Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Alloy with High Boron Content for the Pre-Sintered Preform (PSP) Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
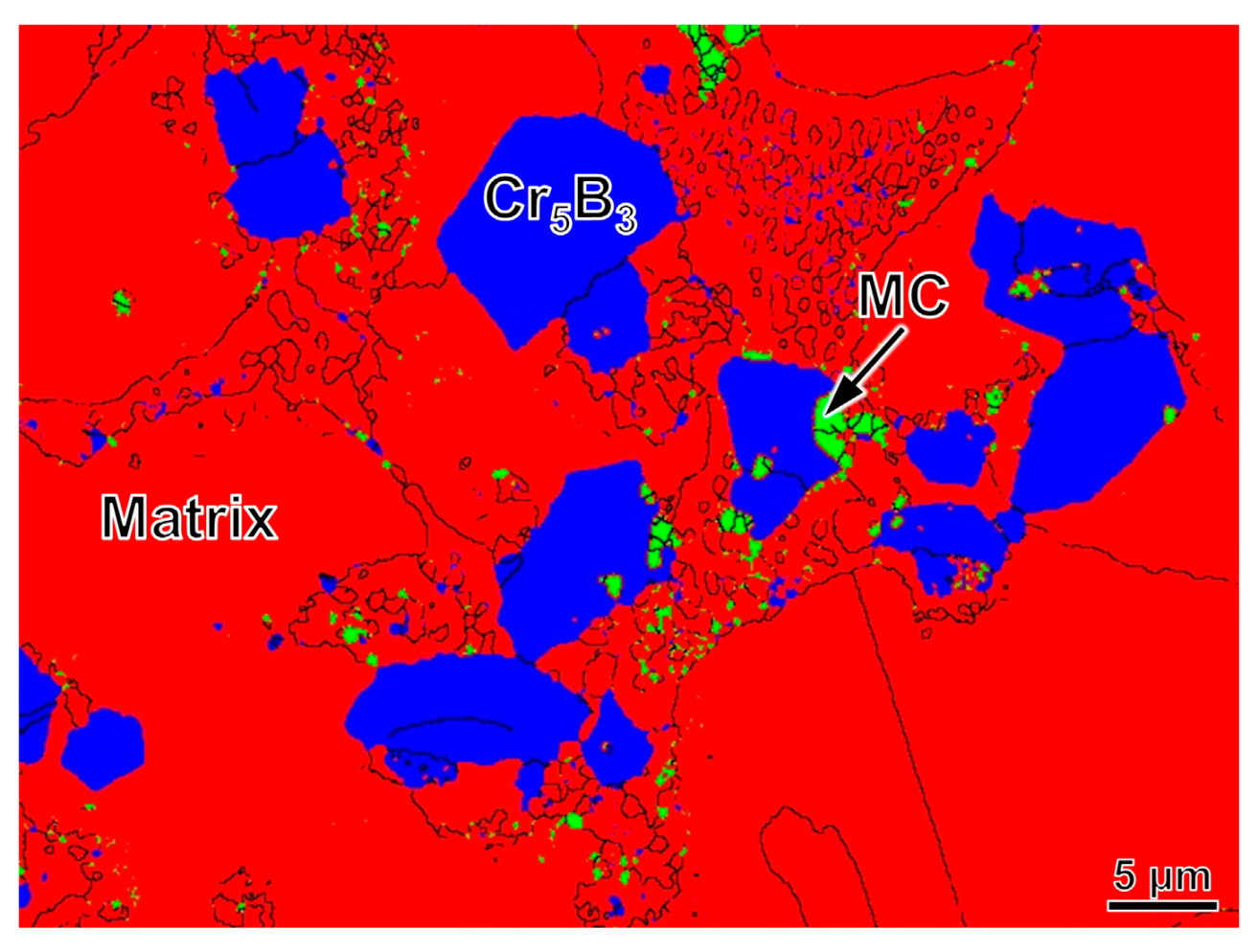
3.1. Microstructures
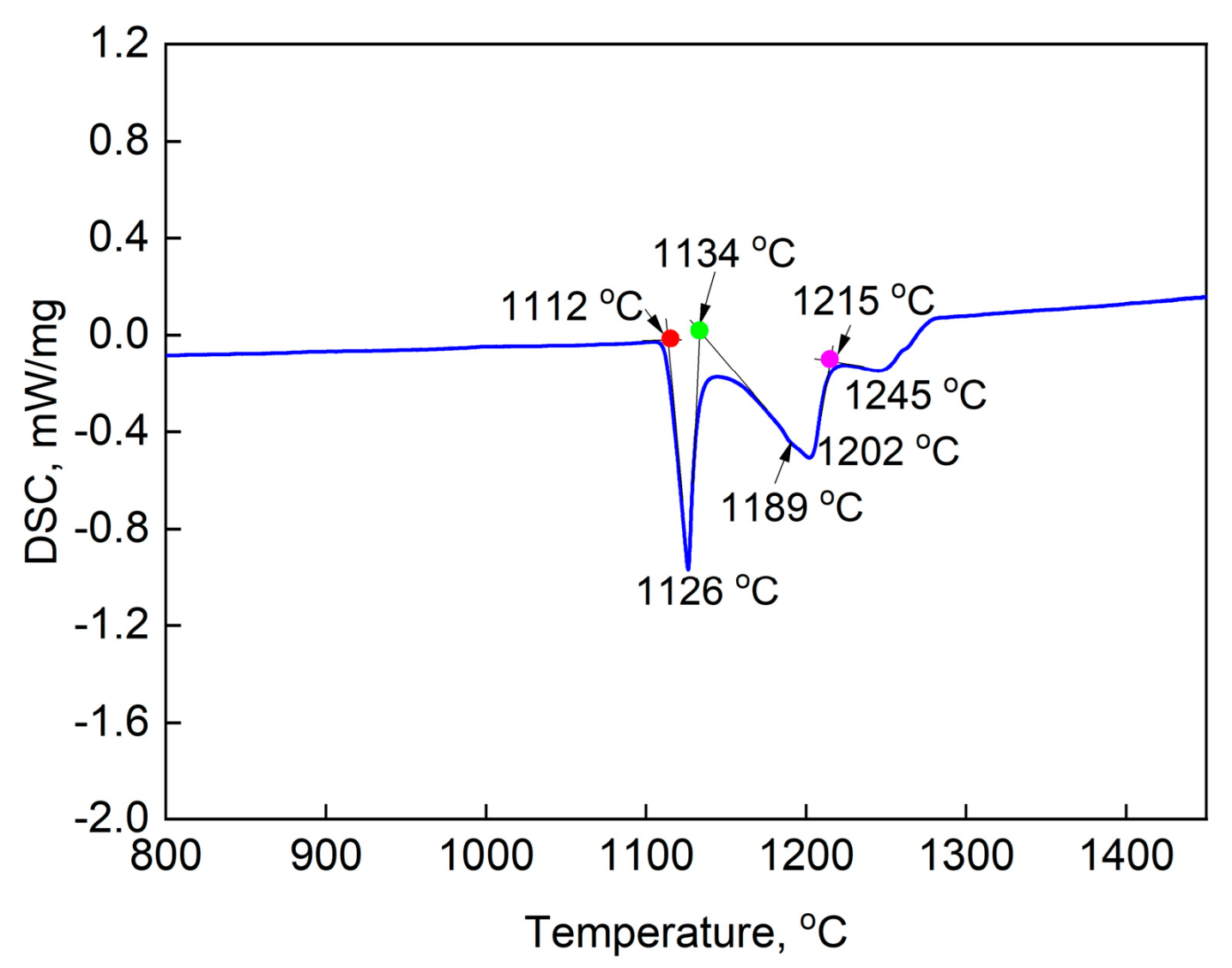
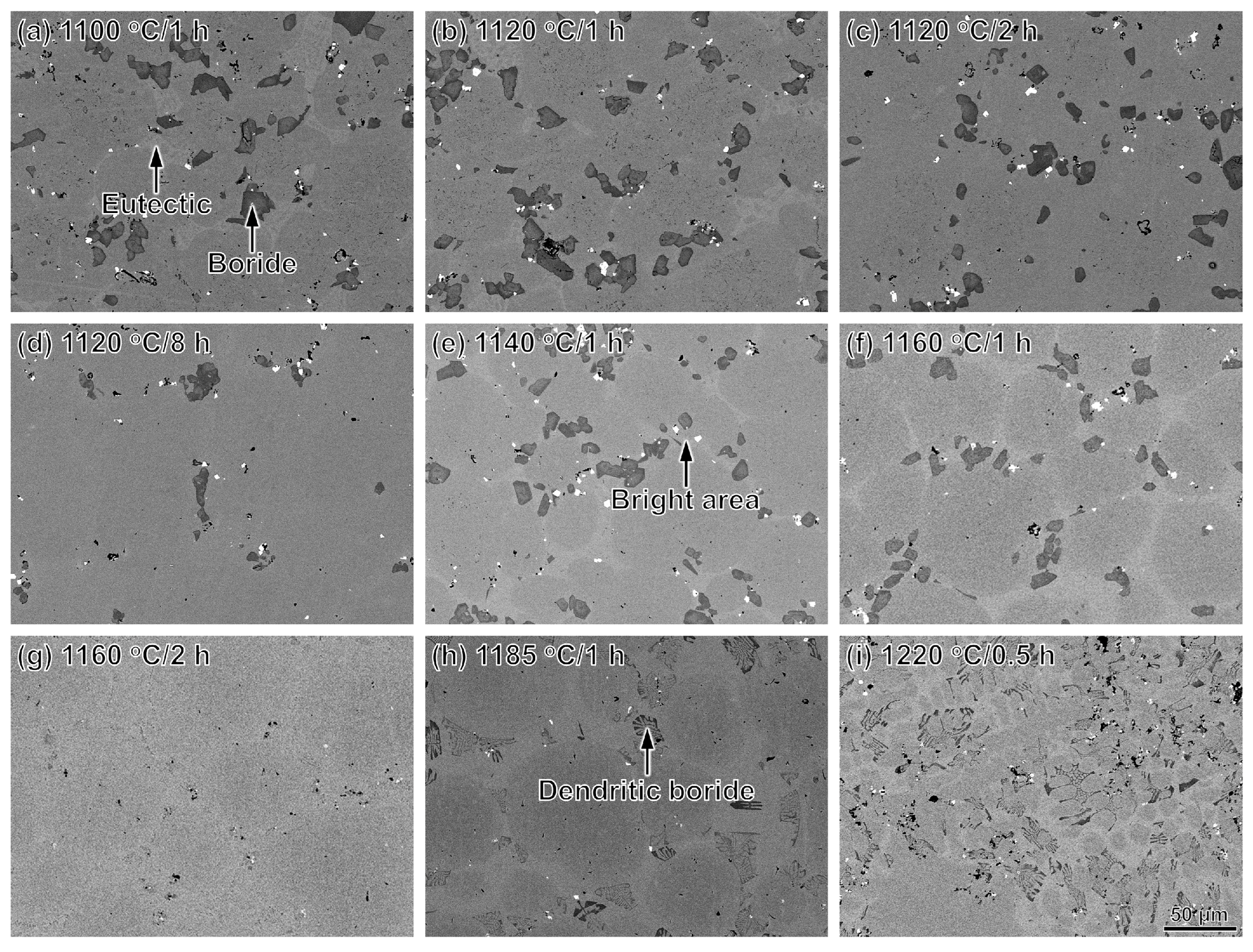
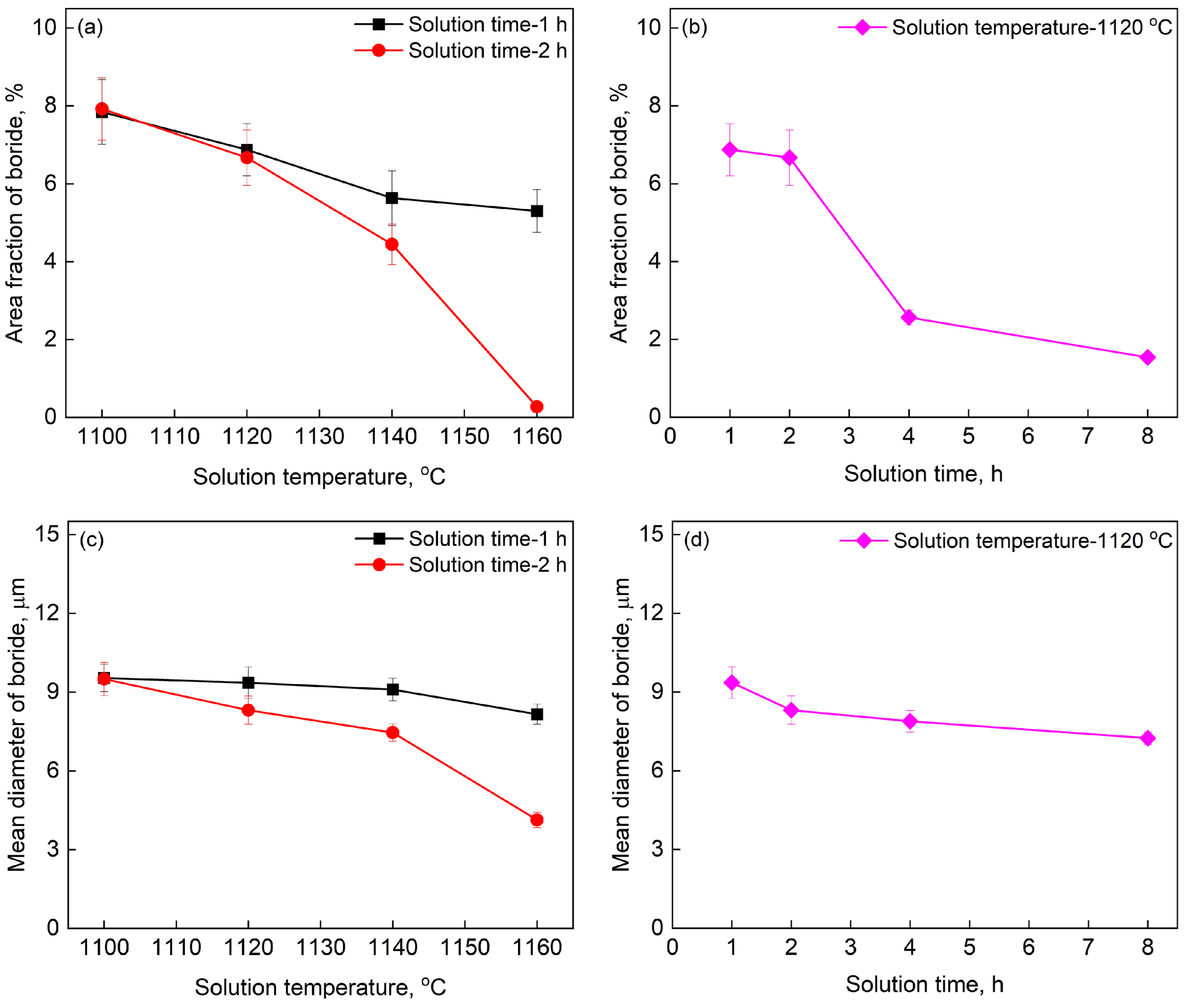
3.2. Solution Heat Treatment
3.3. Microhardness
3.4. Tensile Strength
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cr, W and Mo-rich M5B3 type borides precipitate from the matrix and its area fraction reaches up to about 8% in the PSP work-blank with high B content (>1.0 wt.%).
- (2)
- The area fraction of boride decreases with the prolonging of solution time and the increase of temperature higher than 1120 °C. The borides nearly disappear after solution treatment at 1160 °C for 2 h.
- (3)
- The redissolution of boride and eutectic results in the formation of B-rich bright area with low incipient melting (about 1189 °C). It bonds metallurgically with blade under the melting point of blade, which decreases the precipitation of harmful phases and increase the mechanical properties of the blade after PSP repairing.
- (4)
- The microhardness within the grain in the PSP work blank decreases with the increase of solution temperature lower than 1160 °C due to the dissolving of borides. The dendritic borides precipitate after solution treatment higher than 1185 °C, which increases the microhardness.
- (5)
- The tensile strength of the combination between PSP work-blank and Mar-M247 matrix at room temperature after solution treatment is related to the area fraction of boride, incipient melting and the cohesion between PSP work-blank and Mar-M247 matrix. The tensile strength reduces with the decrease of borides due to the block borides acting as obstacles to the dislocation motion. The cohesion between PSP work-blank and Mar-M247 matrix increases with the prolonging of solution time and the increase of solution temperature, which can increase the tensile strength. The dendritic borides precipitating after incipient melting will lead to the stress concentration and decrease the tensile strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontis, P.; Yusof, H.M.; Pedrazzini, S.; Danaie, M.; Moore, K.; Bagot, P.; Moody, M.; Grovenor, C.; Reed, R. On the effect of boron on grain boundary character in a new polycrystalline superalloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 103, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontis, P.; Alabort, E.; Barba, D.; Collins, D.M.; Wilkinson, A.J.; Reed, R.C. On the role of boron on improving ductility in a new polycrystalline superalloy. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tytko, D.; Choi, P.-P.; Klöwer, J.; Kostka, A.; Inden, G.; Raabe, D. Microstructural evolution of a Ni-based superalloy (617B) at 700°C studied by electron microscopy and atom probe tomography. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.; Felfer, P.J.; Chaturvedi, M.; Stephenson, L.T.; Kilburn, M.R.; Cairney, J.M. Segregation of B, P, and C in the Ni-based superalloy, inconel 718. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.-I.; Han, C.-H.; Shin, Y.-K.; Youn, J.-I.; Kim, Y.-J. Effects of boron and zirconium on grain boundary morphology and creep resistance in nickel-based superalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 7025–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ou, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K. Effect of boron addition on the microstructure and mechanical properties of K4750 nickel-based superalloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 60, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.C.; Zhang, J.; Lou, L.H. Effect of boron additions on the microstructure and transverse properties of a directionally solidified superalloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 474, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ojo, O.; Chaturvedi, M. Nanosize boride particles in heat-treated nickel base superalloys. Scr. Mater. 2008, 58, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadel, E.; Lemarchand, D.; Chambreland, S.; Blavette, D. Atom probe tomography investigation of the microstructure of superalloys N18. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theska, F.; Street, S.; Lison-Pick, M.; Primig, S. Grain boundary microstructure-property relationships in the cast & wrought Ni-based superalloy René 41 with boron and carbon additions. Acta Mater. 2023, 258, 119235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chaturvedi, M.C.; Richards, N.L.; McMahon, G. Grain boundary segregation of boron in INCONEL 718. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1998, 29, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chaturvedi, M.; Richards, N.; Jackman, J. The effect of grain boundary segregation of boron in cast alloy 718 on HAZ microfissuring—A SIMS analysis. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 3095–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theska, F.; Tse, W.F.; Schulz, B.; Buerstmayr, R.; Street, S.R.; Lison-Pick, M.; Primig, S. Review of microstructure–mechanical property relationships in cast and wrought Ni-based superalloys with boron, carbon, and zirconium microalloying additions. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 25, 2201514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delargy, K.M.; Smith, G.D.W. Phase composition and phase stability of a high-chromium nickel-based superalloy, IN939. Met. Trans. A 1983, 14, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, D.; Chaturvedi, M.C. Effect of boron and carbon on the fracture toughness of in 718 superalloy at room temperature and 650 °C. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2005, 14, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garosshen, T.J.; Tillman, T.D.; McCarthy, G.P. Effects of B, C, and Zr on the structure and properties of a P/M nickel base superalloy. Met. Trans. A 1987, 18, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.L.; Schneibel, J.H.; Padgett, R.A. High temperature embrittlement of NI and Ni-Cr alloys by trace elements. Met. Trans. A 1983, 14, 595–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, M.; Strang, A. Effects of trace elements on mechanical properties of superalloys. Met. Technol. 1984, 11, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, M.; Greggi, J.; Whitlow, G. The effect of boron and carbon on the microstructural chemistries of two wrought nickel base superalloys. Scr. Met. 1984, 18, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinville, J.C.; Gallup, K.; Pollock, T.M. Transverse creep of nickel-base superalloy bicrystals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 2516–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, G.; Sarosi, P.; Henry, M.; Whitis, D.; Milligan, W.; Mills, M. Investigation of creep deformation mechanisms at intermediate temperatures in René 88 DT. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3041–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jones, N.; Knowles, D. The microstructures of base/modified RR2072 SX superalloys and their effects on creep properties at elevated temperatures. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xie, J.; Yu, J.; Shu, D.; Hou, G.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Y. Solidification behavior and segregation characteristics of high W-content cast Ni-Based superalloy K416B. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 854, 156027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, S.; Jiang, Z. Segregation and homogenization for a new nickel-based superalloy. Vacuum 2020, 177, 109379. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Hu, R.; Kou, H. Elements segregation and phase precipitation behavior at grain boundary in a Ni-Cr-W based superalloy. Mater. Charact. 2016, 122, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Song, Z.-F.; He, B.; Zhou, L.-Z.; Hou, J.-S. Effect of Ta addition on solidification microstructure and element segregation of IN617B nickel-base superalloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; He, B.; Zhou, L.; Hou, J. Effects of Ta on the high temperature oxidation behavior of IN617 alloy in air. Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Xue, F.; Zhou, X.; Xie, J. Effects of boron or carbon on solidification behavior of Co-Ni-Al-W-based superalloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 891, 161965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, L. Effect of phosphorus segregation on carbides and creep damage of Ni–Fe-based GH984G alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qin, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, L. Influence of phosphorus on hot deformation microstructure of a Ni-Fe-Cr based alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 768, 138454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Temperature/°C | 1100 | 1120 | 1140 | 1160 | 1185 | 1200 | 1220 |
| Time/h | 1, 2, 4 | 1, 2, 4, 8 | 1, 2 | 1, 2 | 1, 2 | 1, 2 | 0.5 |
| Elements | Light Grey Boride | Dark Grey Boride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | |
| B | 10.45 | 38.37 | 10.65 | 38.16 |
| Cr | 68.14 | 52.92 | 69.63 | 52.78 |
| W | 9.77 | 2.14 | 5.78 | 1.24 |
| Mo | 5.05 | 2.12 | 5.55 | 2.28 |
| Ni | 3.78 | 2.59 | 4.66 | 3.11 |
| Co | 2.44 | 1.67 | 3.31 | 2.21 |
| Ti | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.16 |
| Ta | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.04 |
| Nb | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Al | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Elements | Eutectic in Figure 5a | Matrix in Figure 5a | Bright Area in Figure 5e | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | |
| B | 4.34 | 19.83 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.08 | 10.32 |
| Cr | 4.35 | 4.20 | 9.81 | 11.33 | 6.32 | 6.63 |
| W | 0.63 | 1.10 | 4.47 | 1.46 | 1.39 | 0.41 |
| Mo | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.53 | 0.30 |
| Ni | 67.80 | 57.70 | 70.75 | 72.04 | 69.29 | 64.08 |
| Co | 11.72 | 9.98 | 8.61 | 8.77 | 11.55 | 10.68 |
| Ti | 4.48 | 4.69 | 2.51 | 3.14 | 3.94 | 4.48 |
| Ta | 3.62 | 3.62 | 2.00 | 0.66 | 2.97 | 0.90 |
| Nb | 2.18 | 1.18 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 1.21 | 0.71 |
| Al | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.90 | 2.00 | 0.74 | 1.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Guan, Y.; Guan, X.; Qin, X.; Hou, J.; Zhou, L. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Alloy with High Boron Content for the Pre-Sintered Preform (PSP) Application. Materials 2023, 16, 7483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237483
Gong X, Wu Y, Gao Z, Sun Y, Guan Y, Guan X, Qin X, Hou J, Zhou L. Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Alloy with High Boron Content for the Pre-Sintered Preform (PSP) Application. Materials. 2023; 16(23):7483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237483
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Xiufang, Yunsheng Wu, Zhenhuan Gao, Youbei Sun, Yingbo Guan, Xianjun Guan, Xuezhi Qin, Jieshan Hou, and Lanzhang Zhou. 2023. "Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Alloy with High Boron Content for the Pre-Sintered Preform (PSP) Application" Materials 16, no. 23: 7483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237483
APA StyleGong, X., Wu, Y., Gao, Z., Sun, Y., Guan, Y., Guan, X., Qin, X., Hou, J., & Zhou, L. (2023). Microstructural Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Ni-Based Alloy with High Boron Content for the Pre-Sintered Preform (PSP) Application. Materials, 16(23), 7483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16237483






