Out-of-Plane Compression Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy Large-Scale Super-Stub Honeycomb Cellular Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Study
2.1. Testing Specimens
2.2. Material Properties
2.3. Out-of-Plane Compression Tests
3. Numerical Simulation
3.1. Numerical Modelling
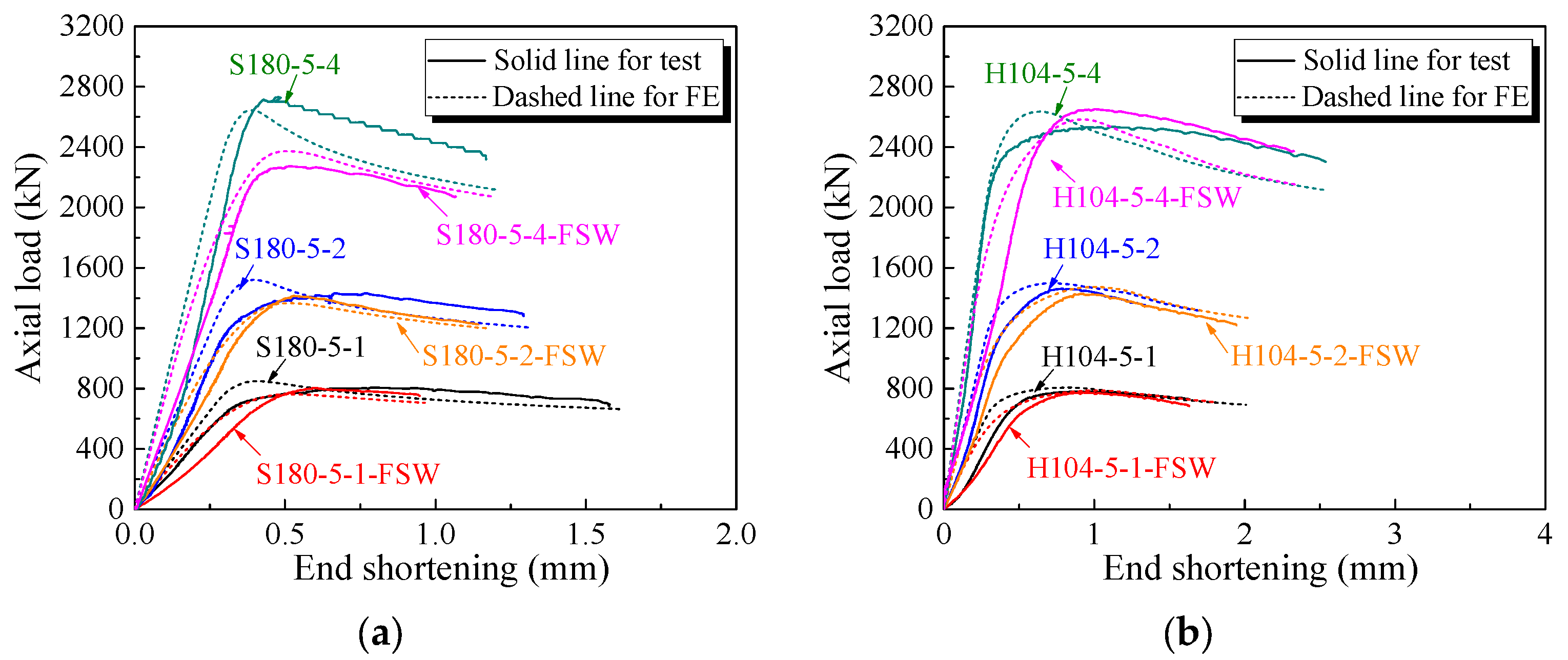
3.2. Validation of FE Models
3.3. Parametric Analysis
4. Out-of-Plane Compression Design
4.1. GB 50429-2007
4.2. EN 1999-1-1: 2007
4.3. The American Aluminum Design Manual (AADM-2015)
4.4. Evaluation of Current Codified Design Methods
4.5. Improved Design Approach
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The non-welded and welded SHS honeycomb specimens failed by local buckling before cross-section yielding, while the non-welded and welded HHS honeycomb specimens failed by local buckling after cross-section yielding.
- (2)
- The design rules set out in GB 50429-2007, EN 1999-1-1: 2007 and AADM-2015 generally yielded very conservative predictions for the out-of-plane compression resistances of aluminium alloy SHS and HHS super-stub honeycomb cores without and with FSW facesheets by about 30–37%, based on the experimental and parametric analysis results.
- (3)
- Modifications to the cross-section effective thickness within the framework of GB 50429-2007 method, applicable to single, double and four SHS and HHS super-stub cells without and with FSW facesheets, were proposed and shown to provide much more accurate and consistent predictions than current design methods.
- (4)
- Facesheets can be effectively fixed to the end of SHS and HHS honeycomb cores to form a sandwich configuration by FSW without failure occurring at the weld zone and with a strength reduction of less than 11% compared with non-welded specimens.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, M.Y.; Han, D.; Chen, N.K.; Wang, D.; Li, X.B. Recent progress in double-layer honeycomb structure: A new type of two-dimensional material. Materials 2022, 15, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yu, G.; Wu, L. Fabrication and mechanical behaviors of quartz fiber composite honeycomb with extremely low permittivity. Compos. Struct. 2021, 271, 114129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciepielewski, R.; Gieleta, R.; Miedzin’ska, D. Experimental study on static and dynamic response of aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures. Materials 2022, 15, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, C.C.; Seah, L.K.; Chai, G.B. Low-velocity impact failure of aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels. Compos. Struct. 2008, 85, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.S.; Sun, Z.; Hu, X.Z.; Chen, H.R. Flexural strength and energy absorption of carbon-fiber-aluminum honeycomb composite sandwich reinforced by aluminum grid. Thin-Walled Struct. 2014, 84, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.D.; Ruan, D.; Lu, G.X.; Guillow, S.; Yoon, J.W. Crushing response of square aluminium tubes filled with polyurethane foam and aluminium honeycomb. Thin-Walled Struct. 2017, 110, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.J.; Ye, H.Y.; Yang, W.; Qi, J.K.; Liu, Y.B.; Yuan, T.Y.; Wang, Y. Mechanical behaviors of inner and outer sidewalls of honeycomb cores subjected to out-of-plane compression. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 107659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Ren, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, F. Impact Response of the Honeycomb Sandwich Structure with Different Poisson’s Ratios. Materials 2022, 15, 6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langseth, M.; Hopperstad, O.S. Local buckling of square thin-walled aluminium extrusions. Thin-Walled Struct. 1997, 27, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faella, C.; Mazzolani, F.M.; Piluso, V.; Rizzano, G. Local buckling of aluminum members: Testing and classification. J. Struct. Eng. 2000, 126, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Young, B. Experimental investigation of aluminum alloy circular hollow section columns. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.N.; Yound, B.; Gardner, L. Testing and design of aluminum alloy cross sections in compression. J. Struct. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chang, T.; Du, X.X.; Bu, Y.D.; Shi, Y.J. Local buckling and postbuckling strength of extruded aluminium alloy stub columns with slender I-sections. Thin-Walled Struct. 2015, 90, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, B.B.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, Y.W. Axial compression behaviour of 7A04-T6 high-strength aluminium alloy SHS and RHS stub columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 180, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.B.; Ouyang, Y.W. Study of local buckling performance of 7075-T6 high-strength aluminium alloy H-section stub columns. Thin-Walled Struct. 2022, 180, 109925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 50429-2007; Code for Design of Aluminium Structures. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- EN 1999-1-1:2007; Eurocode 9: Design of Aluminium Structures; Part 1-1: General Structural Rules. European Committee for Standarization: Brussels, Belgium, 2007.
- Aluminum Association (AA). Aluminum Design Manual; Aluminum Association (AA): Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- ABAQUS. ABAQUS Standard User’s Manual, Version 6.14; Dassault Systemes Corp.: Providence, RI, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.B.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhi, X.H.; Zhang, Y.; Baniotopoulos, C.C. Testing, modelling and design of 7A04-T6 high-strength aluminium alloy RHS columns under axial compression. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
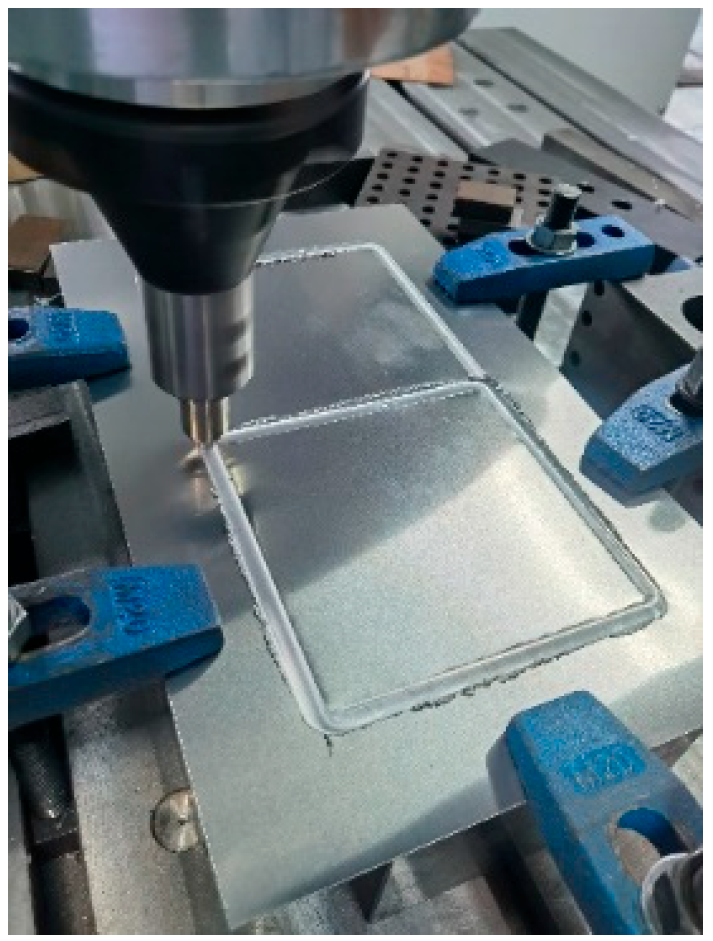
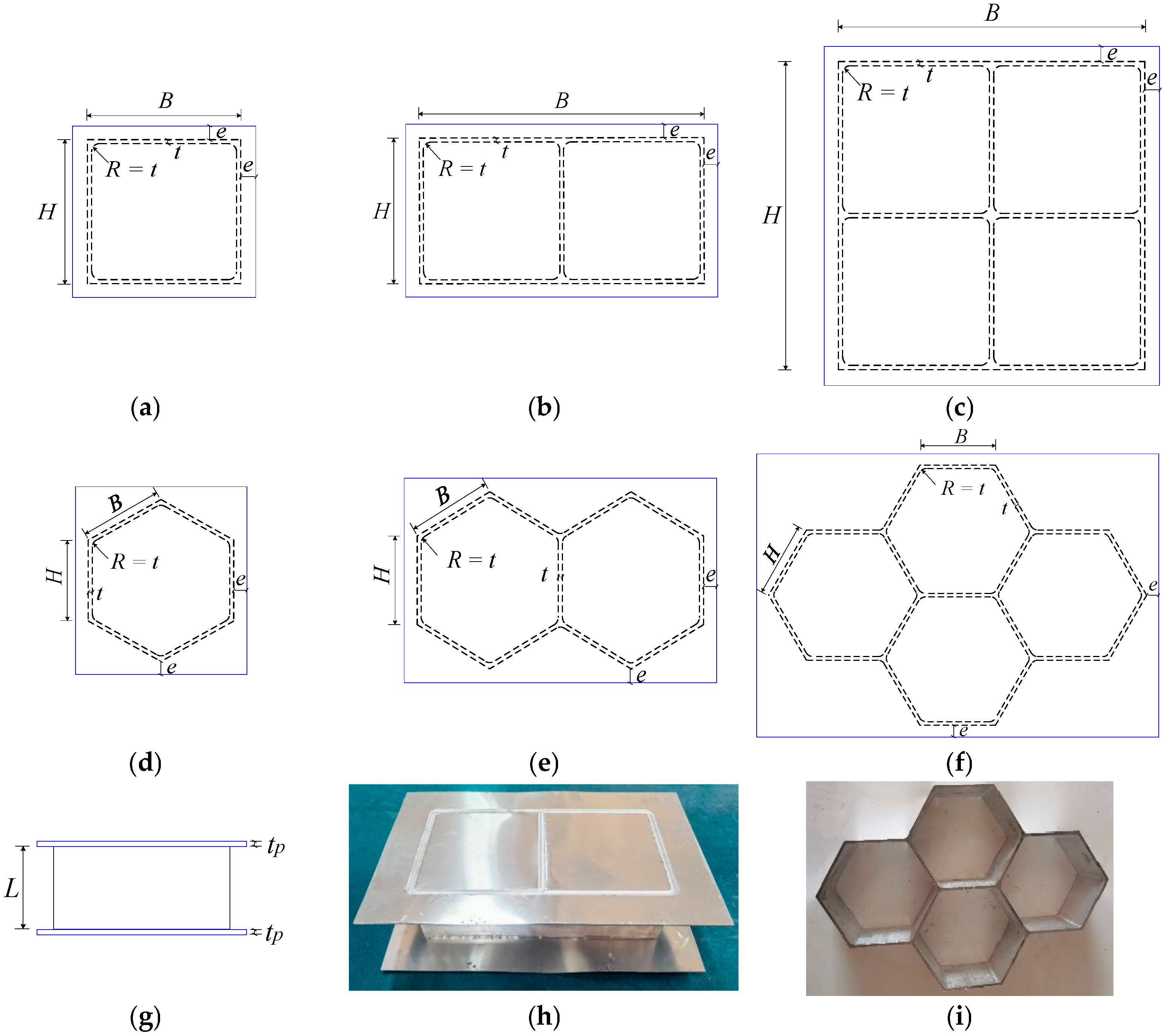
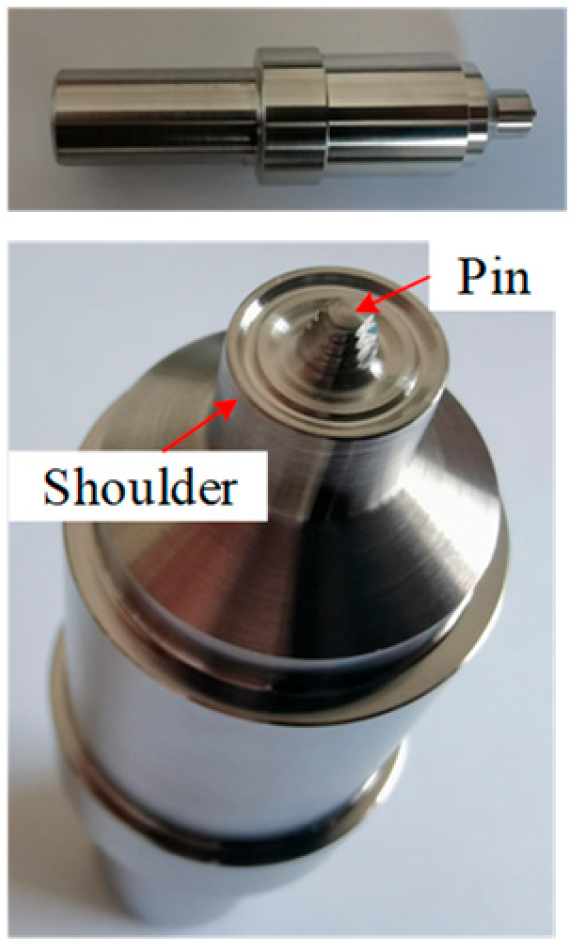


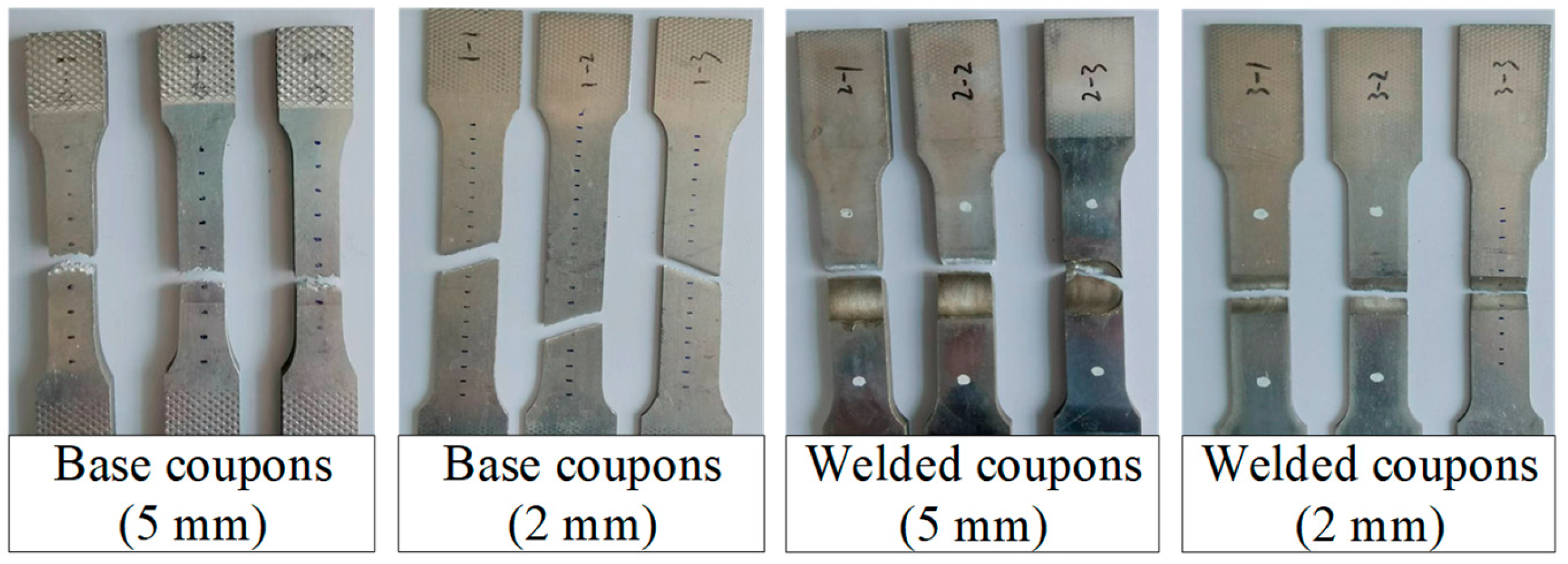

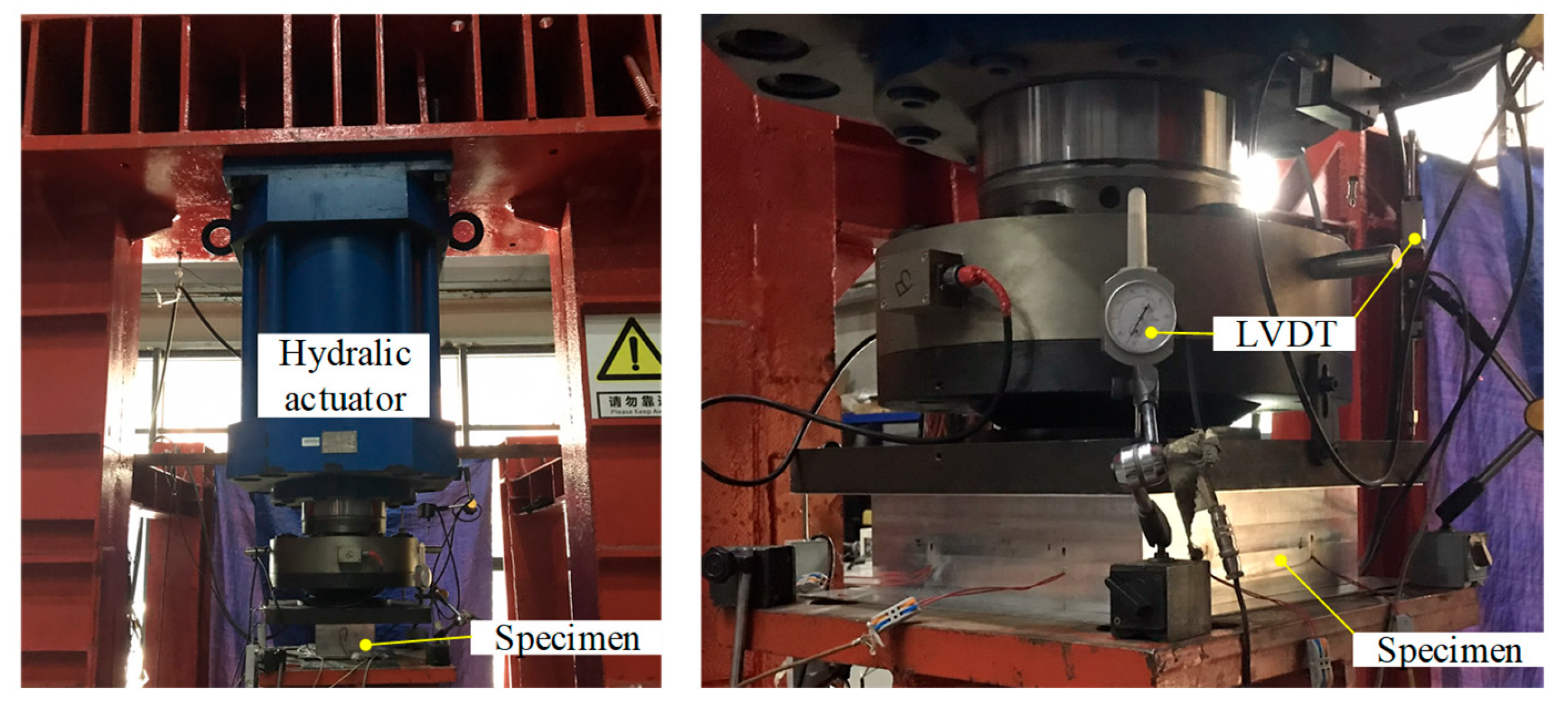
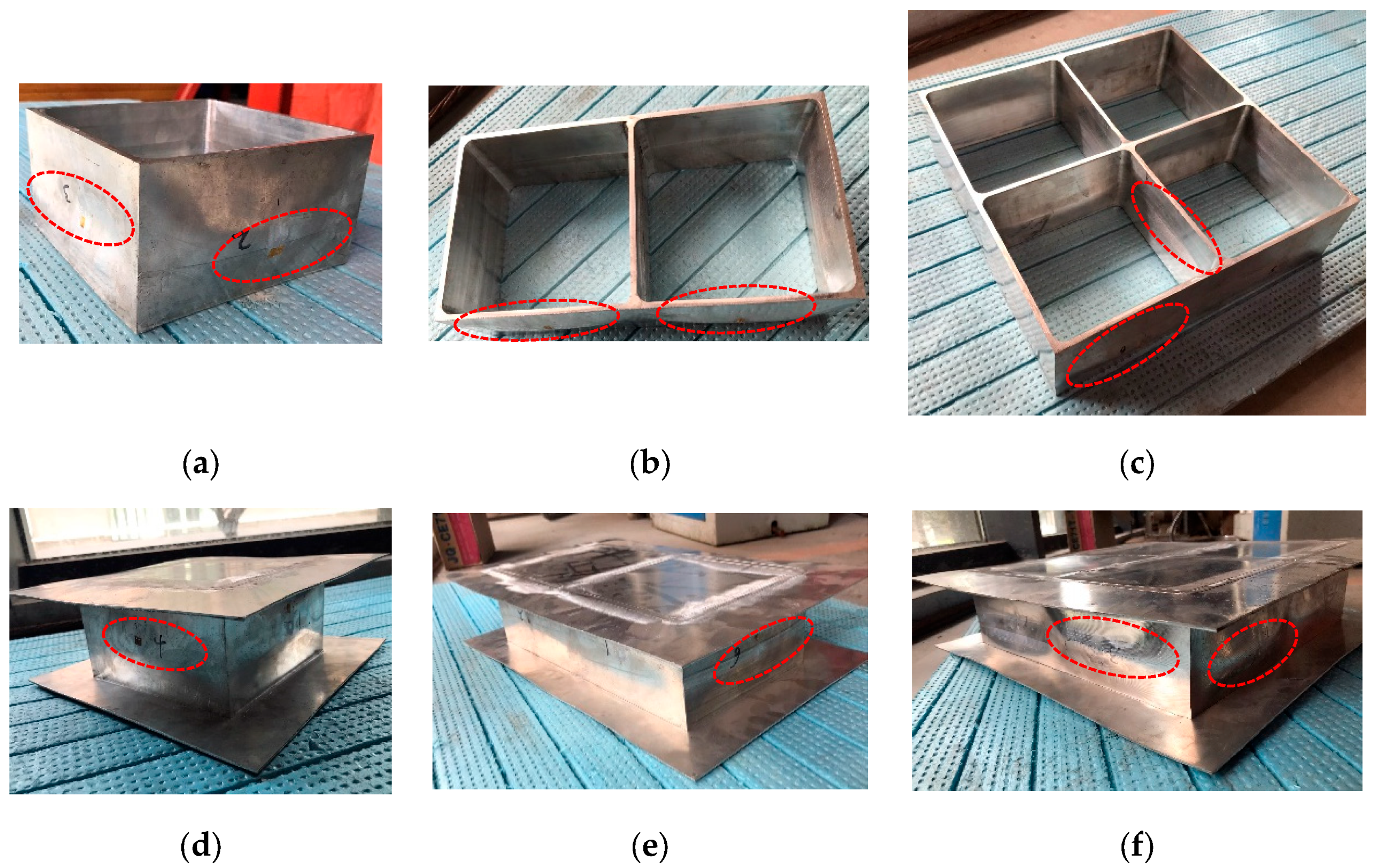
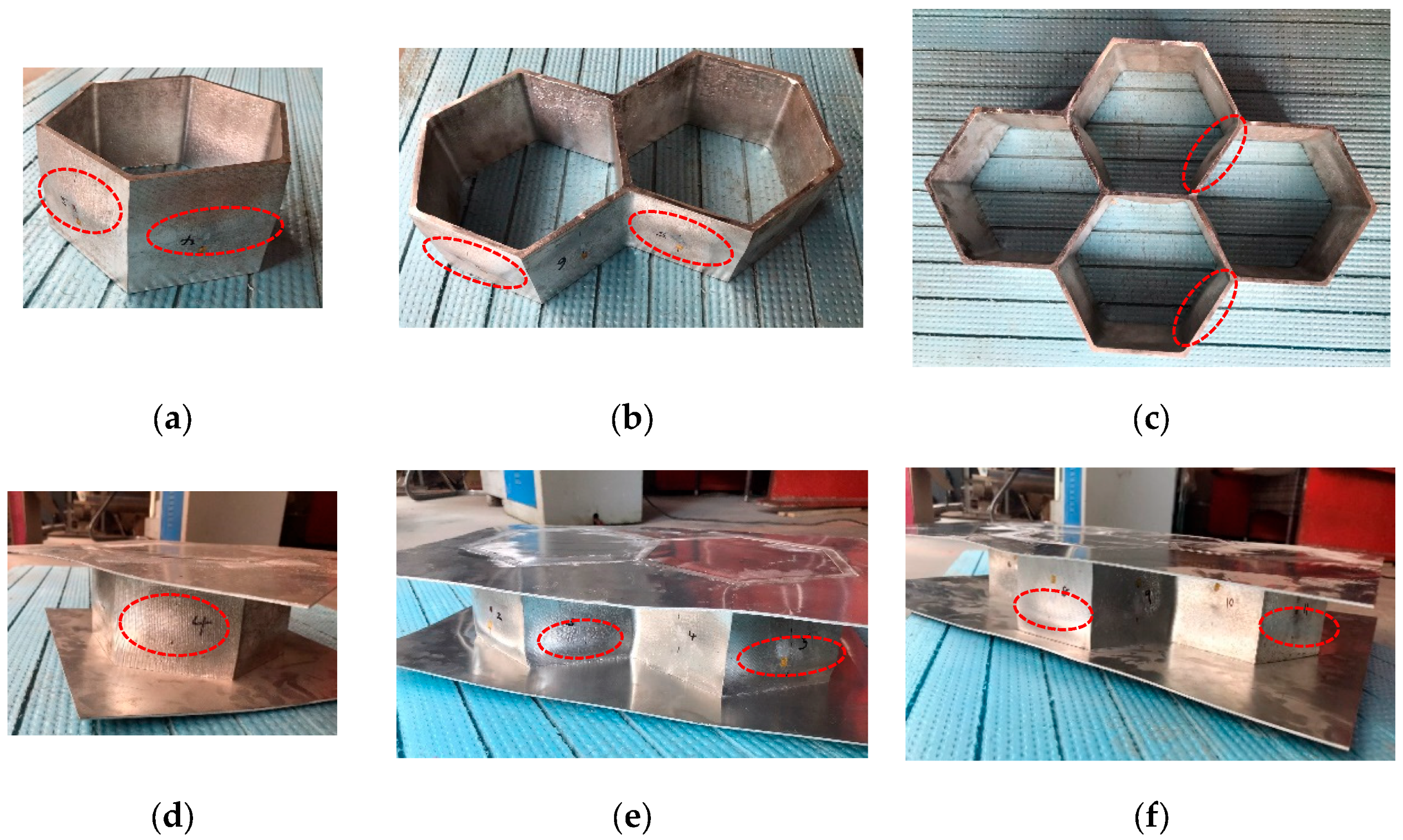





| Specimen | B (mm) | H (mm) | t (mm) | tp (mm) | Ag (mm2) | L (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S180-5-1 | 180.2 | 180.4 | 5.0 | — | 3585.8 | 100.4 |
| S180-5-2 | 354.7 | 180.2 | 4.9 | — | 6318.4 | 101.0 |
| S180-5-4 | 355.3 | 355.0 | 4.9 | — | 10,912.7 | 100.7 |
| H104-5-1 | 104.1 | 104.4 | 5.1 | — | 3069.6 | 100.5 |
| H104-5-2 | 103.7 | 103.8 | 5.0 | — | 5614.8 | 100.4 |
| H104-5-4 | 104.3 | 104.2 | 4.8 | — | 9812.7 | 100.6 |
| S180-5-1-FSW | 179.6 | 180.1 | 5.1 | 2.0 | 3588.5 | 101.2 |
| S180-5-2-FSW | 355.2 | 180.3 | 5.0 | 1.9 | 6321.7 | 100.8 |
| S180-5-4-FSW | 355.2 | 355.2 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 10,919.4 | 99.2 |
| H104-5-1-FSW | 104.6 | 105.2 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 3061.7 | 100.5 |
| H104-5-2-FSW | 105.1 | 105.1 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 5611.4 | 100.6 |
| H104-5-4-FSW | 104.8 | 105.3 | 5.1 | 2.0 | 9821.2 | 100.4 |
| Category | Specimen | Thickness (mm) | E | f0.2 | fu | εu (%) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (GPa) | (MPa) | (MPa) | |||||
| Base aluminium alloy coupons | 0-1 | 5.02 | 71,783 | 245.63 | 299.82 | 5.37 | 16.12 |
| 0-2 | 4.93 | 67,276 | 250.11 | 302.92 | 5.60 | 16.89 | |
| 0-3 | 4.91 | 67,712 | 251.20 | 304.16 | 5.18 | 16.78 | |
| SD | 0.048 | 2030 | 2.41 | 1.83 | 0.17 | 0.34 | |
| 1-1 | 2.04 | 66,721 | 172.07 | 225.78 | 11.23 | 14.91 | |
| 1-2 | 2.07 | 67,626 | 171.65 | 225.09 | 10.67 | 14.75 | |
| 1-3 | 1.96 | 65,707 | 171.34 | 224.38 | 12.48 | 14.88 | |
| SD | 0.046 | 784 | 0.30 | 0.57 | 0.76 | 0.07 | |
| Welded aluminium alloy coupons | 2-1 | 5.08 | 68,942 | 146.17 | 241.87 | 4.01 | 5.71 |
| 2-2 | 5.04 | 68,615 | 153.51 | 240.30 | 4.12 | 5.89 | |
| 2-3 | 5.03 | 71,162 | 159.15 | 236.07 | 3.89 | 6.56 | |
| SD | 0.022 | 1131 | 5.31 | 2.45 | 0.09 | 0.37 | |
| 3-1 | 2.06 | 68,225 | 130.19 | 190.16 | 3.96 | 7.74 | |
| 3-2 | 2.01 | 67,188 | 131.79 | 169.42 | 2.43 | 9.42 | |
| 3-3 | 1.95 | 71,173 | 130.14 | 188.20 | 3.67 | 7.36 | |
| SD | 0.045 | 1688 | 0.77 | 9.35 | 0.66 | 0.90 |
| Specimen | Nexp (kN) | NFE (kN) | NFE /Nexp | Specimen | Nexp (kN) | NFE (kN) | NFE /Nexp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S180-5-1 | 806.66 | 849.50 | 1.05 | H104-5-1 | 781.22 | 806.16 | 1.03 |
| S180-5-1-FSW | 804.62 | 762.26 | 0.95 | H104-5-1-FSW | 773.25 | 786.51 | 1.02 |
| S180-5-2 | 1431.01 | 1521.37 | 1.06 | H104-5-2 | 1462.03 | 1497.84 | 1.02 |
| S180-5-2-FSW | 1414.53 | 1366.81 | 0.97 | H104-5-2-FSW | 1428.72 | 1473.32 | 1.03 |
| S180-5-4 | 2731.05 | 2645.16 | 0.97 | H104-5-4 | 2534.97 | 2634.86 | 1.04 |
| S180-5-4-FSW | 2273.35 | 2374.61 | 1.04 | H104-5-4-FSW | 2650.53 | 2582.97 | 0.97 |
| Mean | 1.01 | ||||||
| COV | 0.037 |
| bf/t | B × H | bf/t | B × H | bf/t | B × H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 90 × 90 | 38 | 200 × 200 | 60 | 310 × 310 |
| 18 | 100 × 100 | 40 | 210 × 210 | 62 | 320 × 320 |
| 20 | 110 × 110 | 42 | 220 × 220 | 64 | 330 × 330 |
| 22 | 120 × 120 | 44 | 230 × 230 | 66 | 340 × 340 |
| 24 | 130 × 130 | 46 | 240 × 240 | 68 | 350 × 350 |
| 26 | 140 × 140 | 48 | 250 × 250 | 70 | 360 × 360 |
| 28 | 150 × 150 | 50 | 260 × 260 | 72 | 370 × 370 |
| 30 | 160 × 160 | 52 | 270 × 270 | 74 | 380 × 380 |
| 32 | 170 × 170 | 54 | 280 × 280 | 76 | 390 × 390 |
| 34 | 180 × 180 | 56 | 290 × 290 | 78 | 400 × 400 |
| 36 | 190 × 190 | 58 | 300 × 300 | 80 | 410 × 410 |
| bf/t | B × H | bf/t | B × H | bf/t | B × H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16.05 | 86 × 86 | 38.05 | 196 × 196 | 60.05 | 306 × 306 |
| 18.05 | 96 × 96 | 40.05 | 206 × 206 | 62.05 | 316 × 316 |
| 20.05 | 106 × 106 | 42.05 | 216 × 216 | 64.05 | 326 × 326 |
| 22.05 | 116 × 116 | 44.05 | 226 × 226 | 66.05 | 336 × 336 |
| 24.05 | 126 × 126 | 46.05 | 236 × 236 | 68.05 | 346 × 346 |
| 26.05 | 136 × 136 | 48.05 | 246 × 246 | 70.05 | 356 × 356 |
| 28.05 | 146 × 146 | 50.05 | 256 × 256 | 72.05 | 366 × 366 |
| 30.05 | 156 × 156 | 52.05 | 266 × 266 | 74.05 | 376 × 376 |
| 32.05 | 166 × 166 | 54.05 | 276 × 276 | 76.05 | 386 × 386 |
| 34.05 | 176 × 176 | 56.05 | 286 × 286 | 78.05 | 396 × 396 |
| 36.05 | 186 × 186 | 58.05 | 296 × 296 |
| Non-welded honeycomb specimens | |||
| Ratio | NGB/Nexp/FE | NEC9/Nexp/FE | NAADM/Nexp/FE |
| Mean | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.67 |
| COV | 0.258 | 0.256 | 0.294 |
| Honeycomb specimens with FSW facesheets | |||
| Ratio | NGB/Nexp/FE | NEC9/Nexp/FE | NAADM/Nexp/FE |
| Mean | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.70 |
| COV | 0.178 | 0.173 | 0.276 |
| Non-welded honeycomb specimens | |||
| Case | Single SHS or HHS | Double or four SHSs | Double or four HHSs |
| Ratio | NMGB/Nexp/FE | NMGB/Nexp/FE | NMGB/Nexp/FE |
| Mean | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| COV | 0.022 | 0.026 | 0.022 |
| Honeycomb specimens with FSW facesheets | |||
| Case | Single SHS or HHS | Double or four SHSs | Double or four HHSs |
| Ratio | NMGB/Nexp/FE | NMGB/Nexp/FE | NMGB/Nexp/FE |
| Mean | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.99 |
| COV | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Yuan, M.; Zhao, B.; Li, B. Out-of-Plane Compression Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy Large-Scale Super-Stub Honeycomb Cellular Structures. Materials 2023, 16, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031241
Lin S, Yuan M, Zhao B, Li B. Out-of-Plane Compression Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy Large-Scale Super-Stub Honeycomb Cellular Structures. Materials. 2023; 16(3):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031241
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Song, Meini Yuan, Bing Zhao, and Beibei Li. 2023. "Out-of-Plane Compression Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy Large-Scale Super-Stub Honeycomb Cellular Structures" Materials 16, no. 3: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031241
APA StyleLin, S., Yuan, M., Zhao, B., & Li, B. (2023). Out-of-Plane Compression Behaviour of Aluminum Alloy Large-Scale Super-Stub Honeycomb Cellular Structures. Materials, 16(3), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031241






