canovic, M. Purification of natural zeolite-clinoptilolite for medical application-extraction of lead. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2005, 70, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Miu, I. Mercury determination in natural zeolites by thermal decomposition atomic absorption spectrometry: Method validation in compliance with eequirements for use as dietary supplements. Molecules 2019, 24, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicinas, P.R.; Bedelean, H.; Maicaneanu, A. Romanian (Măcicaş) zeolitic volcanic tuff for malachite green removal. Studia UBB Chem. 2016, LXI, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Maicaneanu, S.A.; Bedelean, H. Na+—NH4+ cation exchange study on treated zeolitic volcanic tuff in fixed bed column. Studia UBB Chem. 2020, LXV, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Neag, E.; Cadar, O.; Hoaghia, M.A.; Roman, M.; Moldovan, A.; Hosu, A.; Lupas, A.; Kovacs, E.D. Characteristics of volcanic tuff from Macicasu (Romania) and its capacity to remove ammonia from contaminated air. Molecules 2022, 27, 3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Brewery Convention (EBC). Analytica EBC; Fachverlag Hans Carl: Nürnberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, D.; Vecseri, B.H.; Kun-Farkas, G.; Urbin, A.; Nyitrai, A.; Sipos, L. How to objectively determine the color of beer? J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Miu, I. Development and validation of a spectrometric method for Cd and Pb determination in zeolites and safety evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, H.; Kaya, A. Factors affecting adsorption characteristics of Zn2+ on two natural zeolites. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 131, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, L.E.; Juenger, M.C.G. Milling as a pretreatment method for increasing the reactivity of natural zeolites for use as supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2016, 65, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margeta, K.; Zabukovec, N.; Siljeg, M.; Farkas, A. Natural zeolites in water treatment—How effective is their use. In Water Treatment; Elshorbagy, W., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; pp. 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Krol, M.; Mozgawa, W.; Jastrzebski, W. Theoretical and experimental study of ion-exchange process on zeolites from 5-1 structural group. J. Porous. Mater. 2016, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simancas, R.; Chokkalingam, A.; Elangovan, S.P.; Liu, Z.; Sano, T.; Iyoki, K.; Wakihara, T.; Okubo, T. Recent progress in the improvement of hydrothermal stability of zeolites. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7677–7695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bish, D.L.; Carey, J.W. Thermal behavior of natural zeolites. In Natural Zeolites: Occurrence, Properties, Applications (Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry); Bish, D.L., Ming, D.W., Eds.; Mineralogical Society of America: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; Volume 45, pp. 403–452. [Google Scholar]
- Guyot-Declerck, C.; Francois, N.; Ritter, C.; Govaerts, B.; Collin, S. Influence of pH and ageing on beer organoleptic properties. A sensory analysis based on AEDA data. Food. Qual. Prefer. 2005, 16, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schur, F. Beer stabilization before filtration. Brauwelt 1980, 120, 1712–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Cimini, A.; Moresi, M. Beer clarification using ceramic tubular membranes. Food. Bioprocess. Technol. 2014, 7, 2694–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Moresi, M. Innovative rough beer conditioning process free from diatomaceous earth and polyvinylpolypyrrolidone. Foods 2020, 9, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, P. Determination and fractionation of metals in beer—A review. Food Addit. Contam. 2008, 25, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senila, M.; Cadar, O.; Senila, L.; Angyus, B.S. Simulated bioavailability of heavy metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Zn) in contaminated soil amended with natural zeolite using diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique. Agriculture 2022, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Turek, A.; Szczesio, M.; Wolf, W.M. Comprehensive evaluation of metal pollution in urban soils of a post-industrial city—A case of Lodz, Poland. Molecules 2019, 25, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentiu, T.; Ponta, M.; Senila, M.; Mihaltan, A.I.; Darvasi, E.; Frentiu, M.; Cordos, E. Evaluation of figures of merit for Zn determination in environmental and biological samples using EDL excited AFS in a new radiofrequency capacitively coupled plasma. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2010, 25, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Hans, N.; Kumar, S.; Radha, R. A critical review on speciation, mobilization and toxicity of lead in soil microbeplant system and bioremediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senila, M. Real and simulated bioavailability of lead in contaminated and uncontaminated soils. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, H.; Esmaeili, A.; Razaeian, M.; Salari, M.; Hosseini, A.N.; Mobini, M.; Barani, A. Potentially toxic metal concentration, spatial distribution, and health risk assessment in drinking groundwater resources of southeast Iran. Geosci. Front. 2022, 13, 101276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.J.; Rathinasabapathi, B.; Wu, B.; Luo, J.; Pu, L.-P.; LMa, Q. Arsenic and selenium toxicity and their interactive effects in humans. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, C.K.; Hopfer, H.; Ebeler, S.E.; Nelson, J.; Conklin, S.D.; Kubachka, K.M.; Wilson, R.A. Matrix extension and multilaboratory validation of arsenic speciation method EAM to include wine. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2017, 65, 4193–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Journal of the European Union, DIRECTIVE (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32020L2184&from=EN (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Charehsaz, M.; Helvacioglu, S.; Cetinkaya, S.; Demir, R.; Erdem, O.; Aydin, A. Heavy metal and essential elements in beers from turkey market: A risk assessment study. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, D.; Mitic, S.; Miletic, G. The concentrations of Fe, Cu and Zn in selected wines from South-East Serbia. J. Serbian. Chem. 2010, 75, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redan, B.W.; Jablonski, J.E.; Halverson, C.; Jaganathan, J.; Mabud, M.A.; Jackson, L.S. Factors affecting transfer of the heavy metals arsenic, lead, and cadmium from diatomaceous-earth filter aids to alcoholic beverages during laboratory-scale filtration. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2019, 67, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadini, G.; Spalla, S.; Beone, G.M. Arsenic, cadmium and lead in beers from the Italian market. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.B. New evidence against chromium as an essential trace element. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 2212–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnew, U.M.; Slesinger, T.L. Zinc Toxicity. [Updated 19 October 2022]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554548/ (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Gong, W.; Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.; Qiao, K.; Zhao, J. Biological regeneration of brewery spent diatomite and its reuse in basic dye and chromium (III) ions removal. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 128, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadar, O.; Stupar, Z.; Senila, M.; Levei, L.; Moldovan, A.; Becze, A.; Ozunu, A.; Levei, E.A. Zeolites reduce the transfer of potentially toxic elements from soil to leafy vegetables. Materials 2022, 15, 5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, W.Y.; Hui, T.H. Regeneration of the brewing spent diatomite. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 998–999, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, R.D.; Gunathilake, C.; Dassanayakec, R.S. Suitability of reusing the spent diatomaceous earth in brick production: A review. Adv. Technol. 2022, 2, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Experiment | Filter Cake | Filtration Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| E1 | 3 g DIF BO | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E2 | 3 g DIF BO | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E3 | 3 g DIF BO | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E4 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP100 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E5 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E6 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS100 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E7 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E8 | 2 g VP100 + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E9 | 2 g CS100 + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g CBL3 |
| E10 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP100 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E11 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E12 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS100 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E13 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E14 | 2 g VP100 + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E15 | 2 g CS100 + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g VP40 |
| E16 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP100 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E17 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E18 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS100 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E19 | 2 g DIF BO + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E20 | 2 g VP100 + 1 g VP40 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| E21 | 2 g CS100 + 1 g CS40 | 0.5 g CS40 |
| Parameter | CS100 | CS40 | VP100 | VP40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total surface area (m2 g−1) | 73 | 72 | 55 | 53 |
| Total pore volume (cm3 g−1) | 0.187 | 0.160 | 0.119 | 0.114 |
| Average pore radius (Å) | 27 | 27 | 31 | 31 |
| Bulk density (g cm−3) | 0.726 | 0.617 | 0.680 | 0.598 |
| Parameter | Measurement Units | CS100 | CS40 | VP100 | VP40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH | 8.04 ± 0.15 | 8.09 ± 0.17 | 8.31 ± 0.20 | 8.42 ± 0.18 |
| SiO2 | wt.% | 68.4 ± 1.7 | 68.3 ± 2.5 | 68.0 ± 1.8 | 67.5 ± 2.1 |
| Al2O3 | 10.5 ± 0.8 | 10.3 ± 0.7 | 11.6 ± 0.9 | 12.4 ± 0.8 | |
| Fe2O3 | 1.22 ± 0.22 | 1.30 ± 0.15 | 1.80 ± 0.21 | 1.66 ± 0.19 | |
| CaO | 1.62 ± 0.25 | 1.95 ± 0.23 | 2.33 ± 0.31 | 2.21 ± 0.32 | |
| MgO | 0.79 ± 0.08 | 0.65 ± 0.07 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 0.74 ± 0.09 | |
| K2O | 2.36 ± 0.43 | 2.41 ± 0.35 | 3.66 ± 0.31 | 3.52 ± 0.40 | |
| Na2O | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 1.14 ± 0.09 | 1.09 ± 0.10 | |
| MnO | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | |
| Na | mg kg−1 | 1890 ± 340 | 2045 ± 236 | 8458 ± 987 | 8087 ± 926 |
| Mg | 3910 ± 603 | 4740 ± 559 | 5520 ± 734 | 4440 ± 643 | |
| Ca | 11,600 ± 1175 | 13,800 ± 1486 | 16,640 ± 1266 | 15,790 ± 1920 | |
| K | 19,600 ± 3571 | 19,960 ± 2899 | 30,370 ± 2572 | 29,210 ± 3319 | |
| Fe | 8560 ± 1027 | 9110 ± 1301 | 12,600 ± 995 | 11,620 ± 1066 | |
| Mn | 331 ± 63 | 282 ± 51 | 542 ± 79 | 465 ± 80 | |
| As | <0.50 | <0.50 | <0.50 | <0.50 | |
| Cd | <0.10 | <0.10 | <0.10 | <0.10 | |
| Cr | 3.30 ± 0.31 | 3.18 ± 0.30 | 5.44 ± 0.43 | 6.20 ± 0.52 | |
| Cu | 10.3 ± 0.8 | 8.55 ± 0.7 | 20.1 ± 1.6 | 23.6 ± 1.7 | |
| Co | <0.20 | <0.20 | 1.33 ± 0.11 | 1.27 ± 0.10 | |
| Ni | 2.76 ± 0.23 | 3.11 ± 0.25 | 3.82 ± 0.28 | 4.04 ± 0.31 | |
| Pb | 5.84 ± 0.45 | 5.11 ± 0.40 | 7.80 ± 0.63 | 8.43 ± 0.71 | |
| Zn | 23.5 ± 1.53 | 21.4 ± 1.46 | 36.5 ± 2.11 | 34.6 ± 2.23 | |
| Exc. Na+ | mEq 100 g−1 | 1.94 ± 0.25 | 2.05 ± 0.18 | 4.12 ± 0.33 | 4.20 ± 0.35 |
| Exc. Mg2+ | 4.80 ± 0.31 | 4.75 ± 0.32 | 1.48 ± 0.15 | 2.06 ± 0.18 | |
| Exc. Ca2+ | 56.8 ± 3.5 | 60.0 ± 3.1 | 43.3 ± 2.6 | 44.3 ± 2.7 | |
| Exc. K+ | 17.7 ± 1.2 | 18.1 ± 1.3 | 18.5 ± 1.2 | 18.1 ± 1.0 | |
| CEC | 81.3 ± 3.7 | 84.9 ± 3.4 | 67.5 ± 2.9 | 68.6 ± 2.9 |
| Experiment | Filtration Time (min) | pH | Beer Color (EBC) | Beer Turbidity (EBC) | Beer Taste and Flavor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unfiltered beer | - | 4.20 | 14.1 | 10.33 | normal |
| E1 | 17 | 4.31 | 12.3 | 1.51 | normal |
| E2 | 16 | 4.40 | 11.2 | 1.25 | normal |
| E3 | 18 | 4.34 | 9.37 | 1.12 | normal |
| E4 | 22 | 4.40 | 9.29 | 0.93 | normal |
| E5 | 24 | 4.40 | 9.32 | 0.95 | normal |
| E6 | 20 | 4.35 | 9.44 | 0.83 | normal |
| E7 | 26 | 4.36 | 9.41 | 0.80 | normal |
| E8 | 25 | 4.36 | 8.64 | 0.67 | normal |
| E9 | 27 | 4.38 | 6.78 | 0.74 | normal |
| E10 | 21 | 4.38 | 8.95 | 1.00 | normal |
| E11 | 23 | 4.40 | 8.94 | 0.94 | normal |
| E12 | 20 | 4.36 | 8.56 | 1.11 | normal |
| E13 | 22 | 4.28 | 8.32 | 1.05 | normal |
| E14 | 28 | 4.36 | 7.55 | 0.58 | normal |
| E15 | 28 | 4.30 | 6.05 | 0.49 | normal |
| E16 | 20 | 4.46 | 8.93 | 0.61 | normal |
| E17 | 23 | 4.30 | 8.62 | 0.55 | normal |
| E18 | 19 | 4.36 | 8.32 | 0.90 | normal |
| E19 | 23 | 4.31 | 8.16 | 0.75 | normal |
| E20 | 26 | 4.33 | 6.95 | 0.44 | normal |
| E21 | 27 | 4.38 | 6.51 | 0.37 | normal |
| Experiment | Na | K | Ca | Mg | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | |||||
| E0 (unfiltered beer) | 13.1 | 459 | 21.0 | 69.4 | 1.33 |
| E1 | 18.2 | 436 | 28.2 | 65.0 | 1.13 |
| E2 | 12.9 | 399 | 18.9 | 61.9 | 0.88 |
| E3 | 11.9 | 416 | 23.1 | 67.1 | 1.16 |
| E4 | 15.9 | 513 | 22.6 | 77.7 | 1.46 |
| E5 | 16.4 | 520 | 23.5 | 78.7 | 1.53 |
| E6 | 12.5 | 523 | 26.6 | 80.4 | 0.89 |
| E7 | 14.5 | 546 | 30.2 | 70.1 | 1.19 |
| E8 | 11.6 | 580 | 53.8 | 70.9 | 0.81 |
| E9 | 20.5 | 615 | 69.1 | 78.3 | 1.39 |
| E10 | 18.0 | 569 | 53.4 | 72.9 | 0.81 |
| E11 | 19.3 | 556 | 54.6 | 83.6 | 0.89 |
| E12 | 15.9 | 540 | 41.1 | 79.0 | 0.82 |
| E13 | 18.9 | 554 | 50.2 | 75.4 | 0.80 |
| E14 | 13.0 | 518 | 43.6 | 79.4 | 0.58 |
| E15 | 12.0 | 521 | 35.8 | 64.1 | 0.47 |
| E16 | 13.6 | 483 | 37.7 | 71.9 | 0.52 |
| E17 | 17.1 | 453 | 49.8 | 66.1 | 0.74 |
| E18 | 14.2 | 502 | 30.9 | 75.8 | 0.40 |
| E19 | 11.9 | 512 | 29.8 | 77.4 | 1.08 |
| E20 | 10.9 | 491 | 29.3 | 75.6 | 0.38 |
| E21 | 15.1 | 506 | 28.9 | 76.0 | 0.55 |
| Experiment | As | Cd | Co | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µg L−1 | ||||||||
| E0 (unfiltered beer) | <0.50 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 2.80 | 57.9 | 10.9 | 5.55 | 10.6 |
| E1 | 1.35 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 26.6 | 50.9 | 6.87 | 3.26 | 40.3 |
| E2 | 1.30 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 23.1 | 33.9 | 5.27 | 1.18 | 29.5 |
| E3 | 1.09 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 20.4 | 40.5 | 8.77 | 4.23 | 34.8 |
| E4 | 0.89 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 21.4 | 43.2 | 10.7 | 5.36 | 44.1 |
| E5 | 0.77 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 22.0 | 44.6 | 11.2 | 6.02 | 40.6 |
| E6 | 0.68 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 18.4 | 26.3 | 5.74 | 4.02 | 28.8 |
| E7 | 1.02 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 16.5 | 26.0 | 6.02 | 5.11 | 29.4 |
| E8 | 2.44 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 18.1 | 25.4 | 9.28 | 8.14 | 35.8 |
| E9 | 1.65 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 12.3 | 22.3 | 3.74 | 3.00 | 29.2 |
| E10 | 1.89 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 17.9 | 28.4 | 8.28 | 7.44 | 30.6 |
| E11 | 2.04 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 15.2 | 20.5 | 7.23 | 6.63 | 27.4 |
| E12 | 3.20 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 17.2 | 28.8 | 3.24 | 4.29 | 24.6 |
| E13 | 2.02 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 15.6 | 26.4 | 3.11 | 5.23 | 30.5 |
| E14 | 1.12 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 11.6 | 20.2 | 3.91 | 3.18 | 19.7 |
| E15 | 3.49 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 13.0 | 23.9 | 4.01 | 6.13 | 38.5 |
| E16 | 3.11 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 17.9 | 28.4 | 4.54 | 1.88 | 36.6 |
| E17 | 4.05 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 20.8 | 22.6 | 3.48 | 1.44 | 28.8 |
| E18 | 3.21 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 22.3 | 24.3 | 3.79 | 1.61 | 35.0 |
| E19 | 1.89 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 13.5 | 21.4 | 6.05 | 3.23 | 23.7 |
| E20 | 1.76 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 13.3 | 28.3 | 4.53 | 4.43 | 26.4 |
| E21 | 1.45 | <0.26 | <0.65 | 11.2 | 16.5 | 3.79 | 5.51 | 17.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cadar, O.; Vagner, I.; Miu, I.; Scurtu, D.; Senila, M. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration. Materials 2023, 16, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051914
Cadar O, Vagner I, Miu I, Scurtu D, Senila M. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration. Materials. 2023; 16(5):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051914
Chicago/Turabian StyleCadar, Oana, Irina Vagner, Ion Miu, Daniela Scurtu, and Marin Senila. 2023. "Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration" Materials 16, no. 5: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051914
APA StyleCadar, O., Vagner, I., Miu, I., Scurtu, D., & Senila, M. (2023). Preparation, Characterization, and Performance of Natural Zeolites as Alternative Materials for Beer Filtration. Materials, 16(5), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051914









