Investigation of the Functional Ageing of Conductive Coated Fabrics under Simulated Washing Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
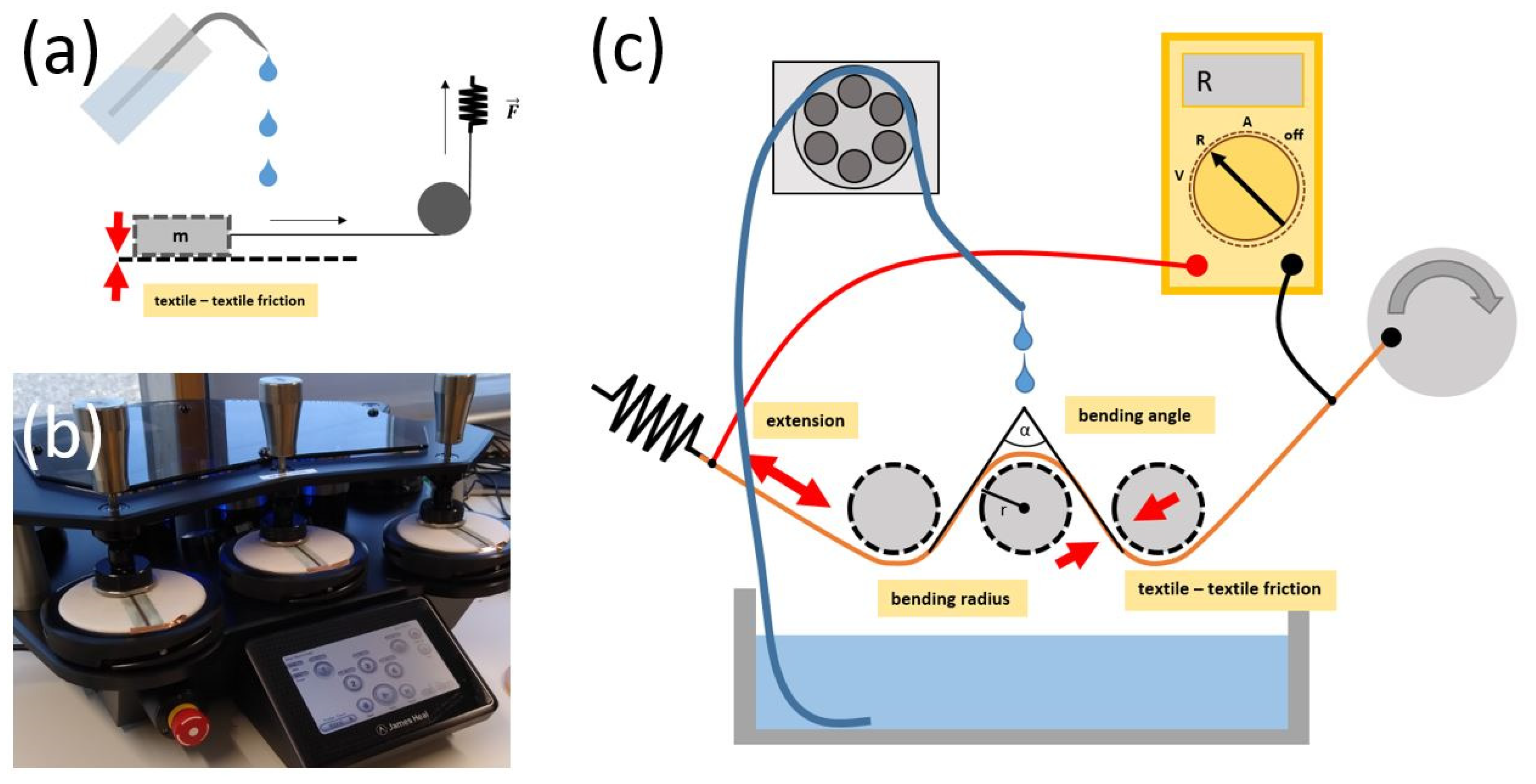
2.2. Tribological Investigation
2.3. Conductive Coating of the Fabrics
2.4. Cyclic Abrasion
2.5. Cyclic Extension
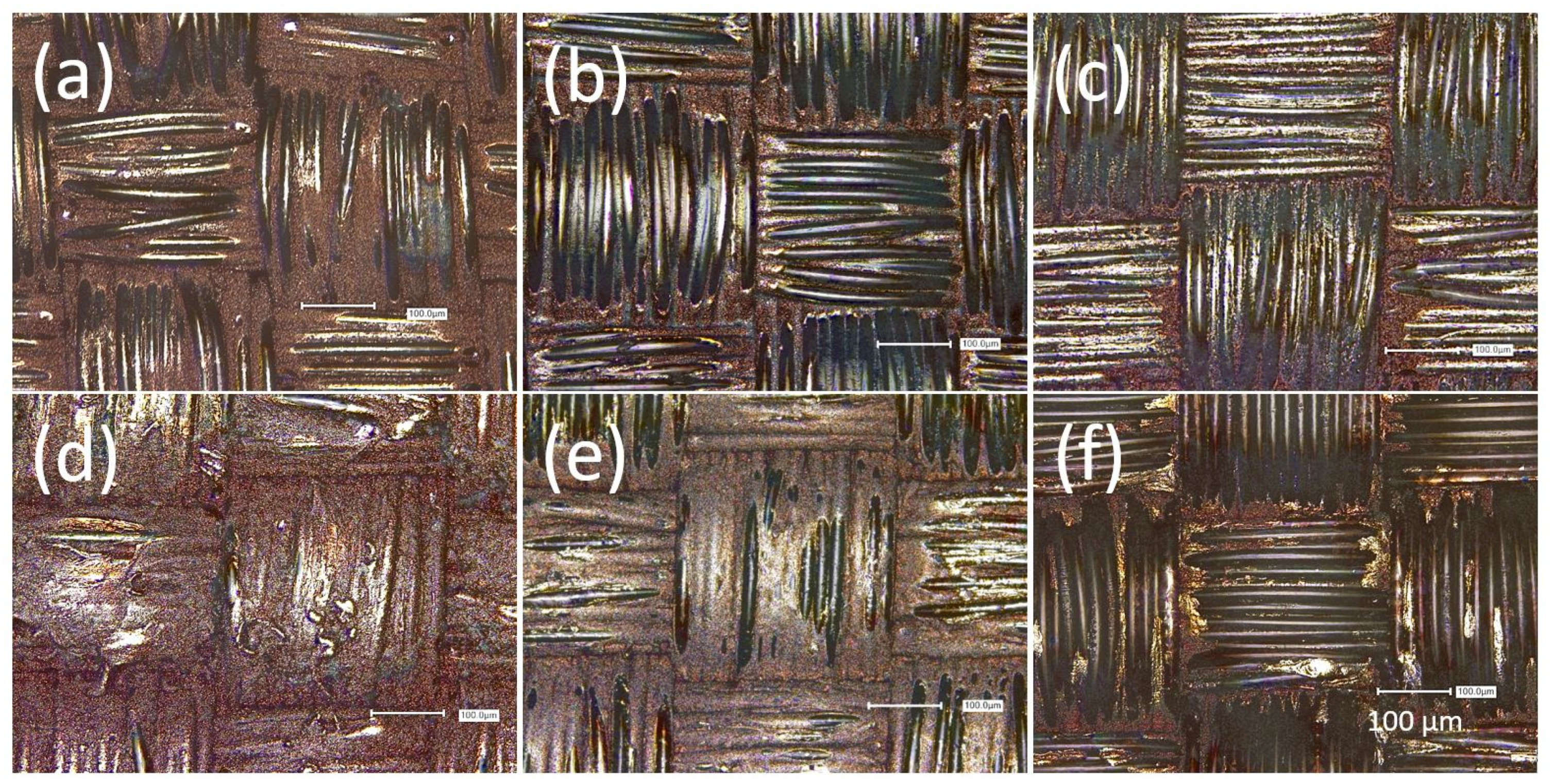
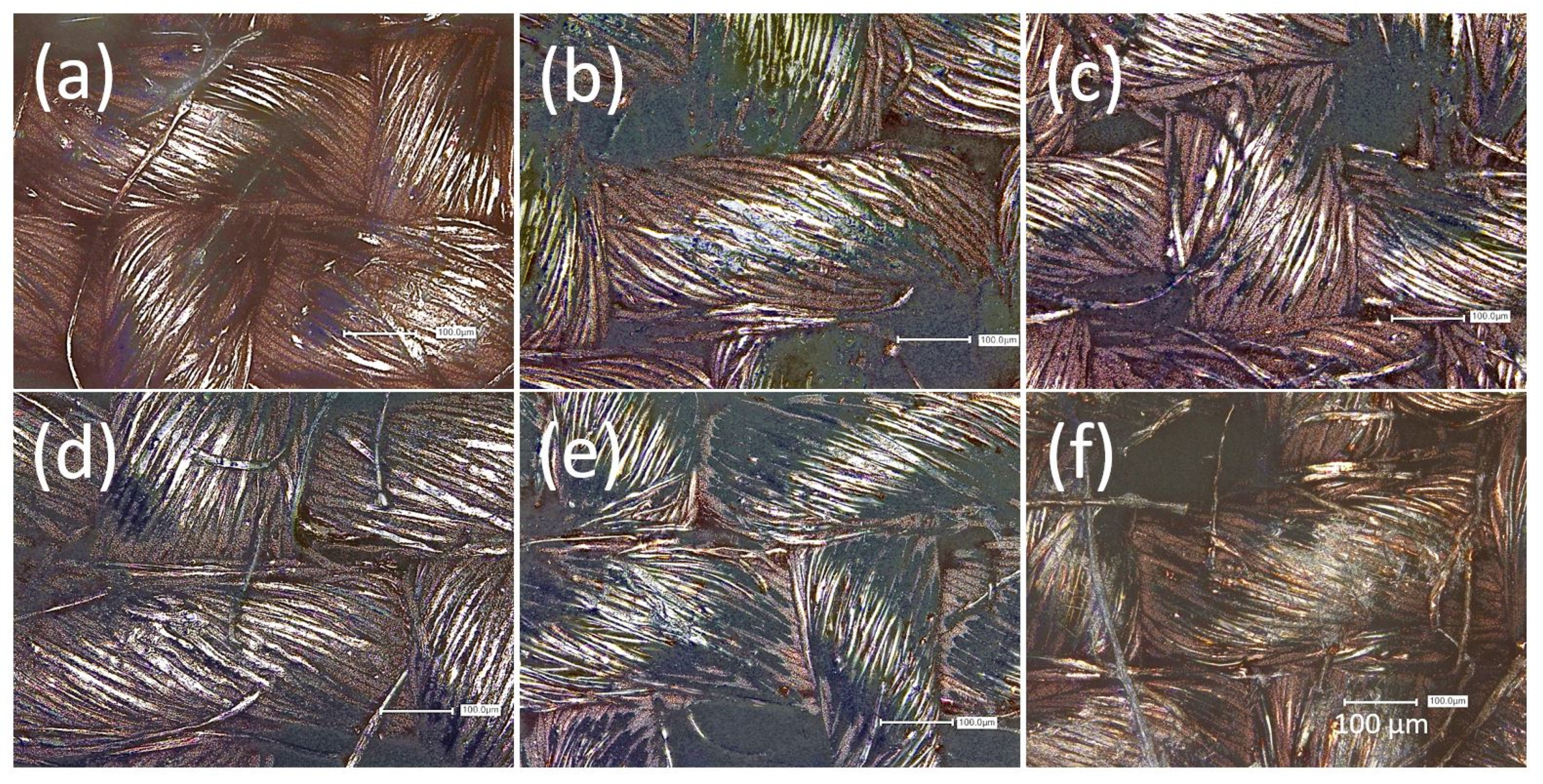
2.6. Laser Scanning Microscopy (LSM)
2.7. Dynamic Flex Tester
3. Results and Discussion
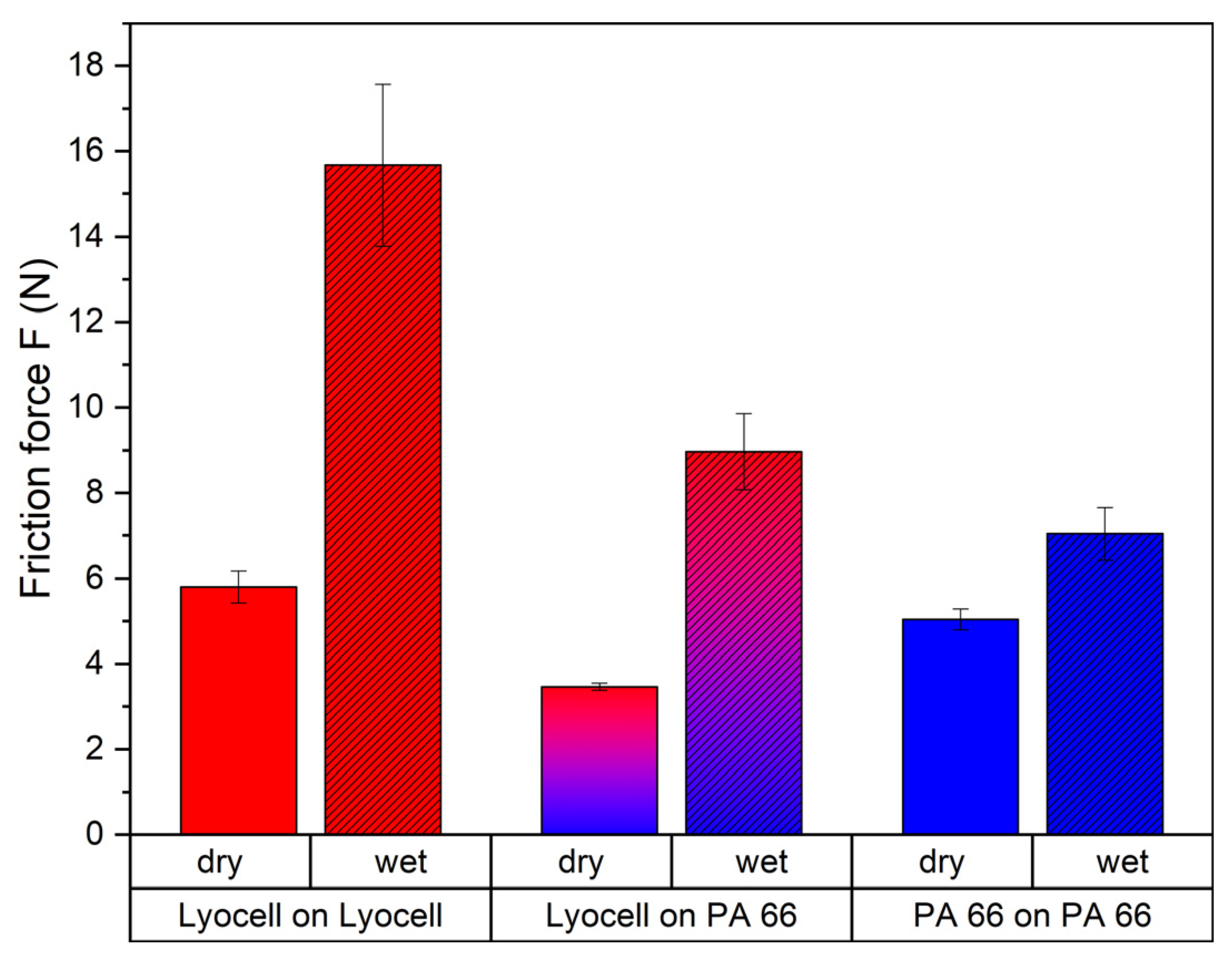
3.1. Dry and Wet Textile–Textile Friction
3.2. Cyclic Extension and Abrasion Testing
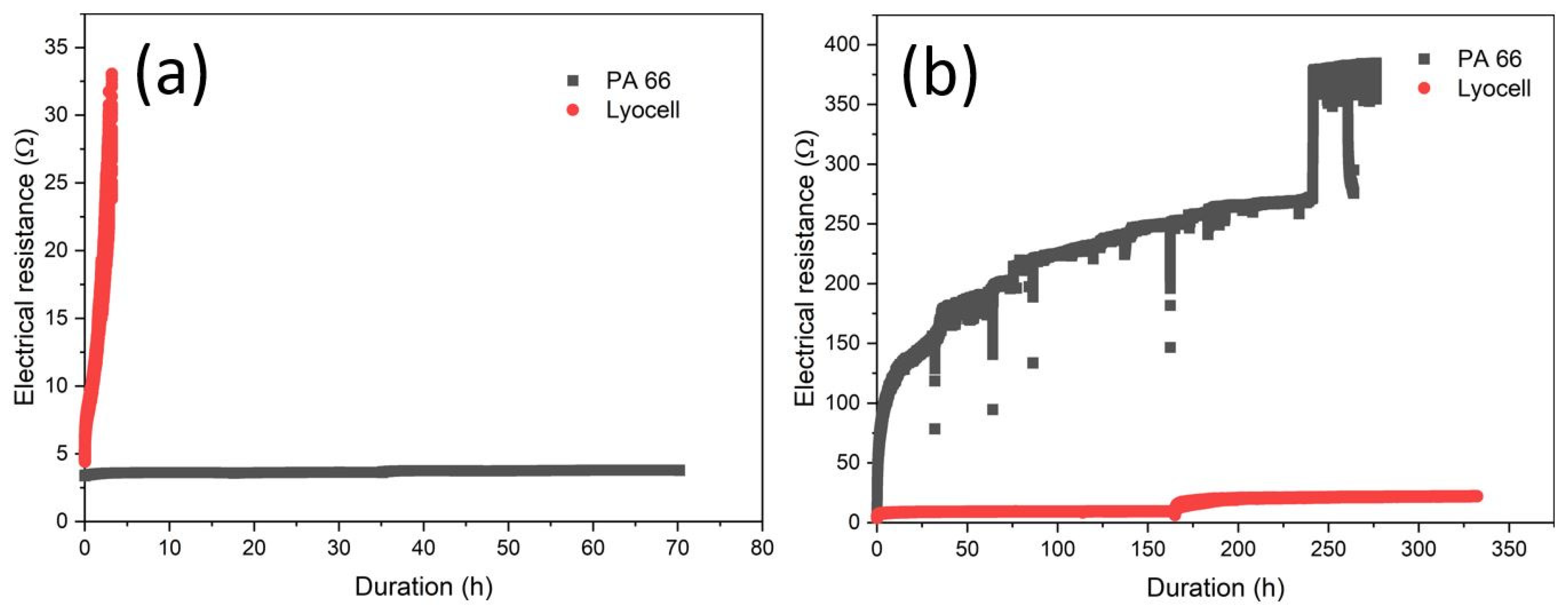
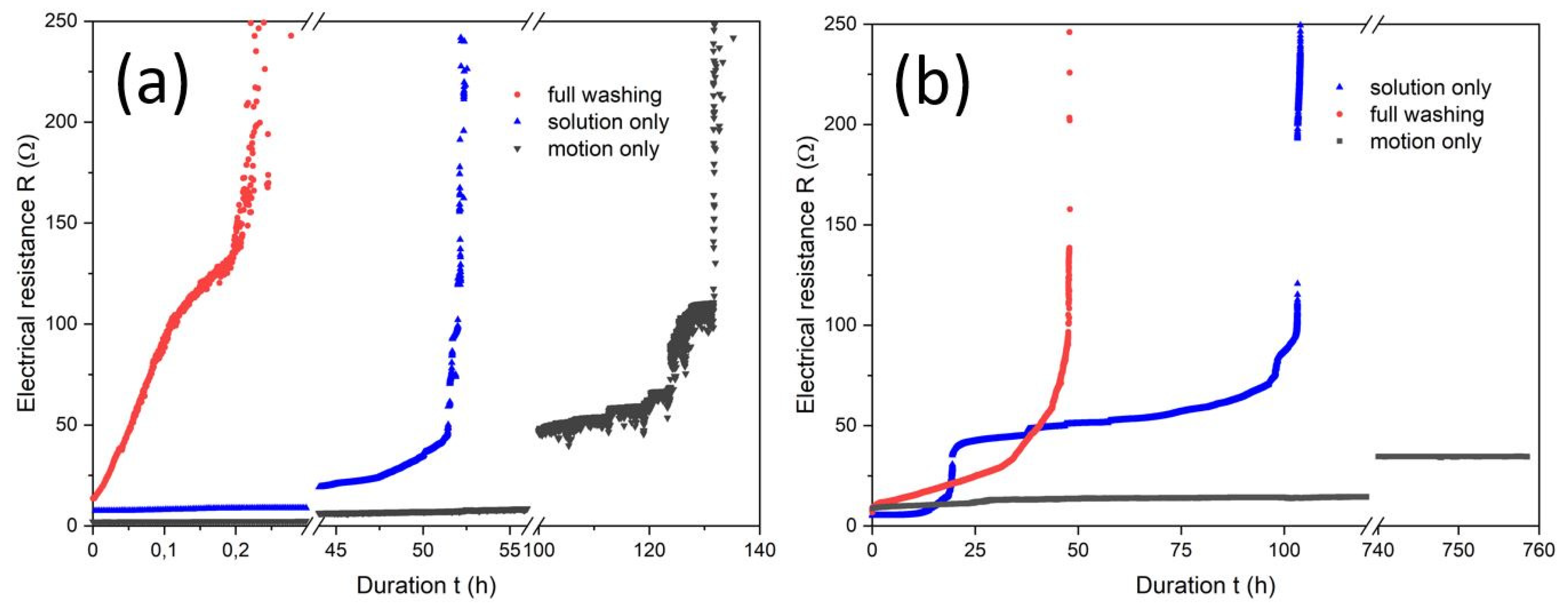
3.3. Ageing under Simulated Conditions in the Dynamic Flex Tester
3.4. Damage Modelling Theory
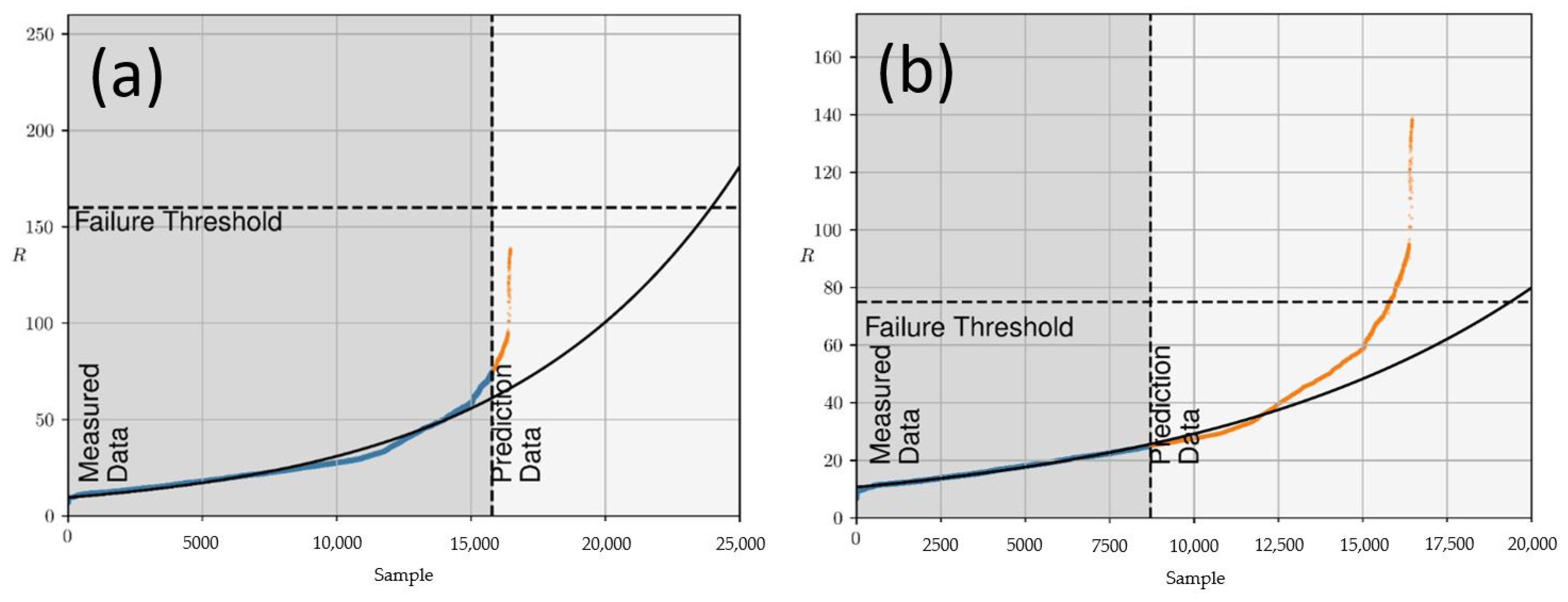
3.5. Prediction of Ageing
4. Conclusions
- Using the electrical resistance as an indicator for function, i.e., conductive percolation.
- The online resistance recording during treatment action.
- The time dependence of the chemical ageing via the corrosion rate and the time dependence of the mechanical ageing via the motor drive of 60 rpm.
- The separation of the ageing compartments, i.e., dry dynamic flex testing, wet dynamic flex testing and chemical ageing without motion.
- The imaging of the surficial damages and comparison with conventional ageing treatment, e.g., classical abrasion testing.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wepner, B.; Rhomberg, W.; Schartinger, D.; Zahradnik, G. Smart Textiles Studie; Bundesministerium für Klimaschutz, Umwelt, Energie, Mobilität, Innovation und Technologie: Vienna, Austria, 2020. (In Germany) [Google Scholar]
- Root, W.; Aguiló-Aguayo, N.; Pham, T.; Bechtold, T. Conductive Layers through Electroless Deposition of Copper on Woven Cellulose Lyocell Fabrics. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 348, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilampi, S.; Laine-Ma, T.; Ruuskanen, P. The Characterization of Electrically Conductive Silver Ink Patterns on Flexible Substrates. Microelectron. Reliab. 2009, 49, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, S.; Petz, P.; Eibensteiner, F. Feasibility Analysis of a Textile Metal Detector Utilizing a Conductive Yarn. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 July 2022; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, P.; Eibensteiner, F.; Langer, J. Performance Evaluation of Conductive Textiles for Movement Pattern Recognition in Smart Socks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Digital Technologies (IDT), Zilina, Slovakia, 25–27 June 2019; pp. 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petz, P.; Eibensteiner, F.; Langer, J. Sensor Shirt as Universal Platform for Real-Time Monitoring of Posture and Movements for Occupational Health and Ergonomics. In Procedia Computer Science; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 180, pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, W.; Wright, T.; Caven, B.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Flexible Textile Strain Sensor Based on Copper-Coated Lyocell Type Cellulose Fabric. Polymers 2019, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Root, W.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Textile-Integrated Thermocouples for Temperature Measurement. Materials 2020, 13, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, J.; Root, W.; Aguiló-Aguayo, N.; Duelli, H.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Multi-Point Flexible Temperature Sensor Array and Thermoelectric Generator Made from Copper-Coated Textiles. Sensors 2021, 21, 3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biermaier, C.; Gleißner, C.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Localised Catalyst Printing for Flexible Conductive Lines by Electroless Copper Deposition on Textiles. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Vienna, Austria, 10–13 July 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleissner, C.; Biermaier, C.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Complexation-Mediated Surface Modification of Polyamide-66 Textile to Enhance Electroless Copper Deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 288, 126383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermaier, C.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Towards the Functional Ageing of Electrically Conductive and Sensing Textiles: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Yao, D.; Hu, S.; Du, D.; Shao, W.; Tang, B.; Fan, J.M.; Tang, X.G.; Gao, J. Highly Conductive, Washable and Super-Hydrophobic Wearable Carbon Nanotubes e-Textile for Vacuum Pressure Sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 303, 111710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Mechael, S.S.; Chen, Y.; Carmichael, T.B. Solution Deposition of Conformal Gold Coatings on Knitted Fabric for E-Textiles and Electroluminescent Clothing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Otley, M.T.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Sinha, S.K.; Treich, G.M.; Sotzing, G.A. PEDOT:PSS “Wires” Printed on Textile for Wearable Electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Int. 2016, 8, 26998–27005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Hakuzimana, J.; Westbroek, P.; de Mey, G.; Priniotakis, G.; Nyokong, T.; van Langenhove, L. A Study on the Morphology of Thin Copper Films on Para-Aramid Yarns and Their Influence on the Yarn’s Electro-Conductive and Mechanical Properties. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 1587–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Hakuzimana, J.; Kaczynska, A.; Banaszczyk, J.; Westbroek, P.; McAdams, E.; Moody, G.; Chronis, Y.; Priniotakis, G.; de Mey, G.; et al. Gold Coated Para-Aramid Yarns through Electroless Deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1412–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Coulon, D.; Koncar, V. Washable and Reliable Textile Electrodes Embedded into Underwear Fabric for Electrocardiography (ECG) Monitoring. Materials 2018, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotzler, S.; von Krshiwoblozki, M.; Schneider-Ramelow, M. Washability of E-Textiles: Current Testing Practices and the Need for Standardization. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2401–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismar, E.; uz Zaman, S.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V. Effect of Water and Chemical Stresses on the Silver Coated Polyamide Yarns. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaubert, V.; Gidik, H.; Bodart, N.; Koncar, V. Investigating the Impact of Washing Cycles on Silver-Plated Textile Electrodes: A Complete Study. Sensors 2020, 20, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- uz Zaman, S.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V. Launderability of Conductive Polymer Yarns Used for Connections of E-Textile Modules: Mechanical Stresses. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 2355–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Seo, M.H.; Yang, S.; Koh, J.; Kim, H. The Effects of Mechanical Actions on Washing Efficiency. Fibers Polym. 2008, 9, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, R.; Acikgoz Tufan, H.; uz Zaman, S.; Cochrane, C.; Kursun Bahadir, S.; Koncar, V.; Kalaoglu, F. Protocol to Assess the Quality of Transmission Lines within Smart Textile Structures. Measurement 2020, 152, 107194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz Zaman, S.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V. Understanding the Washing Damage to Textile ECG Dry Skin Electrodes, Embroidered and Fabric-Based; Set up of Equivalent Laboratory Tests. Sensors 2020, 20, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Zaman, S.U.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Koncar, V.; Coulon, D. How to Connect Conductive Flexible Textile Tracks to Skin Electrocardiography Electrodes and Protect Them against Washing. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 11995–12002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.; Han, K.S. Cumulative Damage Models and Multi-Stress Fatigue Life Prediction. J. Compos. Mater. 1986, 20, 125–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Found, M.S.; Quaresimin, M.; Quaresimin, M. Two-Stage Fatigue Loading of Woven Carbon Fibre Reinforced Laminates. Fatigue Fract. Eging. Mater. Struct. 2003, 26, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Kok, M.; de Vries, H.; Pacheco, K.; van Heck, G. Failure Modes of Conducting Yarns in Electronic-Textile Applications. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, A.; Ahmed, I.-U.; Schaefer, J.A.; Scherge, M. Friction of Thin Water Films: A Nanotribological Study. Surf. Sci. 2002, 504, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Kreze, T.; Ribitsch, V.; Strnad, S. Reactivity and Electrokinetical Properties of Different Types of Regenerated Cellulose Fibres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 195, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashian, F.; Yaghoobi, Z.; Wilding, M.A. Thermal Behaviour of Lyocell Fibres. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komolafe, A.O.; Torah, R.N.; Tudor, M.J.; Beeby, S.P. Modelling and Experimental Validation of the Effect of the Elastic Properties of Fabrics on the Durability of Screen Printed E-Textiles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 75046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, M.; Berger, R.; Andersson, Y.; Hahlin, M.; Björefors, F.; Gustafsson, T.; Ottosson, M. Corrosion of Copper in Water Free from Molecular Oxygen. Corr. Engin. Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, D.J.G.; Rawson, E. Copper Corrosion III: Electrochemical Theory of General Corrosion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1962, 109, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, D.J.G.; Rawson, A.E. Copper Corrosion II. Kinetic Studies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1962, 109, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Okubayashi, S.; Bechtold, T. Fibrillation Tendency of Cellulosic Fibers. Part 1: Effects of Swelling. Cellulose 2005, 12, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongdee, A.; Bechtold, T.; Burtscher, E.; Scheinecker, M. The Influence of Wet/Dry Treatment on Pore Structure-the Correlation of Pore Parameters, Water Retention and Moisture Regain Values. Carbohyd. Polym. 2004, 57, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rous, M.; Varga, K.; Bechtold, T.; Schuster, K.C. A New Method to Visualize and Characterize the Pore Structure of TENCEL® (Lyocell) and Other Man-Made Cellulosic Fibres Using a Fluorescent Dye Molecular Probe. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtold, T.; Manian, A.P.; Öztürk, H.B.; Paul, U.; Široká, B.; Široký, J.; Soliman, H.; Vo, L.T.T.; Vu-Manh, H. Ion-Interactions as Driving Force in Polysaccharide Assembly. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, T.C.; Paulapuro, H.; Steinius, P. Hydration and Swelling of Pulp Fibers Measured with Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Nord. Pulp Paper Res. J. 2018, 13, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, H.; Hatakeyama, T. Interaction between Water and Hydrophilic Polymers. Thermochim. Acta 1998, 308, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driemeier, C.; Mendes, F.M.; Oliveira, M.M. Dynamic Vapor Sorption and Thermoporometry to Probe Water in Celluloses. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Venditti, R.A.; Jameel, H.; Pawlak, J.J. Studies of the Heat of Vaporization of Water Associated with Cellulose Fibers Characterized by Thermal Analysis. Cellulose 2007, 14, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczeniewski, E.; Bryk, P.; Koter, S.; Kowalczyk, P.; Kujawski, W.; Kujawa, J.; Terzyk, A.P. Revisiting Wetting, Freezing, and Evaporation Mechanisms of Water on Copper. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37893–37903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, A.; Haq, S. Water Adsorption and the Wetting of Metal Surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2009, 64, 381–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisner, A.; Rainert, K.T.; Ferrari, F.; Nau, C.T.; Barcellos, I.O.; Pezzin, S.H.; Andreaus, J. Chemical Functionalization of Polyamide 6.6 Fabrics. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Xu, F.; Liu, W.; Zhou, M.; Li, W.; Hui, D.; Qiu, Y. Influence of Cryogenic Treatment on Mechanical and Interfacial Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fiber/Bisphenol-F Epoxy Composite. Compos. B Eng. 2017, 125, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Li, W.; Du, X.; Chen, N.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, J. Electrically Conductive Silver/Polyimide Fabric Composites Fabricated by Spray-Assisted Electroless Plating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Yin, L.; Zhang, S. Copper Corrosion Inhibition by Combined Effect of Inhibitor and Passive Film in Alkaline Solution. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2015, 41, 8557–8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Construction Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| roll length | 55 mm |
| final roll diameter | 16 mm (with wrapped fabric) |
| roll–roll centre distance | 22 mm |
| abradant | Lyocell, plain woven |
| bending angle α | 86° |
| diameter crank rotation | 50 mm |
| spring stiffness | 0.046 ± 0.002 N/mm |
| maximum spring force in exp. setup | 3 N |
| distance centre of roll and centre of crank | 120 mm vertical/115 mm horizontal |
| distance spring attachment—roll | 250 mm |
| power (motor) | 72 W |
| rotation speed | 60 rpm |
| Resistance of a Conductive Line (Ω) | Lost Energy in Textile (W) | Max. Baud Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 mA | 80 mA | 160 mA | ||
| 10 | 0.032 | 0.128 | 0.512 | 921,000 |
| 160 | 0.512 | 2.048 | 8.192 | 921,000 |
| 250 | 0.800 | 3.200 | 12.800 | 921,000 |
| 500 | 1.600 | 6.400 | 25.600 | 576,000 |
| 1250 | 4.000 | 16.000 | 64.000 | 256,000 |
| 2700 | 8.640 | 34.560 | 138.240 | 115,200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biermaier, C.; Petz, P.; Bechtold, T.; Pham, T. Investigation of the Functional Ageing of Conductive Coated Fabrics under Simulated Washing Conditions. Materials 2023, 16, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030912
Biermaier C, Petz P, Bechtold T, Pham T. Investigation of the Functional Ageing of Conductive Coated Fabrics under Simulated Washing Conditions. Materials. 2023; 16(3):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030912
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiermaier, Christian, Phillip Petz, Thomas Bechtold, and Tung Pham. 2023. "Investigation of the Functional Ageing of Conductive Coated Fabrics under Simulated Washing Conditions" Materials 16, no. 3: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030912
APA StyleBiermaier, C., Petz, P., Bechtold, T., & Pham, T. (2023). Investigation of the Functional Ageing of Conductive Coated Fabrics under Simulated Washing Conditions. Materials, 16(3), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16030912







